584eb60c14a370b69f6ee4f38185d539.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 “SIKU” Sea Ice Mapping System The DMI Approach Henrik Steen Andersen Danish Meteorological Institute, Ice Charting and Remote Sensing Division
“SIKU” Sea Ice Mapping System The DMI Approach Henrik Steen Andersen Danish Meteorological Institute, Ice Charting and Remote Sensing Division
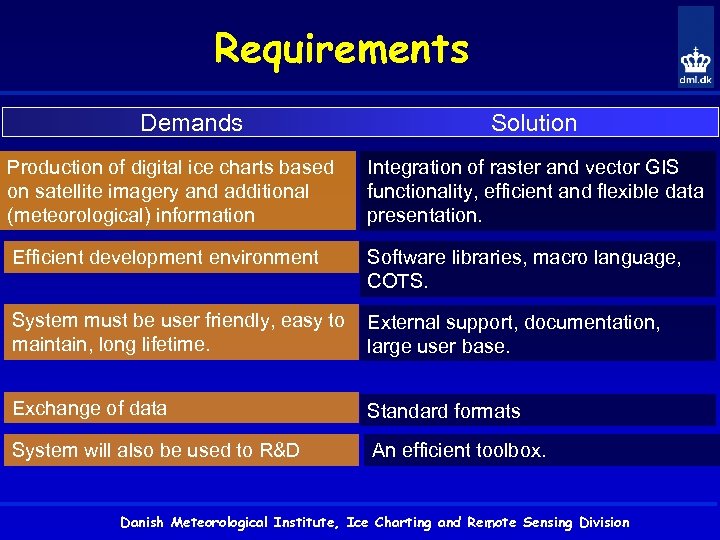 Requirements Demands Solution Production of digital ice charts based on satellite imagery and additional (meteorological) information Integration of raster and vector GIS functionality, efficient and flexible data presentation. Efficient development environment Software libraries, macro language, COTS. System must be user friendly, easy to maintain, long lifetime. External support, documentation, large user base. Exchange of data Standard formats System will also be used to R&D An efficient toolbox. Danish Meteorological Institute, Ice Charting and Remote Sensing Division
Requirements Demands Solution Production of digital ice charts based on satellite imagery and additional (meteorological) information Integration of raster and vector GIS functionality, efficient and flexible data presentation. Efficient development environment Software libraries, macro language, COTS. System must be user friendly, easy to maintain, long lifetime. External support, documentation, large user base. Exchange of data Standard formats System will also be used to R&D An efficient toolbox. Danish Meteorological Institute, Ice Charting and Remote Sensing Division
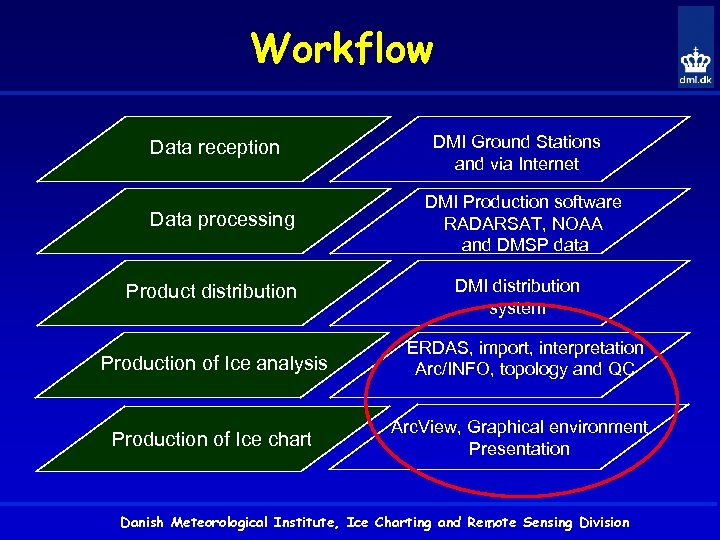 Workflow Data reception Data processing Product distribution Production of Ice analysis Production of Ice chart DMI Ground Stations and via Internet DMI Production software RADARSAT, NOAA and DMSP data DMI distribution system ERDAS, import, interpretation Arc/INFO, topology and QC Arc. View, Graphical environment Presentation Danish Meteorological Institute, Ice Charting and Remote Sensing Division
