1dda8de58643fdcaedebb9944da1c465.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Shocking Regions: Estimating the Temporal and Spatial Effects of One-Time Events Michael Beenstock Daniel Felsenstein Hebrew University of Jerusalem
Shocking Regions: Estimating the Temporal and Spatial Effects of One-Time Events Michael Beenstock Daniel Felsenstein Hebrew University of Jerusalem
 The Issues • Rising interest in the spatial dynamics of shocks and disasters (Katrina, Tsunami, acts of warfare and terrorism). • Shocks have a spatial and temporal impact: onetime effect and cumulative effects • Much interest in the temporal effects: can cities bounce back? how long does it take? is there a size threshold for shocks? 2
The Issues • Rising interest in the spatial dynamics of shocks and disasters (Katrina, Tsunami, acts of warfare and terrorism). • Shocks have a spatial and temporal impact: onetime effect and cumulative effects • Much interest in the temporal effects: can cities bounce back? how long does it take? is there a size threshold for shocks? 2
 The Methods • Control groups and trend analysis (Bram et al 2002, WTC 9/11). • Expanded I-O models (SIM) (Okuyama, Hewings and Sonis 2004, Kobe earthquake 1995) • CGE models (Rose et al 2004, electricity losses from Tennesse earthquake) • NEG models- path dependence and temporary equilibria (Brakman et al 2004, Davis and Weinstein 2002, wars and bombing damage: Hiroshima, Dresden) What about abrupt socio-econ processes and not just natural and man-made ‘disasters’? 3
The Methods • Control groups and trend analysis (Bram et al 2002, WTC 9/11). • Expanded I-O models (SIM) (Okuyama, Hewings and Sonis 2004, Kobe earthquake 1995) • CGE models (Rose et al 2004, electricity losses from Tennesse earthquake) • NEG models- path dependence and temporary equilibria (Brakman et al 2004, Davis and Weinstein 2002, wars and bombing damage: Hiroshima, Dresden) What about abrupt socio-econ processes and not just natural and man-made ‘disasters’? 3
 The State of the Literature • Spatial Panel Models: Pfeifer & Deutsch (1980), univariate context temporal lags, ‘lagged’ spatial lags • Static Spatial Panel Models: Elhorst (2003) SAC and spatial lags Elhorst (2004) SAC and TAC 4
