2ac7cf4eb246f7af81e53313921cc6ed.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29
 Shell Pilot Project PRODML Work Group 2007 n DTS Reconciliation Workflow
Shell Pilot Project PRODML Work Group 2007 n DTS Reconciliation Workflow
 Overview • DTS (Distributed Temperature Sensing) gives a continuous temperature profile along a well • One way to improve accuracy is to reconcile the DTS profile to a single point-source temperature sensor • Energy company assets can have DTS and PT sensors from multiple vendors • A standardised method to transfer raw and calibrated DTS logs To/From a DTS database as well as point temperature readings - typically from a well-agnostic process historian is beneficial. • In case there is a need to change the DTS or PT sensors, this can be done seamlessly without affecting the subsequent process flows. PRODML WG 2007
Overview • DTS (Distributed Temperature Sensing) gives a continuous temperature profile along a well • One way to improve accuracy is to reconcile the DTS profile to a single point-source temperature sensor • Energy company assets can have DTS and PT sensors from multiple vendors • A standardised method to transfer raw and calibrated DTS logs To/From a DTS database as well as point temperature readings - typically from a well-agnostic process historian is beneficial. • In case there is a need to change the DTS or PT sensors, this can be done seamlessly without affecting the subsequent process flows. PRODML WG 2007
 Shell DTS Pilot • The Shell DTS Pilot components • Shell DTS Database • Repository for raw and reconciled DTS logs • Weatherford DTS Viewer / Manager • Carries out reconciliation and curve shifting • OSIsoft Historian • Master source for all point temperature data • Data transferred to DTS database and historian continuously, asynchronously from the DTS-PT reconciliation loop • Network model provides: • Information required to match DTS trace to point temperature source • Position of the point-source temperature in well relative to a depth datum • Not physically implemented but required functionality was hard-coded into each web service PRODML WG 2007
Shell DTS Pilot • The Shell DTS Pilot components • Shell DTS Database • Repository for raw and reconciled DTS logs • Weatherford DTS Viewer / Manager • Carries out reconciliation and curve shifting • OSIsoft Historian • Master source for all point temperature data • Data transferred to DTS database and historian continuously, asynchronously from the DTS-PT reconciliation loop • Network model provides: • Information required to match DTS trace to point temperature source • Position of the point-source temperature in well relative to a depth datum • Not physically implemented but required functionality was hard-coded into each web service PRODML WG 2007
 Description of Webservices • Shell Web Service • In order to interface with the Shell DTS Data Server, two web services have been developed: • One for requesting and returning DTS traces that are stored in the Shell DTS Data Server. • Another for storing reconciled DTS traces in the Shell DTS Data Server. • The initial and terminal messages that start and end the entire communication protocol are handled directly by the Shell DTS Data Server. PRODML WG 2007
Description of Webservices • Shell Web Service • In order to interface with the Shell DTS Data Server, two web services have been developed: • One for requesting and returning DTS traces that are stored in the Shell DTS Data Server. • Another for storing reconciled DTS traces in the Shell DTS Data Server. • The initial and terminal messages that start and end the entire communication protocol are handled directly by the Shell DTS Data Server. PRODML WG 2007
