medical ethic.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 26

SIW: Ethical medicine problems associated with public health Tuleutemir D. 337 GM Astana 2015

• Medical ethics is a system of moral principles that apply values and judgments to the practice of medicine. • As a scholarly discipline, medical ethics encompasses its practical application in clinical settings as well as work on its history, philosophy, theology, and sociology.

Values in medical ethics • There are 4 principles in medical ethic postulated by Tom Beauchamp and James Childress in their textbook Principles of biomedical ethics.

James Childress Tom Beauchamp

• Respect for autonomy - the patient has the right to refuse or choose their treatment. (Voluntas aegroti suprema lex. ) • Beneficence - a practitioner should act in the best interest of the patient. (Salus aegroti suprema lex. ) • Non-maleficence - "first, do no harm" (primum non nocere). • Justice - concerns the distribution of scarce health resources, and the decision of who gets what treatment (fairness and equality).

Other values that are sometimes discussed include: • Respect for persons - the patient (and the person treating the patient) have the right to be treated with dignity. • Truthfulness and honesty

The main problem remains is the relationship between doctor and patient It also owns medical ethics problems as medical confidentiality, medical errors, euthanasia, the right to experiment on themselves (physician, physician), medical intervention without the consent of the patient, experiment on human beings, organ and tissue transplantation, genetic engineering, quackery, Paramedical, etc. .

According to the Korotkih R. V. `s research • 61% of physicians break moral norms of relationships with patients and colleagues, • 30% do not comply with medical confidentiality, are constantly, regardless of the situation, talk about patients, calling their names. • Among the causes of moral character, causing dissatisfaction with medical care, 37% of respondents complained about the negligence of doctors, 6% - for rudeness. • It was found that 11% of doctors have difficulty in collecting history, contacts with patients, 14% at the definition of assignments, 52% - in the control and execution of assignments.
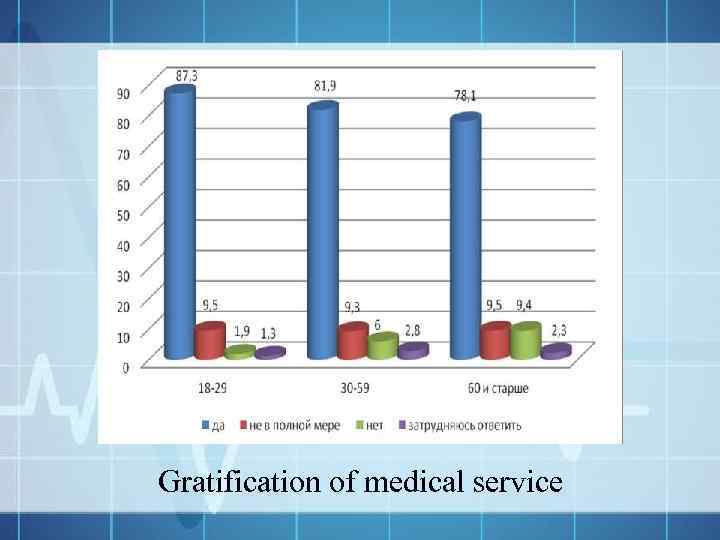
Gratification of medical service

Importance of communication • Many so-called "ethical conflicts" in medical ethics are traceable back to a lack of communication. Communication breakdowns between patients and their healthcare team, between family members, or between members of the medical community, can all lead to disagreements and strong feelings. These breakdowns should be remedied, and many apparently insurmountable "ethics" problems can be solved with open lines of communication.


Confidentiality • Confidentiality is a set of rules or a promise that limits access or places restrictions on certain types of information. • This rule existed since ancient times as one of the most important provisions in the Hippocratic Oath, come in all ethical codes and other documents on the principles and rules of behavior of physicians. After many centuries, the confidentiality has been included in the legislation.


Medical error • A medical error is a preventable adverse effect of care, whether or not it is evident or harmful to the patient. This might include an inaccurate or incomplete diagnosis or treatment of a disease, injury, syndrome, behavior, infection, or other ailment.



Euthanasia • Also called mercy killing. • the act of putting to death painlessly or allowing to die, as by withholding extreme medical measures, a person_or animal suffering from an incurable, especially a painful, disease or condition



There a lot of life examples. For example, medical emergencies or military field medical services when performed triage. According to the rules, all the wounded are divided into three groups: minor injuries, severe injuries and hopeless. Slightly wounded bandage and sent to the rear. Seriously wounded first have the greatest possible assistance in place, and then also sent to the rear. "Hopeless" alleviate suffering, but not transferred to the rear.

• In fact, some of the wounded who fell into the category of "bad" can still be saved if they will be engaged in highly qualified doctors with specialized medical equipment. To do this, they urgently need to be evacuated in the support staff. In such a case, without adequate medical care can remain slightly wounded and seriously wounded, whose condition will deteriorate.


• Also, the medical ethical problem is education of students on human beings. Students, in their inability may inadvertently hurt the patient. However, as much as possible to prepare highly qualified specialists without practice on human beings ? ! No dummies, no practice on cadavers will not be able to prepare a specialist so as to work with a human. This ethical problem is insoluble.


Conclusion • Medical ethical principles aimed at protecting the rights and interests of the patient, and they must be absolutely humane. However, in real life is not so simple. Physicians are often put in a situation where they have to make decisions contrary to the rules of medical ethics. In this case, the doctor tries to make a decision that will cause less harm.

medical ethic.pptx