042b05ce593d625a24955742d46e34b1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35

Short-Term Memory Kimberley Clow kclow 2@uwo. ca http: //instruct. uwo. ca/psychology/130/
Outline What is Memory? Structure l STM vs. LTM l Capacity of STM Forgetting l Decay vs. Interference Structure of STM

What Is Memory? Two different types of memory Short-Term Memory l Long-Term Memory l Important Terms Structure l Encoding l Retrieval l Forgetting l
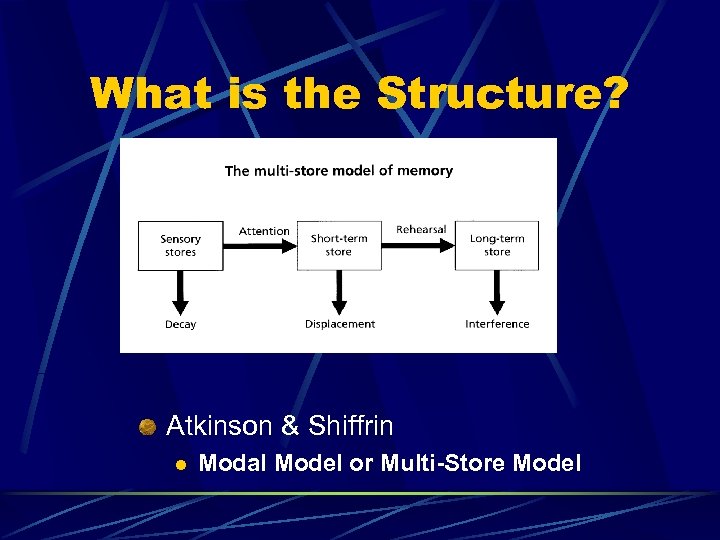
What is the Structure? Atkinson & Shiffrin l Modal Model or Multi-Store Model

What Words? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. drum 2. curtain bell coffee school parent moon garden hat farmer nose turkey colour house river quite good recall bad recall best recall
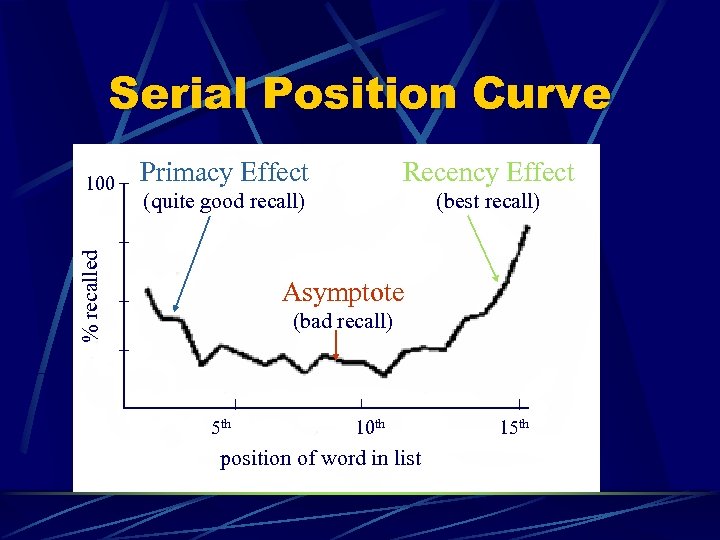
Serial Position Curve Primacy Effect Recency Effect (quite good recall) (best recall) % recalled 100 Asymptote (bad recall) 5 th 10 th position of word in list 15 th
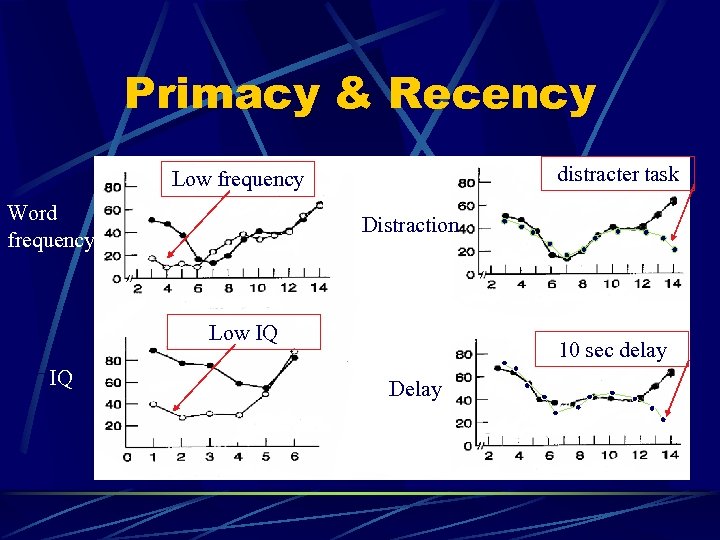
Primacy & Recency distracter task Low frequency Word frequency Distraction Low IQ IQ 10 sec delay Delay