 Description of Webservices II • Weatherford • The Weatherford contribution to the Shell pilot project is on two front: 1. A Web Service (Weatherford DTS Manager) was developed that supports Get. Data. Async. Initiate web method. This Web Service is responsible for getting the temperature data from different Web Services, perform reconciliation of data and store the new DTS trace data in Shell database. 2. A visualization tool (DTSPlus) was provided for plotting the DTS trace before and after reconciliation. The visualization tool also supports configuring the network model information PRODML WG 2007
Description of Webservices II • Weatherford • The Weatherford contribution to the Shell pilot project is on two front: 1. A Web Service (Weatherford DTS Manager) was developed that supports Get. Data. Async. Initiate web method. This Web Service is responsible for getting the temperature data from different Web Services, perform reconciliation of data and store the new DTS trace data in Shell database. 2. A visualization tool (DTSPlus) was provided for plotting the DTS trace before and after reconciliation. The visualization tool also supports configuring the network model information PRODML WG 2007
 Description of Webservices III • OSISoft webservice • The OSIsoft contribution to the Shell pilot project is an update to the Get. Data. Sync web method for the product. Volume schema. Implementation is identical to the PRODML 1. 0 specification, but includes the specification of a port element within the parameter. Set element so that sensor depth down wellbore can be properly represented. Retrieval of actual temperature at depth is consistent with the representation of the data in PRODML 1. 0. • Infosys Orchestration • The Infosys contribution is to track all the web services and to handle any exceptions or errors that may occur, such as if a web service response does not come, thereby triggering an alert and a log entry for reconciliation. PRODML WG 2007
Description of Webservices III • OSISoft webservice • The OSIsoft contribution to the Shell pilot project is an update to the Get. Data. Sync web method for the product. Volume schema. Implementation is identical to the PRODML 1. 0 specification, but includes the specification of a port element within the parameter. Set element so that sensor depth down wellbore can be properly represented. Retrieval of actual temperature at depth is consistent with the representation of the data in PRODML 1. 0. • Infosys Orchestration • The Infosys contribution is to track all the web services and to handle any exceptions or errors that may occur, such as if a web service response does not come, thereby triggering an alert and a log entry for reconciliation. PRODML WG 2007
 Statoil. Hydro Pilot Project PRODML Work Group 2007 Pilot Smart Well Zonal Allocation PRODML WG 2007
Statoil. Hydro Pilot Project PRODML Work Group 2007 Pilot Smart Well Zonal Allocation PRODML WG 2007
 The Problem n To run smart wells at its optimum level it must be possible to determine the zonal reservoir pressure at any time and compare those with theoretical expected pressure calculated from your well and network models. A comparison of theoretical value with the actual calculated value is a key performance indicator if the well/reservoir behaved as expected. If not the system needs to be recalibrated. PRODML WG 2007
The Problem n To run smart wells at its optimum level it must be possible to determine the zonal reservoir pressure at any time and compare those with theoretical expected pressure calculated from your well and network models. A comparison of theoretical value with the actual calculated value is a key performance indicator if the well/reservoir behaved as expected. If not the system needs to be recalibrated. PRODML WG 2007
