Ильхом Мирсабитович.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 20

Shanghai Cooperation Organisation Presented by: Elubayeva M. Checked by : Umarov I. M

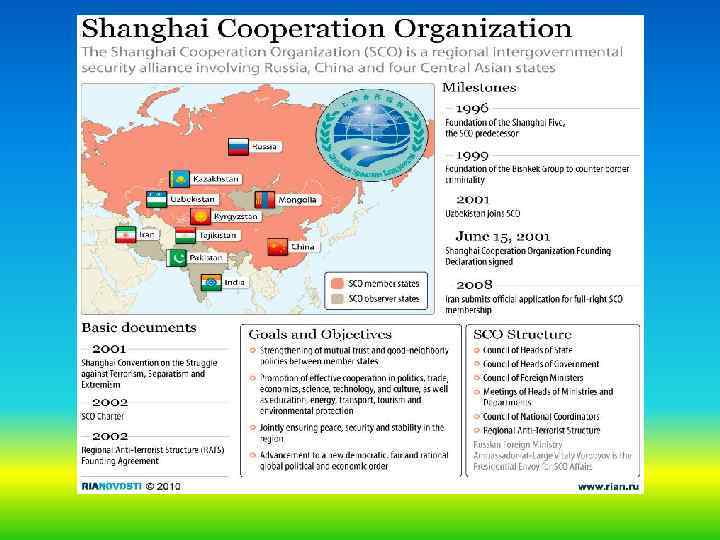
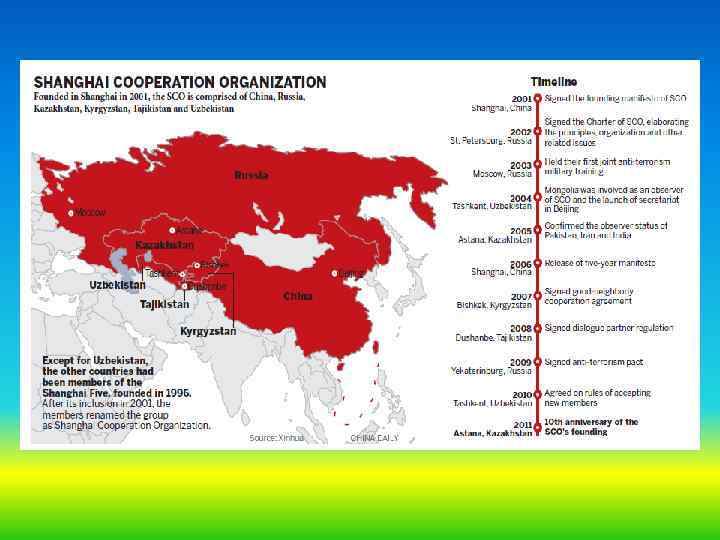
The Shanghai Cooperation Organisation or SCO is a Eurasian political, economic and military organisation which was founded in 2001 in Shanghai by the leaders of China, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan. Except for Uzbekistan, the other countries had been members of the Shanghai Five, founded in 1996; after the inclusion of Uzbekistan in 2001, the members renamed the organisation.

Official languages • Chineese Simplified Chinese: 上海合作组织 ( 上合组织) • Russian Cyrillic: Шанхайская организация сотрудничества (ШОС)

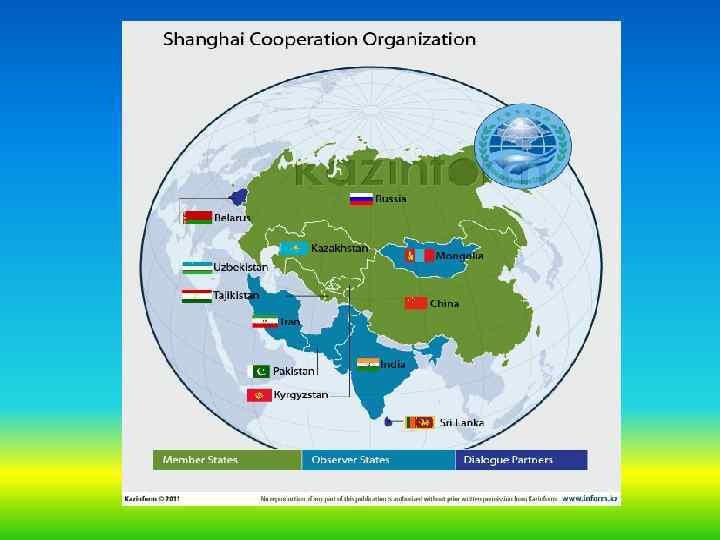
Member states of Shanghai Cooperation Organisation 26 April 1996 China Kazakhstan Kyrgyzstan Russia Tajikistan Founders 15 June 2011 Uzbekistan First

Observer States : Afghanistan, India , Iran , Mongolia, Pakistan. Dialogue Partners : Belarus , Sri Lanka , Turkey. Guest Attendances : ASEAN , CIS , Turkmenistan.

