cea68cb0428249387a8c7df77c22eabb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 50
 SIMULTANEOUS DETECTION OF EXPLOSIVES AND NUCLEAR MATERIALS USING MONO-ENERGETIC HIGH ENERGY GAMMA RAYS Scientific Innovations, Inc. Joseph Brondo President and CEO Brookhaven National Laboratory Lucian Wielopolski, P. I. Inc. Office of Science and Technology Policy (OSTP) Innovations Executive Office of the President SCIENTIFIC January 11, 2006 SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
SIMULTANEOUS DETECTION OF EXPLOSIVES AND NUCLEAR MATERIALS USING MONO-ENERGETIC HIGH ENERGY GAMMA RAYS Scientific Innovations, Inc. Joseph Brondo President and CEO Brookhaven National Laboratory Lucian Wielopolski, P. I. Inc. Office of Science and Technology Policy (OSTP) Innovations Executive Office of the President SCIENTIFIC January 11, 2006 SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
 PURPOSE 1. Obtain Funding sufficient to provide a full scale demonstration system for all applications of gamma resonance technology. 2. Explosives and IED detection in transmission and standoff modes. 3. Demonstration of simultaneous detection of explosives and nuclear materials. SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
PURPOSE 1. Obtain Funding sufficient to provide a full scale demonstration system for all applications of gamma resonance technology. 2. Explosives and IED detection in transmission and standoff modes. 3. Demonstration of simultaneous detection of explosives and nuclear materials. SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
 CAPABILITY n n n Open architecture allows for specific designs for each application Applications include vehicles , containers, borders, perimeters, luggage, cargo, IEDs Detection configurations for portal, standoff and remote Multiple Mono-energetic Gamma Beam Capability 3 -D tomographic imaging of total contents with simultaneous imaging by element Fully automated decision capability without operator interpretation of image or data SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
CAPABILITY n n n Open architecture allows for specific designs for each application Applications include vehicles , containers, borders, perimeters, luggage, cargo, IEDs Detection configurations for portal, standoff and remote Multiple Mono-energetic Gamma Beam Capability 3 -D tomographic imaging of total contents with simultaneous imaging by element Fully automated decision capability without operator interpretation of image or data SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
 Physics –Radiation Interaction with Matter Gamma Resonance Technology, GRT is based on resonance interaction of gamma radiation with a specific level in a nucleus of an element of interest, e. g. , N, O, Cl, and detection of the transmitted incident radiation or that induced by nuclear fluorescence. Photo-Fission Technology, PFT is based on nuclear absorption of energetic gamma rays that above threshold energy induce fission in fissile materials, e. g. , U-235, Pu-239, Th-232, and subsequent detection of the emitted delayed neutrons. High-Z Detection Technology, HZT is based on attenuation of dual or triple high energy gamma beams and solving simultaneous transmission equations for resolving high- and low-z materials. SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
Physics –Radiation Interaction with Matter Gamma Resonance Technology, GRT is based on resonance interaction of gamma radiation with a specific level in a nucleus of an element of interest, e. g. , N, O, Cl, and detection of the transmitted incident radiation or that induced by nuclear fluorescence. Photo-Fission Technology, PFT is based on nuclear absorption of energetic gamma rays that above threshold energy induce fission in fissile materials, e. g. , U-235, Pu-239, Th-232, and subsequent detection of the emitted delayed neutrons. High-Z Detection Technology, HZT is based on attenuation of dual or triple high energy gamma beams and solving simultaneous transmission equations for resolving high- and low-z materials. SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
 Basic Characteristics • Simultaneous inspection for explosives and nuclear materials • Monoenergetic high energy gamma rays ~ 10 Me. V • High throughput • Specific signature for explosives • Fully automated decision making • Single source can feed multiple inspection stations • Low false alarm rate (<5%) • No residual activation or site contamination • Elemental 3 -D imaging capability SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
