893f9983fb7b0152d158d9177ce264c1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26

SHB 30215 Certificate III in Makeup SHB 30315 Certificate III in Nail Technology WRB 20104 SHB 50115 Diploma of Beauty Therapy WRBCS 201 B – PROVIDE MANICURE AND PEDICURE SERVICES BSBSMB 403 Market the small business LEARNING MATERIAL Initial Impact P/L PO Box 301 Balnarring 3926 © 2016 ABN 37 006 210 920 Initial Impact P/L Student name: . . . . Student ID: . . . Date: . . . Student name: . . . . Student ID: . . . Advise on beauty products and services Date: . . . 1
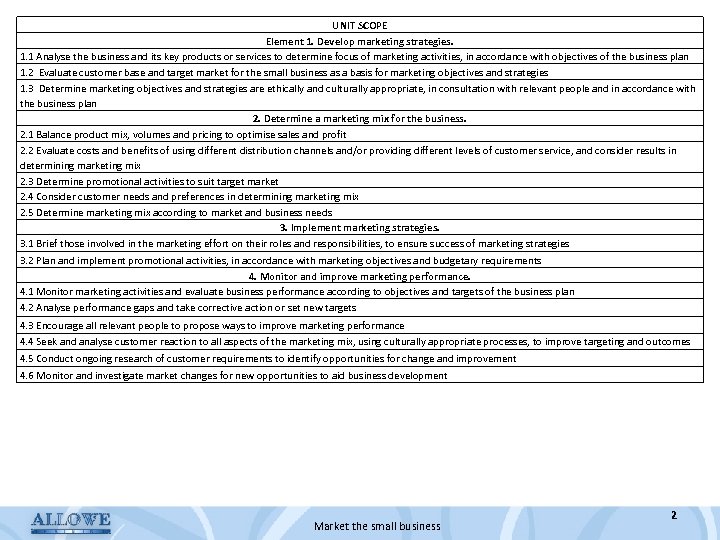
UNIT SCOPE Element 1. Develop marketing strategies. 1. 1 Analyse the business and its key products or services to determine focus of marketing activities, in accordance with objectives of the business plan 1. 2 Evaluate customer base and target market for the small business as a basis for marketing objectives and strategies 1. 3 Determine marketing objectives and strategies are ethically and culturally appropriate, in consultation with relevant people and in accordance with the business plan 2. Determine a marketing mix for the business. 2. 1 Balance product mix, volumes and pricing to optimise sales and profit 2. 2 Evaluate costs and benefits of using different distribution channels and/or providing different levels of customer service, and consider results in determining marketing mix 2. 3 Determine promotional activities to suit target market 2. 4 Consider customer needs and preferences in determining marketing mix 2. 5 Determine marketing mix according to market and business needs 3. Implement marketing strategies. 3. 1 Brief those involved in the marketing effort on their roles and responsibilities, to ensure success of marketing strategies 3. 2 Plan and implement promotional activities, in accordance with marketing objectives and budgetary requirements 4. Monitor and improve marketing performance. 4. 1 Monitor marketing activities and evaluate business performance according to objectives and targets of the business plan 4. 2 Analyse performance gaps and take corrective action or set new targets 4. 3 Encourage all relevant people to propose ways to improve marketing performance 4. 4 Seek and analyse customer reaction to all aspects of the marketing mix, using culturally appropriate processes, to improve targeting and outcomes 4. 5 Conduct ongoing research of customer requirements to identify opportunities for change and improvement 4. 6 Monitor and investigate market changes for new opportunities to aid business development Market the small business 2
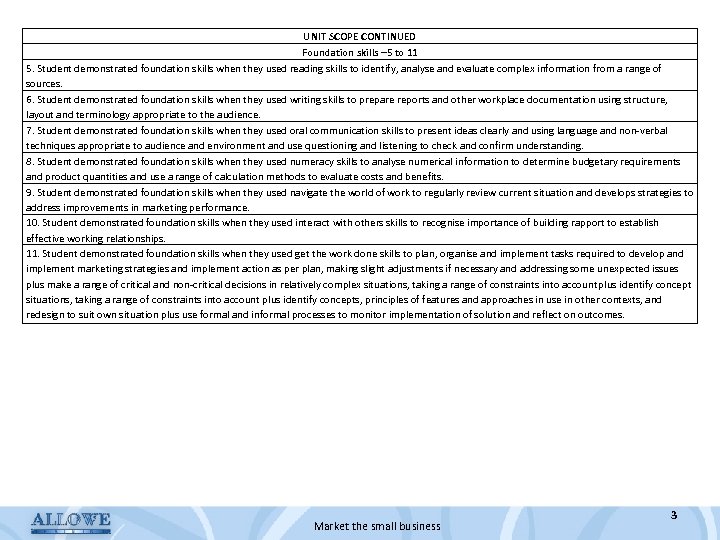
UNIT SCOPE CONTINUED Foundation skills – 5 to 11 5. Student demonstrated foundation skills when they used reading skills to identify, analyse and evaluate complex information from a range of sources. 6. Student demonstrated foundation skills when they used writing skills to prepare reports and other workplace documentation using structure, layout and terminology appropriate to the audience. 7. Student demonstrated foundation skills when they used oral communication skills to present ideas clearly and using language and non-verbal techniques appropriate to audience and environment and use questioning and listening to check and confirm understanding. 8. Student demonstrated foundation skills when they used numeracy skills to analyse numerical information to determine budgetary requirements and product quantities and use a range of calculation methods to evaluate costs and benefits. 9. Student demonstrated foundation skills when they used navigate the world of work to regularly review current situation and develops strategies to address improvements in marketing performance. 10. Student demonstrated foundation skills when they used interact with others skills to recognise importance of building rapport to establish effective working relationships. 11. Student demonstrated foundation skills when they used get the work done skills to plan, organise and implement tasks required to develop and implement marketing strategies and implement action as per plan, making slight adjustments if necessary and addressing some unexpected issues plus make a range of critical and non-critical decisions in relatively complex situations, taking a range of constraints into account plus identify concepts, principles of features and approaches in use in other contexts, and redesign to suit own situation plus use formal and informal processes to monitor implementation of solution and reflect on outcomes. Market the small business 3