Neurological Evidence CW l Problems with short-term memory l Anterograde amnesia HM Short-term memory was good l Problems with long-term memory l KF l Short-term memory impaired l Span of apprehension was 1 item

Short-Term Memory What is Short-Term Memory? The information that is in consciousness right now l The limited-capacity memory component for temporary information storage and manipulation l The mental workplace for retrieval and use of already known information l

The Magical Number 7 (± 2) “My problem is that I have been persecuted by an integer. For seven years this number has followed me around, has intruded in my most private data, and has assaulted me from the pages of our most public journals. This number assumes a variety of disguises, being sometimes a little larger and sometimes a little smaller than usual, but never changing so much as to be unrecognizable… Eithere really is something unusual about the number or else I am suffering from delusions of persecution. ”
Capacity of STM How can we function on such a small short-term memory capacity? Techniques that aid memory l Rehearsal l l Eases transfer to LTM Mnemonic Devices l Strategies for increasing STM capacity

Chunking IFYOUGROUPTOGETHERYOUREMEMBERBETTER

Which is Easier? CHJ MLK ODW

Which is Easier? FBI PHD IBM

Which is Easier? AFGHANISTAN VENEZUELA NICARAGUA

Which is Easier? CUBA MALTA GREECE

Individual Differences Mnemonic Differences l Novice vs. Expert
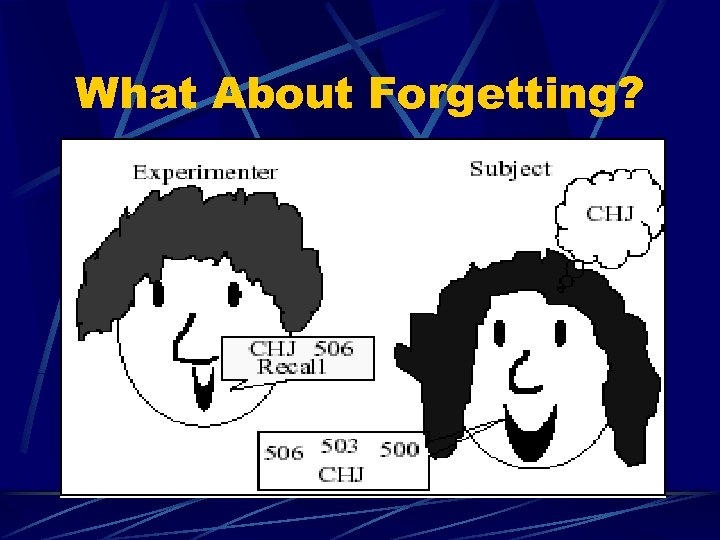
What About Forgetting?