Basic Characteristics • Simultaneous inspection for explosives and nuclear materials • Monoenergetic high energy gamma rays ~ 10 Me. V • High throughput • Specific signature for explosives • Fully automated decision making • Single source can feed multiple inspection stations • Low false alarm rate (<5%) • No residual activation or site contamination • Elemental 3 -D imaging capability SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
 Public Safety • Accelerator produces low energy x-rays. • Target produces only gamma radiation, no neutrons. • Shielded highly collimated beam. • Dose to image N in human body 0. 026 mrem. • Dose to stowaway will be considerable lower. • Gamma flux is two to three orders of magnitude lower than for VACIS or CT systems. SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
Public Safety • Accelerator produces low energy x-rays. • Target produces only gamma radiation, no neutrons. • Shielded highly collimated beam. • Dose to image N in human body 0. 026 mrem. • Dose to stowaway will be considerable lower. • Gamma flux is two to three orders of magnitude lower than for VACIS or CT systems. SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
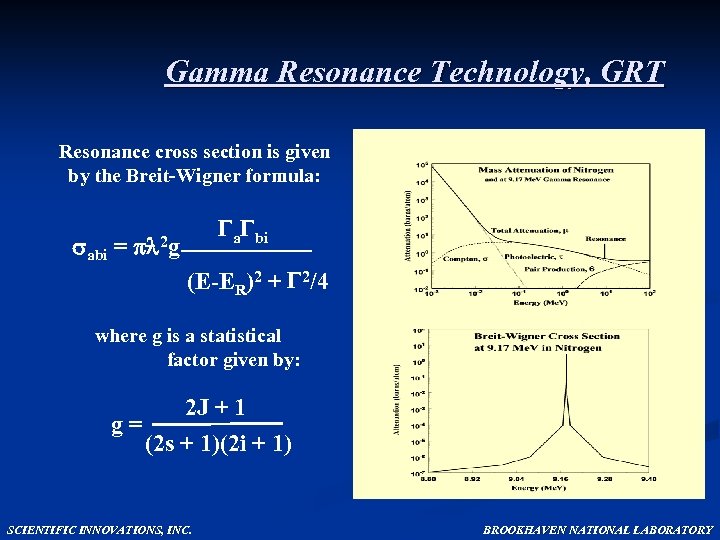 Gamma Resonance Technology, GRT Resonance cross section is given by the Breit-Wigner formula: abi a bi = 2 g (E-ER)2 + 2/4 where g is a statistical factor given by: 2 J + 1 g = (2 s + 1)(2 i + 1) SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
Gamma Resonance Technology, GRT Resonance cross section is given by the Breit-Wigner formula: abi a bi = 2 g (E-ER)2 + 2/4 where g is a statistical factor given by: 2 J + 1 g = (2 s + 1)(2 i + 1) SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
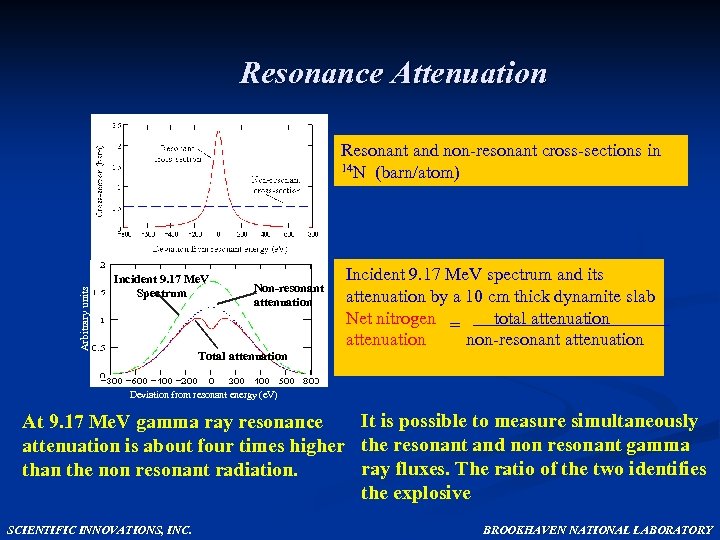 Resonance Attenuation Arbitrary units Resonant and non-resonant cross-sections in 14 N (barn/atom) Incident 9. 17 Me. V Spectrum Non-resonant attenuation Incident 9. 17 Me. V spectrum and its attenuation by a 10 cm thick dynamite slab Net nitrogen = total attenuation non-resonant attenuation Total attenuation Deviation from resonant energy (e. V) It is possible to measure simultaneously At 9. 17 Me. V gamma ray resonance attenuation is about four times higher the resonant and non resonant gamma ray fluxes. The ratio of the two identifies than the non resonant radiation. the explosive SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
Resonance Attenuation Arbitrary units Resonant and non-resonant cross-sections in 14 N (barn/atom) Incident 9. 17 Me. V Spectrum Non-resonant attenuation Incident 9. 17 Me. V spectrum and its attenuation by a 10 cm thick dynamite slab Net nitrogen = total attenuation non-resonant attenuation Total attenuation Deviation from resonant energy (e. V) It is possible to measure simultaneously At 9. 17 Me. V gamma ray resonance attenuation is about four times higher the resonant and non resonant gamma ray fluxes. The ratio of the two identifies than the non resonant radiation. the explosive SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
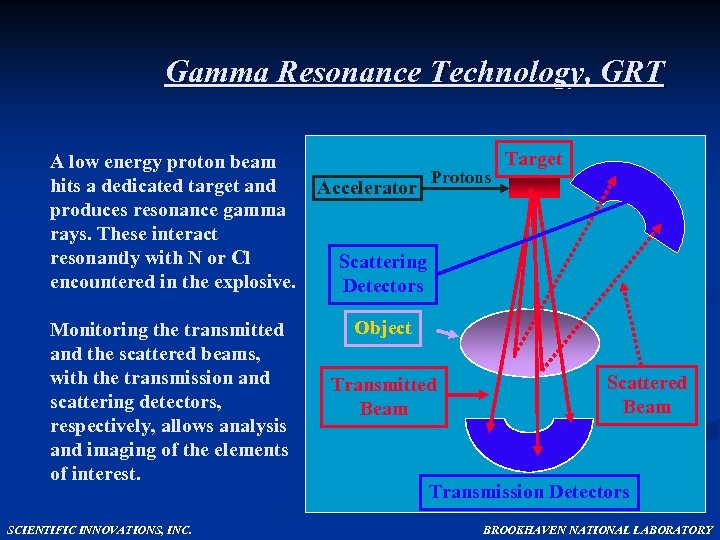 Gamma Resonance Technology, GRT A low energy proton beam hits a dedicated target and produces resonance gamma rays. These interact resonantly with N or Cl encountered in the explosive. Monitoring the transmitted and the scattered beams, with the transmission and scattering detectors, respectively, allows analysis and imaging of the elements of interest. SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. Accelerator Protons Target Scattering Detectors Object Transmitted Beam Scattered Beam Transmission Detectors BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
Gamma Resonance Technology, GRT A low energy proton beam hits a dedicated target and produces resonance gamma rays. These interact resonantly with N or Cl encountered in the explosive. Monitoring the transmitted and the scattered beams, with the transmission and scattering detectors, respectively, allows analysis and imaging of the elements of interest. SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. Accelerator Protons Target Scattering Detectors Object Transmitted Beam Scattered Beam Transmission Detectors BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
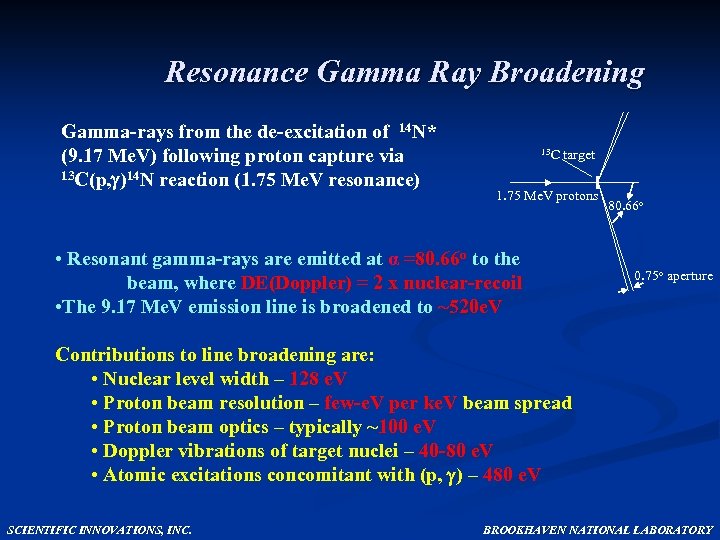 Resonance Gamma Ray Broadening Gamma-rays from the de-excitation of 14 N* (9. 17 Me. V) following proton capture via 13 C(p, )14 N reaction (1. 75 Me. V resonance) 13 C target 1. 75 Me. V protons • Resonant gamma-rays are emitted at α =80. 66 o to the beam, where DE(Doppler) = 2 x nuclear-recoil • The 9. 17 Me. V emission line is broadened to ~520 e. V 80. 66 o 0. 75 o aperture Contributions to line broadening are: • Nuclear level width – 128 e. V • Proton beam resolution – few-e. V per ke. V beam spread • Proton beam optics – typically ~100 e. V • Doppler vibrations of target nuclei – 40 -80 e. V • Atomic excitations concomitant with (p, ) – 480 e. V SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
