ab24dd4067a8f64a0de36cd8791d0069.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 79

SEVICES: GOING GLOBAL? Lecturer: Dr. Truong Thi Kim Chuyen

CONTENT I. Defining and theorizing services II. National and global stimuli to the growth of services III. Service outsourcing: benefits and drawbacks for all? IV. Limits to service export growth in the semiperiphery and periphery V. Geography of services VI. Variety in the internationalization of services

Group members Thái Thụy Tường Vy Đỗ Bảo Khánh Phạm Bình Dương Đoàn Anh Việt Nguyễn Thị Anh Thư

11. 1/ Defining and theorizing services

I. Defining and theorizing services Following Fisher – Clark thesis, services have been defined: Ø Comprising what remains after agriculture, mining and manufacturing are excluded. (1 st defined way) Ø Production and consumption of intangible inputs and outputs. (2 nd defined way)

st 1 defined way Differences between manufacturing and services play important implications For LDCs and the DCs For measuring and studying services

Services are categorized into 7 major components Finance, insurance and real estate Business services Transportation and communications Wholesale and retail trade Entertainment, hotels and motels Public services at all government levels Non-profit services

2 nd defined way • The distinction between tangible manufactured goods and intangible services is not clear cut • Many manufactured products have come to be offered not in their own right to consumers, but in terms of their wider service attributes. This has occurred in 2 ways − The manufactured products can be offered along with closely aligned service products in a single package − Instead of buying a manufactured product in a single one-time purchase, a consumer can buy the service which the manufactured product provides as part of a continuing process involving long-term customer contact through service delivery
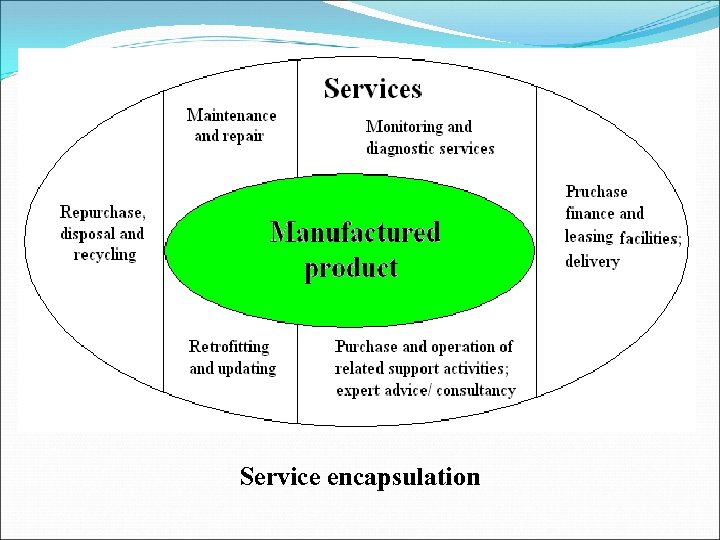
Service encapsulation

11. 2/ National and global stimuli to the growth of services

II. National and global stimuli to the growth of services Rising per capita incomes Growing demand for healthcare and educational services Increasingly complex division of labor Growing size and role of the public sector Increasing international trade in services Rapid growth in outsourcing service functions

11. 3/ SERVICE OUTSOURCING: BENEFITS AND DRAWBACKS FOR ALL?
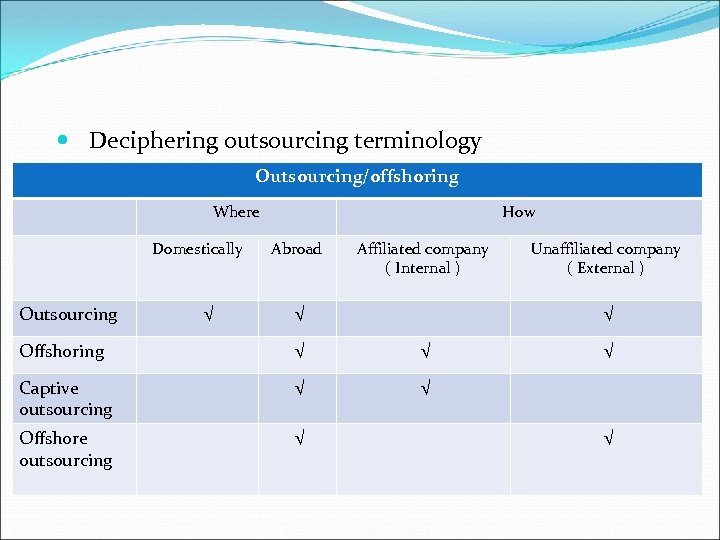
Deciphering outsourcing terminology Outsourcing/offshoring Where Domestically Outsourcing √ How Abroad Affiliated company ( Internal ) √ Unaffiliated company ( External ) √ Offshoring √ √ Captive outsourcing √ √ Offshore outsourcing √ √ √

Outsourcing can be done domestically or abroad, involves work done externally Offshoring is always done abroad, the work can be done either internally External outsourcing – where the work is done by unaffiliated companies ( including independent foreign subcontractors, as in offshore outsourcings ) Internai outsourcing – where the work is done by affiliated companies as in captive outsourcing

While the outsourcing of services is still at a relatively early age, it is seen as representing the leading edge of changes in global production UNCTAD : Reflect a shift to a new internal division of labour in the production of services OECD : The total number of jobs could be affected by international and domestic outsourcing

Service and manufacturing activities, important differences are expected to fuel an acceleration in service outsourcing First, There is significant room for growth Second, The rate of increase in the amount of services that has become tradable Third, Manufacturing companies have primarily carried out the outsourcing of goods production Fourth, Skill levels are typically higher Fifth, Services may be more mobile than outsourced manufacturing activities

The benefits of service outsourcing for LDCs include the criterion of higher skill jobs involving better pay, training and transferable skills and associated infrastructure investment that can contribute to further local job growth The drawback for some LDCs include the possible relocation of outsourced service activities to other more competitive LDC locations unless worker skills and local infrastructure are continuously upgraded

11. 4/ LIMITS TO SERVICE EXPORT GROWTH IN THE SEMI-PERIPHERY AND PERIPHERY

Semi-periphery and periphery The semi-periphery countries are the industrializing, mostly capitalist countries which are positioned between the periphery and core countries The periphery countries (sometimes referred to as just the periphery) are those that are less developed than the semi-periphery and core countries.