Marketing is the process of supplying or satisfying the wants and needs of the customer. It involves all the decisions and actions required to create sales for the business. Marketing aims to give people what they want in the most profitable way for the business. Effective marketing produces satisfied customers who return and tell others about the business. Marketing requires the establishment of an effective and achievable plan in order to make sales and achieve profits. The marketing plan is a written document detailing marketing and financial objectives for each product and service the business provides. It sets out programs, costs and timings as a guide for the marketing activities of the business. The marketing plan is concerned with actual budgets and marketing tactics that will be employed. Marketing funds should be allocated to business promotions, consumer promotions or more advertising. There are benefits a business can expect to achieve as a result of developing a marketing plan which; 1. Provides a clear marketing action plan to follow. 2. Establishes priorities. 3. Allows all aspects of the business to support the marketing programme. 4. Sets measureable business goals against which marketing performance may be judged. 5. Establishes a base for follow-up planning. 6. Allows examination of the assumptions behind the profit and loss statement. 7. Provides an avenue to sell new and innovative products and services to customers. 8. Provides for marketing continuity during staff changes. 9. Enables business owners and managers to test marketing activities for consistency with business objectives. A market trend is a common direction an industry may be moving in over a period of time. A business may be influenced by these trends. Consumers may be influenced by these trends. These trends are classified in long time frames, medium time frames, and short time frames. Market the small business 4

