without video.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 15
 SIX DEGREES COULD CHANGE THE WORLD MGIMO University The faculty of applied economics and commerce Tsibrova Anna THANKS TO:
SIX DEGREES COULD CHANGE THE WORLD MGIMO University The faculty of applied economics and commerce Tsibrova Anna THANKS TO:
 While there’s no way to predict the future, scientific research and powerful climate models give us insight into what the next century may bring if we continue down the present path of emissions. What follows is a hypothetical look at how our world might change, degree by degree. What we are seeing now, in regard to climate change, are the consequences of what we did some time ago. We cannot see directly the impact of what we are doing right now. It is our problem. What the scientists are saying is complicated, of course, but generally it boils down to this: Anything more than a rise of something like 2 degrees Centigrade (3. 6° Fahrenheit) in average global temperature is bad news. (For graphics that say it all, go to the fifth page of this document or the second page of this one. ) The good news is that many sane people and some large institutions recognize this. The European Union, for example, has championed 2°C for some time. Empty words from politicians or part of a basic charter for the twenty-first century? As long as everyone else gets serious about reducing the probability of a temperature rise exceeding about 2°C, there's a chance that climate change will be manageable. So much for theory. In practice, what to do?
While there’s no way to predict the future, scientific research and powerful climate models give us insight into what the next century may bring if we continue down the present path of emissions. What follows is a hypothetical look at how our world might change, degree by degree. What we are seeing now, in regard to climate change, are the consequences of what we did some time ago. We cannot see directly the impact of what we are doing right now. It is our problem. What the scientists are saying is complicated, of course, but generally it boils down to this: Anything more than a rise of something like 2 degrees Centigrade (3. 6° Fahrenheit) in average global temperature is bad news. (For graphics that say it all, go to the fifth page of this document or the second page of this one. ) The good news is that many sane people and some large institutions recognize this. The European Union, for example, has championed 2°C for some time. Empty words from politicians or part of a basic charter for the twenty-first century? As long as everyone else gets serious about reducing the probability of a temperature rise exceeding about 2°C, there's a chance that climate change will be manageable. So much for theory. In practice, what to do?
 , we ture u ar f d e ne th s an. In urie 30 s nt t, r ce 19 Wes ades o an the n a e dec e of eric r th t th reas the Am ast for r large. A e c l fa b n in n ears of a ughts i ts could scale ral y s could ope, lts ve a e Eur resu ega-dro drough nts on tate or s the ns f ntire s fugees. ta e m i g s io ssin icipate ns. The d inhab s. E ndit -re t itne i t co aquifer on eco ges. e. w la an ac wl rough y i can Great P e displ ustbo g d llen entl ted mill d rc in curr eple everal ilar cha he o d nc are to t nd f fs im e to erie We rnia lture a exp ter du nflux o l face s n lifo ricu e a Ca wil an i s be of w from tate ag s ha rtage ly to be ustralia e as Stat sho is like dev nd A ited ll be a n ia, a re U s e e wi. Th tern st, A wes e ther storms dle Ea The e tim Mid ust sam ed by d ica, the ulf Afr eng 1 C ree deg
, we ture u ar f d e ne th s an. In urie 30 s nt t, r ce 19 Wes ades o an the n a e dec e of eric r th t th reas the Am ast for r large. A e c l fa b n in n ears of a ughts i ts could scale ral y s could ope, lts ve a e Eur resu ega-dro drough nts on tate or s the ns f ntire s fugees. ta e m i g s io ssin icipate ns. The d inhab s. E ndit -re t itne i t co aquifer on eco ges. e. w la an ac wl rough y i can Great P e displ ustbo g d llen entl ted mill d rc in curr eple everal ilar cha he o d nc are to t nd f fs im e to erie We rnia lture a exp ter du nflux o l face s n lifo ricu e a Ca wil an i s be of w from tate ag s ha rtage ly to be ustralia e as Stat sho is like dev nd A ited ll be a n ia, a re U s e e wi. Th tern st, A wes e ther storms dle Ea The e tim Mid ust sam ed by d ica, the ulf Afr eng 1 C ree deg

 two degrees At Celsius, cities across China won’t have enough drinking water. Seas will continue to warm due to less efficiency to absorb additional greenhouse gas emissions. This will radically alter ecosystems covering 70 % of the globe. Ocean alkalinity will change and severely impact plankton, which is the base of coastal and deep water food chains. Lower calcium levels will kill off mussel, scallop and oyster populations. By 2040 Europe will experience temperatures similar to North Africa today. Death tolls will soar. Hundreds of thousands will die each year because of searing summer heat waves at 2 degrees Celsius. Imagine 114 degree summers in the Swiss Alps.
