334a0ed32521ba4dd70e4b4eb9971442.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 57
 Sex Determination and Sex -Linked Traits
Sex Determination and Sex -Linked Traits
 How do we determine sex? What is the role of biology, specifically genetics? • What are some other factors in sex determination? • What is the “Gender Revolution”?
How do we determine sex? What is the role of biology, specifically genetics? • What are some other factors in sex determination? • What is the “Gender Revolution”?
 The Gender Revolution http: //channel. nationalgeographic. com/gender-revolution-a-journey-withkatie-couric/videos/gender-revolution-extended-trailer/
The Gender Revolution http: //channel. nationalgeographic. com/gender-revolution-a-journey-withkatie-couric/videos/gender-revolution-extended-trailer/
 Understanding Sex-linked Inheritance • How sex is determined • How characteristics encoded by genes on the sex chromosomes are inherited.
Understanding Sex-linked Inheritance • How sex is determined • How characteristics encoded by genes on the sex chromosomes are inherited.
 Sex is determined by a number of different mechanisms • The term sex refers to sexual phenotype. ex – a XXY person may have a female anatomy and is considered a “female” • Hermaphroditism – organisms that bear both male and female reproductive structures…. . they are “monoecious” …. one house • Organisms that are either male OR female are “ dioecious” meaning two houses. • Sex can be determined by: chromosomes, genes, and environment.
Sex is determined by a number of different mechanisms • The term sex refers to sexual phenotype. ex – a XXY person may have a female anatomy and is considered a “female” • Hermaphroditism – organisms that bear both male and female reproductive structures…. . they are “monoecious” …. one house • Organisms that are either male OR female are “ dioecious” meaning two houses. • Sex can be determined by: chromosomes, genes, and environment.
 Chromosomal Sex-Determining Systems • Chromosome Theory of Inheritance: Genes are located on chromosomes. • Proved by discovery that sex of certain insects is determined by presence or absence of particular chromosomes • Ex – in grasshoppers female XX male XO
Chromosomal Sex-Determining Systems • Chromosome Theory of Inheritance: Genes are located on chromosomes. • Proved by discovery that sex of certain insects is determined by presence or absence of particular chromosomes • Ex – in grasshoppers female XX male XO
 Types of chromosomes • Sex-chromosomes • Autosomes Even though we think sex is determined by the presence of the sex chromosomes, the individual genes located on the sex chromosomes are usually responsible for the sexual phenotypes.
Types of chromosomes • Sex-chromosomes • Autosomes Even though we think sex is determined by the presence of the sex chromosomes, the individual genes located on the sex chromosomes are usually responsible for the sexual phenotypes.
 • Heterogametic sex – if two types of gametes are produced in respect to the sex chromosomes (for us, males) • Homogametic sex – gametes all the same (for us, females)
• Heterogametic sex – if two types of gametes are produced in respect to the sex chromosomes (for us, males) • Homogametic sex – gametes all the same (for us, females)
 Chromosomal Sex determination Systems • XX-XO • XX-XY • ZZ-ZW • Haplodiploidy
Chromosomal Sex determination Systems • XX-XO • XX-XY • ZZ-ZW • Haplodiploidy
 XX – XO systems • XX (females) are homogametic • XO (males) are heterogametic • Males have only one sex chromosome.
XX – XO systems • XX (females) are homogametic • XO (males) are heterogametic • Males have only one sex chromosome.
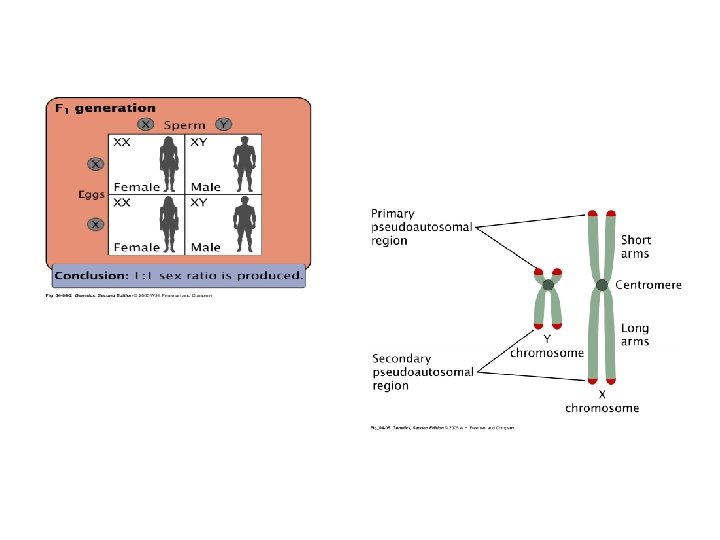
 XX-XY Sex Determination • X and Y NOT generally homologous • They pair because their chromosomes are homologous in small regions called the pseudoautosomal regions in which they carry the same genes. • In humans at both tips of X and Y.
XX-XY Sex Determination • X and Y NOT generally homologous • They pair because their chromosomes are homologous in small regions called the pseudoautosomal regions in which they carry the same genes. • In humans at both tips of X and Y.
