0f9cfe8a184b9d7183e53e79b4342602.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 Single Window Concepts and Models Ag Naden Vencatachellum Head of Information Technology, Customs Mauritius Revenue Authority Tel: (230) 202 20501 Mob: (230) 727 3384 Naden. vencatachellum@mra. mu (30 th March 2011, Antigua, Guatemala)
Single Window Concepts and Models Ag Naden Vencatachellum Head of Information Technology, Customs Mauritius Revenue Authority Tel: (230) 202 20501 Mob: (230) 727 3384 Naden. vencatachellum@mra. mu (30 th March 2011, Antigua, Guatemala)
 Single Window To comply with imports, exports and transitrelated requirements, traders need to ◦ Submit large amount of info to different authorities ◦ Provide info as early as possible (advanced information) Increasingly complex to coordinate effectively with other agencies in our trade facilitation endeavour. Single Window is the solution Trade facilitation tool – effective way of reducing non-tariff barriers
Single Window To comply with imports, exports and transitrelated requirements, traders need to ◦ Submit large amount of info to different authorities ◦ Provide info as early as possible (advanced information) Increasingly complex to coordinate effectively with other agencies in our trade facilitation endeavour. Single Window is the solution Trade facilitation tool – effective way of reducing non-tariff barriers
 Single Window Definition – UN/CEFACT A Single Window is defined as a facility that allows parties involved in trade and transport to lodge standardized information and documents with a single entry point to fulfill all import, export, and transit-related regulatory requirements. If information is electronic, then individual data elements should only be submitted once. ” UN/CEFACT RECOMMENDATION No. 33
Single Window Definition – UN/CEFACT A Single Window is defined as a facility that allows parties involved in trade and transport to lodge standardized information and documents with a single entry point to fulfill all import, export, and transit-related regulatory requirements. If information is electronic, then individual data elements should only be submitted once. ” UN/CEFACT RECOMMENDATION No. 33
 Single Window Benefits Helps improve a country’s economic index by ◦ Reducing costs of doing business. ◦ Eliminating clearance delays – improve dwell time. Win – win concept Offers benefits both to the Government and traders
Single Window Benefits Helps improve a country’s economic index by ◦ Reducing costs of doing business. ◦ Eliminating clearance delays – improve dwell time. Win – win concept Offers benefits both to the Government and traders
 Benefits to Gov Enhance Traders compliance, and encourage further trade and open competition. More trade will automatically yield more revenue to the Government and, therefore, improve the economic health of the country. Transparency and predictability of doing business will attract further investments. Information are centralized at submission and, thereby, promoting effective risk assessment and management. More efficient and effective deployment of resources.
Benefits to Gov Enhance Traders compliance, and encourage further trade and open competition. More trade will automatically yield more revenue to the Government and, therefore, improve the economic health of the country. Transparency and predictability of doing business will attract further investments. Information are centralized at submission and, thereby, promoting effective risk assessment and management. More efficient and effective deployment of resources.
 Benefits to trading community Reduce delays and costs of trading. Enable Just-in-time philosophy Encourage business growth and expansion. Establishes a bond of trust between the Government and trading community. Improve dwell time drastically. Elements of uncertainty are removed, hence, more predictable business. Better usage of resources.
Benefits to trading community Reduce delays and costs of trading. Enable Just-in-time philosophy Encourage business growth and expansion. Establishes a bond of trust between the Government and trading community. Improve dwell time drastically. Elements of uncertainty are removed, hence, more predictable business. Better usage of resources.
 Single Window models Many classification criteria possible ◦ Physical v/s automation ◦ Ownership and funding: Solely Gov, solely private, partnership-PPP ◦ National Single Window v/s regional Single Window ◦ Design and architectural
Single Window models Many classification criteria possible ◦ Physical v/s automation ◦ Ownership and funding: Solely Gov, solely private, partnership-PPP ◦ National Single Window v/s regional Single Window ◦ Design and architectural
 Single Window models 3 clear models emerge – UN/CEFACT (Rec 33) ◦ Single Authority ◦ Single Automated system ◦ Automated Transaction system Though different flavours of a model have also been implemented.
