ad234d8cb62108bd941c6615c6e7094b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 55
 Severe Weather Guide How to Recognize, Identify, and Report Severe Weather
Severe Weather Guide How to Recognize, Identify, and Report Severe Weather
 Definitions and Terms • Watch: conditions are favorable for severe weather • Warning: severe weather is currently occurring in the area • Watches and warnings are issued for: severe thunderstorms, hail, flash floods, and tornadoes
Definitions and Terms • Watch: conditions are favorable for severe weather • Warning: severe weather is currently occurring in the area • Watches and warnings are issued for: severe thunderstorms, hail, flash floods, and tornadoes
 Thunderstorms • Every Thunderstorm Needs: – Moisture – Unstable Air (warm air to rise rapidly) – Lift (cold front) • There are three stages in the life cycle of a thunderstorm – Developing (Cumulus) stage – Mature stage – Dissipating stage
Thunderstorms • Every Thunderstorm Needs: – Moisture – Unstable Air (warm air to rise rapidly) – Lift (cold front) • There are three stages in the life cycle of a thunderstorm – Developing (Cumulus) stage – Mature stage – Dissipating stage
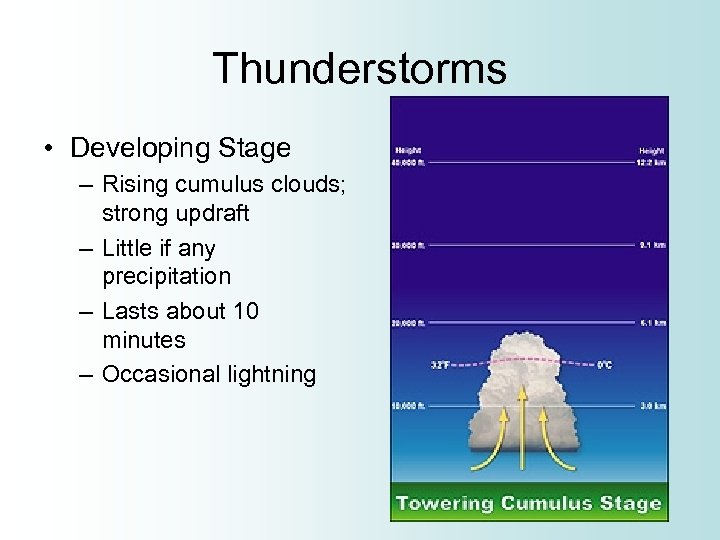 Thunderstorms • Developing Stage – Rising cumulus clouds; strong updraft – Little if any precipitation – Lasts about 10 minutes – Occasional lightning
Thunderstorms • Developing Stage – Rising cumulus clouds; strong updraft – Little if any precipitation – Lasts about 10 minutes – Occasional lightning
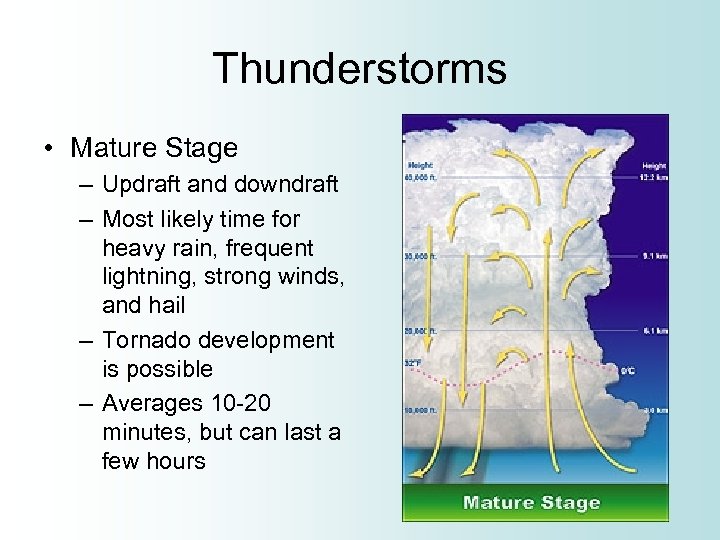 Thunderstorms • Mature Stage – Updraft and downdraft – Most likely time for heavy rain, frequent lightning, strong winds, and hail – Tornado development is possible – Averages 10 -20 minutes, but can last a few hours
Thunderstorms • Mature Stage – Updraft and downdraft – Most likely time for heavy rain, frequent lightning, strong winds, and hail – Tornado development is possible – Averages 10 -20 minutes, but can last a few hours
