a5acace579a30e89c1043fdc3d72ecac.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 44
 Sim. Millennium: Computer Systems, Computational Science and Engineering in the Large Jim Demmel, David Culler E. Brewer, J. Canny, A. Joseph, J. Landay, S. Mc. Canne A. Neureuther, C. Papadimitrou, C. Sequin, K. Yelick EECS, UC Berkeley www. millennium. berkeley. edu NSF CISE EIA RI and MII PI’s Workshop Aug 7 -9 1999 Millennium
Sim. Millennium: Computer Systems, Computational Science and Engineering in the Large Jim Demmel, David Culler E. Brewer, J. Canny, A. Joseph, J. Landay, S. Mc. Canne A. Neureuther, C. Papadimitrou, C. Sequin, K. Yelick EECS, UC Berkeley www. millennium. berkeley. edu NSF CISE EIA RI and MII PI’s Workshop Aug 7 -9 1999 Millennium
 Project Goals • Enable major advances in Computational Science and Engineering – Simulation, Modeling, and Information Processing becoming ubiquitous – Many participants outside CS • Explore novel design techniques for large, complex systems – Fundamental Computer Science problems ahead are problems of scale – Use Capitalism, not Socialism (i. e. not Computer Center) • Develop fundamentally better ways of assimilating and interacting with large volumes of information – and with each other • Explore emerging technologies – networking, OS, devices Millennium 2
Project Goals • Enable major advances in Computational Science and Engineering – Simulation, Modeling, and Information Processing becoming ubiquitous – Many participants outside CS • Explore novel design techniques for large, complex systems – Fundamental Computer Science problems ahead are problems of scale – Use Capitalism, not Socialism (i. e. not Computer Center) • Develop fundamentally better ways of assimilating and interacting with large volumes of information – and with each other • Explore emerging technologies – networking, OS, devices Millennium 2
 Outline • • Background on UC Berkeley Millennium infrastructure description Other infrastructure contributions Systems research – Networking – Computational Economy • Applications – List of all participants – A few highlights • Conclusions Millennium 3
Outline • • Background on UC Berkeley Millennium infrastructure description Other infrastructure contributions Systems research – Networking – Computational Economy • Applications – List of all participants – A few highlights • Conclusions Millennium 3
 Background at UC Berkeley • Mammoth NSF RI (1988 -1993) – CM-5 • Titan NSF RI (1994 -1999) – Culler, spoke yesterday – NOW = Network of Workstations • Curriculum – CS 267 - Applications of Parallel Computing – MS in Comp Sci & Eng Curriculum – Proposed Comp Eng Sci undergrad program • NERSC at LBNL – National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center – Supercomputer center next to campus • Sim. Millennium (1998 -2003) Millennium 4
Background at UC Berkeley • Mammoth NSF RI (1988 -1993) – CM-5 • Titan NSF RI (1994 -1999) – Culler, spoke yesterday – NOW = Network of Workstations • Curriculum – CS 267 - Applications of Parallel Computing – MS in Comp Sci & Eng Curriculum – Proposed Comp Eng Sci undergrad program • NERSC at LBNL – National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center – Supercomputer center next to campus • Sim. Millennium (1998 -2003) Millennium 4
 Planned Millennium Infrastructure Millennium 5
