29bf86fd6902561d5ed6a402b0f40d8c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 12

Simplicity and Automation in Reconfigurable Optical Networks Dr. Tom Mc. Dermott Director, CTO Office, Fujitsu tom. mcdermott@us. fujitsu. com Fujitsu Proprietary and Confidential All Rights Reserved, © 2006 Fujitsu Network Communications
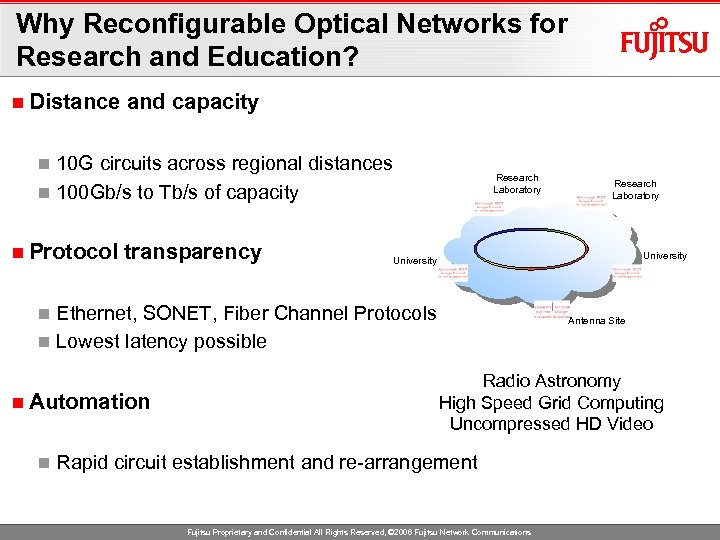
Why Reconfigurable Optical Networks for Research and Education? n Distance and capacity 10 G circuits across regional distances n 100 Gb/s to Tb/s of capacity n n Protocol transparency Research Laboratory University Ethernet, SONET, Fiber Channel Protocols n Lowest latency possible n n Automation n Research Laboratory Antenna Site Radio Astronomy High Speed Grid Computing Uncompressed HD Video Rapid circuit establishment and re-arrangement Fujitsu Proprietary and Confidential All Rights Reserved, © 2006 Fujitsu Network Communications

Optical Networking Evolution Simplicity • Arbitrary topologies • Dynamic wavelength assignment • Automatic power balancing • Universal amplifiers • Tunable components • x. WDM access integration • Sub-wavelength integration • Simpler than SONET Operations • Single Ring Topologies • Reconfigurable wavelength assignment • Automatic power balancing • Operational ease equivalent to SONET ADMs ROADM ROADM 0 -1000 km 10 G - 1. 6 T WDM ROADM 0 -600 km 10 G-400 G 0 -300 km 2. 5 G - 160 G WDM • Point topologies • Static wavelength assignment • Manual power adjustments • Heavy operational burden Fujitsu Proprietary and Confidential All Rights Reserved, © 2006 Fujitsu Network Communications Flexibility/ Distance Capacity
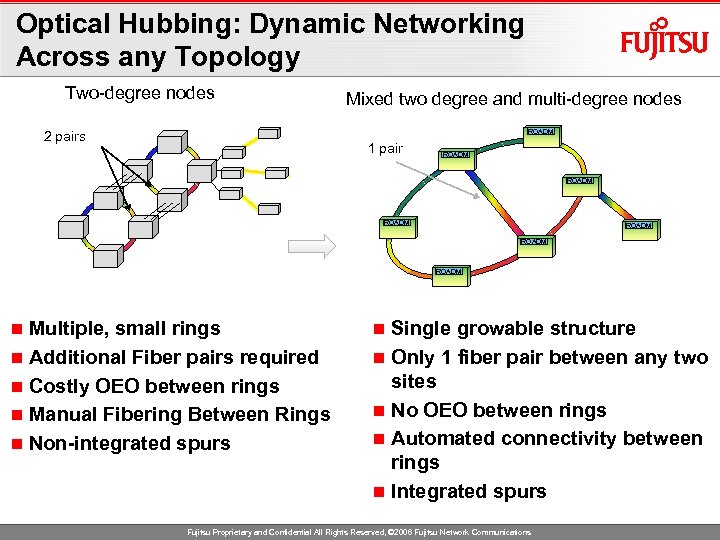
