33968b63203feecae1b561f35069cdf7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 12
 SIER Game Goals: 1. Understand how various key economic concepts may be linked in a market oriented society; 2. Understand how difficult proper policy making may be. 1
SIER Game Goals: 1. Understand how various key economic concepts may be linked in a market oriented society; 2. Understand how difficult proper policy making may be. 1
 Steps 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Game format Welfare: what makes voters happy? The structure of the economy: consumers, firms and government (= teams) What determines firm behaviour? What determines consumer behaviour? Which tools of economic policy do the players have? Examples: how do tools affect the economy and, as a result, welfare? 2
Steps 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Game format Welfare: what makes voters happy? The structure of the economy: consumers, firms and government (= teams) What determines firm behaviour? What determines consumer behaviour? Which tools of economic policy do the players have? Examples: how do tools affect the economy and, as a result, welfare? 2
 1. Game Format n n A world with 4 independent countries Teams of 3 or 4 students form the governments In period 0, all countries are equal The countries are economically linked. Period 1: n All governments submit policies for period 1 computer calculates impact on economies and on welfare levels = results for period 1 = starting levels of period 2. n All governments submit policies for period 2, etc. n Final round = election time: country with highest welfare level wins, provided that its welfare > 100. 00 (starting level). 3
1. Game Format n n A world with 4 independent countries Teams of 3 or 4 students form the governments In period 0, all countries are equal The countries are economically linked. Period 1: n All governments submit policies for period 1 computer calculates impact on economies and on welfare levels = results for period 1 = starting levels of period 2. n All governments submit policies for period 2, etc. n Final round = election time: country with highest welfare level wins, provided that its welfare > 100. 00 (starting level). 3
 2. Welfare: what makes voters happy? n Welfare starts at 100. 00 and goes up if: 1. More real private cons. of goods + services (each civil servant produces 1 service period) 2. Unemployment < 3% ideal: 0 3. Price changes are smaller than 1% ideal: no inflation or deflation 4. Balance on government account < 1% of national income ideal: no surplus, no deficit Note: balance government = tax revenue – government spending 5. Surplus on balance of internat. payments between 2 and 4 ideal: + 3 Note: here, surplus on balance of internat. payments = export – import. n If no country pursues any policy welfare constant (100. 00). 4
2. Welfare: what makes voters happy? n Welfare starts at 100. 00 and goes up if: 1. More real private cons. of goods + services (each civil servant produces 1 service period) 2. Unemployment < 3% ideal: 0 3. Price changes are smaller than 1% ideal: no inflation or deflation 4. Balance on government account < 1% of national income ideal: no surplus, no deficit Note: balance government = tax revenue – government spending 5. Surplus on balance of internat. payments between 2 and 4 ideal: + 3 Note: here, surplus on balance of internat. payments = export – import. n If no country pursues any policy welfare constant (100. 00). 4
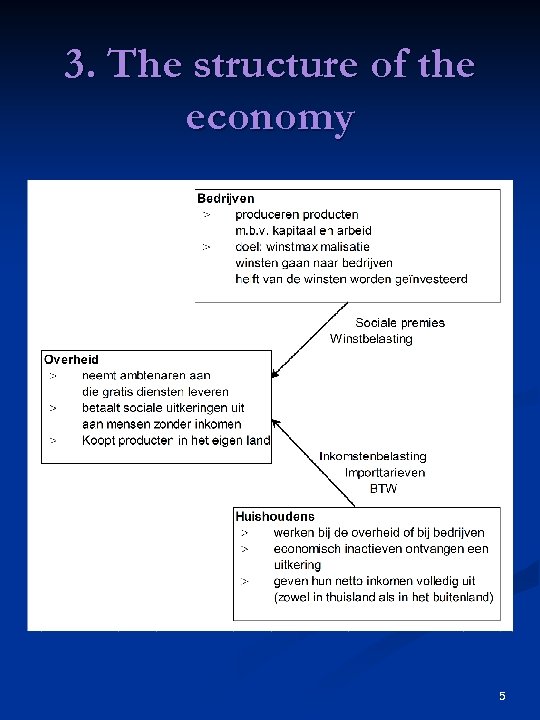 3. The structure of the economy 5
3. The structure of the economy 5
