2f21a8970cc8d1fe37e03651131f4662.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 Shaping our Future: Towards a Pan-Canadian e. Learning Research Agenda On-line Conference, from Montreal, May 22 nd, 2008 The Case for an e. Learning Research and Innovation Strategy Gilbert Paquette LORNET Scientific Director CRC in Instructional and Cognitive Engineering LICEF Research Center, Télé-université www. licef. teluq. uquebec. ca/gp
Shaping our Future: Towards a Pan-Canadian e. Learning Research Agenda On-line Conference, from Montreal, May 22 nd, 2008 The Case for an e. Learning Research and Innovation Strategy Gilbert Paquette LORNET Scientific Director CRC in Instructional and Cognitive Engineering LICEF Research Center, Télé-université www. licef. teluq. uquebec. ca/gp
 Study on International e. Learning Initiatives Financed by CCL/CCA in 2005
Study on International e. Learning Initiatives Financed by CCL/CCA in 2005
 Obstacles to an e-Learning strategy in Canada n n n Education is not a federal competency ? Too many provincial jurisdictions with tight budgets ? E-learning is already sufficiently disseminated ? Insufficient awareness on the importance of e. Learning in the knowledge society ? No need for sustained, coordinated programs and initiatives; no need for a e. Learning strategy ?
Obstacles to an e-Learning strategy in Canada n n n Education is not a federal competency ? Too many provincial jurisdictions with tight budgets ? E-learning is already sufficiently disseminated ? Insufficient awareness on the importance of e. Learning in the knowledge society ? No need for sustained, coordinated programs and initiatives; no need for a e. Learning strategy ?
 Organizations & Multiple Jurisdictions n JISC_UK (since 1993) – England, Scotland, Wales & Northern Ireland n Education. au (since 1997) – All Australian states and territories education authorities (8); n n European Union – e. Learning programs (since 2003) – 27 countries; Multilingual Educause - USA – 50 states
Organizations & Multiple Jurisdictions n JISC_UK (since 1993) – England, Scotland, Wales & Northern Ireland n Education. au (since 1997) – All Australian states and territories education authorities (8); n n European Union – e. Learning programs (since 2003) – 27 countries; Multilingual Educause - USA – 50 states
 Main Findings n n n E-learning seen as a productive part of the new economy Strategies and actions are government initiated Embrace a wide scope of activities and stakeholders Substantial public funding Research, a fundamental dimension in the elearning strategy Jurisdictional competencies and cultural diversity are not constraints to collaboration
Main Findings n n n E-learning seen as a productive part of the new economy Strategies and actions are government initiated Embrace a wide scope of activities and stakeholders Substantial public funding Research, a fundamental dimension in the elearning strategy Jurisdictional competencies and cultural diversity are not constraints to collaboration
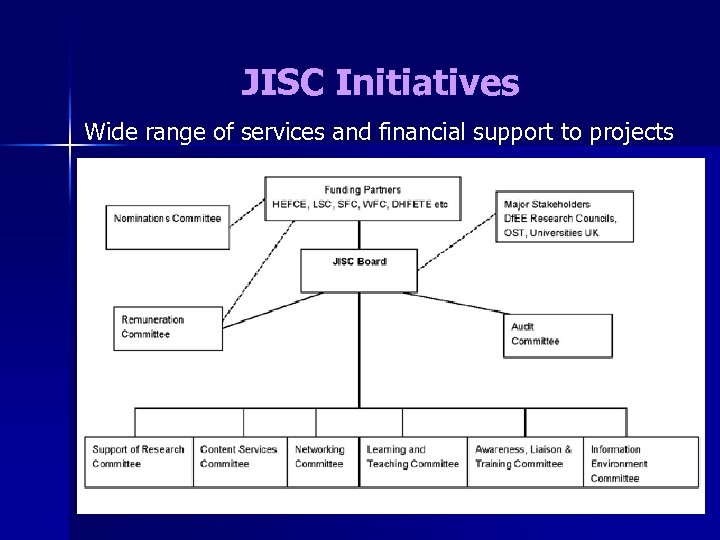 JISC Initiatives Wide range of services and financial support to projects
JISC Initiatives Wide range of services and financial support to projects
 Education. au Initiatives n Wide range of services & capacities centered around accessing, developing and sharing online content & services : – – – n Business services (user needs) Technical services and solutions Comprehensive web services Scalable web solutions Standards and interoperability Web desk services Main current projects : – – – Ed. NA Learning Object Repository myfuture. edu. au - Australia's career information service The Le@rning Federation : Australia / New Zealand, 2001 -2006 Government Education Portal (Commonwealth) Interoperability standards development <. edu. au> domain name management
