b56810cd8e3f4f883d3d80648416b721.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 Settling the Northern Colonies Chapter 3/4 AP U. S. History
Settling the Northern Colonies Chapter 3/4 AP U. S. History
 The Protestant Reformation Produces Puritanism Background: • Catholic Church – Divine grace – to sinners through sacraments, blessings through “indulgences” for “good works” like donating $ – Popular! But materialistic, corrupt • Martin Luther (1517) – Church gave people false confidence they could “earn” salvation – initiated the Protestant Reformation
The Protestant Reformation Produces Puritanism Background: • Catholic Church – Divine grace – to sinners through sacraments, blessings through “indulgences” for “good works” like donating $ – Popular! But materialistic, corrupt • Martin Luther (1517) – Church gave people false confidence they could “earn” salvation – initiated the Protestant Reformation
 • Trust God alone, “reborn”/conversion experience (will be heart of Protestant religion) • High emphasis on reading (thanks to? ? ) – study Bible • 95 Thesis – 1517 – statements on abuses of church
• Trust God alone, “reborn”/conversion experience (will be heart of Protestant religion) • High emphasis on reading (thanks to? ? ) – study Bible • 95 Thesis – 1517 – statements on abuses of church
 • King Henry 8 th – Made himself head of the church, led to some wanting total reform in church – Edward Protestant but… “Bloody” Mary Elizabeth Catholic • Puritanism – wanted “purification” of Church of England from Catholic abuses • Membership – conversion exp. – “Saint”
• King Henry 8 th – Made himself head of the church, led to some wanting total reform in church – Edward Protestant but… “Bloody” Mary Elizabeth Catholic • Puritanism – wanted “purification” of Church of England from Catholic abuses • Membership – conversion exp. – “Saint”
 The Pilgrims End their Pilgrimage at Plymouth • 1620 – VA Co. – Thomas Weston • 24 families (102 people) – Mayflower – Separatist Puritans • Nov. - Plymouth Bay • Mayflower Compact – civil government • 1 st Winter – ½ died • Miles Standish
The Pilgrims End their Pilgrimage at Plymouth • 1620 – VA Co. – Thomas Weston • 24 families (102 people) – Mayflower – Separatist Puritans • Nov. - Plymouth Bay • Mayflower Compact – civil government • 1 st Winter – ½ died • Miles Standish
 “A City Upon a Hill” • 1628 – Mass Bay Co • 1629/1630 – more – called? ? • John Winthrop – “City on a Hill” – holy society, model to everyone – Rich/poor depended on one another (social reciprocity) • Economy - Fur trading, fishing, shipbuilding • In few months 6 towns • Only one bad winter
“A City Upon a Hill” • 1628 – Mass Bay Co • 1629/1630 – more – called? ? • John Winthrop – “City on a Hill” – holy society, model to everyone – Rich/poor depended on one another (social reciprocity) • Economy - Fur trading, fishing, shipbuilding • In few months 6 towns • Only one bad winter
 Building the Bay Colony Self-governing congregations Franchise – Male saints (church members) All adults – attend services, pay taxes One building for church and town business – the meetinghouse • Government – Male church members • Who had real power? Religious leaders • •
Building the Bay Colony Self-governing congregations Franchise – Male saints (church members) All adults – attend services, pay taxes One building for church and town business – the meetinghouse • Government – Male church members • Who had real power? Religious leaders • •
 “New England Way” • Membership – Conversion Experience • Literacy – Town with 50 or more households – teacher – 100 or more – grammar school – Harvard (ministers)
