f78b223f6f6afecd3d36a974d9339c87.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24

Seven Keys 16 September 2009 © Pv. N 1 45
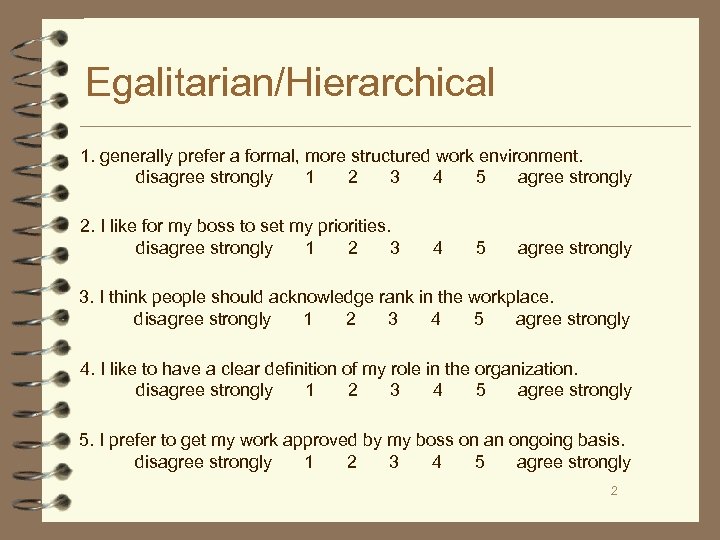
Egalitarian/Hierarchical 1. generally prefer a formal, more structured work environment. disagree strongly 1 2 3 4 5 agree strongly 2. I like for my boss to set my priorities. disagree strongly 1 2 3 4 5 agree strongly 3. I think people should acknowledge rank in the workplace. disagree strongly 1 2 3 4 5 agree strongly 4. I like to have a clear definition of my role in the organization. disagree strongly 1 2 3 4 5 agree strongly 5. I prefer to get my work approved by my boss on an ongoing basis. disagree strongly 1 2 3 4 5 agree strongly 2

Group Focus 1. When confronted with a challenge, I prefer to it solve with a group. disagree strongly 1 2 3 4 5 agree strongly 2. I believe that team members should clear their work with each other disagree strongly 1 2 3 4 5 agree strongly 3. I prefer to be recognized as part of a team (rather than alone). disagree strongly 1 2 3 4 5 agree strongly 4. I like to sit in an open office environment. disagree strongly 1 2 3 4 5 agree strongly 5. I am most comfortable presenting a business plan as part of a team. disagree strongly 1 2 3 4 5 agree strongly 3

Relationships 1. I make friends easily. disagree strongly 1 2 3 4 5 agree strongly 2. I need to build trust with people before working with them. disagree strongly 1 2 3 4 5 agree strongly 3. When I make friends, I tend to keep them for a very long time. disagree strongly 1 2 3 4 5 agree strongly 4. I will try very hard to avoid a disagreement, even when that seems necessary. disagree strongly 1 2 3 4 5 agree strongly 5. When choosing team members, I pick my friends first. disagree strongly 1 2 3 4 5 agree strongly 4

Communication Styles 1. I like to communicate the full story with all the details to be sure I'm understood. disagree strongly 1 2 3 4 5 agree strongly 2. When giving feedback, I'm very careful not to hurt someone's feelings. disagree strongly 1 2 3 4 5 agree strongly 3. I look for more in a message than the words spoken. disagree strongly 1 2 3 4 5 agree strongly 4. I hate when people get right to the point without concern for the listener. disagree strongly 1 2 3 4 5 agree strongly 5. I don't think that being brief and concise is as important as being thorough and sensitive. disagree strongly 1 2 3 4 5 agree strongly 5