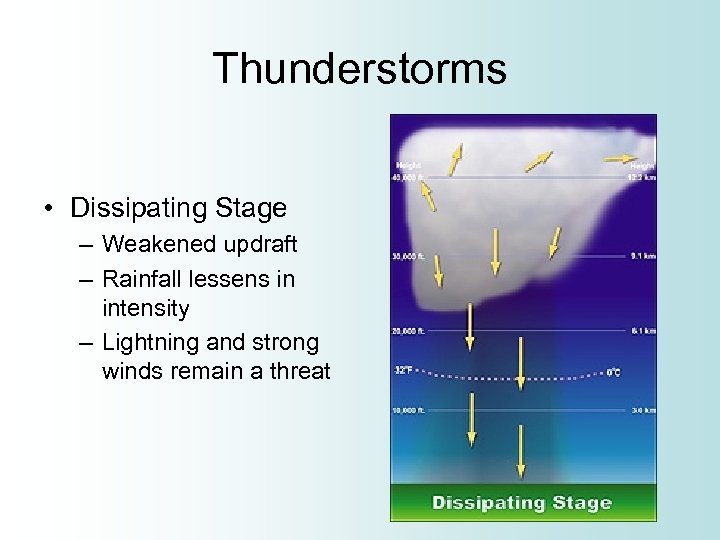 Thunderstorms • Dissipating Stage – Weakened updraft – Rainfall lessens in intensity – Lightning and strong winds remain a threat
Thunderstorms • Dissipating Stage – Weakened updraft – Rainfall lessens in intensity – Lightning and strong winds remain a threat
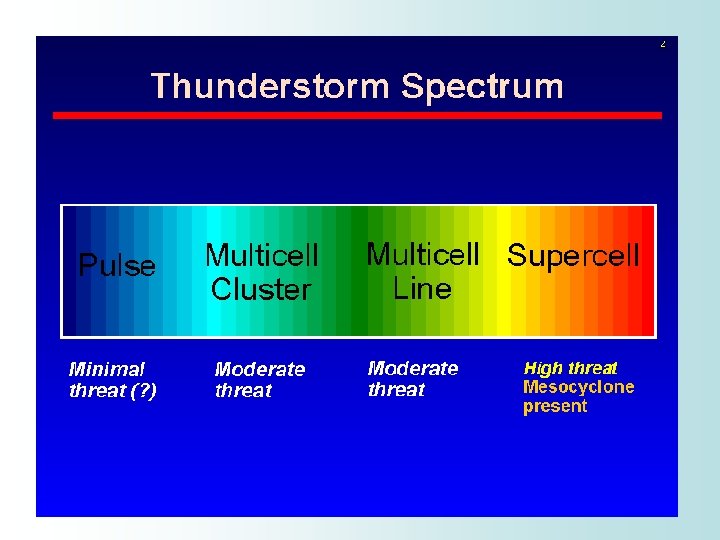
 Types of Thunderstorms • Single Cell (Pulse): – Generally weak, short lived, and poorly organized • Multicell Cluster: – Most common type – Series of cells moving as one unit • Multicell Line: – AKA “Squall Line” – Long line of storms with gust front at leading edge • Supercell: – Very strong and produce severe weather
Types of Thunderstorms • Single Cell (Pulse): – Generally weak, short lived, and poorly organized • Multicell Cluster: – Most common type – Series of cells moving as one unit • Multicell Line: – AKA “Squall Line” – Long line of storms with gust front at leading edge • Supercell: – Very strong and produce severe weather
 Types of Thunderstorms • A thunderstorm is classified as severe if it has any of the following characteristics – Hail greater than 0. 75” in diameter (dime size) – Winds greater than 58 miles per hour – Tornado
Types of Thunderstorms • A thunderstorm is classified as severe if it has any of the following characteristics – Hail greater than 0. 75” in diameter (dime size) – Winds greater than 58 miles per hour – Tornado
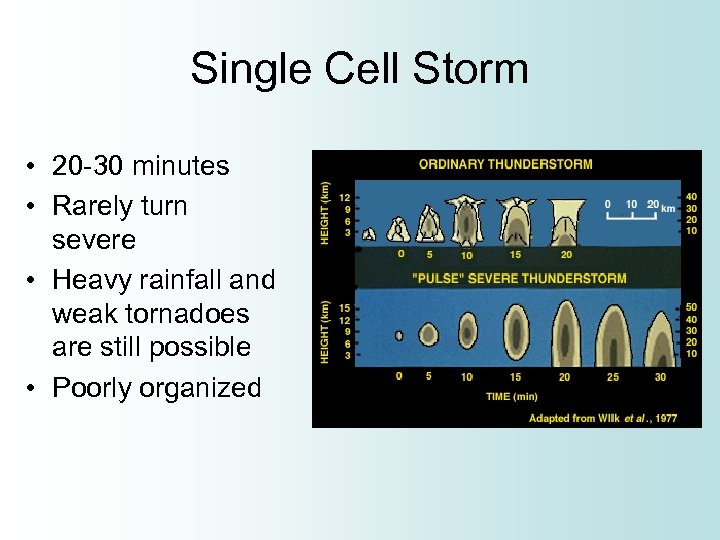 Single Cell Storm • 20 -30 minutes • Rarely turn severe • Heavy rainfall and weak tornadoes are still possible • Poorly organized
Single Cell Storm • 20 -30 minutes • Rarely turn severe • Heavy rainfall and weak tornadoes are still possible • Poorly organized
 Single Cell Storm
Single Cell Storm
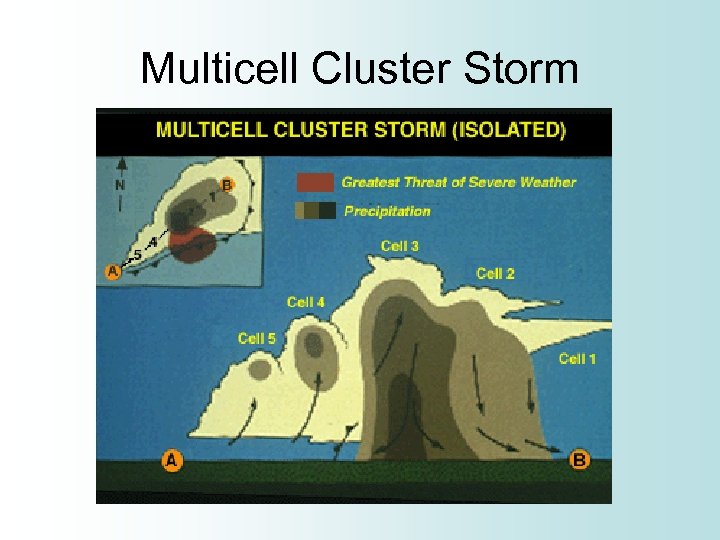
 Multicell Cluster Storm • Most common type of thunderstorm • Each cell in the cluster is at a different stage of the thunderstorm life cycle • Each cell may last 20 minutes, but each cluster can last several hours • Heavy rain, downbursts, moderate sized hail, occasional weak tornadoes
