bfc70e6641c5bfe0ea84def5163c7c83.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37

SIP- Session Initiation Protocol Kari-Anne Bakke Morten Biering Elisabeth Klaveness Ingvild Risvik Hege Tunheim Håvard Voldsund

Agenda w Introduksjon n n Hva er SIP? Hvorfor SIP? w Arkitektur w SIP versus mobil IP w Mobilitet w ”Hvordan SIP kunne hindret krig”

Hva er SIP? w SIP er en applikasjonslagsprotokoll for oppsetting, kontroll og nedkobling av interaktive sesjoner. n IKKE transport-, reservering- eller tjenestekvalitetsprotokoll w Signalleringsprotokoll w Utombåndssignallering

Hva er SIP? (2) w Tillater to eller flere brukere å etablere en sesjon bestående av en eller flere mediestrømmer. w En brukers mediestrømmer kan bli distribuert over et sett terminaler. w Kan invitere brukere både til unicast og multicast- sesjoner, og nye brukere kan inviteres underveis.

Hva er SIP? (3) w En del av IETFs overordnede multimedia data- og kontrollarktitektur sammen med RSVP, RTSP, SAP og SDP w Uavhengig av de underliggende protokollene.

Hvorfor SIP? w Dagens brukere n n n Benytter gjerne flere forskjellige terminaler Ofte adresserbare under flere navn Vil kommunisere gjennom forskjellige media samtidig w Standardisert av IETF for å imøtekomme det økende kravet til terminal, person, sesjon og tjeneste mobilitet.

Hvorfor SIP? (2) w SIP er enkelt w Intelligens i endenodene w Nettverksnodene er tilstandsløse w Teksbaserte meldinger

Bruksområder w Eksempler på bruksområder: n n n IP-telefoni (Vo. IP) Instant messaging Nettverksspill Multimediakonferanser (lyd, video, tekst, osv. ) Multimediadistribusjon w Ett av målene er sømløs mobilitet!

Adressering w SIP gir deg en globalt tilgjengelig adresse. w Adressen er på URL-format: sip: ola@normann. no w Kan bruke telefonnr i stedet for navn: sip: 73500000@normann. no; user=phone;

