43e95a38fb69f772351fee18e5608e01.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
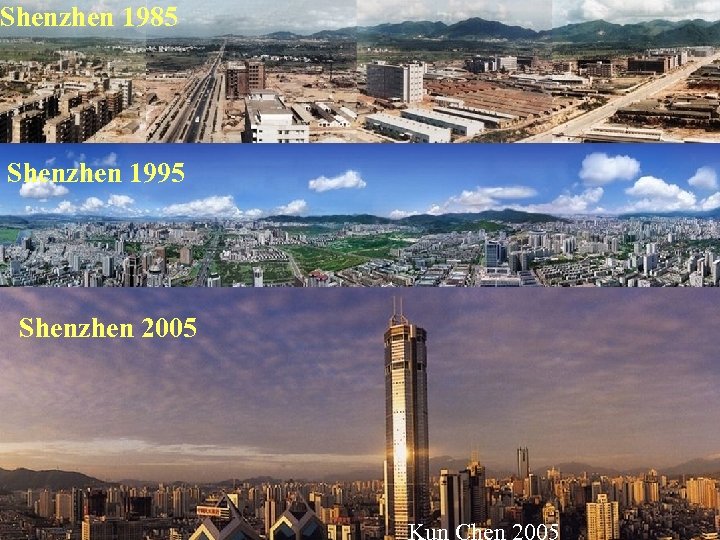 Shenzhen 1985 Shenzhen 1995 Shenzhen 2005
Shenzhen 1985 Shenzhen 1995 Shenzhen 2005
 Offshored Services, Innovation, and Knowledge Intensity* Martin Kenney UC Davis & Berkeley Roundtable on the International Economy & Rafiq Dossani Stanford University *Keynote presentation at the Innovation in Services Conference, Manchester, UK, June 15 -18, 2006.
Offshored Services, Innovation, and Knowledge Intensity* Martin Kenney UC Davis & Berkeley Roundtable on the International Economy & Rafiq Dossani Stanford University *Keynote presentation at the Innovation in Services Conference, Manchester, UK, June 15 -18, 2006.
 The Story Is No Longer. . . • about domestic markets • confined to call centers, simple software coding, or data entry • about only large MNCs, small knowledgeintensive firms are rapidly building capabilities abroad • about India alone (Martha shows)
The Story Is No Longer. . . • about domestic markets • confined to call centers, simple software coding, or data entry • about only large MNCs, small knowledgeintensive firms are rapidly building capabilities abroad • about India alone (Martha shows)
 It Is Also About. . . • high value-adding capabilities being developed in low-wage economies • interesting entrepreneurial initiatives in developing nations • interesting entrepreneurial initiatives in the developed nations to use low cost “think” workers • MNCs creating global centers of excellence offshore • new business models (virtual receptionist) • global knowledge networks – Different mix-and-match (in-house/external)
It Is Also About. . . • high value-adding capabilities being developed in low-wage economies • interesting entrepreneurial initiatives in developing nations • interesting entrepreneurial initiatives in the developed nations to use low cost “think” workers • MNCs creating global centers of excellence offshore • new business models (virtual receptionist) • global knowledge networks – Different mix-and-match (in-house/external)
 The Discussion of Whether Knowledge-Intensive Services Will Be Relocated to Developing Nations Is Over
