bdc7f6fa4a0815052823b44b56c9ff86.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35
 SFD EXPERIMENTAL TESTING & ANALYTICAL METHODS DEVELOPMENT High Load SFD Test Rig Identification of SFD force coefficients Luis San Andrés Mast-Childs Professor May 2011 1
SFD EXPERIMENTAL TESTING & ANALYTICAL METHODS DEVELOPMENT High Load SFD Test Rig Identification of SFD force coefficients Luis San Andrés Mast-Childs Professor May 2011 1
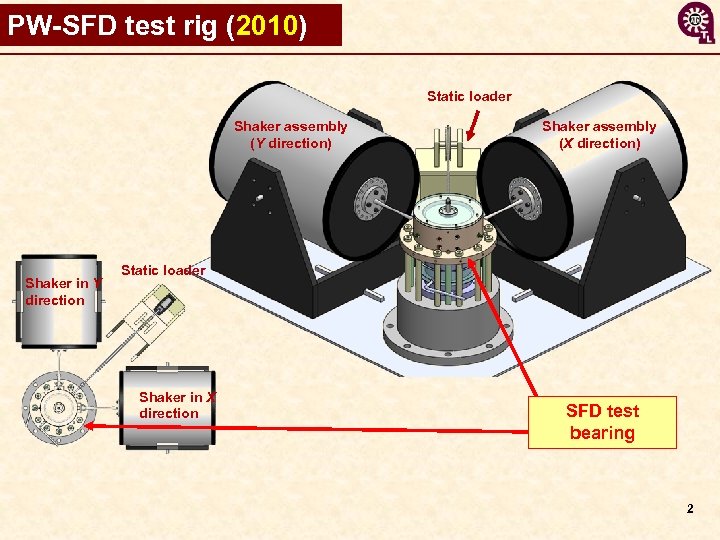 PW-SFD test rig (2010) Static loader Shaker assembly (Y direction) Shaker in Y direction Shaker assembly (X direction) Static loader Shaker in X direction SFD test bearing 2
PW-SFD test rig (2010) Static loader Shaker assembly (Y direction) Shaker in Y direction Shaker assembly (X direction) Static loader Shaker in X direction SFD test bearing 2
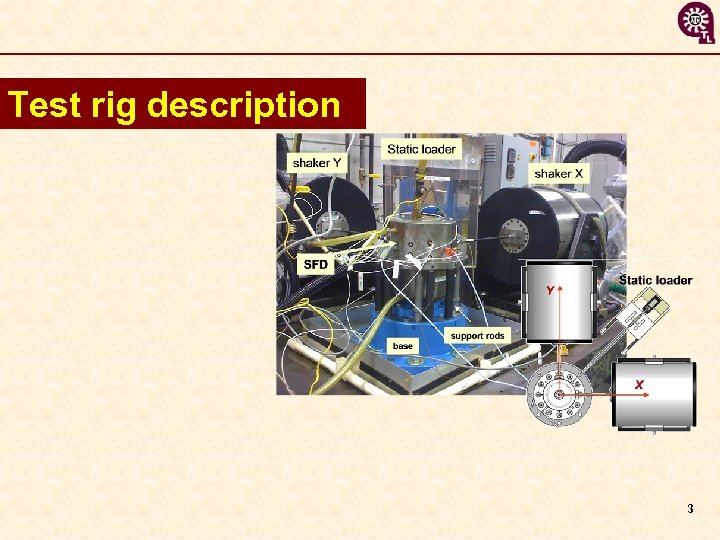 Test rig description 3
Test rig description 3
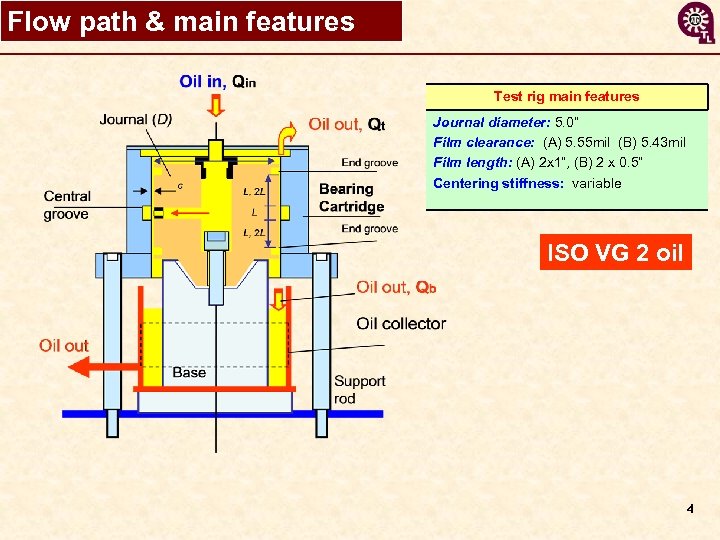 Flow path & main features Test rig main features in Journal diameter: 5. 0” Film clearance: (A) 5. 55 mil (B) 5. 43 mil Film length: (A) 2 x 1”, (B) 2 x 0. 5“ Centering stiffness: variable ISO VG 2 oil 4
Flow path & main features Test rig main features in Journal diameter: 5. 0” Film clearance: (A) 5. 55 mil (B) 5. 43 mil Film length: (A) 2 x 1”, (B) 2 x 0. 5“ Centering stiffness: variable ISO VG 2 oil 4
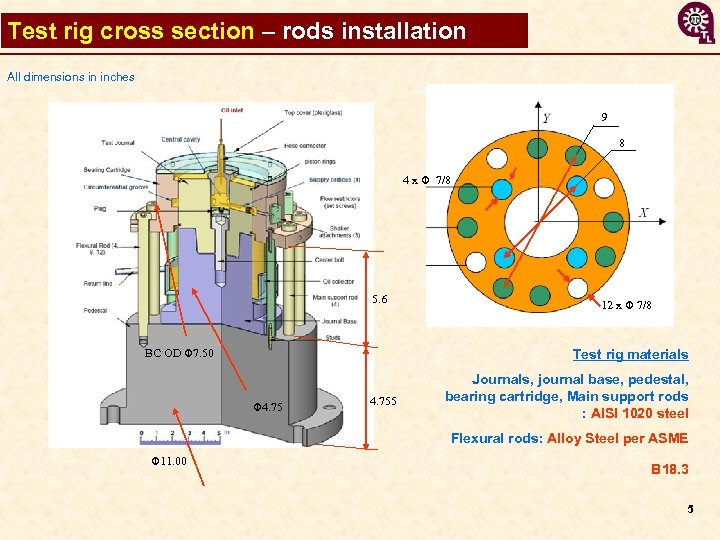 Test rig cross section – rods installation All dimensions in inches 9 8 4 x Φ 7/8 5. 6 BC OD Φ 7. 50 12 x Φ 7/8 Test rig materials Φ 4. 755 Journals, journal base, pedestal, bearing cartridge, Main support rods : AISI 1020 steel Flexural rods: Alloy Steel per ASME Φ 11. 00 B 18. 3 5
Test rig cross section – rods installation All dimensions in inches 9 8 4 x Φ 7/8 5. 6 BC OD Φ 7. 50 12 x Φ 7/8 Test rig materials Φ 4. 755 Journals, journal base, pedestal, bearing cartridge, Main support rods : AISI 1020 steel Flexural rods: Alloy Steel per ASME Φ 11. 00 B 18. 3 5