The State of the Literature • Spatial Panel Models: Pfeifer & Deutsch (1980), univariate context temporal lags, ‘lagged’ spatial lags • Static Spatial Panel Models: Elhorst (2003) SAC and spatial lags Elhorst (2004) SAC and TAC 4
 The State of the Literature (cont. ) • Dynamic Spatial Panel Models – 2 stage process 1. spatial filtering 2. estimate dynamic panel Badinger, Muller and Tondl (2004) • Dynamic Spatial Panel Models – joint estimation, multivariate Spatial lags and spatial (auto)correlation estimated jointly with temporal lags and temporal autocorrelation. Beenstock and Felsenstein (2007) 5
The State of the Literature (cont. ) • Dynamic Spatial Panel Models – 2 stage process 1. spatial filtering 2. estimate dynamic panel Badinger, Muller and Tondl (2004) • Dynamic Spatial Panel Models – joint estimation, multivariate Spatial lags and spatial (auto)correlation estimated jointly with temporal lags and temporal autocorrelation. Beenstock and Felsenstein (2007) 5
 The Questions • Method: can temporal and spatial dynamics of shocks be integrated (using spatial panel data)? • Temporary or permanent effects: What are the impulse responses? How long do they last? • Spatial issues: are shocks independent or spatially correlated? 6
The Questions • Method: can temporal and spatial dynamics of shocks be integrated (using spatial panel data)? • Temporary or permanent effects: What are the impulse responses? How long do they last? • Spatial issues: are shocks independent or spatially correlated? 6
 Notation Regions: n = 1, 2, …. . , N Time Periods: t = 1, 2, . . …, T Endogenous Variables (Yk) k = 1, 2, . . …, K Exogenous Variables (XP) p = 1, 2, . . …, P Temporal Lag (Yt-q) q = 1, 2, . . …, Q 7
Notation Regions: n = 1, 2, …. . , N Time Periods: t = 1, 2, . . …, T Endogenous Variables (Yk) k = 1, 2, . . …, K Exogenous Variables (XP) p = 1, 2, . . …, P Temporal Lag (Yt-q) q = 1, 2, . . …, Q 7
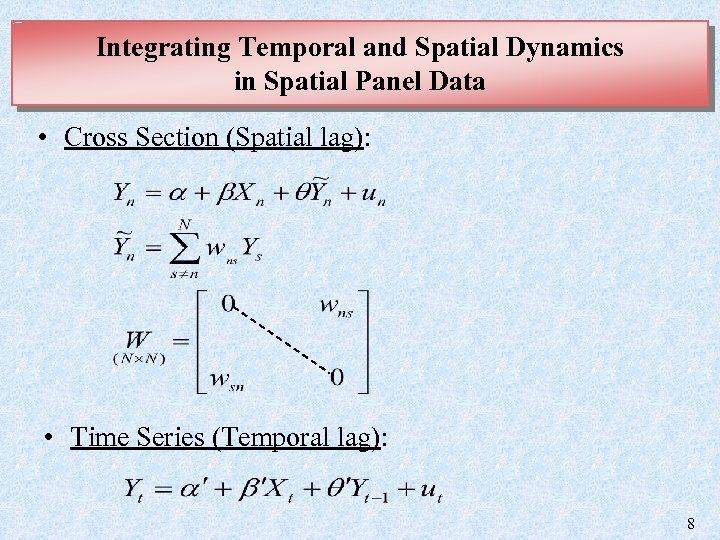 Integrating Temporal and Spatial Dynamics in Spatial Panel Data • Cross Section (Spatial lag): • Time Series (Temporal lag): 8
Integrating Temporal and Spatial Dynamics in Spatial Panel Data • Cross Section (Spatial lag): • Time Series (Temporal lag): 8