SIP registrering Her registreres brukeren med adressen jiri@iptel. org. Denne adressen bindes til brukerens nåværende lokasjon som er: 195. 37. 78. 173
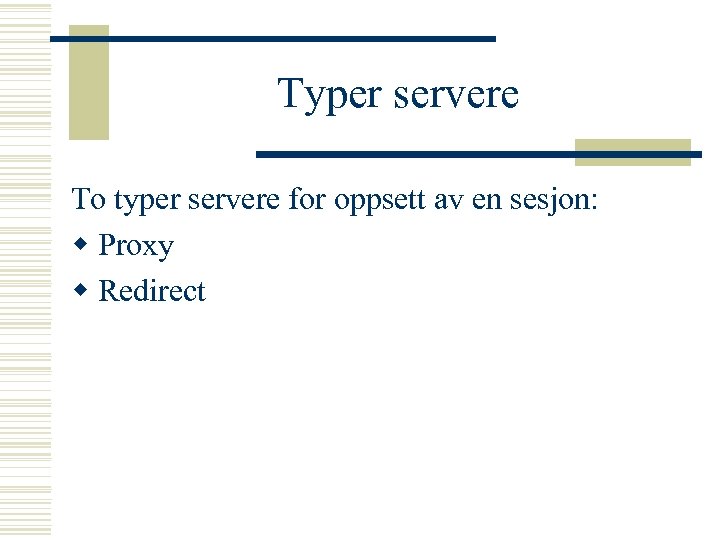
Typer servere To typer servere for oppsett av en sesjon: w Proxy w Redirect
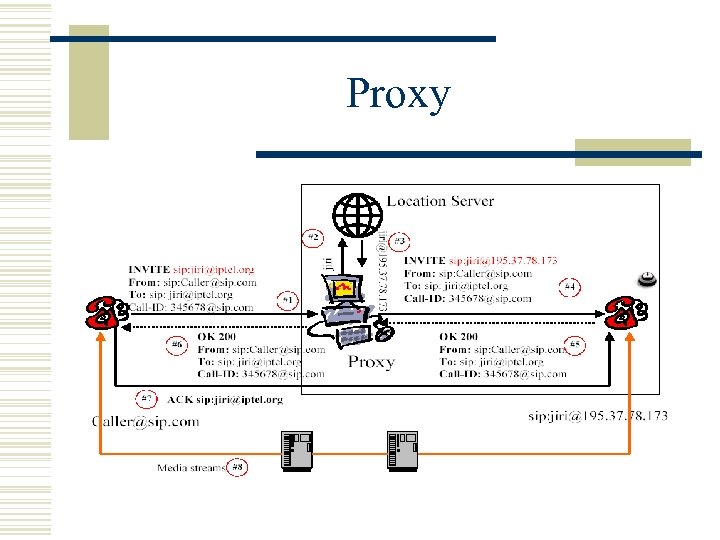
Proxy
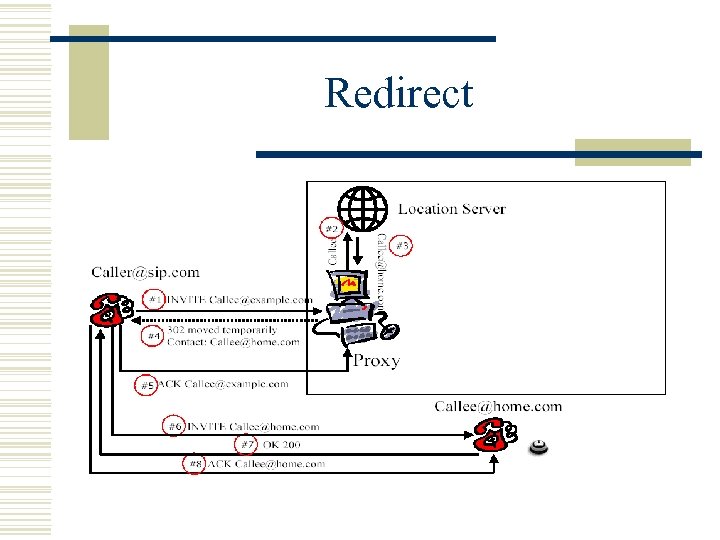
Redirect

SIP vs H. 323 w SIP blir ofte sammenlignet med H. 323 w H. 323 er en komplett vertikalintegrert samling protokoller som muliggjør multimediakonferanser. w H. 323 er en etablert protokoll
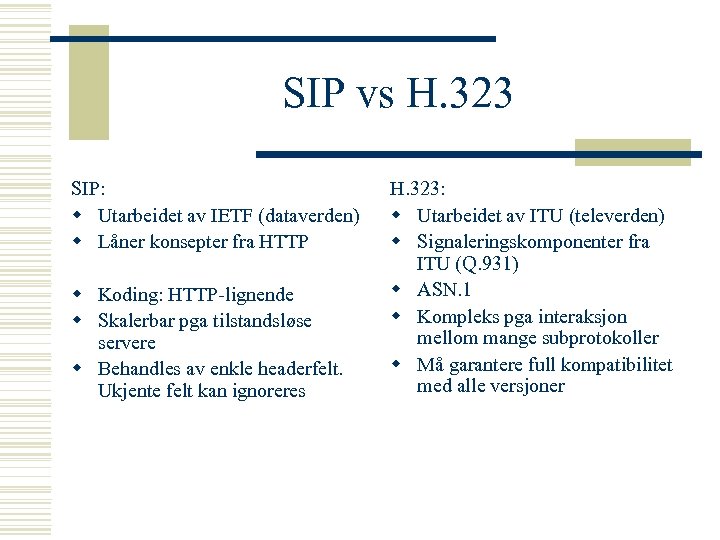
SIP vs H. 323 SIP: w Utarbeidet av IETF (dataverden) w Låner konsepter fra HTTP w Koding: HTTP-lignende w Skalerbar pga tilstandsløse servere w Behandles av enkle headerfelt. Ukjente felt kan ignoreres H. 323: w Utarbeidet av ITU (televerden) w Signaleringskomponenter fra ITU (Q. 931) w ASN. 1 w Kompleks pga interaksjon mellom mange subprotokoller w Må garantere full kompatibilitet med alle versjoner