two degrees At Celsius, cities across China won’t have enough drinking water. Seas will continue to warm due to less efficiency to absorb additional greenhouse gas emissions. This will radically alter ecosystems covering 70 % of the globe. Ocean alkalinity will change and severely impact plankton, which is the base of coastal and deep water food chains. Lower calcium levels will kill off mussel, scallop and oyster populations. By 2040 Europe will experience temperatures similar to North Africa today. Death tolls will soar. Hundreds of thousands will die each year because of searing summer heat waves at 2 degrees Celsius. Imagine 114 degree summers in the Swiss Alps.
 consequences
consequences
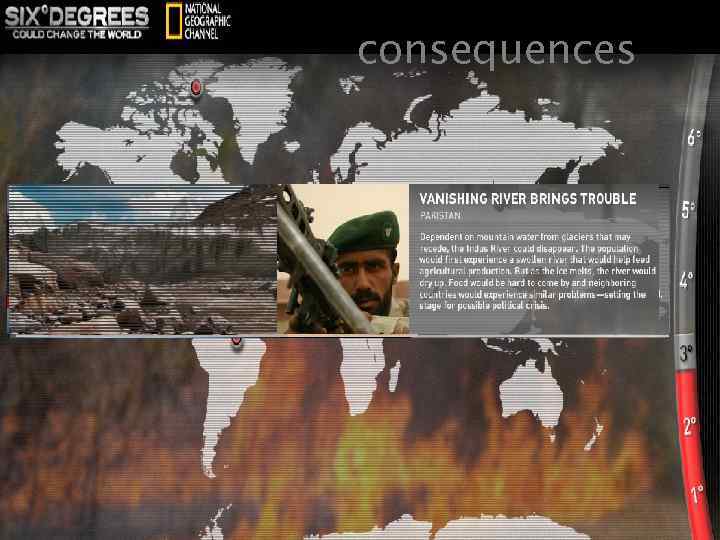
 3 degrees C At our children and grandchildren will see a return to Pliocene norms when the Transantarctic Mountains were covered with beech trees. Global sea levels will rise 25 meters. There will be hyper-hurricanes; an ice-free arctic, dry Indus and Colorado rivers, and New York City will be inundated. Rice, wheat, and maize yields will decline by 10% for every 1 degree Celsius temperature increase.
3 degrees C At our children and grandchildren will see a return to Pliocene norms when the Transantarctic Mountains were covered with beech trees. Global sea levels will rise 25 meters. There will be hyper-hurricanes; an ice-free arctic, dry Indus and Colorado rivers, and New York City will be inundated. Rice, wheat, and maize yields will decline by 10% for every 1 degree Celsius temperature increase.