Limits to service export growth in the semi-periphery and periphery TECHNOLOGY AND INFRASTRUCTURE EDUCATION AND TRAINING GOVRNMENT REGULATIONS AND POLICIES CORPORATE STRATEGIES
TECHNOLOGY AND INFRASTRUCTURE TECHNOLOGICAL LIMITATIONS: USE BY COMPUTER DIGITAL FORM MADE TO OUTSORCING

TECHNOLOGICAL LIMITATIONS: Ex: Africa has less than 1 internet host per 1000 inhabitants
LIMITED INFRASTRUCTURE: TELECOMMUNICATIONS RELIABLE POWER SOURCES FINANCIAL SERVICES DISTRIBUTION LOGISTIC

LIMITED INFRASTRUCTURE: EX: LDCs cannot link into telecommunications network in submarine cables => They are limited in their ability to develop competitive base for services exports

EDUCATION AND TRAINING Lack of education and training is a limiting factor in knowledge-intense services.
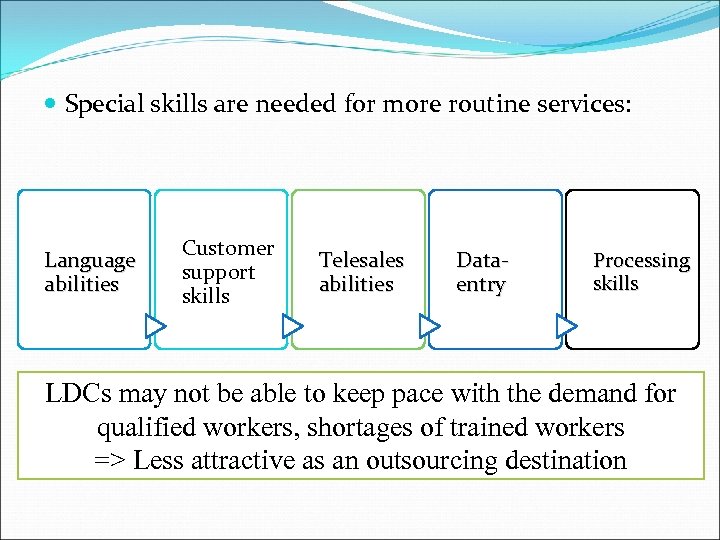
Special skills are needed for more routine services: Language abilities Customer support skills Telesales abilities Dataentry Processing skills LDCs may not be able to keep pace with the demand for qualified workers, shortages of trained workers => Less attractive as an outsourcing destination

GOVERNMENT AND POLICIES Competitive regulatory environment is need to encourage competition among service providers The regulatory and legal framework in some less developed countries can place limits on the growth of export services. => they need to be concern about poor data security and intellectual property protection.

WTO’s General Agreement on Trade in services (GATS) covers all internationally traded services. However, it still proceeds extremely slowly to help a greater competition and non-discrimination.
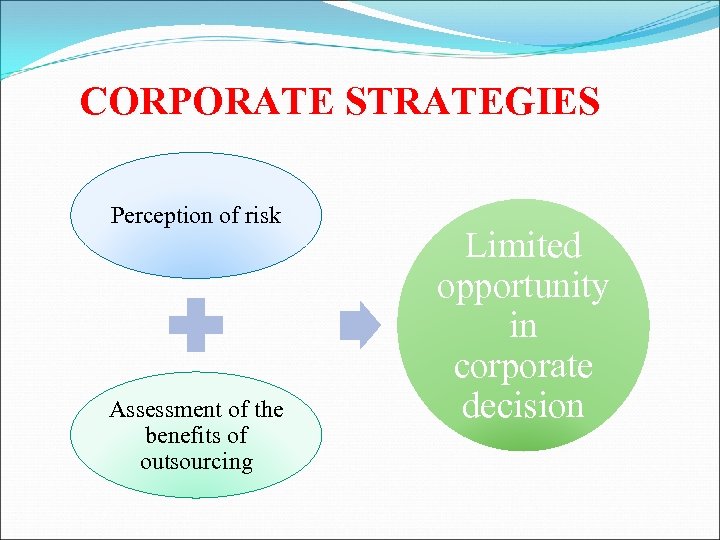
CORPORATE STRATEGIES Perception of risk Assessment of the benefits of outsourcing Limited opportunity in corporate decision

Any assessment of the potential for service outsourcing needs to include analysis of corporate strategies and organizational limitations Ex: some information that is to be processed can be confidental. However, this can increase transation cost and limit desirability of outsourcing. The royal Bank of Scotland in UK are right when deciding not to outsource certain financial service abroad while LDCs is limited in decision of outsourcing.

