 Seven Principles of the United States Constitution
Seven Principles of the United States Constitution
 Poor Ruth Feels She Can’t Like Insects P R R F S R C L I
Poor Ruth Feels She Can’t Like Insects P R R F S R C L I
 P= Popular Sovereignty The people are in charge – show this by voting for or against laws
P= Popular Sovereignty The people are in charge – show this by voting for or against laws
 Example: schools have bond elections to approve raising school taxes in order to build more schools or buy more technology
Example: schools have bond elections to approve raising school taxes in order to build more schools or buy more technology
 R= Republicanism People vote for representatives to speak for us and make decisions for our government
R= Republicanism People vote for representatives to speak for us and make decisions for our government
 Example: House of Reps, Senate, Texas House of Reps, Texas Senate
Example: House of Reps, Senate, Texas House of Reps, Texas Senate
 F= Federalism The sharing of power between the national (Washington, D. C. ) and state governments (Austin, TX)
F= Federalism The sharing of power between the national (Washington, D. C. ) and state governments (Austin, TX)
 There are 3 types of powers:
There are 3 types of powers:
 Delegated powers - given only to the national government by the constitution Power to coin money Power to declare war
Delegated powers - given only to the national government by the constitution Power to coin money Power to declare war
 Reserved powers – powers only the state have Power to establish schools Power to build roads
Reserved powers – powers only the state have Power to establish schools Power to build roads
 Concurrent powers are powers shared by the national and state governments Power to tax Power to make laws
Concurrent powers are powers shared by the national and state governments Power to tax Power to make laws
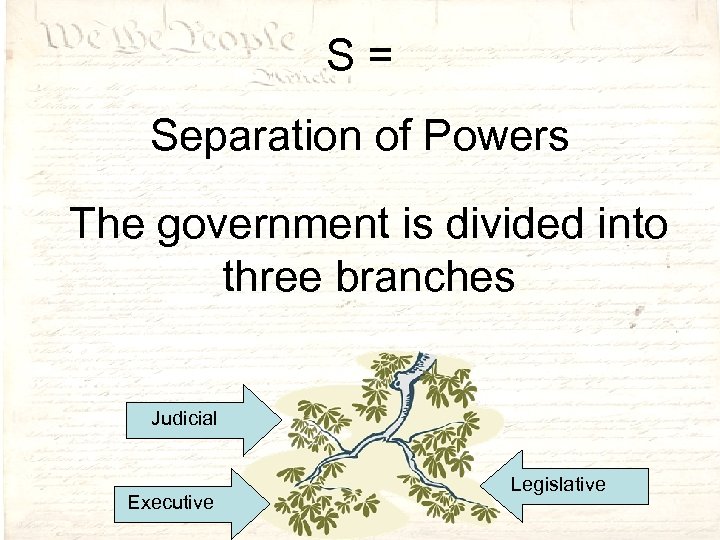 S= Separation of Powers The government is divided into three branches Judicial Executive Legislative
S= Separation of Powers The government is divided into three branches Judicial Executive Legislative
 Judicial branch: All federal courts including the Supreme Court, interpret the laws
Judicial branch: All federal courts including the Supreme Court, interpret the laws
 Executive branch: The President and his Cabinet – enforce the laws
Executive branch: The President and his Cabinet – enforce the laws
 Legislative branch: The two parts of Congress – the House of Representatives and the Senate – make the laws
Legislative branch: The two parts of Congress – the House of Representatives and the Senate – make the laws
 C= Checks and Balances No branch has more power than the other two
C= Checks and Balances No branch has more power than the other two
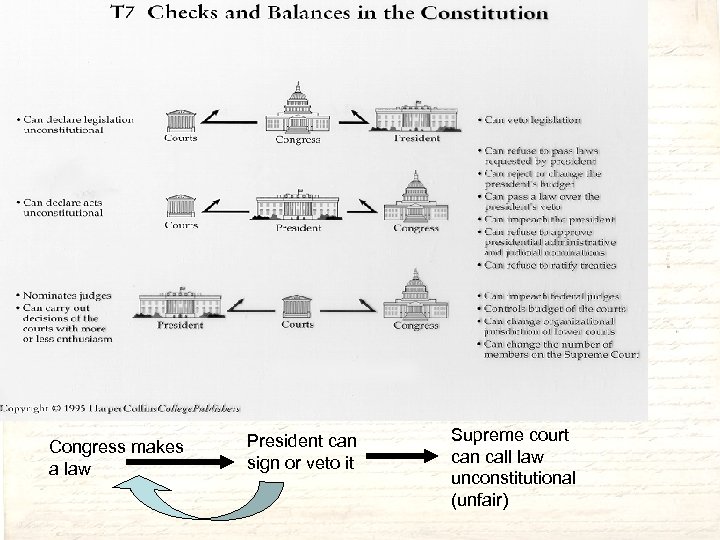 Congress makes a law President can sign or veto it Supreme court can call law unconstitutional (unfair)
Congress makes a law President can sign or veto it Supreme court can call law unconstitutional (unfair)
 L= Limited Government Everyone must obey the same laws Yes, we pay I still have to can! my taxes?
L= Limited Government Everyone must obey the same laws Yes, we pay I still have to can! my taxes?
 I= Individual Rights Personal liberties and privileges
I= Individual Rights Personal liberties and privileges
 The Bill of Rights protects the individual rights of citizens.
The Bill of Rights protects the individual rights of citizens.