 The Team n n n IP 21 by Aspentech is the data historian Energy. Components by Tieto. Enator is the production database Prosper by Petroleum Experts is a Well modelling application DECIDE! By Schlumberger is the orchestrator of automated workflows and data consolidation Avocet Production Surveillance by Schlumberger is the visualization tool Avocet - Integrated Asset Modeller (IAM) by Schlumberger is the optimizer and forecaster PRODML WG 2007
The Team n n n IP 21 by Aspentech is the data historian Energy. Components by Tieto. Enator is the production database Prosper by Petroleum Experts is a Well modelling application DECIDE! By Schlumberger is the orchestrator of automated workflows and data consolidation Avocet Production Surveillance by Schlumberger is the visualization tool Avocet - Integrated Asset Modeller (IAM) by Schlumberger is the optimizer and forecaster PRODML WG 2007
 Statoil. Hydro Pilot Project PRODML Work Group 2007 JV Reporting - Algeria PRODML WG 2007
Statoil. Hydro Pilot Project PRODML Work Group 2007 JV Reporting - Algeria PRODML WG 2007
 The context n Statoil. Hydro partner in 2 Algerian fields (In. Salah, In. Amenas) operated by BP. Field is operated as joint venture between BP and Statoil. Hydro. n Sonatrach is the goverment equivalent requiring different types of reports each day n Currently the network infrastructure is almost non-existing, ftp the only viable connection variant n Today reports are faxed to Sonatrach – the different reports covers different views of the same data n Data is shipped in a wide range of different formats n Involved software Energy Components (Tieto. Enator) and Production Monitoring and Reporting (Tieto. Enator) PRODML WG 2007
The context n Statoil. Hydro partner in 2 Algerian fields (In. Salah, In. Amenas) operated by BP. Field is operated as joint venture between BP and Statoil. Hydro. n Sonatrach is the goverment equivalent requiring different types of reports each day n Currently the network infrastructure is almost non-existing, ftp the only viable connection variant n Today reports are faxed to Sonatrach – the different reports covers different views of the same data n Data is shipped in a wide range of different formats n Involved software Energy Components (Tieto. Enator) and Production Monitoring and Reporting (Tieto. Enator) PRODML WG 2007
 The business benefits n n n n Data is structured in a computer readable form – making it possible to load, publish to different formats, make subsets of data e. g. only extract gas composition for a given pipeline Data is transfered in a more optimal manner to the different parties involved Data is timely distributed without needed human intervention Data can be published to different production systems utilising the same format e. g. well tests are required for a lot of different applications The data stream is just published once to multiple sources Data can be more easily shared between involved parties – no need to manual punching of excel spreadsheets, txt – files and so on The different reports are based on the same datastream and one file Joint venture partners gain access to data in a more timely and structured manner PRODML WG 2007
The business benefits n n n n Data is structured in a computer readable form – making it possible to load, publish to different formats, make subsets of data e. g. only extract gas composition for a given pipeline Data is transfered in a more optimal manner to the different parties involved Data is timely distributed without needed human intervention Data can be published to different production systems utilising the same format e. g. well tests are required for a lot of different applications The data stream is just published once to multiple sources Data can be more easily shared between involved parties – no need to manual punching of excel spreadsheets, txt – files and so on The different reports are based on the same datastream and one file Joint venture partners gain access to data in a more timely and structured manner PRODML WG 2007