The Brown-Peterson Task l Forget the letters very quickly l l l 70% accuracy after 3 s 10% accuracy after 15 s Concluded that items decay out of short term memory very quickly
Decay vs. Interference Two reasons why we may forget things l Decay l l l Information fades from memory Not influenced by other information Interference l Other information disrupts learning l l Proactive Interference Retroactive Interference

Probe Digit Task
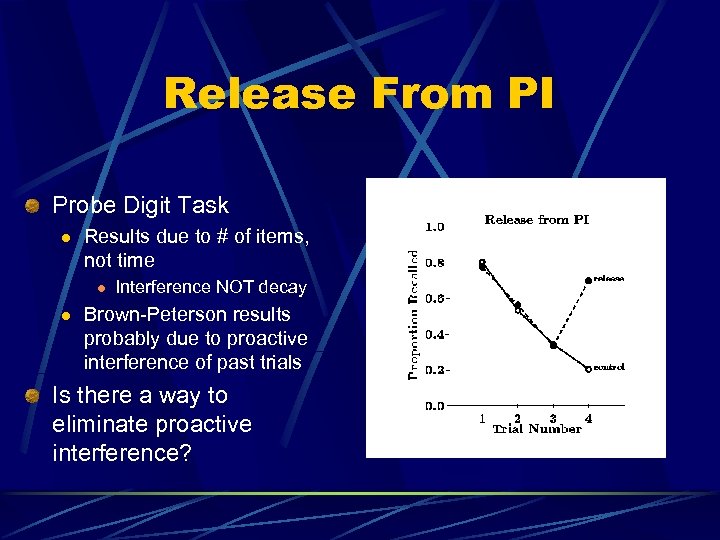
Release From PI Probe Digit Task l Results due to # of items, not time l l Interference NOT decay Brown-Peterson results probably due to proactive interference of past trials Is there a way to eliminate proactive interference?

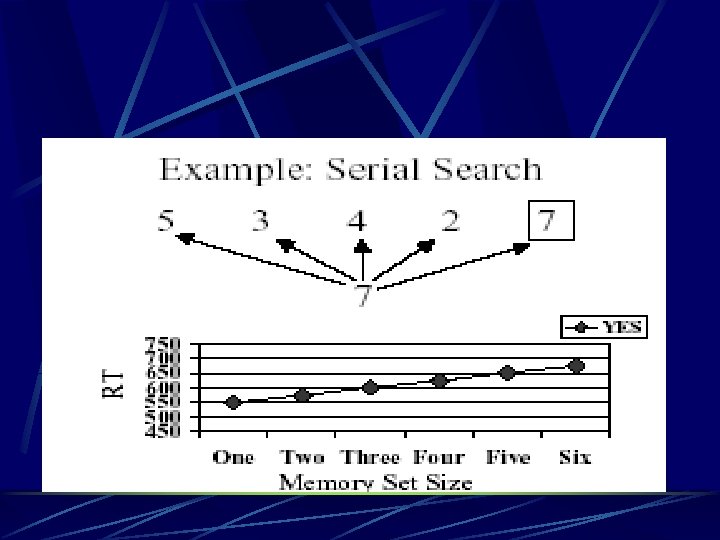
Searching STM Sternberg l Shown a string of characters (1 -6) l l Then a single character appears (probe) l l l 53427 7 Was the probe in the string? Measure speed of response depending upon… l l l How many characters were presented The sequential position of the probed character Whether the answer was yes or no
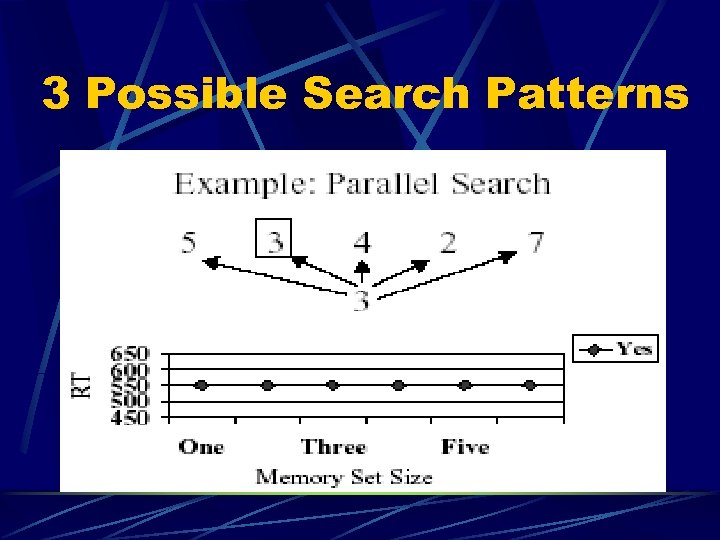
3 Possible Search Patterns