Single Window models 3 clear models emerge – UN/CEFACT (Rec 33) ◦ Single Authority ◦ Single Automated system ◦ Automated Transaction system Though different flavours of a model have also been implemented.
 Single Window model Single Authority ◦ One authority takes the lead and accepts all the information or documents at a single entry point. ◦ Redirects them to the proper agencies or authorities accordingly. ◦ Very often Customs will play this coordinating role and will be the contact point for the trading community. ◦ Another flavour of that model – Customs performs the tasks on behalf of the agencies, e. g Sweden.
Single Window model Single Authority ◦ One authority takes the lead and accepts all the information or documents at a single entry point. ◦ Redirects them to the proper agencies or authorities accordingly. ◦ Very often Customs will play this coordinating role and will be the contact point for the trading community. ◦ Another flavour of that model – Customs performs the tasks on behalf of the agencies, e. g Sweden.
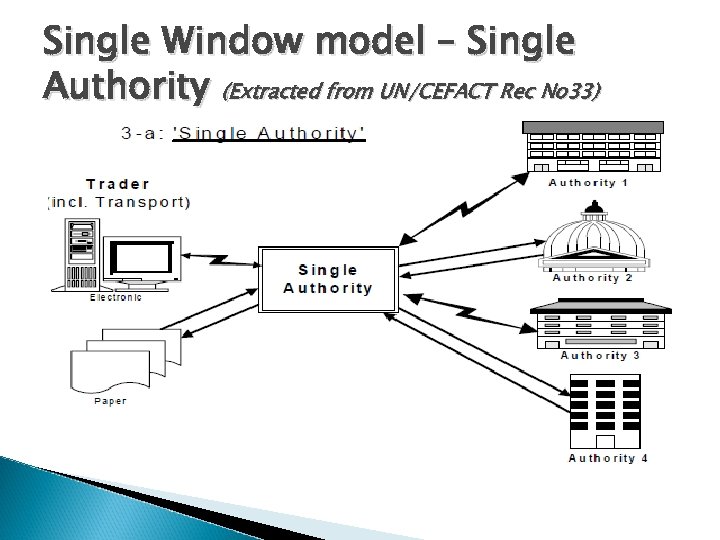 Single Window model – Single Authority (Extracted from UN/CEFACT Rec No 33)
Single Window model – Single Authority (Extracted from UN/CEFACT Rec No 33)
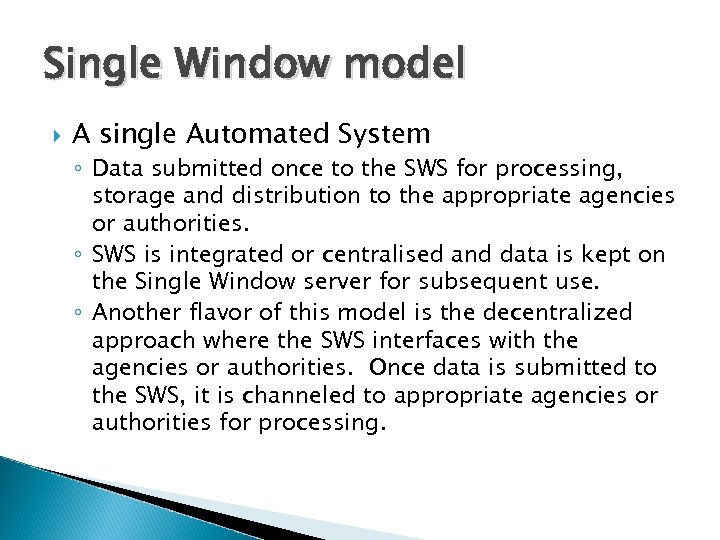 Single Window model A single Automated System ◦ Data submitted once to the SWS for processing, storage and distribution to the appropriate agencies or authorities. ◦ SWS is integrated or centralised and data is kept on the Single Window server for subsequent use. ◦ Another flavor of this model is the decentralized approach where the SWS interfaces with the agencies or authorities. Once data is submitted to the SWS, it is channeled to appropriate agencies or authorities for processing.
