Система крови 1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29
Система крови

• oxygen transportation (by hemoglobin) • mobile elements of the body’s defense system • important for blood clotting
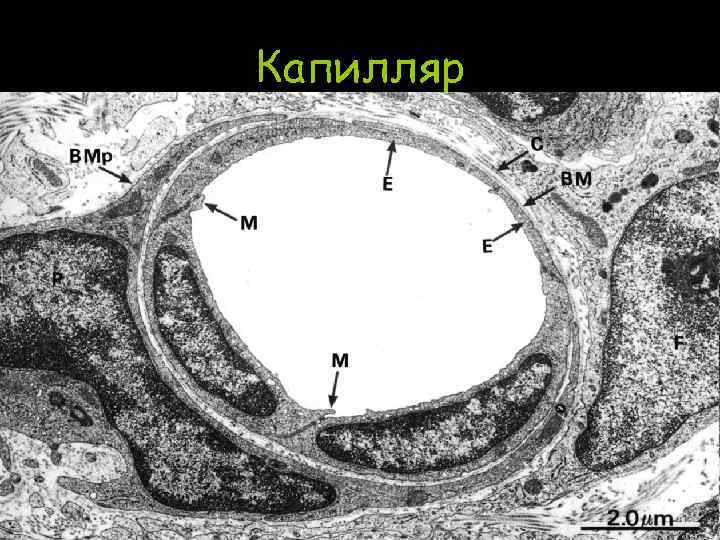
Капилляр
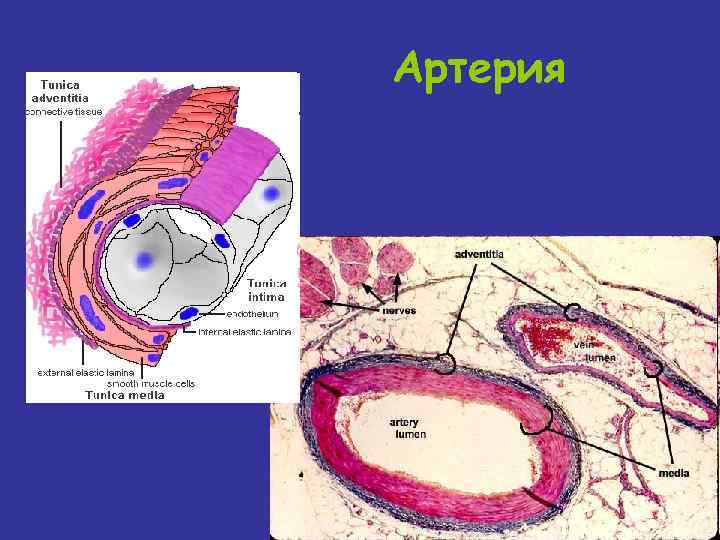
Артерия
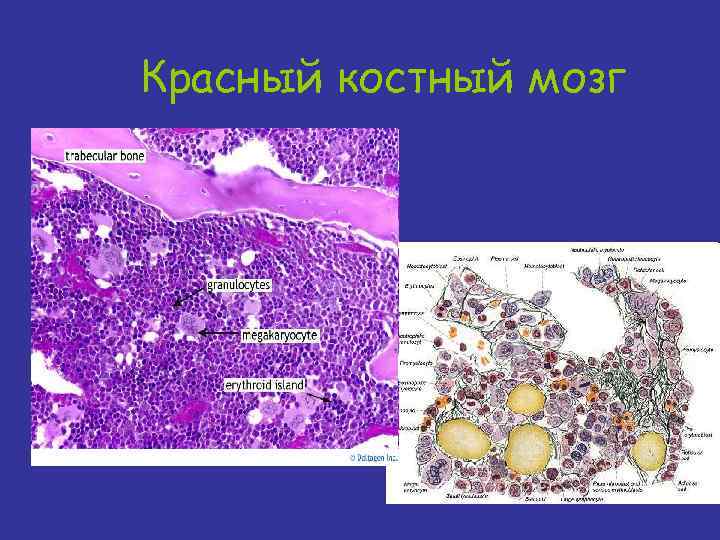
Красный костный мозг
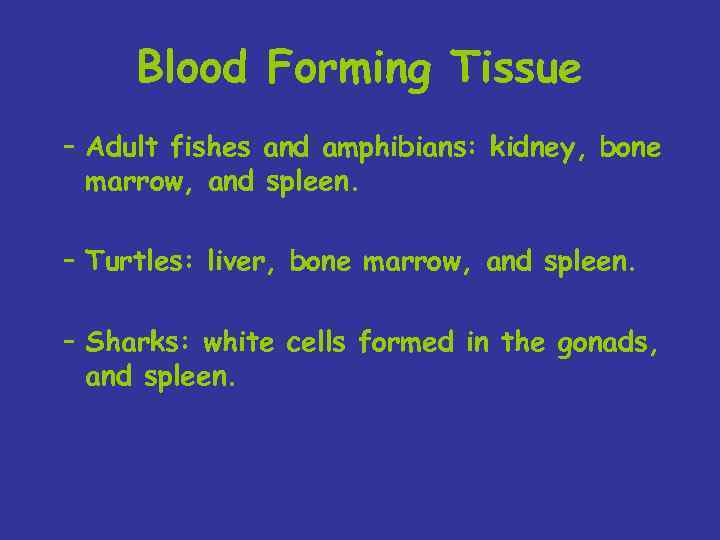
Blood Forming Tissue – Adult fishes and amphibians: kidney, bone marrow, and spleen. – Turtles: liver, bone marrow, and spleen. – Sharks: white cells formed in the gonads, and spleen.