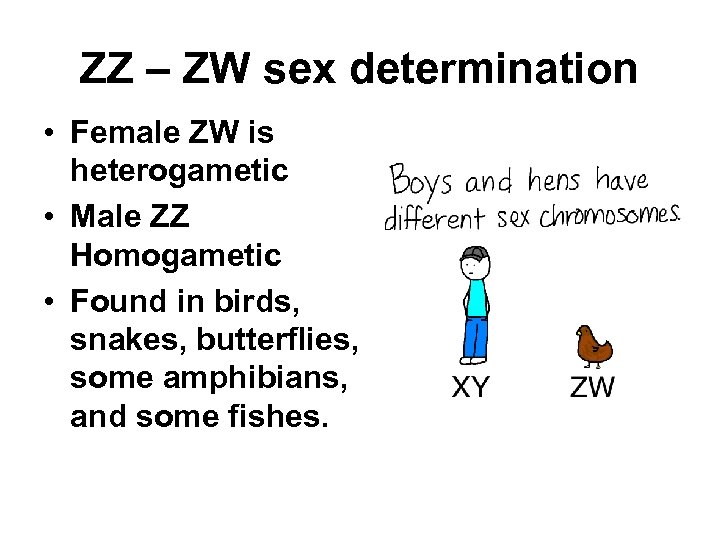 ZZ – ZW sex determination • Female ZW is heterogametic • Male ZZ Homogametic • Found in birds, snakes, butterflies, some amphibians, and some fishes.
ZZ – ZW sex determination • Female ZW is heterogametic • Male ZZ Homogametic • Found in birds, snakes, butterflies, some amphibians, and some fishes.
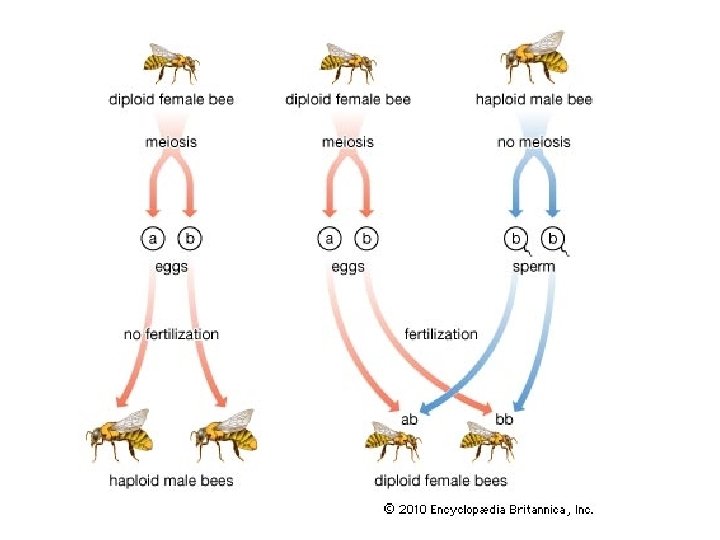
 Haplodiploidy • Haplodiploidy is a sex-determination system in which males develop from unfertilized eggs and are haploid, and females develop from fertilized eggs and are diploid.
Haplodiploidy • Haplodiploidy is a sex-determination system in which males develop from unfertilized eggs and are haploid, and females develop from fertilized eggs and are diploid.
 What about sex determination in plants? • Most plants have both sexes on each plant. • Some plants have one sex per plant. Ex – Bryophytes (mosses) have separate sexes in their gametophyte stages.
What about sex determination in plants? • Most plants have both sexes on each plant. • Some plants have one sex per plant. Ex – Bryophytes (mosses) have separate sexes in their gametophyte stages.