Multicell Cluster Storm • Most common type of thunderstorm • Each cell in the cluster is at a different stage of the thunderstorm life cycle • Each cell may last 20 minutes, but each cluster can last several hours • Heavy rain, downbursts, moderate sized hail, occasional weak tornadoes
 Multicell Cluster Storm
Multicell Cluster Storm
 Multicell Cluster Storm
Multicell Cluster Storm
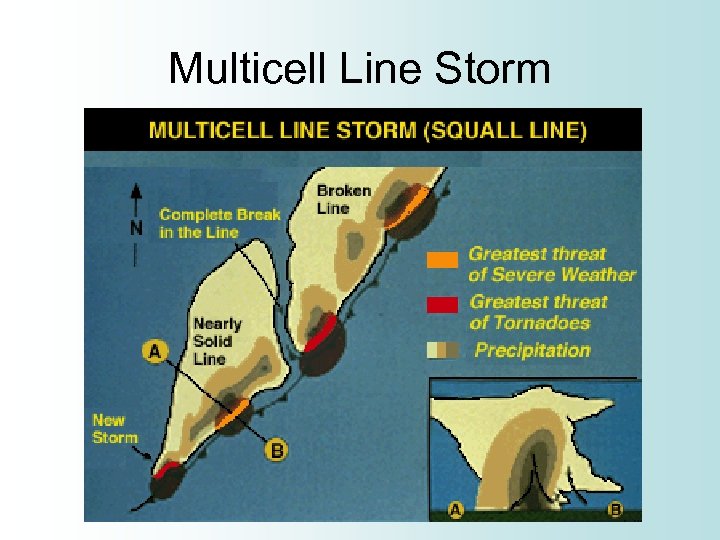
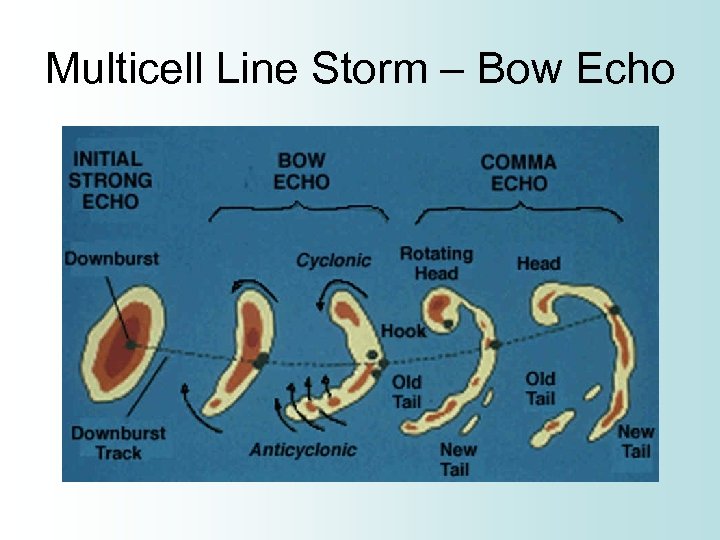
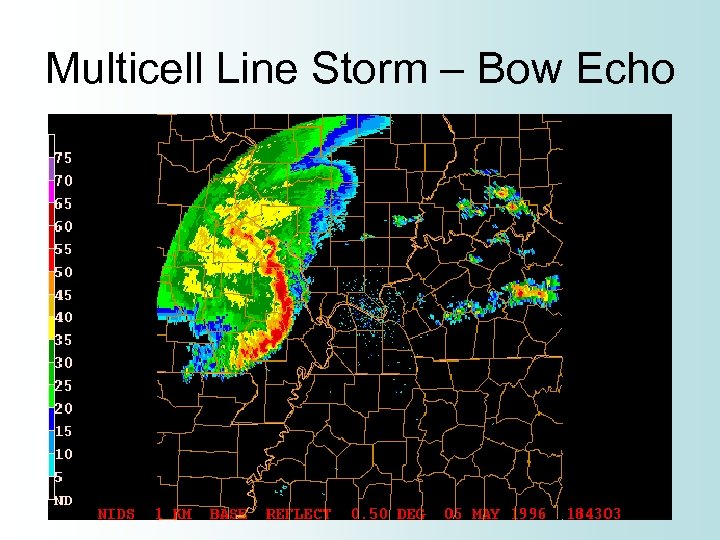
 Multicell Line Storm • Squall Line • Long line of storms with a continuous, well developed gust front at leading edge of the line • Heaviest rain is at center of line • Produce heavy rain, hail, and tornadoes • Strong downbursts can cause line to bend and become a “bow echo”
Multicell Line Storm • Squall Line • Long line of storms with a continuous, well developed gust front at leading edge of the line • Heaviest rain is at center of line • Produce heavy rain, hail, and tornadoes • Strong downbursts can cause line to bend and become a “bow echo”
 Multicell Line Storm
Multicell Line Storm
 Multicell Line Storm
Multicell Line Storm
 Multicell Line Storm – Bow Echo
Multicell Line Storm – Bow Echo
 Multicell Line Storm – Bow Echo
Multicell Line Storm – Bow Echo
 Supercell Thunderstorm • Rarest type of thunderstorm, but the most dangerous • The updraft rotates (called mesocyclone) • Large hail • Heavy downpours • Strong downbursts • Strong to violent tornadoes
Supercell Thunderstorm • Rarest type of thunderstorm, but the most dangerous • The updraft rotates (called mesocyclone) • Large hail • Heavy downpours • Strong downbursts • Strong to violent tornadoes
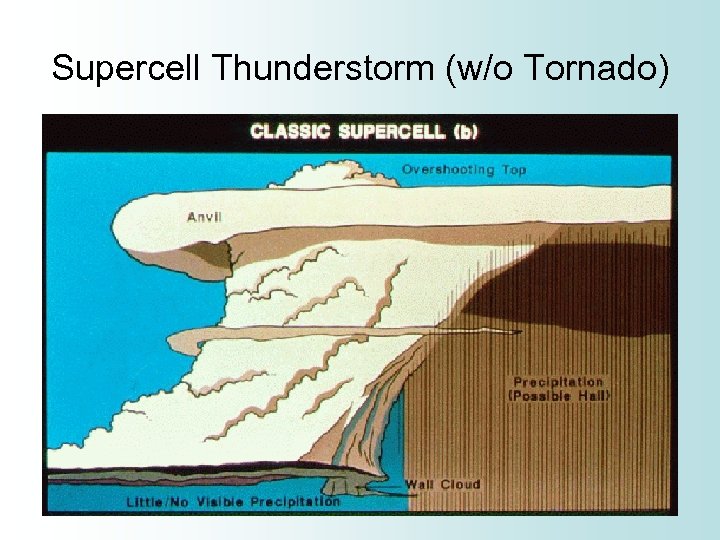 Supercell Thunderstorm (w/o Tornado)
Supercell Thunderstorm (w/o Tornado)
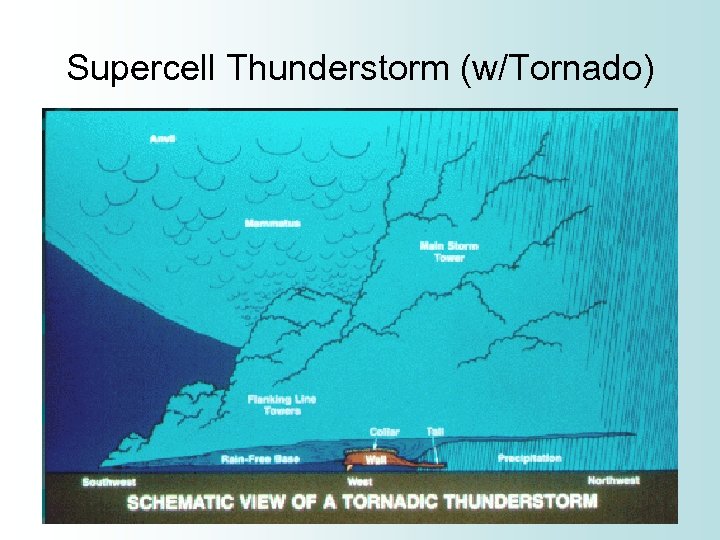 Supercell Thunderstorm (w/Tornado)
Supercell Thunderstorm (w/Tornado)
