04efe3e1a22ff6dd964ecbf5bad8f845.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 Simdis Course AC Analytical Controls January 2001
Simdis Course AC Analytical Controls January 2001
 Simdis - Introduction l Distillation is the most widely used separation process in the petrol industry l Knowledge of the boiling range is essential for quality assurance regulatory compliance refinery process control physical property predictions
Simdis - Introduction l Distillation is the most widely used separation process in the petrol industry l Knowledge of the boiling range is essential for quality assurance regulatory compliance refinery process control physical property predictions
 Simdis Vs. Physical Distillation l D 86, D 1160 generates an average boiling point of a mixture at a given point l D 2892, 15 theoretical plate, true boiling point l Time consuming, labor intensive, imprecise
Simdis Vs. Physical Distillation l D 86, D 1160 generates an average boiling point of a mixture at a given point l D 2892, 15 theoretical plate, true boiling point l Time consuming, labor intensive, imprecise
 Simdis Vs Physical Distallation l GC analysis simulates a “true boiling point” l Simdis provides TBP of the individual components in a mixture at a given point l Automated l Accurate results l Fast l Detection of contamination or entrainment
Simdis Vs Physical Distallation l GC analysis simulates a “true boiling point” l Simdis provides TBP of the individual components in a mixture at a given point l Automated l Accurate results l Fast l Detection of contamination or entrainment