 Conoco. Phillips Onshore PRODML Work Group 2007 Pilot Project Allocation Reporting PRODML WG 2007
Conoco. Phillips Onshore PRODML Work Group 2007 Pilot Project Allocation Reporting PRODML WG 2007
 Conoco. Phillips Daily Volume Reporting PRODML Pilot Team Conoco. Phillips Don Van Speybroeck, Pilot Lead Jose Rivas, Reporting Lead Thomas Vanya, Test Environment Lead Aspen. Tech Chris Hewitt, Technical Lead Norbert Meierhoefer, Functional Lead Kongsberg Per Arild Andresen, Ph. D, Technical Lead P 2 Energy Solutions Kiran Vajrala, Technical Lead Dave Johnson, Functional Lead Iain Saunderson, Test Environment Lead PRODML WG 2007
Conoco. Phillips Daily Volume Reporting PRODML Pilot Team Conoco. Phillips Don Van Speybroeck, Pilot Lead Jose Rivas, Reporting Lead Thomas Vanya, Test Environment Lead Aspen. Tech Chris Hewitt, Technical Lead Norbert Meierhoefer, Functional Lead Kongsberg Per Arild Andresen, Ph. D, Technical Lead P 2 Energy Solutions Kiran Vajrala, Technical Lead Dave Johnson, Functional Lead Iain Saunderson, Test Environment Lead PRODML WG 2007
 Conoco. Phillips Daily Volume Reporting PRODML Pilot Problem Statement • Rebuilding and remapping software application interfaces to produce daily production reports should not be so complicated. • Software applications and database systems in the Upstream Production environment have different data requirements for collection, analysis, and reporting functions. • The systems data flow and analysis requirements change in size and functionality as the assets grow and evolve. • Continuous data mapping and custom interface development efforts between applications and systems can be eliminated through the adoption of industry standard network and volume models defined in PRODML WG 2007
Conoco. Phillips Daily Volume Reporting PRODML Pilot Problem Statement • Rebuilding and remapping software application interfaces to produce daily production reports should not be so complicated. • Software applications and database systems in the Upstream Production environment have different data requirements for collection, analysis, and reporting functions. • The systems data flow and analysis requirements change in size and functionality as the assets grow and evolve. • Continuous data mapping and custom interface development efforts between applications and systems can be eliminated through the adoption of industry standard network and volume models defined in PRODML WG 2007
 BP Pilot Project PRODML Work Group 2007 Network Model Management PRODML WG 2007
BP Pilot Project PRODML Work Group 2007 Network Model Management PRODML WG 2007
 BP Network Model Team • Joe Palatka BP • Jim Bettencourt BP (SAIC) • Ray Verhoeff OSIsoft • Per Arild Anderson Kongsberg Intellifield • Duncan Ord Matrikon • Laurence Ormerod Weatherford • Jason Clarke Weatherford PRODML WG 2007
BP Network Model Team • Joe Palatka BP • Jim Bettencourt BP (SAIC) • Ray Verhoeff OSIsoft • Per Arild Anderson Kongsberg Intellifield • Duncan Ord Matrikon • Laurence Ormerod Weatherford • Jason Clarke Weatherford PRODML WG 2007
 Definition of the Network Model A description of the processing units in an oil field, the product flow connections between them and the property measurement points that exist. This includes active units, planned units and historic units that are not currently active. This model can be dynamically shared between applications that require knowledge of the network topology in order to add value. Standards-based sharing of the network model allows for accurate propagation of the topology and for dynamic maintenance. This provides a common understanding of the system configuration and scope. PRODML WG 2007