Education. au Initiatives n Wide range of services & capacities centered around accessing, developing and sharing online content & services : – – – n Business services (user needs) Technical services and solutions Comprehensive web services Scalable web solutions Standards and interoperability Web desk services Main current projects : – – – Ed. NA Learning Object Repository myfuture. edu. au - Australia's career information service The Le@rning Federation : Australia / New Zealand, 2001 -2006 Government Education Portal (Commonwealth) Interoperability standards development <. edu. au> domain name management
 European Initiatives n EC e. Learning program (2004 -2006): – – – – n Education, training and lifelong learning Teachers, trainers, learners Schools and higher education institutions Promoting digital literacy European virtual campuses e-Twinning of schools & promotion of teacher training Transversal actions for the promotion of e-learning in Europe (including elearningeuropa - e. Learning portal) European Schoolnet – School networking and services – Policy and Practice – Interoperability and Content exchange
European Initiatives n EC e. Learning program (2004 -2006): – – – – n Education, training and lifelong learning Teachers, trainers, learners Schools and higher education institutions Promoting digital literacy European virtual campuses e-Twinning of schools & promotion of teacher training Transversal actions for the promotion of e-learning in Europe (including elearningeuropa - e. Learning portal) European Schoolnet – School networking and services – Policy and Practice – Interoperability and Content exchange
 EDUCAUSE (USA) Initiatives n n n n Professional development activities Applied research Strategic policy advocacy Teaching and learning initiatives Online information services Print and electronic publications, including books, monographs, and the magazines EDUCAUSE Quarterly and EDUCAUSE Review Special interest collaborative communities Awards for leadership and exemplary practices
EDUCAUSE (USA) Initiatives n n n n Professional development activities Applied research Strategic policy advocacy Teaching and learning initiatives Online information services Print and electronic publications, including books, monographs, and the magazines EDUCAUSE Quarterly and EDUCAUSE Review Special interest collaborative communities Awards for leadership and exemplary practices
 Type of organizations n JISC A NFP Organization led by Higher Education Councils of UK countries, Research Councils and UK universities representatives n Education. au ltd. Non-profit Corporation put in place by a federal Australian Law in agreement with the Ministers of Education of the 8 States and Territories governments n European Union initiatives They are projects put in place by EU Education Ministries decrees, funded by EU Governments n EDUCAUSE : member-driven initiative Non profit association of 2, 000 colleges, universities, educational organizations, 200 corporations, and 15, 000 active members
Type of organizations n JISC A NFP Organization led by Higher Education Councils of UK countries, Research Councils and UK universities representatives n Education. au ltd. Non-profit Corporation put in place by a federal Australian Law in agreement with the Ministers of Education of the 8 States and Territories governments n European Union initiatives They are projects put in place by EU Education Ministries decrees, funded by EU Governments n EDUCAUSE : member-driven initiative Non profit association of 2, 000 colleges, universities, educational organizations, 200 corporations, and 15, 000 active members
 Funding n JISC – 2004 -05: 137 M$ CAN funding from HE councils Education. au – 2005 : 10 M$ CAN European Union – e. Learning prog. 2004 -2006: 63 M$ CAN – Eur. Schoolnet, 2006: 5, 46 M$ CAN – « e. Content plus » 2005– 08 : 214 M$ CAN – Te. Learn, 2005 -06 : 78 M$ CAN n EDUCAUSE n n – 2006 : 13, 6 M $US (only for central management)