Workflow Data reception Data processing Product distribution Production of Ice analysis Production of Ice chart DMI Ground Stations and via Internet DMI Production software RADARSAT, NOAA and DMSP data DMI distribution system ERDAS, import, interpretation Arc/INFO, topology and QC Arc. View, Graphical environment Presentation Danish Meteorological Institute, Ice Charting and Remote Sensing Division
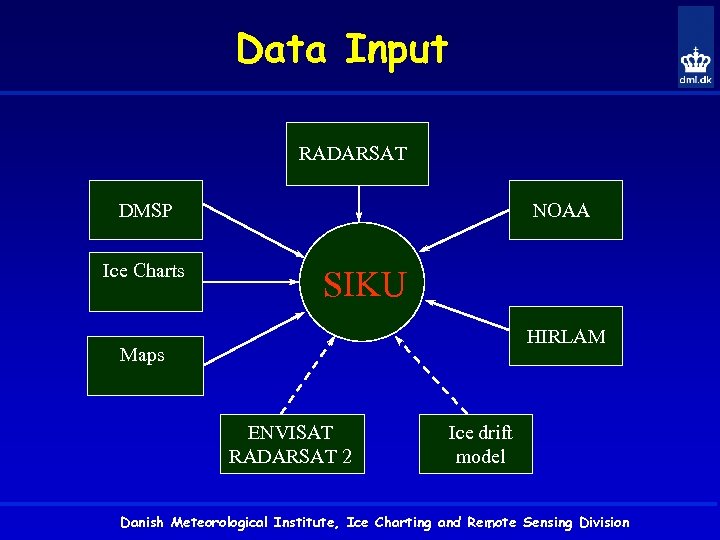 Data Input RADARSAT NOAA DMSP Ice Charts SIKU HIRLAM Maps ENVISAT RADARSAT 2 Ice drift model Danish Meteorological Institute, Ice Charting and Remote Sensing Division
Data Input RADARSAT NOAA DMSP Ice Charts SIKU HIRLAM Maps ENVISAT RADARSAT 2 Ice drift model Danish Meteorological Institute, Ice Charting and Remote Sensing Division
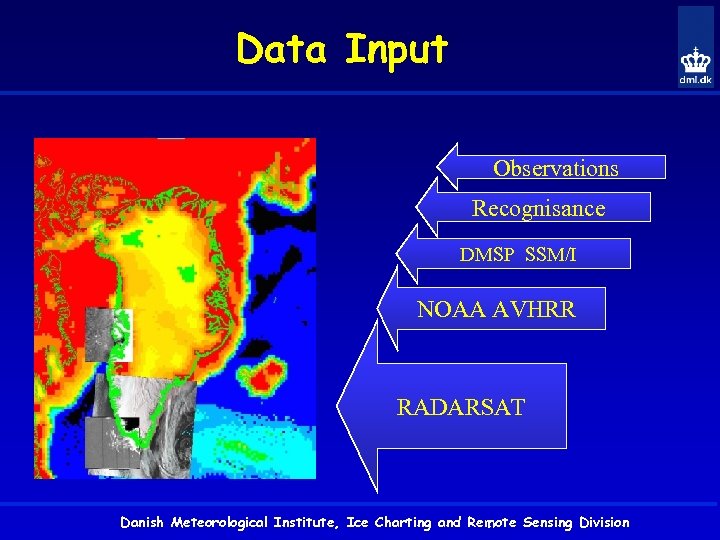 Data Input Observations Recognisance DMSP SSM/I NOAA AVHRR RADARSAT Danish Meteorological Institute, Ice Charting and Remote Sensing Division
Data Input Observations Recognisance DMSP SSM/I NOAA AVHRR RADARSAT Danish Meteorological Institute, Ice Charting and Remote Sensing Division
 Current Status • Hardware – SGI O 2 Front end, two screens. – Connected to DMI operational production system • OS – UNIX (front end and production) • Software – – DMI software, satellite data ingest and production ERDAS Imagine, version 8. 3 Arc/INFO, version 8. 1 Arc. View, version 3. 3 Danish Meteorological Institute, Ice Charting and Remote Sensing Division
Current Status • Hardware – SGI O 2 Front end, two screens. – Connected to DMI operational production system • OS – UNIX (front end and production) • Software – – DMI software, satellite data ingest and production ERDAS Imagine, version 8. 3 Arc/INFO, version 8. 1 Arc. View, version 3. 3 Danish Meteorological Institute, Ice Charting and Remote Sensing Division