Mobile ip w. Mobil ip funksjonalitet w. Ulemper w. Hvordan SIP kan brukes i forbindelse med mobil ip

Binding update w Route optimization solves the triangular routing problem by using binding updates to inform the correspondent host about the current ip-adress. w Binding updates is sent from the home agent to the correspondent host
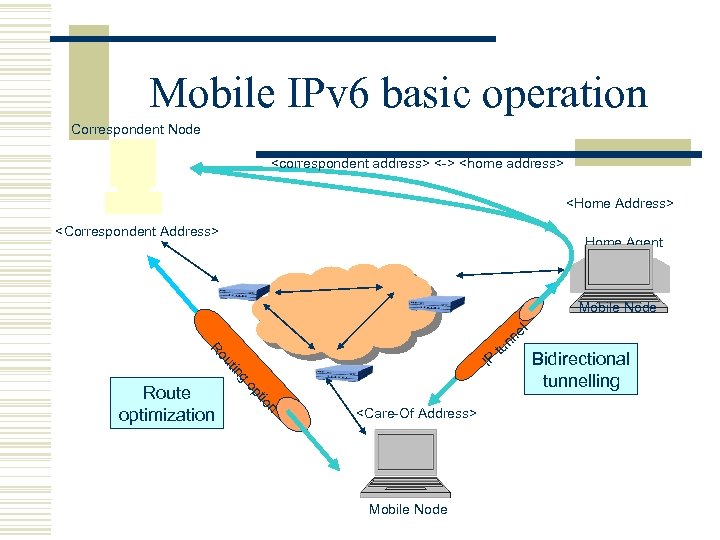
Mobile IPv 6 basic operation Correspondent Node <correspondent address> <-> <home address> <Home Address> <Correspondent Address> Home Agent Mobile Node Ro e nn n tio op Route optimization g in ut IP <Care-Of Address> Mobile Node tu l Bidirectional tunnelling
Disadvantages with route optimization w Route optimization requires changes in the ip -stack of the correspondent host. w The correspondent host must be able to store the care of adress of the mobile node. w CH must be able to tunnel (encapsulate ippackets) directly to the mobile node.

Disadvantages with route optimization(2) w The home agent sends binding updates to the correspondent node. There will be a delay before the CN gets hold of the new location of the mobile node. The old foreign agent must then forward these packets recieved in this delay before the CN starts sending to the new foreign agent. There is no requirement saying the foreign agent must do so…

Disadvantages with route optimization(3) w Also: heavy response on the home agent and the foreign agent in mobile ip. This can be a bottleneck? The reason for this is that these servers are involved in the whole transaction conserning getting the message to the correct location. w The home- and foreign agents must handle the tunnels of a large number of mobile hosts.

Advantage with mobile IP w Mobile IP provides transparent mobility which is needed to keep TCP connections alive as the user is moving

SIP mobility support w Each new SIP transaction has a unique call identifier, which identifies the session. w A redirect server returns the location of the host rather than relaying the SIP message. w This makes it possible to make higly scalable servers, since it only has to send back a response with the correct location, instead of participating in the whole transaction which is the case for the SIP proxy

SIP mobility support(2) w The load on a redirect server can be expected to be lower since it only needs to send an answer with the users location. w SIP redirect server has properties resembling those of the home agent in mobile IP with route optimization, in that it tells the caller where to send the invitation.