Marrow Production • All bones - 0 -5 years of age • Pelvis (40%), vertebrae (28%), cranium/mandible (13%), ribs (8%), sternum (2%) - 20+ years of age

Embryogenesis • 3 rd gestational week - stem cells in yolk sac • 3 rd gestational month - liver becomes site blood cell formation, with the help of spleen, lymph nodes, and thymus • 4 th gestational month - bone marrow becomes functional
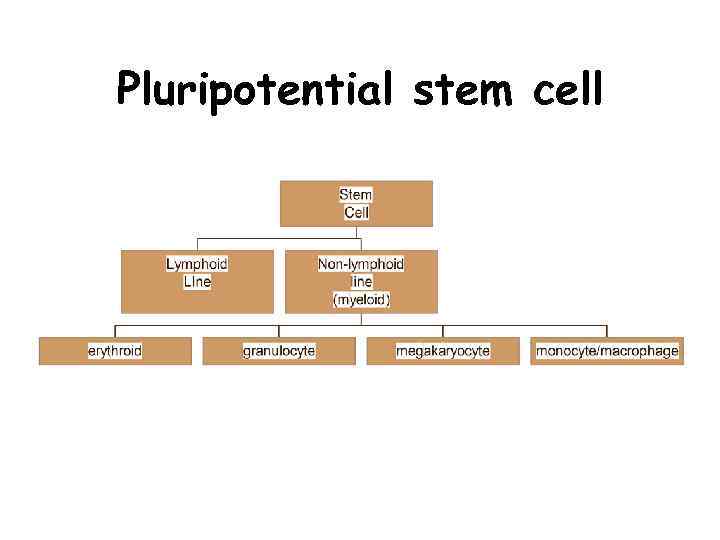
Pluripotential stem cell
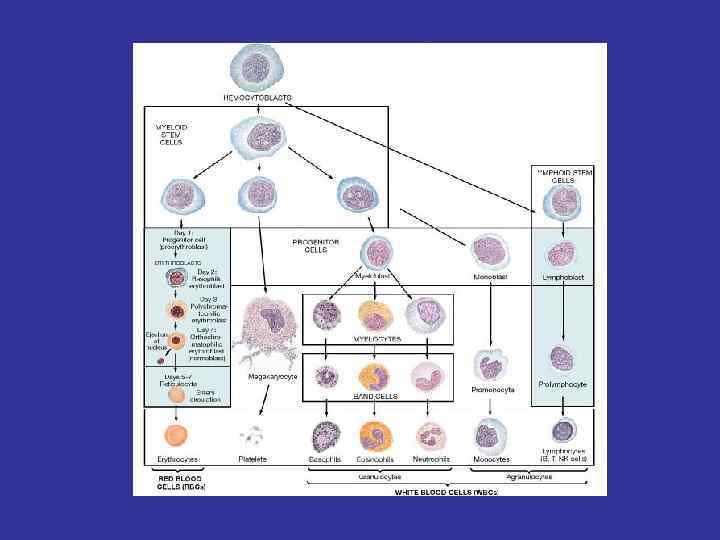

Erythropoesis
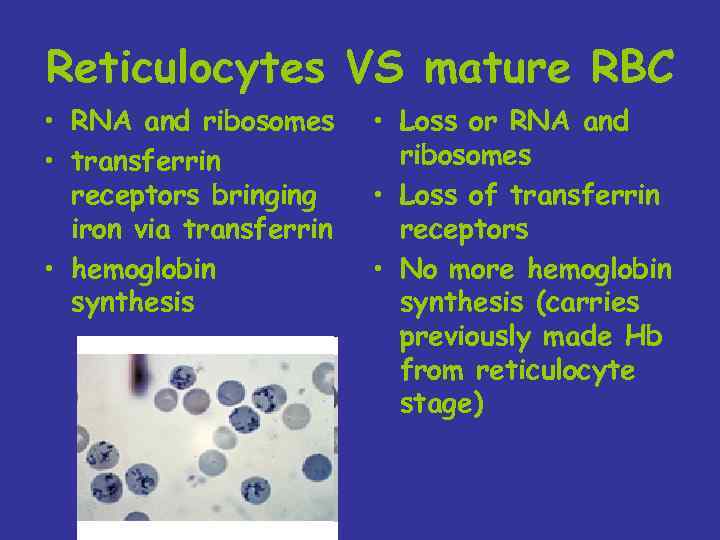