Brief introduction to the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation • The Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) is a permanent intergovernmental international organisation creation of which was proclaimed on 15 June 2001 in Shanghai (China) by the Republic of Kazakhstan, the People’s Republic of China, the Kyrgyz Republic, the Russian Federation, the Republic of Tajikistan and the Republic of Uzbekistan. Its prototype is the Shanghai Five mechanism. • The Heads of State Council (HSC) is the highest decision-making body in the SCO. It meets once every year to take decisions and give instructions on all important issues of SCO activity. • The SCO member states occupy a territory of around 30 million 189 thousand square kilometers, which makes up three fifths of the Eurasian continent, and have a population of 1. 5 billion, which makes up a quarter of the planet’s population.
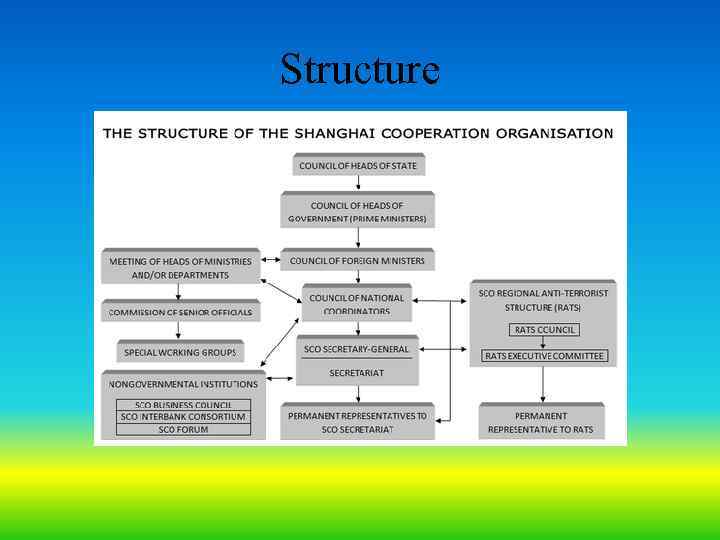
Structure

Cooperation on security • The SCO is primarily centered on its member nations' Central Asian security-related concerns, often describing the main threats it confronts as being terrorism, separatism and extremism. At 16– 17 June 2004 SCO summit, held in Tashkent, Uzbekistan, the Regional Antiterrorism Structure (RATS) was established. On 21 April 2006, the SCO announced plans to fight cross-border drug crimes under the counterterrorism rubric. • Grigory Logninov claimed in April 2006 that the SCO has no plans to become a military bloc; nonetheless he argued that the increased threats of "terrorism, extremism and separatism" make necessary a full-scale involvement of armed forces. • In October 2007, the SCO signed an agreement with the Collective Securite Threat Organsation (CSTO), in the Tajik capital Dushanbe, to broaden cooperation on issues such as security, crime, and drug trafficking.

Putin and Hu Jintao Peace Mission 2007

Military activities • There have been a number of SCO joint military exercises. The first of these was held in 2003, with the first phase taking place in Kazakhstan and the second in China. Since then China and Russia have teamed up for largescale war games in 2005 (Peace Mission 2005), 2007 and 2009, under the auspices of the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation. More than 4, 000 Chinese soldiers participated at the joint military exercises in 2007 (known as "Peace Mission 2007") which took place in Chelyabinsk Russia near the Ural Mountains, as was agreed upon in April 2006 at a meeting of SCO Defence Ministers. Air forces and precision-guided weapons were also likely to be used. Peace Mission 2010, conducted September 9– 25 at Kazakhstan's Matybulak training area, saw over 5, 000 personnel from China, Russia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan conduct joint planning and operational maneuvers.

Economic cooperation On 26 October 2005, during the Moscow Summit of the SCO, the Secretary General of the Organisation said that the SCO will prioritise joint energy projects; such will include the oil and gas sector, the exploration of new hydrocarbon reserves, and joint use of water resources. The creation of an Inter-bank SCO Council was also agreed upon at that summit in order to fund future joint projects. The first meeting of the SCO Interbank Association was held in Beijing on 21– 22 February 2006. On 30 November 2006, at The SCO: Results and Perspectives, an international conference held in Almaty, the representative of the Russian Foreign Ministry announced that Russia is developing plans for an SCO "Energy Club". • Leaders present at the SCO summit in Yekaterinburg, Russia in 2009.