11. 5/ GEOGRAPHY OF SERVICES

1. 2. 3. 4. 5. PATTERNS AND TRAJECTORIES INTERNATIONAL TRADE IN SERVICES TRANSNATIONAL INVESTMENT PATTERNS EXPORT PROCESSING ZONES (EPZS) AGGLOMERATION AND NEW BUSINESS SERVICE CONCENTRATIONS
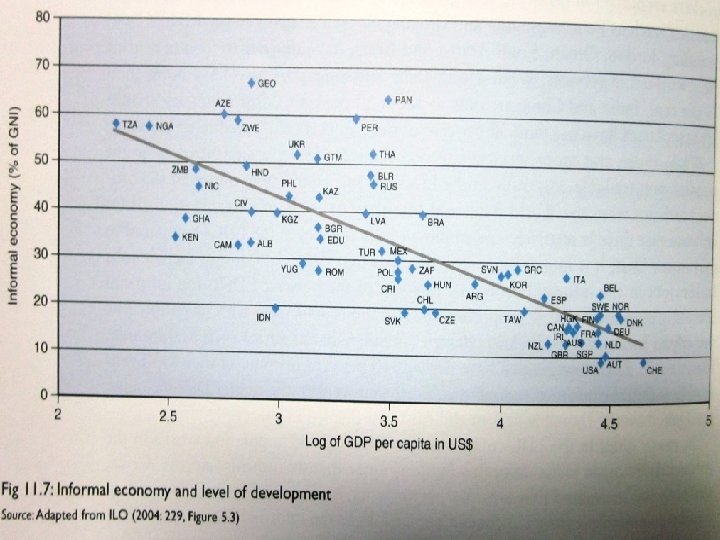
PATTERNS AND TRAJECTORIES 2006: milestone for service Low employment in services ? Economy Informal Formal
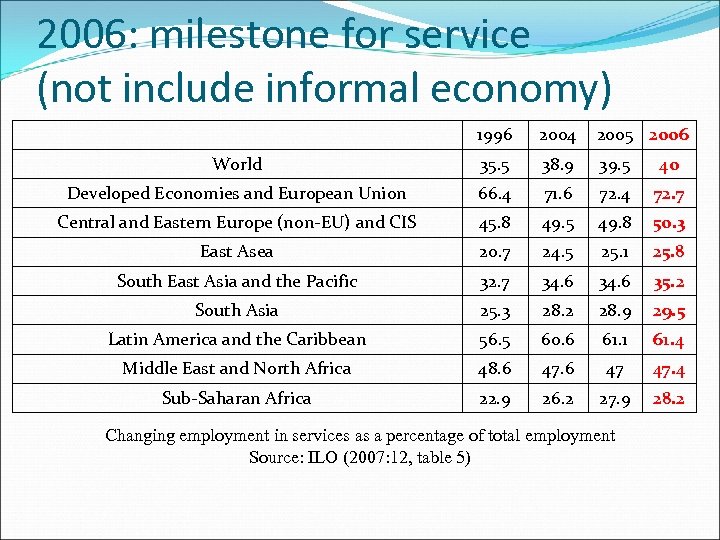
2006: milestone for service (not include informal economy) 1996 2004 2005 2006 World 35. 5 38. 9 39. 5 40 Developed Economies and European Union 66. 4 71. 6 72. 4 72. 7 Central and Eastern Europe (non-EU) and CIS 45. 8 49. 5 49. 8 50. 3 East Asea 20. 7 24. 5 25. 1 25. 8 South East Asia and the Pacific 32. 7 34. 6 35. 2 South Asia 25. 3 28. 2 28. 9 29. 5 Latin America and the Caribbean 56. 5 60. 6 61. 1 61. 4 Middle East and North Africa 48. 6 47 47. 4 Sub-Saharan Africa 22. 9 26. 2 27. 9 28. 2 Changing employment in services as a percentage of total employment Source: ILO (2007: 12, table 5)
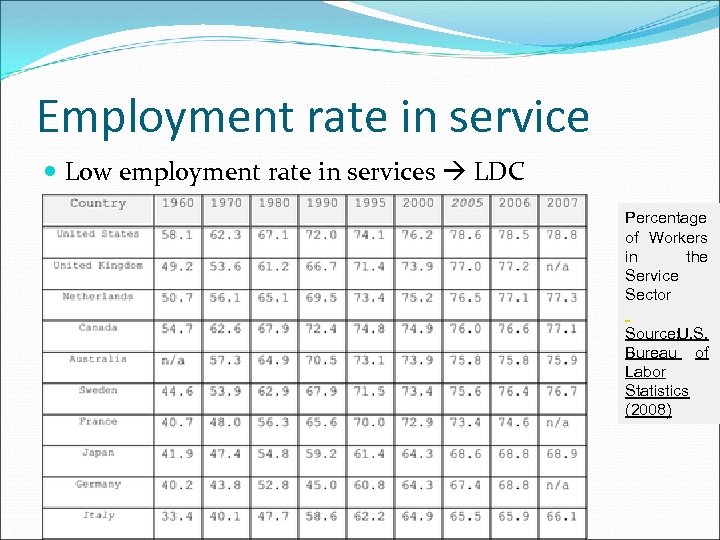
Employment rate in service Low employment rate in services LDC Percentage of Workers in the Service Sector Source: U. S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (2008)
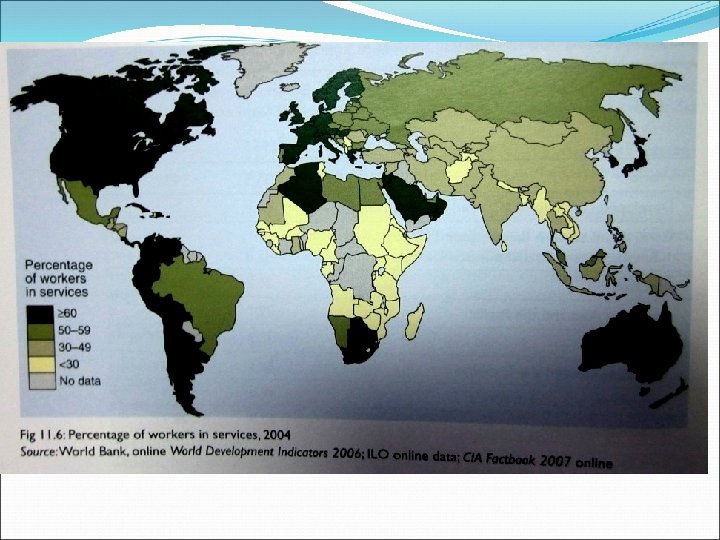

The connection between two kinds of economy Informal economy: informal sector, informal employment, LDC employment without labour or social protection— both inside and outside informal enterprises, including both self-employment in small unregistered enterprises and wage employment in unprotected jobs. (D E S A W o r k i n g P a p e r N o. 4 6) Formal economy: formal sector, formal employment, DC