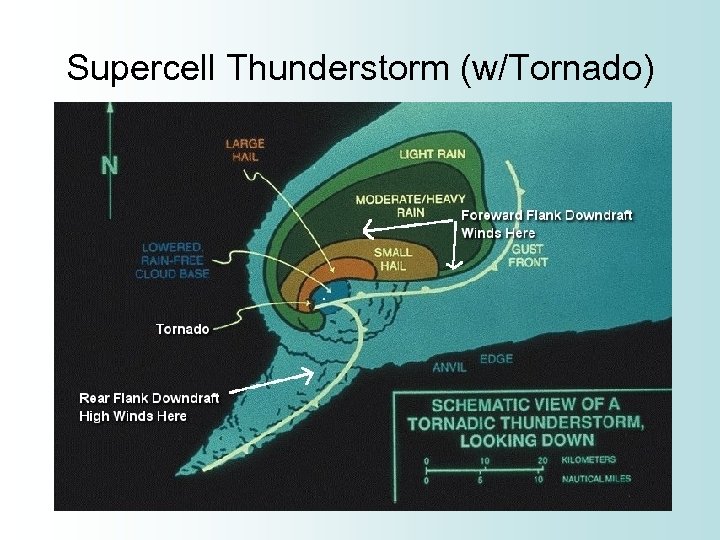 Supercell Thunderstorm (w/Tornado)
Supercell Thunderstorm (w/Tornado)
 Supercell Thunderstorm
Supercell Thunderstorm
 Dangers of Thunderstorms • • • Flash Floods Lightning Hail Downbursts Tornadoes
Dangers of Thunderstorms • • • Flash Floods Lightning Hail Downbursts Tornadoes
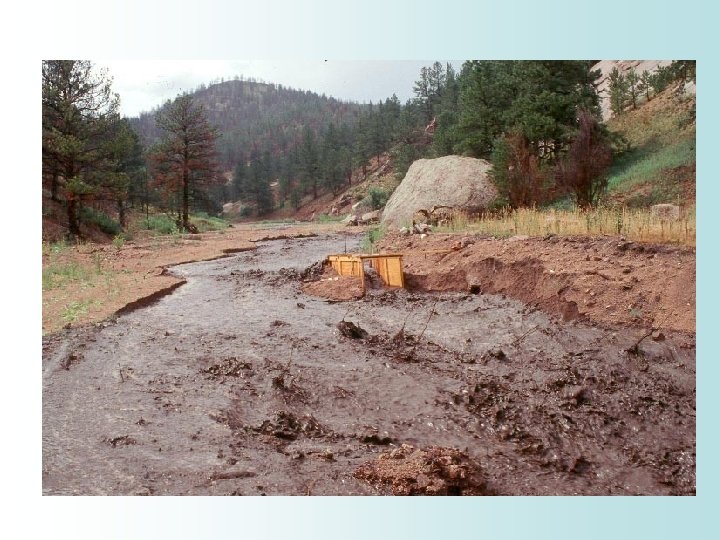
 Flash Floods • #1 cause of death associated with thunderstorms • An average of 140 fatalities every year (in US) • Definition: a rapid rise in water (creeks, streams, drainage ditches) within 12 hours of a period of heavy rain – – As little as 6 inches can knock a human over Two feet of water can move a car “Turn Around, Don’t Drown” Get to higher ground immediately
Flash Floods • #1 cause of death associated with thunderstorms • An average of 140 fatalities every year (in US) • Definition: a rapid rise in water (creeks, streams, drainage ditches) within 12 hours of a period of heavy rain – – As little as 6 inches can knock a human over Two feet of water can move a car “Turn Around, Don’t Drown” Get to higher ground immediately

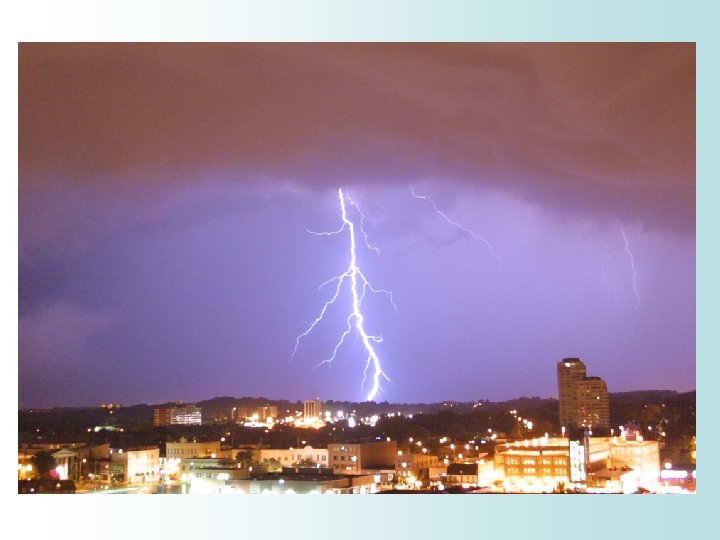
 Lightning • Lightning occurs in all thunderstorms • Causes an average of 80 fatalities and 300 injuries per year (in the US) • Lightning strikes the tallest object – If caught outside crouch down in a ball • 30/30 Rule – Go indoors if you hear thunder before counting to 30 after you see lightning – Wait inside for 30 minutes after you last hear thunder
Lightning • Lightning occurs in all thunderstorms • Causes an average of 80 fatalities and 300 injuries per year (in the US) • Lightning strikes the tallest object – If caught outside crouch down in a ball • 30/30 Rule – Go indoors if you hear thunder before counting to 30 after you see lightning – Wait inside for 30 minutes after you last hear thunder

 Hail • Rarely causes fatalities, but causes significant damage to property and crops • Can fall at rates up to 100 miles per hour • Created by strong updrafts in thunderstorm
