79207c468f9563acbc0ed2a5c4cf2df5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19

SHB 30215 Certificate III in Makeup SHB 30315 Certificate III in Nail Technology SHB 50115 WRB 20104 Beauty Therapy Diploma of WRBCS 201 B – PROVIDE MANICURE AND PEDICURE SERVICES BSBSMB 304 Determine resource requirements for the micro business LEARNING MATERIAL Initial Impact P/L PO Box 301 Balnarring 3926 © 2016 ABN 37 006 210 Initial Impact P/L 920 Student name: . . . . Student ID: . . . Date: . . . Student name: . . . . Student ID: . . . Advise on beauty products and services Date: . . . 1
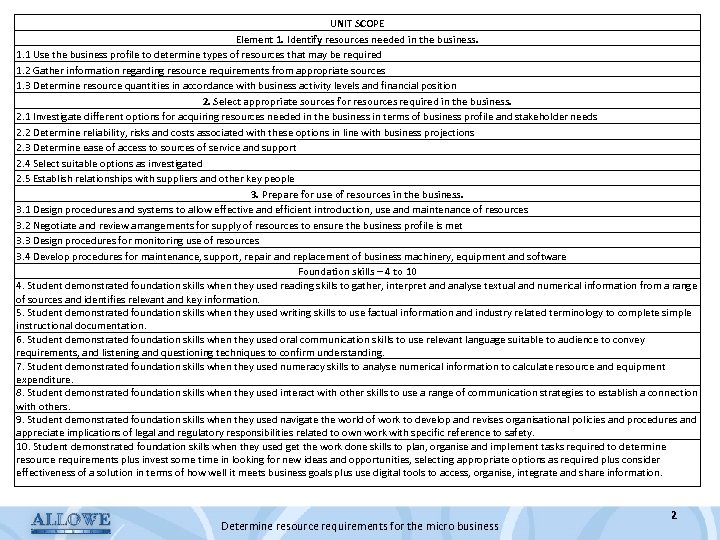
UNIT SCOPE Element 1. Identify resources needed in the business. 1. 1 Use the business profile to determine types of resources that may be required 1. 2 Gather information regarding resource requirements from appropriate sources 1. 3 Determine resource quantities in accordance with business activity levels and financial position 2. Select appropriate sources for resources required in the business. 2. 1 Investigate different options for acquiring resources needed in the business in terms of business profile and stakeholder needs 2. 2 Determine reliability, risks and costs associated with these options in line with business projections 2. 3 Determine ease of access to sources of service and support 2. 4 Select suitable options as investigated 2. 5 Establish relationships with suppliers and other key people 3. Prepare for use of resources in the business. 3. 1 Design procedures and systems to allow effective and efficient introduction, use and maintenance of resources 3. 2 Negotiate and review arrangements for supply of resources to ensure the business profile is met 3. 3 Design procedures for monitoring use of resources 3. 4 Develop procedures for maintenance, support, repair and replacement of business machinery, equipment and software Foundation skills – 4 to 10 4. Student demonstrated foundation skills when they used reading skills to gather, interpret and analyse textual and numerical information from a range of sources and identifies relevant and key information. 5. Student demonstrated foundation skills when they used writing skills to use factual information and industry related terminology to complete simple instructional documentation. 6. Student demonstrated foundation skills when they used oral communication skills to use relevant language suitable to audience to convey requirements, and listening and questioning techniques to confirm understanding. 7. Student demonstrated foundation skills when they used numeracy skills to analyse numerical information to calculate resource and equipment expenditure. 8. Student demonstrated foundation skills when they used interact with other skills to use a range of communication strategies to establish a connection with others. 9. Student demonstrated foundation skills when they used navigate the world of work to develop and revises organisational policies and procedures and appreciate implications of legal and regulatory responsibilities related to own work with specific reference to safety. 10. Student demonstrated foundation skills when they used get the work done skills to plan, organise and implement tasks required to determine resource requirements plus invest some time in looking for new ideas and opportunities, selecting appropriate options as required plus consider effectiveness of a solution in terms of how well it meets business goals plus use digital tools to access, organise, integrate and share information. Determine resource requirements for the micro business 2
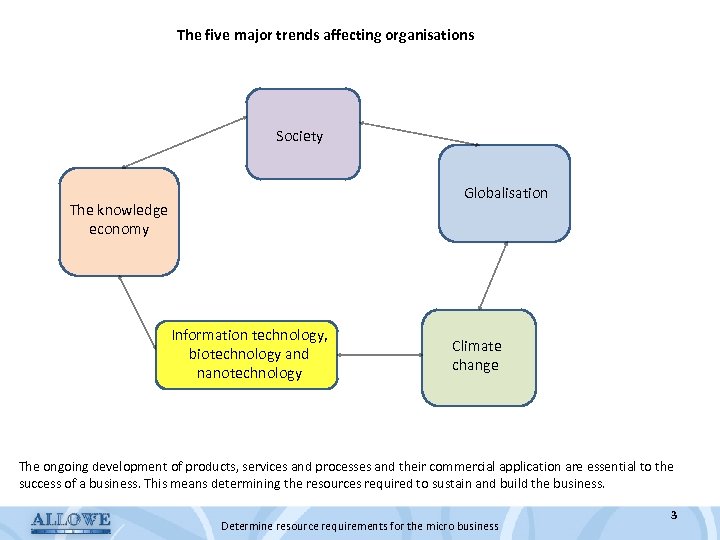
The five major trends affecting organisations Society Globalisation The knowledge economy Information technology, biotechnology and nanotechnology Climate change The ongoing development of products, services and processes and their commercial application are essential to the success of a business. This means determining the resources required to sustain and build the business. Determine resource requirements for the micro business 3