Informal sector resource for the formal sector. Reason: informal sector provides a huge range of cheap services for employees in the formal sector reduce the living cost of them reduce the wages reduce the goods price good formal economy
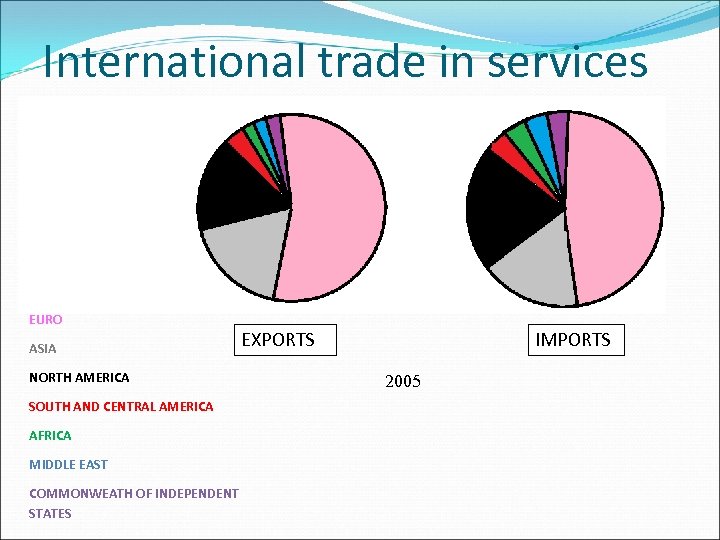
International trade in services EURO ASIA NORTH AMERICA SOUTH AND CENTRAL AMERICA AFRICA MIDDLE EAST COMMONWEATH OF INDEPENDENT STATES EXPORTS IMPORTS 2005
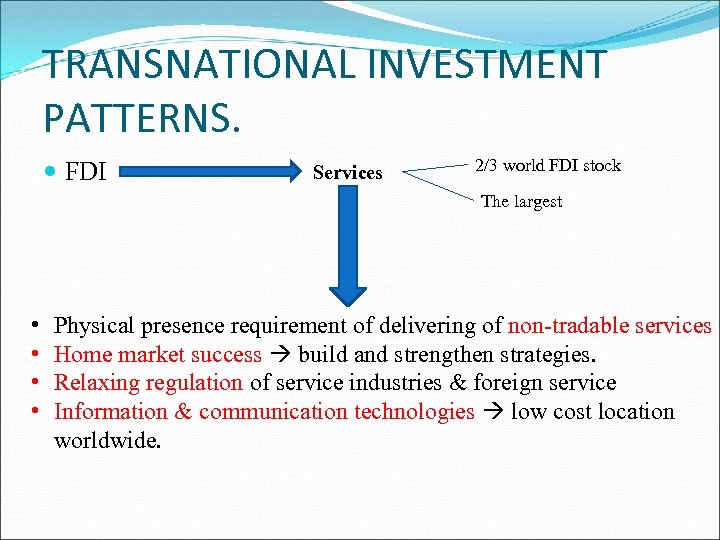
TRANSNATIONAL INVESTMENT PATTERNS. FDI Services 2/3 world FDI stock The largest • • Physical presence requirement of delivering of non-tradable services Home market success build and strengthen strategies. Relaxing regulation of service industries & foreign service Information & communication technologies low cost location worldwide.

EXPORT PROCESSING ZONES (EPZS) LCDs use subsidies and EPZs attract investment. Subsidies: variety of service industries. EPZs: manufacturing (traditional), export-oriented services
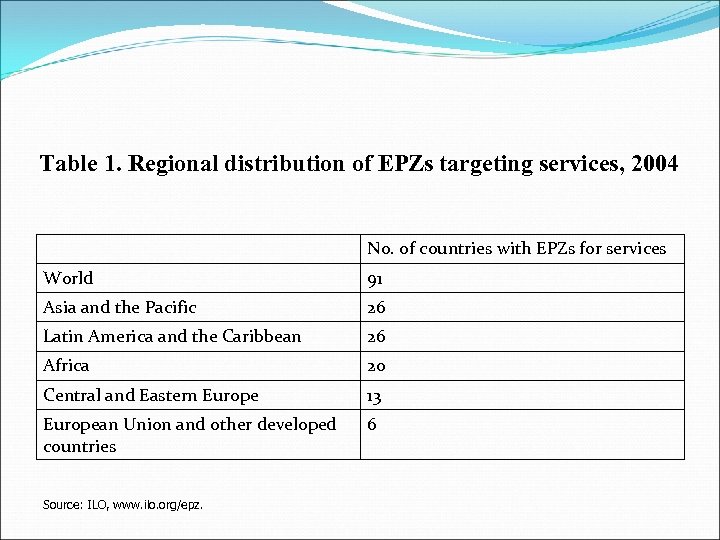
Table 1. Regional distribution of EPZs targeting services, 2004 No. of countries with EPZs for services World 91 Asia and the Pacific 26 Latin America and the Caribbean 26 Africa 20 Central and Eastern Europe 13 European Union and other developed countries 6 Source: ILO, www. ilo. org/epz.

Most EPZs for service industries are located in the LDCs. The kinds of these EPZs have growth rapidly: commercial services, simple data entry, call centres, medical diagnoses, architectural, business, engineering and financial services. Modern communication technologies EPZs Reliable power supplies Highly skilled work-force.
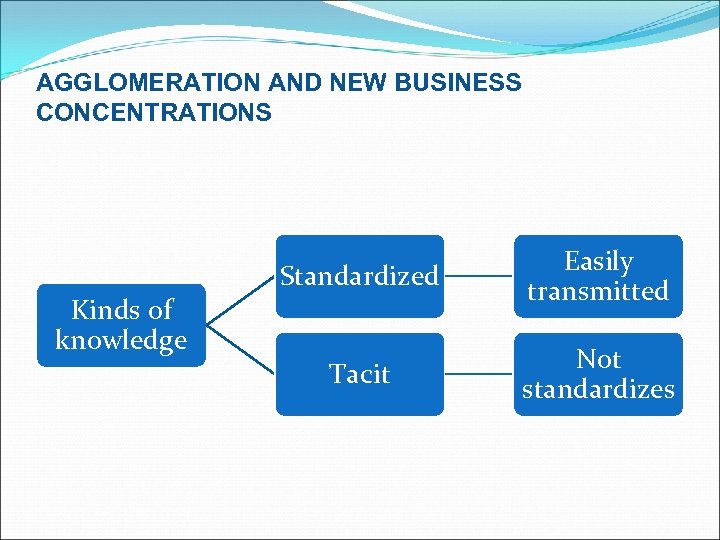
AGGLOMERATION AND NEW BUSINESS CONCENTRATIONS Kinds of knowledge Standardized Easily transmitted Tacit Not standardizes

Actor-network theory High value-added services + skilled labor + tacit information = world’s global cities. Low value-added services + standardized knownledge = world’s low wage.

11. 6/ Variety in the Internationalization of Services

The Internalization of Services Retailing Tourism Financial Business
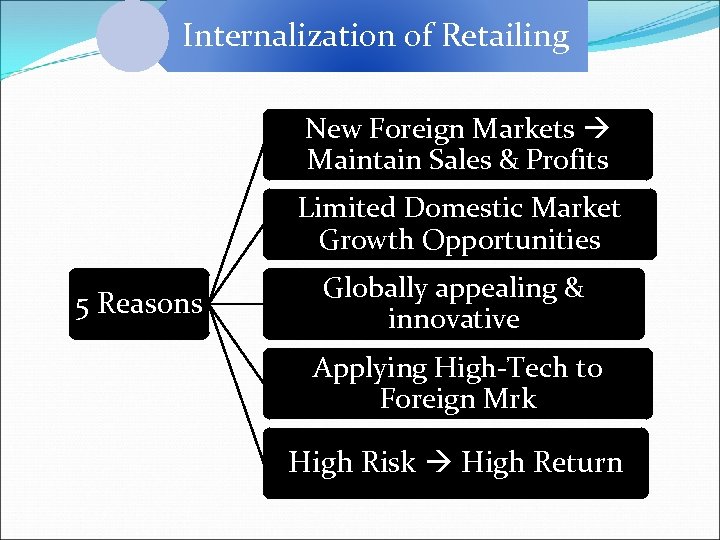
Internalization of Retailing New Foreign Markets Maintain Sales & Profits Limited Domestic Market Growth Opportunities 5 Reasons Globally appealing & innovative Applying High-Tech to Foreign Mrk High Risk High Return