The Discussion of Whether Knowledge-Intensive Services Will Be Relocated to Developing Nations Is Over
 And That Is Why This Conference Is So Exciting and the Reason We All Came -- We Are Studying a Major Shift the Organization and Geography of Value Creation Blinder (2006) claims that it will be a new Industrial Revolution. Will it be like China in manufacturing, was that an industrial revolution
And That Is Why This Conference Is So Exciting and the Reason We All Came -- We Are Studying a Major Shift the Organization and Geography of Value Creation Blinder (2006) claims that it will be a new Industrial Revolution. Will it be like China in manufacturing, was that an industrial revolution
 Consider the Issues With Which Our Work Intersects • The boundaries of the firm • The reorganization of the firm (e. g. , Sako 2005) – Vertical disintegration – Dismantling the Chandlerian firm’s staff function • Changing location of work – Division of labor • Changing organization of work • What does information technology enable
Consider the Issues With Which Our Work Intersects • The boundaries of the firm • The reorganization of the firm (e. g. , Sako 2005) – Vertical disintegration – Dismantling the Chandlerian firm’s staff function • Changing location of work – Division of labor • Changing organization of work • What does information technology enable
 The Enabling Conditions -- We All Know • Increasingly accessible workers in developing nations • Standardized platforms & now open source • Digitization – data and info fluidized – increasing volume – plummeting transfer and telecom costs – copying and use costs zero w/t state protection • Corporate reengineering and outsourcing domestically becomes normal practice
The Enabling Conditions -- We All Know • Increasingly accessible workers in developing nations • Standardized platforms & now open source • Digitization – data and info fluidized – increasing volume – plummeting transfer and telecom costs – copying and use costs zero w/t state protection • Corporate reengineering and outsourcing domestically becomes normal practice
 Patents as a Measure of Knowledge Creation
Patents as a Measure of Knowledge Creation
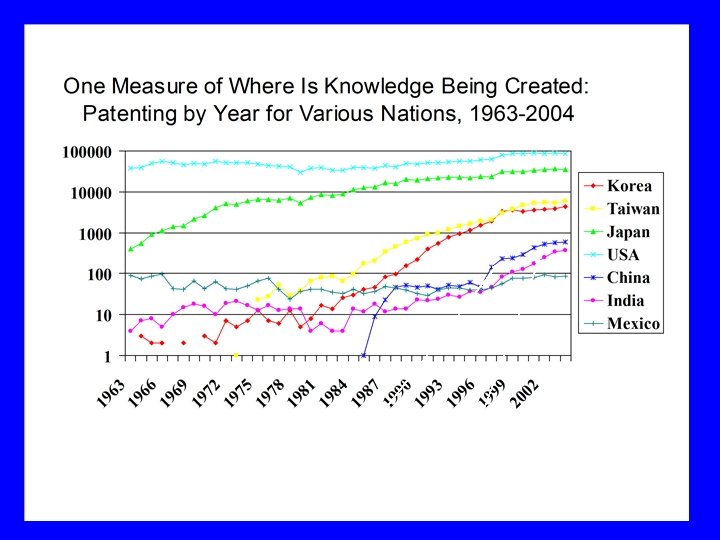 China India
China India