 Simdis Theory l The technique of simulated distillation is based upon the assumption that individual components of a sample elute from a GC column in order of their boiling point.
Simdis Theory l The technique of simulated distillation is based upon the assumption that individual components of a sample elute from a GC column in order of their boiling point.
 Available Simdis Methods Final boiling point l ASTM 3710 l ASTM 2887 l 2887 extended l Ht 750 260 °C 538 °C 620 °C 750 °C
Available Simdis Methods Final boiling point l ASTM 3710 l ASTM 2887 l 2887 extended l Ht 750 260 °C 538 °C 620 °C 750 °C
 ASTM D 3710 l Gasoline, naphtha, kerosene l Final boiling point (FBP)<260°C l Packed or capillary column
ASTM D 3710 l Gasoline, naphtha, kerosene l Final boiling point (FBP)<260°C l Packed or capillary column
 ASTM D 2887 l Petroleum products l Final boiling point (FBP)<538°C l Packed or capillary column l Cryogenic option
ASTM D 2887 l Petroleum products l Final boiling point (FBP)<538°C l Packed or capillary column l Cryogenic option
 ASTM D 2887 Extended l Petroleum products l Final boiling point (FBP)<620°C l Capillary column l Cryogenic option
ASTM D 2887 Extended l Petroleum products l Final boiling point (FBP)<620°C l Capillary column l Cryogenic option
 Ht 750 l Crude's and crude fractions, petroleum products l Boiling range from 35°C-750°C l Capillary column l Cryogenic option
Ht 750 l Crude's and crude fractions, petroleum products l Boiling range from 35°C-750°C l Capillary column l Cryogenic option