Reticulocytes VS mature RBC • RNA and ribosomes • transferrin receptors bringing iron via transferrin • hemoglobin synthesis • Loss or RNA and ribosomes • Loss of transferrin receptors • No more hemoglobin synthesis (carries previously made Hb from reticulocyte stage)

Peripheral Blood: Erythrocytes • RBCs constitute the largest number of cells in the blood • Biconcave discs • NO NUCLEUS • Contain Hemoglobin
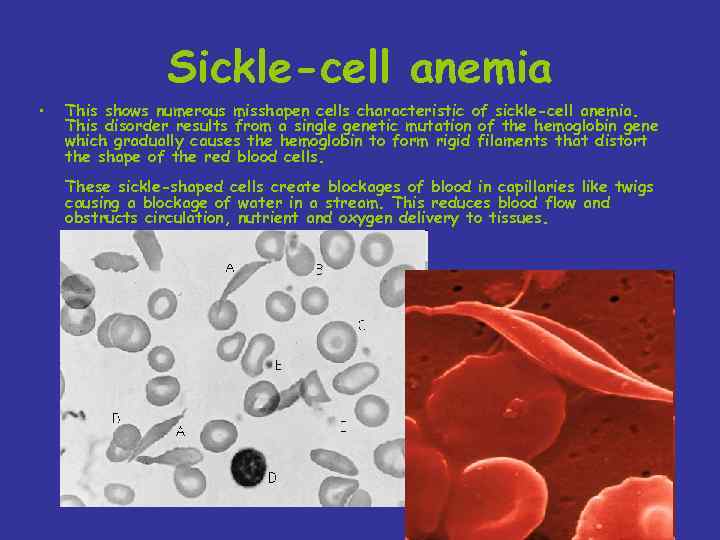
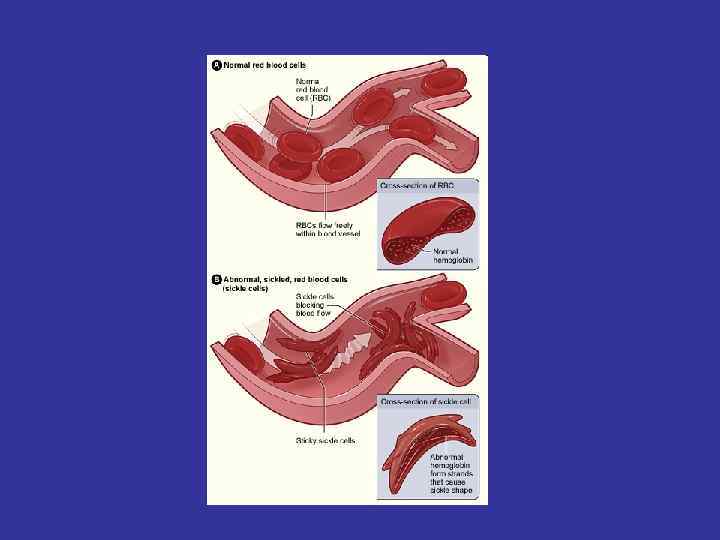
Sickle-cell anemia • This shows numerous misshapen cells characteristic of sickle-cell anemia. This disorder results from a single genetic mutation of the hemoglobin gene which gradually causes