Hail • Rarely causes fatalities, but causes significant damage to property and crops • Can fall at rates up to 100 miles per hour • Created by strong updrafts in thunderstorm
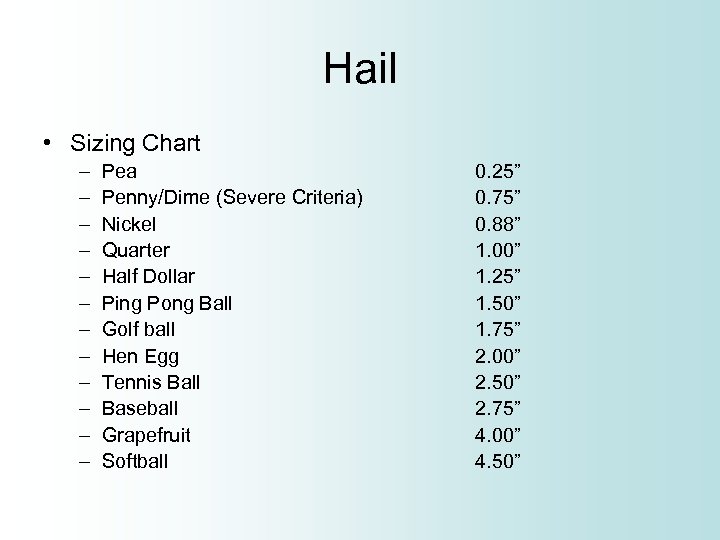 Hail • Sizing Chart – – – Pea Penny/Dime (Severe Criteria) Nickel Quarter Half Dollar Ping Pong Ball Golf ball Hen Egg Tennis Ball Baseball Grapefruit Softball 0. 25” 0. 75” 0. 88” 1. 00” 1. 25” 1. 50” 1. 75” 2. 00” 2. 50” 2. 75” 4. 00” 4. 50”
Hail • Sizing Chart – – – Pea Penny/Dime (Severe Criteria) Nickel Quarter Half Dollar Ping Pong Ball Golf ball Hen Egg Tennis Ball Baseball Grapefruit Softball 0. 25” 0. 75” 0. 88” 1. 00” 1. 25” 1. 50” 1. 75” 2. 00” 2. 50” 2. 75” 4. 00” 4. 50”
 Downbursts • A strong downdraft with an outrush of damaging winds at the surface • Winds can reach 100 miles per hour or more • Straight line winds • Winds speed and direction can change rapidly
Downbursts • A strong downdraft with an outrush of damaging winds at the surface • Winds can reach 100 miles per hour or more • Straight line winds • Winds speed and direction can change rapidly
 Downbursts
Downbursts
 Downbursts • Wind Speed Estimates (mph) – 25 -31: large branches in motion; whistling in telephone wires – 32 -38: whole trees in motion – 39 -54: twigs break off of trees; wind impedes walking – 55 -72: damage to chimneys and TV antennas; pushes over shallow rooted trees – 73 -112: peels surface off roofs; windows broken; trailer houses overturned – 113+: roofs torn off houses; weak building destroyed; large trees uprooted
Downbursts • Wind Speed Estimates (mph) – 25 -31: large branches in motion; whistling in telephone wires – 32 -38: whole trees in motion – 39 -54: twigs break off of trees; wind impedes walking – 55 -72: damage to chimneys and TV antennas; pushes over shallow rooted trees – 73 -112: peels surface off roofs; windows broken; trailer houses overturned – 113+: roofs torn off houses; weak building destroyed; large trees uprooted