Customer oriented marketing The correct approach to marketing is to be customer oriented. The process is to put the customers needs first in all customer dealings. This includes personal selling, customer enquiries, servicing and customer complaints. The main characteristics of a customer oriented business are; • Marketing decisions are based on a knowledge and an understanding of what customers want. • Profitable sales volume. • Wide product or service range. • New additions to the product and services provided. • There are high standards of customer service and good customer relations. • Market research is conducted frequently. • Competitors are continually monitored. • New opportunities are sought to expand the business. There are three categories that divide products. Product differences. This involves the ingredients used in the product, how those ingredients work, the ways to use the product and the different types of packaging of the product. Pricing differences. This is the retail price of the product, the size of the packaging, the amount of product you get in the packaging and if they are discounted or have a gift with purchase as an incentive. People differences. This is based on the skills of the sales person to sell more to the customers through providing good customer service. Market the small business 5
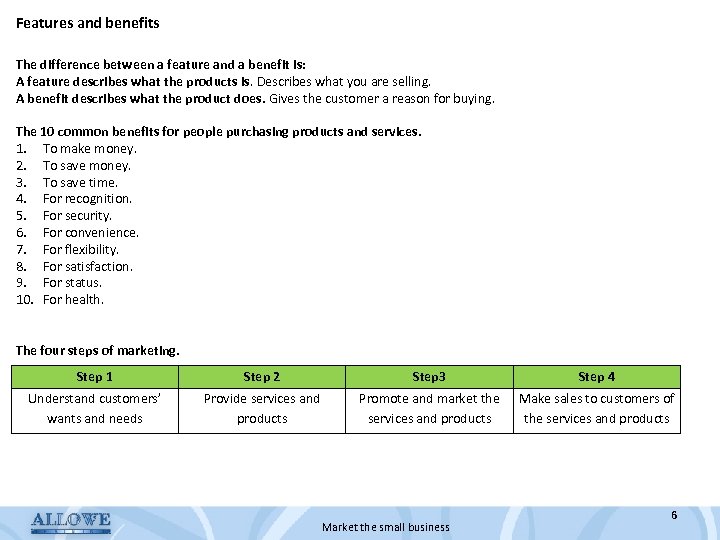
Features and benefits The difference between a feature and a benefit is: A feature describes what the products is. Describes what you are selling. A benefit describes what the product does. Gives the customer a reason for buying. The 10 common benefits for people purchasing products and services. 1. To make money. 2. To save money. 3. To save time. 4. For recognition. 5. For security. 6. For convenience. 7. For flexibility. 8. For satisfaction. 9. For status. 10. For health. The four steps of marketing. Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 Step 4 Understand customers’ wants and needs Provide services and products Promote and market the services and products Make sales to customers of the services and products Market the small business 6

Demographics of consumers Demographic is the process of defining and subdividing a large homogenous market into clearly identifiable segments having similar needs, wants or demand characteristics. Its objective is to design a marketing mix that precisely matches the expectation of customers in the targeted segment. Demographics allows a business to divide customers into; • Age. • Gender. • Family size. • Family life cycle - single, married with or without children. • Income. • Occupation. • Education. • Religion. • Race. • Nationality. • Social status; lower, middle class etc. Promotional activities. • Personal selling is verbal or face-to-face communication with potential buyers of the product or service with the intention of making a sale. Personal selling may focus initially on developing a relationship with the potential buyer, but will always ultimately end with an attempt to 'close the sale‘. • Direct marketing is targeting a person or a company by sending things such as fliers, emails, postcards or sales presentation letters with the objective of generating new business or raising the profile of an organisation or product. • Advertising is paid messages which can be delivered using newspapers, radio, television, magazines or through the web. • Public relations, or publicity, is messages sent to the media or general public to build a good corporate image. The important thing is to have a newsworthy item to tell people about. Market the small business 7
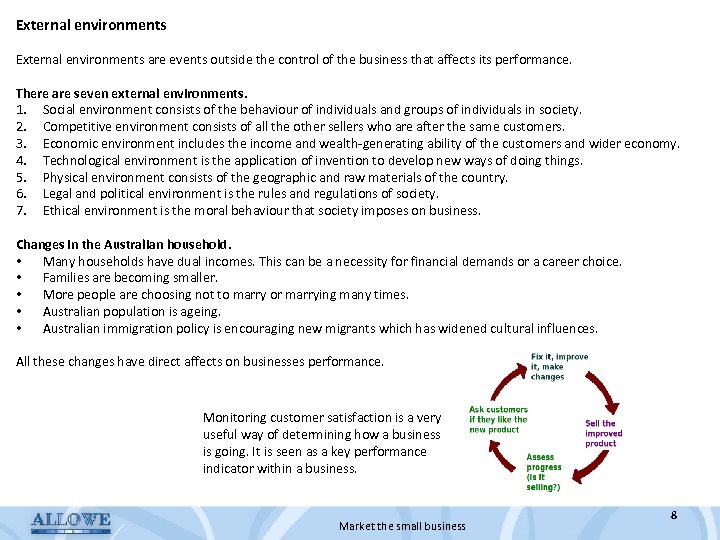
External environments are events outside the control of the business that affects its performance. There are seven external environments. 1. Social environment consists of the behaviour of individuals and groups of individuals in society. 2. Competitive environment consists of all the other sellers who are after the same customers. 3. Economic environment includes the income and wealth-generating ability of the customers and wider economy. 4. Technological environment is the application of invention to develop new ways of doing things. 5. Physical environment consists of the geographic and raw materials of the country. 6. Legal and political environment is the rules and regulations of society. 7. Ethical environment is the moral behaviour that society imposes on business. Changes in the Australian household. • Many households have dual incomes. This can be a necessity for financial demands or a career choice. • Families are becoming smaller. • More people are choosing not to marry or marrying many times. • Australian population is ageing. • Australian immigration policy is encouraging new migrants which has widened cultural influences. All these changes have direct affects on businesses performance. Monitoring customer satisfaction is a very useful way of determining how a business is going. It is seen as a key performance indicator within a business. Market the small business 8