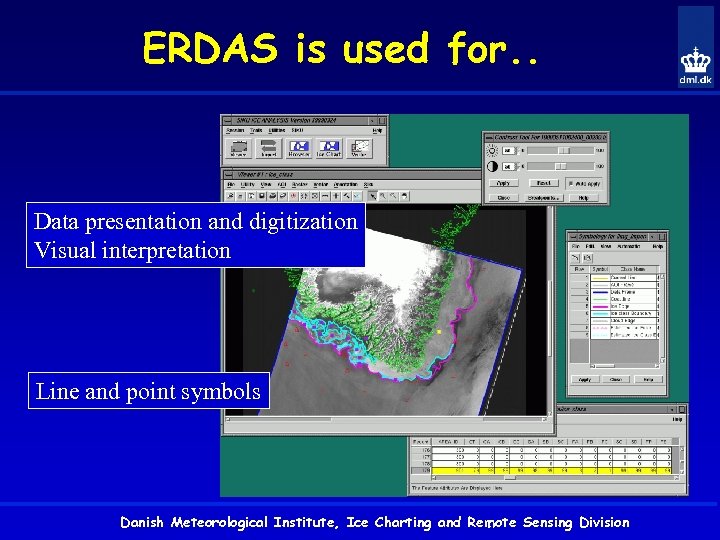 ERDAS is used for. . Data presentation and digitization Visual interpretation Line and point symbols Danish Meteorological Institute, Ice Charting and Remote Sensing Division
ERDAS is used for. . Data presentation and digitization Visual interpretation Line and point symbols Danish Meteorological Institute, Ice Charting and Remote Sensing Division
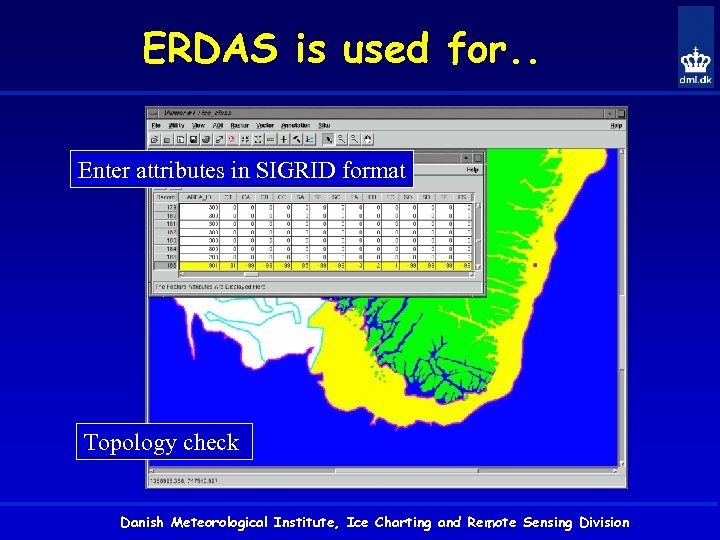 ERDAS is used for. . Enter attributes in SIGRID format Topology check Danish Meteorological Institute, Ice Charting and Remote Sensing Division
ERDAS is used for. . Enter attributes in SIGRID format Topology check Danish Meteorological Institute, Ice Charting and Remote Sensing Division
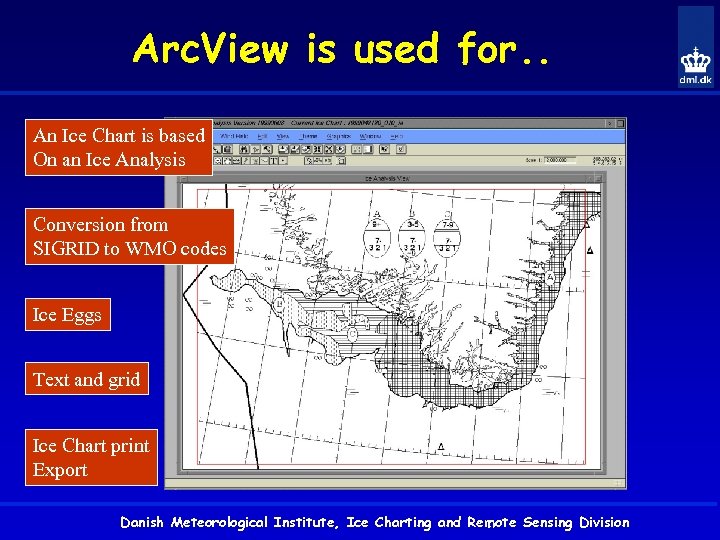 Arc. View is used for. . An Ice Chart is based On an Ice Analysis Conversion from SIGRID to WMO codes Ice Eggs Text and grid Ice Chart print Export Danish Meteorological Institute, Ice Charting and Remote Sensing Division
Arc. View is used for. . An Ice Chart is based On an Ice Analysis Conversion from SIGRID to WMO codes Ice Eggs Text and grid Ice Chart print Export Danish Meteorological Institute, Ice Charting and Remote Sensing Division
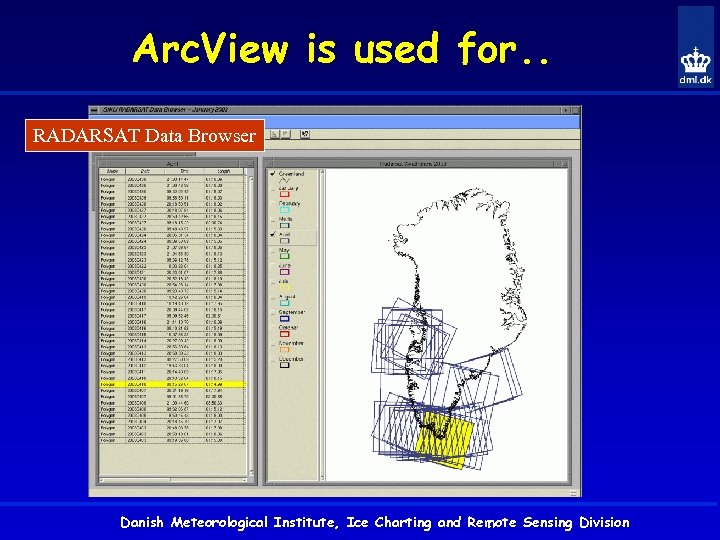 Arc. View is used for. . RADARSAT Data Browser Danish Meteorological Institute, Ice Charting and Remote Sensing Division
Arc. View is used for. . RADARSAT Data Browser Danish Meteorological Institute, Ice Charting and Remote Sensing Division
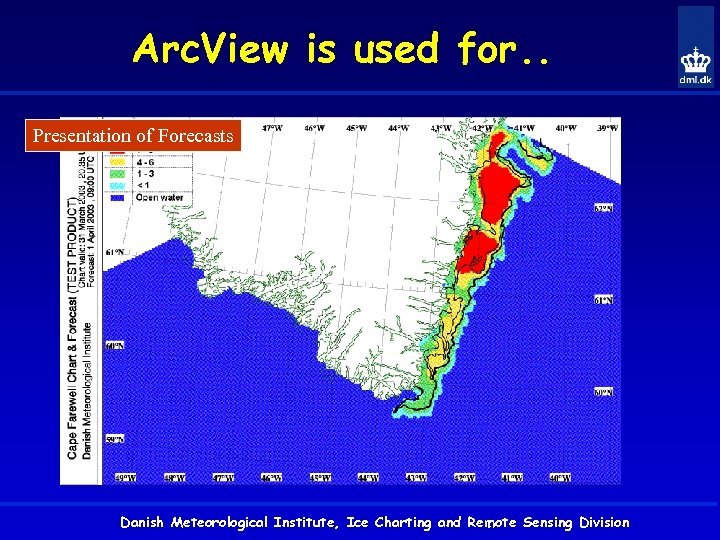 Arc. View is used for. . Presentation of Forecasts Danish Meteorological Institute, Ice Charting and Remote Sensing Division
Arc. View is used for. . Presentation of Forecasts Danish Meteorological Institute, Ice Charting and Remote Sensing Division
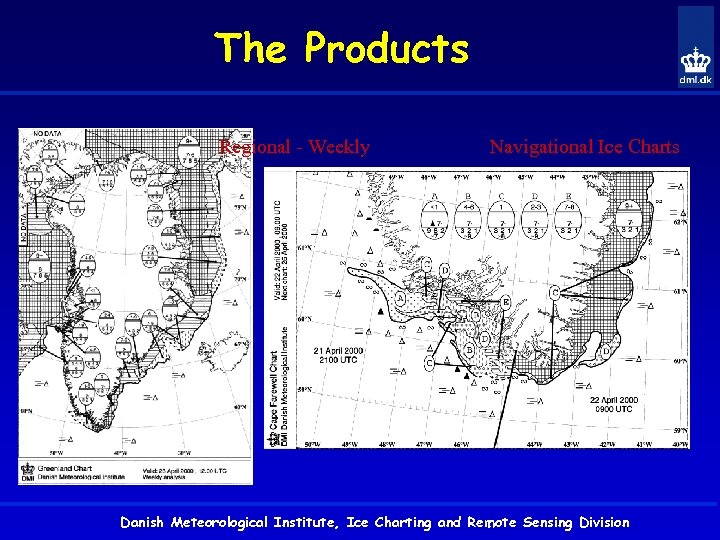 The Products Regional - Weekly Navigational Ice Charts Danish Meteorological Institute, Ice Charting and Remote Sensing Division