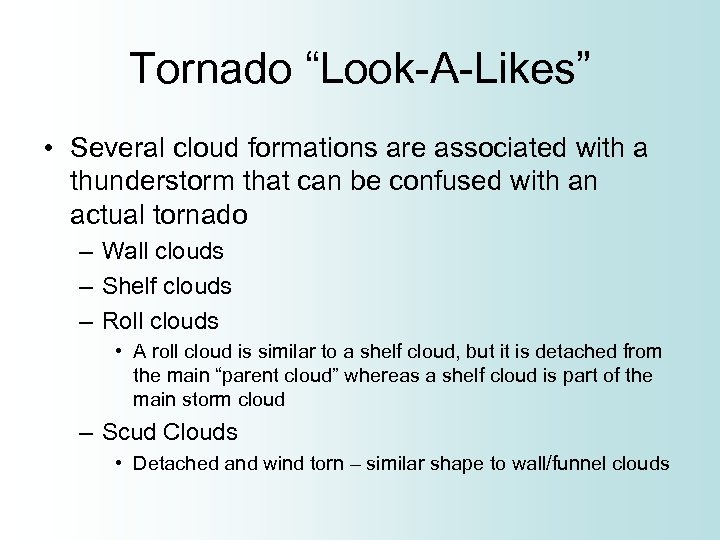 Tornado “Look-A-Likes” • Several cloud formations are associated with a thunderstorm that can be confused with an actual tornado – Wall clouds – Shelf clouds – Roll clouds • A roll cloud is similar to a shelf cloud, but it is detached from the main “parent cloud” whereas a shelf cloud is part of the main storm cloud – Scud Clouds • Detached and wind torn – similar shape to wall/funnel clouds
Tornado “Look-A-Likes” • Several cloud formations are associated with a thunderstorm that can be confused with an actual tornado – Wall clouds – Shelf clouds – Roll clouds • A roll cloud is similar to a shelf cloud, but it is detached from the main “parent cloud” whereas a shelf cloud is part of the main storm cloud – Scud Clouds • Detached and wind torn – similar shape to wall/funnel clouds
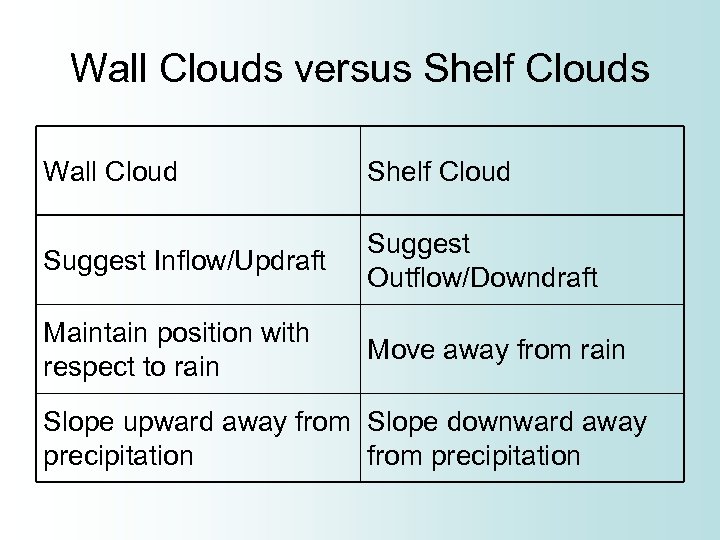 Wall Clouds versus Shelf Clouds Wall Cloud Shelf Cloud Suggest Inflow/Updraft Suggest Outflow/Downdraft Maintain position with respect to rain Move away from rain Slope upward away from Slope downward away precipitation from precipitation
Wall Clouds versus Shelf Clouds Wall Cloud Shelf Cloud Suggest Inflow/Updraft Suggest Outflow/Downdraft Maintain position with respect to rain Move away from rain Slope upward away from Slope downward away precipitation from precipitation
 Wall Cloud
Wall Cloud
 Wall Cloud • What is the tornado potential for a wall cloud? – It will be consistent, lasting 10 -20 minutes – It will have persistent rotation – Strong winds will blow into the wall cloud from the south or southeast (25 -35 mph) – It will exhibit evidence of rapid vertical motion • These are rules of thumb – there always exceptions!
Wall Cloud • What is the tornado potential for a wall cloud? – It will be consistent, lasting 10 -20 minutes – It will have persistent rotation – Strong winds will blow into the wall cloud from the south or southeast (25 -35 mph) – It will exhibit evidence of rapid vertical motion • These are rules of thumb – there always exceptions!