 Requirements l non-polar stationery phase l linear temperature program l compensation of column bleeding
Requirements l non-polar stationery phase l linear temperature program l compensation of column bleeding
 Hardware l Gas chromatograph l Programmable temperature vaporizer (PTV injector) l FID detector l Column
Hardware l Gas chromatograph l Programmable temperature vaporizer (PTV injector) l FID detector l Column
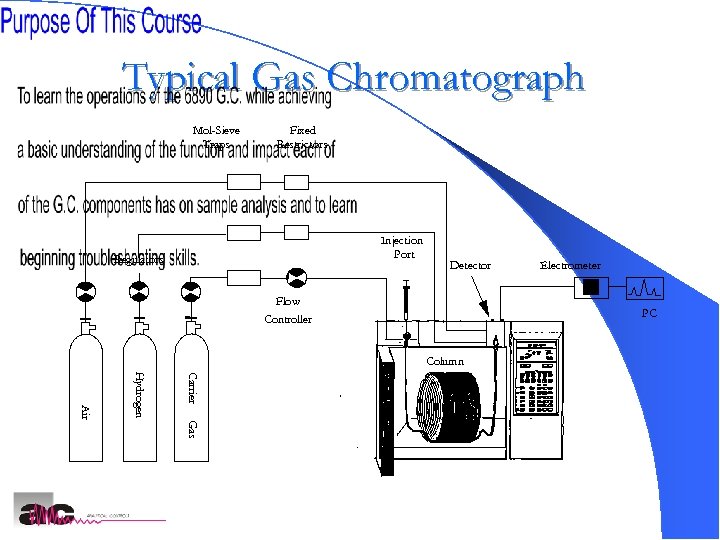 Typical Gas Chromatograph Mol-Sieve Traps Fixed Restrictors Injection Port Regulators Detector Flow Controller Electrometer PC Column Carrier Hydrogen Gas Air
Typical Gas Chromatograph Mol-Sieve Traps Fixed Restrictors Injection Port Regulators Detector Flow Controller Electrometer PC Column Carrier Hydrogen Gas Air
 PTV
PTV
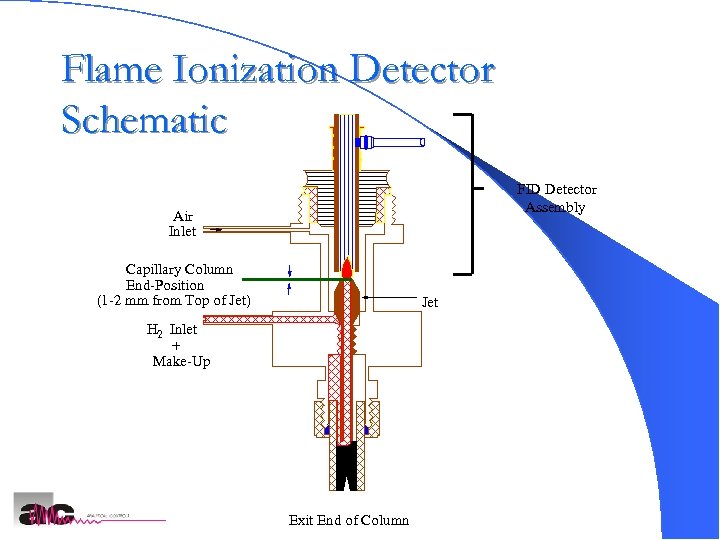 Flame Ionization Detector Schematic FID Detector Assembly Air Inlet Capillary Column End-Position (1 -2 mm from Top of Jet) Jet H 2 Inlet + Make-Up Exit End of Column
Flame Ionization Detector Schematic FID Detector Assembly Air Inlet Capillary Column End-Position (1 -2 mm from Top of Jet) Jet H 2 Inlet + Make-Up Exit End of Column
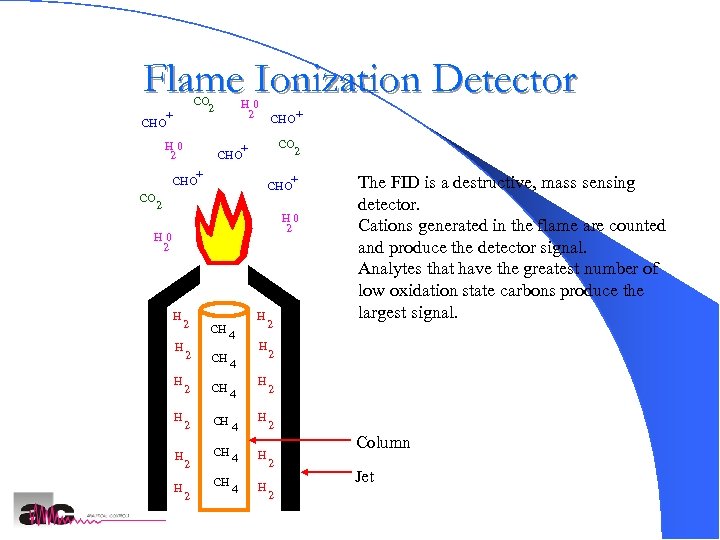 Flame Ionization Detector CO 2 + CHO H 0 2 CHO+ CO 2 + CHO CO + CHO 2 H 0 2 H H H H CH 4 2 CH CH 2 2 H 4 4 H 4 H The FID is a destructive, mass sensing detector. Cations generated in the flame are counted and produce the detector signal. Analytes that have the greatest number of low oxidation state carbons produce the largest signal. 2 2 2 Column 2 2 Jet