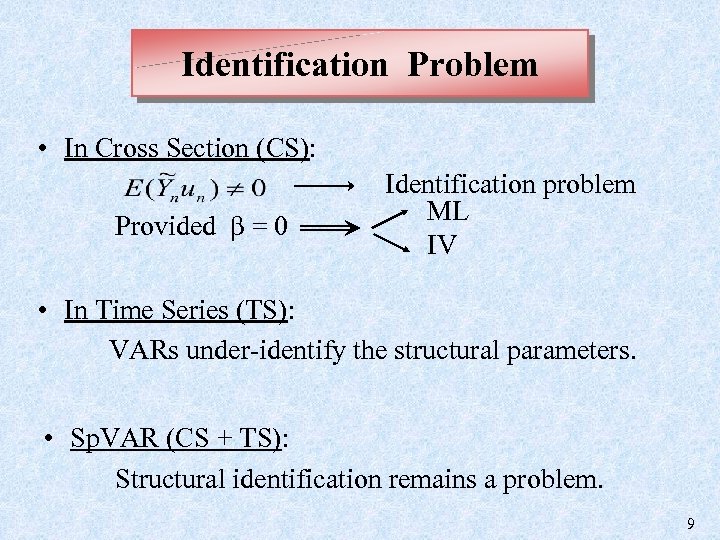 Identification Problem • In Cross Section (CS): Provided β = 0 Identification problem ML IV • In Time Series (TS): VARs under-identify the structural parameters. • Sp. VAR (CS + TS): Structural identification remains a problem. 9
Identification Problem • In Cross Section (CS): Provided β = 0 Identification problem ML IV • In Time Series (TS): VARs under-identify the structural parameters. • Sp. VAR (CS + TS): Structural identification remains a problem. 9
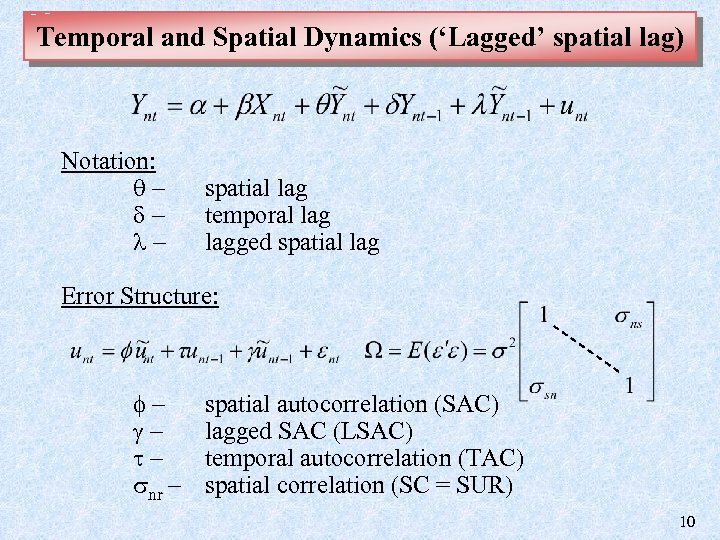 Temporal and Spatial Dynamics (‘Lagged’ spatial lag) Notation: – – – spatial lag temporal lagged spatial lag Error Structure: – – – nr – spatial autocorrelation (SAC) lagged SAC (LSAC) temporal autocorrelation (TAC) spatial correlation (SC = SUR) 10
Temporal and Spatial Dynamics (‘Lagged’ spatial lag) Notation: – – – spatial lag temporal lagged spatial lag Error Structure: – – – nr – spatial autocorrelation (SAC) lagged SAC (LSAC) temporal autocorrelation (TAC) spatial correlation (SC = SUR) 10
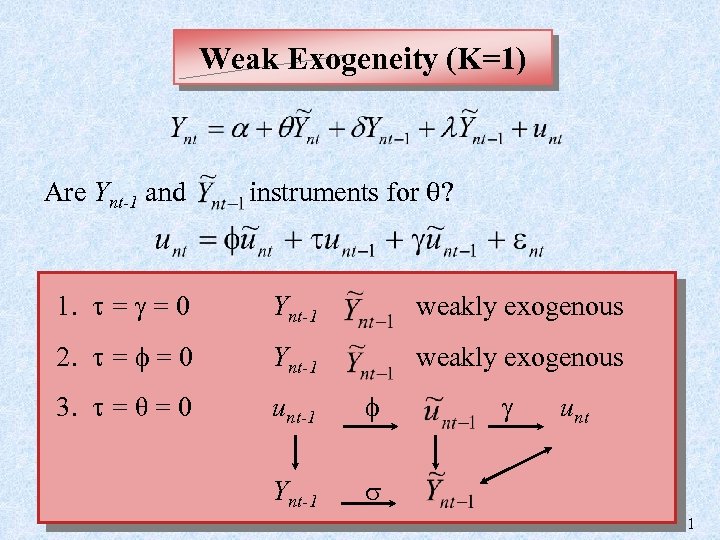 Weak Exogeneity (K=1) Are Ynt-1 and instruments for ? 1. = = 0 Ynt-1 weakly exogenous 2. = = 0 Ynt-1 weakly exogenous 3. = θ = 0 unt-1 unt Ynt-1 11
Weak Exogeneity (K=1) Are Ynt-1 and instruments for ? 1. = = 0 Ynt-1 weakly exogenous 2. = = 0 Ynt-1 weakly exogenous 3. = θ = 0 unt-1 unt Ynt-1 11
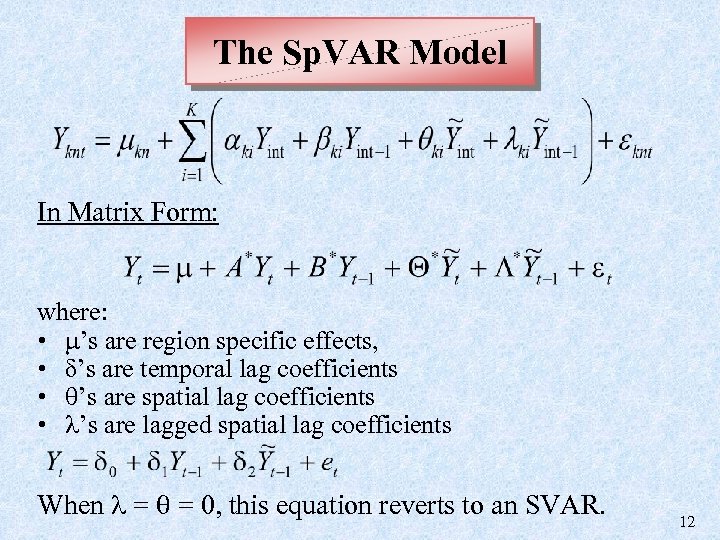 The Sp. VAR Model In Matrix Form: where: • ’s are region specific effects, • δ’s are temporal lag coefficients • ’s are spatial lag coefficients • ’s are lagged spatial lag coefficients When = = 0, this equation reverts to an SVAR. 12
The Sp. VAR Model In Matrix Form: where: • ’s are region specific effects, • δ’s are temporal lag coefficients • ’s are spatial lag coefficients • ’s are lagged spatial lag coefficients When = = 0, this equation reverts to an SVAR. 12
 Data Sources • 9 regions, 1987 -2004 • 4 variables: Earnings: Household Income Surveys (CBS) Population: Central Bureau of Statistics House Prices: Central Bureau of Statistics Housing Stock: Housing Completions (CBS) 13
Data Sources • 9 regions, 1987 -2004 • 4 variables: Earnings: Household Income Surveys (CBS) Population: Central Bureau of Statistics House Prices: Central Bureau of Statistics Housing Stock: Housing Completions (CBS) 13