 Shelf Cloud
Shelf Cloud
 Roll Cloud
Roll Cloud
 Scud Cloud
Scud Cloud
 Tornadoes • A tornado is a violently rotating column of air in contact with the ground extending from a thunderstorm • May appear transparent until dirt and debris are picked up in the vortex or until a condensation cloud forms • A tornado that forms over a body of water is called a waterspout
Tornadoes • A tornado is a violently rotating column of air in contact with the ground extending from a thunderstorm • May appear transparent until dirt and debris are picked up in the vortex or until a condensation cloud forms • A tornado that forms over a body of water is called a waterspout
 Tornadoes • Tornadoes can occur at any time, any day, and in any state • They are most common – In tornado alley: Texas north to Nebraska and east to Indiana – During the spring and summer months – During the late afternoon and early evening
Tornadoes • Tornadoes can occur at any time, any day, and in any state • They are most common – In tornado alley: Texas north to Nebraska and east to Indiana – During the spring and summer months – During the late afternoon and early evening
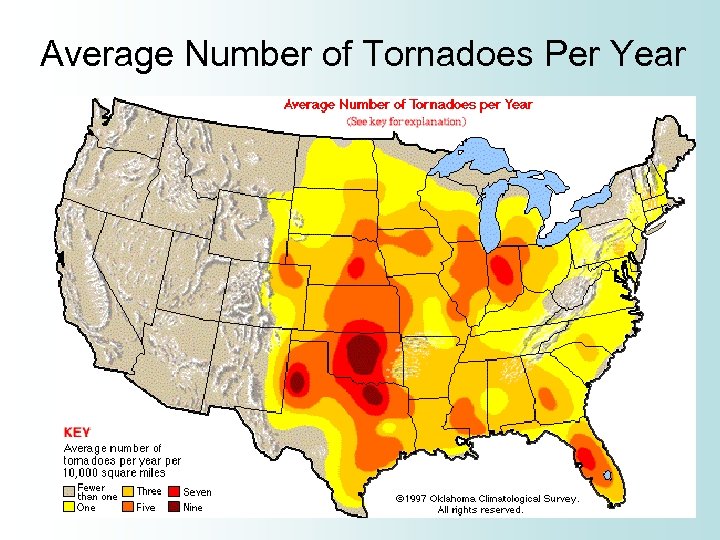 Average Number of Tornadoes Per Year
Average Number of Tornadoes Per Year
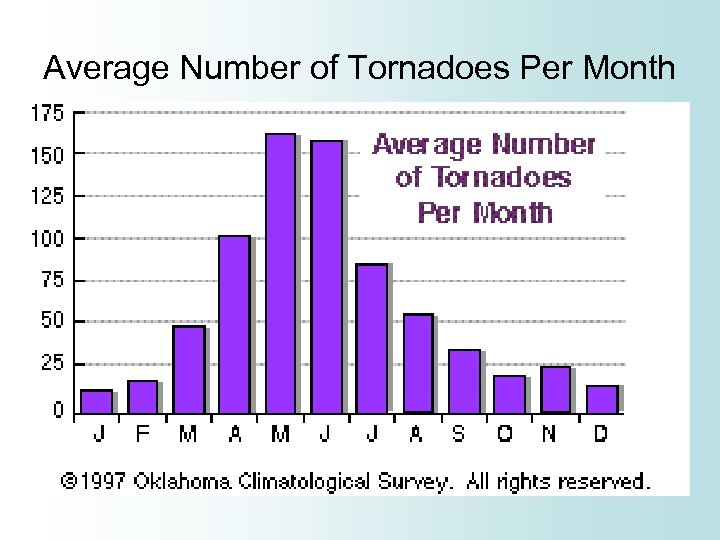 Average Number of Tornadoes Per Month
Average Number of Tornadoes Per Month
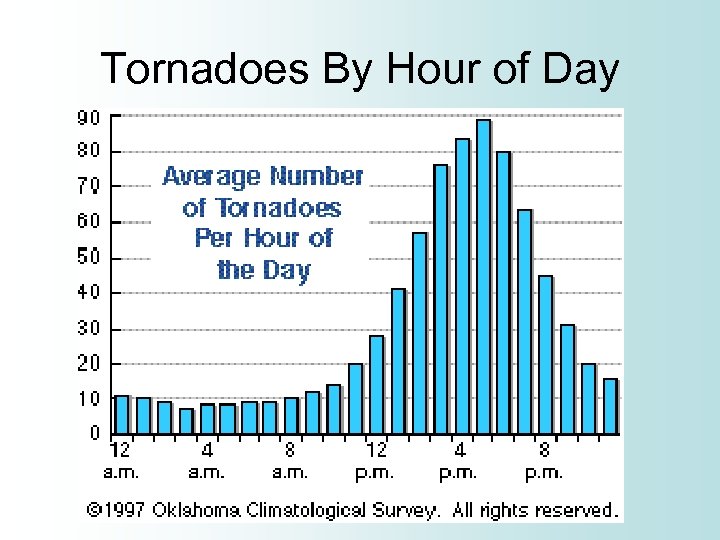 Tornadoes By Hour of Day
Tornadoes By Hour of Day
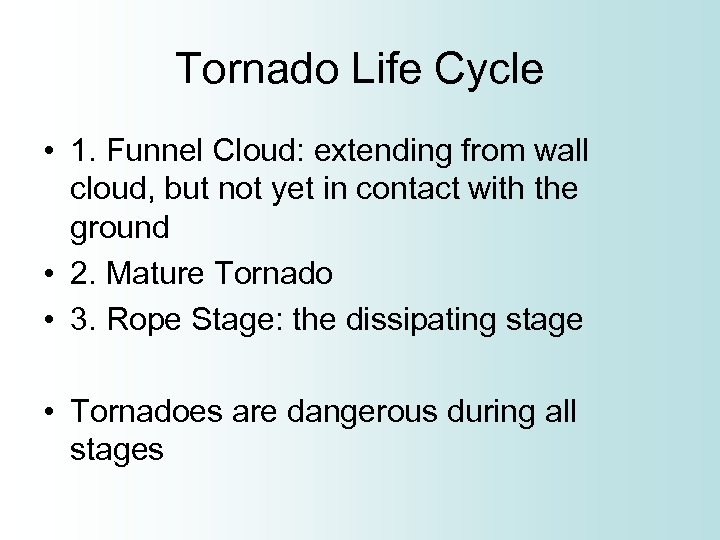 Tornado Life Cycle • 1. Funnel Cloud: extending from wall cloud, but not yet in contact with the ground • 2. Mature Tornado • 3. Rope Stage: the dissipating stage • Tornadoes are dangerous during all stages
Tornado Life Cycle • 1. Funnel Cloud: extending from wall cloud, but not yet in contact with the ground • 2. Mature Tornado • 3. Rope Stage: the dissipating stage • Tornadoes are dangerous during all stages
 Funnel Cloud
Funnel Cloud
 Mature Stage
Mature Stage
 Rope Tornado
Rope Tornado