Planned Millennium Infrastructure Millennium 5
 The Community Business School of Info. Mgmt and Sys. BMRC Chemistry Computer Science Electrical Eng. Biology Astro Mechanical Eng. Physics Nuclear Eng. IEOR Civil Eng. Geo Inst. Of Transport Millennium Economy Math 6
The Community Business School of Info. Mgmt and Sys. BMRC Chemistry Computer Science Electrical Eng. Biology Astro Mechanical Eng. Physics Nuclear Eng. IEOR Civil Eng. Geo Inst. Of Transport Millennium Economy Math 6
 NT Workstations for Sci. & Eng. Business SIMS BMRC Chemistry C. S. E. E. Biology Astro M. E. Physics N. E. IEOR Civil Eng Geo Transport Millennium Economy Math 7
NT Workstations for Sci. & Eng. Business SIMS BMRC Chemistry C. S. E. E. Biology Astro M. E. Physics N. E. IEOR Civil Eng Geo Transport Millennium Economy Math 7
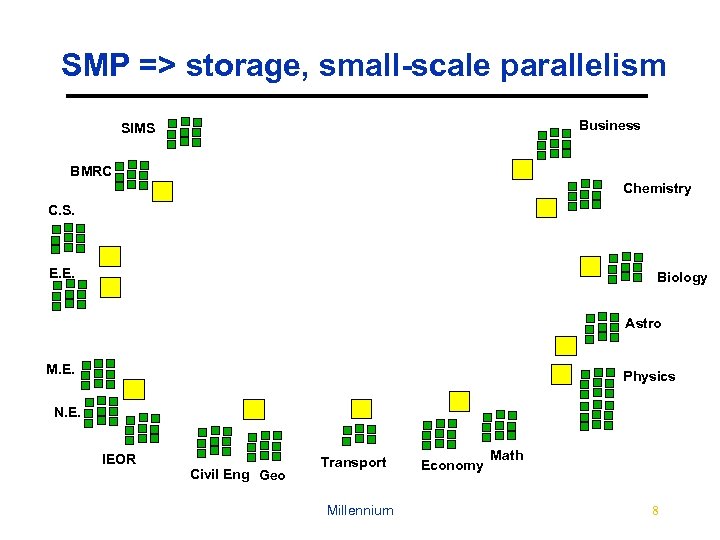 SMP => storage, small-scale parallelism Business SIMS BMRC Chemistry C. S. E. E. Biology Astro M. E. Physics N. E. IEOR Civil Eng Geo Transport Millennium Economy Math 8
SMP => storage, small-scale parallelism Business SIMS BMRC Chemistry C. S. E. E. Biology Astro M. E. Physics N. E. IEOR Civil Eng Geo Transport Millennium Economy Math 8
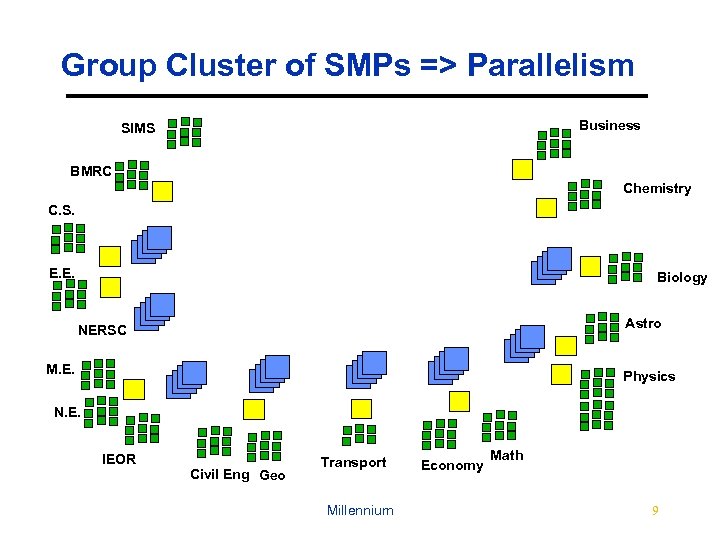 Group Cluster of SMPs => Parallelism Business SIMS BMRC Chemistry C. S. E. E. Biology Astro NERSC M. E. Physics N. E. IEOR Civil Eng Geo Transport Millennium Economy Math 9
Group Cluster of SMPs => Parallelism Business SIMS BMRC Chemistry C. S. E. E. Biology Astro NERSC M. E. Physics N. E. IEOR Civil Eng Geo Transport Millennium Economy Math 9
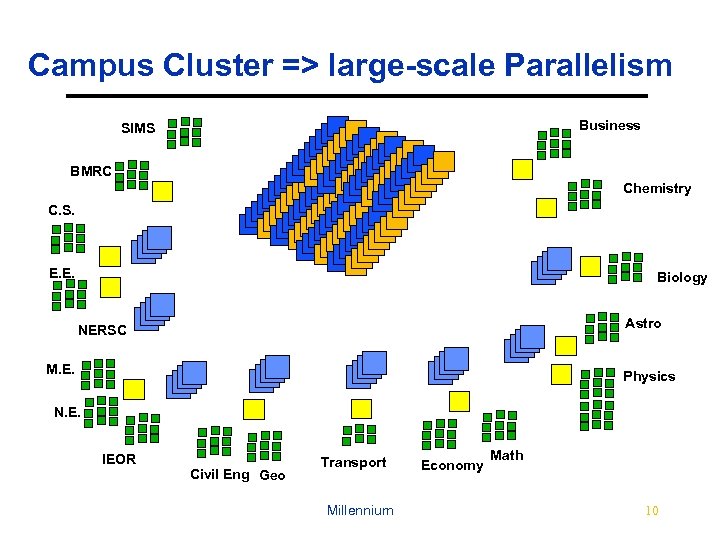 Campus Cluster => large-scale Parallelism Business SIMS BMRC Chemistry C. S. E. E. Biology Astro NERSC M. E. Physics N. E. IEOR Civil Eng Geo Transport Millennium Economy Math 10
Campus Cluster => large-scale Parallelism Business SIMS BMRC Chemistry C. S. E. E. Biology Astro NERSC M. E. Physics N. E. IEOR Civil Eng Geo Transport Millennium Economy Math 10
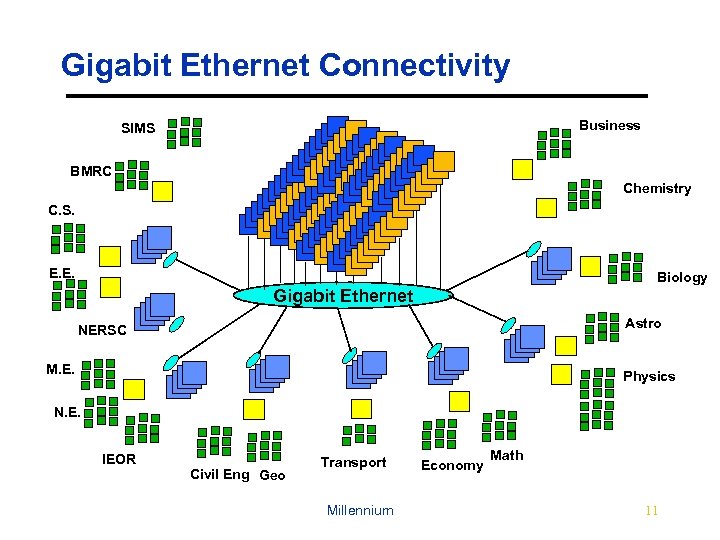 Gigabit Ethernet Connectivity Business SIMS BMRC Chemistry C. S. E. E. Biology Gigabit Ethernet Astro NERSC M. E. Physics N. E. IEOR Civil Eng Geo Transport Millennium Economy Math 11
Gigabit Ethernet Connectivity Business SIMS BMRC Chemistry C. S. E. E. Biology Gigabit Ethernet Astro NERSC M. E. Physics N. E. IEOR Civil Eng Geo Transport Millennium Economy Math 11
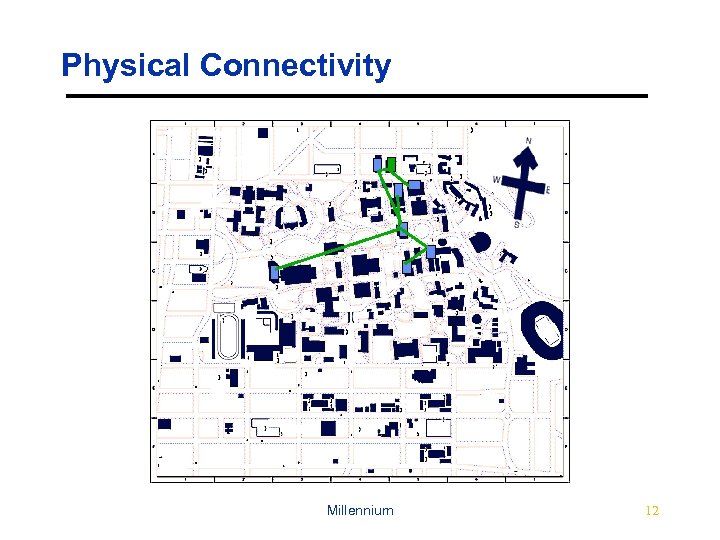 Physical Connectivity Millennium 12
Physical Connectivity Millennium 12
 Visualization and Novel User Interfaces Millennium 13
Visualization and Novel User Interfaces Millennium 13
 Current Infrastructure (by end of 8/99) • All 195 desktops and 20 SMPs delivered • All 18 16 -(or smaller)-processor clusters (8 dual SMPs) – Mostly running Myrinet interconnects, some 100 Mb Ethernet • NOW functioning as large central cluster • Cluster build service • Millennium wide services –. 5 Tbyte file server – distributed system services and software for UNIX and NT • Optical fiber for Gigabit in place • 10 Gigabit switches purchased • 2 Vision Maker Digital Desks purchased Millennium 14