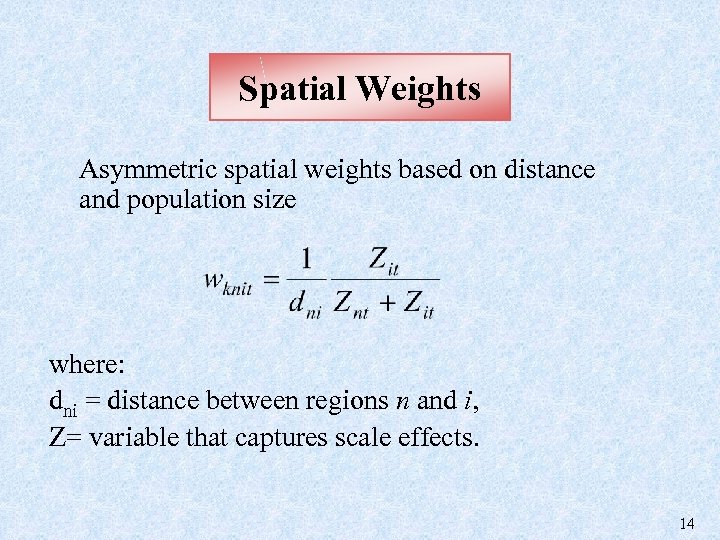 Spatial Weights Asymmetric spatial weights based on distance and population size where: dni = distance between regions n and i, Z= variable that captures scale effects. 14
Spatial Weights Asymmetric spatial weights based on distance and population size where: dni = distance between regions n and i, Z= variable that captures scale effects. 14
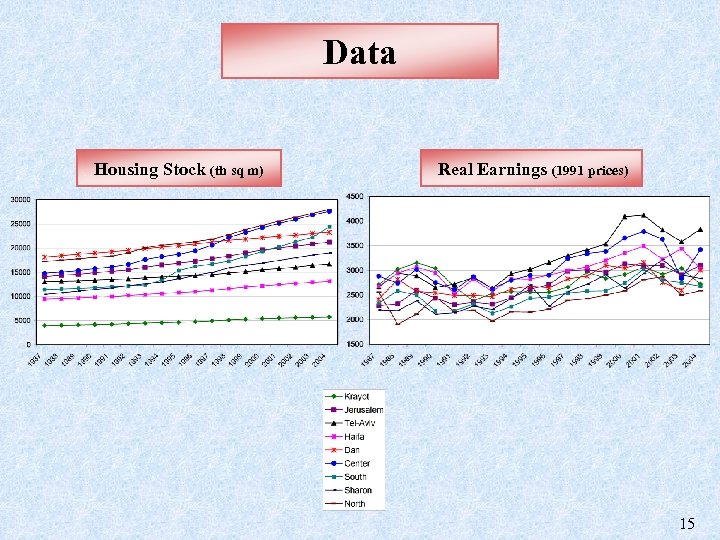 Data Housing Stock (th sq m) Real Earnings (1991 prices) 15
Data Housing Stock (th sq m) Real Earnings (1991 prices) 15
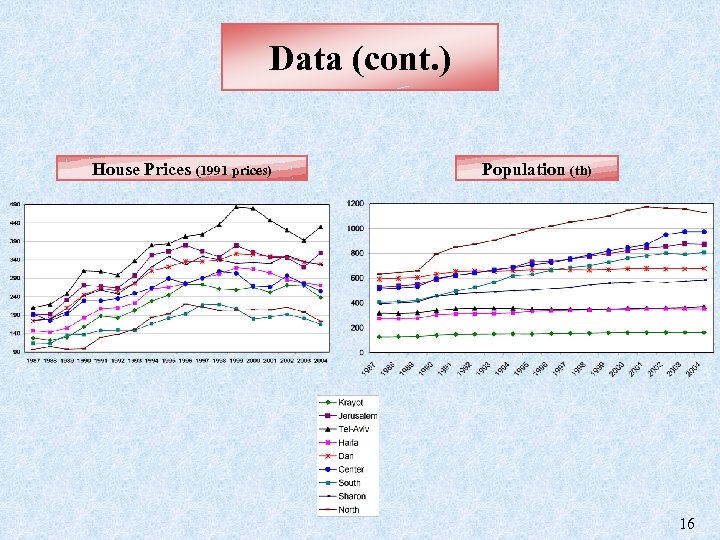 Data (cont. ) House Prices (1991 prices) Population (th) 16
Data (cont. ) House Prices (1991 prices) Population (th) 16
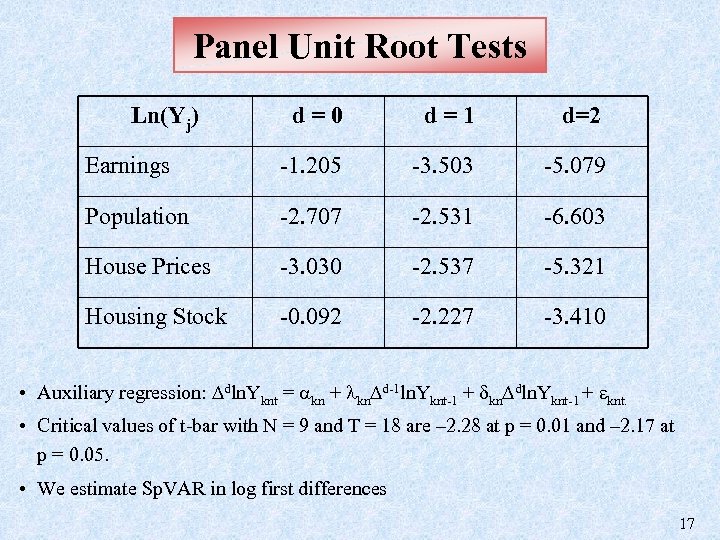 Panel Unit Root Tests Ln(Yj) d=0 d=1 d=2 Earnings -1. 205 -3. 503 -5. 079 Population -2. 707 -2. 531 -6. 603 House Prices -3. 030 -2. 537 -5. 321 Housing Stock -0. 092 -2. 227 -3. 410 • Auxiliary regression: dln. Yknt = kn + kn d-1 ln. Yknt-1 + kn dln. Yknt-1 + knt. • Critical values of t-bar with N = 9 and T = 18 are – 2. 28 at p = 0. 01 and – 2. 17 at p = 0. 05. • We estimate Sp. VAR in log first differences 17
Panel Unit Root Tests Ln(Yj) d=0 d=1 d=2 Earnings -1. 205 -3. 503 -5. 079 Population -2. 707 -2. 531 -6. 603 House Prices -3. 030 -2. 537 -5. 321 Housing Stock -0. 092 -2. 227 -3. 410 • Auxiliary regression: dln. Yknt = kn + kn d-1 ln. Yknt-1 + kn dln. Yknt-1 + knt. • Critical values of t-bar with N = 9 and T = 18 are – 2. 28 at p = 0. 01 and – 2. 17 at p = 0. 05. • We estimate Sp. VAR in log first differences 17
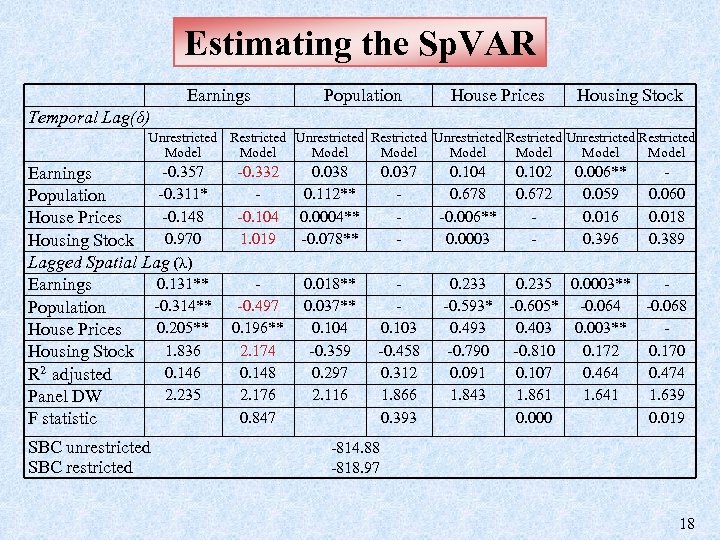 Estimating the Sp. VAR Earnings Temporal Lag(δ) Unrestricted Restricted Model -0. 357 Earnings -0. 311* Population -0. 148 House Prices 0. 970 Housing Stock Lagged Spatial Lag (λ) 0. 131** Earnings -0. 314** Population 0. 205** House Prices 1. 836 Housing Stock 0. 146 R 2 adjusted 2. 235 Panel DW F statistic SBC unrestricted SBC restricted Model Population House Prices Housing Stock Unrestricted Restricted Model Model -0. 332 -0. 104 1. 019 0. 038 0. 112** 0. 0004** -0. 078** 0. 037 - 0. 104 0. 678 -0. 