Description of resource requirements A resource is any physical item or online communication entity. It can be stock, or supply of money, materials, staff and other assets that can be used by a micro business in order to function effectively. There are five types of resources. • Financial - includes money, shares and other assets. • Physical - refers to tangible property such as equipment, stock and office space. • Human resources - includes the knowledge, training, experience, as well as the time of the business owner and employees. • Technological - includes the process, system or physical transformation, unique software products and tailored information system architecture. • Organisational - the business structure, routines and systems. The resources required will vary and depend on the nature, type and size of the business. A business needs to determine the resource requirements in order to effectively operate the business. Many resources are acquired and attained over time. The start-up of the business requires funds, knowledge, work space and any supplies or equipment that is required. The limitations to accessing the resources can greatly affect the nature of the business. As the business grows and establishes, and more resources are acquired, the business will be utilise these resources to expand diversify the business. There are three considerations which will determine the business goals and objectives; • The nature (type) of the business. What are the products or services offered? • The attitudes of the decision makers. How do the decision makers react to risk? • The image of the business. How does the business want to be seen by - customers - staff – suppliers- lenders? Determine resource requirements for the micro business 4

Financing resources Before seeking finance options, a business should firstly determine the amount of money it requires. This is done by identifying all of the start-up and ongoing running costs for the business. Start-up costs are the initial one-off outlays when starting the business. These costs include purchase of equipment, office set up, legal and insurance requirements, rent in advance, stock and other costs. Ongoing costs are those continual costs required to operate the business, and include expenses such as wages, rent, electricity and advertising. To calculate the capital that is required to finance the micro-business a budget needs to be developed. This will include all of the start-up and ongoing running costs, a cash-flow statement, as well as working capital. The business then needs to consider the various sources of finances, as well as evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of each. Some of the common sources of finance include; • Personal savings – these are the easiest and cheapest form of finance, but holds a great degree of personal risk. • Credit cards - relatively easy to obtain, however they usually have high interest rates. • Friends and relatives – these can be a cheap and easy form of finance, however, this may potentially affect your relationships. • Angel investors –this is finance that is provided in exchange for a share of the business. • Leases - this involves obtaining equipment from financiers, requiring rental payments during the lease. • Bank loans - this includes term loans, mortgages and bank overdrafts. These usually come with strict qualification requirements. Determine resource requirements for the micro business 5