Flame Ionization Detector CO 2 + CHO H 0 2 CHO+ CO 2 + CHO CO + CHO 2 H 0 2 H H H H CH 4 2 CH CH 2 2 H 4 4 H 4 H The FID is a destructive, mass sensing detector. Cations generated in the flame are counted and produce the detector signal. Analytes that have the greatest number of low oxidation state carbons produce the largest signal. 2 2 2 Column 2 2 Jet
 System Startup l Electrical connections l Gas connections – carrier, FID l GC and auto sampler configuration l Installation of liner & column l Installation of septum and syringe l Check flows
System Startup l Electrical connections l Gas connections – carrier, FID l GC and auto sampler configuration l Installation of liner & column l Installation of septum and syringe l Check flows
 Simdis Theory l. A n-paraffin standard is analyzed to determine retention times l The times relate to the n-paraffin boiling points l A boiling point calibration curve is created by the software
Simdis Theory l. A n-paraffin standard is analyzed to determine retention times l The times relate to the n-paraffin boiling points l A boiling point calibration curve is created by the software
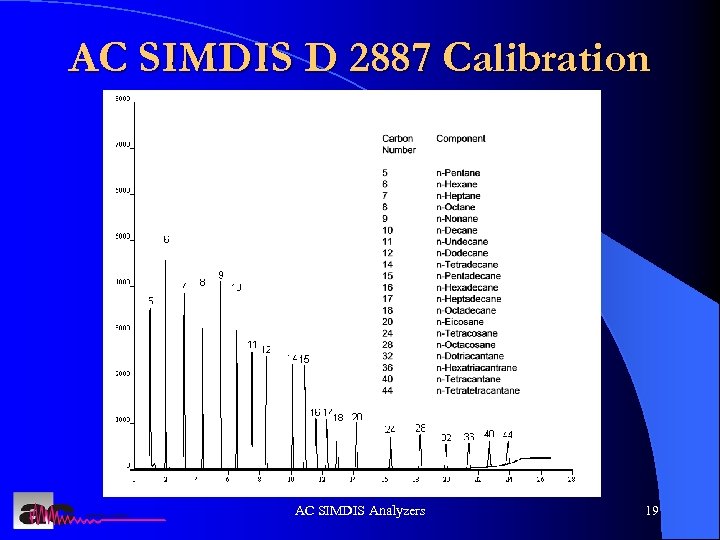 AC SIMDIS D 2887 Calibration AC SIMDIS Analyzers 19
AC SIMDIS D 2887 Calibration AC SIMDIS Analyzers 19
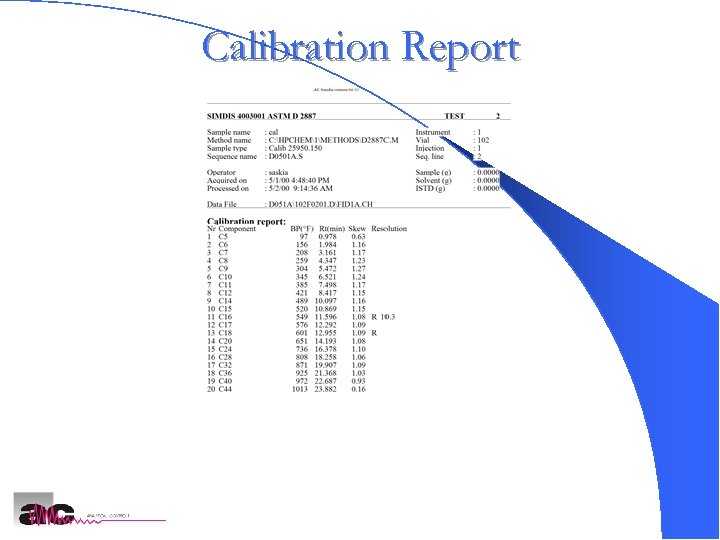 Calibration Report AC SIMDIS Analyzers 20
Calibration Report AC SIMDIS Analyzers 20
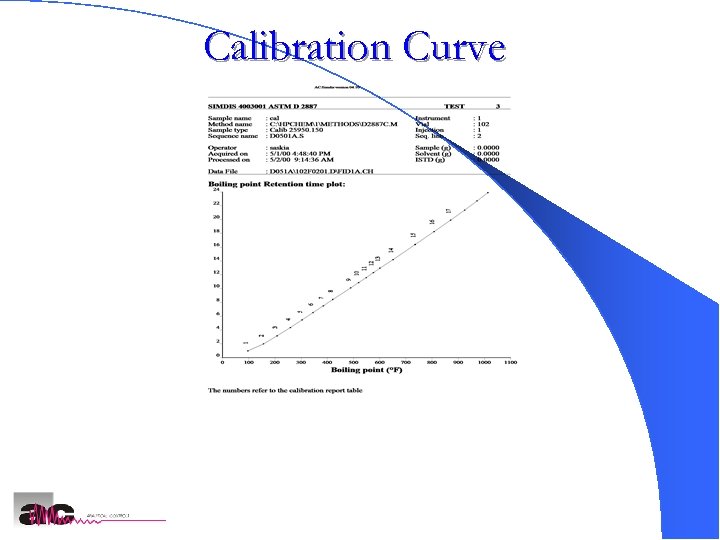 Calibration Curve AC SIMDIS Analyzers 21