Time Orientation 1. I think that being prompt is a sign of respect and competence. disagree strongly 1 2 3 4 5 agree strongly 2. I think deadlines should be met regardless of the personal cost. disagree strongly 1 2 3 4 5 agree strongly 3. I think that meetings should start and end on time. disagree strongly 1 2 3 4 5 agree strongly 4. I think it's OK to interrupt people who take too long. disagree strongly 1 2 3 4 5 agree strongly 5. I see time as being completely in my control. disagree strongly 1 2 3 4 5 agree strongly 6. I think time management is an important skill. disagree strongly 1 2 3 4 5 agree strongly 6
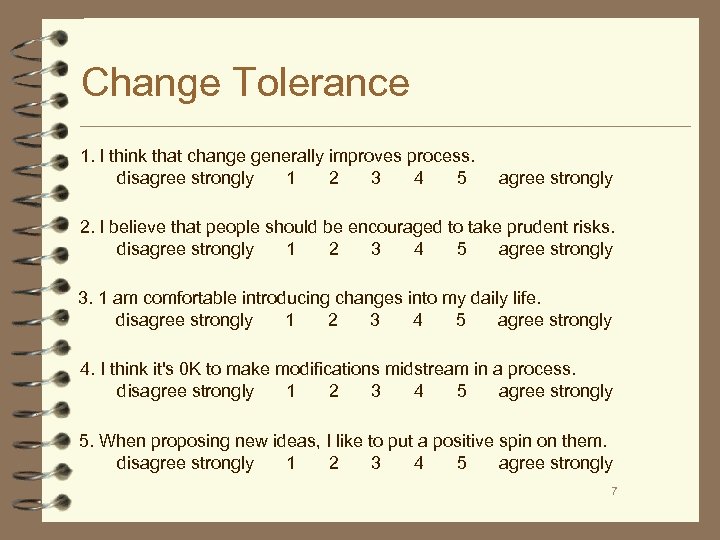
Change Tolerance 1. I think that change generally improves process. disagree strongly 1 2 3 4 5 agree strongly 2. I believe that people should be encouraged to take prudent risks. disagree strongly 1 2 3 4 5 agree strongly 3. 1 am comfortable introducing changes into my daily life. disagree strongly 1 2 3 4 5 agree strongly 4. I think it's 0 K to make modifications midstream in a process. disagree strongly 1 2 3 4 5 agree strongly 5. When proposing new ideas, I like to put a positive spin on them. disagree strongly 1 2 3 4 5 agree strongly 7

Motivation/Work-Life Balance 1. I don't think that work should intrude on personal time. disagree strongly 1 2 3 4 5 agree strongly 2. I identify myself more by my personal life than my work life. disagree strongly 1 2 3 4 5 agree strongly 3. I believe the adage "I work to live, not live to work" is correct. disagree strongly 1 2 3 4 5 agree strongly 4. I believe that personal stature is gained by my interests and my education, not from the workplace. disagree strongly 1 2 3 4 5 agree strongly 5. I am not prepared to sacrifice family time for promotions at work. disagree strongly 1 2 3 4 5 agree strongly 8
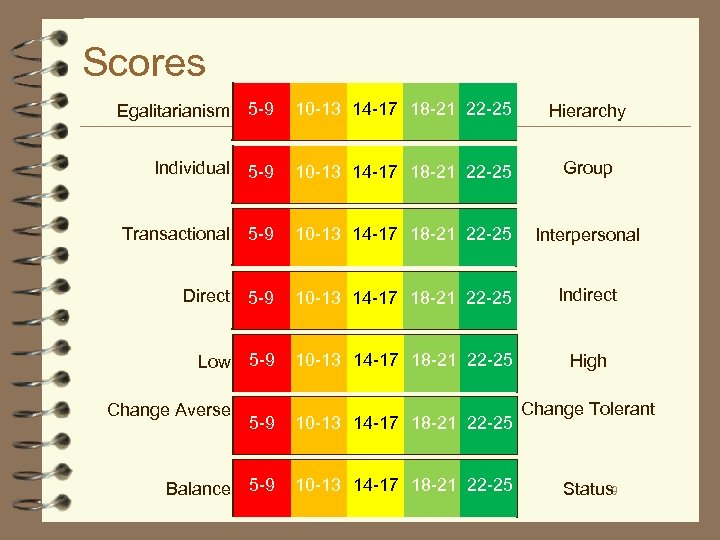
Scores Egalitarianism 5 -9 10 -13 14 -17 18 -21 22 -25 Hierarchy Individual 5 -9 10 -13 14 -17 18 -21 22 -25 Group Transactional 5 -9 10 -13 14 -17 18 -21 22 -25 Interpersonal Direct 5 -9 10 -13 14 -17 18 -21 22 -25 Indirect Low 5 -9 10 -13 14 -17 18 -21 22 -25 High Change Averse Balance 5 -9 10 -13 14 -17 18 -21 22 -25 Change Tolerant Status 9
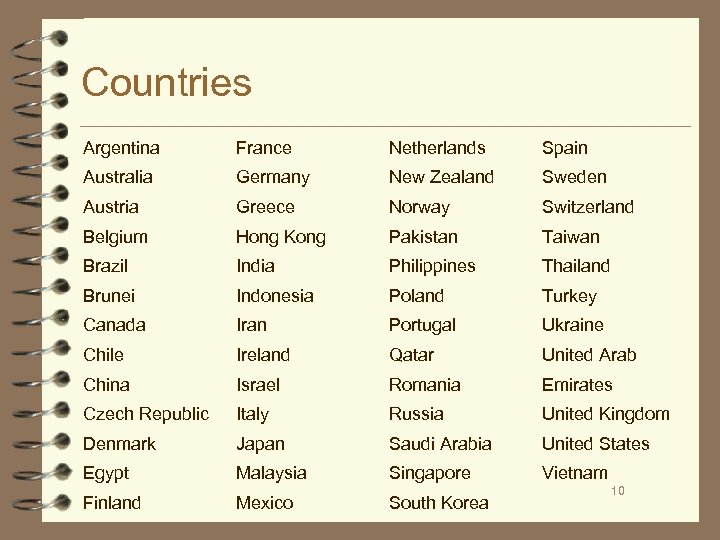
Countries Argentina France Netherlands Spain Australia Germany New Zealand Sweden Austria Greece Norway Switzerland Belgium Hong Kong Pakistan Taiwan Brazil India Philippines Thailand Brunei Indonesia Poland Turkey Canada Iran Portugal Ukraine Chile Ireland Qatar United Arab China Israel Romania Emirates Czech Republic Italy Russia United Kingdom Denmark Japan Saudi Arabia United States Egypt Malaysia Singapore Vietnam Finland Mexico South Korea 10