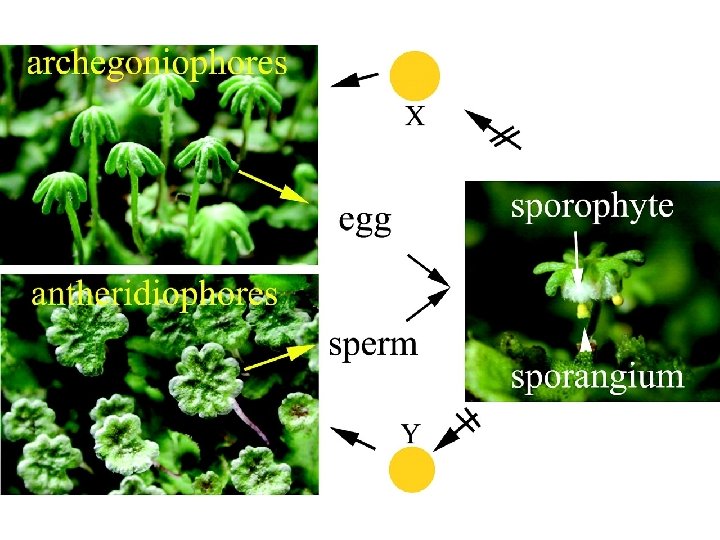
 Silene latiflora has X and Y chromosomes
Silene latiflora has X and Y chromosomes
 Environment and Sex Determination • Sex can be determined by the environment • Limpets’ sex is determined by their order in a stack; the uppermost animals are always males. Slipper limpet
Environment and Sex Determination • Sex can be determined by the environment • Limpets’ sex is determined by their order in a stack; the uppermost animals are always males. Slipper limpet
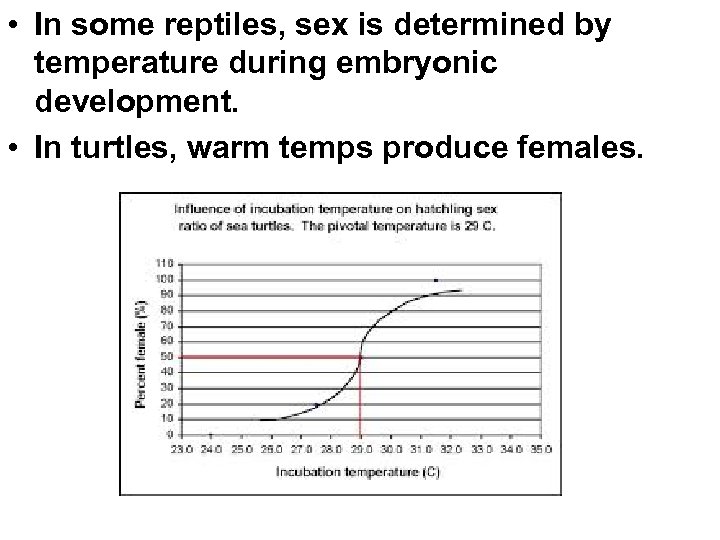 • In some reptiles, sex is determined by temperature during embryonic development. • In turtles, warm temps produce females.
• In some reptiles, sex is determined by temperature during embryonic development. • In turtles, warm temps produce females.
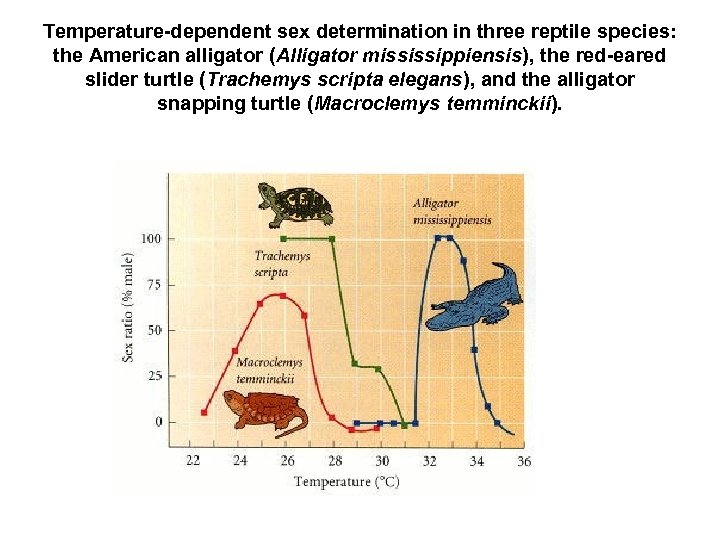 Temperature-dependent sex determination in three reptile species: the American alligator (Alligator mississippiensis), the red-eared slider turtle (Trachemys scripta elegans), and the alligator snapping turtle (Macroclemys temminckii).
Temperature-dependent sex determination in three reptile species: the American alligator (Alligator mississippiensis), the red-eared slider turtle (Trachemys scripta elegans), and the alligator snapping turtle (Macroclemys temminckii).
 • So it seems there is no genetic predisposition for the embryo of a temperature-sensitive reptile to develop as either male or female, so the early embryo does not have a "sex" until it enters thermosensitive period of its development.
• So it seems there is no genetic predisposition for the embryo of a temperature-sensitive reptile to develop as either male or female, so the early embryo does not have a "sex" until it enters thermosensitive period of its development.
 And then there are the spoon worms. • As a larvae, it is sexually undifferentiated, where it settles determines its sex. If the spoon worm larvae lands on the seafloor it becomes female. • Should the larvae come in contact with a female, it will be masculinized and sucked into the spoonworm’s body through her feeding proboscis, where it will spend the rest of its life in her uterus.
And then there are the spoon worms. • As a larvae, it is sexually undifferentiated, where it settles determines its sex. If the spoon worm larvae lands on the seafloor it becomes female. • Should the larvae come in contact with a female, it will be masculinized and sucked into the spoonworm’s body through her feeding proboscis, where it will spend the rest of its life in her uterus.
 What about fruit flies? • Y does not determine maleness. Each fly’s sex is determined by a balance between the genes on their autosomes and genes on the X chromosome. • Sex is primarily determined by the X: A ratio, or the ratio of the number of X chromosomes to the number of sets of autosomes.
What about fruit flies? • Y does not determine maleness. Each fly’s sex is determined by a balance between the genes on their autosomes and genes on the X chromosome. • Sex is primarily determined by the X: A ratio, or the ratio of the number of X chromosomes to the number of sets of autosomes.