Single Window model A single Automated System ◦ Data submitted once to the SWS for processing, storage and distribution to the appropriate agencies or authorities. ◦ SWS is integrated or centralised and data is kept on the Single Window server for subsequent use. ◦ Another flavor of this model is the decentralized approach where the SWS interfaces with the agencies or authorities. Once data is submitted to the SWS, it is channeled to appropriate agencies or authorities for processing.
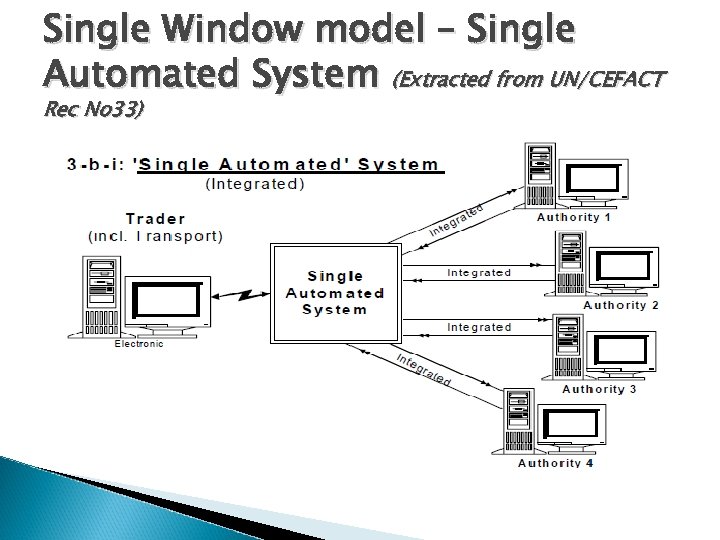 Single Window model – Single Automated System (Extracted from UN/CEFACT Rec No 33)
Single Window model – Single Automated System (Extracted from UN/CEFACT Rec No 33)
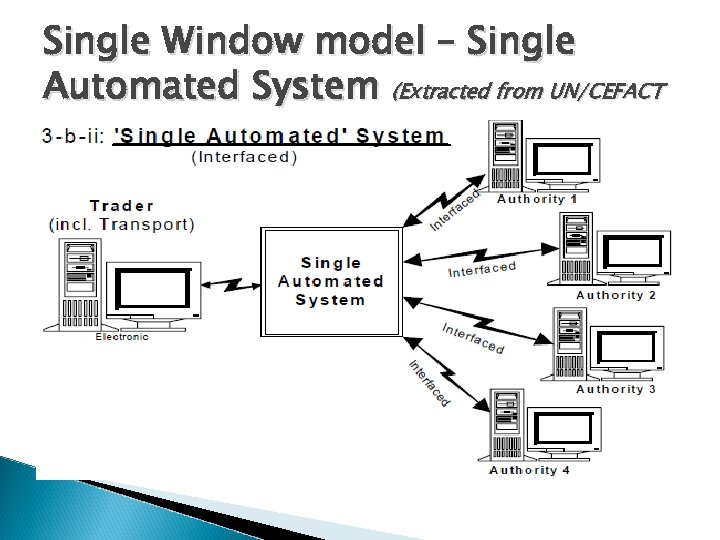 Single Window model – Single Automated System (Extracted from UN/CEFACT
Single Window model – Single Automated System (Extracted from UN/CEFACT
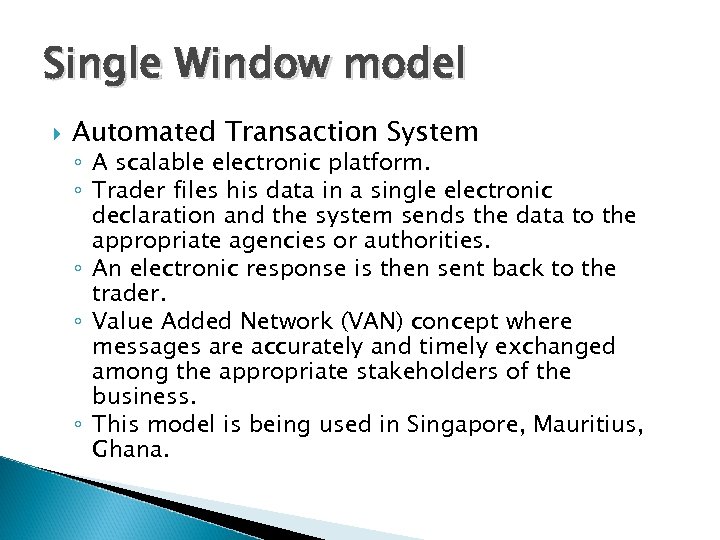 Single Window model Automated Transaction System ◦ A scalable electronic platform. ◦ Trader files his data in a single electronic declaration and the system sends the data to the appropriate agencies or authorities. ◦ An electronic response is then sent back to the trader. ◦ Value Added Network (VAN) concept where messages are accurately and timely exchanged among the appropriate stakeholders of the business. ◦ This model is being used in Singapore, Mauritius, Ghana.
Single Window model Automated Transaction System ◦ A scalable electronic platform. ◦ Trader files his data in a single electronic declaration and the system sends the data to the appropriate agencies or authorities. ◦ An electronic response is then sent back to the trader. ◦ Value Added Network (VAN) concept where messages are accurately and timely exchanged among the appropriate stakeholders of the business. ◦ This model is being used in Singapore, Mauritius, Ghana.