Resonance Gamma Ray Broadening Gamma-rays from the de-excitation of 14 N* (9. 17 Me. V) following proton capture via 13 C(p, )14 N reaction (1. 75 Me. V resonance) 13 C target 1. 75 Me. V protons • Resonant gamma-rays are emitted at α =80. 66 o to the beam, where DE(Doppler) = 2 x nuclear-recoil • The 9. 17 Me. V emission line is broadened to ~520 e. V 80. 66 o 0. 75 o aperture Contributions to line broadening are: • Nuclear level width – 128 e. V • Proton beam resolution – few-e. V per ke. V beam spread • Proton beam optics – typically ~100 e. V • Doppler vibrations of target nuclei – 40 -80 e. V • Atomic excitations concomitant with (p, ) – 480 e. V SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
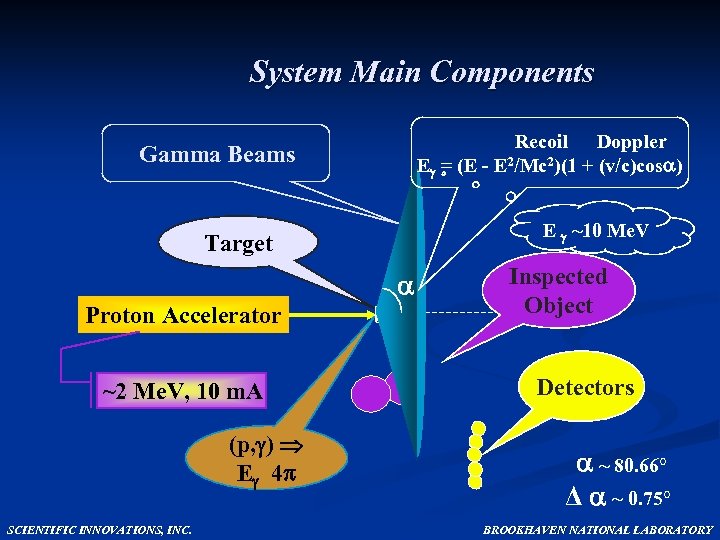 System Main Components Recoil Doppler E = (E - E 2/Mc 2)(1 + (v/c)cos ) Gamma Beams E ~10 Me. V Target Proton Accelerator ~2 Me. V, 10 m. A (p, ) E 4 SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. Inspected Object Detectors ~ 80. 66° Δ ~ 0. 75° BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
System Main Components Recoil Doppler E = (E - E 2/Mc 2)(1 + (v/c)cos ) Gamma Beams E ~10 Me. V Target Proton Accelerator ~2 Me. V, 10 m. A (p, ) E 4 SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. Inspected Object Detectors ~ 80. 66° Δ ~ 0. 75° BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
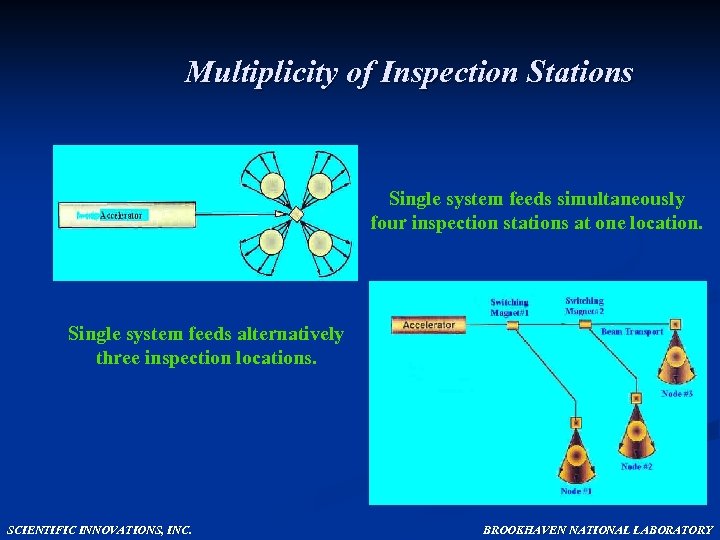 Multiplicity of Inspection Stations Single system feeds simultaneously four inspection stations at one location. Single system feeds alternatively three inspection locations. SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
Multiplicity of Inspection Stations Single system feeds simultaneously four inspection stations at one location. Single system feeds alternatively three inspection locations. SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
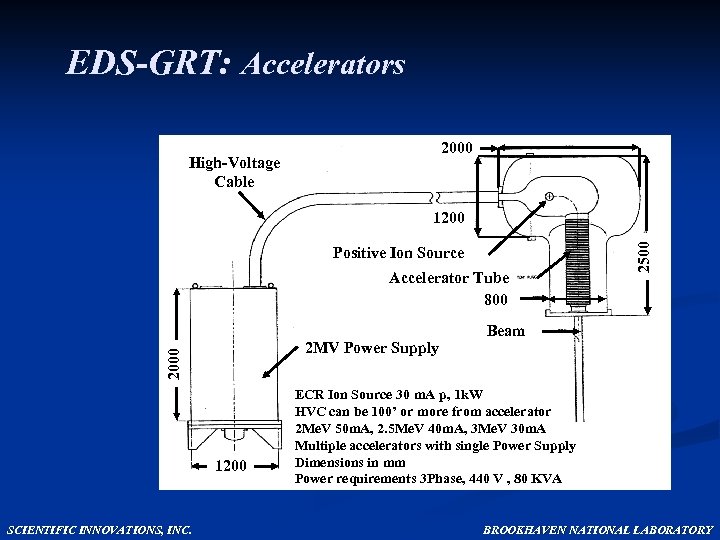 EDS-GRT: Accelerators 2000 High-Voltage Cable Positive Ion Source Accelerator Tube 800 2000 2 MV Power Supply 1200 SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. 2500 1200 Beam ECR Ion Source 30 m. A p, 1 k. W HVC can be 100’ or more from accelerator 2 Me. V 50 m. A, 2. 5 Me. V 40 m. A, 3 Me. V 30 m. A Multiple accelerators with single Power Supply Dimensions in mm Power requirements 3 Phase, 440 V , 80 KVA BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
EDS-GRT: Accelerators 2000 High-Voltage Cable Positive Ion Source Accelerator Tube 800 2000 2 MV Power Supply 1200 SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. 2500 1200 Beam ECR Ion Source 30 m. A p, 1 k. W HVC can be 100’ or more from accelerator 2 Me. V 50 m. A, 2. 5 Me. V 40 m. A, 3 Me. V 30 m. A Multiple accelerators with single Power Supply Dimensions in mm Power requirements 3 Phase, 440 V , 80 KVA BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
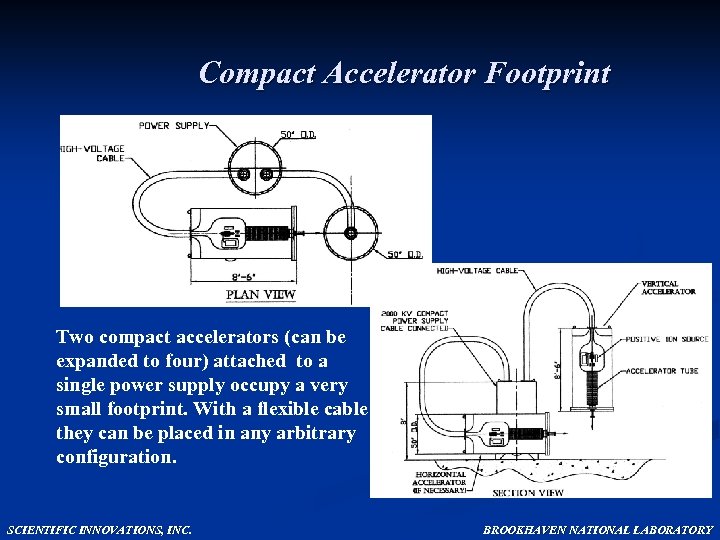 Compact Accelerator Footprint Two compact accelerators (can be expanded to four) attached to a single power supply occupy a very small footprint. With a flexible cable they can be placed in any arbitrary configuration. SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
Compact Accelerator Footprint Two compact accelerators (can be expanded to four) attached to a single power supply occupy a very small footprint. With a flexible cable they can be placed in any arbitrary configuration. SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
 Accelerator Specifications High Voltage Beam Current Energy Stability (including ripple) Beam Intensity Stability Normalized Emittance Electron suppression on column Energy regulation Auxiliary voltage regulation Ripple detection Beam diagnostics Operation and display SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. ~2 MV 10 m. A per head ± 1 ke. V ± 5% <6 mm-mrad in each plane reduce x-ray radiation based on 90 deg. doublefocusing magnet and slit system based on generating voltmeter based on capacitive pick-up two beam profiles monitors, two Faraday cups with electrometer digital, PC controlled BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