the hemoglobin to form rigid filaments that distort the shape of the red blood cells. These sickle-shaped cells create blockages of blood in capillaries like twigs causing a blockage of water in a stream. This reduces blood flow and obstructs circulation, nutrient and oxygen delivery to tissues.

Peripheral Blood: Leukocytes • GRANULOCYTES – Neutrophils – Basophils – Eosinophils • AGRANULOCYTES – Lymphocytes (T and B cells) – Monocytes (Macrophages)
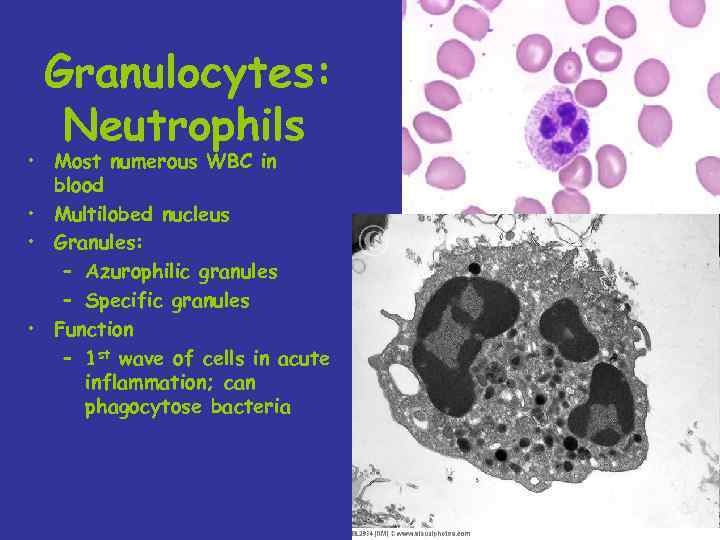
Granulocytes: Neutrophils • Most numerous WBC in blood • Multilobed nucleus • Granules: – Azurophilic granules – Specific granules • Function – 1 st wave of cells in acute inflammation; can phagocytose bacteria
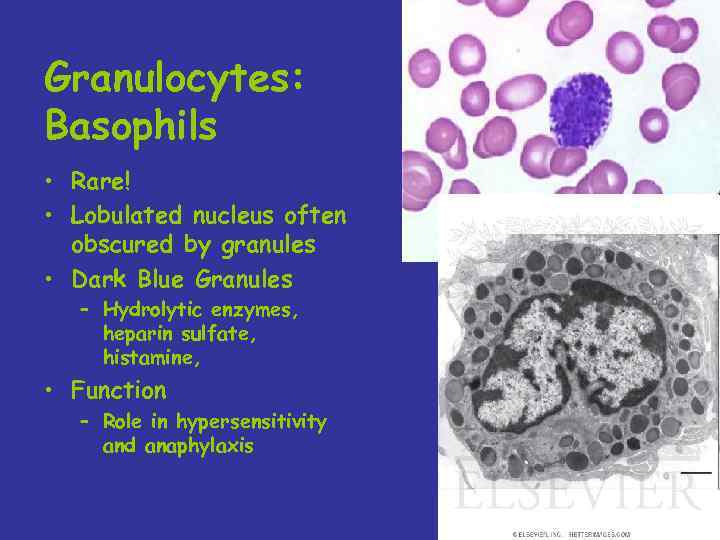
Granulocytes: Basophils • Rare! • Lobulated nucleus often obscured by granules • Dark Blue Granules – Hydrolytic enzymes, heparin sulfate, histamine, • Function – Role in hypersensitivity and anaphylaxis
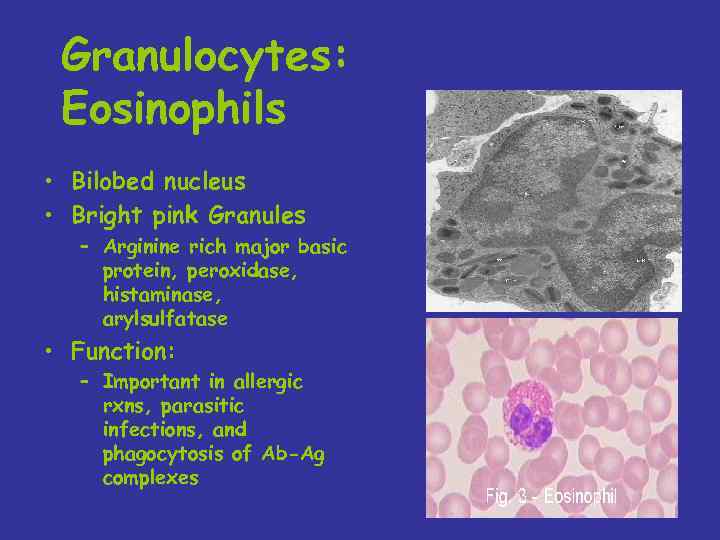
Granulocytes: Eosinophils • Bilobed nucleus • Bright pink Granules – Arginine rich major basic protein, peroxidase, histaminase, arylsulfatase • Function: – Important in allergic rxns, parasitic infections, and phagocytosis of Ab-Ag complexes