What Info Is in Memory? Verbal l Confuse E with D (auditory information) l Not E with F (visual information) Semantic l Release from proactive interference (PI) l Changing categories is semantic info Visual l Mental rotation tasks
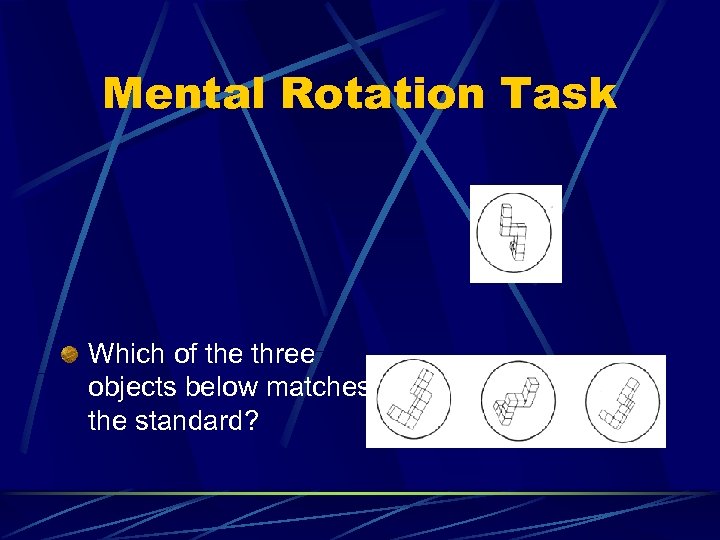
Mental Rotation Task Which of the three objects below matches the standard?
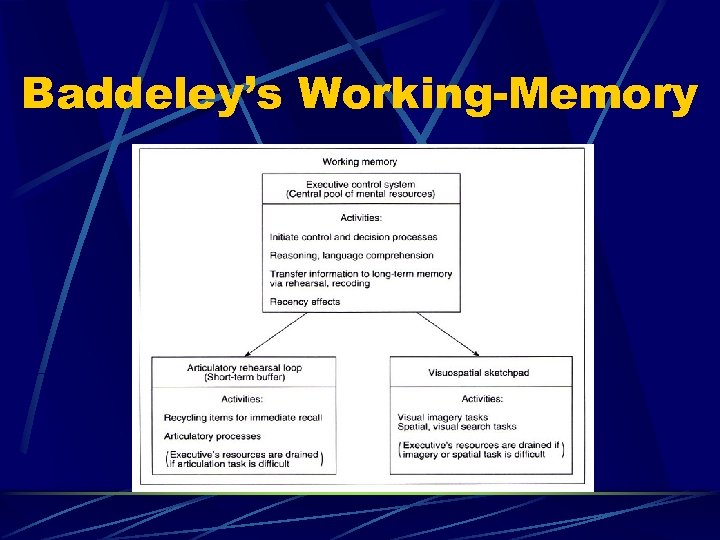
Baddeley’s Working-Memory