Egalitarian/Hierarchical ■ Hierarchy/egalitarianism is the way individuals view authority and power (deference to people in authority). ■ whether people are entitled to express themselves ■ how empowered people feel to make independent decisions and take the initiative ■ Are people in authority better or have they earned that status by merit, and is it open to other with the same degree of effort? ■ Hierarchy/egalitarianism refers to ■ how people view their relationship to people in power ■ how casually or formally people relate one another ■ whether a culture believes all people are created equal ■ how much social mobility exists ■ who is responsible for decision making ■ the degree of authority and personal initiative people feel they have 11
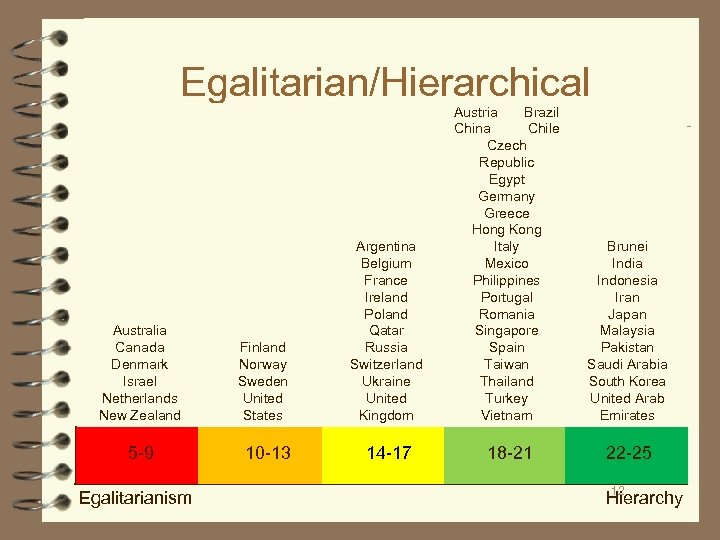
Egalitarian/Hierarchical Australia Canada Denmark Israel Netherlands New Zealand 5 -9 Egalitarianism Finland Norway Sweden United States 10 -13 Argentina Belgium France Ireland Poland Qatar Russia Switzerland Ukraine United Kingdom Austria Brazil China Chile Czech Republic Egypt Germany Greece Hong Kong Italy Mexico Philippines Portugal Romania Singapore Spain Taiwan Thailand Turkey Vietnam Brunei India Indonesia Iran Japan Malaysia Pakistan Saudi Arabia South Korea United Arab Emirates 14 -17 18 -21 22 -25 12 Hierarchy