Government registration requirements To check for relevant licenses and business registrations as well as state and local government regulations you need to contact your state business centre. Four main business structures. - Sole Trader: an individual trading on their own. - Partnership: an association of people or entities running a business together, but not as a company. - Trust: an entity that holds property or income for the benefit of others. - Company: a legal entity separate from its shareholders. • • A sole trader, partnership or trust needs to register the business name in the state or territory that you operate in, unless you are operating the business under your name. Business name registration is administered by the Department of Fair Trading. A company must register your company with the Australian Securities and Investments Commission. There also various taxes that the business may register and comply with. Refer to Australian Taxation Office and the Office of State for the state that the business is in. These may include; - Australian Business Number. - Fringe Benefits Tax. - Goods & Services Tax. - Pay As You Go (PAYG) Withholding. - Tax File Number. - Payroll Tax. Determine resource requirements for the micro business 6

Government registration requirements continued Depending on the type of business, various licences and permits may be required. . These vary from state to state. Check your state’s Business and License Information Service for information relating to licences, business regulations and permits. Also check local council requirements as these vary from region to region. A business owner must be aware of the Trade Practices Act. The Trade Practices Act applies to just about every aspect of the business including advertising, price setting, and transactions with other businesses or consumers. Complying with obligations relating to the Privacy Act sets rules for businesses handling personal information. It also allows individuals to make a complaint if personal information is mishandled. Business insurance minimises the risks to the business in the instance of unforeseen events. There are some types of insurance that are compulsory, while others are optional. There is a wide range of insurances available. - Assets and revenue insurance protects assets and revenue-generating capacity. - People insurance insures business owners and employees against injury, illness, accidents and death. - Liability insurance protects business owners and the business from legal action being taken in relation to damage or injury to a third party due to negligence, faulty products or advice you have offered. There is also professional indemnity insurance especially important in the hair and beauty industry. - Work. Cover insurance provides employers with cover if employees of the business, which includes the business owners and directors, are injured or become ill because of their work. Determine resource requirements for the micro business 7

Salon products and services It is the job of the manager or owner of the business to think about new ideas, new products and new services for the business. For this information it would be wise to consult; • Specialists in the hair and beauty industry – industry associations. • Existing salons who may have similar customers. • Research into industry trends. • Industry magazines, television, commercial printed material. • Customers. • Internet. You can also use Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). • Sales figures on specific products. • Repeat sales rates. Persons involved in the salon’s policy may include; • Staff members. • Owner operator/partners. • Product suppliers. The manager or owner has to decide how much to charge the customer to cover the cost of promotions, additional staff wages and new products and services so that the business makes money. This is seen in a cash flow forecast. Budget setting. All salons need to set selling targets for each product or service they provide. These targets are established by the number of expected sales of each product or service in a given time. These are then used in calculating the salon’s overall budget figures. The aim is to make a profit. Determine resource requirements for the micro business 8

Products and services Your customers will have specific needs and wants that change over time so it is vital that you keep up to date with product knowledge as well as introducing new products and services into the salon. Investigate trends by; • Asking questions of your customers about their wants and needs. • Looking at current and past sales figures in your business. • Recording client requests. • Reviewing customer cards and seeing how often they visited your business or contacted you. • Talking to suppliers and sales persons. • Fashion trends, seasonal colours or clothing styles. • Talking to other hair and beauty salon owners. • Talking to staff and industry associations. • Looking at magazines, attending beauty trade shows, using the internet to source what is happening internationally. • Market research data collected from independent sources. Services. Hair and beauty services are also affected by time, fashion, technology and the entertainment industry. Many techniques become outdated and you will always need to know the latest popular services and how to conduct the service. Visiting trade shows and beauty exhibitions will give you this information. Determine resource requirements for the micro business 9