Current Infrastructure (by end of 8/99) • All 195 desktops and 20 SMPs delivered • All 18 16 -(or smaller)-processor clusters (8 dual SMPs) – Mostly running Myrinet interconnects, some 100 Mb Ethernet • NOW functioning as large central cluster • Cluster build service • Millennium wide services –. 5 Tbyte file server – distributed system services and software for UNIX and NT • Optical fiber for Gigabit in place • 10 Gigabit switches purchased • 2 Vision Maker Digital Desks purchased Millennium 14
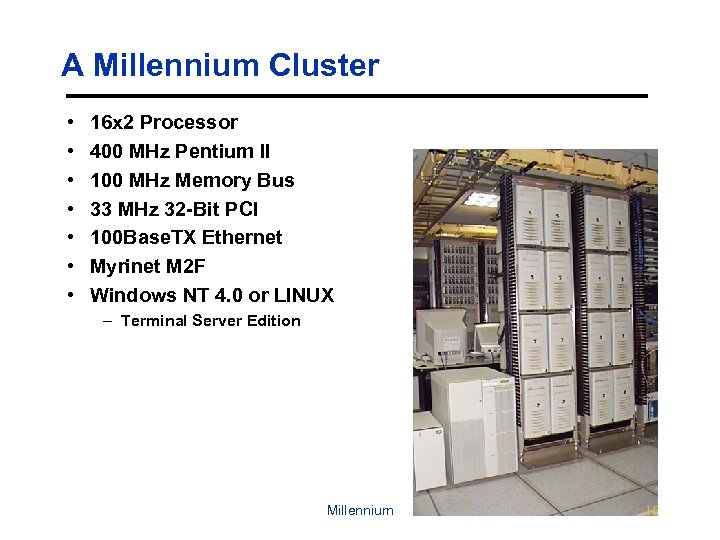 A Millennium Cluster • • 16 x 2 Processor 400 MHz Pentium II 100 MHz Memory Bus 33 MHz 32 -Bit PCI 100 Base. TX Ethernet Myrinet M 2 F Windows NT 4. 0 or LINUX – Terminal Server Edition Millennium 15
A Millennium Cluster • • 16 x 2 Processor 400 MHz Pentium II 100 MHz Memory Bus 33 MHz 32 -Bit PCI 100 Base. TX Ethernet Myrinet M 2 F Windows NT 4. 0 or LINUX – Terminal Server Edition Millennium 15
 Industrial / Academic Collaboration • Computers via Intel Technology 2000 grant – 200 NT desktops – 16 department 4 -way SMPs – 10+ 8 x 2 Group Clusters, – 1 ~200 x 2 Campus Cluster – PPro => Pentium III 200 Gflop/s 150 GB memory 8 TB disk • Additional storage via IBM SUR grant – 0. 5 TB this year => 4 TB • • • NT tools via Microsoft grant Solaris x 86 tools via SMCC grant Nortel discounts the gigabit Ethernet 70% Campus provides 3 technical staff, fiber Research provides the prog. and system support Millennium 16
Industrial / Academic Collaboration • Computers via Intel Technology 2000 grant – 200 NT desktops – 16 department 4 -way SMPs – 10+ 8 x 2 Group Clusters, – 1 ~200 x 2 Campus Cluster – PPro => Pentium III 200 Gflop/s 150 GB memory 8 TB disk • Additional storage via IBM SUR grant – 0. 5 TB this year => 4 TB • • • NT tools via Microsoft grant Solaris x 86 tools via SMCC grant Nortel discounts the gigabit Ethernet 70% Campus provides 3 technical staff, fiber Research provides the prog. and system support Millennium 16
 What NSF is paying for • Fast internal networks for clusters • Gigabit ethernet switches • Interesting I/O devices – – Large displays 3 D glasses Haptic mice Position sensors • One staff person Millennium 17
What NSF is paying for • Fast internal networks for clusters • Gigabit ethernet switches • Interesting I/O devices – – Large displays 3 D glasses Haptic mice Position sensors • One staff person Millennium 17
 Primary Faculty Participants - 1 • CS – D. Culler, J. Demmel, E. Brewer, J. Canny, A. Joseph, R. Katz, J. Landay, S. Mc. Canne, C. Papadimitriou, C. Sequin, R. Wilensky, K. Yelick – Systems, Numerical Methods, Services, HCI, Networking, Computational Economics, Digital libraries, Parallel languages • EE – A. Neureuther – Technology CAD for EBEAM Lithography • Civil Engineering – S. Govindjee, G. Fenves – Earthquake Engineering, Finite Element Modeling • Physics – B. Price, J. Wurtele, D. Lowder – Processing neutrinos and muons at South Pole • SIMS – H. Varian, R. Larson, M. Hearst – Computational Economics, User Interfaces Millennium 18
Primary Faculty Participants - 1 • CS – D. Culler, J. Demmel, E. Brewer, J. Canny, A. Joseph, R. Katz, J. Landay, S. Mc. Canne, C. Papadimitriou, C. Sequin, R. Wilensky, K. Yelick – Systems, Numerical Methods, Services, HCI, Networking, Computational Economics, Digital libraries, Parallel languages • EE – A. Neureuther – Technology CAD for EBEAM Lithography • Civil Engineering – S. Govindjee, G. Fenves – Earthquake Engineering, Finite Element Modeling • Physics – B. Price, J. Wurtele, D. Lowder – Processing neutrinos and muons at South Pole • SIMS – H. Varian, R. Larson, M. Hearst – Computational Economics, User Interfaces Millennium 18