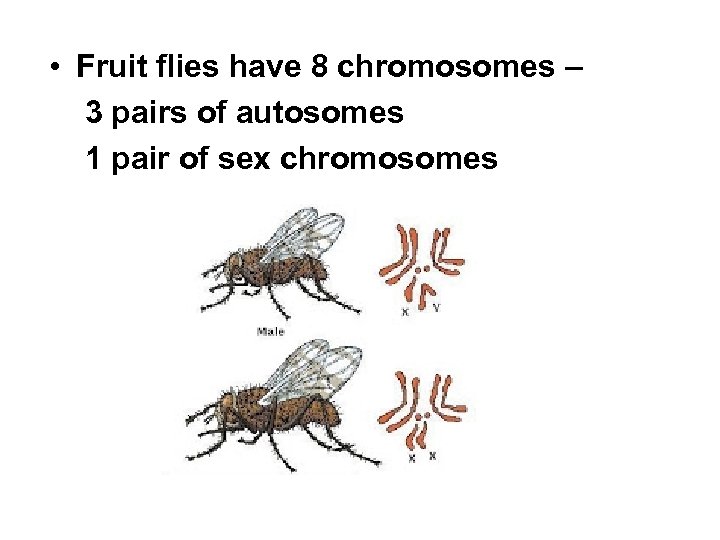 • Fruit flies have 8 chromosomes – 3 pairs of autosomes 1 pair of sex chromosomes
• Fruit flies have 8 chromosomes – 3 pairs of autosomes 1 pair of sex chromosomes
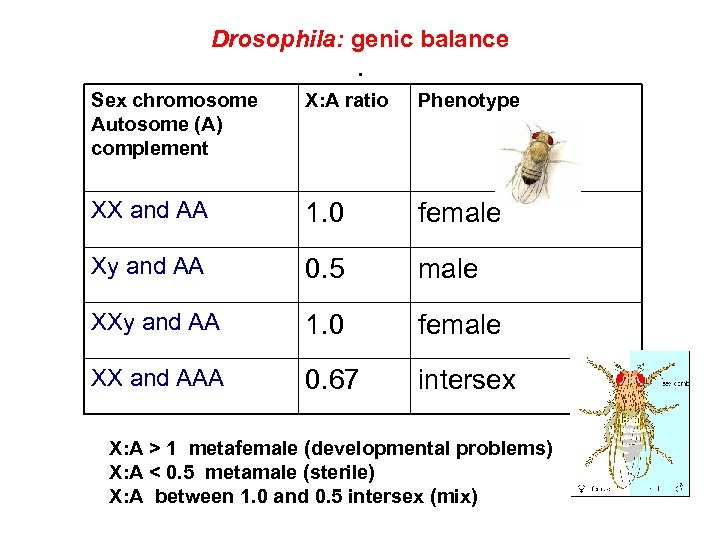 Drosophila: genic balance. Sex chromosome Autosome (A) complement X: A ratio Phenotype XX and AA 1. 0 female Xy and AA 0. 5 male XXy and AA 1. 0 female XX and AAA 0. 67 intersex X: A > 1 metafemale (developmental problems) X: A < 0. 5 metamale (sterile) X: A between 1. 0 and 0. 5 intersex (mix)
Drosophila: genic balance. Sex chromosome Autosome (A) complement X: A ratio Phenotype XX and AA 1. 0 female Xy and AA 0. 5 male XXy and AA 1. 0 female XX and AAA 0. 67 intersex X: A > 1 metafemale (developmental problems) X: A < 0. 5 metamale (sterile) X: A between 1. 0 and 0. 5 intersex (mix)
 Am I a male or female? I have no idea. I can’t do math!
Am I a male or female? I have no idea. I can’t do math!
 How number of sex chromosomes affect human development • Turner syndrome (XO) female • Klinefelters (XXY) male • sterile, phenotypic traits related to secondary sexual characteristics, and frequently developmental problems
How number of sex chromosomes affect human development • Turner syndrome (XO) female • Klinefelters (XXY) male • sterile, phenotypic traits related to secondary sexual characteristics, and frequently developmental problems
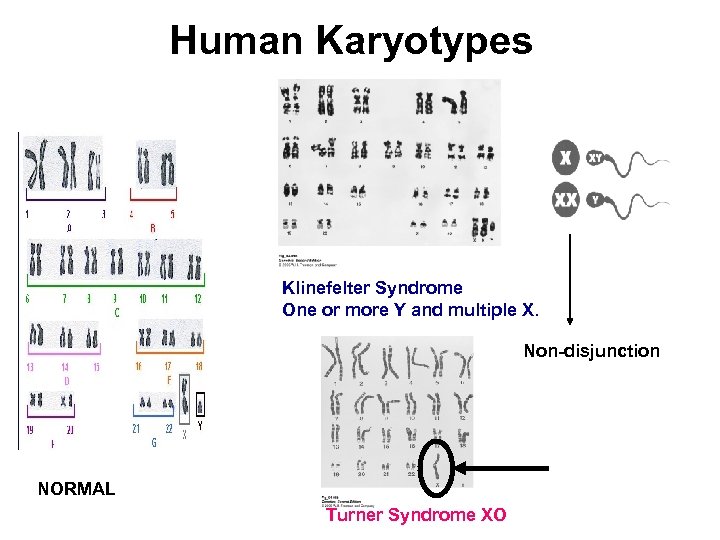 Human Karyotypes Klinefelter Syndrome One or more Y and multiple X. Non-disjunction NORMAL Turner Syndrome XO
Human Karyotypes Klinefelter Syndrome One or more Y and multiple X. Non-disjunction NORMAL Turner Syndrome XO