Definition of the Network Model A description of the processing units in an oil field, the product flow connections between them and the property measurement points that exist. This includes active units, planned units and historic units that are not currently active. This model can be dynamically shared between applications that require knowledge of the network topology in order to add value. Standards-based sharing of the network model allows for accurate propagation of the topology and for dynamic maintenance. This provides a common understanding of the system configuration and scope. PRODML WG 2007
 Pilot Goals • Increase the speed of data propagation through out the field management system • Increase the integrity of the analysis and optimization in the operation of fields by enabling automated propagation of the current Network Product Flow Model PRODML WG 2007
Pilot Goals • Increase the speed of data propagation through out the field management system • Increase the integrity of the analysis and optimization in the operation of fields by enabling automated propagation of the current Network Product Flow Model PRODML WG 2007
 Pilot Objectives • Define an Authorities Source in the system for the Network Model • Create an active Network Product Flow Model and make it available for propagation to other applications in the system • Change the network model in the Authoritative Source and expose it for propagation to other applications in the system PRODML WG 2007
Pilot Objectives • Define an Authorities Source in the system for the Network Model • Create an active Network Product Flow Model and make it available for propagation to other applications in the system • Change the network model in the Authoritative Source and expose it for propagation to other applications in the system PRODML WG 2007
 Conclusion • The BP Network Product Flow Model Demonstrated : − Automated availability and dynamic propagation of the model to users/applications on the system − Automated updating of application with the latest configuration − The ability to get historic active models in a dynamic and automated manner PRODML WG 2007
Conclusion • The BP Network Product Flow Model Demonstrated : − Automated availability and dynamic propagation of the model to users/applications on the system − Automated updating of application with the latest configuration − The ability to get historic active models in a dynamic and automated manner PRODML WG 2007
 Conoco. Phillips Offshore Work Group 2007 Pilot Project Allocation Reporting PRODML WG 2007
Conoco. Phillips Offshore Work Group 2007 Pilot Project Allocation Reporting PRODML WG 2007
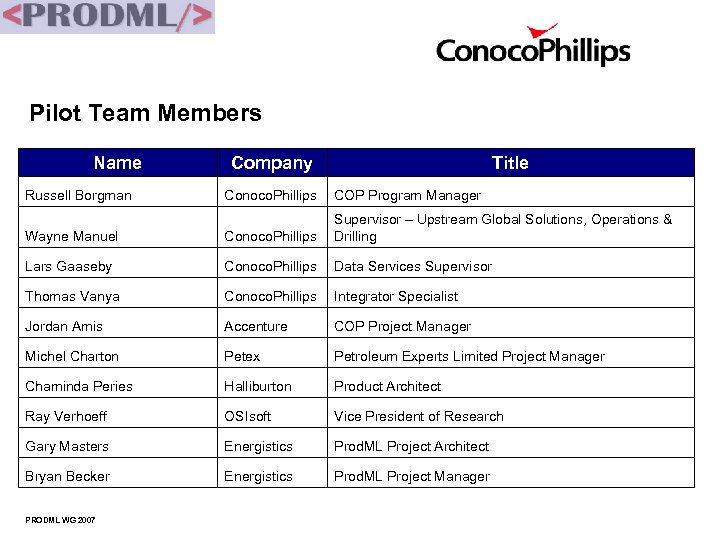 Pilot Team Members Name Russell Borgman Company Title Conoco. Phillips COP Program Manager Wayne Manuel Conoco. Phillips Supervisor – Upstream Global Solutions, Operations & Drilling Lars Gaaseby Conoco. Phillips Data Services Supervisor Thomas Vanya Conoco. Phillips Integrator Specialist Jordan Amis Accenture COP Project Manager Michel Charton Petex Petroleum Experts Limited Project Manager Chaminda Peries Halliburton Product Architect Ray Verhoeff OSIsoft Vice President of Research Gary Masters Energistics Prod. ML Project Architect Bryan Becker Energistics Prod. ML Project Manager PRODML WG 2007
Pilot Team Members Name Russell Borgman Company Title Conoco. Phillips COP Program Manager Wayne Manuel Conoco. Phillips Supervisor – Upstream Global Solutions, Operations & Drilling Lars Gaaseby Conoco. Phillips Data Services Supervisor Thomas Vanya Conoco. Phillips Integrator Specialist Jordan Amis Accenture COP Project Manager Michel Charton Petex Petroleum Experts Limited Project Manager Chaminda Peries Halliburton Product Architect Ray Verhoeff OSIsoft Vice President of Research Gary Masters Energistics Prod. ML Project Architect Bryan Becker Energistics Prod. ML Project Manager PRODML WG 2007