 Primary Faculty Participants - 2 • Astronomy – J. Arons, C. Mc. Kee. P. Marcus – Star Formation, Geophysical Turbulence • Transportation Studies – S. Sastry, A. Kanafani – Redesign of Nation’s Air Traffic Control System Millennium 19
Primary Faculty Participants - 2 • Astronomy – J. Arons, C. Mc. Kee. P. Marcus – Star Formation, Geophysical Turbulence • Transportation Studies – S. Sastry, A. Kanafani – Redesign of Nation’s Air Traffic Control System Millennium 19
 Secondary Faculty Participants - 1 • Geology/Geophysics – M. Richards, D. Dreger – Mantle modeling • Math – D. Eisenbud, B. Poonen, A. Grunbaum, T. Slaman, B. Sturmfels, P. Vojta – Crystal growth modeling, tomography, symbolic computing • Berkeley Multimedia Research Center – L. Rowe – Video effects processing • Mechanical Engineering – V. Carey, M. Frenklach, A. Packard, P. Papadopoulos, P. Marcus – Modeling Automated Highways, Material Processing • Biology – D. Lindberg, S. Brenner – Reconstruct Phylogenetic Tree of Life, Genome studies • Nuclear Engineering – J. Vujic – Planning radiotherapy for Brain Tumors Millennium 20
Secondary Faculty Participants - 1 • Geology/Geophysics – M. Richards, D. Dreger – Mantle modeling • Math – D. Eisenbud, B. Poonen, A. Grunbaum, T. Slaman, B. Sturmfels, P. Vojta – Crystal growth modeling, tomography, symbolic computing • Berkeley Multimedia Research Center – L. Rowe – Video effects processing • Mechanical Engineering – V. Carey, M. Frenklach, A. Packard, P. Papadopoulos, P. Marcus – Modeling Automated Highways, Material Processing • Biology – D. Lindberg, S. Brenner – Reconstruct Phylogenetic Tree of Life, Genome studies • Nuclear Engineering – J. Vujic – Planning radiotherapy for Brain Tumors Millennium 20
 Secondary Faculty Participants - 2 • NERSC – W. Saphir • Business – N. Hakansson – Computational Finance Laboratory • Chemistry – K. Durkin, D. Chandler, D. Harris, W. Lester, W. Miller, R. Stevens, B. Whaley – Computational Chemistry, Molecular Dynamics Visualization • Economics – A. Nevo – Market Modeling Millennium 21
Secondary Faculty Participants - 2 • NERSC – W. Saphir • Business – N. Hakansson – Computational Finance Laboratory • Chemistry – K. Durkin, D. Chandler, D. Harris, W. Lester, W. Miller, R. Stevens, B. Whaley – Computational Chemistry, Molecular Dynamics Visualization • Economics – A. Nevo – Market Modeling Millennium 21
 The CS Research Agenda • High Performance Cluster Computing Environment – Fast communication on Clusters of SMPs – Compiler Techniques for Performance and Ease of use – Numerical Techniques and Solvers » Particles, FFT, AMR, Multigrid, Sparse and Dense Lin. Alg. • Novel System Design Techniques – Clusters of clusters – Computational Economy – Open infrastructure services • Novel modes of interacting with large amounts of data – User interfaces, Digital Libraries Millennium 22
The CS Research Agenda • High Performance Cluster Computing Environment – Fast communication on Clusters of SMPs – Compiler Techniques for Performance and Ease of use – Numerical Techniques and Solvers » Particles, FFT, AMR, Multigrid, Sparse and Dense Lin. Alg. • Novel System Design Techniques – Clusters of clusters – Computational Economy – Open infrastructure services • Novel modes of interacting with large amounts of data – User interfaces, Digital Libraries Millennium 22