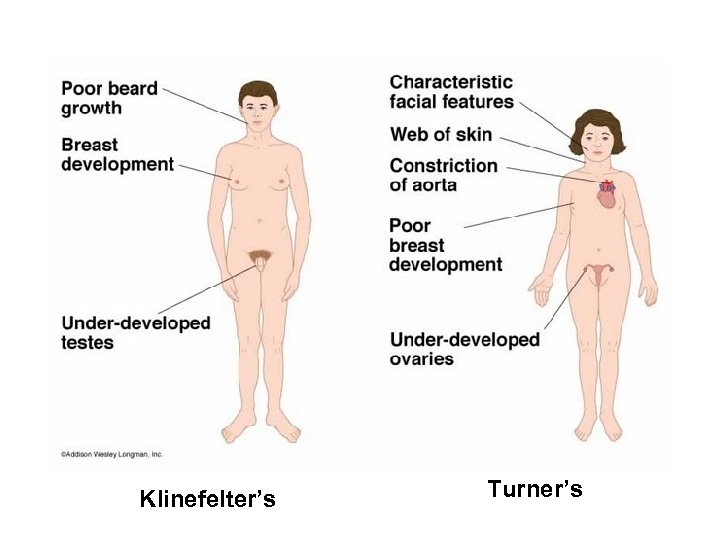 Klinefelter’s Turner’s
Klinefelter’s Turner’s
 Maleness Determination of maleness is due to sry gene of Y chromosome
Maleness Determination of maleness is due to sry gene of Y chromosome
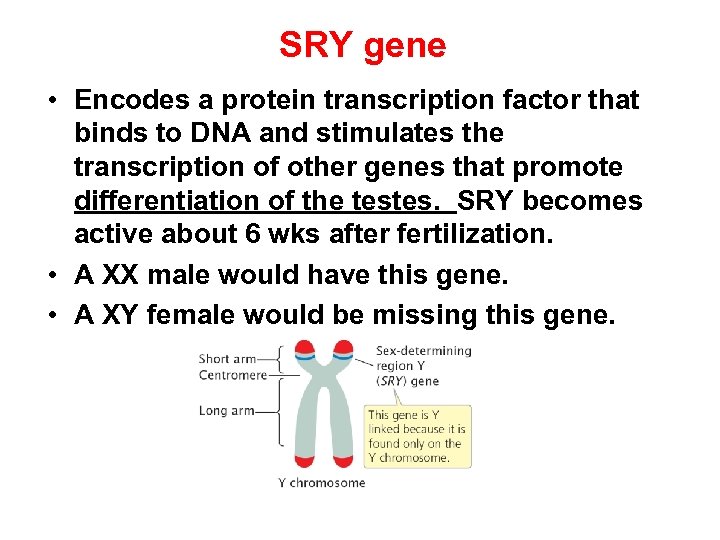 SRY gene • Encodes a protein transcription factor that binds to DNA and stimulates the transcription of other genes that promote differentiation of the testes. SRY becomes active about 6 wks after fertilization. • A XX male would have this gene. • A XY female would be missing this gene.
SRY gene • Encodes a protein transcription factor that binds to DNA and stimulates the transcription of other genes that promote differentiation of the testes. SRY becomes active about 6 wks after fertilization. • A XX male would have this gene. • A XY female would be missing this gene.
 How does this work? • Upon SRY activation, the former neutral gonads develop into testes, which secrete testosterone and Mullerianinhibiting substance which causes the degeneration of the female reproductive ducts.
How does this work? • Upon SRY activation, the former neutral gonads develop into testes, which secrete testosterone and Mullerianinhibiting substance which causes the degeneration of the female reproductive ducts.
 • SRY is the primary determinant of maleness in humans, other genes (some X-linked, others Y-linked, and others autosomal) also have roles in fertility and development of sex differences.
• SRY is the primary determinant of maleness in humans, other genes (some X-linked, others Y-linked, and others autosomal) also have roles in fertility and development of sex differences.