Accelerator Specifications High Voltage Beam Current Energy Stability (including ripple) Beam Intensity Stability Normalized Emittance Electron suppression on column Energy regulation Auxiliary voltage regulation Ripple detection Beam diagnostics Operation and display SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. ~2 MV 10 m. A per head ± 1 ke. V ± 5% <6 mm-mrad in each plane reduce x-ray radiation based on 90 deg. doublefocusing magnet and slit system based on generating voltmeter based on capacitive pick-up two beam profiles monitors, two Faraday cups with electrometer digital, PC controlled BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
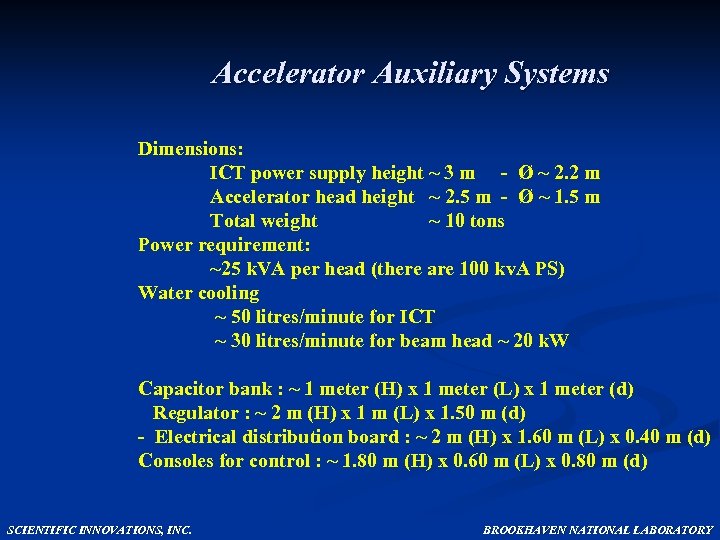 Accelerator Auxiliary Systems Dimensions: ICT power supply height ~ 3 m - Ø ~ 2. 2 m Accelerator head height ~ 2. 5 m - Ø ~ 1. 5 m Total weight ~ 10 tons Power requirement: ~25 k. VA per head (there are 100 kv. A PS) Water cooling ~ 50 litres/minute for ICT ~ 30 litres/minute for beam head ~ 20 k. W Capacitor bank : ~ 1 meter (H) x 1 meter (L) x 1 meter (d) Regulator : ~ 2 m (H) x 1 m (L) x 1. 50 m (d) - Electrical distribution board : ~ 2 m (H) x 1. 60 m (L) x 0. 40 m (d) Consoles for control : ~ 1. 80 m (H) x 0. 60 m (L) x 0. 80 m (d) SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
Accelerator Auxiliary Systems Dimensions: ICT power supply height ~ 3 m - Ø ~ 2. 2 m Accelerator head height ~ 2. 5 m - Ø ~ 1. 5 m Total weight ~ 10 tons Power requirement: ~25 k. VA per head (there are 100 kv. A PS) Water cooling ~ 50 litres/minute for ICT ~ 30 litres/minute for beam head ~ 20 k. W Capacitor bank : ~ 1 meter (H) x 1 meter (L) x 1 meter (d) Regulator : ~ 2 m (H) x 1 m (L) x 1. 50 m (d) - Electrical distribution board : ~ 2 m (H) x 1. 60 m (L) x 0. 40 m (d) Consoles for control : ~ 1. 80 m (H) x 0. 60 m (L) x 0. 80 m (d) SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
 Accelerator Operation Hydrogen gas refilling, annually Target unknown ECR ion source inspected annually PC Controlled 7/24 operation automated unattended Tube 5000 h beam time Minimal training SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
Accelerator Operation Hydrogen gas refilling, annually Target unknown ECR ion source inspected annually PC Controlled 7/24 operation automated unattended Tube 5000 h beam time Minimal training SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
 PC Controlled SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
PC Controlled SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
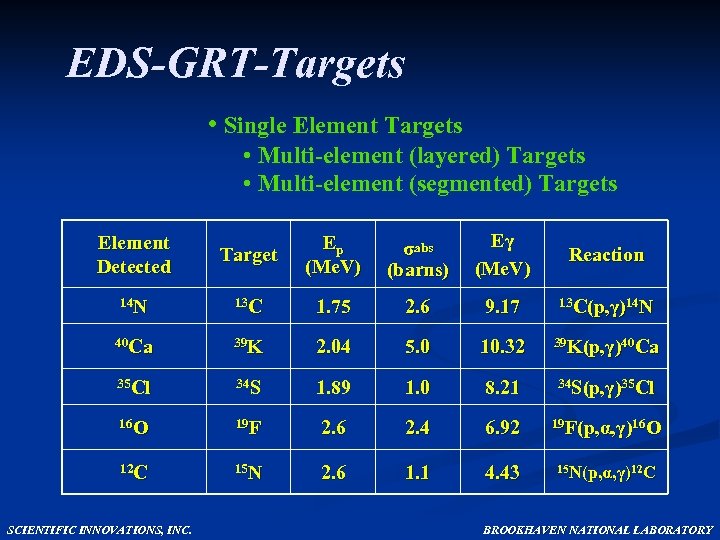 EDS-GRT-Targets • Single Element Targets • Multi-element (layered) Targets • Multi-element (segmented) Targets Target Ep (Me. V) σabs (barns) Eγ (Me. V) Reaction 14 N 13 C 1. 75 2. 6 9. 17 13 C(p, γ)14 N 40 Ca 39 K 2. 04 5. 0 10. 32 39 K(p, γ)40 Ca 35 Cl 34 S 1. 89 1. 0 8. 21 34 S(p, γ)35 Cl 16 O 19 F 2. 6 2. 4 6. 92 19 F(p, α, γ)16 O 12 C 15 N 2. 6 1. 1 4. 43 15 N(p, α, γ)12 C Element Detected SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
EDS-GRT-Targets • Single Element Targets • Multi-element (layered) Targets • Multi-element (segmented) Targets Target Ep (Me. V) σabs (barns) Eγ (Me. V) Reaction 14 N 13 C 1. 75 2. 6 9. 17 13 C(p, γ)14 N 40 Ca 39 K 2. 04 5. 0 10. 32 39 K(p, γ)40 Ca 35 Cl 34 S 1. 89 1. 0 8. 21 34 S(p, γ)35 Cl 16 O 19 F 2. 6 2. 4 6. 92 19 F(p, α, γ)16 O 12 C 15 N 2. 6 1. 1 4. 43 15 N(p, α, γ)12 C Element Detected SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
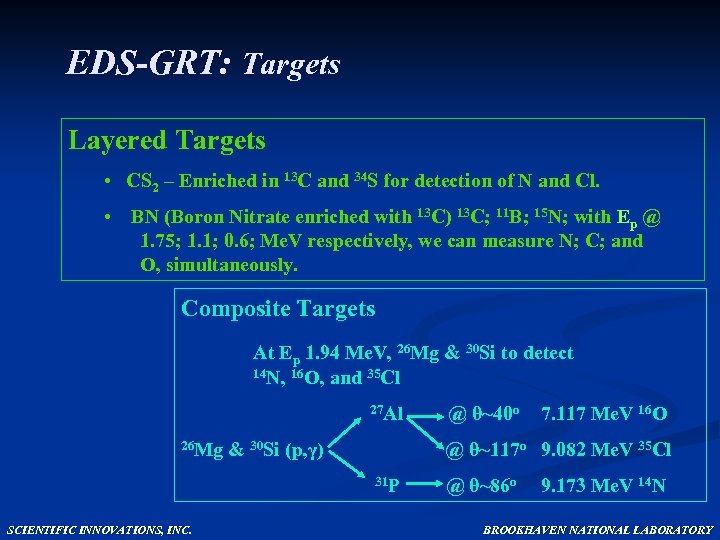 EDS-GRT: Targets Layered Targets • CS 2 – Enriched in 13 C and 34 S for detection of N and Cl. • BN (Boron Nitrate enriched with 13 C) 13 C; 11 B; 15 N; with Ep @ 1. 75; 1. 1; 0. 6; Me. V respectively, we can measure N; C; and O, simultaneously. Composite Targets At Ep 1. 94 Me. V, 26 Mg & 30 Si to detect 14 N, 16 O, and 35 Cl 27 Al @ θ~40 o 26 Mg & 30 Si (p, γ) @ θ~117 o 31 P @ θ~86 o SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. 7. 117 Me. V 16 O 9. 082 Me. V 35 Cl 9. 173 Me. V 14 N BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
EDS-GRT: Targets Layered Targets • CS 2 – Enriched in 13 C and 34 S for detection of N and Cl. • BN (Boron Nitrate enriched with 13 C) 13 C; 11 B; 15 N; with Ep @ 1. 75; 1. 1; 0. 6; Me. V respectively, we can measure N; C; and O, simultaneously. Composite Targets At Ep 1. 94 Me. V, 26 Mg & 30 Si to detect 14 N, 16 O, and 35 Cl 27 Al @ θ~40 o 26 Mg & 30 Si (p, γ) @ θ~117 o 31 P @ θ~86 o SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. 7. 117 Me. V 16 O 9. 082 Me. V 35 Cl 9. 173 Me. V 14 N BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
 Detectors Linear array of: Na. I, Resonance Detectors Bulk Detection: Liquid Scintillator Sandwich Detectors SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