Summits • According to the Charter of the SCO, summits of the Council of Heads of State shall be held annually at alternating venues. The locations of these summits follow the alphabetical order of the member state's name in Russian. The charter also dictates that the Council of Heads of Government (that is, the Prime Ministers) shall meet annually in a place previously decided upon by the council members. The Council of Foreign Ministers is supposed to hold a summit one month before the annual summit of Heads of State. Extraordinary meetings of the Council of Foreign Ministers can be called by any two member states.
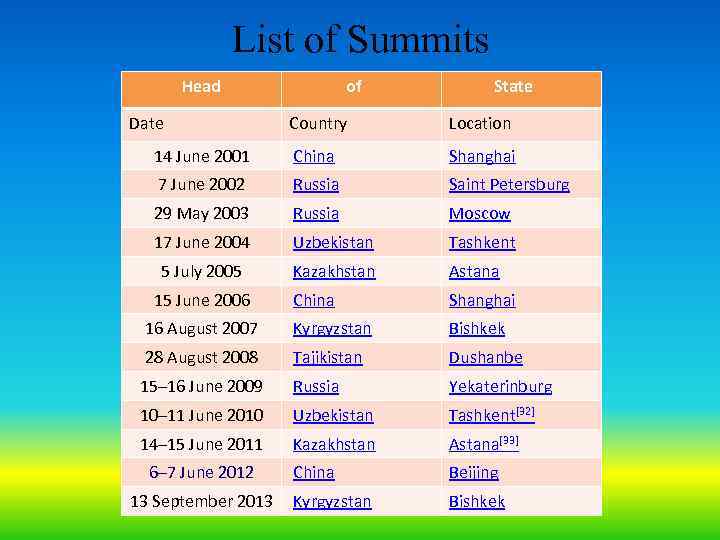
List of Summits Head Date of State Country Location 14 June 2001 China Shanghai 7 June 2002 Russia Saint Petersburg 29 May 2003 Russia Moscow 17 June 2004 Uzbekistan Tashkent 5 July 2005 Kazakhstan Astana China Shanghai 16 August 2007 Kyrgyzstan Bishkek 28 August 2008 Tajikistan Dushanbe 15– 16 June 2009 Russia Yekaterinburg 10– 11 June 2010 Uzbekistan Tashkent[32] 14– 15 June 2011 Kazakhstan Astana[33] China Beijing 15 June 2006 6– 7 June 2012 13 September 2013 Kyrgyzstan Bishkek

The Executive Committee of the Regional Counter-Terrorism Structure Director is the chief administrative officer of the RCTS Executive Committee. The nominee, a citizen of an SCO member state, is appointed by the Council of Heads of State upon the recommendation of the RCTS Council for a period of three years. The Regional Counter-Terrorism Structure operates in accordance with the SCO Charter, the Shanghai Convention on Combating Terrorism, Separatism and Extremism, the Agreement among the SCO member states on the Regional Anti-Terrorism Structure, as well as documents and decisions adopted in the SCO framework. Zhang Xinfeng was appointed Director of the SCO RCTS Executive Committee on 1 January 2013.

Current Observers • Afghanistan received observer status at the 2012 SCO summit in Beijing, China on June 6, 2012. • India currently has observer status in the SCO. Russia has encouraged India to join the organisation as a full-time member, because they see it as a crucial future strategic partner. China has "welcomed" India's accession to the SCO. • Iran currently has observer status in the organisation, and applied for full membership on 24 March 2008. However, because of ongoing sanctions levied by the United Nations, it is blocked from admission as a new member. 4 Tashkent Summit. Pakistan, India and Iran received observer status at the 2005 SCO summit in Astana, Kazakhstan on 5 July 2005. • Pakistan currently has observer status in the SCO. Former Pakistani President Pervez Musharraf argued in favour of Pakistan's qualification to join the organisation as a full member during a joint summit with China in 2006.

Dialogue Parner The position of Dialogue Partner was created in 2008 in accordance with Article 14 of the SCO Charter of 7 June 2002. Belarus was granted dialogue partner status in the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) at the group's 2009 summit in Yekaterinburg. Hamid Karzai at SCO Summit

Thank you for attention !!!
Ильхом Мирсабитович.pptx