Large global retailers Internationalizing their Supply Networks Applying Buyerdriven commodity chain What is Buyer- driven commodity chains ? v. Labour- Intensive v. Consumer goods industries
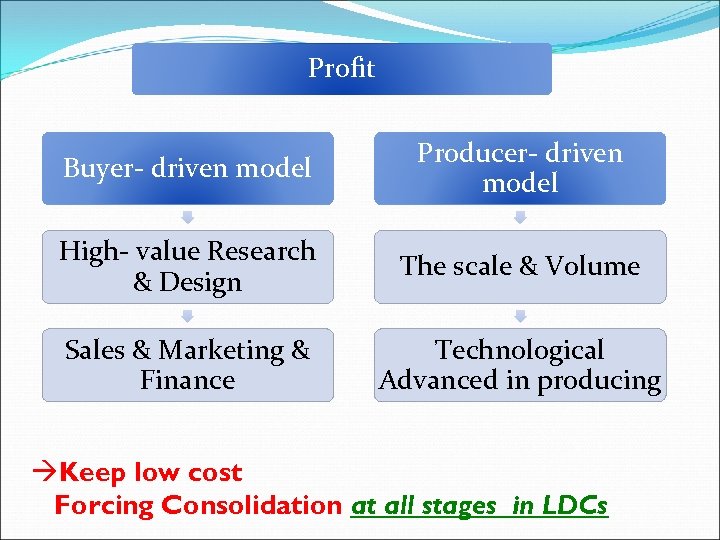
Profit Buyer- driven model Producer- driven model High- value Research & Design The scale & Volume Sales & Marketing & Finance Technological Advanced in producing Keep low cost Forcing Consolidation at all stages in LDCs
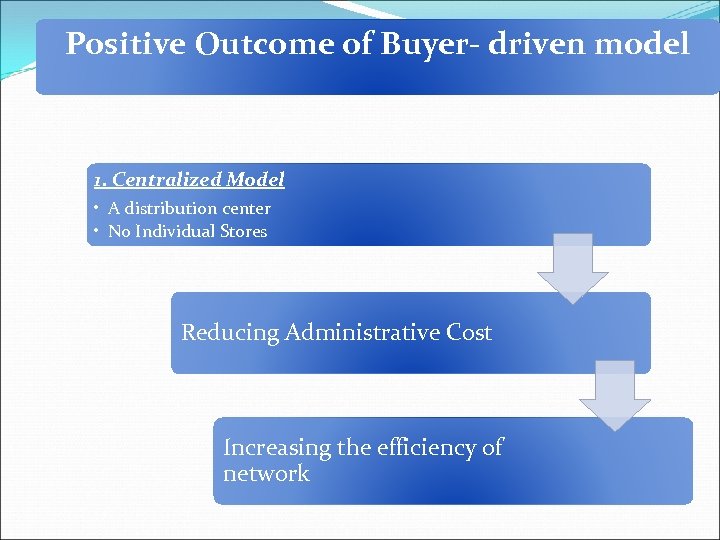
Positive Outcome of Buyer- driven model 1. Centralized Model • A distribution center • No Individual Stores Reducing Administrative Cost Increasing the efficiency of network
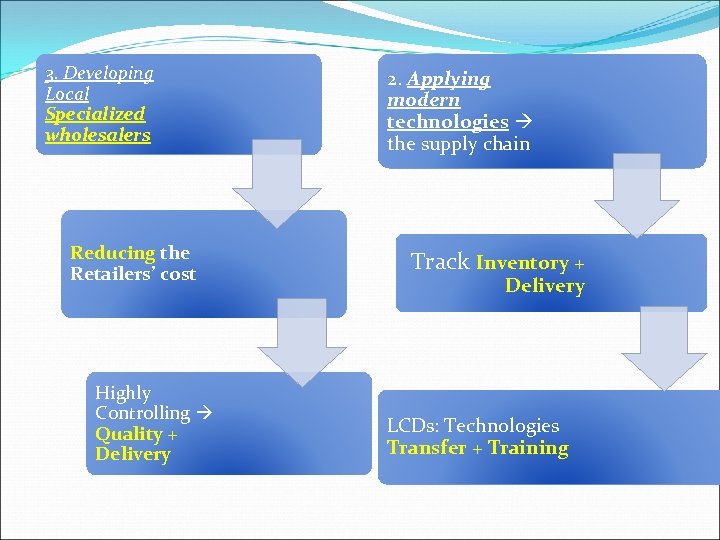
3. Developing Local Specialized wholesalers Reducing the Retailers’ cost Highly Controlling Quality + Delivery 2. Applying modern technologies the supply chain Track Inventory + Delivery LCDs: Technologies Transfer + Training
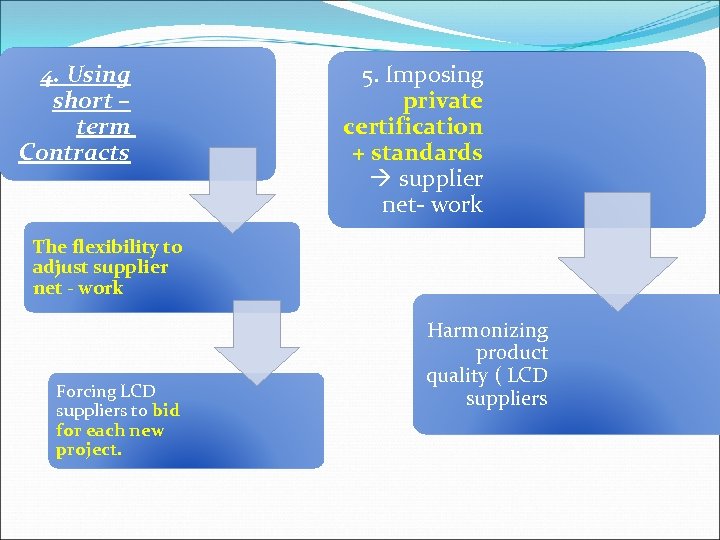
4. Using short – term Contracts 5. Imposing private certification + standards supplier net- work The flexibility to adjust supplier net - work Forcing LCD suppliers to bid for each new project. Harmonizing product quality ( LCD suppliers
Negative Outcome of Buyer- driven model u. Power in hands of a few major retailers. Ex: Wal- Mart u. Tighter Control over inputs and standards
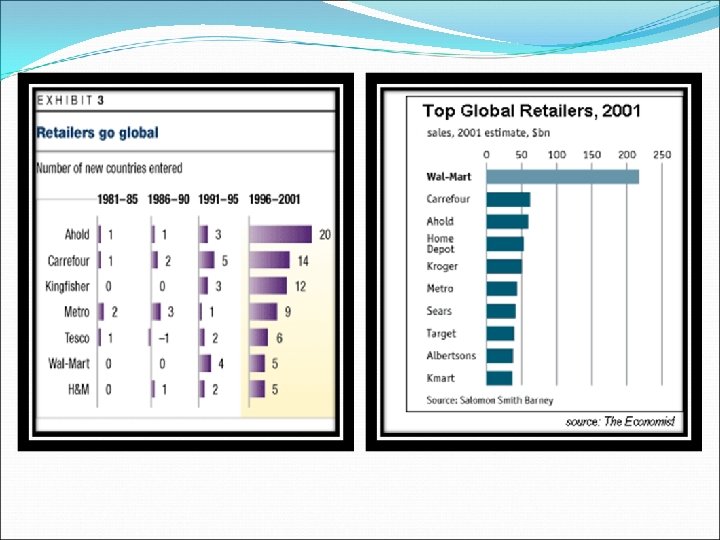