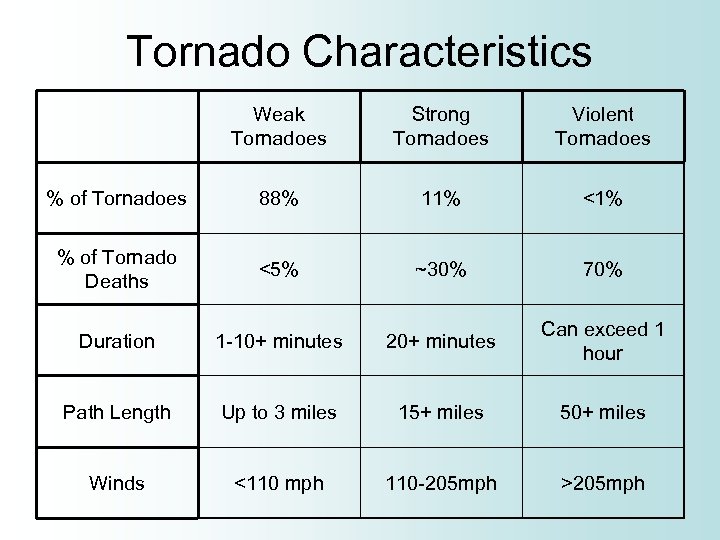 Tornado Characteristics Weak Tornadoes Strong Tornadoes Violent Tornadoes % of Tornadoes 88% 11% <1% % of Tornado Deaths <5% ~30% 70% Duration 1 -10+ minutes 20+ minutes Can exceed 1 hour Path Length Up to 3 miles 15+ miles 50+ miles Winds <110 mph 110 -205 mph >205 mph
Tornado Characteristics Weak Tornadoes Strong Tornadoes Violent Tornadoes % of Tornadoes 88% 11% <1% % of Tornado Deaths <5% ~30% 70% Duration 1 -10+ minutes 20+ minutes Can exceed 1 hour Path Length Up to 3 miles 15+ miles 50+ miles Winds <110 mph 110 -205 mph >205 mph
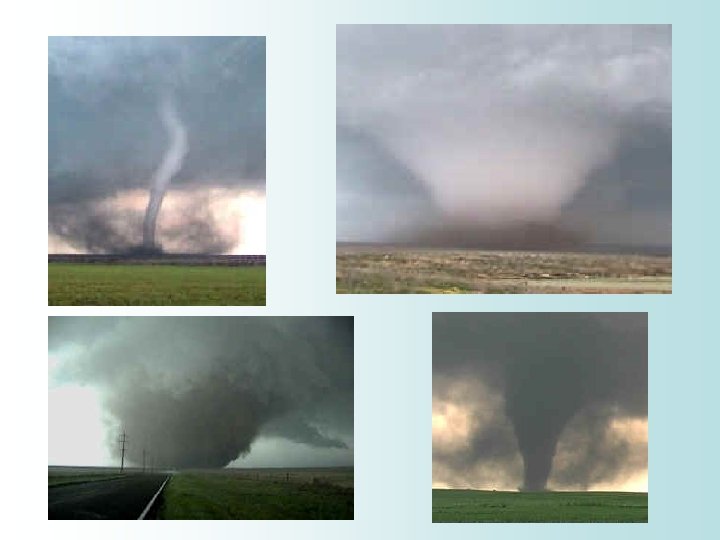

 Tornadoes • Tornadoes are always dangerous regardless of shape, size, or color • Large cities and mountains are just as prone to tornadoes as wide open fields • Average tornado speed is 30 mph, but they can move as fast as 70 mph – Do not attempt to outrun a tornado, find shelter immediately
Tornadoes • Tornadoes are always dangerous regardless of shape, size, or color • Large cities and mountains are just as prone to tornadoes as wide open fields • Average tornado speed is 30 mph, but they can move as fast as 70 mph – Do not attempt to outrun a tornado, find shelter immediately
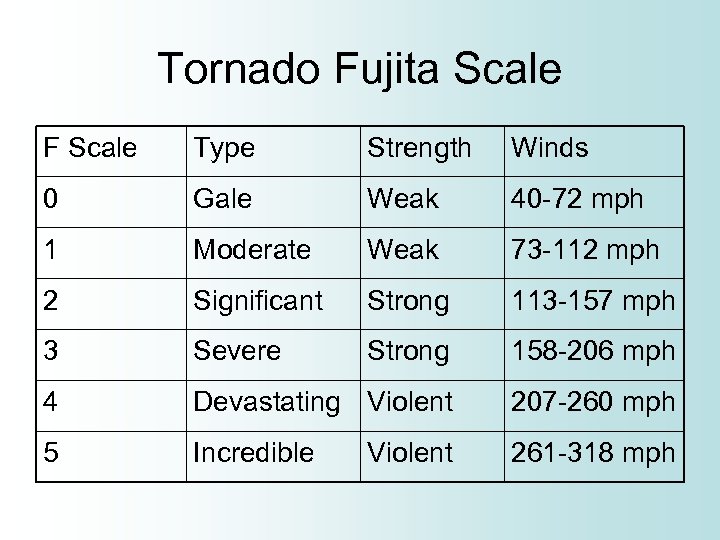 Tornado Fujita Scale F Scale Type Strength Winds 0 Gale Weak 40 -72 mph 1 Moderate Weak 73 -112 mph 2 Significant Strong 113 -157 mph 3 Severe Strong 158 -206 mph 4 Devastating Violent 207 -260 mph 5 Incredible 261 -318 mph Violent
Tornado Fujita Scale F Scale Type Strength Winds 0 Gale Weak 40 -72 mph 1 Moderate Weak 73 -112 mph 2 Significant Strong 113 -157 mph 3 Severe Strong 158 -206 mph 4 Devastating Violent 207 -260 mph 5 Incredible 261 -318 mph Violent
 Severe Weather Alerts • During periods of severe weather it is important to keep an eye on the sky • Local television, radio, and the Internet are vital sources of information • A S. A. M. E NOAA weather radio is essential for immediate watches and warnings
Severe Weather Alerts • During periods of severe weather it is important to keep an eye on the sky • Local television, radio, and the Internet are vital sources of information • A S. A. M. E NOAA weather radio is essential for immediate watches and warnings