Funding n JISC – 2004 -05: 137 M$ CAN funding from HE councils Education. au – 2005 : 10 M$ CAN European Union – e. Learning prog. 2004 -2006: 63 M$ CAN – Eur. Schoolnet, 2006: 5, 46 M$ CAN – « e. Content plus » 2005– 08 : 214 M$ CAN – Te. Learn, 2005 -06 : 78 M$ CAN n EDUCAUSE n n – 2006 : 13, 6 M $US (only for central management)
 The Situation in Canada -Key issues and concerns
The Situation in Canada -Key issues and concerns
 Canadian Initiatives n n n Huge investments in the ICT infrastructure CANARIE’S e. Learning : 32 projects through its 29 millions $ cost-shared; Program ended after 5 years Industry Canada funded Canadian participation in IMS and IEEE, now absent from these decision centers School. Net had a huge impact on K-12 and was ended while it was more and more productive Canadian participation to international initiatives like GLOBE is fragile The LORNET research network has achieved important R&D results that need to be transferred and disseminated; no funding for that
Canadian Initiatives n n n Huge investments in the ICT infrastructure CANARIE’S e. Learning : 32 projects through its 29 millions $ cost-shared; Program ended after 5 years Industry Canada funded Canadian participation in IMS and IEEE, now absent from these decision centers School. Net had a huge impact on K-12 and was ended while it was more and more productive Canadian participation to international initiatives like GLOBE is fragile The LORNET research network has achieved important R&D results that need to be transferred and disseminated; no funding for that
 Why Are We Behind ? n n n n Discontinuity of major initiatives Short-terms financing of small projects Duplication and waste of efforts Separation of research and innovations projects from implementation and deployment initiatives Multiplicity of centers of decision Lack of strategy, long-term vision, determination and continuity Funding totally insufficient
Why Are We Behind ? n n n n Discontinuity of major initiatives Short-terms financing of small projects Duplication and waste of efforts Separation of research and innovations projects from implementation and deployment initiatives Multiplicity of centers of decision Lack of strategy, long-term vision, determination and continuity Funding totally insufficient
 Proposals for an e. Learning Strategy and a Research Agenda
Proposals for an e. Learning Strategy and a Research Agenda
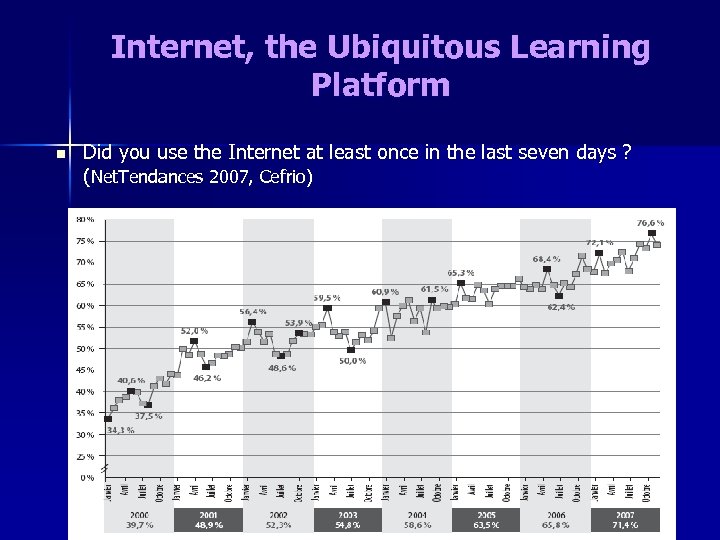 Internet, the Ubiquitous Learning Platform n Did you use the Internet at least once in the last seven days ? (Net. Tendances 2007, Cefrio)
Internet, the Ubiquitous Learning Platform n Did you use the Internet at least once in the last seven days ? (Net. Tendances 2007, Cefrio)
 Needed: A Vision and a Strategy for the Quality of Learning n n Learner centered approaches must be instrumented across boundaries, in a life long learning perspective Repositories of content resources, design resources, and interoperable tools must be made available to learners and educators and evaluated by them to ensure more quality Programs for the development of high-quality content and learning designs should be put in place systematically in workplace sectors and subject matters in universities, colleges and schools Programs for the professional development of teachers and trainers must be supported using e. Learning technologies, including competency selfassessment resources.
Needed: A Vision and a Strategy for the Quality of Learning n n Learner centered approaches must be instrumented across boundaries, in a life long learning perspective Repositories of content resources, design resources, and interoperable tools must be made available to learners and educators and evaluated by them to ensure more quality Programs for the development of high-quality content and learning designs should be put in place systematically in workplace sectors and subject matters in universities, colleges and schools Programs for the professional development of teachers and trainers must be supported using e. Learning technologies, including competency selfassessment resources.