006** 0. 0003 -0. 497 0. 196** 2. 174 0. 148 2. 176 0. 847 0. 018** 0. 037** 0. 104 -0. 359 0. 297 2. 116 0. 103 -0. 458 0. 312 1. 866 0. 393 0. 233 -0. 593* 0. 493 -0. 790 0. 091 1. 843 0. 102 0. 672 - 0. 006** 0. 059 0. 016 0. 396 0. 060 0. 018 0. 389 0. 235 0. 0003** -0. 605* -0. 064 -0. 068 0. 403 0. 003** -0. 810 0. 172 0. 170 0. 107 0. 464 0. 474 1. 861 1. 641 1. 639 0. 000 0. 019 -814. 88 -818. 97 18
Estimating the Sp. VAR Earnings Temporal Lag(δ) Unrestricted Restricted Model -0. 357 Earnings -0. 311* Population -0. 148 House Prices 0. 970 Housing Stock Lagged Spatial Lag (λ) 0. 131** Earnings -0. 314** Population 0. 205** House Prices 1. 836 Housing Stock 0. 146 R 2 adjusted 2. 235 Panel DW F statistic SBC unrestricted SBC restricted Model Population House Prices Housing Stock Unrestricted Restricted Model Model -0. 332 -0. 104 1. 019 0. 038 0. 112** 0. 0004** -0. 078** 0. 037 - 0. 104 0. 678 -0. 006** 0. 0003 -0. 497 0. 196** 2. 174 0. 148 2. 176 0. 847 0. 018** 0. 037** 0. 104 -0. 359 0. 297 2. 116 0. 103 -0. 458 0. 312 1. 866 0. 393 0. 233 -0. 593* 0. 493 -0. 790 0. 091 1. 843 0. 102 0. 672 - 0. 006** 0. 059 0. 016 0. 396 0. 060 0. 018 0. 389 0. 235 0. 0003** -0. 605* -0. 064 -0. 068 0. 403 0. 003** -0. 810 0. 172 0. 170 0. 107 0. 464 0. 474 1. 861 1. 641 1. 639 0. 000 0. 019 -814. 88 -818. 97 18
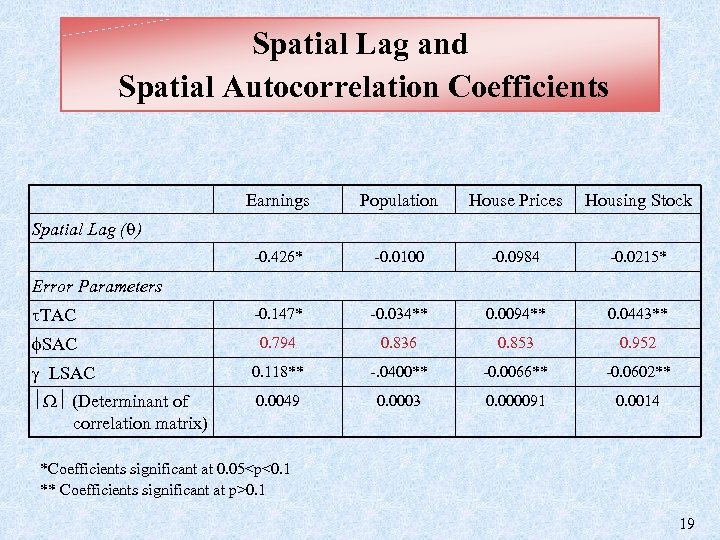 Spatial Lag and Spatial Autocorrelation Coefficients Earnings Population House Prices Housing Stock -0. 426* -0. 0100 -0. 0984 -0. 0215* TAC -0. 147* -0. 034** 0. 0094** 0. 0443** SAC 0. 794 0. 836 0. 853 0. 952 LSAC 0. 118** -. 0400** -0. 0066** -0. 0602** (Determinant of correlation matrix) 0. 0049 0. 0003 0. 000091 0. 0014 Spatial Lag ( ) Error Parameters *Coefficients significant at 0. 05
Spatial Lag and Spatial Autocorrelation Coefficients Earnings Population House Prices Housing Stock -0. 426* -0. 0100 -0. 0984 -0. 0215* TAC -0. 147* -0. 034** 0. 0094** 0. 0443** SAC 0. 794 0. 836 0. 853 0. 952 LSAC 0. 118** -. 0400** -0. 0066** -0. 0602** (Determinant of correlation matrix) 0. 0049 0. 0003 0. 000091 0. 0014 Spatial Lag ( ) Error Parameters *Coefficients significant at 0. 05