Setting business objectives An important step in marketing is to have a clear idea of what you want to achieve. Objectives are the targets the business wishes to reach. They help focus energy towards the results the business wants to achieve. Research has proven that clear objectives lead to increased performance. To develop objectives it would be wise to consult; • Specialists in the industry – industry associations. • Staff and complementary business. • Research into industry trends. • Suppliers and customers. • Accountants and bankers. Persons involved in the marketing effort may include; • Advertising and graphic designer professionals. • Owner operator/partners. • Product suppliers. • Photographers and printers. • Customers and staff. SWOT ANALYSIS – strengths, weaknesses, opportunity, threats. 1. Strengths - This is an internal audit of the business. What is the business good at? What does the business do well? 2. Weaknesses - This is an internal audit of the business. What is currently lacking in the business? What are the weak aspects of the business that competitors do better? Could be staff, lack of funds, location etc. 3. Opportunity -This is an external audit of the business. What opportunities can management see from the research it has conducted? These are opportunities that the business has control over. 4. Threats -This is an external audit of the business. What is happening outside the business that directly effects the business? Can these threats be overcome by activities the business conducts or are they out of the control of the business? Market the small business 9
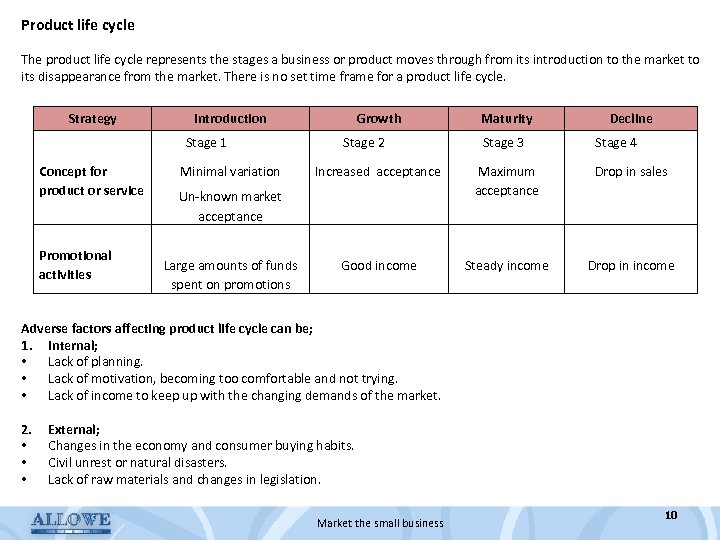
Product life cycle The product life cycle represents the stages a business or product moves through from its introduction to the market to its disappearance from the market. There is no set time frame for a product life cycle. Strategy Introduction Stage 1 Concept for product or service Stage 2 Maturity Stage 3 Decline Stage 4 Increased acceptance Maximum acceptance Drop in sales Promotional activities Minimal variation Growth Good income Steady income Drop in income Un-known market acceptance Large amounts of funds spent on promotions Adverse factors affecting product life cycle can be; 1. Internal; • Lack of planning. • Lack of motivation, becoming too comfortable and not trying. • Lack of income to keep up with the changing demands of the market. 2. External; • Changes in the economy and consumer buying habits. • Civil unrest or natural disasters. • Lack of raw materials and changes in legislation. Market the small business 10
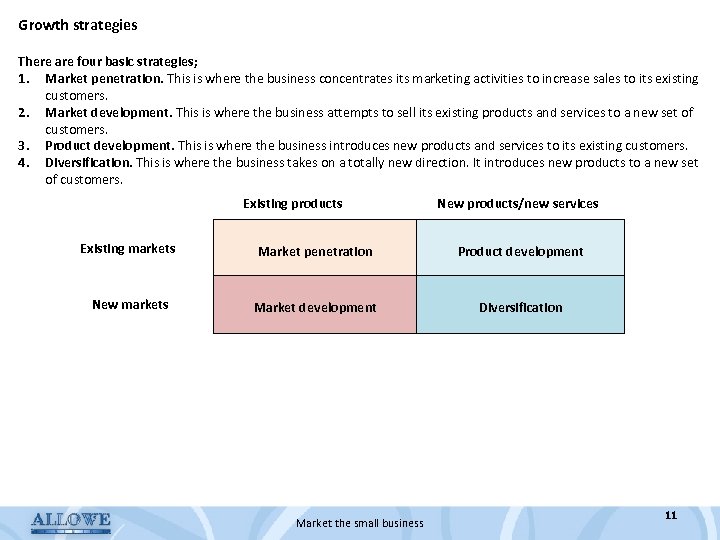
Growth strategies There are four basic strategies; 1. Market penetration. This is where the business concentrates its marketing activities to increase sales to its existing customers. 2. Market development. This is where the business attempts to sell its existing products and services to a new set of customers. 3. Product development. This is where the business introduces new products and services to its existing customers. 4. Diversification. This is where the business takes on a totally new direction. It introduces new products to a new set of customers. Existing products New products/new services Existing markets Market penetration Product development New markets Market development Diversification Market the small business 11