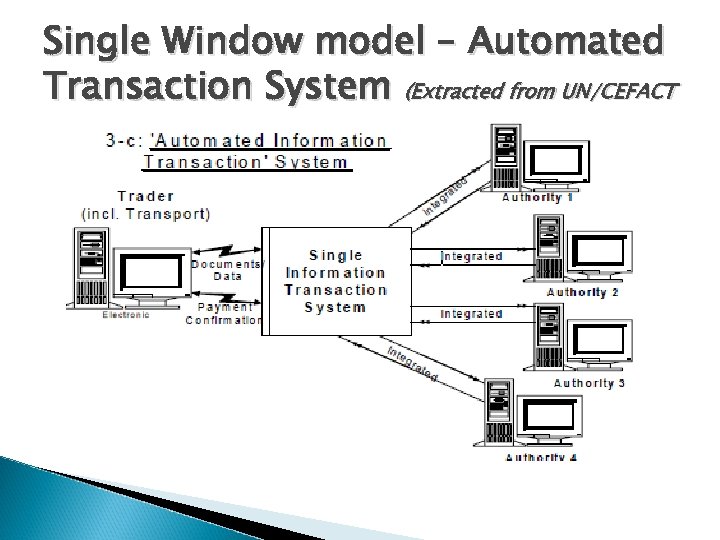 Single Window model – Automated Transaction System (Extracted from UN/CEFACT
Single Window model – Automated Transaction System (Extracted from UN/CEFACT
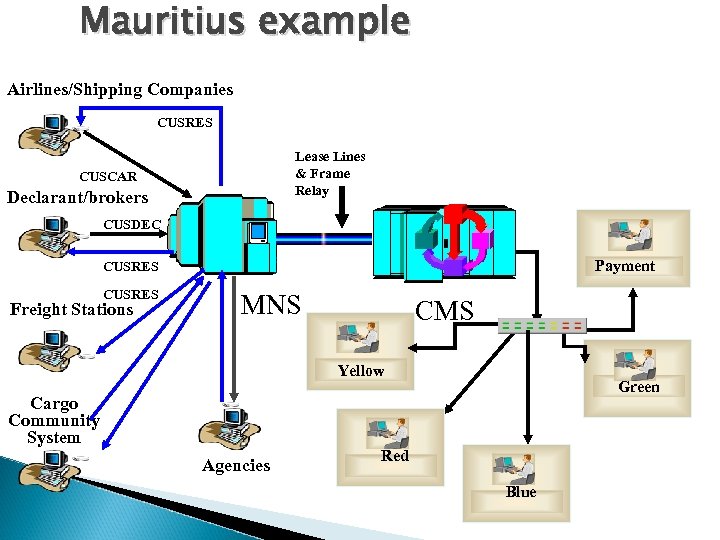 Mauritius example Airlines/Shipping Companies CUSRES Lease Lines & Frame Relay CUSCAR Declarant/brokers CUSDEC Payment CUSRES Freight Stations MNS CMS Yellow Cargo Community System Agencies Green Red Blue
Mauritius example Airlines/Shipping Companies CUSRES Lease Lines & Frame Relay CUSCAR Declarant/brokers CUSDEC Payment CUSRES Freight Stations MNS CMS Yellow Cargo Community System Agencies Green Red Blue
 Mauritius example Closed and secured environment. E-export certificates issued by Customs and hosted on Trade. Net website ◦ Eliminate risk of fake exports certificates Trade. Net moving towards web portal New security features will be in place ◦ Encryption ◦ DS ◦ Authentication etc
Mauritius example Closed and secured environment. E-export certificates issued by Customs and hosted on Trade. Net website ◦ Eliminate risk of fake exports certificates Trade. Net moving towards web portal New security features will be in place ◦ Encryption ◦ DS ◦ Authentication etc
 Trends in Single Window A country cannot operate in isolation now! Globalisation urges regional cooperation From National Single window to Regional Single Window. ◦ Effective sharing of information in the region for enhanced trade facilitation and better risk assessment. ◦ Single Window should be fully automated and support paperless trade.
Trends in Single Window A country cannot operate in isolation now! Globalisation urges regional cooperation From National Single window to Regional Single Window. ◦ Effective sharing of information in the region for enhanced trade facilitation and better risk assessment. ◦ Single Window should be fully automated and support paperless trade.