Three categories that divide products and services Products differences. This involves the ingredients used in the products, how those ingredients work, the ways to use the product, the different types of packaging of the products and what services are provided with the products. Pricing differences. This is the retail price of the product or service, the size of the product packaging, the amount of product you get in the packaging and if they are on special or have gift with purchase as an incentive. People differences. This is based of the sales skills of the business owner or staff to sell better and more to the customers. demonstrating good customer service skills. Four ways for identifying competitor strengths. • Similar services and products. • Cheaper prices on similar services and products. • Greater variety of services and products. • Better promotions and communication with clients. Where sales and services can be improved. You will need to watch how often your customers return for their products and services. Do you need to add an extra service so that your customers will return more often? Do you need to add in additional products so that you can offer more variety to your customers? Reduction of prices known as sales. This greatly affects your business. If other hair or beauty businesses are offering big price reductions on products and services, even if they are not the same as what you have, your business will be affected. It will depend on the relationship you have with your customers. This level of loyalty from your customers is seen from the customer’s point of view. It may be that the cheaper price is more important to the customer than loyalty to your business. Determine resource requirements for the micro business 10
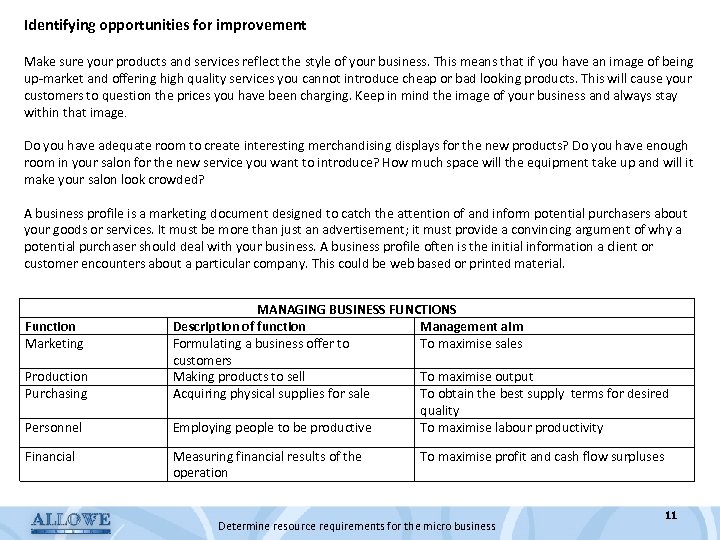
Identifying opportunities for improvement Make sure your products and services reflect the style of your business. This means that if you have an image of being up-market and offering high quality services you cannot introduce cheap or bad looking products. This will cause your customers to question the prices you have been charging. Keep in mind the image of your business and always stay within that image. Do you have adequate room to create interesting merchandising displays for the new products? Do you have enough room in your salon for the new service you want to introduce? How much space will the equipment take up and will it make your salon look crowded? A business profile is a marketing document designed to catch the attention of and inform potential purchasers about your goods or services. It must be more than just an advertisement; it must provide a convincing argument of why a potential purchaser should deal with your business. A business profile often is the initial information a client or customer encounters about a particular company. This could be web based or printed material. Function Marketing Production Purchasing Personnel Financial MANAGING BUSINESS FUNCTIONS Description of function Management aim Formulating a business offer to To maximise sales customers Making products to sell To maximise output Acquiring physical supplies for sale To obtain the best supply terms for desired quality Employing people to be productive To maximise labour productivity Measuring financial results of the operation To maximise profit and cash flow surpluses Determine resource requirements for the micro business 11

Maintaining supplier relations Keeping a good relationship with the suppliers of your stock and equipment is a vital component for your business. You need to pay invoices on time, be friendly and professional in all your dealings with the suppliers. They should be seen as part of your business. Successful order of stock. There are two types of products (known as stock) in the hair and beauty industry. 1. The stock you use in treatments. This is not sold to customers. 2. The stock that is sold to customers. This is sold at retail prices so that the salon makes money on each sale. Having the products in the right quantities. Before setting up a merchandising display, a salon needs to know what products their customers are likely to buy. The number of stock items that a salon buys from the supplier depends on the number of sales they believe they will make to customers. What is the salon’s budget for the purchase of these products? Receiving the products at the right place. When stock arrives at the salon it needs to be unpacked. Unpacking needs to take into consideration Occupational Health and Safety issues. • Correct lifting techniques. • Using cutting and opening equipment correctly. • Wearing protective clothing if required. • Correct and safe storage of stock and equipment. • Disposal of packing material. • Unpacking in a safe and secure area. Determine resource requirements for the micro business 12