Agranulocytes: Monocytes • Largest WBCs in blood smear • Migrate through blood to the tissues; once in tissues they differentiate into phagocytes (macrophages)
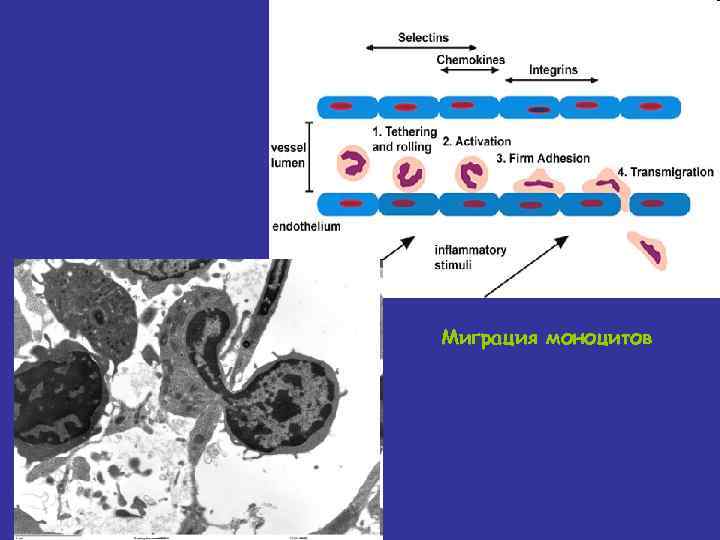
Миграция моноцитов
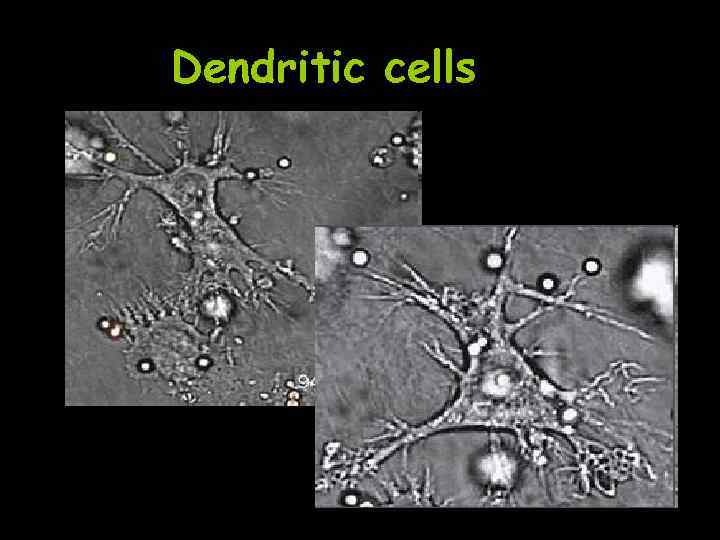
Dendritic cells
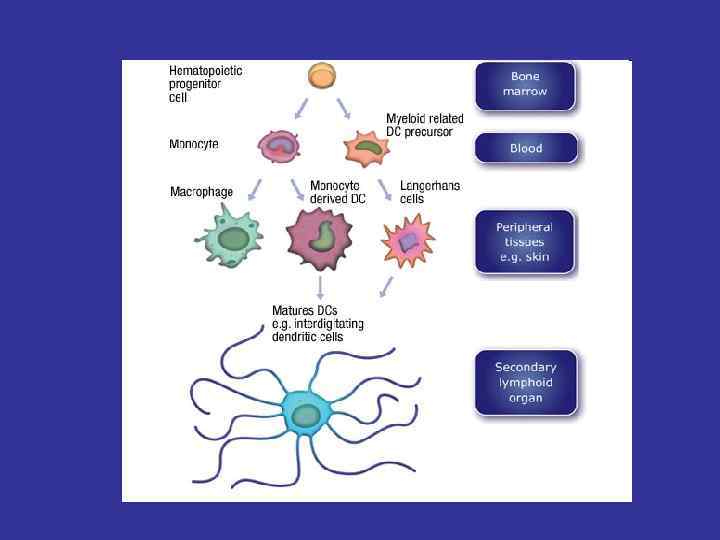
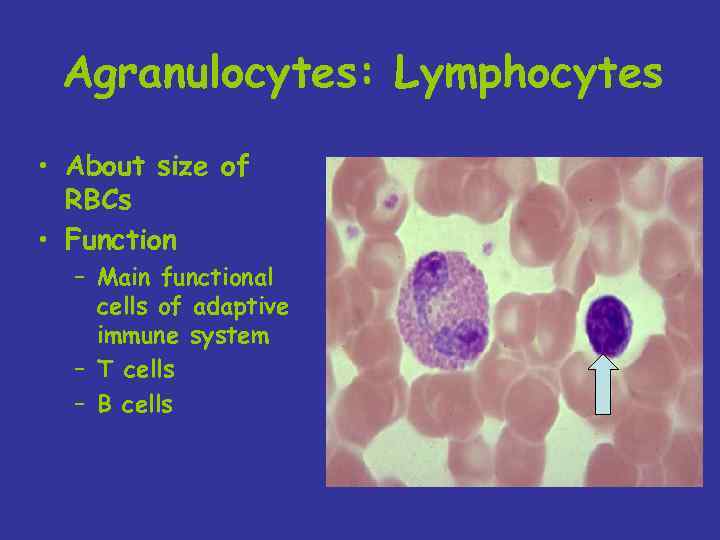
Agranulocytes: Lymphocytes • About size of RBCs • Function – Main functional cells of adaptive immune system – T cells – B cells
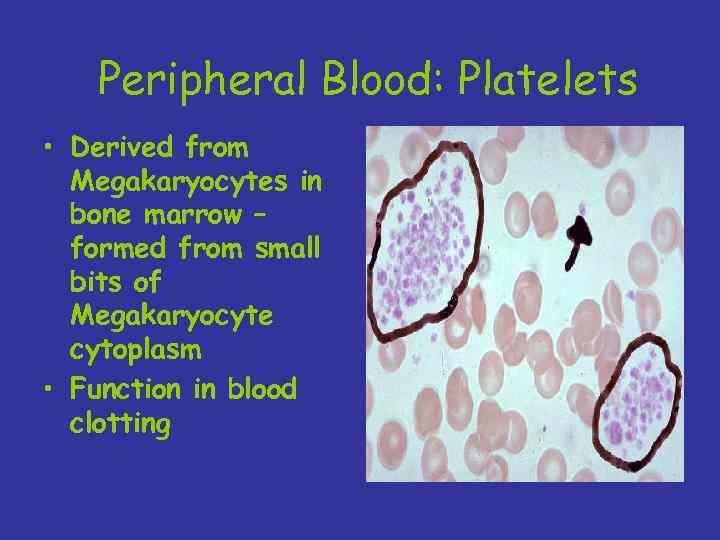