 Communication Interface Revolution • Low Overhead Communication “Happens” • Academic Research put it on the map – Active Messages (AM), FM, PM, … Unet – Memory Messaging (Get/Put, Reflective, VMMC, Mem. Chan. ) • Intel / Microsoft / Compaq recognized it – Virtual Interface Architecture 1. 0 released 12/16/97 • Berkeley VIA over Myrinet released on NT and Linux Millennium 23
Communication Interface Revolution • Low Overhead Communication “Happens” • Academic Research put it on the map – Active Messages (AM), FM, PM, … Unet – Memory Messaging (Get/Put, Reflective, VMMC, Mem. Chan. ) • Intel / Microsoft / Compaq recognized it – Virtual Interface Architecture 1. 0 released 12/16/97 • Berkeley VIA over Myrinet released on NT and Linux Millennium 23
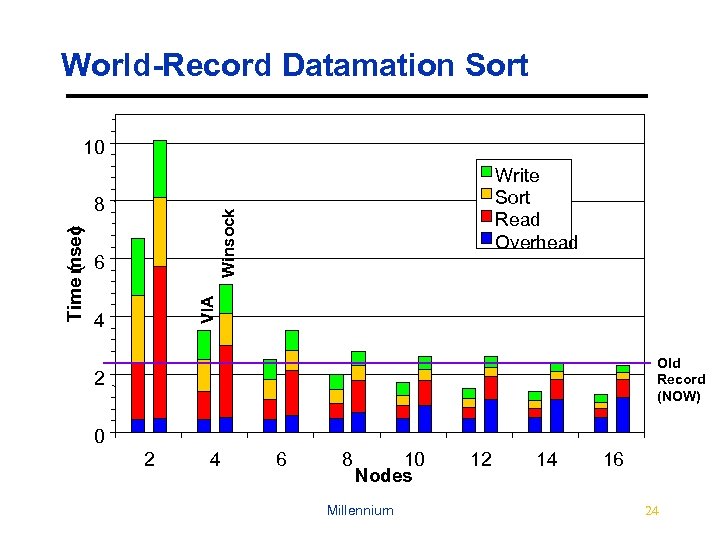 World-Record Datamation Sort 10 Winsock 6 VIA Time msec ( ) 8 Write Sort Read Overhead 4 Old Record (NOW) 2 0 2 4 6 8 10 Nodes Millennium 12 14 16 24
World-Record Datamation Sort 10 Winsock 6 VIA Time msec ( ) 8 Write Sort Read Overhead 4 Old Record (NOW) 2 0 2 4 6 8 10 Nodes Millennium 12 14 16 24
 Computational Economy Approach • System has a supply of various resources • Demand on resources revealed in price – distinct from the cost of acquiring the resources • User has unique assessment of value • Client agent negotiates for system resources on user’s behalf – submits requests, receives bids or participates in auctions – selects resources of highest value at least cost Millennium 25
Computational Economy Approach • System has a supply of various resources • Demand on resources revealed in price – distinct from the cost of acquiring the resources • User has unique assessment of value • Client agent negotiates for system resources on user’s behalf – submits requests, receives bids or participates in auctions – selects resources of highest value at least cost Millennium 25
 Advantages of the Approach • Decentralized load balancing – according to user’s perception of what is important, not system’s own metric – adapts to system and workload changes • Creates incentive to adopt efficient modes of use – exploit under-utilized resources – maximize flexibility (e. g. , migratable, restartable applications) • Establishes user-to-user feedback on resource usage – basis for exchange rate across resources • Powerful framework for system design – Natural for client to be watchful, proactive, and wary – Generalizes from resources to services • Rich body of theory ready for application Millennium 26
Advantages of the Approach • Decentralized load balancing – according to user’s perception of what is important, not system’s own metric – adapts to system and workload changes • Creates incentive to adopt efficient modes of use – exploit under-utilized resources – maximize flexibility (e. g. , migratable, restartable applications) • Establishes user-to-user feedback on resource usage – basis for exchange rate across resources • Powerful framework for system design – Natural for client to be watchful, proactive, and wary – Generalizes from resources to services • Rich body of theory ready for application Millennium 26