SIP mobility support(3) w When the correspondent host sends an INVITE to the mobile host, the redirect server has the current information about the mobile hosts location and redirects the INVITE there. w If the mobile host moves during a session, it must send a new INVITE to the CH using the same call identifier as in the original call setup. w Finally, the mobile host should update its registration at the home SIP server, so that new calls can be correctly redirected

SIP and mobile IP w If the mohile host is using mobile IP, it is not necessary for the SIP server to have knowledge about the current location of the mobile host. w Waste of recourses to keep duplicated information both in the SIP server and in the home agent. w Solution: co-locate the SIP server and the home agent
Summary w By introducing SIP mobility support, we will avoid many of the problems with mobile IP. w However, SIP mobility cannot support TCP connections. w Solution: Use SIP mobility for real time traffic over UDP, and mobile IP for TCP connections

Where to buy these foils w These foils are ofcourse not for free, but you can buy them on Stripa tomorrow 12 -13 w Income go straight in own pocket. w THANKS!

SIP and Mobility w Different modes of mobility: n n n Terminal mobility Personal mobility Service mobility

SIP and Terminal Mobility w Terminal can move between subnetworks w Realised today with GSM and WLAN w Terminal mobility and SIP: n n Mobile hosts inform their home proxy about their new locations using REGISTER Mid-call mobility (session mobility) is dealt with using re. INVITE
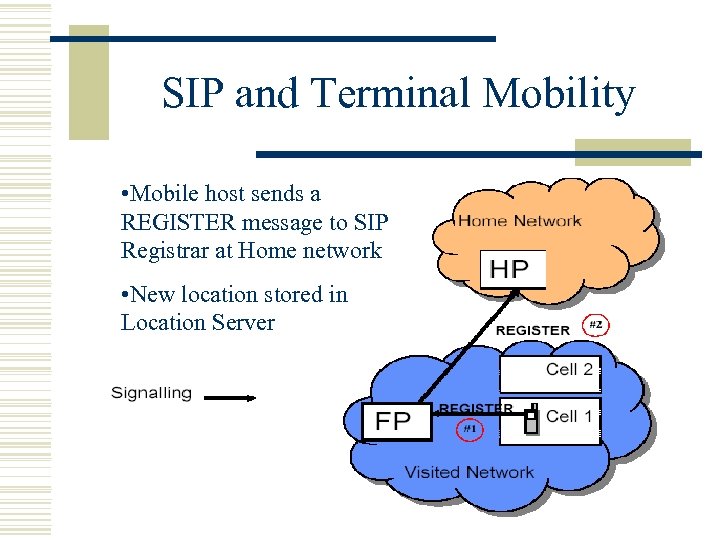
SIP and Terminal Mobility • Mobile host sends a REGISTER message to SIP Registrar at Home network • New location stored in Location Server
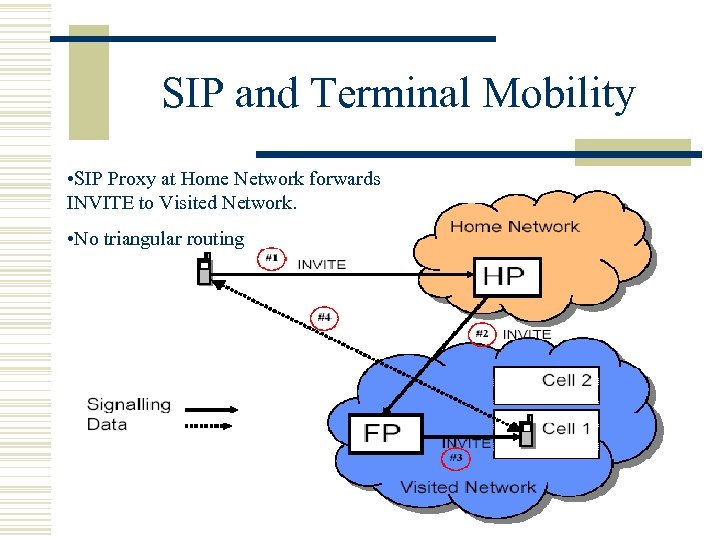
SIP and Terminal Mobility • SIP Proxy at Home Network forwards INVITE to Visited Network. • No triangular routing
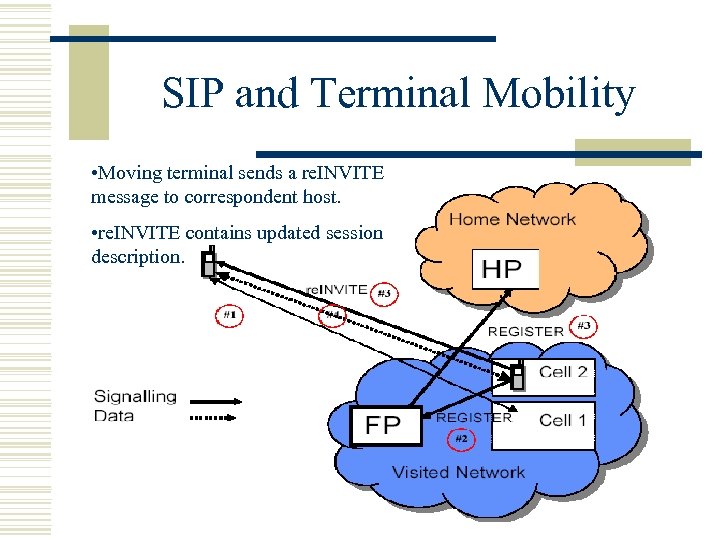
SIP and Terminal Mobility • Moving terminal sends a re. INVITE message to correspondent host. • re. INVITE contains updated session description.