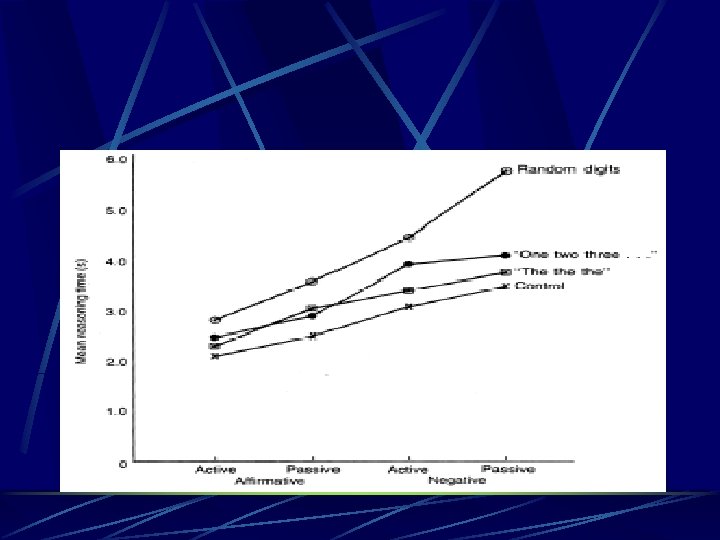
Evidence Remember a string of 6 numbers or letters Simultaneously do a reasoning task Shown stimuli like “AB” l Then asked a true or false question l A precedes B l B is preceded by A l B does not precede A l A is not preceded by B l B precedes A A is preceded by B A does not precede B B is not preceded by A
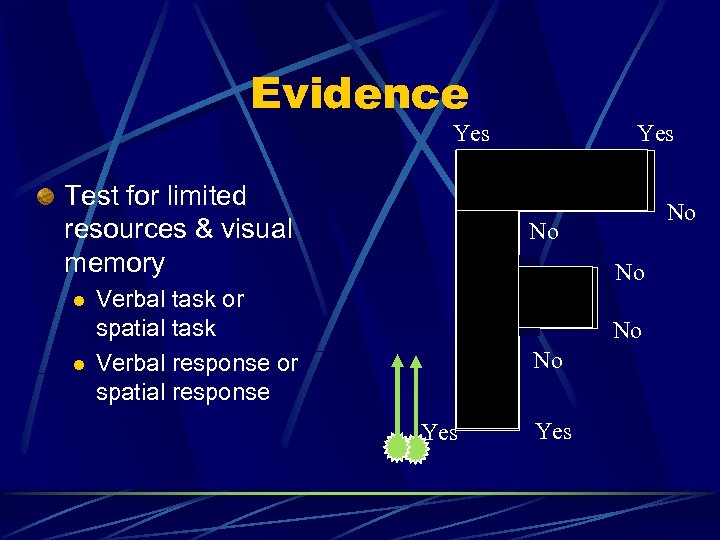
Evidence Yes Test for limited resources & visual memory l l Yes No No No Verbal task or spatial task Verbal response or spatial response No No Yes
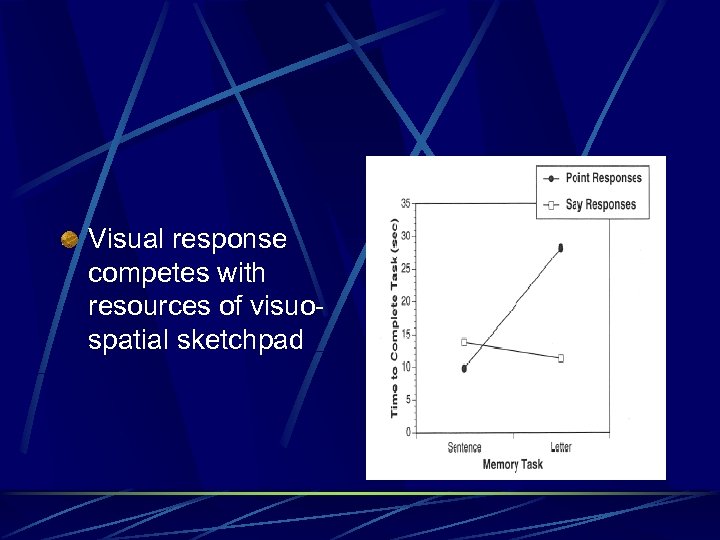
Visual response competes with resources of visuospatial sketchpad

Summary Short-term memory is limited in capacity l Decay vs. Interference Short-term memory is where information is consciously manipulated l l Rehearse to maintain information temporarily or to transfer to long-term memory Workbench for manipulating current conscious information Short-term memory specializes in verbal and visuo-spatial information
042b05ce593d625a24955742d46e34b1.ppt