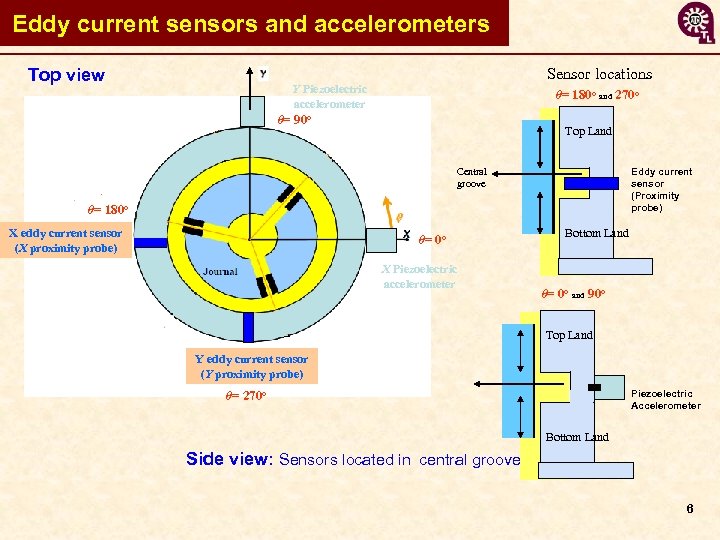 Eddy current sensors and accelerometers Top view Sensor locations Y Piezoelectric accelerometer θ= 180 o and 270 o θ= 90 o Top Land Eddy current sensor (Proximity probe) Central groove θ= 180 o X eddy current sensor (X proximity probe) θ= 0 o Journal B X Piezoelectric accelerometer Bottom Land θ= 0 o and 90 o Top Land Y eddy current sensor (Y proximity probe) Piezoelectric Accelerometer θ= 270 o Bottom Land Side view: Sensors located in central groove 6
Eddy current sensors and accelerometers Top view Sensor locations Y Piezoelectric accelerometer θ= 180 o and 270 o θ= 90 o Top Land Eddy current sensor (Proximity probe) Central groove θ= 180 o X eddy current sensor (X proximity probe) θ= 0 o Journal B X Piezoelectric accelerometer Bottom Land θ= 0 o and 90 o Top Land Y eddy current sensor (Y proximity probe) Piezoelectric Accelerometer θ= 270 o Bottom Land Side view: Sensors located in central groove 6
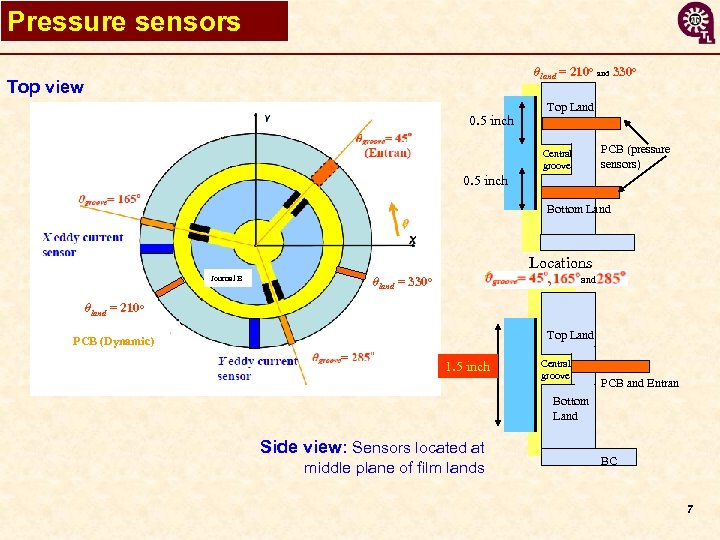 Pressure sensors θland = 210 o and 330 o Top view 0. 5 inch Top Land PCB (pressure sensors) Central groove 0. 5 inch Bottom Land Locations Journal B , θland = 330 o and θland = 210 o Top Land PCB (Dynamic) 1. 5 inch Central groove PCB and Entran Bottom Land Side view: Sensors located at middle plane of film lands BC 7
Pressure sensors θland = 210 o and 330 o Top view 0. 5 inch Top Land PCB (pressure sensors) Central groove 0. 5 inch Bottom Land Locations Journal B , θland = 330 o and θland = 210 o Top Land PCB (Dynamic) 1. 5 inch Central groove PCB and Entran Bottom Land Side view: Sensors located at middle plane of film lands BC 7
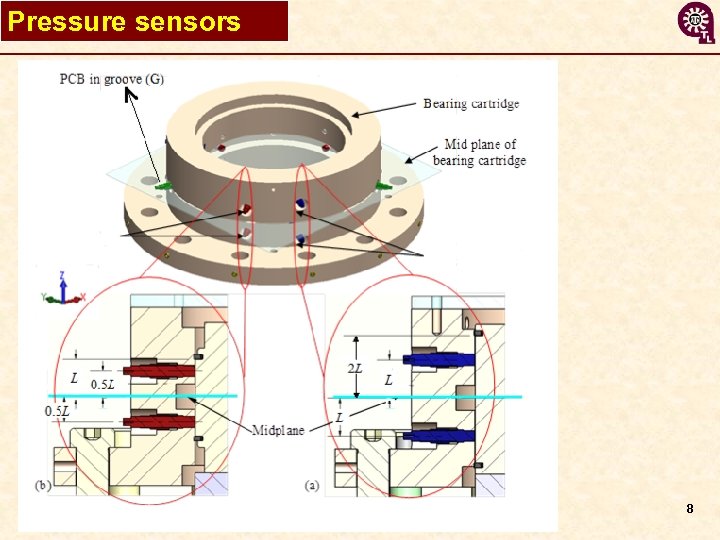 Pressure sensors 8
Pressure sensors 8
 Test results for (c) SFD force coefficients – Comparison between short and long open ends dampers 9
Test results for (c) SFD force coefficients – Comparison between short and long open ends dampers 9
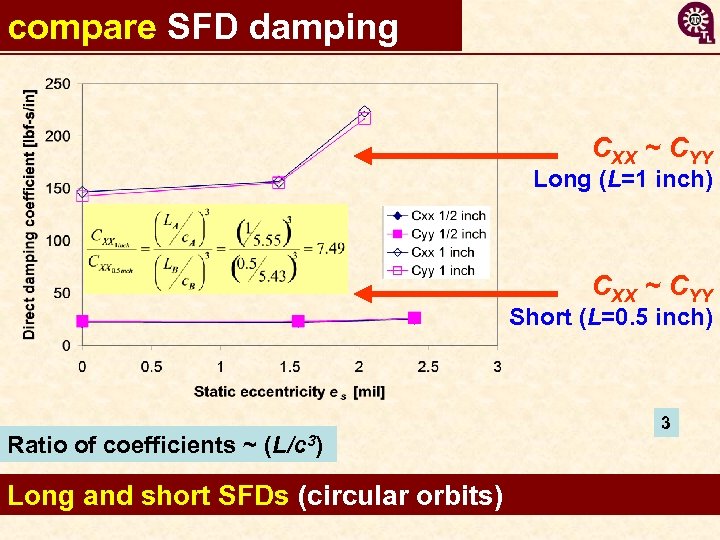 compare SFD damping CXX ~ CYY Long (L=1 inch) CXX ~ CYY Short (L=0. 5 inch) Ratio of coefficients ~ (L/c 3) Long and short SFDs (circular orbits) 3 10