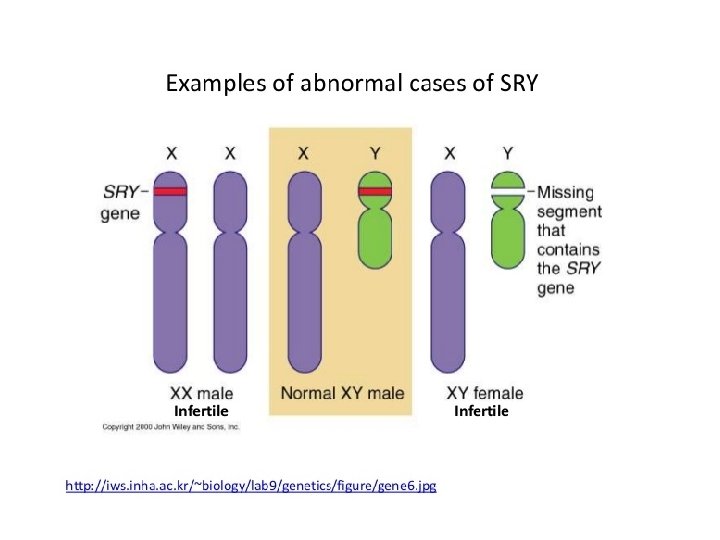
 What about crossing-over involving the SRY gene? • When crossing over extends past the boundary of the pseudoautosomal region and includes the SRY gene, sexual development will most likely be adversely affected. • The rare occurrences of chromosomally XX males and XY females are due to such aberrant crossing over, in which the Y chromosome has lost—and the X chromosome has gained—this sexdetermining gene.
What about crossing-over involving the SRY gene? • When crossing over extends past the boundary of the pseudoautosomal region and includes the SRY gene, sexual development will most likely be adversely affected. • The rare occurrences of chromosomally XX males and XY females are due to such aberrant crossing over, in which the Y chromosome has lost—and the X chromosome has gained—this sexdetermining gene.
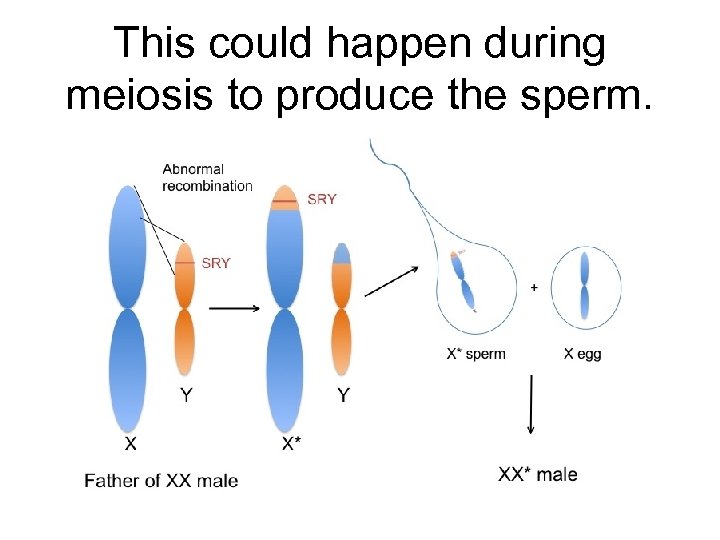 This could happen during meiosis to produce the sperm.
This could happen during meiosis to produce the sperm.
 • Expression of gender is more complex than just sry gene. • Example: androgen insensitivity – XY genotype – Many female characteristics!
• Expression of gender is more complex than just sry gene. • Example: androgen insensitivity – XY genotype – Many female characteristics!
 Androgen-insensitivity syndrome • In XY females • Vagina ends blindly, no uterus, oviducts, or ovaries • Pair of testes in abdominal area that produce testosterone • Cells have X and Y • Testosterone is produced (has SRY gene) but receptor is missing • Androgen-receptor gene on X chromosome
Androgen-insensitivity syndrome • In XY females • Vagina ends blindly, no uterus, oviducts, or ovaries • Pair of testes in abdominal area that produce testosterone • Cells have X and Y • Testosterone is produced (has SRY gene) but receptor is missing • Androgen-receptor gene on X chromosome

 • So, the key to maleness and femaleness lies not in the genes, but in the control of their expression! OR NOT!
• So, the key to maleness and femaleness lies not in the genes, but in the control of their expression! OR NOT!