Future trends The world global trend is that people are working harder and for longer hours. This will have an effect on your business as there will be less time to visit a salon or store. This may require you to open for longer hours, be flexible in what you offer your customers or change your opening hours. You may have to visit your customers and offer services in their home or provide a home delivery service for products. The entertainment industry. This has a big impact on the hair and beauty industry. Actors, singers and models influence beauty trends. International trends. Overseas fashion in make-up colours and skin treatments, hair colours and techniques, health requirements and environmental issues with ingredients and packaging will also affect your business. Seasonal trends. These are the changes that occur at special times each year. It can be summer, winter, spring, autumn, religious festivals, Father’s Day, Mother’s Day, Valentines Day and all other special occasions that retailers create so that they can sell more product. Your hair or beauty business will also be affected by these seasonal trends. Reduction of prices known as sales. This greatly affects your business. If other hair or beauty businesses are offering big price reductions on products and services, even if they are not the same as what you have, your business will be affected. It will depend on the relationship you have with your customers. This level of loyalty from your customers is seen from the customer’s point of view. It may be that the cheaper price is more important to the customer than loyalty to your business. Market the small business 12

Market research is an essential part of a business. The research may involve the following; • Observing and discussing client requirements. • Recording and reviewing client requests, enquiries and client personal cards. • Reviewing frequency of purchases of services and products. • Talking to colleagues and sales representatives. • Reading industry magazines and other publications. • Sourcing suppliers of products for the industry. • Collecting market research data from independent sources. You can use; • Telephone surveys – questionnaire over the telephone. • Mail surveys – questionnaire through the mail. • Interviews – personal administration of questionnaire. Market the small business 13

Marketing mix A marketing mix is the variety of activities and promotions chosen by the business to create sales. Marketing activities consist of the 4 P’S. Product – an item, service or idea that is created to fill the needs of customers. Look at the product or service through the eyes of the customer. A business should sell products and provide services that they know the customers are needing or wanting. Price – the price charged for the product or services. What does the product or service cost the business to produce? What price will the customer pay? The true price for a service or product is as much as the customer can stand as long as the customer believes they are getting value for money. Promotion – the communication and activities created to attract customers. An advertisement must have a benefit in it for the customer the business is trying to attract. It must create interest and stimulate the customers desires to have the products and services being offered. Promotional strategies could be to; Provide information – brochures, price lists etc. Differentiate – how much better your business is compared to your competitors. Stabilise sales – offer discounts in down times. Place – also known as the distribution of the product. How or where will the customers receive the products or services? Will it be in store, mail order, internet sales or door to door? The places where products and services are distributed can include business association meetings, school councils, local offices, shops or factories. Market the small business 14