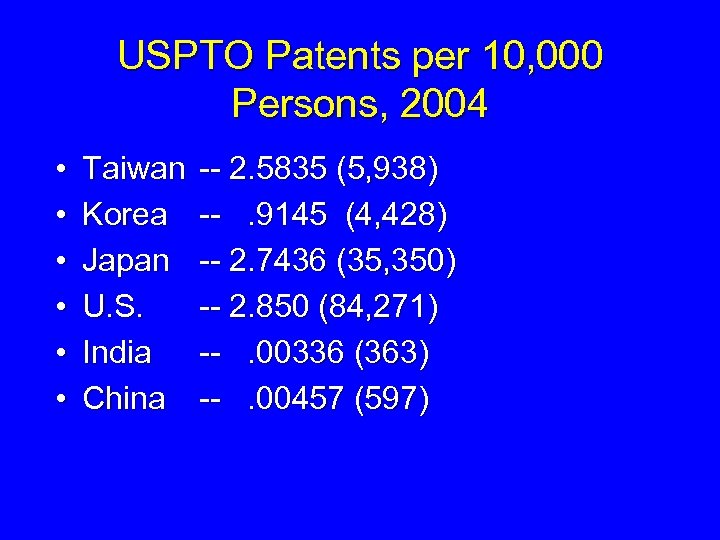 USPTO Patents per 10, 000 Persons, 2004 • • • Taiwan Korea Japan U. S. India China -- 2. 5835 (5, 938) --. 9145 (4, 428) -- 2. 7436 (35, 350) -- 2. 850 (84, 271) --. 00336 (363) --. 00457 (597)
USPTO Patents per 10, 000 Persons, 2004 • • • Taiwan Korea Japan U. S. India China -- 2. 5835 (5, 938) --. 9145 (4, 428) -- 2. 7436 (35, 350) -- 2. 850 (84, 271) --. 00336 (363) --. 00457 (597)
 India as an Exemplar
India as an Exemplar
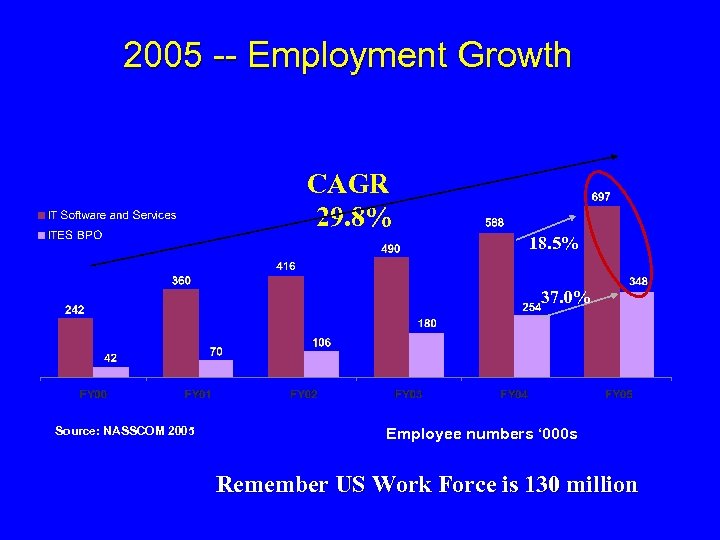 2005 -- Employment Growth CAGR 29. 8% 18. 5% 37. 0% Source: NASSCOM 2005 Employee numbers ‘ 000 s Remember US Work Force is 130 million
2005 -- Employment Growth CAGR 29. 8% 18. 5% 37. 0% Source: NASSCOM 2005 Employee numbers ‘ 000 s Remember US Work Force is 130 million
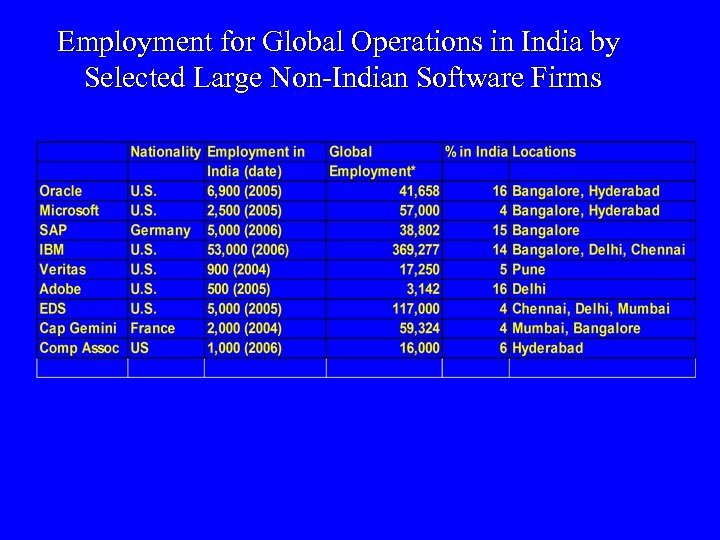 Employment for Global Operations in India by Selected Large Non-Indian Software Firms
Employment for Global Operations in India by Selected Large Non-Indian Software Firms
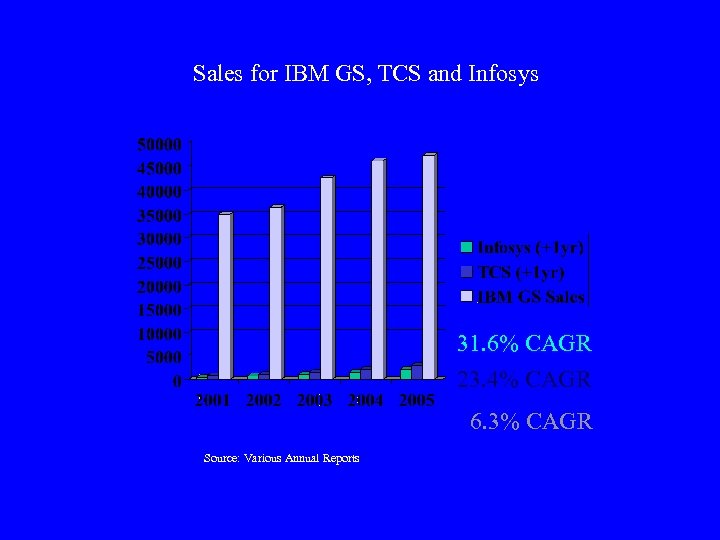 Sales for IBM GS, TCS and Infosys 31. 6% CAGR 23. 4% CAGR 6. 3% CAGR Source: Various Annual Reports
Sales for IBM GS, TCS and Infosys 31. 6% CAGR 23. 4% CAGR 6. 3% CAGR Source: Various Annual Reports
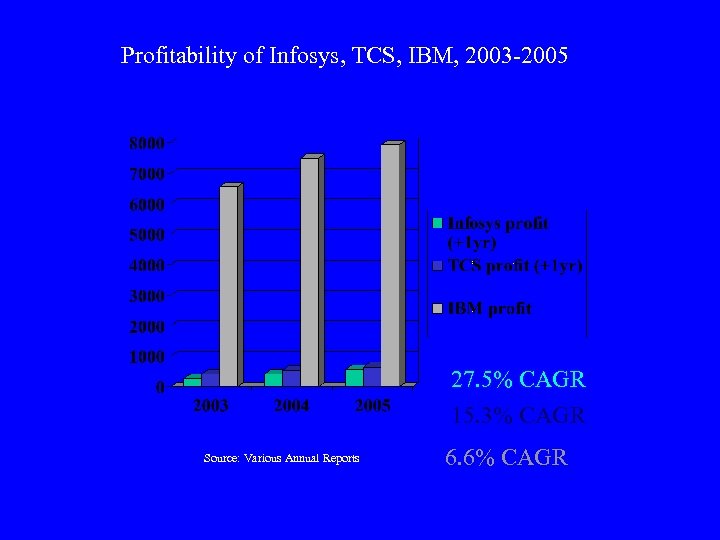 Profitability of Infosys, TCS, IBM, 2003 -2005 27. 5% CAGR 15. 3% CAGR Source: Various Annual Reports 6. 6% CAGR
Profitability of Infosys, TCS, IBM, 2003 -2005 27. 5% CAGR 15. 3% CAGR Source: Various Annual Reports 6. 6% CAGR
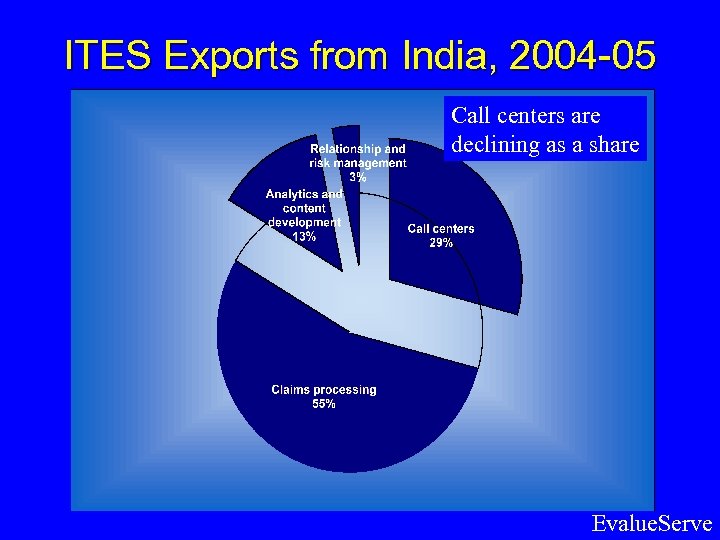 ITES Exports from India, 2004 -05 Call centers are declining as a share Evalue. Serve
ITES Exports from India, 2004 -05 Call centers are declining as a share Evalue. Serve
 By the year 2010, several new KPO services will become prominent in the global offshoring space … Source: Evalueserve 2005
By the year 2010, several new KPO services will become prominent in the global offshoring space … Source: Evalueserve 2005
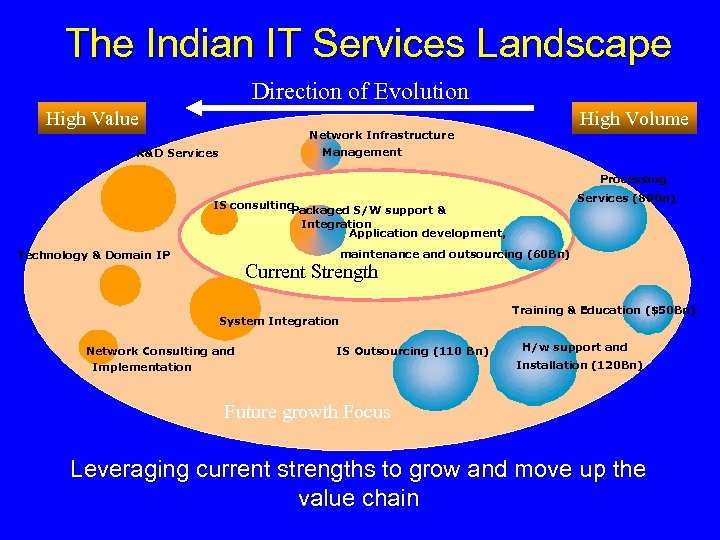 The Indian IT Services Landscape Direction of Evolution High Value High Volume Network Infrastructure Management R&D Services Processing Services (80 Bn) IS consulting Packaged S/W support & Integration Application development, maintenance and outsourcing (60 Bn) Technology & Domain IP Current Strength System Integration Network Consulting and Implementation IS Outsourcing (110 Bn) Training & Education ($50 Bn) H/w support and Installation (120 Bn) Future growth Focus Leveraging current strengths to grow and move up the value chain