compare SFD damping CXX ~ CYY Long (L=1 inch) CXX ~ CYY Short (L=0. 5 inch) Ratio of coefficients ~ (L/c 3) Long and short SFDs (circular orbits) 3 10
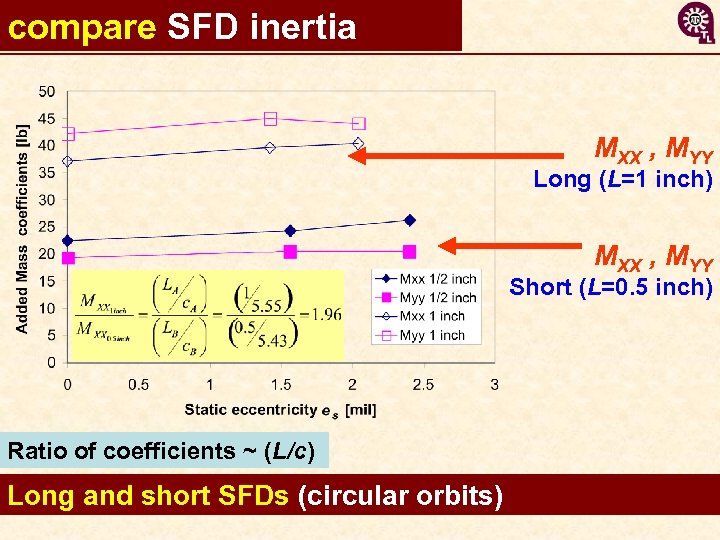 compare SFD inertia MXX , MYY Long (L=1 inch) MXX , MYY Short (L=0. 5 inch) Ratio of coefficients ~ (L/c) Long and short SFDs (circular orbits) 11
compare SFD inertia MXX , MYY Long (L=1 inch) MXX , MYY Short (L=0. 5 inch) Ratio of coefficients ~ (L/c) Long and short SFDs (circular orbits) 11
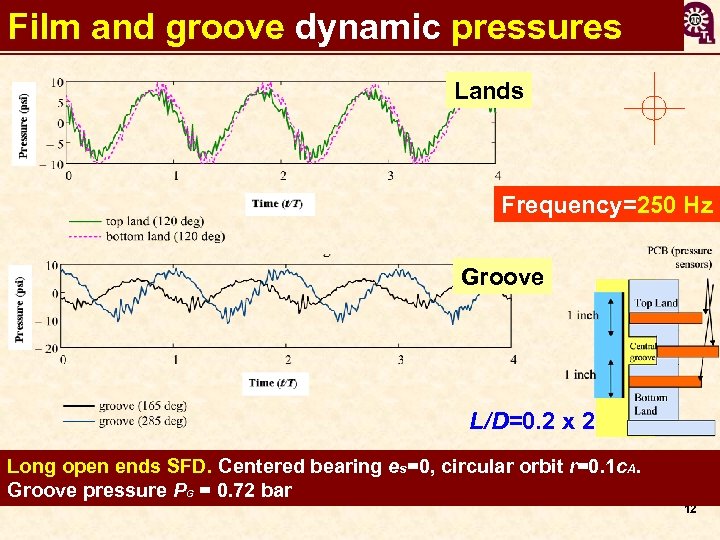 Film and groove dynamic pressures Lands Frequency=250 Hz Groove L/D=0. 2 x 2 Long open ends SFD. Centered bearing es=0, circular orbit r=0. 1 c. A. Groove pressure PG = 0. 72 bar 12
Film and groove dynamic pressures Lands Frequency=250 Hz Groove L/D=0. 2 x 2 Long open ends SFD. Centered bearing es=0, circular orbit r=0. 1 c. A. Groove pressure PG = 0. 72 bar 12
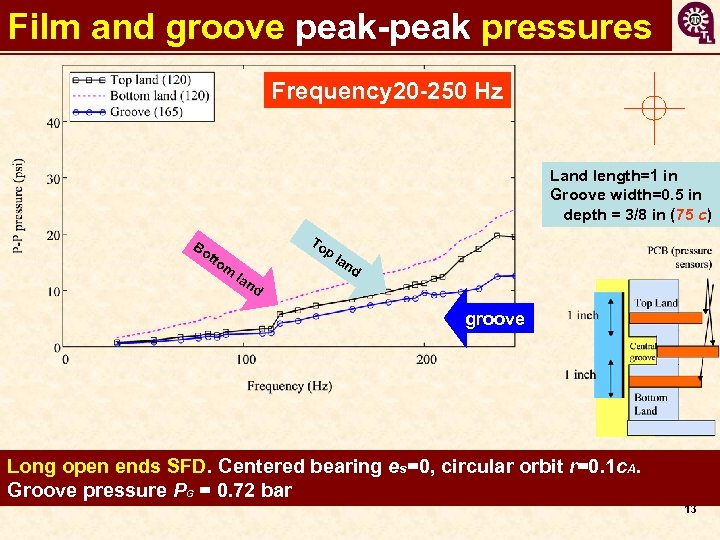 Film and groove peak-peak pressures Frequency 20 -250 Hz Land length=1 in Groove width=0. 5 in depth = 3/8 in (75 c) To p Bo tto m la nd groove Long open ends SFD. Centered bearing es=0, circular orbit r=0. 1 c. A. Groove pressure PG = 0. 72 bar 13
Film and groove peak-peak pressures Frequency 20 -250 Hz Land length=1 in Groove width=0. 5 in depth = 3/8 in (75 c) To p Bo tto m la nd groove Long open ends SFD. Centered bearing es=0, circular orbit r=0. 1 c. A. Groove pressure PG = 0. 72 bar 13
 Test results for (d) SFD force coefficients – Comparison between open ends and sealed ends long dampers 14
Test results for (d) SFD force coefficients – Comparison between open ends and sealed ends long dampers 14
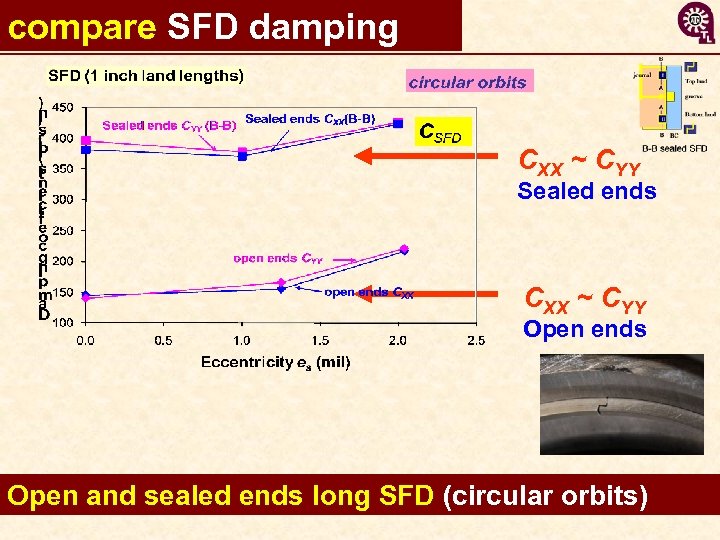 compare SFD damping CXX ~ CYY Sealed ends CXX ~ CYY Open ends Open and sealed ends long SFD (circular orbits) 15
compare SFD damping CXX ~ CYY Sealed ends CXX ~ CYY Open ends Open and sealed ends long SFD (circular orbits) 15