Detectors Linear array of: Na. I, Resonance Detectors Bulk Detection: Liquid Scintillator Sandwich Detectors SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
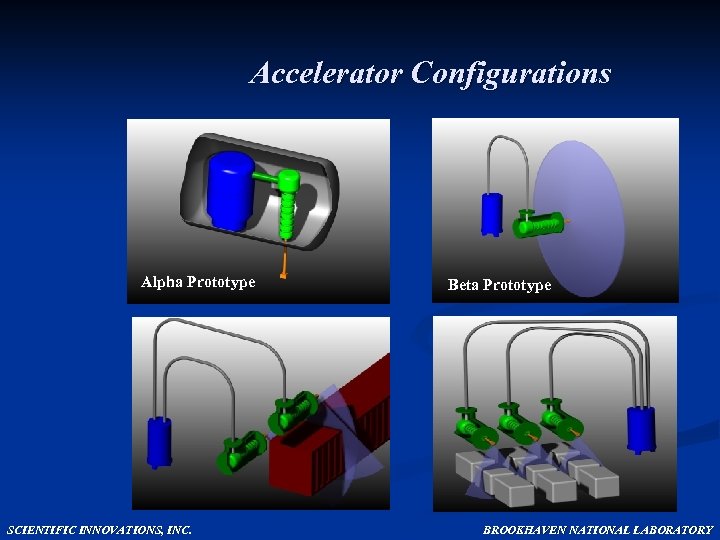 Accelerator Configurations Alpha Prototype SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. Beta Prototype BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
Accelerator Configurations Alpha Prototype SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. Beta Prototype BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
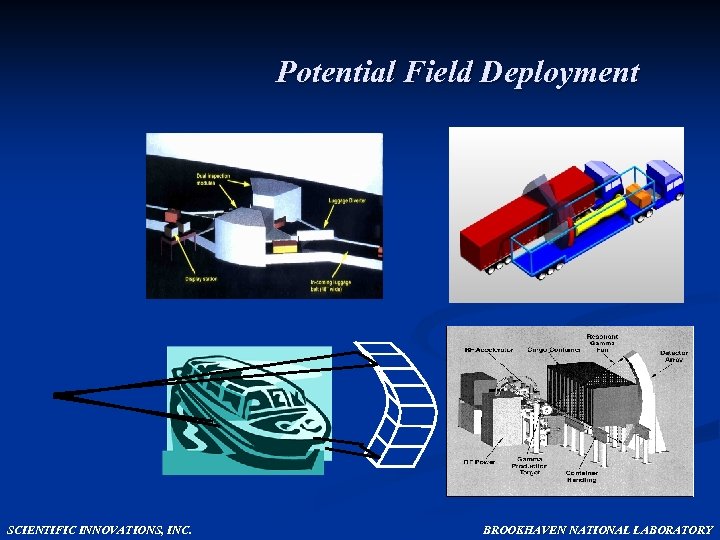 Potential Field Deployment SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
Potential Field Deployment SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
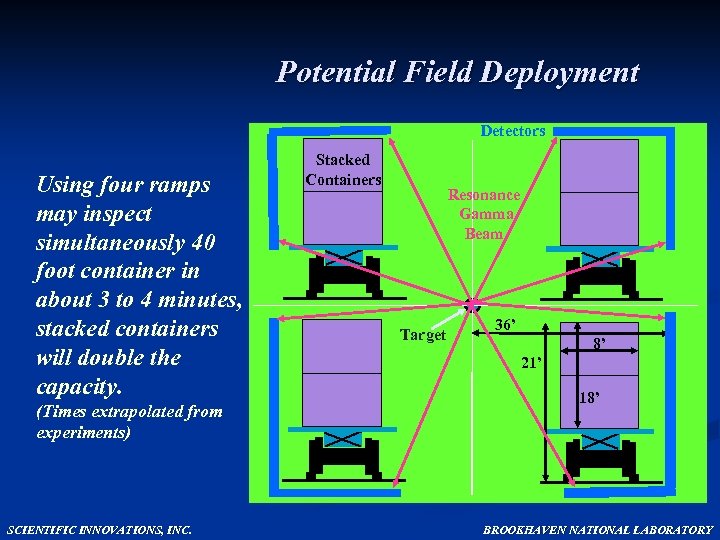 Potential Field Deployment Detectors Using four ramps may inspect simultaneously 40 foot container in about 3 to 4 minutes, stacked containers will double the capacity. (Times extrapolated from experiments) SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. Stacked Containers Resonance Gamma Beam Target 36’ 8’ 21’ 18’ BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
Potential Field Deployment Detectors Using four ramps may inspect simultaneously 40 foot container in about 3 to 4 minutes, stacked containers will double the capacity. (Times extrapolated from experiments) SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. Stacked Containers Resonance Gamma Beam Target 36’ 8’ 21’ 18’ BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
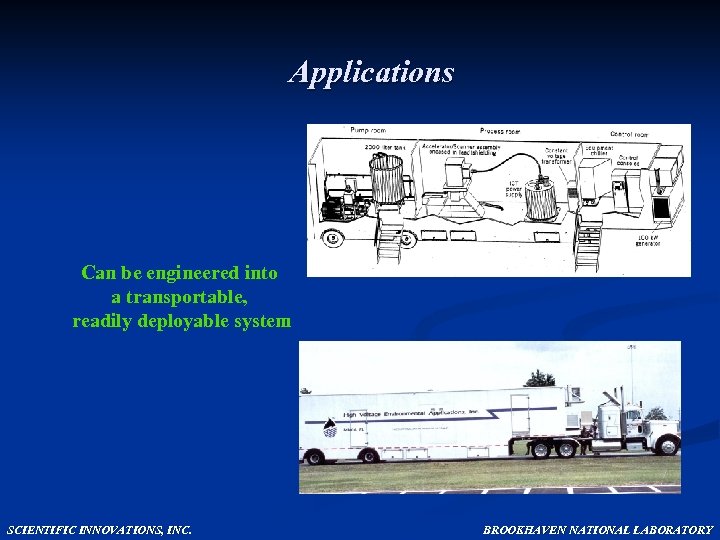 Applications Can be engineered into a transportable, readily deployable system SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
Applications Can be engineered into a transportable, readily deployable system SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
 GRT: Proof-of-Principle Nitrogenous and non-nitrogenous objects placed in a beam. Experiments carried out by Nahal Soreq Group Images: Out of resonance In resonance SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
GRT: Proof-of-Principle Nitrogenous and non-nitrogenous objects placed in a beam. Experiments carried out by Nahal Soreq Group Images: Out of resonance In resonance SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
 GRT: Demonstration on LD-3 Six explosives were hidden in a LD-3 container loaded with a mixed cargo. NRC Nahal Soreq group carried out these experiments using resonance detectors for nitrogen detection. Two images are created simultaneously. The upper image shows a regular gamma transmission radiograph. The lower image shows nitrogen image that clearly identifies the explosives. SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
GRT: Demonstration on LD-3 Six explosives were hidden in a LD-3 container loaded with a mixed cargo. NRC Nahal Soreq group carried out these experiments using resonance detectors for nitrogen detection. Two images are created simultaneously. The upper image shows a regular gamma transmission radiograph. The lower image shows nitrogen image that clearly identifies the explosives. SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
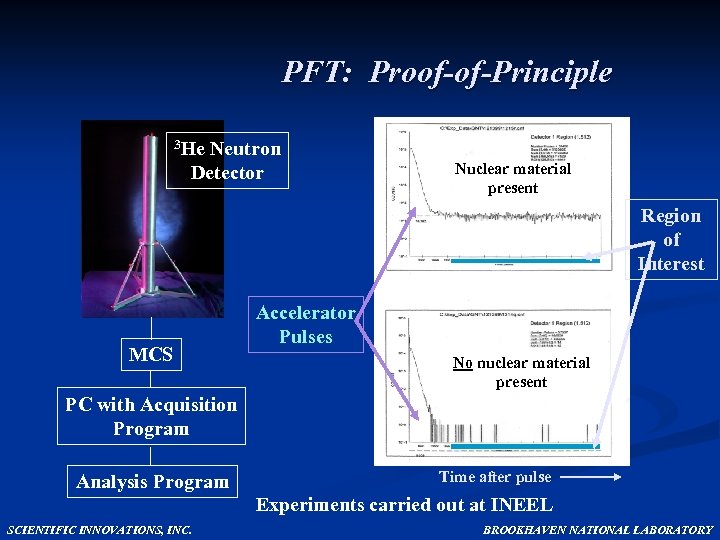 PFT: Proof-of-Principle 3 He Neutron Detector Nuclear material present Region of Interest MCS Accelerator Pulses No nuclear material present PC with Acquisition Program Analysis Program Time after pulse Experiments carried out at INEEL SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
PFT: Proof-of-Principle 3 He Neutron Detector Nuclear material present Region of Interest MCS Accelerator Pulses No nuclear material present PC with Acquisition Program Analysis Program Time after pulse Experiments carried out at INEEL SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
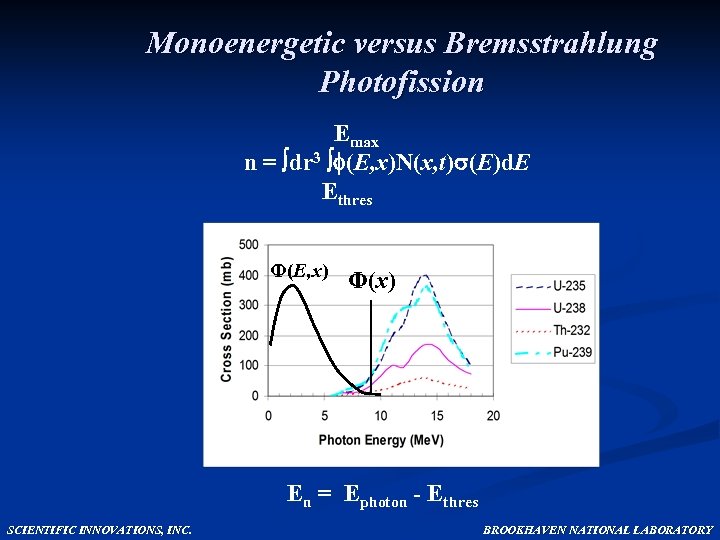 Monoenergetic versus Bremsstrahlung Photofission Emax n = dr 3 (E, x)N(x, t) (E)d. E Ethres Φ(E, x) Φ(x) En = Ephoton - Ethres SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
Monoenergetic versus Bremsstrahlung Photofission Emax n = dr 3 (E, x)N(x, t) (E)d. E Ethres Φ(E, x) Φ(x) En = Ephoton - Ethres SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