Group Focus ■ Group focus describes whether people identify themselves as part of a group or by their individual responsibility and whether work would be a collective output or a series of individual contributions. ■ Group focus refers to ■ the importance of the group in relation to the individual ■ whether people want to be distinguished from the group or considered part of a particular group ■ the idea that group harmony is necessary to achieve business goals ■ the importance of living and working together in harmony 13

Group Focus Canada New Zealand United States 5 -9 Individual Australia Belgium Czech Republic Denmark Finland Netherlands Norway Poland Switzerland 10 -13 Argentina Chile France Germany Hong Kong India Iran Ireland Israel Portugal Romania Russia Spain Sweden Ukraine United Kingdom Austria Brazil China Egypt Greece Italy Mexico Pakistan Philippines Saudi Arabia Singapore Taiwan Thailand Turkey United Arab Emirates Brunei Indonesia Japan Malaysia Qatar South Korea Vietnam 14 -17 18 -21 22 -25 14 Group

Relationships ■ The relationships dimension describes the importance a society ascribes to building extensive connections and developing trust and how central relationships are as a prerequisite to working with someone. ■ Relationships refer to ■ the importance of developing a personal relationship before conducting business ■ the implied expectations and obligations of a relationship ■ whether trust is assumed or earned ■ whether rules are interpreted equally or there are special conditiions for friends ■ the value of connections 15
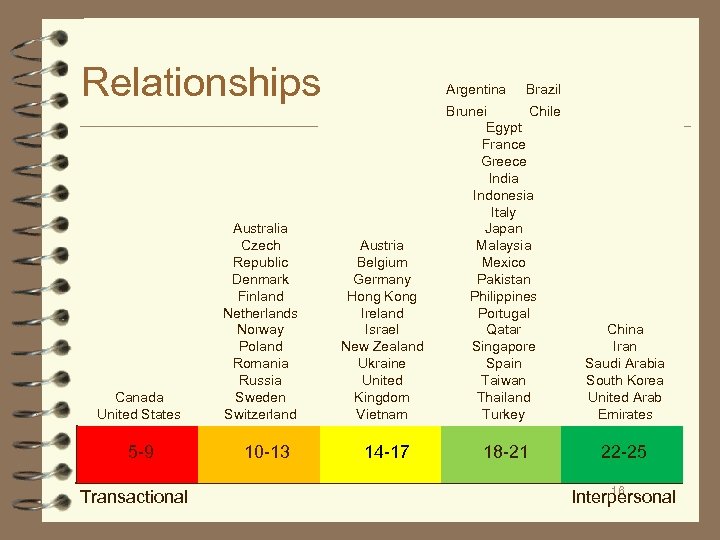
Relationships Canada United States 5 -9 Transactional Australia Czech Republic Denmark Finland Netherlands Norway Poland Romania Russia Sweden Switzerland 10 -13 Argentina Austria Belgium Germany Hong Kong Ireland Israel New Zealand Ukraine United Kingdom Vietnam 14 -17 Brazil Brunei Chile Egypt France Greece India Indonesia Italy Japan Malaysia Mexico Pakistan Philippines Portugal Qatar Singapore Spain Taiwan Thailand Turkey China Iran Saudi Arabia South Korea United Arab Emirates 18 -21 22 -25 16 Interpersonal