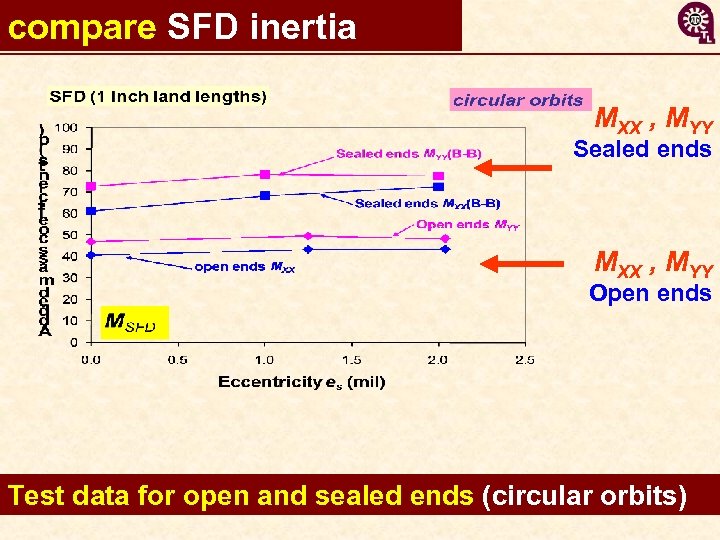 compare SFD inertia MXX , MYY Sealed ends MXX , MYY Open ends Test data for open and sealed ends (circular orbits)16
compare SFD inertia MXX , MYY Sealed ends MXX , MYY Open ends Test data for open and sealed ends (circular orbits)16
 Conclusions: Learning from tests and predictions 17
Conclusions: Learning from tests and predictions 17
 Summary of learning Open ends long damper shows ~ 7 times more damping than short length damper. Inertia coefficients are two times larger. SFD force coefficients are more a function of static eccentricity (max. 40%c) than amplitude of whirl (max 40%c) changing little with ellipticity of orbit (aspect ratios 1: 1, 2: 1 & 5: 1) Piston ring faces orientation affects leakage and force coefficients. Long Sealed SFD shows ~2. 6 times more damping than open ends SFD Code benchmarked for long and short SFDs (open and sealed ends). 18
Summary of learning Open ends long damper shows ~ 7 times more damping than short length damper. Inertia coefficients are two times larger. SFD force coefficients are more a function of static eccentricity (max. 40%c) than amplitude of whirl (max 40%c) changing little with ellipticity of orbit (aspect ratios 1: 1, 2: 1 & 5: 1) Piston ring faces orientation affects leakage and force coefficients. Long Sealed SFD shows ~2. 6 times more damping than open ends SFD Code benchmarked for long and short SFDs (open and sealed ends). 18
 Proposed work (TRC) Linear-Nonlinear Force Coefficients for Squeeze Film Dampers Whirl Orbit Analysis for Identification of SFD force coefficients 19
Proposed work (TRC) Linear-Nonlinear Force Coefficients for Squeeze Film Dampers Whirl Orbit Analysis for Identification of SFD force coefficients 19
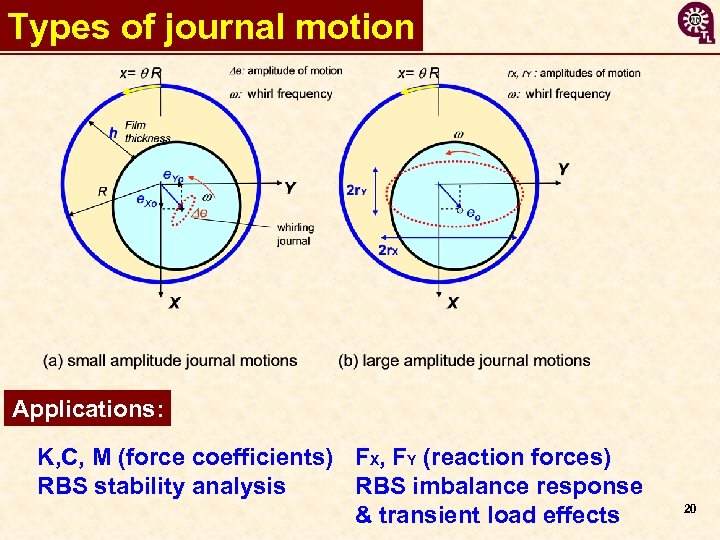 Types of journal motion Applications: K, C, M (force coefficients) FX, FY (reaction forces) RBS stability analysis RBS imbalance response & transient load effects 20
Types of journal motion Applications: K, C, M (force coefficients) FX, FY (reaction forces) RBS stability analysis RBS imbalance response & transient load effects 20