Marketing strategies can include; • Increasing the average client bill through staff incentives. • Incentives to attract new clients. • Off-peak promotion ideas. • Incentive schemes to encourage re-booking by clients. • Pricing, presentation and display of products and services. • Promotion and advertising. • Changing the service and professional product and retail range. • Pursuing cost leadership and/or product differentiation within a specialist market segment. • Creating a very different product line or service so that the business becomes a leader in the industry. Promotional activities may include; • Website. • Word of mouth, referrals and testimonials. • Professional and industry journals. • Advertising in newspapers, on radio or on television (paid media). • Mail drops (direct marketing). • Display posters and telephone canvassing. • Exhibitions and in-store promotions. • Sponsorship and donations. • Consumer promotions – competitions, coupons, samples, demonstrations, in-store displays. • Public relations – unpaid media exposure. • The development of networks and strategic alliances. • Staff development programs to enhance customer service orientation, staff incentives. • Client incentives, including loyalty programs and discounting. Market the small business 15
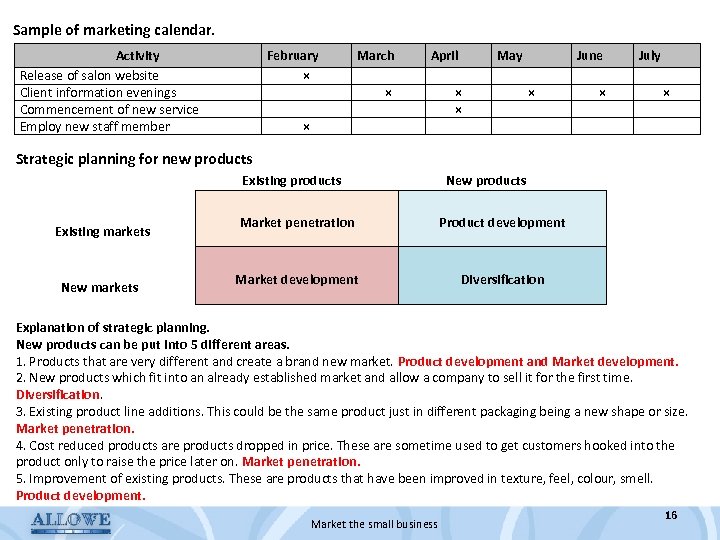
Sample of marketing calendar. Activity Release of salon website Client information evenings Commencement of new service Employ new staff member February × March April × × May June × × July × Strategic planning for new products Existing products New products Existing markets New markets Market penetration Product development Market development Diversification Explanation of strategic planning. New products can be put into 5 different areas. 1. Products that are very different and create a brand new market. Product development and Market development. 2. New products which fit into an already established market and allow a company to sell it for the first time. Diversification. 3. Existing product line additions. This could be the same product just in different packaging being a new shape or size. Market penetration. 4. Cost reduced products are products dropped in price. These are sometime used to get customers hooked into the product only to raise the price later on. Market penetration. 5. Improvement of existing products. These are products that have been improved in texture, feel, colour, smell. Product development. Market the small business 16
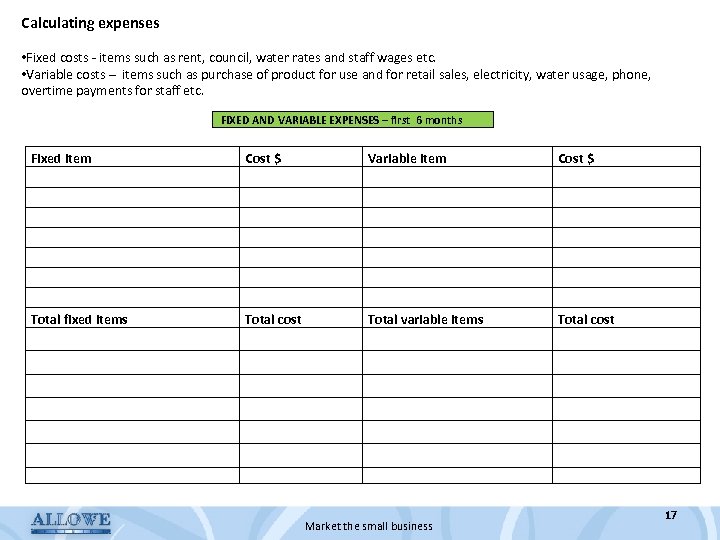
Calculating expenses • Fixed costs - items such as rent, council, water rates and staff wages etc. • Variable costs – items such as purchase of product for use and for retail sales, electricity, water usage, phone, overtime payments for staff etc. FIXED AND VARIABLE EXPENSES – first 6 months Fixed item Total fixed items Cost $ Total cost Variable item Total variable items Cost $ Total cost Market the small business 17