 Needed Initiatives n n n e. Learning R&D Dissemination Fund Action Research Joint Funding Program by the Canadian Research Councils Research Program on e. Learning standards Implementation and Professional Training Sustain a Network of Learning Object Repositories Linked to the Globe Project. Support Communities of Practice to Develop Highquality Content and Learning Designs. Implement a User-based Evaluation Process. Develop e. Learning Modules for educators e. Learning professionals and Create Competency Assessment Programs
Needed Initiatives n n n e. Learning R&D Dissemination Fund Action Research Joint Funding Program by the Canadian Research Councils Research Program on e. Learning standards Implementation and Professional Training Sustain a Network of Learning Object Repositories Linked to the Globe Project. Support Communities of Practice to Develop Highquality Content and Learning Designs. Implement a User-based Evaluation Process. Develop e. Learning Modules for educators e. Learning professionals and Create Competency Assessment Programs
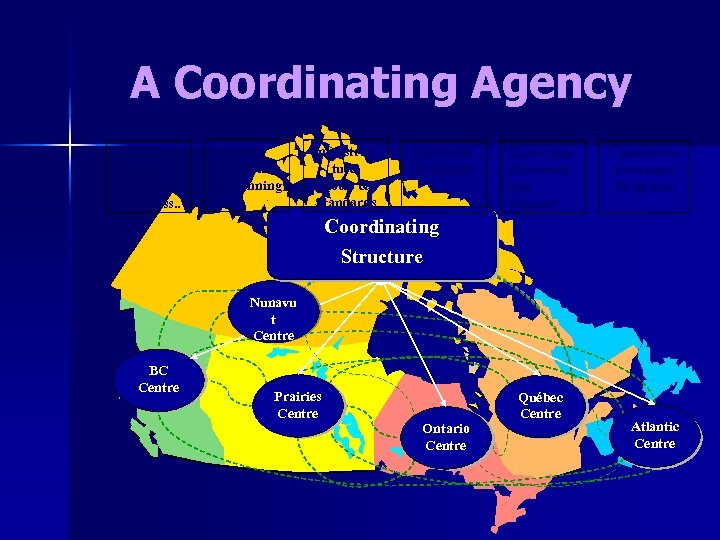 A Coordinating Agency Business Intelligence Progress & Needs. Ass. . Policy orientation & Planning Infrastructure, Tools & Standards Research Programs ELearning Dissemination Support Community Awareness Programs Coordinating Structure Nunavu t Centre BC Centre Prairies Centre Ontario Centre Québec Centre Atlantic Centre
A Coordinating Agency Business Intelligence Progress & Needs. Ass. . Policy orientation & Planning Infrastructure, Tools & Standards Research Programs ELearning Dissemination Support Community Awareness Programs Coordinating Structure Nunavu t Centre BC Centre Prairies Centre Ontario Centre Québec Centre Atlantic Centre
 Some Research Priorities
Some Research Priorities
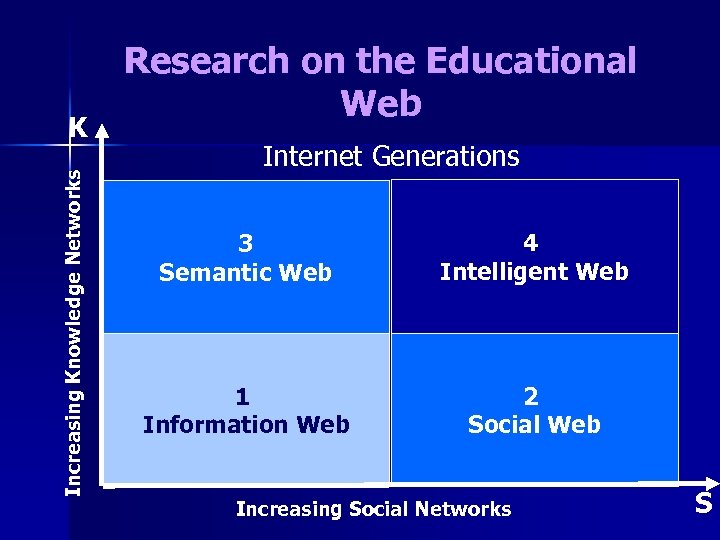 Increasing Knowledge Networks K Research on the Educational Web Internet Generations 3 Semantic Web 4 Intelligent Web 1 Information Web 2 Social Web Increasing Social Networks S
Increasing Knowledge Networks K Research on the Educational Web Internet Generations 3 Semantic Web 4 Intelligent Web 1 Information Web 2 Social Web Increasing Social Networks S
 Web 1. 0 - The Technical Challenges: Interoperability, Reusability, Scalability, Flexibility SCORM QTI Etc. IMS-LD
Web 1. 0 - The Technical Challenges: Interoperability, Reusability, Scalability, Flexibility SCORM QTI Etc. IMS-LD
 Leaning Object Respositories: Networking Worldwide for Quality MERLOT (USA) LORNET (CANADA) FRANCO : RAFAEL LACLO (South America) SCHOOLNET ARIADNE (EUROPE) NIME (JAPAN) EDNA (AUSTRALIA)
Leaning Object Respositories: Networking Worldwide for Quality MERLOT (USA) LORNET (CANADA) FRANCO : RAFAEL LACLO (South America) SCHOOLNET ARIADNE (EUROPE) NIME (JAPAN) EDNA (AUSTRALIA)
 Web 2. 0 - Social Interactivity
Web 2. 0 - Social Interactivity
 Mobility - Pod. Casting
Mobility - Pod. Casting
 Web 3. 0 – The Knowledge Web
Web 3. 0 – The Knowledge Web
 Mega. Trends – The Future is Here 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. New communication means and interfaces Collective creation and sharing of knowledge Prosumerism: Content production by users New forms of socialization Augmented and Virtual Reality Environments Personal mobile multimedia assistant Internet as the unique and ubiquitous educational platform
Mega. Trends – The Future is Here 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. New communication means and interfaces Collective creation and sharing of knowledge Prosumerism: Content production by users New forms of socialization Augmented and Virtual Reality Environments Personal mobile multimedia assistant Internet as the unique and ubiquitous educational platform