The Products Regional - Weekly Navigational Ice Charts Danish Meteorological Institute, Ice Charting and Remote Sensing Division
 What’s New ? • The current version of SIKU has been working operationally since 1999 • The front end hardware is from 1998 • Only minor changes have been made since Danish Meteorological Institute, Ice Charting and Remote Sensing Division
What’s New ? • The current version of SIKU has been working operationally since 1999 • The front end hardware is from 1998 • Only minor changes have been made since Danish Meteorological Institute, Ice Charting and Remote Sensing Division
 Are the Ice Analysts Happy ? • The ice analysts find SIKU satisfactory – The system is stable – The workflow is logical – Normally the system is not the limiting factor – We are getting the job done Danish Meteorological Institute, Ice Charting and Remote Sensing Division
Are the Ice Analysts Happy ? • The ice analysts find SIKU satisfactory – The system is stable – The workflow is logical – Normally the system is not the limiting factor – We are getting the job done Danish Meteorological Institute, Ice Charting and Remote Sensing Division
 Are the Ice Analysts Happy ? • On the other hand. . – Basic functionality should be improved • Easier selection of lines and symbols • A better way to enter area attributes • Optimize the digitization process – Faster hardware would be nice – Add new information layers Danish Meteorological Institute, Ice Charting and Remote Sensing Division
Are the Ice Analysts Happy ? • On the other hand. . – Basic functionality should be improved • Easier selection of lines and symbols • A better way to enter area attributes • Optimize the digitization process – Faster hardware would be nice – Add new information layers Danish Meteorological Institute, Ice Charting and Remote Sensing Division