 Current Prototype • Specify #procs p and value on job – rexec -n 16 -value 20 fft. mpi • Market-based Proportional Sharing – Bidder i gets fraction bi / Sk bk of resource – If one bidder, no cost to use resource – Resource may be CPU, Memory, Network, I/O • Existing OS mechanisms/policies insufficient – New proportional CPU schedule for LINUX – New page replacement policy – Game theoretic analysis • Preliminary experience in CS 267 – Students trusted system to allocate fairly, so they did not try to flood system with jobs • Future work – other mechanisms and analysis (Vikrey auction, batch vs interactive) – package up and market services (make, popular simulators, DB search) Millennium 27
Current Prototype • Specify #procs p and value on job – rexec -n 16 -value 20 fft. mpi • Market-based Proportional Sharing – Bidder i gets fraction bi / Sk bk of resource – If one bidder, no cost to use resource – Resource may be CPU, Memory, Network, I/O • Existing OS mechanisms/policies insufficient – New proportional CPU schedule for LINUX – New page replacement policy – Game theoretic analysis • Preliminary experience in CS 267 – Students trusted system to allocate fairly, so they did not try to flood system with jobs • Future work – other mechanisms and analysis (Vikrey auction, batch vs interactive) – package up and market services (make, popular simulators, DB search) Millennium 27
 Application Highlights • PEER - NSF Earthquake Engineering Center – FE modeling of Bay Area during Big One – Need better parallel sparse linear system solvers • EBEAM - Electron Beam Lithography – Simulate next generation chip manufacturing – Need better parallel N-body force calculation • AMANDA – Antarctic Muon and Neutrino Detector Array – Need to process many detector tracks for events • Web Page Design – Better human interfaces using novel devices • Digital Library – Support access to large active document collection Millennium 28
Application Highlights • PEER - NSF Earthquake Engineering Center – FE modeling of Bay Area during Big One – Need better parallel sparse linear system solvers • EBEAM - Electron Beam Lithography – Simulate next generation chip manufacturing – Need better parallel N-body force calculation • AMANDA – Antarctic Muon and Neutrino Detector Array – Need to process many detector tracks for events • Web Page Design – Better human interfaces using novel devices • Digital Library – Support access to large active document collection Millennium 28
 Earthquake Modeling • • • PEER = Pacific Earthquake Engineering Research Center UC, Caltech, Stanford, USC, U Washington Model behavior of civil infrastructure in Big One Improve earthquake resistant designs Requires large scale FE models – Buildings, roads, bridges, etc. coupled to ground – Simulate effects of earthquakes – Requires solution of very large sparse linear systems • Collaboration on software – G. Fenves - OO Finite Element Modeling System – J. Demmel - direct and iterative parallel linear equation solvers » Prometheus - a multigrid solver for FE problems (M. Adams) » Super. LU - sparse Gaussian elimination (X. Li) • Port from Cray T 3 E to Millennium 29