Communication Styles ■ Communication styles refer to ■ the ways societies use language, both verbal and non-verbal ■ the amount of information people need to receive or share in order to understand a message. Is it brief and task-relevant, or does it include background information as well? ■ the directness or subtleness of the language people use ■ the way people use words or gestures to express feeling or moods ■ the importance of harmony and saving face 17
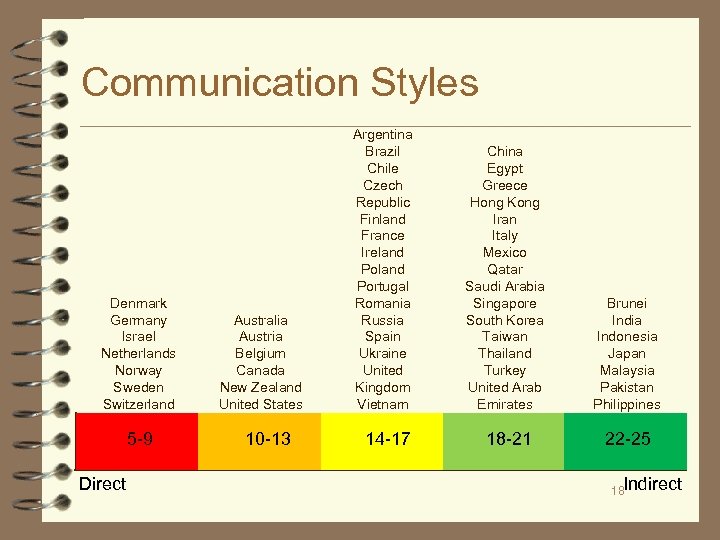
Communication Styles Denmark Germany Israel Netherlands Norway Sweden Switzerland 5 -9 Direct Australia Austria Belgium Canada New Zealand United States 10 -13 Argentina Brazil Chile Czech Republic Finland France Ireland Portugal Romania Russia Spain Ukraine United Kingdom Vietnam 14 -17 China Egypt Greece Hong Kong Iran Italy Mexico Qatar Saudi Arabia Singapore South Korea Taiwan Thailand Turkey United Arab Emirates Brunei India Indonesia Japan Malaysia Pakistan Philippines 18 -21 22 -25 18 Indirect

Time Orientation ■ Time orientation is the degree to which people believe they can control time and whether schedules or people are more important. It affects time management, long- and short-term planning, schedules, and adherence to agendas and deadlines. ■ Time orientation refers to ■ the amount of control people feel they have over time. Do you control time, or is it out of your control? ■ the importance society places on relationships versus keeping schedules ■ attitude toward timekeeping and punctuality ■ comfort level with short-range versus longer-term planning ■ the appropriateness of assigning set times for social functions or business meeting to start and finish 19
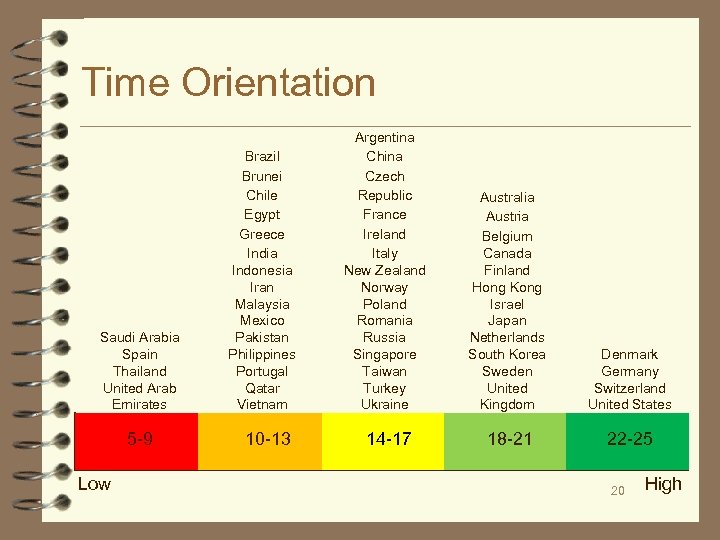
Time Orientation Saudi Arabia Spain Thailand United Arab Emirates 5 -9 Low Brazil Brunei Chile Egypt Greece India Indonesia Iran Malaysia Mexico Pakistan Philippines Portugal Qatar Vietnam 10 -13 Argentina China Czech Republic France Ireland Italy New Zealand Norway Poland Romania Russia Singapore Taiwan Turkey Ukraine 14 -17 Australia Austria Belgium Canada Finland Hong Kong Israel Japan Netherlands South Korea Sweden United Kingdom Denmark Germany Switzerland United States 18 -21 22 -25 20 High