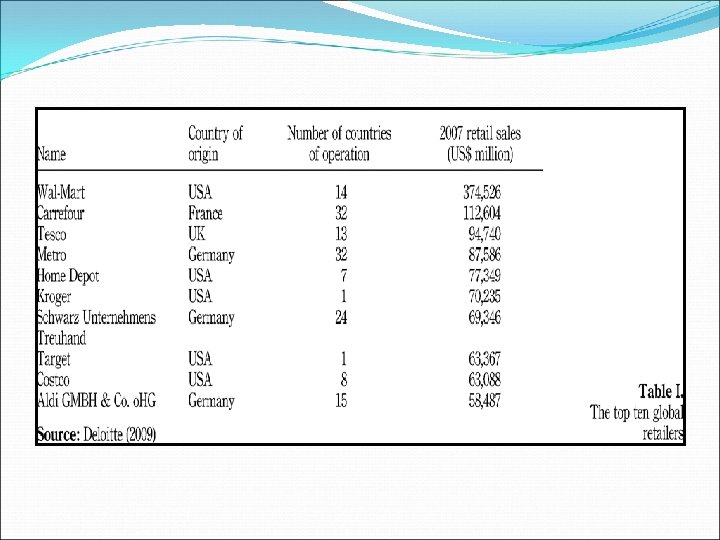
The World’s Largest retailer today
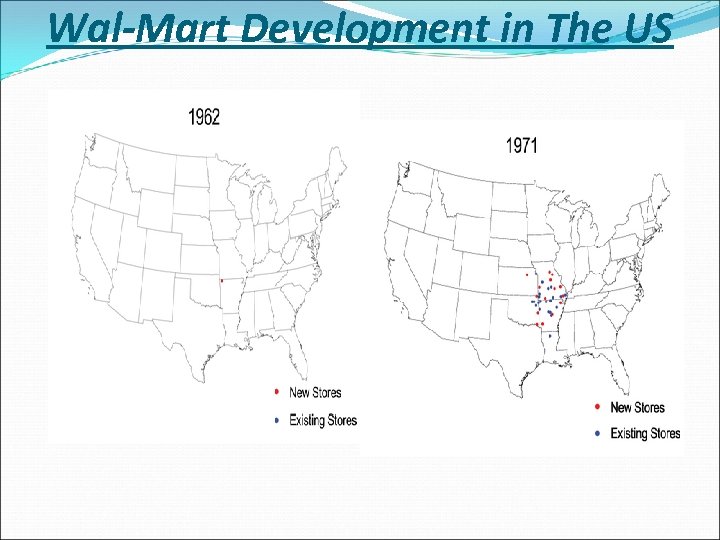
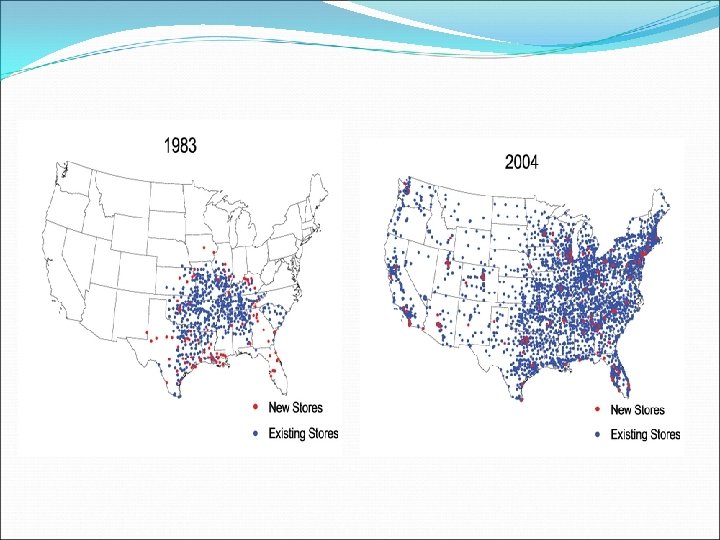
Wal-Mart Development in The US
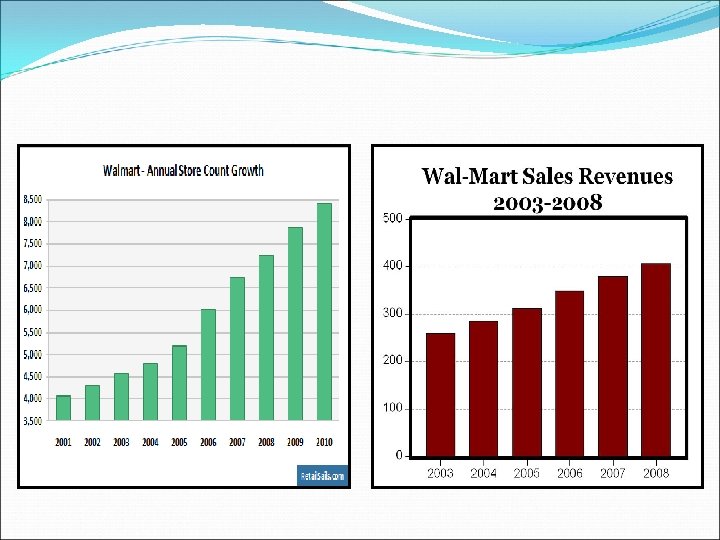

How did Wal- Mart solve its difficulties in Germany?