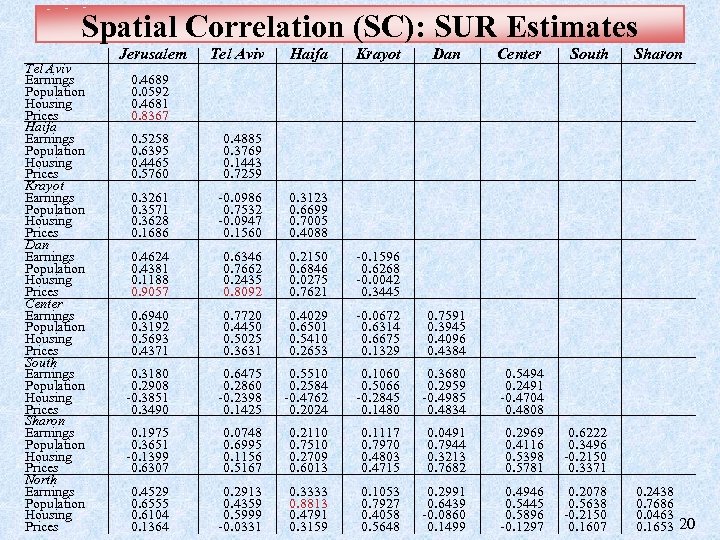 Spatial Correlation (SC): SUR Estimates Tel Aviv Earnings Population Housing Prices Haifa Earnings Population Housing Prices Krayot Earnings Population Housing Prices Dan Earnings Population Housing Prices Center Earnings Population Housing Prices South Earnings Population Housing Prices Sharon Earnings Population Housing Prices North Earnings Population Housing Prices Jerusalem 0. 4689 0. 0592 0. 4681 0. 8367 0. 5258 0. 6395 0. 4465 0. 5760 0. 3261 0. 3571 0. 3628 0. 1686 0. 4624 0. 4381 0. 1188 0. 9057 0. 6940 0. 3192 0. 5693 0. 4371 0. 3180 0. 2908 -0. 3851 0. 3490 0. 1975 0. 3651 -0. 1399 0. 6307 0. 4529 0. 6555 0. 6104 0. 1364 Tel Aviv Haifa Krayot 0. 4885 0. 3769 0. 1443 0. 7259 -0. 0986 0. 7532 -0. 0947 0. 1560 0. 6346 0. 7662 0. 2435 0. 8092 0. 7720 0. 4450 0. 5025 0. 3631 0. 6475 0. 2860 -0. 2398 0. 1425 0. 0748 0. 6995 0. 1156 0. 5167 0. 2913 0. 4359 0. 5999 -0. 0331 0. 3123 0. 6699 0. 7005 0. 4088 0. 2150 0. 6846 0. 0275 0. 7621 0. 4029 0. 6501 0. 5410 0. 2653 0. 5510 0. 2584 -0. 4762 0. 2024 0. 2110 0. 7510 0. 2709 0. 6013 0. 3333 0. 8813 0. 4791 0. 3159 Center South Sharon -0. 1596 0. 6268 -0. 0042 0. 3445 -0. 0672 0. 6314 0. 6675 0. 1329 0. 1060 0. 5066 -0. 2845 0. 1480 0. 1117 0. 7970 0. 4803 0. 4715 0. 1053 0. 7927 0. 4058 0. 5648 0. 7591 0. 3945 0. 4096 0. 4384 0. 3680 0. 2959 -0. 4985 0. 4834 0. 0491 0. 7944 0. 3213 0. 7682 0. 2991 0. 6439 -0. 0860 0. 1499 0. 5494 0. 2491 -0. 4704 0. 4808 0. 2969 0. 4116 0. 5398 0. 5781 0. 4946 0. 5445 0. 5896 -0. 1297 0. 6222 0. 3496 -0. 2150 0. 3371 0. 2078 0. 5638 -0. 2150 0. 1607 Dan 0. 2438 0. 7686 0. 0463 0. 1653 20
Spatial Correlation (SC): SUR Estimates Tel Aviv Earnings Population Housing Prices Haifa Earnings Population Housing Prices Krayot Earnings Population Housing Prices Dan Earnings Population Housing Prices Center Earnings Population Housing Prices South Earnings Population Housing Prices Sharon Earnings Population Housing Prices North Earnings Population Housing Prices Jerusalem 0. 4689 0. 0592 0. 4681 0. 8367 0. 5258 0. 6395 0. 4465 0. 5760 0. 3261 0. 3571 0. 3628 0. 1686 0. 4624 0. 4381 0. 1188 0. 9057 0. 6940 0. 3192 0. 5693 0. 4371 0. 3180 0. 2908 -0. 3851 0. 3490 0. 1975 0. 3651 -0. 1399 0. 6307 0. 4529 0. 6555 0. 6104 0. 1364 Tel Aviv Haifa Krayot 0. 