 Maintenance and Development • The struggle between new ideas and resources – The system is customizable – The knowledge is available – We have plenty of new ideas – BUT human and economic resources are limited Danish Meteorological Institute, Ice Charting and Remote Sensing Division
Maintenance and Development • The struggle between new ideas and resources – The system is customizable – The knowledge is available – We have plenty of new ideas – BUT human and economic resources are limited Danish Meteorological Institute, Ice Charting and Remote Sensing Division
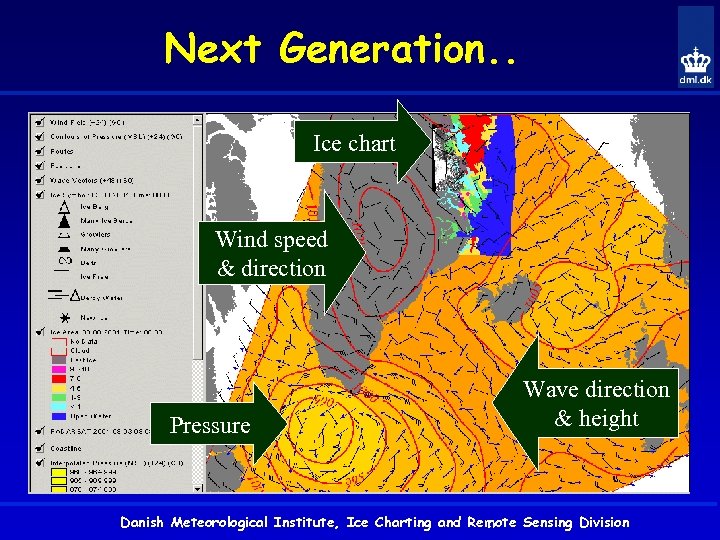 Next Generation. . Ice chart Wind speed & direction Pressure Wave direction & height Danish Meteorological Institute, Ice Charting and Remote Sensing Division
Next Generation. . Ice chart Wind speed & direction Pressure Wave direction & height Danish Meteorological Institute, Ice Charting and Remote Sensing Division
 Next Generation. . • Trends. . – ESRI software development strategy makes WINDOWS mandatory – Arc. GIS may contain all necessary elements – ERDAS may only be used for R&D – Normally it is easier to buy software including support than to pay contractors Danish Meteorological Institute, Ice Charting and Remote Sensing Division
Next Generation. . • Trends. . – ESRI software development strategy makes WINDOWS mandatory – Arc. GIS may contain all necessary elements – ERDAS may only be used for R&D – Normally it is easier to buy software including support than to pay contractors Danish Meteorological Institute, Ice Charting and Remote Sensing Division
 Next Generation. . • Advantages. . – Arc. GIS provides very flexible customization tools – Arc. GIS is scalable – Support and maintenance are simpler – Hardware is cheaper – It is a very interesting job to convert from Avenue to VBA – Other Ice Services use ESRI software Danish Meteorological Institute, Ice Charting and Remote Sensing Division