 4. What determines firm behaviour? Assumptions: n n n Firms act under perfect competition All firms in a country make identical products These products compete with foreign products Firms hire labour and machines How much do they invest ? If net profits 1 period later: investments 2 periods later: - more operational machines - output How many products do they supply? Depends on: profit margin per product (price – labour costs) Note: labour costs = wage + social security tax maximum output. The supply curve. Note: when does it shift rightward? 6
4. What determines firm behaviour? Assumptions: n n n Firms act under perfect competition All firms in a country make identical products These products compete with foreign products Firms hire labour and machines How much do they invest ? If net profits 1 period later: investments 2 periods later: - more operational machines - output How many products do they supply? Depends on: profit margin per product (price – labour costs) Note: labour costs = wage + social security tax maximum output. The supply curve. Note: when does it shift rightward? 6
 What determines consumer behaviour? Assumptions: n Households do not save n Only households buy foreign products (Government buys in home country, only) n If net income rises by 1% consumers buy 1% more of each product. n If the price of a product goes up by 2% consumers buy 3% less of this product and more of the other products. The demand curve Note: when does this curve shift rightward? 7
What determines consumer behaviour? Assumptions: n Households do not save n Only households buy foreign products (Government buys in home country, only) n If net income rises by 1% consumers buy 1% more of each product. n If the price of a product goes up by 2% consumers buy 3% less of this product and more of the other products. The demand curve Note: when does this curve shift rightward? 7
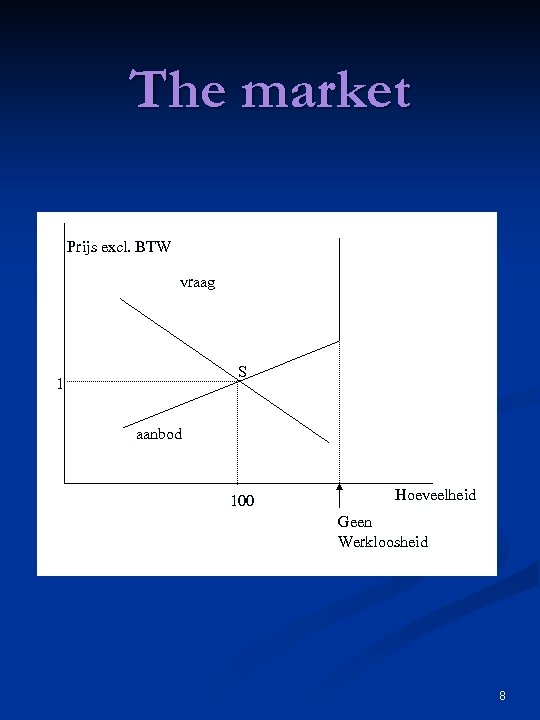 The market Prijs excl. BTW vraag S 1 aanbod 100 Hoeveelheid Geen Werkloosheid 8
The market Prijs excl. BTW vraag S 1 aanbod 100 Hoeveelheid Geen Werkloosheid 8
 5. The tools of economic policy Instruments economy changes welfare changes. Available instruments: n Value Added Tax (VAT) n Income tax n Profit tax n Social security tax n Import tariffs ( trade blocks) n Government purchases n Number of civil servants n Wages paid by firms n Wages of civil servants n social benefit level n Devaluation Which tools make demand curve shift? Which tools make supply curve shift? 9
5. The tools of economic policy Instruments economy changes welfare changes. Available instruments: n Value Added Tax (VAT) n Income tax n Profit tax n Social security tax n Import tariffs ( trade blocks) n Government purchases n Number of civil servants n Wages paid by firms n Wages of civil servants n social benefit level n Devaluation Which tools make demand curve shift? Which tools make supply curve shift? 9
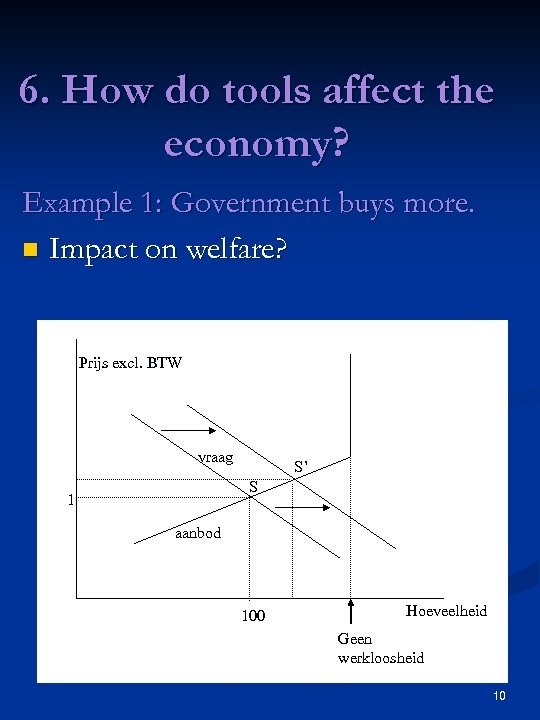 6. How do tools affect the economy? Example 1: Government buys more. n Impact on welfare? Prijs excl. BTW vraag S’ S 1 aanbod 100 Hoeveelheid Geen werkloosheid 10
6. How do tools affect the economy? Example 1: Government buys more. n Impact on welfare? Prijs excl. BTW vraag S’ S 1 aanbod 100 Hoeveelheid Geen werkloosheid 10
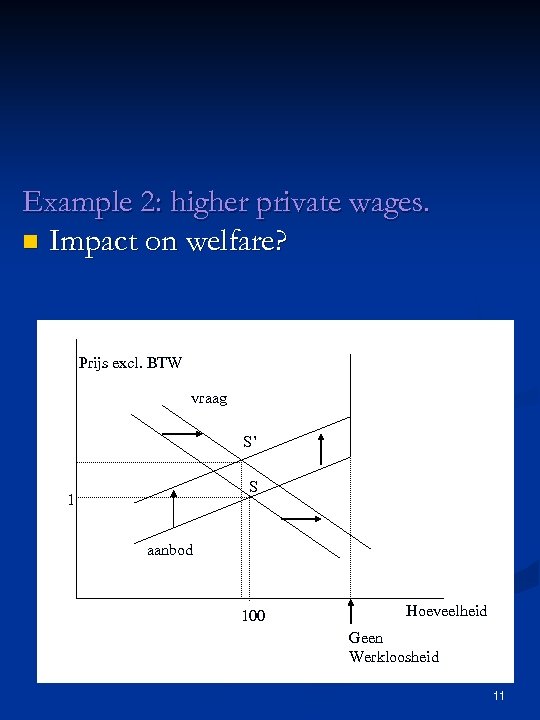 Example 2: higher private wages. n Impact on welfare? Prijs excl. BTW vraag S’ S 1 aanbod 100 Hoeveelheid Geen Werkloosheid 11
Example 2: higher private wages. n Impact on welfare? Prijs excl. BTW vraag S’ S 1 aanbod 100 Hoeveelheid Geen Werkloosheid 11
 Questions? 12
Questions? 12