 SFD predictive code Code & GUI: virtual tool for prediction of SFD forced response (a) Linear force coefficients (K, C, M) (b) Instantaneous reaction forces along orbital path (c) Automated orbit analysis for NL parameter identification 21
SFD predictive code Code & GUI: virtual tool for prediction of SFD forced response (a) Linear force coefficients (K, C, M) (b) Instantaneous reaction forces along orbital path (c) Automated orbit analysis for NL parameter identification 21
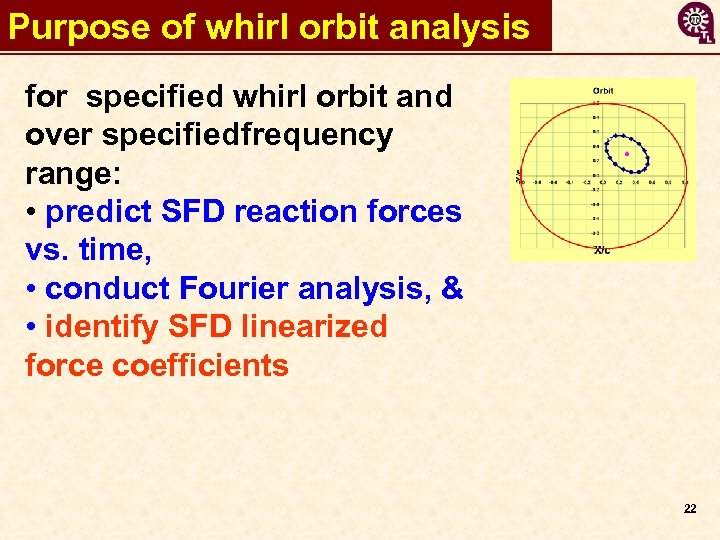 Purpose of whirl orbit analysis for specified whirl orbit and over specifiedfrequency range: • predict SFD reaction forces vs. time, • conduct Fourier analysis, & • identify SFD linearized force coefficients 22
Purpose of whirl orbit analysis for specified whirl orbit and over specifiedfrequency range: • predict SFD reaction forces vs. time, • conduct Fourier analysis, & • identify SFD linearized force coefficients 22
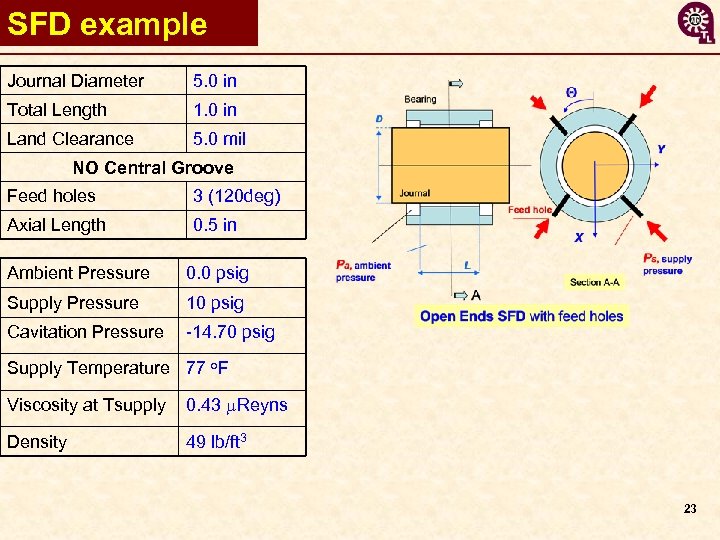 SFD example Journal Diameter 5. 0 in Total Length 1. 0 in Land Clearance 5. 0 mil NO Central Groove Feed holes 3 (120 deg) Axial Length 0. 5 in Ambient Pressure 0. 0 psig Supply Pressure 10 psig Cavitation Pressure -14. 70 psig Supply Temperature 77 o. F Viscosity at Tsupply 0. 43 m. Reyns Density 49 lb/ft 3 23
SFD example Journal Diameter 5. 0 in Total Length 1. 0 in Land Clearance 5. 0 mil NO Central Groove Feed holes 3 (120 deg) Axial Length 0. 5 in Ambient Pressure 0. 0 psig Supply Pressure 10 psig Cavitation Pressure -14. 70 psig Supply Temperature 77 o. F Viscosity at Tsupply 0. 43 m. Reyns Density 49 lb/ft 3 23
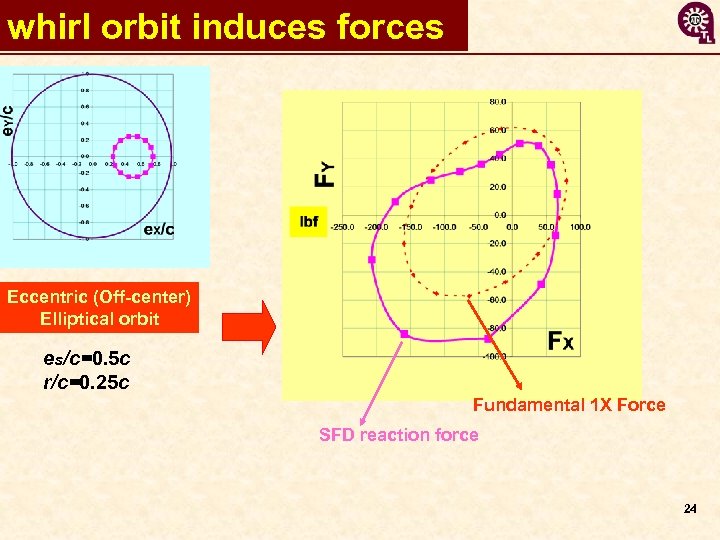 whirl orbit induces forces Eccentric (Off-center) Elliptical orbit es/c=0. 5 c r/c=0. 25 c Fundamental 1 X Force SFD reaction force 24
whirl orbit induces forces Eccentric (Off-center) Elliptical orbit es/c=0. 5 c r/c=0. 25 c Fundamental 1 X Force SFD reaction force 24