Receiving the products at the right time Stock should be ordered from the supplier prior to any promotional activity occurring. Establishing a promotions calendar and ordering stock to arrive not too early before activities, is good financial practice. It is no good having money tied up in stock sitting around in the salon if it is not going to be promoted and sold. When stock arrives it can be sorted in two groups; • Stock that will be displayed in the salon. • Stock that will be placed in the storeroom. Selling the products at the right price. The image of the salon usually dictates the type of customers the salon attracts. This image dictates the price a salon can charge for its services and products. The merchandising displays should reflect the image of the salon. High quality or bargain priced. Negotiate with supplier. To maximise your profits you may need to negotiate with the supplier for better deals. This can include; • Buy a larger number and get some for free. • Payment terms. • Delivery costs reduced or removed for larger orders. Standard salon policies and procedures for investigating new products and services usually include; • Range of products and services within the business model of the salon. • Legislative requirements for the safe application of new technologies. • Current and future stock levels. • Quality control procedures. • Environmental control procedures. • Staff product training procedures. Determine resource requirements for the micro business 13

Product display standards Your salon policy on product display needs to include arranging products, posters, product display stands, maintaining displays and keeping everything clean and in good condition. Sales and merchandising material should consist of; • Price of product. • Packaging or labelling. • Product information brochure or sheet. • Point of sale poster for product. • Display material and props. Keeping your merchandising looking good. • Always make sure your merchandise is clearly displayed and priced. • Make sure colours work together. • Replace products as you remove them from displays. • Make sure that people can understand what you are selling. • Merchandise in such a way that invites customers to touch, feel and try the products. Determine resource requirements for the micro business 14

Monitor quality control of stock Stock count. • Make up a list of all your products, professional and retail, and count each one. • Check for any stock that may be out of date, old, smells bad or has been damaged. • Check to see if the stock you have sold matches with the stock you have counted. • If there is a difference, could it be that you have not recorded every sale or some items may have been stolen? Re-order of stock. • Before ordering more stock check with your sales figures to see if there any sales trends that will tell you which products are the fast or slow sellers. • If you are planning any promotions as part of your marketing concept, allow for extra sales. • Place your order with your supplier making sure you are able to pay for the stock. When stock arrives. • When stock arrives remove packaging materials following OH&S policies. • Check that all stock you ordered has arrived and check to see if any is missing or damaged. • If any items are missing or damaged contact the supplier immediately and make a written report in case there is a dispute over the items. • If you place price stickers on your stock then this is the time to do it. Place all stock where it should be kept. Determine resource requirements for the micro business 15

Rationalising stock Keeping up to date with the latest in products is essential for you to remain competitive. Customers like new things. They like to know that you are knowledgeable about fashion, image and technology. This will require that some of your stock may need to be updated or deleted if it is not selling. The lack of customer sales for those products will tell you what to do. Returning stock to supplier. Sometimes you may need to return stock to a supplier. It may have been damaged when it reached your salon or you may have a special arrangement with the supplier. • Pack the products carefully so that they cannot be damaged. If they do get damaged then the supplier can charge you for the products. • Keep a record of returning the stock in case there is a dispute with the supplier. Deleting products or services to maximise profits. Sometimes you will need to delete products or services that are not bringing in the income that it costs you to offer them. You need to continually check your sales records to determine what is profitable and what is not. There are many ways a business can create a successful mix of products and services. • Expanding the current number of products and services offered if the clients are demanding it. • Changing the current products and services to best suit the clients visiting the salon. • Reducing the current variety of services if some are not profitable. • Replacing expensive products with cheaper ones if the clients are complaining about the price. • Reducing the amount of customer service items that you provide your clients, which cost you money, for no extra return. Determine resource requirements for the micro business 16