The Indian IT Services Landscape Direction of Evolution High Value High Volume Network Infrastructure Management R&D Services Processing Services (80 Bn) IS consulting Packaged S/W support & Integration Application development, maintenance and outsourcing (60 Bn) Technology & Domain IP Current Strength System Integration Network Consulting and Implementation IS Outsourcing (110 Bn) Training & Education ($50 Bn) H/w support and Installation (120 Bn) Future growth Focus Leveraging current strengths to grow and move up the value chain
 BPO maturing and moving up the value chain High Embryonic Growth Mature Aging IT Outsourcing Maturity Call Centers Engineering Accounting HR Admin Insurance Claims • Specialized players emerging • Complexity quickly increasing • From captives to third-party • “Double Sourcing” Tech Support Knowledge Processes Low Time Source: Alok Agarwal/Evalueserve 2005
BPO maturing and moving up the value chain High Embryonic Growth Mature Aging IT Outsourcing Maturity Call Centers Engineering Accounting HR Admin Insurance Claims • Specialized players emerging • Complexity quickly increasing • From captives to third-party • “Double Sourcing” Tech Support Knowledge Processes Low Time Source: Alok Agarwal/Evalueserve 2005
 Case Studies
Case Studies
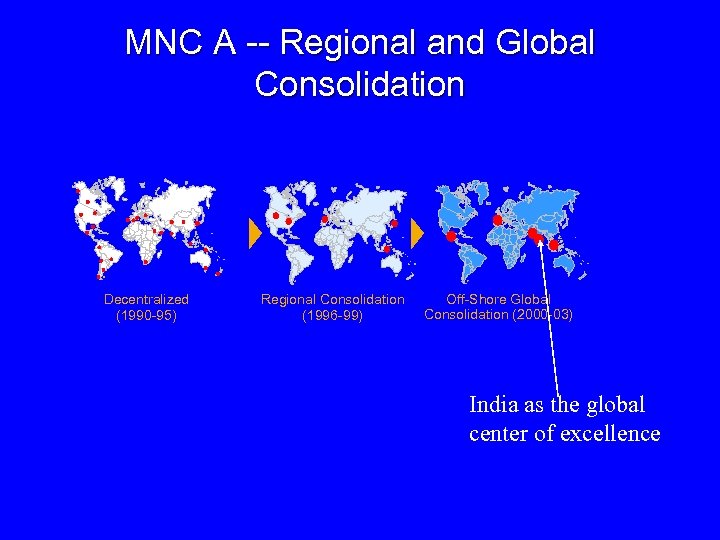 MNC A -- Regional and Global Consolidation Decentralized (1990 -95) Regional Consolidation (1996 -99) Off-Shore Global Consolidation (2000 -03) India as the global center of excellence
MNC A -- Regional and Global Consolidation Decentralized (1990 -95) Regional Consolidation (1996 -99) Off-Shore Global Consolidation (2000 -03) India as the global center of excellence