Optical Hubbing: Dynamic Networking Across any Topology Two-degree nodes Mixed two degree and multi-degree nodes ROADM 2 pairs 1 pair ROADM ROADM Multiple, small rings n Additional Fiber pairs required n Costly OEO between rings n Manual Fibering Between Rings n Non-integrated spurs n Single growable structure n Only 1 fiber pair between any two sites n No OEO between rings n Automated connectivity between rings n Integrated spurs n Fujitsu Proprietary and Confidential All Rights Reserved, © 2006 Fujitsu Network Communications
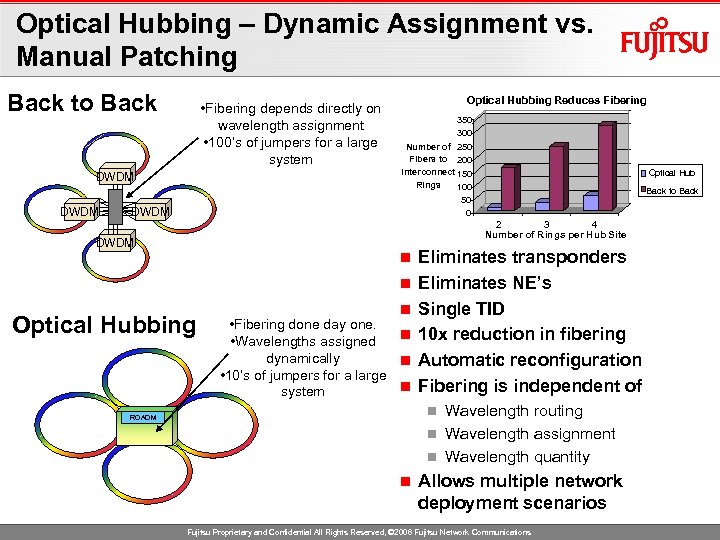
Optical Hubbing – Dynamic Assignment vs. Manual Patching Back to Back • Fibering depends directly on wavelength assignment • 100’s of jumpers for a large system DWDM Optical Hubbing Reduces Fibering 350 300 Number of 250 Fibers to 200 Interconnect 150 Rings 100 50 0 Optical Hub Back to Back 2 3 4 Number of Rings per Hub Site DWDM n n Optical Hubbing n • Fibering done day one. n • Wavelengths assigned dynamically n • 10’s of jumpers for a large n system Eliminates transponders Eliminates NE’s Single TID 10 x reduction in fibering Automatic reconfiguration Fibering is independent of Wavelength routing n Wavelength assignment n Wavelength quantity n ROADM n Allows multiple network deployment scenarios Fujitsu Proprietary and Confidential All Rights Reserved, © 2006 Fujitsu Network Communications
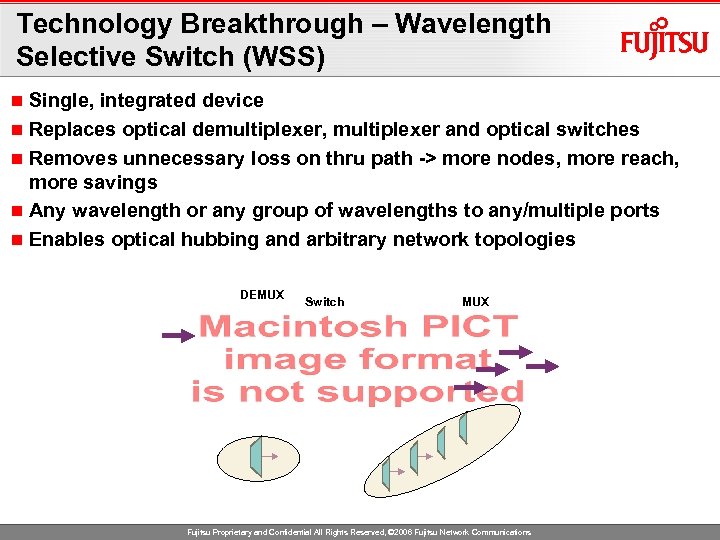
Technology Breakthrough – Wavelength Selective Switch (WSS) Single, integrated device n Replaces optical demultiplexer, multiplexer and optical switches n Removes unnecessary loss on thru path -> more nodes, more reach, more savings n Any wavelength or any group of wavelengths to any/multiple ports n Enables optical hubbing and arbitrary network topologies n DEMUX Switch MUX Fujitsu Proprietary and Confidential All Rights Reserved, © 2006 Fujitsu Network Communications
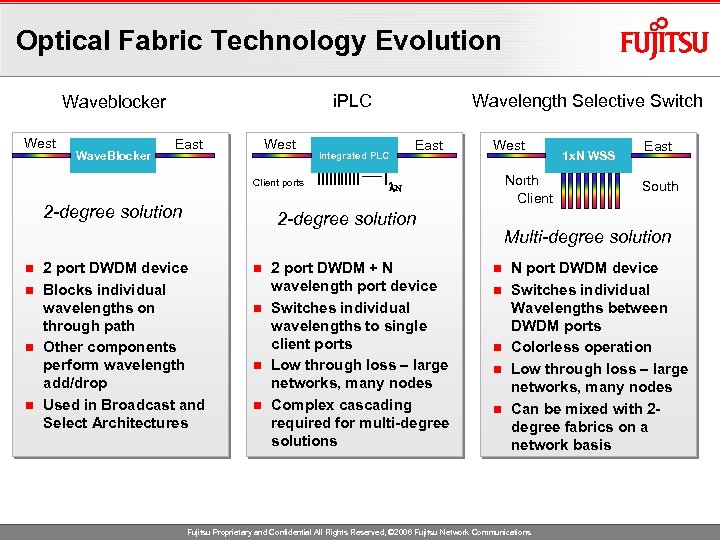