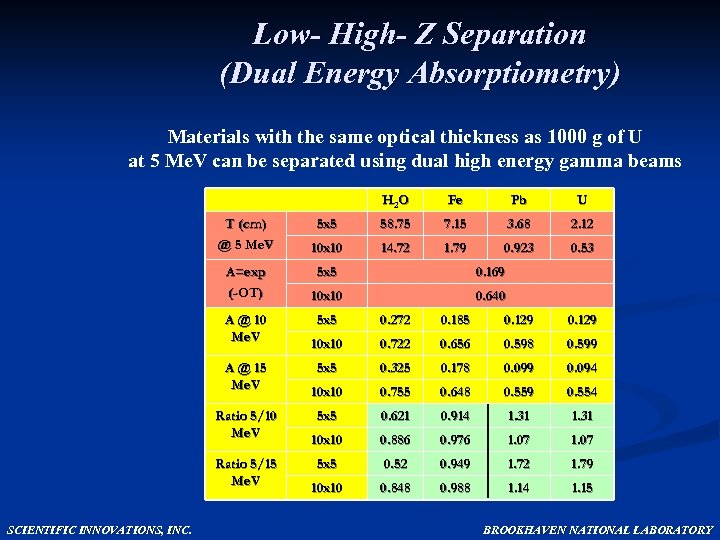 Low- High- Z Separation (Dual Energy Absorptiometry) Materials with the same optical thickness as 1000 g of U at 5 Me. V can be separated using dual high energy gamma beams H 2 O T (cm) @ 5 Me. V A=exp (-OT) A @ 10 Me. V A @ 15 Me. V Ratio 5/10 Me. V Ratio 5/15 Me. V SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. Fe Pb U 5 x 5 58. 75 7. 15 3. 68 2. 12 10 x 10 14. 72 1. 79 0. 923 0. 53 5 x 5 0. 169 10 x 10 0. 640 5 x 5 0. 272 0. 185 0. 129 10 x 10 0. 722 0. 656 0. 598 0. 599 5 x 5 0. 325 0. 178 0. 099 0. 094 10 x 10 0. 755 0. 648 0. 559 0. 554 5 x 5 0. 621 0. 914 1. 31 10 x 10 0. 886 0. 976 1. 07 5 x 5 0. 52 0. 949 1. 72 1. 79 10 x 10 0. 848 0. 988 1. 14 1. 15 BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
Low- High- Z Separation (Dual Energy Absorptiometry) Materials with the same optical thickness as 1000 g of U at 5 Me. V can be separated using dual high energy gamma beams H 2 O T (cm) @ 5 Me. V A=exp (-OT) A @ 10 Me. V A @ 15 Me. V Ratio 5/10 Me. V Ratio 5/15 Me. V SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. Fe Pb U 5 x 5 58. 75 7. 15 3. 68 2. 12 10 x 10 14. 72 1. 79 0. 923 0. 53 5 x 5 0. 169 10 x 10 0. 640 5 x 5 0. 272 0. 185 0. 129 10 x 10 0. 722 0. 656 0. 598 0. 599 5 x 5 0. 325 0. 178 0. 099 0. 094 10 x 10 0. 755 0. 648 0. 559 0. 554 5 x 5 0. 621 0. 914 1. 31 10 x 10 0. 886 0. 976 1. 07 5 x 5 0. 52 0. 949 1. 72 1. 79 10 x 10 0. 848 0. 988 1. 14 1. 15 BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
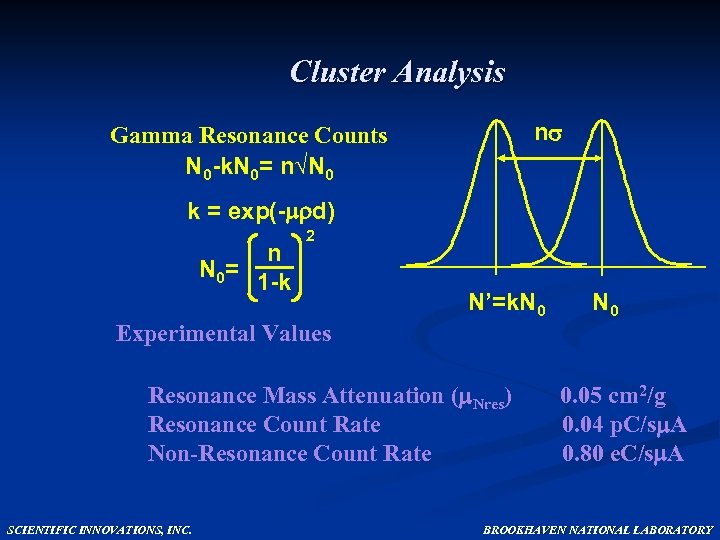 Cluster Analysis Gamma Resonance Counts N 0 -k. N 0= n√N 0 n k = exp(- d) n N 0= 1 -k 2 N’=k. N 0 Experimental Values Resonance Mass Attenuation ( Nres) 0. 05 cm 2/g Resonance Count Rate 0. 04 p. C/s A Non-Resonance Count Rate 0. 80 e. C/s A SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
Cluster Analysis Gamma Resonance Counts N 0 -k. N 0= n√N 0 n k = exp(- d) n N 0= 1 -k 2 N’=k. N 0 Experimental Values Resonance Mass Attenuation ( Nres) 0. 05 cm 2/g Resonance Count Rate 0. 04 p. C/s A Non-Resonance Count Rate 0. 80 e. C/s A SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
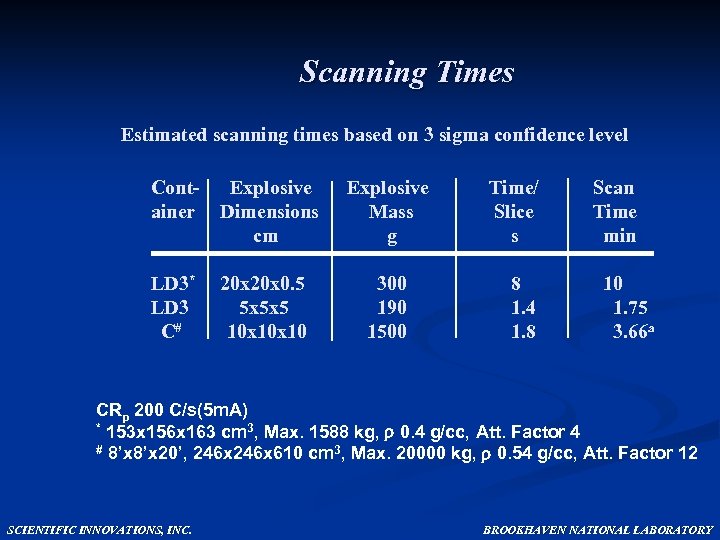 Scanning Times Estimated scanning times based on 3 sigma confidence level Cont- Explosive Time/ ainer Dimensions Mass Slice cm g s Scan Time min LD 3* 20 x 0. 5 LD 3 5 x 5 x 5 C# 10 x 10 10 1. 75 3. 66 a 300 190 1500 8 1. 4 1. 8 CRp 200 C/s(5 m. A) * 153 x 156 x 163 cm 3, Max. 1588 kg, 0. 4 g/cc, Att. Factor 4 # 8’x 20’, 246 x 610 cm 3, Max. 20000 kg, 0. 54 g/cc, Att. Factor 12 SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
Scanning Times Estimated scanning times based on 3 sigma confidence level Cont- Explosive Time/ ainer Dimensions Mass Slice cm g s Scan Time min LD 3* 20 x 0. 5 LD 3 5 x 5 x 5 C# 10 x 10 10 1. 75 3. 66 a 300 190 1500 8 1. 4 1. 8 CRp 200 C/s(5 m. A) * 153 x 156 x 163 cm 3, Max. 1588 kg, 0. 4 g/cc, Att. Factor 4 # 8’x 20’, 246 x 610 cm 3, Max. 20000 kg, 0. 54 g/cc, Att. Factor 12 SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
 Possible Locations SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
Possible Locations SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
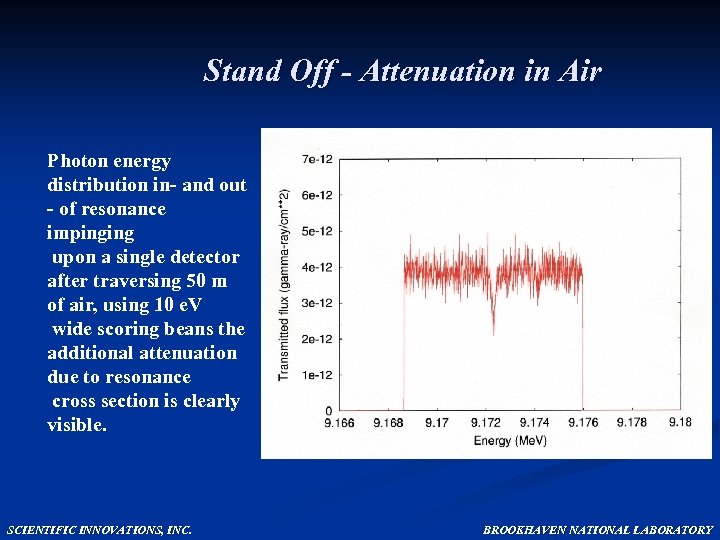 Stand Off - Attenuation in Air Photon energy distribution in- and out - of resonance impinging upon a single detector after traversing 50 m of air, using 10 e. V wide scoring beans the additional attenuation due to resonance cross section is clearly visible. SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
Stand Off - Attenuation in Air Photon energy distribution in- and out - of resonance impinging upon a single detector after traversing 50 m of air, using 10 e. V wide scoring beans the additional attenuation due to resonance cross section is clearly visible. SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
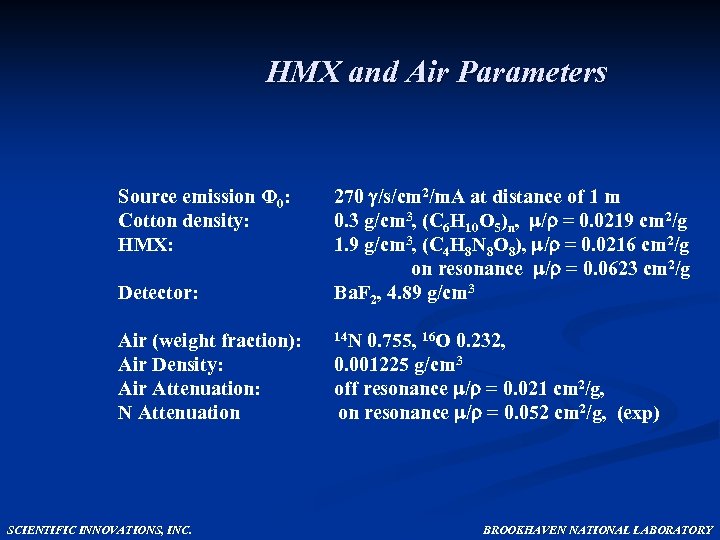 HMX and Air Parameters Source emission Φ 0: Cotton density: HMX: Detector: Air (weight fraction): Air Density: Air Attenuation: N Attenuation SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. 270 /s/cm 2/m. A at distance of 1 m 0. 3 g/cm 3, (C 6 H 10 O 5)n, / = 0. 0219 cm 2/g 1. 9 g/cm 3, (C 4 H 8 N 8 O 8), / = 0. 0216 cm 2/g on resonance / = 0. 0623 cm 2/g Ba. F 2, 4. 89 g/cm 3 14 N 0. 755, 16 O 0. 232, 0. 001225 g/cm 3 off resonance / = 0. 021 cm 2/g, on resonance / = 0. 052 cm 2/g, (exp) BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
HMX and Air Parameters Source emission Φ 0: Cotton density: HMX: Detector: Air (weight fraction): Air Density: Air Attenuation: N Attenuation SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. 270 /s/cm 2/m. A at distance of 1 m 0. 3 g/cm 3, (C 6 H 10 O 5)n, / = 0. 0219 cm 2/g 1. 9 g/cm 3, (C 4 H 8 N 8 O 8), / = 0. 0216 cm 2/g on resonance / = 0. 0623 cm 2/g Ba. F 2, 4. 89 g/cm 3 14 N 0. 755, 16 O 0. 232, 0. 001225 g/cm 3 off resonance / = 0. 021 cm 2/g, on resonance / = 0. 052 cm 2/g, (exp) BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