 consequences
consequences
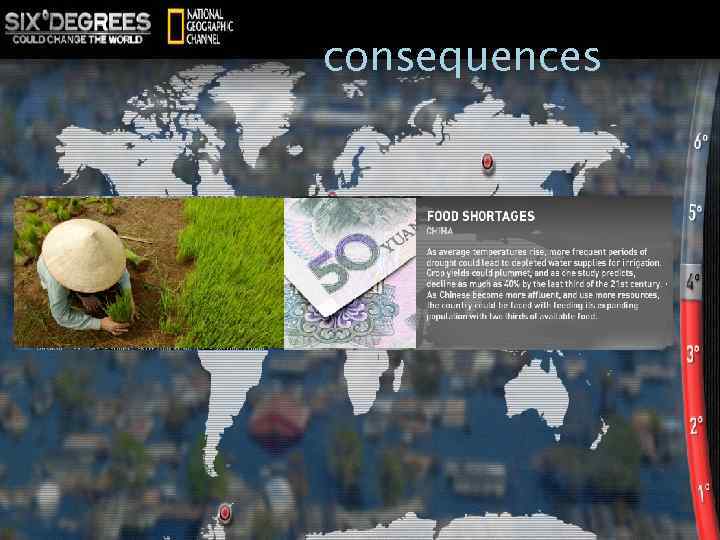
 four degree Celsius
four degree Celsius
 consequences
consequences
 Five degrees Celsius increase will leave our grandchildren with a new planet, indifferent to the needs of humanity. Rain forests will be gone. People will be confined to a few habitability zones which will suffer from drought and flood. At the highest latitudes Alaskan rivers will experience dramatically increased flows due to torrential rain. The United Kingdom will experience severe winter flooding as reset Atlantic weather patterns lash out with ferocity. Conditions on our planet will be like those experienced during the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM). Nearly every academic PETM study published in recent years notes that this epoch presages what anthropogenic global warming might have in store. Massive amounts of methane hydrates may be released, resulting in runaway global warming. Humans will witness the early stages of a Venusian climate. Climate changes that in the past took thousands of years will occur in a century. Ecosystems won’t have time to adapt to new circumstances. Humans won’t have time to adapt.
Five degrees Celsius increase will leave our grandchildren with a new planet, indifferent to the needs of humanity. Rain forests will be gone. People will be confined to a few habitability zones which will suffer from drought and flood. At the highest latitudes Alaskan rivers will experience dramatically increased flows due to torrential rain. The United Kingdom will experience severe winter flooding as reset Atlantic weather patterns lash out with ferocity. Conditions on our planet will be like those experienced during the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM). Nearly every academic PETM study published in recent years notes that this epoch presages what anthropogenic global warming might have in store. Massive amounts of methane hydrates may be released, resulting in runaway global warming. Humans will witness the early stages of a Venusian climate. Climate changes that in the past took thousands of years will occur in a century. Ecosystems won’t have time to adapt to new circumstances. Humans won’t have time to adapt.
 consequences
consequences
 6 degrees C With of warming those left will see an extinction not seen for 251 million years. Ninety percent of all life on Earth will die off. Runaway greenhouse warming will trigger anoxic oceans to release massive amounts of poisonous hydrogen sulfide into the atmosphere. Oxygen levels will plunge and many organisms will suffocate.
6 degrees C With of warming those left will see an extinction not seen for 251 million years. Ninety percent of all life on Earth will die off. Runaway greenhouse warming will trigger anoxic oceans to release massive amounts of poisonous hydrogen sulfide into the atmosphere. Oxygen levels will plunge and many organisms will suffocate.
 consequences
consequences
 To sum it up… I believe that this project will make you more attentive to environmental problems If people want to survive they must solve ecological problems quickly. Man is beginning to understand that his environment is not just his own town or country, but the whole earth. That’s why people all over the world think and speak so much about ecology. The Earth is our home. We must take care of it for next generations and ourselves. Thank you.
To sum it up… I believe that this project will make you more attentive to environmental problems If people want to survive they must solve ecological problems quickly. Man is beginning to understand that his environment is not just his own town or country, but the whole earth. That’s why people all over the world think and speak so much about ecology. The Earth is our home. We must take care of it for next generations and ourselves. Thank you.