Optical Fabric Technology Evolution i. PLC Waveblocker West Wave. Blocker East West Client ports 2 -degree solution Integrated PLC East West North Client l. N 2 -degree solution 2 port DWDM device n Blocks individual wavelengths on through path n Other components perform wavelength add/drop n Used in Broadcast and Select Architectures n Wavelength Selective Switch 2 port DWDM + N wavelength port device n Switches individual wavelengths to single client ports n Low through loss – large networks, many nodes n Complex cascading required for multi-degree solutions n 1 x. N WSS East South Multi-degree solution n n N port DWDM device Switches individual Wavelengths between DWDM ports Colorless operation Low through loss – large networks, many nodes Can be mixed with 2 degree fabrics on a network basis Fujitsu Proprietary and Confidential All Rights Reserved, © 2006 Fujitsu Network Communications
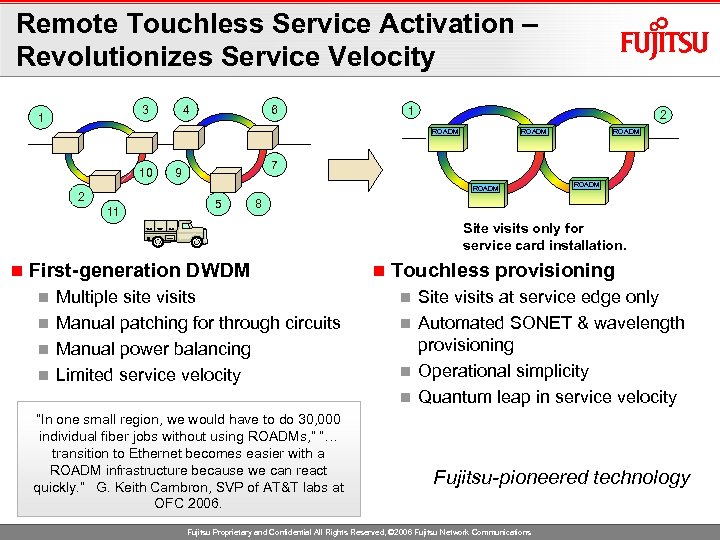
Remote Touchless Service Activation – Revolutionizes Service Velocity 3 1 4 6 1 2 ROADM 10 ROADM 7 9 ROADM 2 11 ROADM 5 ROADM 8 Site visits only for service card installation. n First-generation DWDM Multiple site visits n Manual patching for through circuits n Manual power balancing n Limited service velocity n “In one small region, we would have to do 30, 000 individual fiber jobs without using ROADMs, ” “… transition to Ethernet becomes easier with a ROADM infrastructure because we can react quickly. ” G. Keith Cambron, SVP of AT&T labs at OFC 2006. n Touchless provisioning Site visits at service edge only n Automated SONET & wavelength provisioning n Operational simplicity n Quantum leap in service velocity n Fujitsu-pioneered technology Fujitsu Proprietary and Confidential All Rights Reserved, © 2006 Fujitsu Network Communications