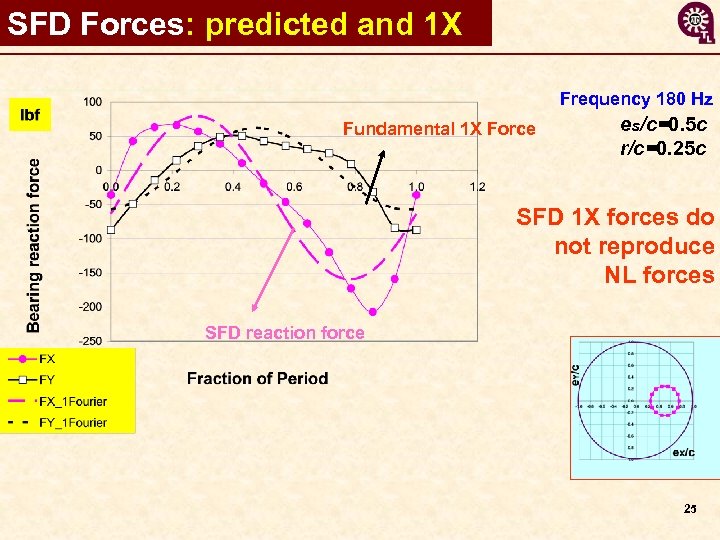 SFD Forces: predicted and 1 X Frequency 180 Hz Fundamental 1 X Force es/c=0. 5 c r/c=0. 25 c SFD 1 X forces do not reproduce NL forces SFD reaction force 25
SFD Forces: predicted and 1 X Frequency 180 Hz Fundamental 1 X Force es/c=0. 5 c r/c=0. 25 c SFD 1 X forces do not reproduce NL forces SFD reaction force 25
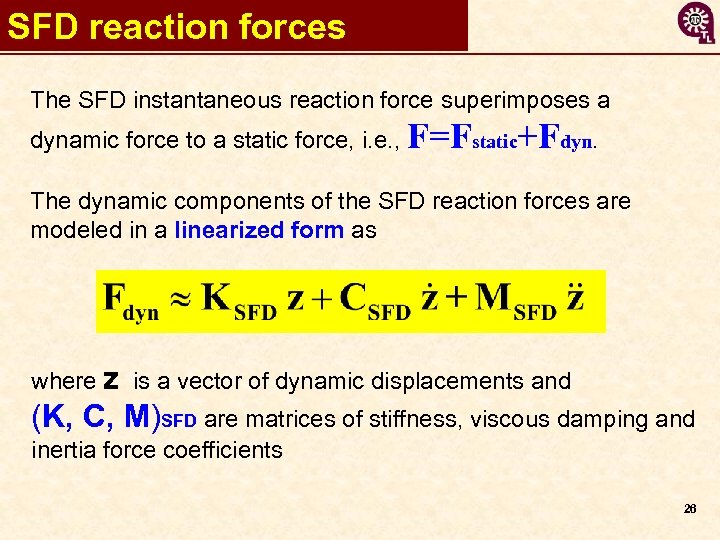 SFD reaction forces The SFD instantaneous reaction force superimposes a dynamic force to a static force, i. e. , F=Fstatic+Fdyn. The dynamic components of the SFD reaction forces are modeled in a linearized form as where z is a vector of dynamic displacements and (K, C, M)SFD are matrices of stiffness, viscous damping and inertia force coefficients 26
SFD reaction forces The SFD instantaneous reaction force superimposes a dynamic force to a static force, i. e. , F=Fstatic+Fdyn. The dynamic components of the SFD reaction forces are modeled in a linearized form as where z is a vector of dynamic displacements and (K, C, M)SFD are matrices of stiffness, viscous damping and inertia force coefficients 26
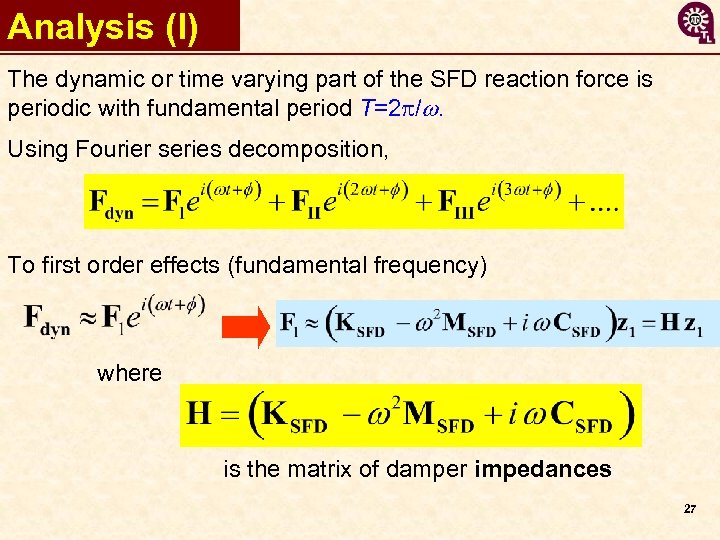 Analysis (I) The dynamic or time varying part of the SFD reaction force is periodic with fundamental period T=2 p/w. Using Fourier series decomposition, To first order effects (fundamental frequency) where is the matrix of damper impedances 27
Analysis (I) The dynamic or time varying part of the SFD reaction force is periodic with fundamental period T=2 p/w. Using Fourier series decomposition, To first order effects (fundamental frequency) where is the matrix of damper impedances 27
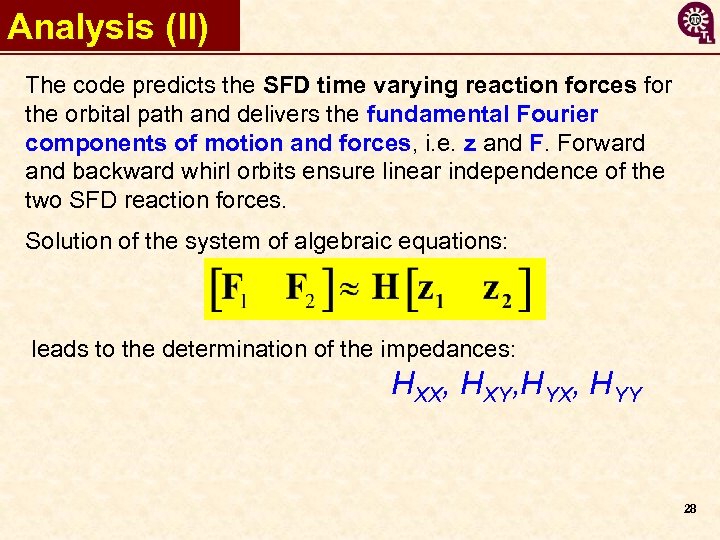 Analysis (II) The code predicts the SFD time varying reaction forces for the orbital path and delivers the fundamental Fourier components of motion and forces, i. e. z and F. Forward and backward whirl orbits ensure linear independence of the two SFD reaction forces. Solution of the system of algebraic equations: leads to the determination of the impedances: HXX, HXY, HYX, HYY 28