Wal- Mart superimposes its own Culture to Germany X No

An Important Lesson

International Tourism The requirements for rising International Tourism Transportation service Hotels Service Entertainment Service
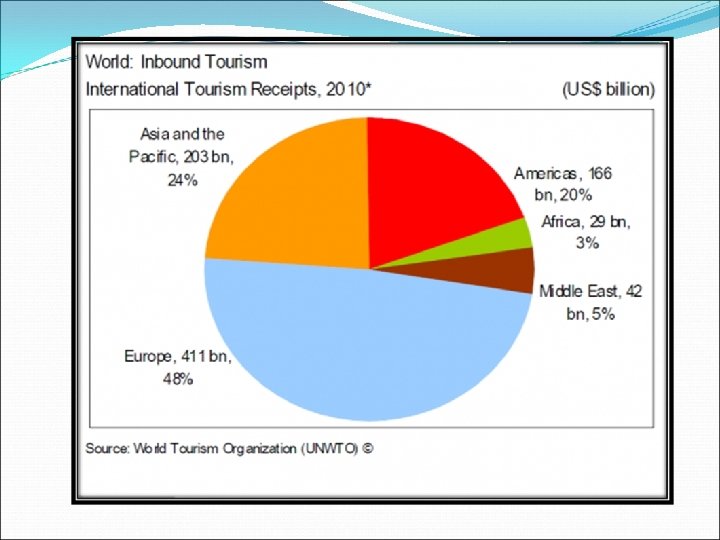
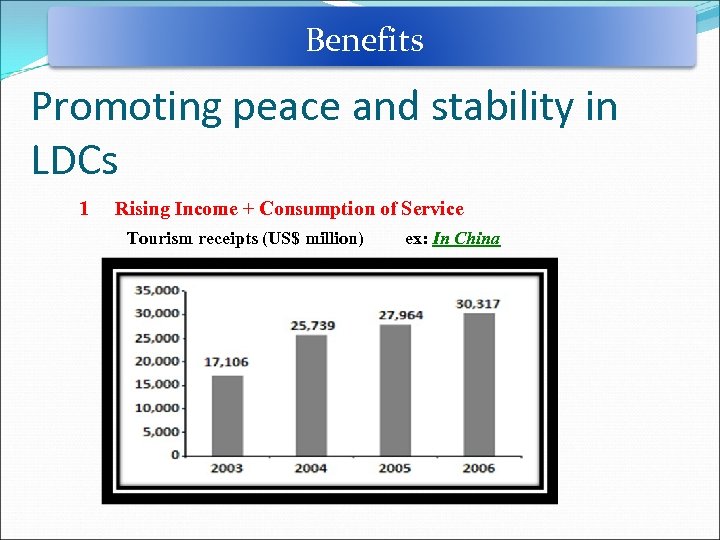
Benefits Promoting peace and stability in LDCs 1 Rising Income + Consumption of Service Tourism receipts (US$ million) ex: In China
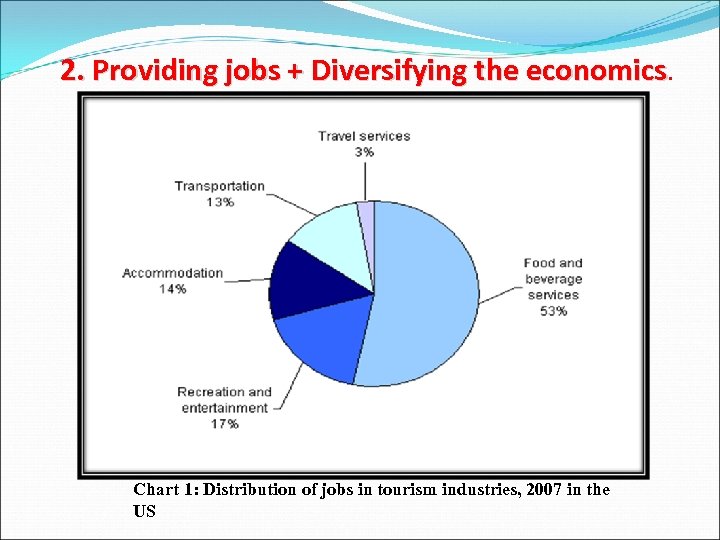
2. Providing jobs + Diversifying the economics. Chart 1: Distribution of jobs in tourism industries, 2007 in the US

3. Promoting cross- culture awareness.

Challenges 1 Producing jobs which are often seasonal. not fixed 1 Pollution / environment degradation 3 Degrade traditional lifestyle + heritage
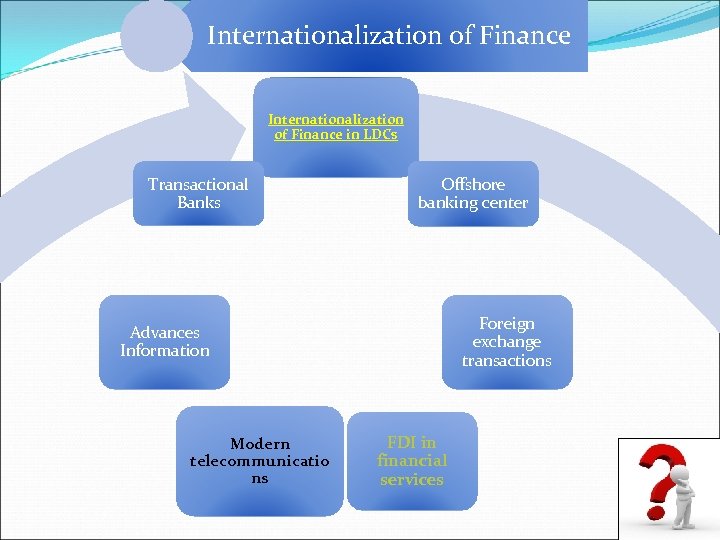
Internationalization of Finance in LDCs Transactional Banks Offshore banking center Foreign exchange transactions Advances Information Modern telecommunicatio ns FDI in financial services