Calibration Curve AC SIMDIS Analyzers 21
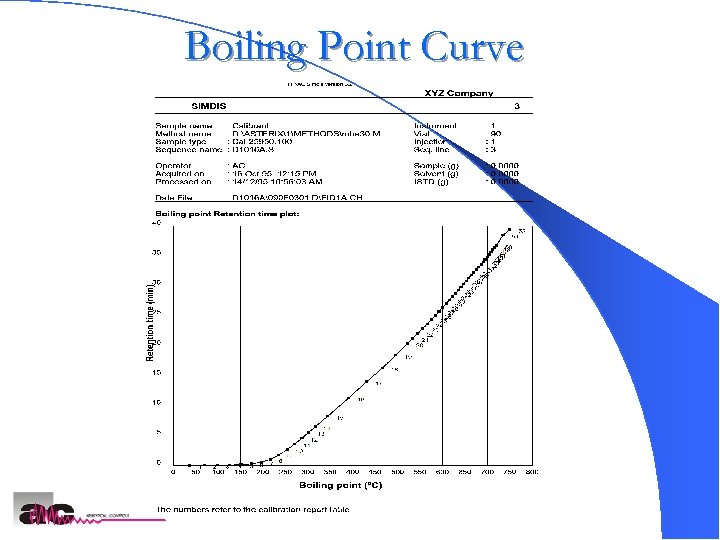 Boiling Point Curve AC SIMDIS Analyzers 22
Boiling Point Curve AC SIMDIS Analyzers 22
 Simdis Theory l Every analysis should be corrected for column bleeding l Analyze a blank in every sequence l The blank signal is automatically subtracted from every sample and reference signal
Simdis Theory l Every analysis should be corrected for column bleeding l Analyze a blank in every sequence l The blank signal is automatically subtracted from every sample and reference signal
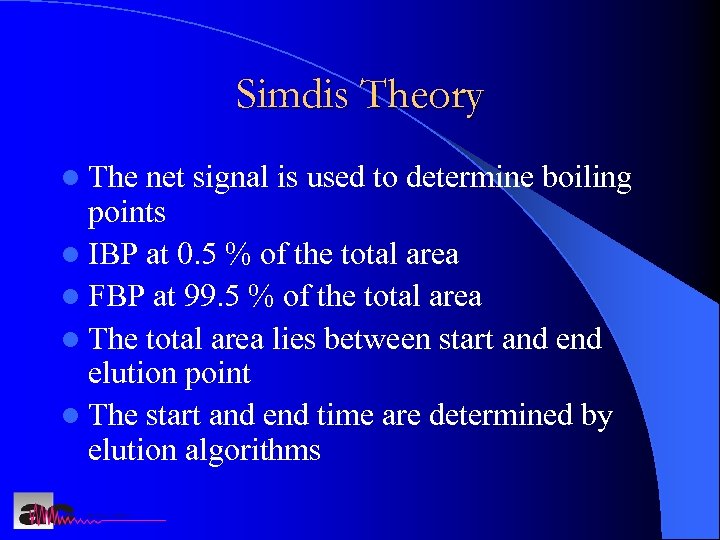 Simdis Theory l The net signal is used to determine boiling points l IBP at 0. 5 % of the total area l FBP at 99. 5 % of the total area l The total area lies between start and elution point l The start and end time are determined by elution algorithms
Simdis Theory l The net signal is used to determine boiling points l IBP at 0. 5 % of the total area l FBP at 99. 5 % of the total area l The total area lies between start and elution point l The start and end time are determined by elution algorithms
 Simdis Theory l. A reference sample is analyzed to check system performance
Simdis Theory l. A reference sample is analyzed to check system performance
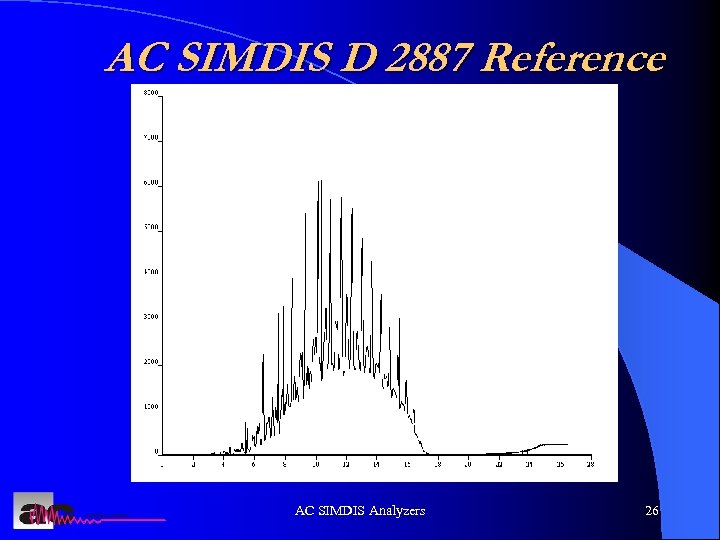 AC SIMDIS D 2887 Reference AC SIMDIS Analyzers 26
AC SIMDIS D 2887 Reference AC SIMDIS Analyzers 26
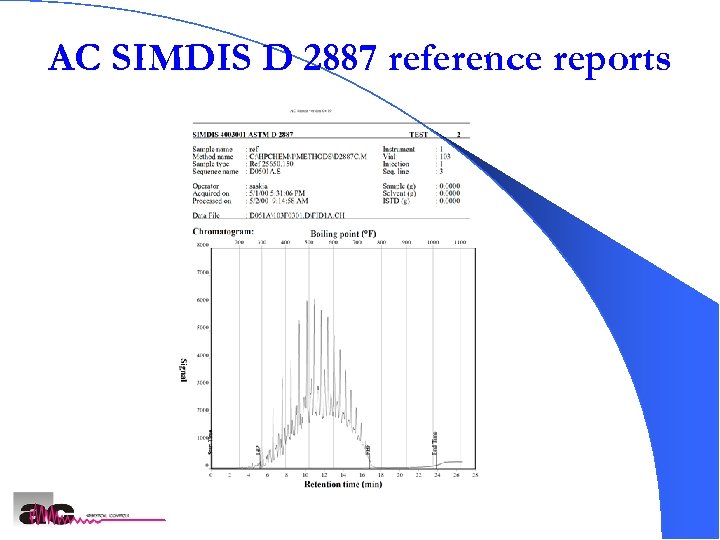 AC SIMDIS D 2887 reference reports AC SIMDIS Analyzers 27