 Profund Impact on Learning 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Learning through personal research – Renewed importance on « Learning to Learn » Multiplicity of (valuable or unreliable) information sources Information management competencies are key Creating a new equilibrium between search/browsing and human interaction, between real and virtual activities New means for an active, constructive pedagogy based on real situation, problem solving, projectbased learning, etc.
Profund Impact on Learning 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Learning through personal research – Renewed importance on « Learning to Learn » Multiplicity of (valuable or unreliable) information sources Information management competencies are key Creating a new equilibrium between search/browsing and human interaction, between real and virtual activities New means for an active, constructive pedagogy based on real situation, problem solving, projectbased learning, etc.
 Evolution of the Tasks and Roles of Educators 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. On-line learning questions traditional models : inevitable focus on learner – team work – facilitation Frontiers between departments, institutions, countries are blurring – shift towards higher competencies – specialization and collaboration are essential Mobility of knowledge diversifies ways, time and places where to learn – Distance Ed is the future Large gap between students and professors towards perceptions and use of technologies - digital divide to evercome The number and the interaction of teaching decisions increases – need for a new ISD methodology
Evolution of the Tasks and Roles of Educators 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. On-line learning questions traditional models : inevitable focus on learner – team work – facilitation Frontiers between departments, institutions, countries are blurring – shift towards higher competencies – specialization and collaboration are essential Mobility of knowledge diversifies ways, time and places where to learn – Distance Ed is the future Large gap between students and professors towards perceptions and use of technologies - digital divide to evercome The number and the interaction of teaching decisions increases – need for a new ISD methodology
 New Institutional Challenges 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Educational institution and training department must change their processes towards networking instead of the industrial model Need to develop new forms of interaction, collaboration, evaluation and work for instructional design, learning resource production and search, and delivery processes Importance to model knowledge and competencies linked to processes and resources Invent services, content and media to be delivered in multiple ways: desktop, mobile devices, F 2 F meetings, … Become learning organizations - Offer means to acquire and develop information, media and method competencies to professors, staff and students – New roles for the libraries linked to knowledge portals
New Institutional Challenges 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Educational institution and training department must change their processes towards networking instead of the industrial model Need to develop new forms of interaction, collaboration, evaluation and work for instructional design, learning resource production and search, and delivery processes Importance to model knowledge and competencies linked to processes and resources Invent services, content and media to be delivered in multiple ways: desktop, mobile devices, F 2 F meetings, … Become learning organizations - Offer means to acquire and develop information, media and method competencies to professors, staff and students – New roles for the libraries linked to knowledge portals
 Shaping our Future: Towards a Pan-Canadian e. Learning Research Agenda On-line Conference, from Montreal, 22 nd, 2008 Merci ! www. licef. teluq. uquebec. ca/gp
Shaping our Future: Towards a Pan-Canadian e. Learning Research Agenda On-line Conference, from Montreal, 22 nd, 2008 Merci ! www. licef. teluq. uquebec. ca/gp