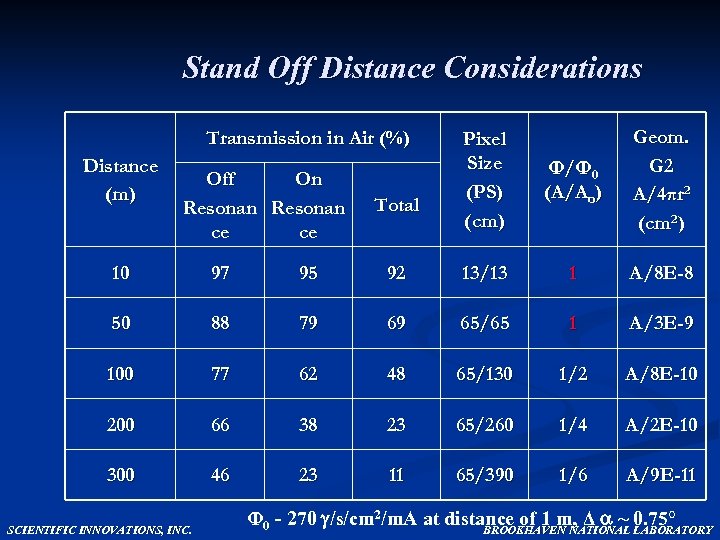 Stand Off Distance Considerations Transmission in Air (%) Distance (m) Off On Resonan ce ce Total Pixel Size (PS) (cm) Φ/ Φ 0 (A/Ao) Geom. G 2 A/4πr 2 (cm 2) 10 97 95 92 13/13 1 A/8 E-8 50 88 79 69 65/65 1 A/3 E-9 100 77 62 48 65/130 1/2 A/8 E-10 200 66 38 23 65/260 1/4 A/2 E-10 300 46 23 11 65/390 1/6 A/9 E-11 SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. Φ 0 - 270 /s/cm 2/m. A at distance of 1 m, Δ ~ 0. 75° BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
Stand Off Distance Considerations Transmission in Air (%) Distance (m) Off On Resonan ce ce Total Pixel Size (PS) (cm) Φ/ Φ 0 (A/Ao) Geom. G 2 A/4πr 2 (cm 2) 10 97 95 92 13/13 1 A/8 E-8 50 88 79 69 65/65 1 A/3 E-9 100 77 62 48 65/130 1/2 A/8 E-10 200 66 38 23 65/260 1/4 A/2 E-10 300 46 23 11 65/390 1/6 A/9 E-11 SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. Φ 0 - 270 /s/cm 2/m. A at distance of 1 m, Δ ~ 0. 75° BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
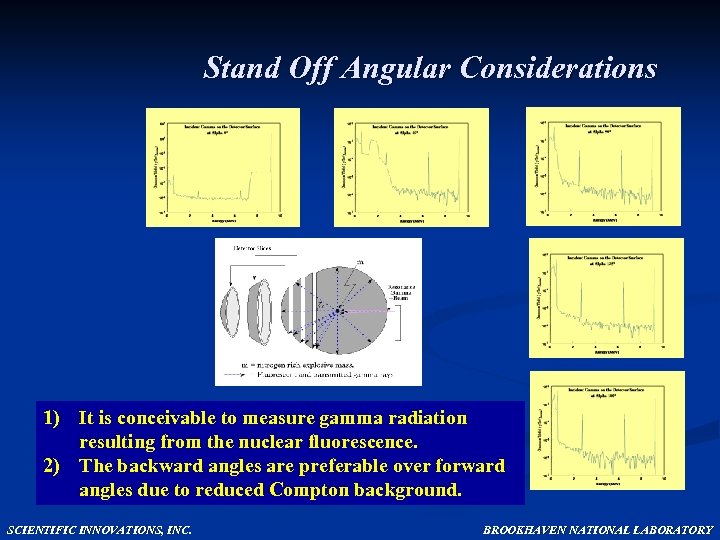 Stand Off Angular Considerations 1) It is conceivable to measure gamma radiation resulting from the nuclear fluorescence. 2) The backward angles are preferable over forward angles due to reduced Compton background. SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
Stand Off Angular Considerations 1) It is conceivable to measure gamma radiation resulting from the nuclear fluorescence. 2) The backward angles are preferable over forward angles due to reduced Compton background. SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
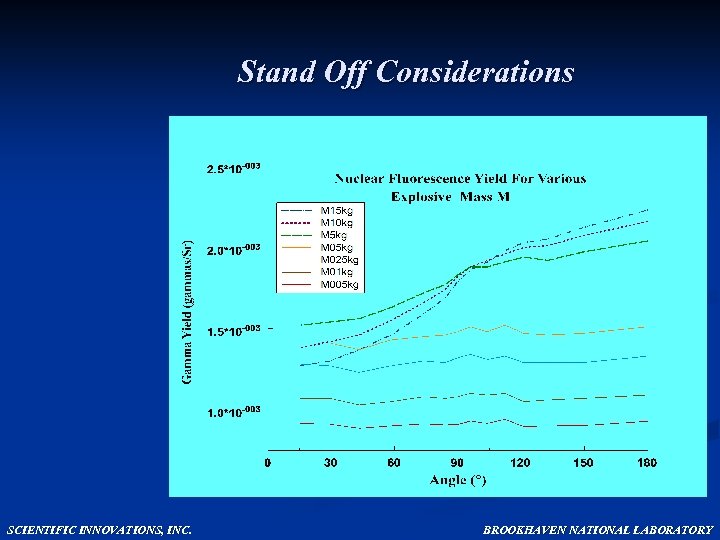 Stand Off Considerations SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
Stand Off Considerations SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
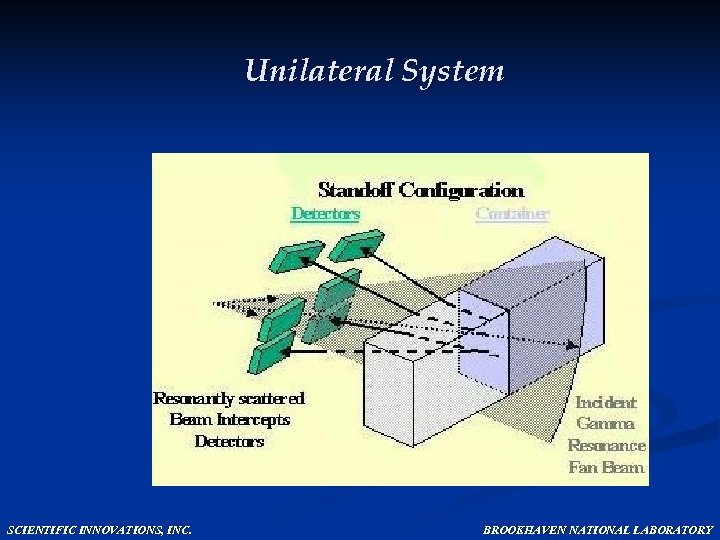 Unilateral System SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
Unilateral System SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
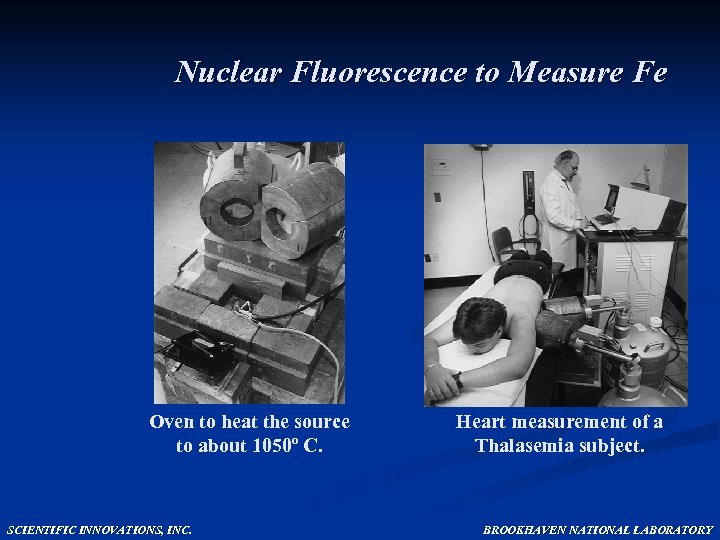 Nuclear Fluorescence to Measure Fe Oven to heat the source to about 1050º C. SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. Heart measurement of a Thalasemia subject. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
Nuclear Fluorescence to Measure Fe Oven to heat the source to about 1050º C. SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. Heart measurement of a Thalasemia subject. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
 Detection of Roadside Explosives SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
Detection of Roadside Explosives SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
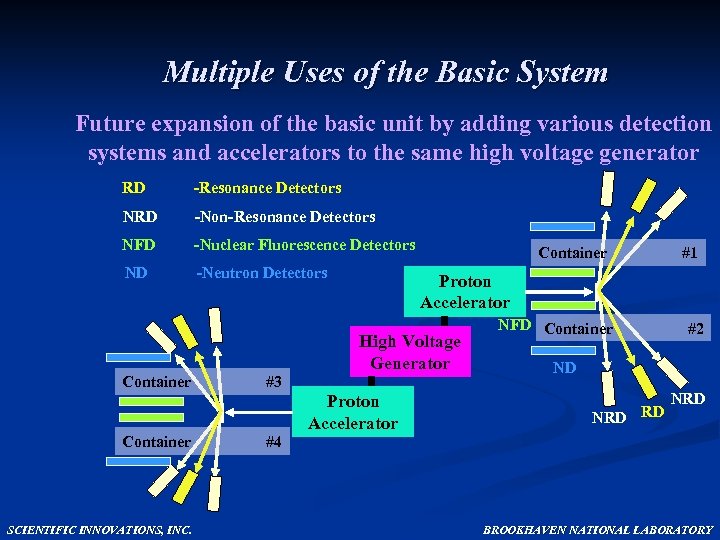 Multiple Uses of the Basic System Future expansion of the basic unit by adding various detection systems and accelerators to the same high voltage generator RD -Resonance Detectors NRD -Non-Resonance Detectors NFD -Nuclear Fluorescence Detectors ND -Neutron Detectors Container Proton Accelerator High Voltage Generator Container SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. #3 #4 #1 Proton Accelerator NFD Container #2 ND NRD RD NRD BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
Multiple Uses of the Basic System Future expansion of the basic unit by adding various detection systems and accelerators to the same high voltage generator RD -Resonance Detectors NRD -Non-Resonance Detectors NFD -Nuclear Fluorescence Detectors ND -Neutron Detectors Container Proton Accelerator High Voltage Generator Container SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. #3 #4 #1 Proton Accelerator NFD Container #2 ND NRD RD NRD BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
 Current Location at BNL The System Has Been Located at BNL in Bldg. 945 9 4 5 SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
Current Location at BNL The System Has Been Located at BNL in Bldg. 945 9 4 5 SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
 Technology Readiness Accelerator: ECR Ion Source ICT Power Supply Target Accelerator Integration T 9 T 5 Detectors: Conventional Resonance Sandwich System Integration SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. T 9 T 5 T 5 BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
Technology Readiness Accelerator: ECR Ion Source ICT Power Supply Target Accelerator Integration T 9 T 5 Detectors: Conventional Resonance Sandwich System Integration SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. T 9 T 5 T 5 BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