 Sex Linked (X-linked) Traits – determined by Thomas Morgan • The mystery of the white-eyed Drosophila male
Sex Linked (X-linked) Traits – determined by Thomas Morgan • The mystery of the white-eyed Drosophila male

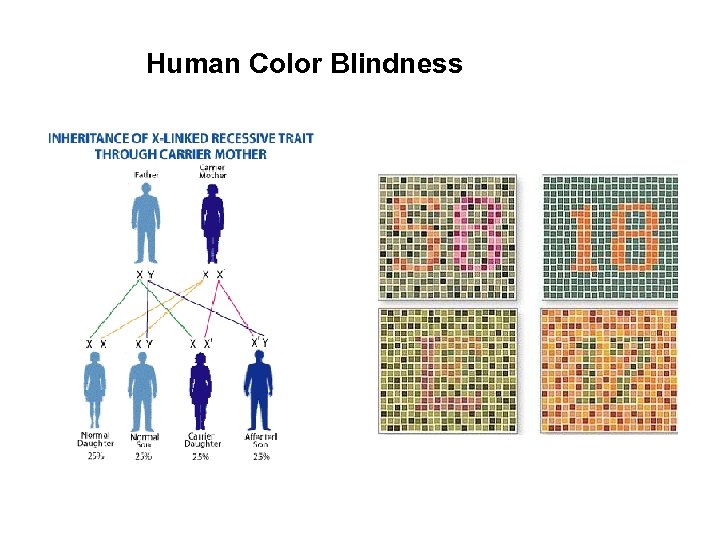 Human Color Blindness
Human Color Blindness
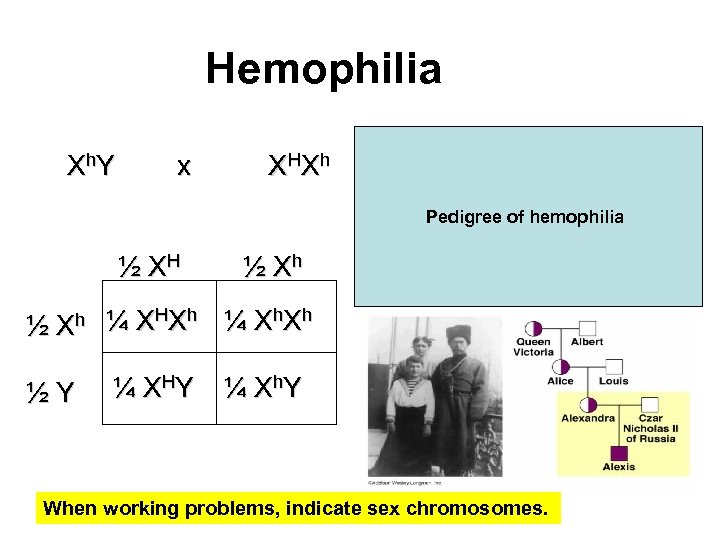 Hemophilia X h. Y x X HX h Pedigree of hemophilia ½ XH ½ Xh ½ X h ¼ X HX h ¼ X h ½Y ¼ X HY ¼ X h. Y When working problems, indicate sex chromosomes.
Hemophilia X h. Y x X HX h Pedigree of hemophilia ½ XH ½ Xh ½ X h ¼ X HX h ¼ X h ½Y ¼ X HY ¼ X h. Y When working problems, indicate sex chromosomes.
 Y-linked characteristics • 2/3 of Y consists of repeated short DNA sequences and contain no active genes • Only about 350 genes in human Y; only half code for proteins • Some genetic elements can influence expression of genes on autosomal and X chromosomes though.
Y-linked characteristics • 2/3 of Y consists of repeated short DNA sequences and contain no active genes • Only about 350 genes in human Y; only half code for proteins • Some genetic elements can influence expression of genes on autosomal and X chromosomes though.
 • Mutations can form Y-linked markers and these can be traced to the male exclusively • Thomas Jefferson’s sons? ?
• Mutations can form Y-linked markers and these can be traced to the male exclusively • Thomas Jefferson’s sons? ?
 Dosage compensation for X chromosomes • Amt of gene product would be 2 X in females • How compensate: In fruit flies, X double activity of genes on the X • Lyon hypothesis: in females one of the two X’s is inactivated and forms a Barr body (observed initially in cats)
Dosage compensation for X chromosomes • Amt of gene product would be 2 X in females • How compensate: In fruit flies, X double activity of genes on the X • Lyon hypothesis: in females one of the two X’s is inactivated and forms a Barr body (observed initially in cats)
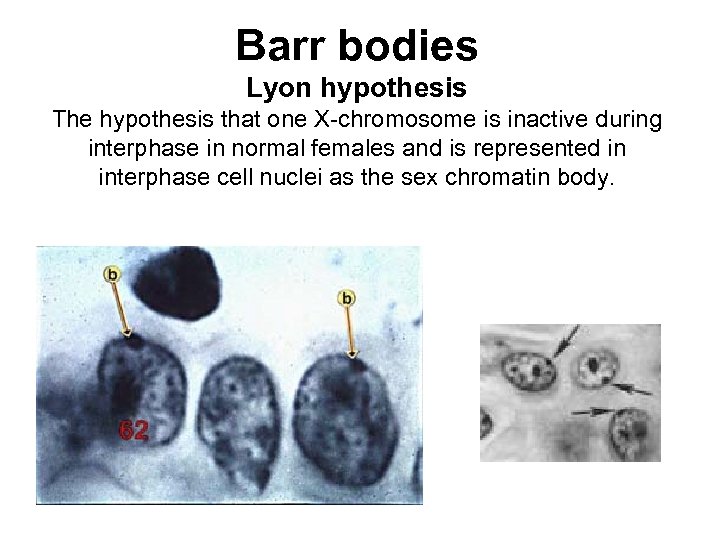 Barr bodies Lyon hypothesis The hypothesis that one X-chromosome is inactive during interphase in normal females and is represented in interphase cell nuclei as the sex chromatin body.
Barr bodies Lyon hypothesis The hypothesis that one X-chromosome is inactive during interphase in normal females and is represented in interphase cell nuclei as the sex chromatin body.