 Introduction • COP Case for Change: – The process of optimizing production in a large offshore gas producing asset in the North Sea is manually intensive and slow to react to changes in the producing system – Major impediments to improving the process include: • The lack of a capability to access an accurate and dynamic model of asset configuration data for use by various engineering applications • The inability to feed real time data to the engineering applications without hard coding system interfaces PRODML WG 2007
Introduction • COP Case for Change: – The process of optimizing production in a large offshore gas producing asset in the North Sea is manually intensive and slow to react to changes in the producing system – Major impediments to improving the process include: • The lack of a capability to access an accurate and dynamic model of asset configuration data for use by various engineering applications • The inability to feed real time data to the engineering applications without hard coding system interfaces PRODML WG 2007
 Objectives • The PRODML COPPR pilot would demonstrate how PRODML enables the capabilities to: – Create a dynamically updateable network model and make changes available for allocation reporting – Facilitate the access of real time data from the appropriate source system – Capture changes in the asset configuration network model for an audit trail, including rationale behind changes – Utilize a network model to support field operations PRODML WG 2007
Objectives • The PRODML COPPR pilot would demonstrate how PRODML enables the capabilities to: – Create a dynamically updateable network model and make changes available for allocation reporting – Facilitate the access of real time data from the appropriate source system – Capture changes in the asset configuration network model for an audit trail, including rationale behind changes – Utilize a network model to support field operations PRODML WG 2007
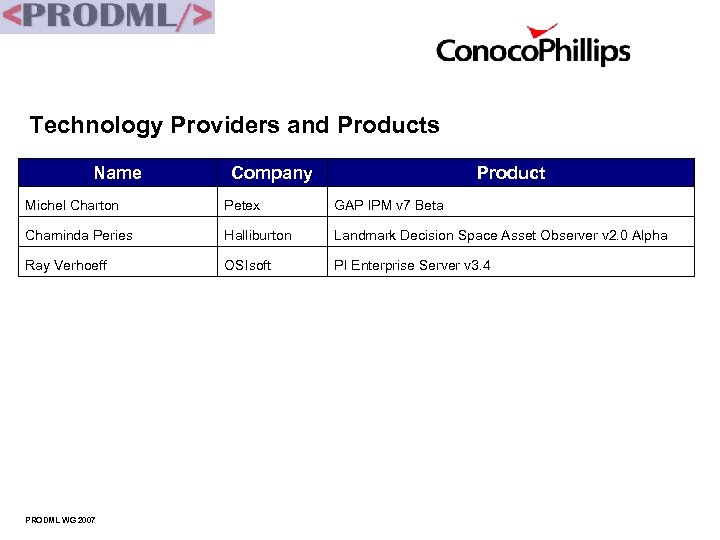 Technology Providers and Products Name Company Product Michel Charton Petex GAP IPM v 7 Beta Chaminda Peries Halliburton Landmark Decision Space Asset Observer v 2. 0 Alpha Ray Verhoeff OSIsoft PI Enterprise Server v 3. 4 PRODML WG 2007
Technology Providers and Products Name Company Product Michel Charton Petex GAP IPM v 7 Beta Chaminda Peries Halliburton Landmark Decision Space Asset Observer v 2. 0 Alpha Ray Verhoeff OSIsoft PI Enterprise Server v 3. 4 PRODML WG 2007
 PRODML WG 07 Chevron Pilot Water Manager Oil and Gas Sales PRODML WG 2007 Water Management Production Management
PRODML WG 07 Chevron Pilot Water Manager Oil and Gas Sales PRODML WG 2007 Water Management Production Management
 Participating Vendors We would like to thank the vendors participating with Chevron in the WG 07 pilot. Each made a significant contribution to its successful implementation PRODML WG 2007
Participating Vendors We would like to thank the vendors participating with Chevron in the WG 07 pilot. Each made a significant contribution to its successful implementation PRODML WG 2007
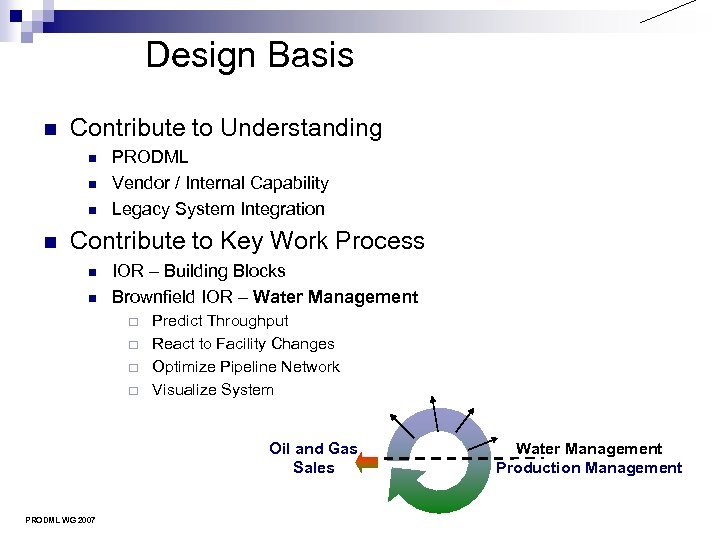 Design Basis n Contribute to Understanding n n PRODML Vendor / Internal Capability Legacy System Integration Contribute to Key Work Process n n IOR – Building Blocks Brownfield IOR – Water Management ¨ ¨ Predict Throughput React to Facility Changes Optimize Pipeline Network Visualize System Oil and Gas Sales PRODML WG 2007 Water Management Production Management
Design Basis n Contribute to Understanding n n PRODML Vendor / Internal Capability Legacy System Integration Contribute to Key Work Process n n IOR – Building Blocks Brownfield IOR – Water Management ¨ ¨ Predict Throughput React to Facility Changes Optimize Pipeline Network Visualize System Oil and Gas Sales PRODML WG 2007 Water Management Production Management