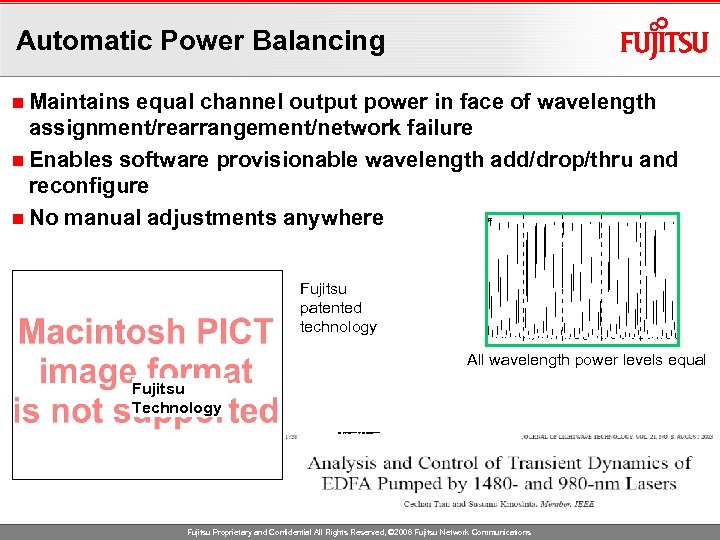
Automatic Power Balancing n Maintains equal channel output power in face of wavelength assignment/rearrangement/network failure n Enables software provisionable wavelength add/drop/thru and reconfigure n No manual adjustments anywhere Fujitsu patented technology All wavelength power levels equal Fujitsu Technology Fujitsu Proprietary and Confidential All Rights Reserved, © 2006 Fujitsu Network Communications
Automating Control and Management n GMPLS enabled topology discovery Populates EMS database for assured inventory tracking n Verifies fiber connectivity n Craft user sees whole network easily n n Circuit provisioning options Point and click from EMS n Activated from EMS with explicit route – signaled using GMPLS n Activated from EMS, computed route using GMPLS n n Circuit tracking with GMPLS Network element layer understands end to end circuit view n Simplifies troubleshooting and alarm correlation n ROADM Fujitsu Proprietary and Confidential All Rights Reserved, © 2006 Fujitsu Network Communications
Summary n Optical Networking provides substantial value for R&E applications n Transparency, distance, capacity, automation n Optical networking surpasses the simplicity of SONET networking n n n Elimination of manual adjustments Zero-lambda turnup In-service wavelength additions to spans, rings In-service addition of nodes to rings In-service addition of rings and spurs to networks n Network automation uniquely enabled by Optical Hubbing n Auto-adjusting amplifiers n Tunable components n GMPLS control plane and EMS n Fujitsu Proprietary and Confidential All Rights Reserved, © 2006 Fujitsu Network Communications

Fujitsu Proprietary and Confidential All Rights Reserved, © 2006 Fujitsu Network Communications
29bf86fd6902561d5ed6a402b0f40d8c.ppt