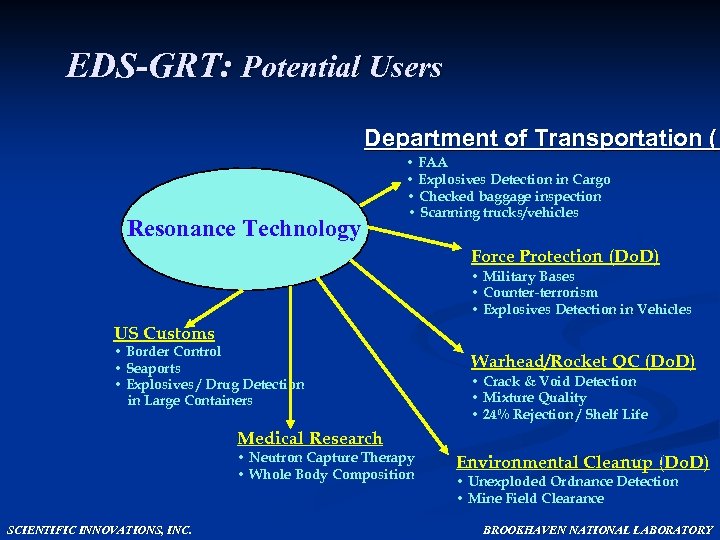 EDS-GRT: Potential Users Department of Transportation (D Resonance Technology • FAA • Explosives Detection in Cargo • Checked baggage inspection • Scanning trucks/vehicles Force Protection (Do. D) • Military Bases • Counter-terrorism • Explosives Detection in Vehicles US Customs • Border Control • Seaports • Explosives / Drug Detection in Large Containers Warhead/Rocket QC (Do. D) • Crack & Void Detection • Mixture Quality • 24% Rejection / Shelf Life Medical Research • Neutron Capture Therapy • Whole Body Composition SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. ) Environmental Cleanup (Do. D) • Unexploded Ordnance Detection • Mine Field Clearance BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
EDS-GRT: Potential Users Department of Transportation (D Resonance Technology • FAA • Explosives Detection in Cargo • Checked baggage inspection • Scanning trucks/vehicles Force Protection (Do. D) • Military Bases • Counter-terrorism • Explosives Detection in Vehicles US Customs • Border Control • Seaports • Explosives / Drug Detection in Large Containers Warhead/Rocket QC (Do. D) • Crack & Void Detection • Mixture Quality • 24% Rejection / Shelf Life Medical Research • Neutron Capture Therapy • Whole Body Composition SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. ) Environmental Cleanup (Do. D) • Unexploded Ordnance Detection • Mine Field Clearance BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
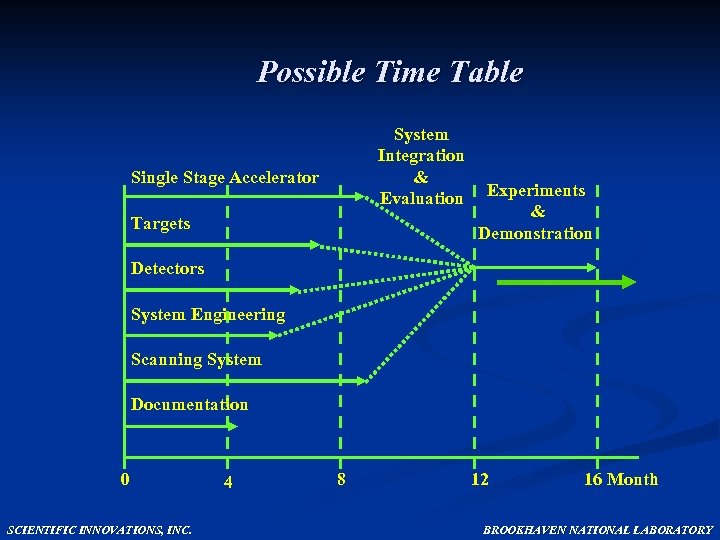 Possible Time Table System Integration & Evaluation Experiments & Demonstration Single Stage Accelerator Targets Detectors System Engineering Scanning System Documentation 0 SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. 4 8 12 16 Month BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
Possible Time Table System Integration & Evaluation Experiments & Demonstration Single Stage Accelerator Targets Detectors System Engineering Scanning System Documentation 0 SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. 4 8 12 16 Month BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
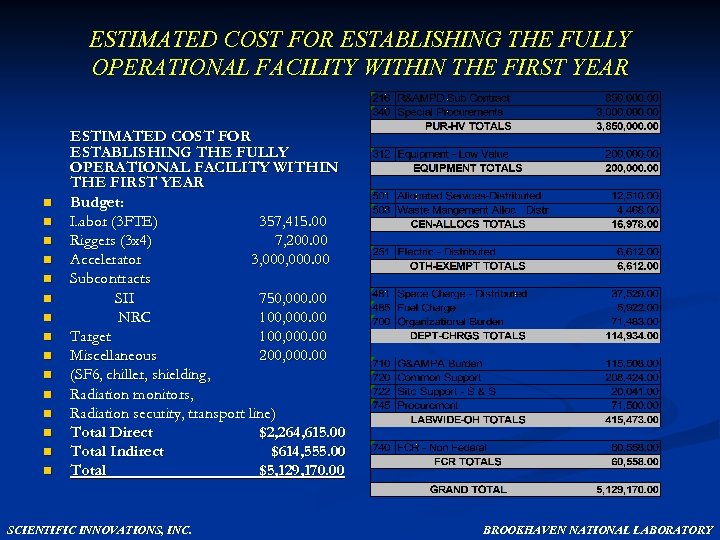 ESTIMATED COST FOR ESTABLISHING THE FULLY OPERATIONAL FACILITY WITHIN THE FIRST YEAR n n n n ESTIMATED COST FOR ESTABLISHING THE FULLY OPERATIONAL FACILITY WITHIN THE FIRST YEAR Budget: Labor (3 FTE) 357, 415. 00 Riggers (3 x 4) 7, 200. 00 Accelerator 3, 000. 00 Subcontracts SII 750, 000. 00 NRC 100, 000. 00 Target 100, 000. 00 Miscellaneous 200, 000. 00 (SF 6, chiller, shielding, Radiation monitors, Radiation security, transport line) Total Direct $2, 264, 615. 00 Total Indirect $614, 555. 00 Total $5, 129, 170. 00 SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
ESTIMATED COST FOR ESTABLISHING THE FULLY OPERATIONAL FACILITY WITHIN THE FIRST YEAR n n n n ESTIMATED COST FOR ESTABLISHING THE FULLY OPERATIONAL FACILITY WITHIN THE FIRST YEAR Budget: Labor (3 FTE) 357, 415. 00 Riggers (3 x 4) 7, 200. 00 Accelerator 3, 000. 00 Subcontracts SII 750, 000. 00 NRC 100, 000. 00 Target 100, 000. 00 Miscellaneous 200, 000. 00 (SF 6, chiller, shielding, Radiation monitors, Radiation security, transport line) Total Direct $2, 264, 615. 00 Total Indirect $614, 555. 00 Total $5, 129, 170. 00 SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
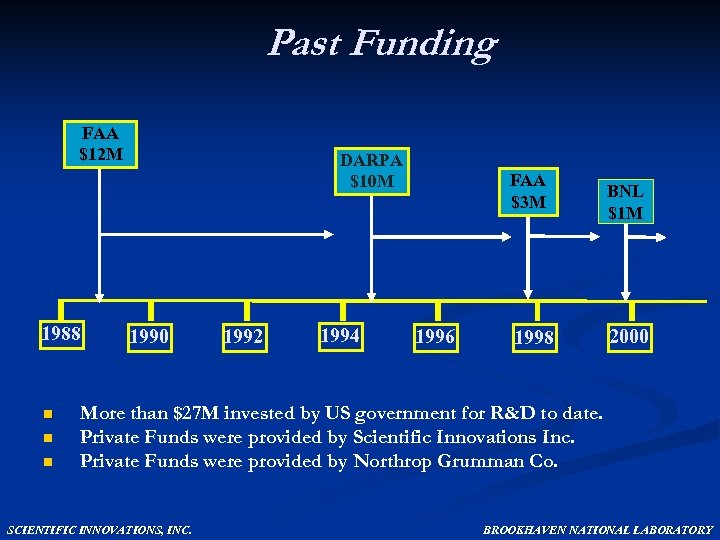 Past Funding FAA $12 M 1988 n n n DARPA $10 M 1990 1992 1994 FAA $3 M 1996 1998 BNL $1 M 2000 More than $27 M invested by US government for R&D to date. Private Funds were provided by Scientific Innovations Inc. Private Funds were provided by Northrop Grumman Co. SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
Past Funding FAA $12 M 1988 n n n DARPA $10 M 1990 1992 1994 FAA $3 M 1996 1998 BNL $1 M 2000 More than $27 M invested by US government for R&D to date. Private Funds were provided by Scientific Innovations Inc. Private Funds were provided by Northrop Grumman Co. SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
 SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
 POINT OF CONTACT Joseph H. Brondo, Jr. President, CEO Scientific Innovations, Inc. 14 Oak Hill Lane East Hampton, New York 11937 Phone: (631)324 -0404 Fax: (631) 324 -8771 E-Mail: jhbrondo@optonline. net SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY
POINT OF CONTACT Joseph H. Brondo, Jr. President, CEO Scientific Innovations, Inc. 14 Oak Hill Lane East Hampton, New York 11937 Phone: (631)324 -0404 Fax: (631) 324 -8771 E-Mail: jhbrondo@optonline. net SCIENTIFIC INNOVATIONS, INC. BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY