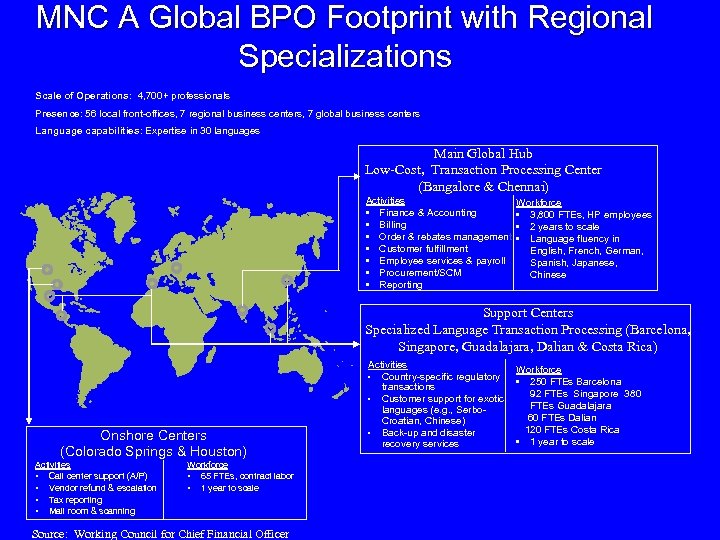 MNC A Global BPO Footprint with Regional Specializations Scale of Operations: 4, 700+ professionals Presence: 56 local front-offices, 7 regional business centers, 7 global business centers Language capabilities: Expertise in 30 languages Main Global Hub Low-Cost, Transaction Processing Center (Bangalore & Chennai) Activities • Finance & Accounting • Billing • Order & rebates management • Customer fulfillment • Employee services & payroll • Procurement/SCM • Reporting Workforce • 3, 800 FTEs, HP employees • 2 years to scale • Language fluency in English, French, German, Spanish, Japanese, Chinese Support Centers Specialized Language Transaction Processing (Barcelona, Singapore, Guadalajara, Dalian & Costa Rica) Onshore Centers (Colorado Springs & Houston) Activities • Call center support (A/P) • Vendor refund & escalation • Tax reporting • Mail room & scanning Workforce • 65 FTEs, contract labor • 1 year to scale Source: Working Council for Chief Financial Officer Activities • Country-specific regulatory transactions • Customer support for exotic languages (e. g. , Serbo. Croatian, Chinese) • Back-up and disaster recovery services Workforce • 250 FTEs Barcelona 92 FTEs Singapore 380 FTEs Guadalajara 60 FTEs Dalian 120 FTEs Costa Rica • 1 year to scale
MNC A Global BPO Footprint with Regional Specializations Scale of Operations: 4, 700+ professionals Presence: 56 local front-offices, 7 regional business centers, 7 global business centers Language capabilities: Expertise in 30 languages Main Global Hub Low-Cost, Transaction Processing Center (Bangalore & Chennai) Activities • Finance & Accounting • Billing • Order & rebates management • Customer fulfillment • Employee services & payroll • Procurement/SCM • Reporting Workforce • 3, 800 FTEs, HP employees • 2 years to scale • Language fluency in English, French, German, Spanish, Japanese, Chinese Support Centers Specialized Language Transaction Processing (Barcelona, Singapore, Guadalajara, Dalian & Costa Rica) Onshore Centers (Colorado Springs & Houston) Activities • Call center support (A/P) • Vendor refund & escalation • Tax reporting • Mail room & scanning Workforce • 65 FTEs, contract labor • 1 year to scale Source: Working Council for Chief Financial Officer Activities • Country-specific regulatory transactions • Customer support for exotic languages (e. g. , Serbo. Croatian, Chinese) • Back-up and disaster recovery services Workforce • 250 FTEs Barcelona 92 FTEs Singapore 380 FTEs Guadalajara 60 FTEs Dalian 120 FTEs Costa Rica • 1 year to scale