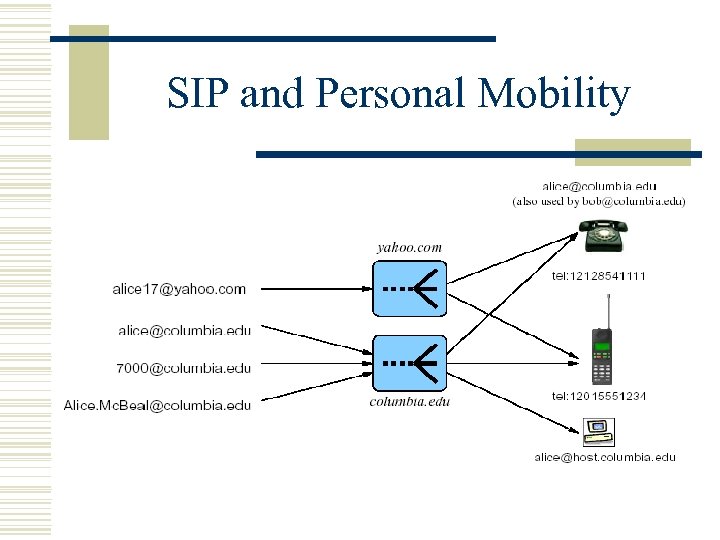
SIP and Personal Mobility w Allows to address a single user located at different terminals by the same logical address. w 1 -to-n (one address, many terminals) w M-to-1(many addresses reaching one terminal)
SIP and Personal Mobility

SIP and Personal Mobility w REGISTER binds a person to a device. w Proxy and Redirect translate address to location and device. w Need mapping mechanisms to recognize registrations as belonging to the same person

SIP and Service Mobility w Allows users to maintain access to their services while moving or changing devices and network service providers. n Speed dial list, address book, buddy list etc. w The services are located at ”home” server, associated with the user’s address. n Only end system can be used to propagate service information.
bfc70e6641c5bfe0ea84def5163c7c83.ppt