There has been a large increase in the presence of banks from developed countries to LCDs countries HSBC Viet Nam Citibank Viet Nam Banks from developed countries strongly develop in China, Korea, Taiwan ( >= 50%) Others : Argentina, Brazil, Colombia, & Venezuela ( higher increase)

United Nations Conference on Trade and Development v. One- third of the world’ s financial TNCs are from LDCs ü Its international standards: Low ü Less international active A physical presence in a few foreign banking markets Ex: Banks ( from LDCs) London: 1996 - 2002 153 - 122 New York: 118 - 90
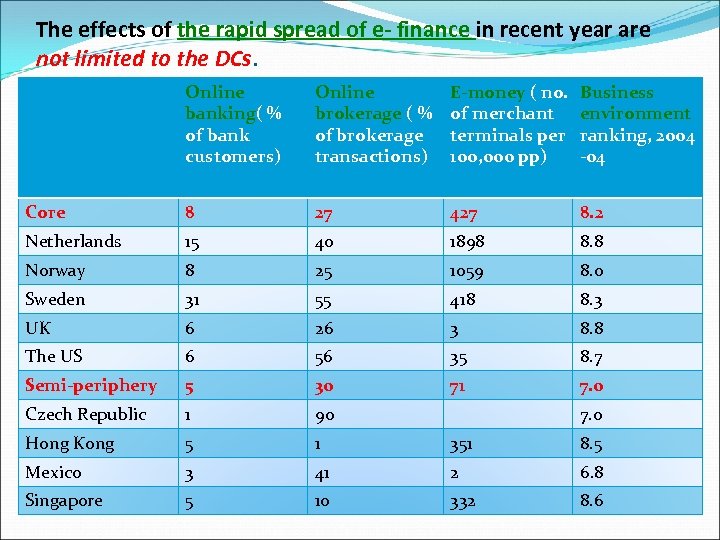
The effects of the rapid spread of e- finance in recent year are not limited to the DCs. Online banking( % of bank customers) Online brokerage ( % of brokerage transactions) E-money ( no. of merchant terminals per 100, 000 pp) Business environment ranking, 2004 -04 Core 8 27 427 8. 2 Netherlands 15 40 1898 8. 8 Norway 8 25 1059 8. 0 Sweden 31 55 418 8. 3 UK 6 26 3 8. 8 The US 6 56 35 8. 7 Semi-periphery 5 30 71 7. 0 Czech Republic 1 90 Hong Kong 5 1 351 8. 5 Mexico 3 41 2 6. 8 Singapore 5 10 332 8. 6 7. 0
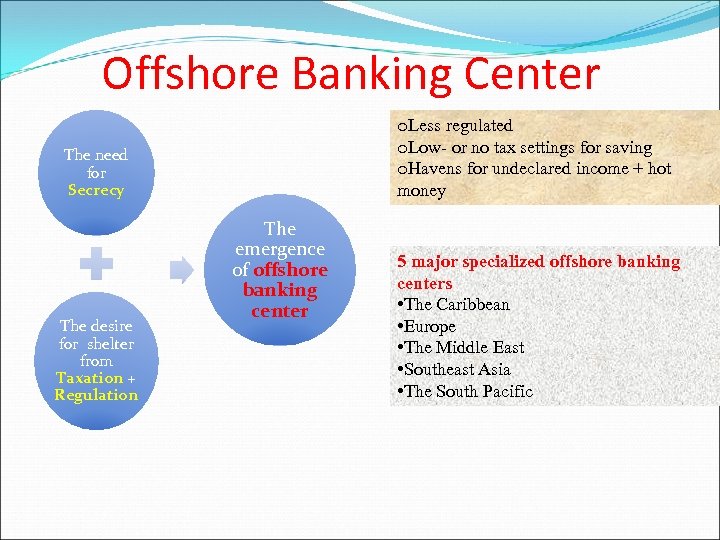
Offshore Banking Center o. Less regulated o. Low- or no tax settings for saving o. Havens for undeclared income + hot money The need for Secrecy The desire for shelter from Taxation + Regulation The emergence of offshore banking center 5 major specialized offshore banking centers • The Caribbean • Europe • The Middle East • Southeast Asia • The South Pacific

Internationalization of Business Service IBOS : in term of BPO to the LDCs in general and to India in particular §Low- cost Indian Programmers §The necessary skills, speed, & attention The US outsources the conversion of custom- made software programs ( 2/3 ) The large IT + BPO providers & intermediaries include companies in: §The DCs : the US ( CSC, EDS, & IBM). §The LDCs: India ( Infosys Technologies, Tata Consultancy services and Wipro).
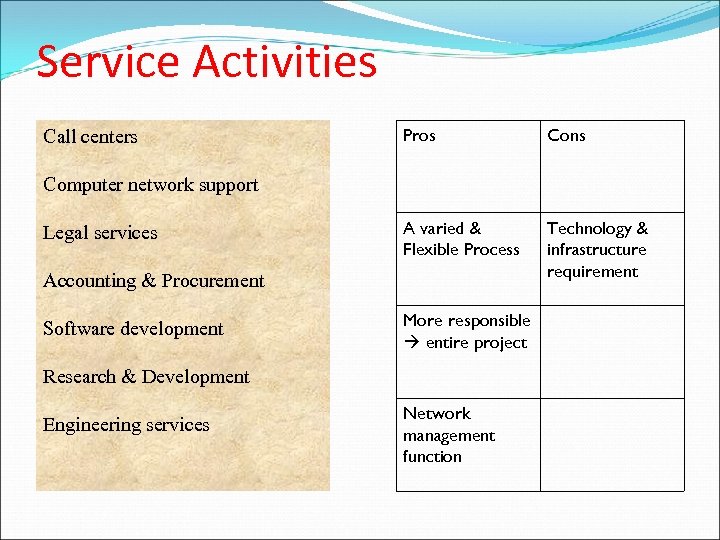
Service Activities Call centers Pros Cons A varied & Flexible Process Technology & infrastructure requirement Computer network support Legal services Accounting & Procurement Software development More responsible entire project Research & Development Engineering services Network management function

REFERENCES: www. g 77. org www. worldbank. org/depweb/beyondco/beg_09. pdf www. deti. ie/trade/marketaccess/singlemarket/05 serv 277. pdf www. ilo. org http: //www. worldcat. org/wcpa/servlet/org. oclc. lac. ui. Dial. ABoo k. Servlet? oclcnum=256533624 www. wto. org UNCTAD wikipedia. org/ The Geography of the World Economy

THANK FOR LISTENING
ab24dd4067a8f64a0de36cd8791d0069.ppt