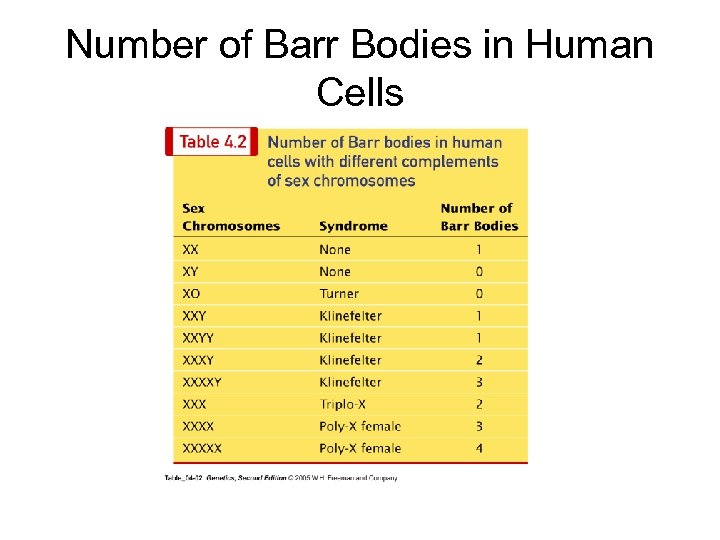 Number of Barr Bodies in Human Cells
Number of Barr Bodies in Human Cells
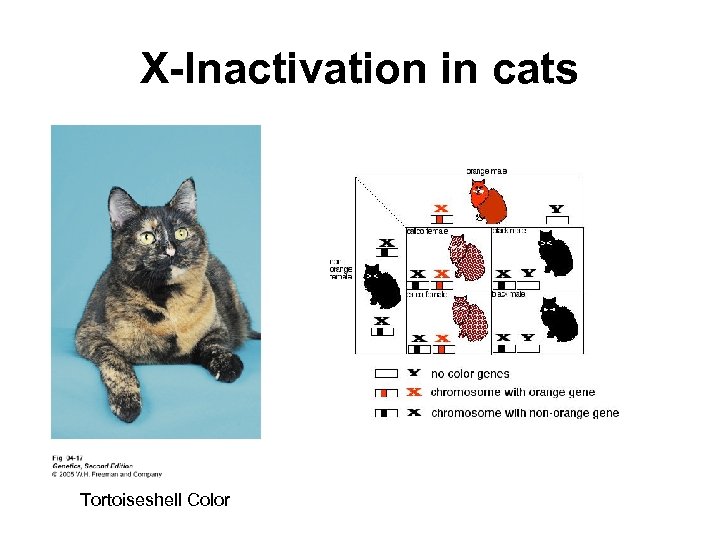 X-Inactivation in cats Tortoiseshell Color
X-Inactivation in cats Tortoiseshell Color
 De-evolution of the Y chromosome • • When is testosterone the highest? Only males have testosterone? Only females have estrogen? SRY begins to be expressed at what age of development? • What is the NRY?
De-evolution of the Y chromosome • • When is testosterone the highest? Only males have testosterone? Only females have estrogen? SRY begins to be expressed at what age of development? • What is the NRY?
 • What percent of functional genes of the genome on the Y? • Breaking that percent down, how many are used to produce sperm? • What is DAZ? • Where did the SRY gene come from? • Why has the Y chromosome become smaller over the years? • Where did DAZ come from? • What is the result if the DAZ gene is deleted in males?
• What percent of functional genes of the genome on the Y? • Breaking that percent down, how many are used to produce sperm? • What is DAZ? • Where did the SRY gene come from? • Why has the Y chromosome become smaller over the years? • Where did DAZ come from? • What is the result if the DAZ gene is deleted in males?
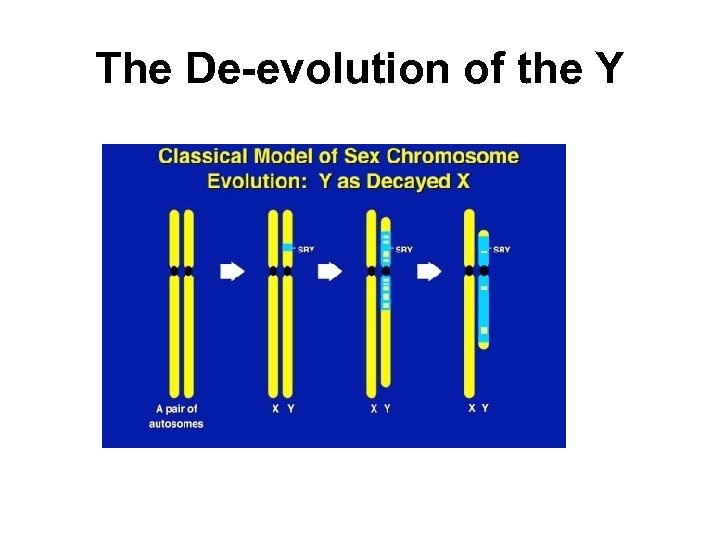 The De-evolution of the Y
The De-evolution of the Y
 Back to the Gender Revolution https: //www. facebook. com/katiecouric/videos/10154790608436005/
Back to the Gender Revolution https: //www. facebook. com/katiecouric/videos/10154790608436005/
 So what does determine sex? • • • Chromosomes Hormones Gene expression Genitalia How you feel about your sex?
So what does determine sex? • • • Chromosomes Hormones Gene expression Genitalia How you feel about your sex?
 The End
The End