Peripheral Blood: Platelets • Derived from Megakaryocytes in bone marrow – formed from small bits of Megakaryocyte cytoplasm • Function in blood clotting
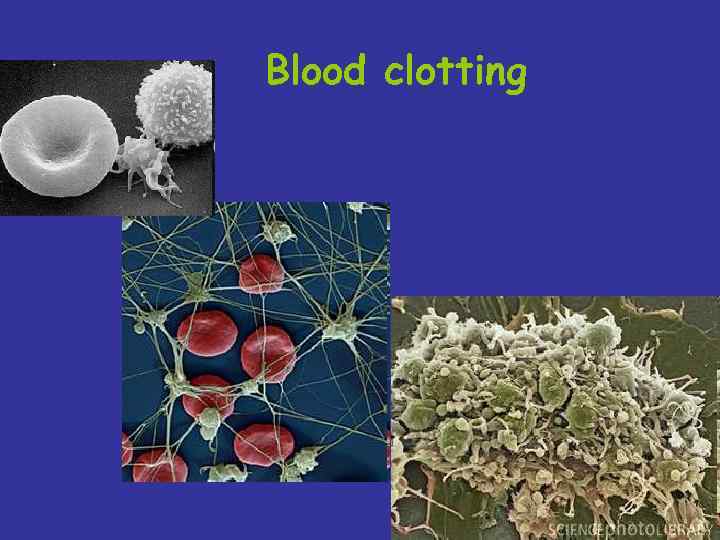
Вlood clotting
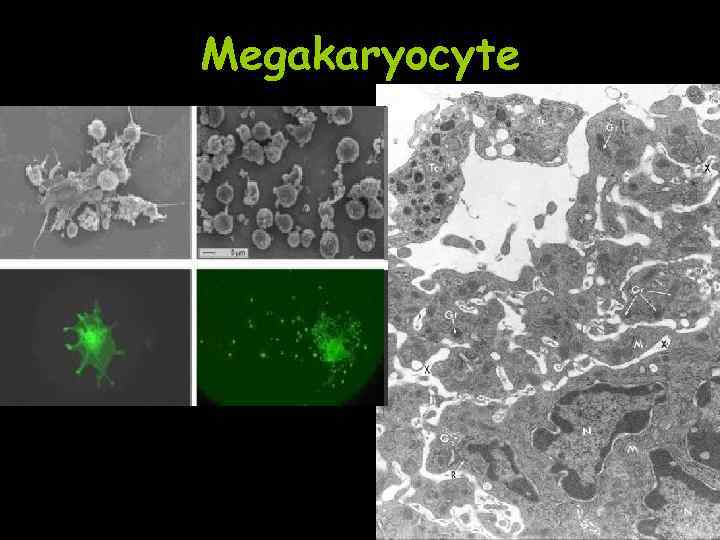
Megakaryocyte
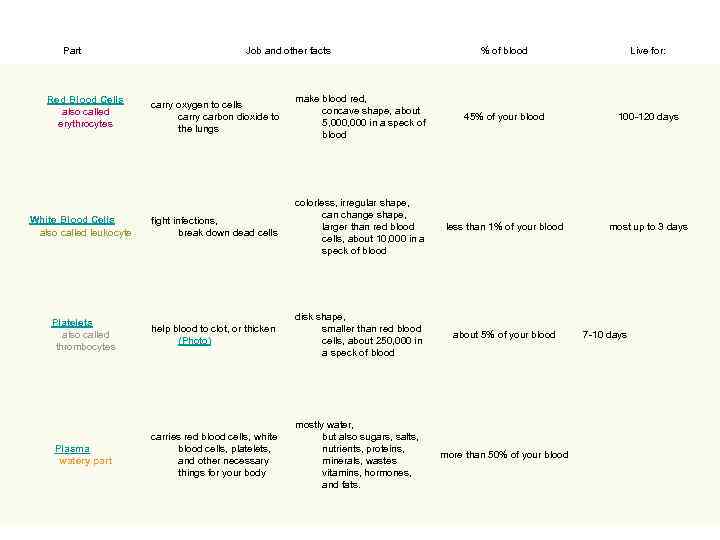
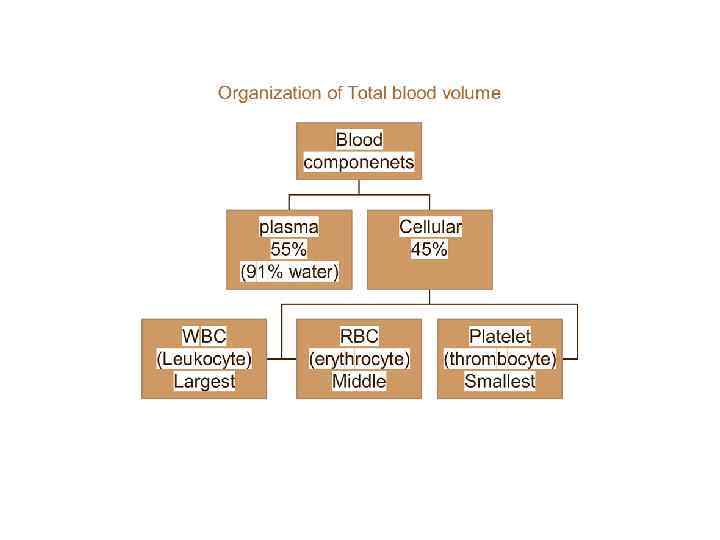
Part Job and other facts % of blood Live for: carry oxygen to cells carry carbon dioxide to the lungs make blood red, concave shape, about 5, 000 in a speck of blood 45% of your blood 100 -120 days White Blood Cells also called leukocyte fight infections, break down dead cells colorless, irregular shape, can change shape, larger than red blood cells, about 10, 000 in a speck of blood less than 1% of your blood most up to 3 days Platelets also called thrombocytes help blood to clot, or thicken (Photo) disk shape, smaller than red blood cells, about 250, 000 in a speck of blood about 5% of your blood Plasma watery part carries red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and other necessary things for your body mostly water, but also sugars, salts, nutrients, proteins, minerals, wastes vitamins, hormones, and fats. more than 50% of your blood Red Blood Cells also called erythrocytes 7 -10 days
Система крови 1.ppt