 Pre-requisites to successful implementation Commitment and support from high level. A leader is fundamental (Usually Customs). Legal framework should be in place. ◦ E. g epayment -> Electronic Transaction Act & regulations. Simplification and streamlining of procedures of all the actors (Customs, OGA etc). Simplication and harmonisation of the data sets to be used. Choose the right technical solution in line with your countries infrastructure. Sound project management & change mgt.
Pre-requisites to successful implementation Commitment and support from high level. A leader is fundamental (Usually Customs). Legal framework should be in place. ◦ E. g epayment -> Electronic Transaction Act & regulations. Simplification and streamlining of procedures of all the actors (Customs, OGA etc). Simplication and harmonisation of the data sets to be used. Choose the right technical solution in line with your countries infrastructure. Sound project management & change mgt.
 Guidance and help Revised Kyoto Convention. UN / CEFACT Recommendation and guidelines on establishing a Single Window, Rec No 33. UN / CEFACT Recommendation No 18 – Alignment of documents WCO Data Model 3. 0 – GOVCBR WCO Single Window Data Harmonisaion Guideline WCO Templates for OGA business process and data mapping. UNe. Docs – standardization of documents. UN/CEFACT Modelling Methodology (UMM) – to model the business process. WCO Unique Consignment Reference (UCR).
Guidance and help Revised Kyoto Convention. UN / CEFACT Recommendation and guidelines on establishing a Single Window, Rec No 33. UN / CEFACT Recommendation No 18 – Alignment of documents WCO Data Model 3. 0 – GOVCBR WCO Single Window Data Harmonisaion Guideline WCO Templates for OGA business process and data mapping. UNe. Docs – standardization of documents. UN/CEFACT Modelling Methodology (UMM) – to model the business process. WCO Unique Consignment Reference (UCR).
 Thank you for your attention
Thank you for your attention