Analysis (II) The code predicts the SFD time varying reaction forces for the orbital path and delivers the fundamental Fourier components of motion and forces, i. e. z and F. Forward and backward whirl orbits ensure linear independence of the two SFD reaction forces. Solution of the system of algebraic equations: leads to the determination of the impedances: HXX, HXY, HYX, HYY 28
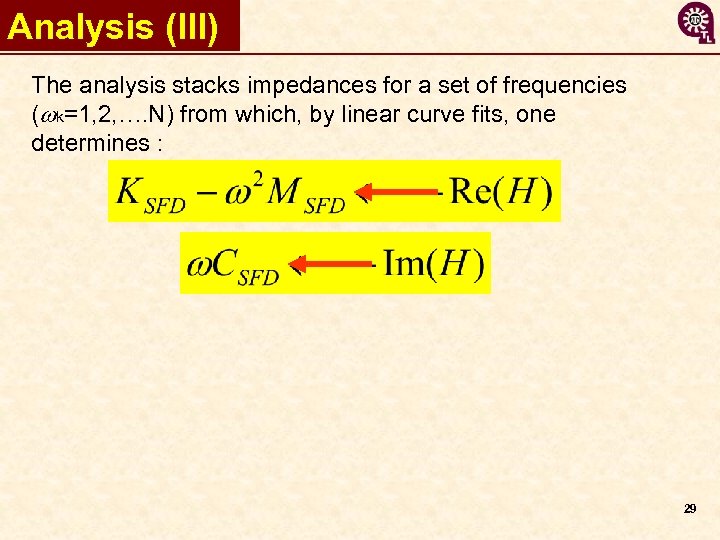 Analysis (III) The analysis stacks impedances for a set of frequencies (wk=1, 2, …. N) from which, by linear curve fits, one determines : 29
Analysis (III) The analysis stacks impedances for a set of frequencies (wk=1, 2, …. N) from which, by linear curve fits, one determines : 29
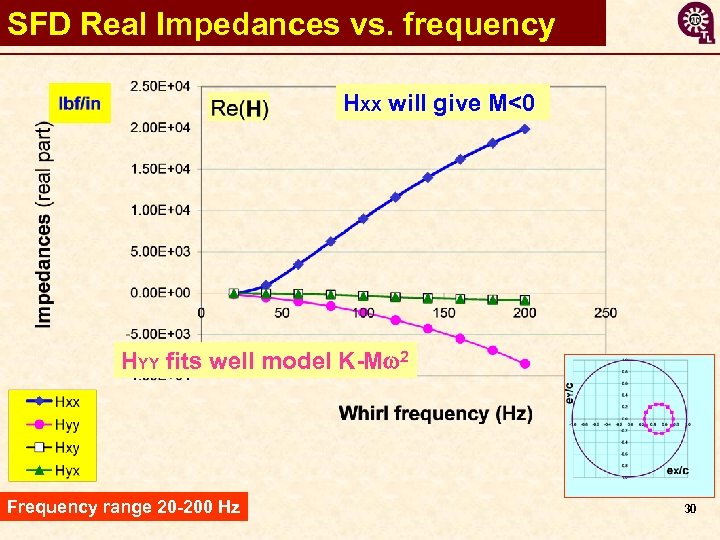 SFD Real Impedances vs. frequency HXX will give M<0 HYY fits well model K-Mw 2 Frequency range 20 -200 Hz 30
SFD Real Impedances vs. frequency HXX will give M<0 HYY fits well model K-Mw 2 Frequency range 20 -200 Hz 30
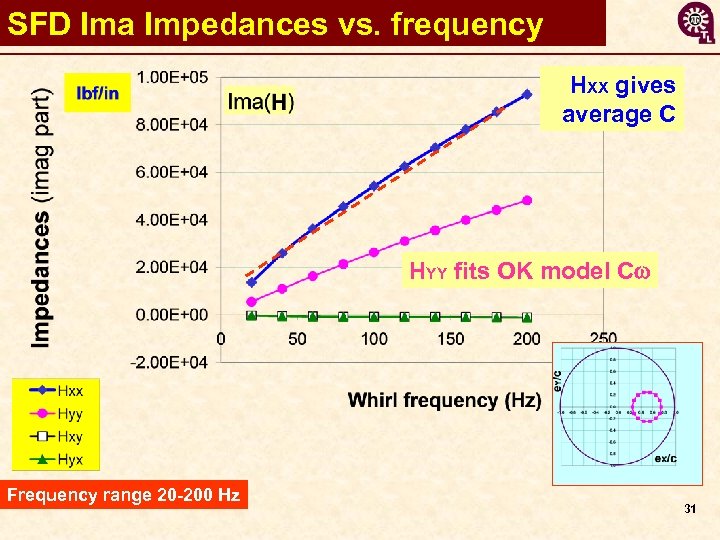 SFD Ima Impedances vs. frequency HXX gives average C HYY fits OK model Cw Frequency range 20 -200 Hz 31
SFD Ima Impedances vs. frequency HXX gives average C HYY fits OK model Cw Frequency range 20 -200 Hz 31
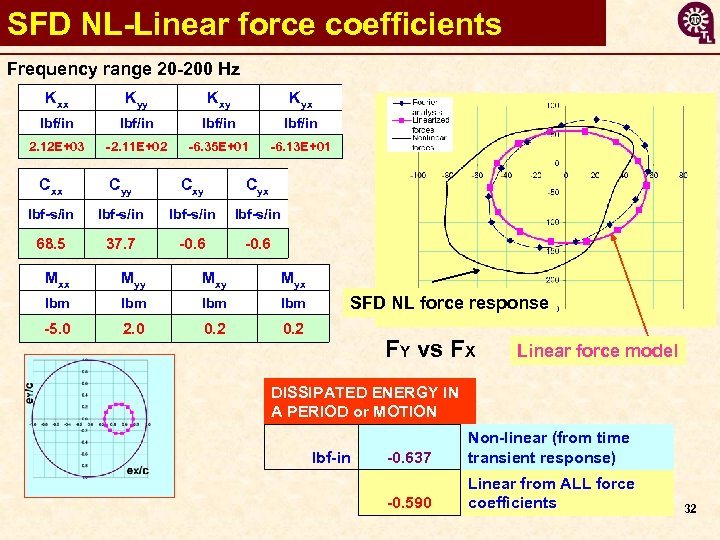 SFD NL-Linear force coefficients Frequency range 20 -200 Hz Kxx Kyy Kxy Kyx lbf/in 2. 12 E+03 -2. 11 E+02 -6. 35 E+01 -6. 13 E+01 Cxx Cyy Cxy Cyx lbf-s/in 68. 5 37. 7 -0. 6 Mxx Myy Mxy Myx lbm lbm -5. 0 2. 0 0. 2 SFD NL force response FY vs FX DISSIPATED ENERGY IN A PERIOD or MOTION lbf-in Linear force model -0. 637 Non-linear (from time transient response) -0. 590 Linear from ALL force coefficients 32
SFD NL-Linear force coefficients Frequency range 20 -200 Hz Kxx Kyy Kxy Kyx lbf/in 2. 12 E+03 -2. 11 E+02 -6. 35 E+01 -6. 13 E+01 Cxx Cyy Cxy Cyx lbf-s/in 68. 5 37. 7 -0. 6 Mxx Myy Mxy Myx lbm lbm -5. 0 2. 0 0. 2 SFD NL force response FY vs FX DISSIPATED ENERGY IN A PERIOD or MOTION lbf-in Linear force model -0. 637 Non-linear (from time transient response) -0. 590 Linear from ALL force coefficients 32