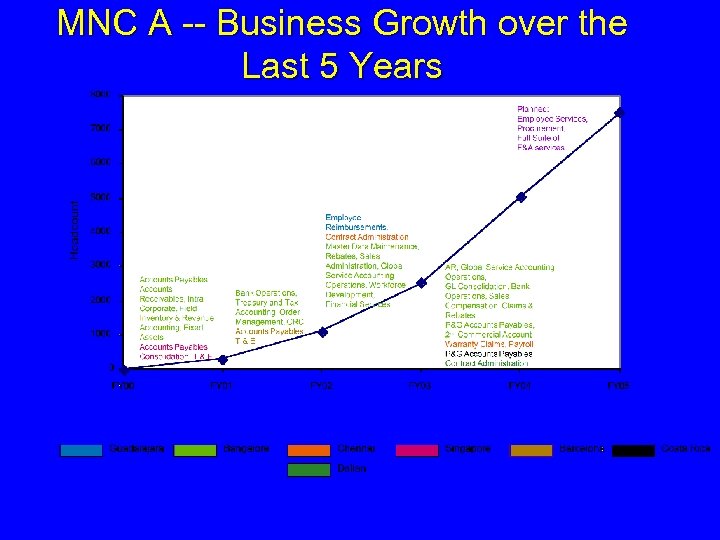 MNC A -- Business Growth over the Last 5 Years
MNC A -- Business Growth over the Last 5 Years
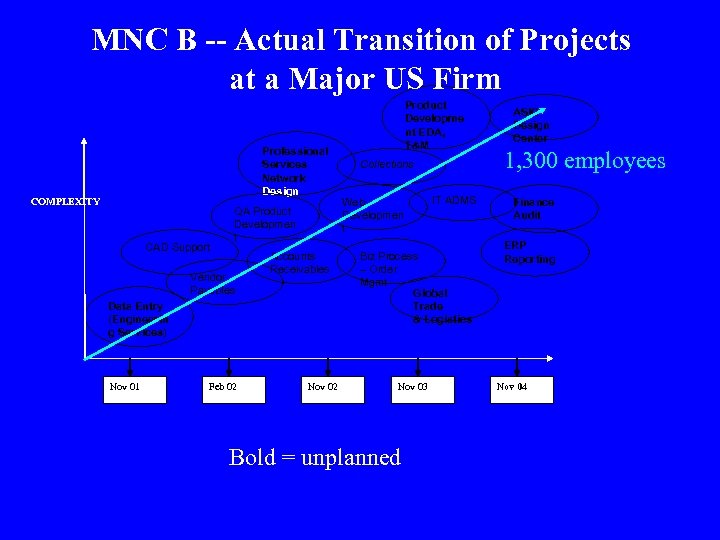 MNC B -- Actual Transition of Projects at a Major US Firm Professional Services Network Design COMPLEXITY CAD Support QA Product Developmen t Vendor Payables Accounts Receivables Data Entry (Engineerin g Services) Nov 01 Feb 02 Nov 02 Product Developme nt EDA, T&M Collections Web Developmen t IT ADMS Biz Process – Order Mgmt Global Trade & Logistics Nov 03 Bold = unplanned ASIC Design Center 1, 300 employees Finance Audit ERP Reporting Nov 04
MNC B -- Actual Transition of Projects at a Major US Firm Professional Services Network Design COMPLEXITY CAD Support QA Product Developmen t Vendor Payables Accounts Receivables Data Entry (Engineerin g Services) Nov 01 Feb 02 Nov 02 Product Developme nt EDA, T&M Collections Web Developmen t IT ADMS Biz Process – Order Mgmt Global Trade & Logistics Nov 03 Bold = unplanned ASIC Design Center 1, 300 employees Finance Audit ERP Reporting Nov 04
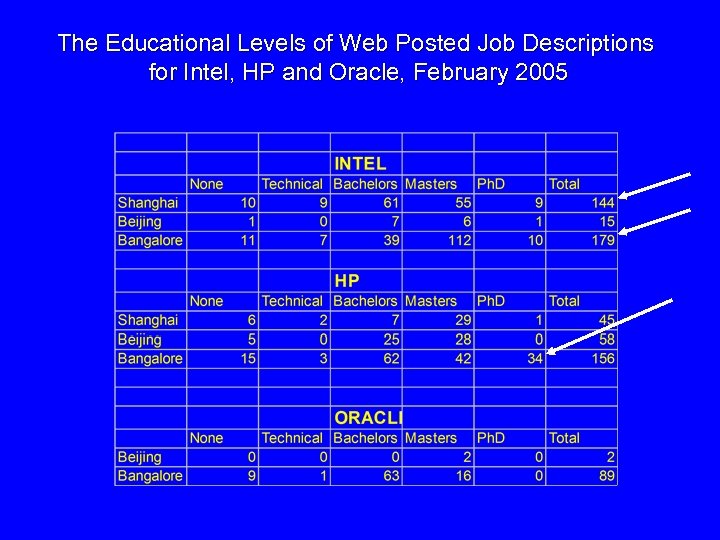 The Educational Levels of Web Posted Job Descriptions for Intel, HP and Oracle, February 2005
The Educational Levels of Web Posted Job Descriptions for Intel, HP and Oracle, February 2005
 A Job at Intel India • CAD Engineer: Hardware Engineering is all about finding solutions. As a CAD (Computer Aided Design) Engineer with the Intel Hardware Engineering team, you'll work on teams designing, developing and implementing solutions. As part of Hardware Engineering at Intel, you'll have the opportunity to be involved from start to finish on the development of world-class innovations. Responsibilities As a CAD Engineer, you will be involved in developing new very large scale integration (VLSI) CAD tools and methodology solutions for design for testability (DFT) and test generation for high volume manufacturing of next generation microprocessor products. You will be responsible for development, deployment and maintenance of in-house fault simulation and test generation tools. This position will be based in Bangalore, India. Qualifications You must possess a Ph. D. or