AC SIMDIS D 2887 reference reports AC SIMDIS Analyzers 27
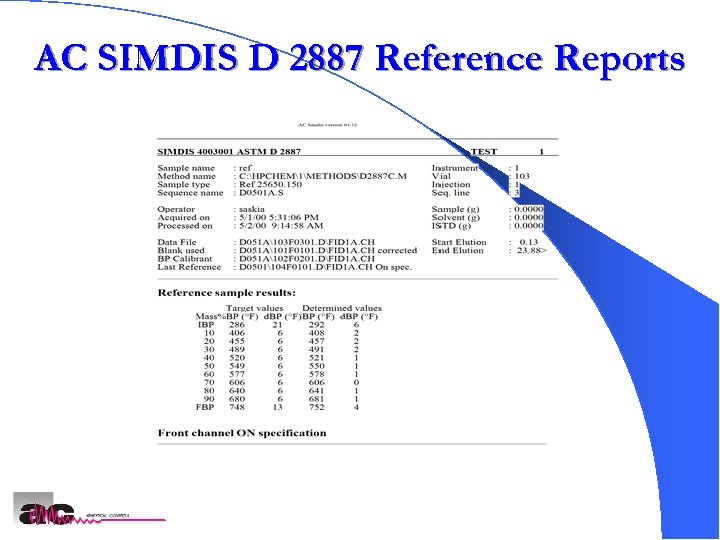 AC SIMDIS D 2887 Reference Reports AC SIMDIS Analyzers 28
AC SIMDIS D 2887 Reference Reports AC SIMDIS Analyzers 28
 Starting Analysis l Make & run a sequence l Calibration l Observe results l Reprocess if necessary
Starting Analysis l Make & run a sequence l Calibration l Observe results l Reprocess if necessary
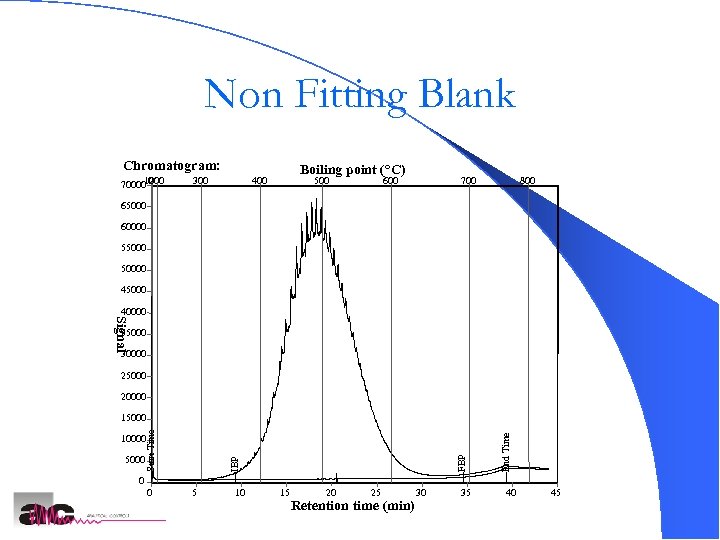 Non Fitting Blank Chromatogram: 100 200 70000 0 300 Boiling point (°C) 400 500 600 700 800 65000 60000 550000 45000 Signal 40000 35000 30000 25000 20000 IBP 5000 FBP 10000 End Time Start Time 15000 0 0 5 10 15 20 25 Retention time (min) 30 35 40 45
Non Fitting Blank Chromatogram: 100 200 70000 0 300 Boiling point (°C) 400 500 600 700 800 65000 60000 550000 45000 Signal 40000 35000 30000 25000 20000 IBP 5000 FBP 10000 End Time Start Time 15000 0 0 5 10 15 20 25 Retention time (min) 30 35 40 45
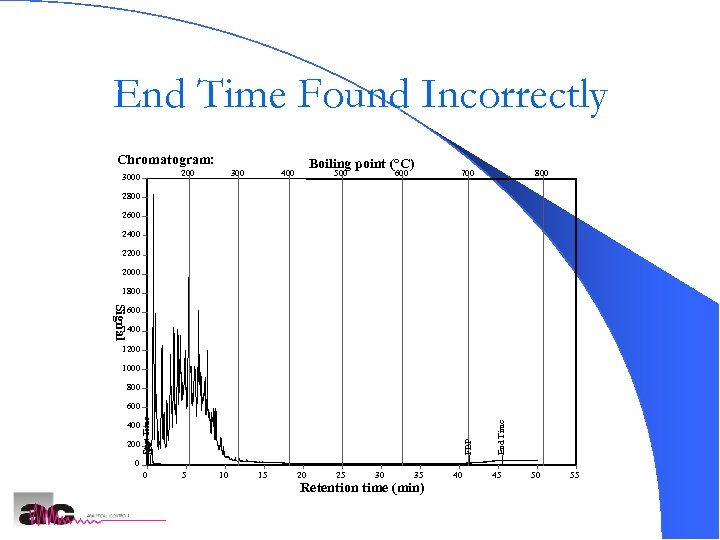 End Time Found Incorrectly Chromatogram: 200 300 Boiling point (°C) 400 500 600 700 800 2600 2400 2200 2000 1800 Signal 1600 1400 1200 1000 800 End Time 200 FBP 400 Start IBP Time 600 0 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 Retention time (min) 40 45 50 55
End Time Found Incorrectly Chromatogram: 200 300 Boiling point (°C) 400 500 600 700 800 2600 2400 2200 2000 1800 Signal 1600 1400 1200 1000 800 End Time 200 FBP 400 Start IBP Time 600 0 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 Retention time (min) 40 45 50 55