Planning staff requirements Workforce action planning requires consideration of; • The problems the business is currently facing. • The future - the business objectives you need to achieve. • The strategies for achieving the objectives. Current business needs. • What skills does the business need right now? Consider the options, up-skilling existing workers or taking on new employees and training them. • What can the business afford? This doesn't just mean wages. You need to think about turnover, loss of training, inexperience and long term vacancies if there is a high turnover of staff. Future business needs. • What skills do you want more of? What are the critical jobs you will need to make the business meet the changing needs of the marketplace? • Prediction of future employees. Will there be shortages of staff who have particular skills? Policies and procedures. Salon policies and procedures should outline the responsibilities and expectations of all staff members. SALON POLICIES AND PROCEDURES Job descriptions Educational and professional requirements of staff Client relations Standards of behaviour for employees Location of M. S. D. S information Guidelines for dealing with organisational problems Guidelines for dealing with clients with disabilities Salon hours and prices for products and services Salon service standards Infection control standards Record keeping Staff absence policy and complaints Care of products, tools and equipment Termination of employment Determine resource requirements for the micro business 17

Sustainability legislation Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme Bill 2009 www. climatechange. gov. au/emissionstrading/legislation/index. html A Bill for an Act to reduce pollution caused by emissions of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases, and for other purposes. National Greenhouse and Energy Reporting Act 2007 www. comlaw. gov. au The National Greenhouse and Energy Reporting Act (Cth) (NGER Act) requires corporations and facilities that emit greenhouse gases above a certain threshold to report their emissions, energy usage and consumption, including some Local Governments. Energy Efficiency Opportunities Act 2006 www. comlaw. gov. au The Energy Efficiencies Opportunities Act encourages greater efficiency in the use of energy by large energy using businesses, and for related purposes. The Act requires large energy using business to report energy use and assess opportunities for improvements. Businesses are not required to implement the energy efficiency opportunities identified. Renewable Energy (Electricity) Act 2000 www. comlaw. gov. au The Renewable Energy (Electricity) Act encourages additional electricity generation from renewable sources by placing a legal liability on the wholesale purchasers of electricity. Liable parties must surrender an annual quota of Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) each year, which are created by accredited renewable energy generators. This Act sets the framework for the Mandatory Renewable Energy Targets (MRET), which must be achieved over the period 2001 to 2020. The legislation is supported by the regulations. A review of the MRET led to the Renewable Energy (Electricity) Amendment Act 2006. Environment Protection and Biodiversity Act 1999 www. comlaw. gov. au The Environment Protection and Biodiversity Act is the Australian Government’s principle piece of legislation for the protection of the environment and conservation of biodiversity. Part IV of this Act establishes the legislative framework for the environmental impact assessment process. This Act gives the Commonwealth jurisdiction over development approvals that impinge upon heritage sites, national heritage places, or nationally threatened species and ecological communities. Determine resource requirements for the micro business 18

Sustainable environmental practices These may include; • Safe disposal of all waste materials to minimise negative impact on the environment. • Efficient use of energy, water and other resources to minimise negative impact on the environment. • Redesigning layout of premises to maximise the use of space and reduce energy costs. • Ensuring the practice of waste minimisation and recycling is conducted to reduce impact on the environment. • Comparing availability of products, equipment and services and adjusting their use to minimise negative impact on the environment. • Using effective time management practices throughout daily work activities. Sustainable business practices. Achieving sustainability in business also involves ethical work practices. These include the responsibilities of staff and management towards evaluating products and services to meet customer’s needs and affordability. Waste management system. A waste management system refers to a specific strategy used to treat waste materials. This may include the collection, transportation, recycling, disposal or processing of waste. The term waste generally means unwanted or unusable material. Waste could be human waste, industrial waste, hazardous waste or biodegradable waste. Four categories of waste reduction. 1. Managing inventory – implement just-in-time procedures by not holding stock and ordering when stocks are low. 2. Modifying production processes – improving current operation and maintenance procedures, changing the materials used in production and modifying existing equipment or purchasing more cost efficient equipment. 3. Reducing waste volume – techniques for separating hazardous waste and/or recoverable waste from overall waste. 4. Recovering waste – recycling activities. This completes the learning material for this unit. Authors copyright is claimed in all forms of media. Moral rights are claimed in all forms of media. Intellectual property rights are asserted and maintained in all forms of media. Determine resource requirements for the micro business 19
79207c468f9563acbc0ed2a5c4cf2df5.ppt