Legislative requirements Australian Consumer Law (ACL). The Australian Consumer Law (ACL) is a national law and replaced any existing State and Territory laws regarding consumer rights and protection and gives all Australian consumers the same rights and protections wherever they are in Australia. The aim of the law is to simplify consumer laws and reduce business compliance burdens and create a national enforcement regime, with consistent enforcement powers for Australia's consumer protection agencies to take effective action for consumers. The ACL includes; - A national law guaranteeing consumer rights when buying goods and services, which replaces existing laws on conditions and warranties. - A national product safety law and enforcement system. - A national unfair contract terms law covering standard form contracts. - A national law for unsolicited consumer agreements replacing existing laws on door-to-door sales and other direct marketing. - Simple national rules for lay-by agreements. - Definitions of penalties, enforcement powers and consumer redress options. The Occupational Health and Safety Act 2004 (the Act). This Act provides legislative and administrative measures to improve occupational health and safety. The Act sets out the key principles, duties and rights in relation to occupational health and safety. The Occupational Health and Safety Regulations 2007 are made under the Act. They specify the ways duties imposed by the Act must be performed, or prescribe procedural or administrative matters to support the Act, such as requiring licenses for specific activities, keeping records, or notifying certain matters. Market the small business 18

Business requirements Permit to erect or remove an advertising sign or notice on a building, road or footpath. You will require this licence if you intend to erect, place or remove an advertising sign or notice on a building, road or footpath. For example, approval may be required for the placement of A-frame sandwich boards, business signage on a building, or temporary or movable signs. Signs also include banners or flag-like materials and signs affixed to buildings, fences, trees and other council property. Permit to distribute handbills. This permit is required if you intend to display, hand out or distribute handbills, notices, pamphlets, flyers or any other form of advertising or promotional material to persons or premises. Refer to your local council for details of any specific requirements for this permit. Registration for payroll tax. You will require this registration if you are an employer who pays wages that exceed $45, 833 monthly or $550, 000 annually. If you are an employer who is a member of a group, the total Australian wages paid or payable by all members of the group determines whether you should register for payroll tax. Registration for Work. Safe injury insurance. You will require this registration if you intend to run a business which employs workers, or contractors, and you pay (or expect to pay) more than $7, 500 a year in rateable remuneration, or if you engage apprentices or trainees. Work. Safe is a public operation and it administers this compulsory insurance scheme. Directors and employees (including apprentices or trainees) of proprietary limited companies who receive salaries or wages are workers and are covered under Work. Safe Injury Insurance. Market the small business 19

Creating a marketing budget A budget is a plan to; • Control your finances. • Enable you to make confident financial decisions and meet your objectives. • To ensure you have enough money for your future projects. A budget outlines what you will spend your money on and how that spending will be financed. It is not a forecast. A forecast is a prediction of the future, whereas a budget is a planned outcome of what you want to achieve in your business. Budgeting. When setting budgets the following items should be considered. Days/ months - Each year has 12 months in the calendar but with holidays, many businesses decide to budget for an 11 month year and take the sales that occur in the 12 months as a bonus. The number of days each month can vary in a 5 day week, changing from 18 days to 23 days depending on the month. The weeks in a month change from 4 to 5 with each quarter having 13 weeks. Holidays - School holidays affect spending habits, while geographic regional holidays affect the number of trading days. Public holidays - Currently there are 11 paid public holidays occurring throughout the year. Easter is celebrated in different months each year while ANZAC day and Australia day are specific days. These holidays can be taken on weekends. This may affect trading and should be noted in the budget. Facts - Always budget based on actual information not guesses. Check the facts for relevance and accuracy. Sales - Included in your plan will be a sales forecast based on the marketing plan. Check your marketing calendar. Expenses - The plan will also include costs or expenses in the budget. Profit - The end result of the sales budget and expense budget is that you should have a surplus of profit to be put to further development of marketing and other areas of the business. Market the small business 20

The selling gap One way to look at selling any product is to see the sale as filling the gap between what the customer is receiving from their current products and what the customer really wants. This means “Is the customer really happy with the products they are currently using? ” There are two selling gap situations. Gap 1. This gap is when a customer is considering the purchase of a product for the very first time. It’s the customers understanding of what the product should provide. This gap occurs even if the customer has never used these types of products before. The customer would have been listening to advertising and come to you for assistance with their product choice. This is called a LARGE SELLING GAP because it allows you to personally demonstrate your products to the customer resulting in an easy sale for you. Gap 2. This gap is when a customer already uses specific products and is reasonably satisfied with those products. This is called a SMALL SELLING GAP. Your sales skills will be needed to demonstrate to the customer that your product is better than the one the customer is currently using. This can be demonstrated through product usage, product results, feel of the product, special ingredients, packaging, value for money, or your skills as a product demonstrator. Performance appraisal. This is a process where the owner/manager of the business examines and evaluates how the business is performing according to targets and budgets. It can be used for evaluating staff performance at work to determine who requires additional training. Market the small business 21