Change Tolerance ■ Change tolerance refers to the perception of how much control we believe we have our lives and destinies (is our life determined by us or by external forces? ) and our comfort level with change, innovation, and risk taking. Do we see change as bringing opportunities or as threats to be avoided? ■ Change tolerance refers to ■ openness to change and innovation ■ willingness to take risks ■ if people feel they control their destiny or if their environment controls them ■ preference for rules and structure ■ how the organization encourages and rewards initiative and deals with failure 21
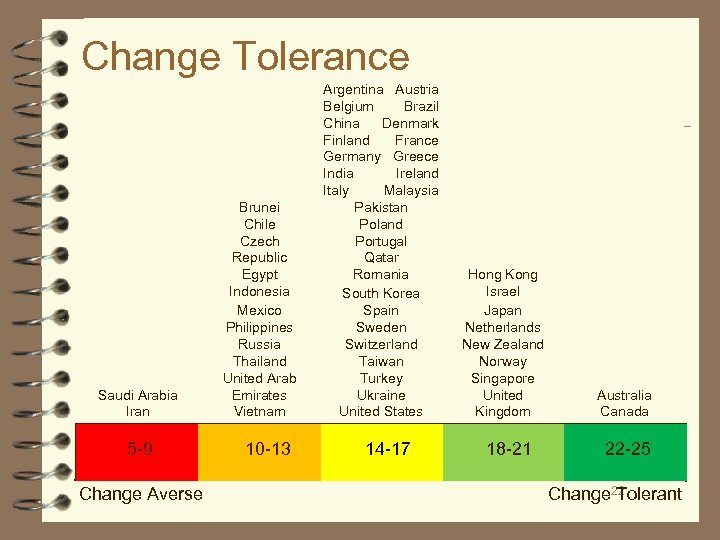
Change Tolerance Saudi Arabia Iran 5 -9 Change Averse Brunei Chile Czech Republic Egypt Indonesia Mexico Philippines Russia Thailand United Arab Emirates Vietnam 10 -13 Argentina Austria Belgium Brazil China Denmark Finland France Germany Greece India Ireland Italy Malaysia Pakistan Poland Portugal Qatar Romania South Korea Spain Sweden Switzerland Taiwan Turkey Ukraine United States 14 -17 Hong Kong Israel Japan Netherlands New Zealand Norway Singapore United Kingdom 18 -21 Australia Canada 22 -25 Change 22 Tolerant

Motivation/Work-Life Balance ■ Motivation/work-life balance describes the emphasis that people in a society place on achievement and status by hard work, versus the focus on personal time and activities. ■ Motivation/work-life balance refers to □ how people identify the ways they gain status, whether through achievement or personal life; how people define their status in society, whether from personal life or work achievements □ how one’s work influences one’s self-image and selfperception □ motivation for success: why people work and what I means □ how much work-life balance is values □ which is more motivating: time off or a promotionthe presence or absence of laws and policies promoting family benefits 23 □ what constitutes status
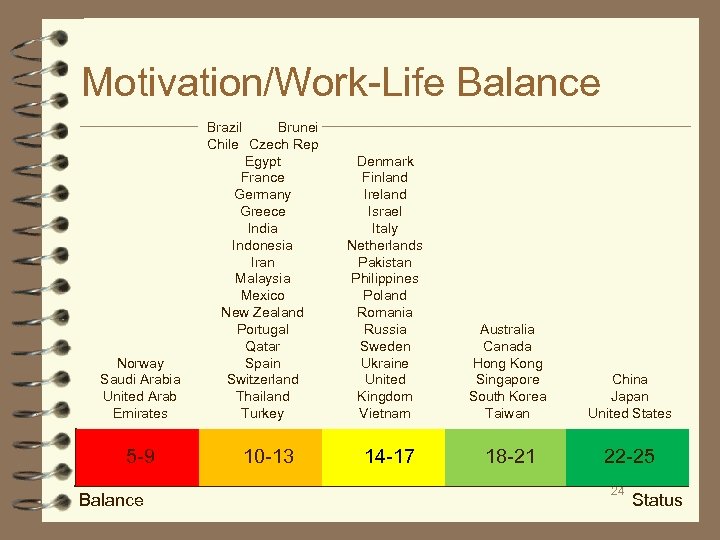
Motivation/Work-Life Balance Norway Saudi Arabia United Arab Emirates 5 -9 Balance Brazil Brunei Chile Czech Rep Egypt France Germany Greece India Indonesia Iran Malaysia Mexico New Zealand Portugal Qatar Spain Switzerland Thailand Turkey 10 -13 Denmark Finland Ireland Israel Italy Netherlands Pakistan Philippines Poland Romania Russia Sweden Ukraine United Kingdom Vietnam 14 -17 Australia Canada Hong Kong Singapore South Korea Taiwan China Japan United States 18 -21 22 -25 24 Status
f78b223f6f6afecd3d36a974d9339c87.ppt