Master of Science degree in Electrical Engineering or Computer Engineering with five to ten years of related work experience. Additional qualifications include: Extensive knowledge of Digital Design and Design-for-test principles, digital circuit/fault simulation and automatic test pattern generation. Good working knowledge in developing CAD tools using C++ in a UNIX*/Linux* environment. Excellent experience in a related people management role would be an added advantage. Accessed April 9, 2004 http: //appzone. intel. com/jobs/u. Requisition. asp? Posting=34339
A Job at Intel India • CAD Engineer: Hardware Engineering is all about finding solutions. As a CAD (Computer Aided Design) Engineer with the Intel Hardware Engineering team, you'll work on teams designing, developing and implementing solutions. As part of Hardware Engineering at Intel, you'll have the opportunity to be involved from start to finish on the development of world-class innovations. Responsibilities As a CAD Engineer, you will be involved in developing new very large scale integration (VLSI) CAD tools and methodology solutions for design for testability (DFT) and test generation for high volume manufacturing of next generation microprocessor products. You will be responsible for development, deployment and maintenance of in-house fault simulation and test generation tools. This position will be based in Bangalore, India. Qualifications You must possess a Ph. D. or Master of Science degree in Electrical Engineering or Computer Engineering with five to ten years of related work experience. Additional qualifications include: Extensive knowledge of Digital Design and Design-for-test principles, digital circuit/fault simulation and automatic test pattern generation. Good working knowledge in developing CAD tools using C++ in a UNIX*/Linux* environment. Excellent experience in a related people management role would be an added advantage. Accessed April 9, 2004 http: //appzone. intel. com/jobs/u. Requisition. asp? Posting=34339
 An Example of Offshore KIS • Evalue. Serve – Business Information & Market Research – Industry and Value Chain Analysis – In-Depth Analysis of Customer Segments, Products, Channels, Technologies – Competitive Intelligence and Benchmarking – Monitoring and Customized Newsletters – Primary Research Surveys of Industry Participants and Experts