Performance gap A performance gap is the difference between what was expected and what was achieved. This means that the sales target figures you expected to achieve were not reached. Large performance gaps mean that there is a big difference from what was expected to what actually occurred in the performance of the service or the product. Small performance gaps mean that there is little difference from what was expected to what actually occurred in the performance of the service or the product. Six large performance gap situations might include; 1. Level of customer service provided by team or individual staff members is below required standard. 2. The average dollar value per client is below the required level. 3. Individual staff members have too much down-time. 4. Under achievement of turnover targets by some team members. 5. Profit margins being set too low. 6. Insufficient allocation of funds to marketing. There are four strategies that may solve performance gap situations. 1. People strategies. 2. Product strategies. 3. Pricing strategies. 4. Promotion strategies. People strategies can include the activities of; • Targeting different demographic or psychographic groups. • Targeting heavy, light or non users. • Targeting those markets that have certain behaviour patterns. • Addressing staff issues for under performance or down times. Market the small business 22

Performance gap situations continued Product strategies can include the activities of; • Changing, modifying or improving products and services. • Changing the product mix. • Introducing new lines or deleting some services or products. • Changing the service procedures. • Changing the manner or style of service. Pricing strategies can include the activities of; • Changing the prices. • Becoming price competitive. • Creating value-added offers. • Introducing flexible payment terms. Promotional strategies can include the activities of; • Improving sales techniques – handling customer enquiries. • Improving sales presentation techniques. • Re-arranging the display mix. • Introducing new promotions. • Changing the advertising approach. • Organising better brochures. • Increasing or decreasing the promotional budget. • Using direct email. • Changing the signage on the business. • Organising publicity – unpaid media. Market the small business 23

Monitor product stock levels Stock count. • Make up a list of all products, professional and retail and count each one. • Check for any stock that may be out of date, old, smells bad or has been damaged. • Check to see if the stock you have sold matches with the stock you have counted. • If there is a difference could it be that you have not recorded every sale or some items may have been stolen? Re-order of stock. • Before ordering more stock check with your sales figures to see in there any sales trends that will tell you which products are the fast or slow sellers. • If you are planning any promotions as part of your marketing concept then allow for extra sales. • Place your order with your supplier making sure you are able to afford to pay for the stock. Rationalising stock. Keeping up to date with the latest in products is essential for you to remain competitive. Customers like new things. This will require that some of your stock may need to be updated or deleted if it is not selling. The lack of customer sales for those products will tell you what to do. Deleting services to maximise profits. Sometimes you will need to delete services that are not bringing in the income that it costs you to offer them. You need to continually check your sales records to determine what is profitable and what is not. Market the small business 24

Monitoring the success of marketing and promotional activities All businesses need to evaluate their marketing goals and strategies in order to grow and become ahead of their competitors. This monitoring can take place by; • Monitoring of the marketing activities conducted over the past year. • Asking staff or other relevant people on ways to improve the marketing performance. • Conducting customer service surveys on the effects of the marketing campaign. • Keeping up to date knowledge on market trends, both local and international. Ongoing research is required. To assist with this process answer the following questions. • Will the business change any of its services? If so what will they be? • Have you noticed any changes in the types of customers coming into the business? • Does the business require additional services and products to keep up with the changing market? If so which ones and what will you be getting rid of? • What new promotional activities do you need to implement? • Will your business be changing its prices in this year? If so why? • Are you planning to expand your business and if so what are those plans? Recording data. It is essential that a business has back-up data facilities for recording all business activities. There are many business management systems available covering a wide variety of industries. These systems can assist with the organisation of marketing research and tracking the progress of the sales towards achieving the marketing goals. Market the small business 25

Sustainable environmental practices These may include; • Safe disposal of all waste materials to minimise negative impact on the environment. • Efficient use of energy, water and other resources to minimise negative impact on the environment. • Redesigning layout of premises to maximise the use of space and reduce energy costs. • Ensuring the practice of waste minimisation and recycling is conducted to reduce impact on the environment. • Comparing availability of products, equipment and services and adjusting their use to minimise negative impact on the environment. • Using effective time management practices throughout daily work activities. Sustainable business practices. Achieving sustainability in business also involves ethical work practices. These include the responsibilities of staff and management towards evaluating products and services to meet customer’s needs and affordability. This completes the learning material for this unit. Authors copyright is claimed in all forms of media. Moral rights are claimed in all forms of media. Intellectual property rights are asserted and maintained in all forms of media. Market the small business 26
893f9983fb7b0152d158d9177ce264c1.ppt