 Proposed tasks (2011 -12) 1. Test ACTUAL short length open ends damper with dynamic loads (20300 Hz) inducing off-centered elliptical orbital motions with amplitude ratios (5: 1) to reach 0. 8 c. 2. Identify SFD force coefficients from test impedances, and correlate coefficients with linear force coefficients and experimental coefficients for smallest whirl amplitude (0. 05 c). 3. Perform numerical experiments, similar to the physical tests, to extract linearized SFD force coefficients from the nonlinear forces. Quantify goodness of linear-nonlinear representation from an equivalence in mechanical energy dissipation. 33
Proposed tasks (2011 -12) 1. Test ACTUAL short length open ends damper with dynamic loads (20300 Hz) inducing off-centered elliptical orbital motions with amplitude ratios (5: 1) to reach 0. 8 c. 2. Identify SFD force coefficients from test impedances, and correlate coefficients with linear force coefficients and experimental coefficients for smallest whirl amplitude (0. 05 c). 3. Perform numerical experiments, similar to the physical tests, to extract linearized SFD force coefficients from the nonlinear forces. Quantify goodness of linear-nonlinear representation from an equivalence in mechanical energy dissipation. 33
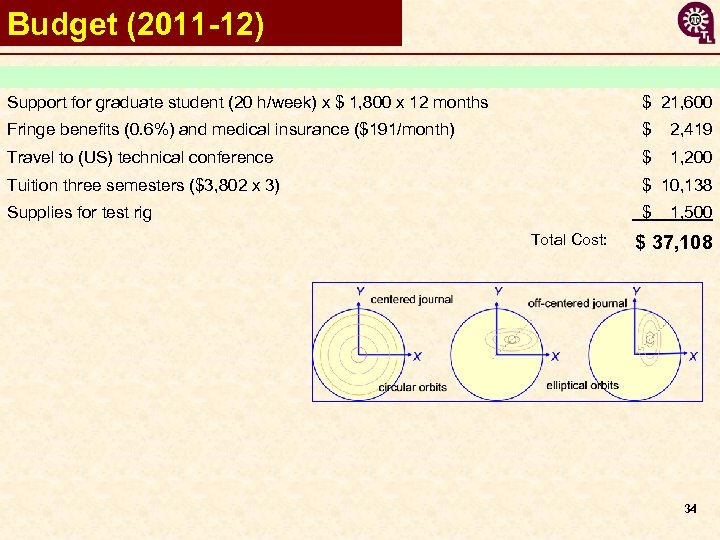 Budget (2011 -12) Support for graduate student (20 h/week) x $ 1, 800 x 12 months $ 21, 600 Fringe benefits (0. 6%) and medical insurance ($191/month) $ 2, 419 Travel to (US) technical conference $ 1, 200 Tuition three semesters ($3, 802 x 3) $ 10, 138 Supplies for test rig $ 1, 500 Total Cost: $ 37, 108 34
Budget (2011 -12) Support for graduate student (20 h/week) x $ 1, 800 x 12 months $ 21, 600 Fringe benefits (0. 6%) and medical insurance ($191/month) $ 2, 419 Travel to (US) technical conference $ 1, 200 Tuition three semesters ($3, 802 x 3) $ 10, 138 Supplies for test rig $ 1, 500 Total Cost: $ 37, 108 34
 Questions (? ) 35
Questions (? ) 35