Earthquake Modeling • • • PEER = Pacific Earthquake Engineering Research Center UC, Caltech, Stanford, USC, U Washington Model behavior of civil infrastructure in Big One Improve earthquake resistant designs Requires large scale FE models – Buildings, roads, bridges, etc. coupled to ground – Simulate effects of earthquakes – Requires solution of very large sparse linear systems • Collaboration on software – G. Fenves - OO Finite Element Modeling System – J. Demmel - direct and iterative parallel linear equation solvers » Prometheus - a multigrid solver for FE problems (M. Adams) » Super. LU - sparse Gaussian elimination (X. Li) • Port from Cray T 3 E to Millennium 29
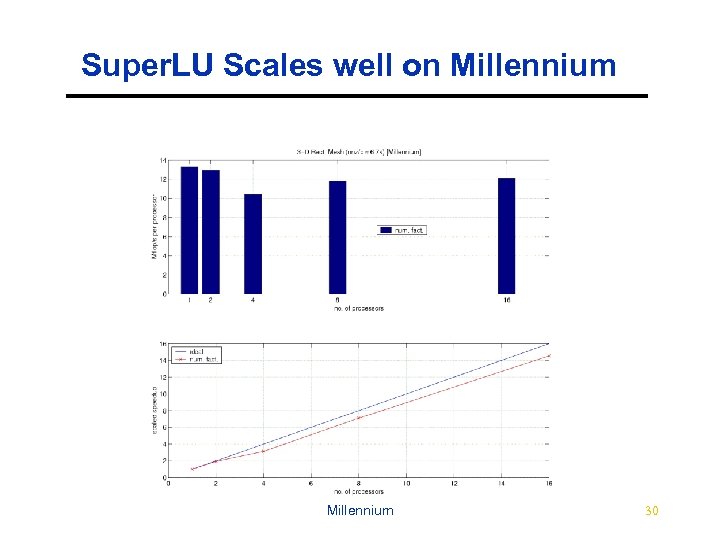 Super. LU Scales well on Millennium 30
Super. LU Scales well on Millennium 30
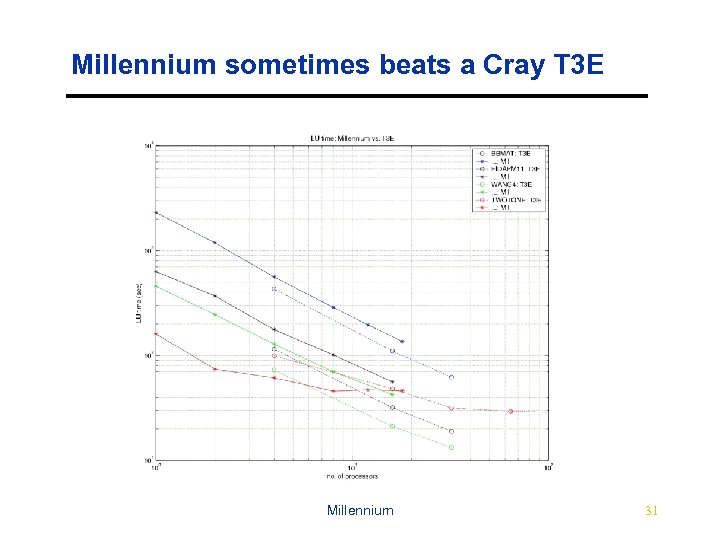 Millennium sometimes beats a Cray T 3 E Millennium 31
Millennium sometimes beats a Cray T 3 E Millennium 31
 EBEAM - Lithography Simulation • A. Neureuther and J. Demmel • Simulate future chip manufacturing devices which will use electron beams instead of light • Computational Bottleneck: computing electrostatic forces on electrons • Pbody (D. Blackston) – Parallel O(N) or O(N log N) N-Body code – Incorporates Barnes-Hut / Fast Multipole Method / Anderson in unified framework – Portable across many platforms – Easy to tune for accuracy and performance • Now used in production runs • Will be packaged as Web service on Millennium, with other TCAD tools 32 Millennium
EBEAM - Lithography Simulation • A. Neureuther and J. Demmel • Simulate future chip manufacturing devices which will use electron beams instead of light • Computational Bottleneck: computing electrostatic forces on electrons • Pbody (D. Blackston) – Parallel O(N) or O(N log N) N-Body code – Incorporates Barnes-Hut / Fast Multipole Method / Anderson in unified framework – Portable across many platforms – Easy to tune for accuracy and performance • Now used in production runs • Will be packaged as Web service on Millennium, with other TCAD tools 32 Millennium
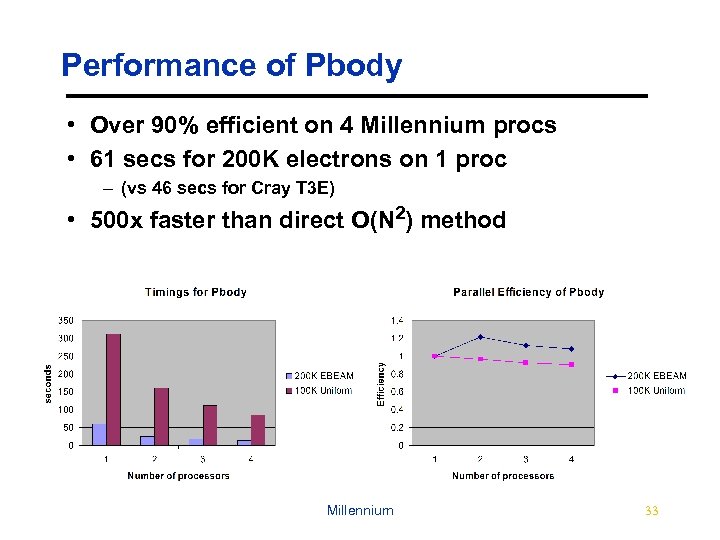 Performance of Pbody • Over 90% efficient on 4 Millennium procs • 61 secs for 200 K electrons on 1 proc – (vs 46 secs for Cray T 3 E) • 500 x faster than direct O(N 2) method Millennium 33
Performance of Pbody • Over 90% efficient on 4 Millennium procs • 61 secs for 200 K electrons on 1 proc – (vs 46 secs for Cray T 3 E) • 500 x faster than direct O(N 2) method Millennium 33
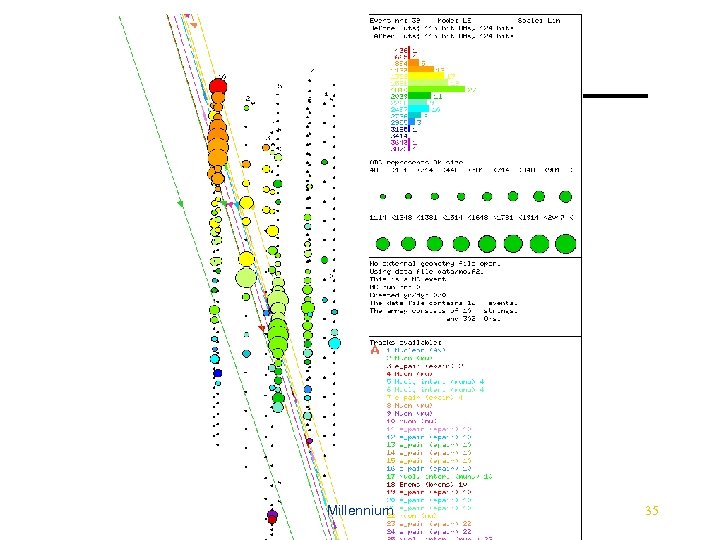
 AMANDA • Antarctic Muon And Neutrino Detector Array • International project to detect particles in 1 km 3 of ice at South Pole • 98 scientists, 15 universities, 4 countries • Millennium uses – Machine at South Pole for data collection, webcast, teleconference – Used in PBS broadcast ``Passport to Knowledge: Live from the Pole” in 1998 linking schoolchildren in Mississippi to South Pole crew – Simulation of AMANDA events and calculating optical properties of the ice Millennium 34
AMANDA • Antarctic Muon And Neutrino Detector Array • International project to detect particles in 1 km 3 of ice at South Pole • 98 scientists, 15 universities, 4 countries • Millennium uses – Machine at South Pole for data collection, webcast, teleconference – Used in PBS broadcast ``Passport to Knowledge: Live from the Pole” in 1998 linking schoolchildren in Mississippi to South Pole crew – Simulation of AMANDA events and calculating optical properties of the ice Millennium 34
 Millennium 35
Millennium 35