4885 0. 3769 0. 1443 0. 7259 -0. 0986 0. 7532 -0. 0947 0. 1560 0. 6346 0. 7662 0. 2435 0. 8092 0. 7720 0. 4450 0. 5025 0. 3631 0. 6475 0. 2860 -0. 2398 0. 1425 0. 0748 0. 6995 0. 1156 0. 5167 0. 2913 0. 4359 0. 5999 -0. 0331 0. 3123 0. 6699 0. 7005 0. 4088 0. 2150 0. 6846 0. 0275 0. 7621 0. 4029 0. 6501 0. 5410 0. 2653 0. 5510 0. 2584 -0. 4762 0. 2024 0. 2110 0. 7510 0. 2709 0. 6013 0. 3333 0. 8813 0. 4791 0. 3159 Center South Sharon -0. 1596 0. 6268 -0. 0042 0. 3445 -0. 0672 0. 6314 0. 6675 0. 1329 0. 1060 0. 5066 -0. 2845 0. 1480 0. 1117 0. 7970 0. 4803 0. 4715 0. 1053 0. 7927 0. 4058 0. 5648 0. 7591 0. 3945 0. 4096 0. 4384 0. 3680 0. 2959 -0. 4985 0. 4834 0. 0491 0. 7944 0. 3213 0. 7682 0. 2991 0. 6439 -0. 0860 0. 1499 0. 5494 0. 2491 -0. 4704 0. 4808 0. 2969 0. 4116 0. 5398 0. 5781 0. 4946 0. 5445 0. 5896 -0. 1297 0. 6222 0. 3496 -0. 2150 0. 3371 0. 2078 0. 5638 -0. 2150 0. 1607 Dan 0. 2438 0. 7686 0. 0463 0. 1653 20
 Sp. VAR Impulse Response Simulations: The effect of shocks to variable k in region n on: • The shocked variable in the region in which the shock occurred • Other variables in which the shock occurred • The shocked variable in other regions • Other variables in other regions 21
Sp. VAR Impulse Response Simulations: The effect of shocks to variable k in region n on: • The shocked variable in the region in which the shock occurred • Other variables in which the shock occurred • The shocked variable in other regions • Other variables in other regions 21
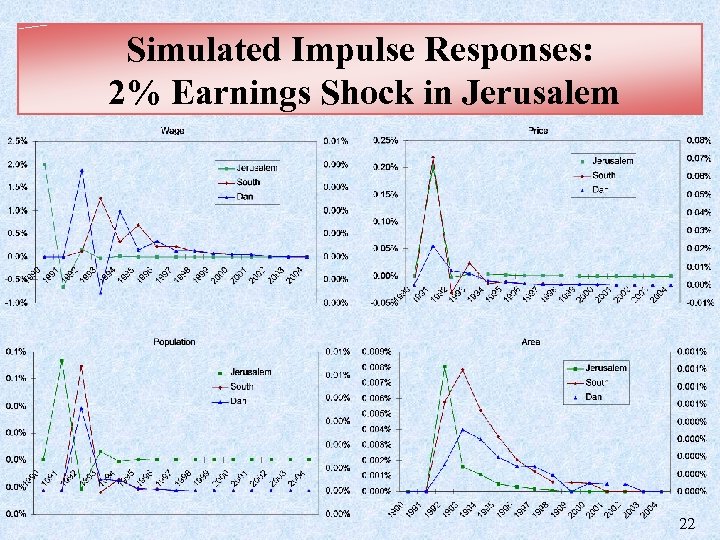 Simulated Impulse Responses: 2% Earnings Shock in Jerusalem 22
Simulated Impulse Responses: 2% Earnings Shock in Jerusalem 22
 Simulated Impulse Responses: 2% Population Shock in Tel Aviv 23
Simulated Impulse Responses: 2% Population Shock in Tel Aviv 23
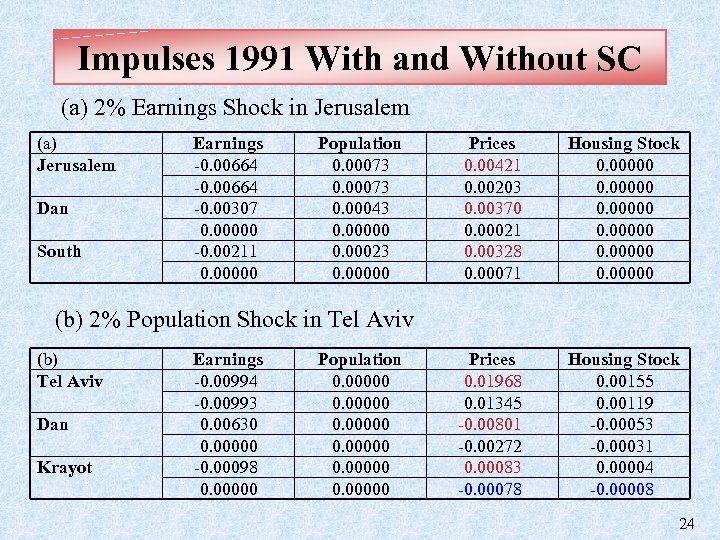 Impulses 1991 With and Without SC (a) 2% Earnings Shock in Jerusalem (a) Jerusalem Dan South Earnings -0. 00664 -0. 00307 0. 00000 -0. 00211 0. 00000 Population 0. 00073 0. 00043 0. 00000 0. 00023 0. 00000 Prices 0. 00421 0. 00203 0. 00370 0. 00021 0. 00328 0. 00071 Housing Stock 0. 00000 Prices 0. 01968 0. 01345 -0. 00801 -0. 00272 0. 00083 -0. 00078 Housing Stock 0. 00155 0. 00119 -0. 00053 -0. 00031 0. 00004 -0. 00008 (b) 2% Population Shock in Tel Aviv (b) Tel Aviv Dan Krayot Earnings -0. 00994 -0. 00993 0. 00630 0. 00000 -0. 00098 0. 00000 Population 0. 00000 24