An Example of Offshore KIS • Evalue. Serve – Business Information & Market Research – Industry and Value Chain Analysis – In-Depth Analysis of Customer Segments, Products, Channels, Technologies – Competitive Intelligence and Benchmarking – Monitoring and Customized Newsletters – Primary Research Surveys of Industry Participants and Experts
 Software As a Service • Why own software and pay consultants to maintain it, when you can buy it as a service – Salesforce. com – Jotspot. com (uses programmers globally)
Software As a Service • Why own software and pay consultants to maintain it, when you can buy it as a service – Salesforce. com – Jotspot. com (uses programmers globally)
 Questions • How much KIS can be created in LDCs? – What are the limits and can we create theories that will tell us what they are? • How does interpersonal knowledge creation across national boundaries work? • Will a global wage be set for work? • How do networks of intermediaries (these are also KIS) get created to facilitate globalization (Howells and others here at UM)? • How is the increasingly encompassing open source movement going to affect KIS?
Questions • How much KIS can be created in LDCs? – What are the limits and can we create theories that will tell us what they are? • How does interpersonal knowledge creation across national boundaries work? • Will a global wage be set for work? • How do networks of intermediaries (these are also KIS) get created to facilitate globalization (Howells and others here at UM)? • How is the increasingly encompassing open source movement going to affect KIS?
 Questions • With digitization, value created from the digital realm itself – Music mashups – Myspace – Web mashups • What is the proper stance toward IP to maximize global value creation? • How will entrepreneurs innovate new value propositions?
Questions • With digitization, value created from the digital realm itself – Music mashups – Myspace – Web mashups • What is the proper stance toward IP to maximize global value creation? • How will entrepreneurs innovate new value propositions?
 Thank You
Thank You