 Better Interfaces for Web Site Design • J. Landay, Raecine Sapien (SUPERB student) • Most web designers do not like to program, edit • Provide a more natural user interface that matches their style • Exploit large displays, position trackers, vision and gesture recognition to make design easier and faster • Prototype (minus vision) built over summer, evaluated on a group of designers Millennium 36
Better Interfaces for Web Site Design • J. Landay, Raecine Sapien (SUPERB student) • Most web designers do not like to program, edit • Provide a more natural user interface that matches their style • Exploit large displays, position trackers, vision and gesture recognition to make design easier and faster • Prototype (minus vision) built over summer, evaluated on a group of designers Millennium 36
 Web Site Design Issues Taken from Contextual Design Beyer & Holtzblatt Millennium 37
Web Site Design Issues Taken from Contextual Design Beyer & Holtzblatt Millennium 37
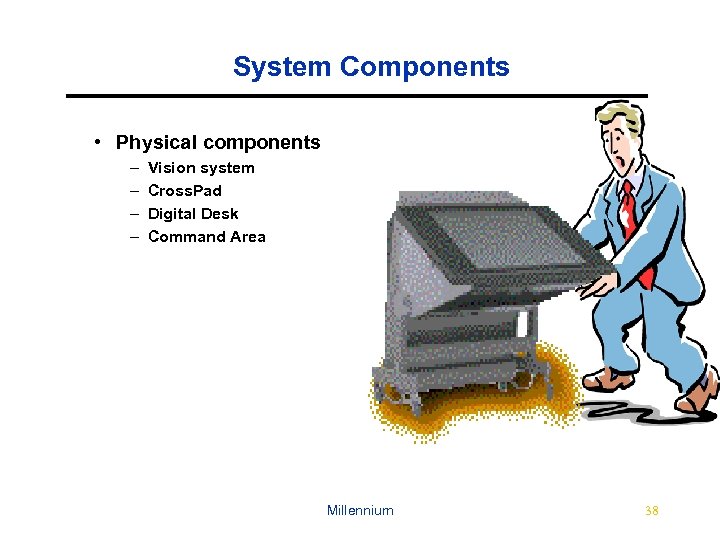 System Components • Physical components – – Vision system Cross. Pad Digital Desk Command Area Millennium 38
System Components • Physical components – – Vision system Cross. Pad Digital Desk Command Area Millennium 38
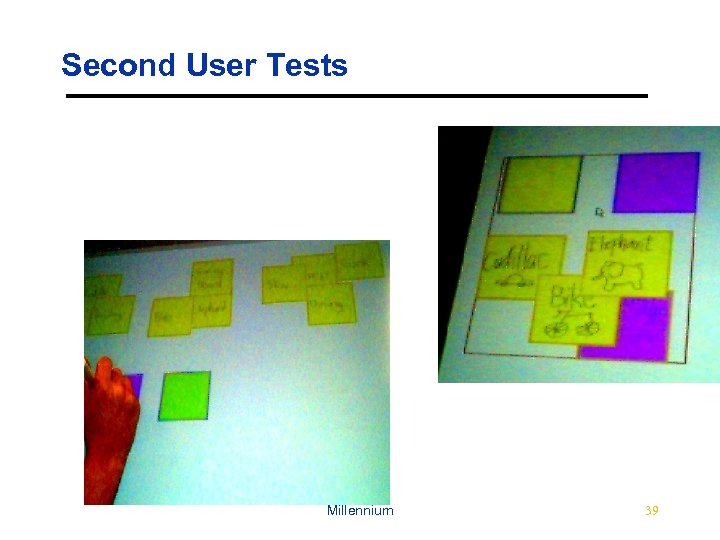 Second User Tests Millennium 39
Second User Tests Millennium 39
 Digital Libraries: Rethinking Scholarly Information Dissemination and Use Robert Wilensky Principal Investigator David Forsyth Co-principal Investigator The UC Berkeley Digital Library Team Millennium
Digital Libraries: Rethinking Scholarly Information Dissemination and Use Robert Wilensky Principal Investigator David Forsyth Co-principal Investigator The UC Berkeley Digital Library Team Millennium
 Goal: Complete Rethinking of How we Use Information • Must support – entire “information cycle”: creation, dissemination and collaboration » in addition to organization, access, presentation and preservation – non-textual material (photos, video, maps) » in addition to text-based content – primary data sources, informal “publication” » as well as traditional archival product – radically new modes of use • Scholarly information use is an especially attractive place to start. Millennium 41
Goal: Complete Rethinking of How we Use Information • Must support – entire “information cycle”: creation, dissemination and collaboration » in addition to organization, access, presentation and preservation – non-textual material (photos, video, maps) » in addition to text-based content – primary data sources, informal “publication” » as well as traditional archival product – radically new modes of use • Scholarly information use is an especially attractive place to start. Millennium 41
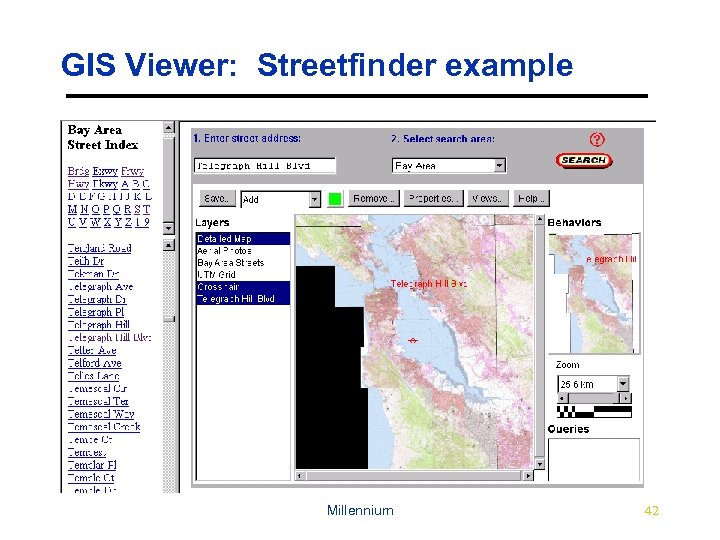 GIS Viewer: Streetfinder example Millennium 42
GIS Viewer: Streetfinder example Millennium 42
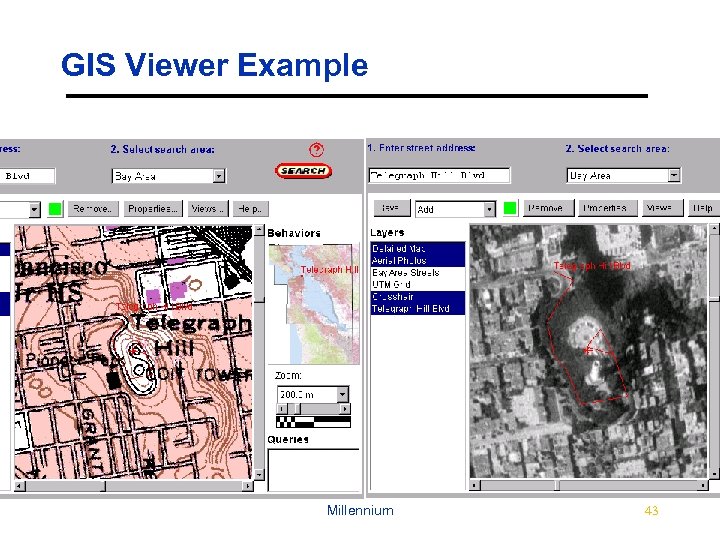 GIS Viewer Example Millennium 43
GIS Viewer Example Millennium 43
 Conclusions: What is Millennium About? • An experiment in large-scale system design • Advance the state of computational science and engineering • Exploring novel design techniques • Exploring important new technologies • NSF support essential Millennium 44
Conclusions: What is Millennium About? • An experiment in large-scale system design • Advance the state of computational science and engineering • Exploring novel design techniques • Exploring important new technologies • NSF support essential Millennium 44