Next Generation. . • Advantages. . – Arc. GIS provides very flexible customization tools – Arc. GIS is scalable – Support and maintenance are simpler – Hardware is cheaper – It is a very interesting job to convert from Avenue to VBA – Other Ice Services use ESRI software Danish Meteorological Institute, Ice Charting and Remote Sensing Division
 Next Generation. . • Questions. . – Do Arc. GIS provide the efficient image presentation environment that we need ? – Will it be possible for DMI to maintain and further develop the software ? – Can DMI benefit from the development in the other ice services ? – Is it possible to exchange / buy customized modules ? Danish Meteorological Institute, Ice Charting and Remote Sensing Division
Next Generation. . • Questions. . – Do Arc. GIS provide the efficient image presentation environment that we need ? – Will it be possible for DMI to maintain and further develop the software ? – Can DMI benefit from the development in the other ice services ? – Is it possible to exchange / buy customized modules ? Danish Meteorological Institute, Ice Charting and Remote Sensing Division
 The Way Forward. . • DMI most upgrade HW / SW within 1 -2 years. • Major DMI development efforts must be financed by external sources. • Customized (front end) modules based on COTS could be a very interesting alternative. • DMI possess the necessary technical skills to maintain the software and implement interfaces Danish Meteorological Institute, Ice Charting and Remote Sensing Division
The Way Forward. . • DMI most upgrade HW / SW within 1 -2 years. • Major DMI development efforts must be financed by external sources. • Customized (front end) modules based on COTS could be a very interesting alternative. • DMI possess the necessary technical skills to maintain the software and implement interfaces Danish Meteorological Institute, Ice Charting and Remote Sensing Division