Impulses 1991 With and Without SC (a) 2% Earnings Shock in Jerusalem (a) Jerusalem Dan South Earnings -0. 00664 -0. 00307 0. 00000 -0. 00211 0. 00000 Population 0. 00073 0. 00043 0. 00000 0. 00023 0. 00000 Prices 0. 00421 0. 00203 0. 00370 0. 00021 0. 00328 0. 00071 Housing Stock 0. 00000 Prices 0. 01968 0. 01345 -0. 00801 -0. 00272 0. 00083 -0. 00078 Housing Stock 0. 00155 0. 00119 -0. 00053 -0. 00031 0. 00004 -0. 00008 (b) 2% Population Shock in Tel Aviv (b) Tel Aviv Dan Krayot Earnings -0. 00994 -0. 00993 0. 00630 0. 00000 -0. 00098 0. 00000 Population 0. 00000 24
 Main Results • Evidence of temporal lags, spatially autocorrelated errors and ‘lagged’ spatial lags. • Impulses: reverberate across space and time, feedback effects. But die out quite quickly • Impulse response across regions: dictated by spatial weighting system, eg Jerusalem has greater spillover effect on South than on Dan region • Spillover effects from Tel Aviv: reflects spatial lag coefficients in magnitude and sign 25
Main Results • Evidence of temporal lags, spatially autocorrelated errors and ‘lagged’ spatial lags. • Impulses: reverberate across space and time, feedback effects. But die out quite quickly • Impulse response across regions: dictated by spatial weighting system, eg Jerusalem has greater spillover effect on South than on Dan region • Spillover effects from Tel Aviv: reflects spatial lag coefficients in magnitude and sign 25
 Conclusions • Integration of time series and spatial econometrics • Joint estimation in Sp. VAR (not 2 -stage estimation) • Difference between spatially correlated errors (SC) and spatially autocorrelated errors (SAC) and lagged SAC • Impulse responses – ripple-through effect within and between regions 26
Conclusions • Integration of time series and spatial econometrics • Joint estimation in Sp. VAR (not 2 -stage estimation) • Difference between spatially correlated errors (SC) and spatially autocorrelated errors (SAC) and lagged SAC • Impulse responses – ripple-through effect within and between regions 26