“New England Way” • Membership – Conversion Experience • Literacy – Town with 50 or more households – teacher – 100 or more – grammar school – Harvard (ministers)
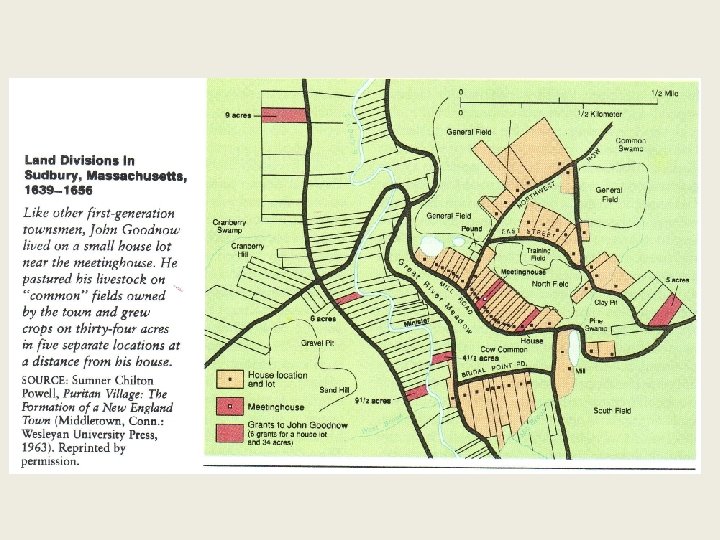
 Community Life • Family – one-acre house lot – near meetinghouse – Strips of land farther out • Reciprocity!! • Women – social force in communities
Community Life • Family – one-acre house lot – near meetinghouse – Strips of land farther out • Reciprocity!! • Women – social force in communities
 Puritan Families • Nuclear family • Marriages subject to state regulation – Divorce rare (between 1639 – 1692 only 27!) – Intervened when serious problems • Disease free environment – longer life span (men – 65, women 62) • Larger families – Apprentices/hired hands for others
Puritan Families • Nuclear family • Marriages subject to state regulation – Divorce rare (between 1639 – 1692 only 27!) – Intervened when serious problems • Disease free environment – longer life span (men – 65, women 62) • Larger families – Apprentices/hired hands for others
 Dissenting Puritans • Quakers – persecution with fines, floggings, and banishments • Anne Hutchison – sharp in theology, predestination, brought to trial for heresy. Banished, went to RI
Dissenting Puritans • Quakers – persecution with fines, floggings, and banishments • Anne Hutchison – sharp in theology, predestination, brought to trial for heresy. Banished, went to RI
 • Roger Williams – wanted separation church/state. • Opposed compulsory church • Wanted Indians compensated for land. Banished Started? ? ?
• Roger Williams – wanted separation church/state. • Opposed compulsory church • Wanted Indians compensated for land. Banished Started? ? ?
 • Merchants – fueled economy but challenged ideals – Challenged social reciprocity with greed – 1635 – Mass General Court forbade sale of any item above 5% its cost – merchants objected – had to sell some goods at higher costs • Would be fined heavily!!
• Merchants – fueled economy but challenged ideals – Challenged social reciprocity with greed – 1635 – Mass General Court forbade sale of any item above 5% its cost – merchants objected – had to sell some goods at higher costs • Would be fined heavily!!
 The Rhode Island Sewer/New England Spreads Out • Offered complete freedom of Religion!! Even for Jews and Catholics. No oaths, no compulsory attendance, no taxes to support state church. • Hartford – CT – river where land was fertile • Thomas Hooker – Fundamental Orders of Conn. – gave power to the people. • New Haven Colony – Puritans wanting a closer church/state relationship. Merged with CT • New Hampshire – separated from MA
The Rhode Island Sewer/New England Spreads Out • Offered complete freedom of Religion!! Even for Jews and Catholics. No oaths, no compulsory attendance, no taxes to support state church. • Hartford – CT – river where land was fertile • Thomas Hooker – Fundamental Orders of Conn. – gave power to the people. • New Haven Colony – Puritans wanting a closer church/state relationship. Merged with CT • New Hampshire – separated from MA
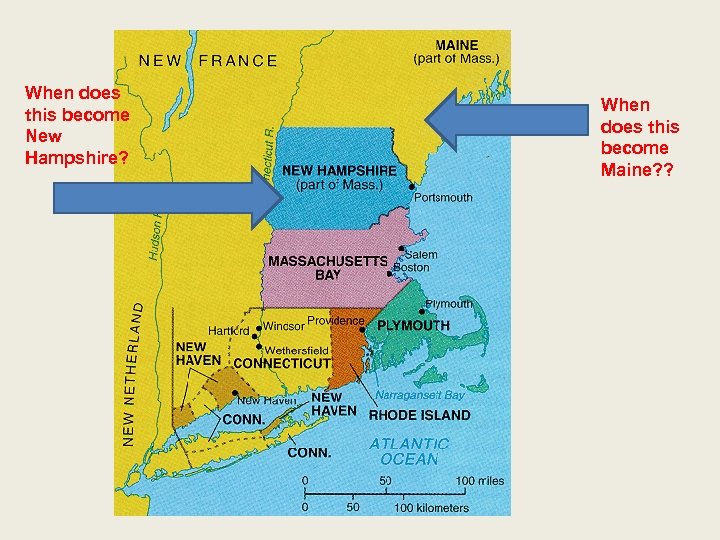 When does this become New Hampshire? When does this become Maine? ?
When does this become New Hampshire? When does this become Maine? ?
 Puritans vs. Indians • Little resistance at first – diseases • “Praying Towns” • Pequot War – 1637 – English set fire to villages, shot Pequots – several hundred killed (mostly women and children) • CT and New Haven could now expand without resistance
Puritans vs. Indians • Little resistance at first – diseases • “Praying Towns” • Pequot War – 1637 – English set fire to villages, shot Pequots – several hundred killed (mostly women and children) • CT and New Haven could now expand without resistance
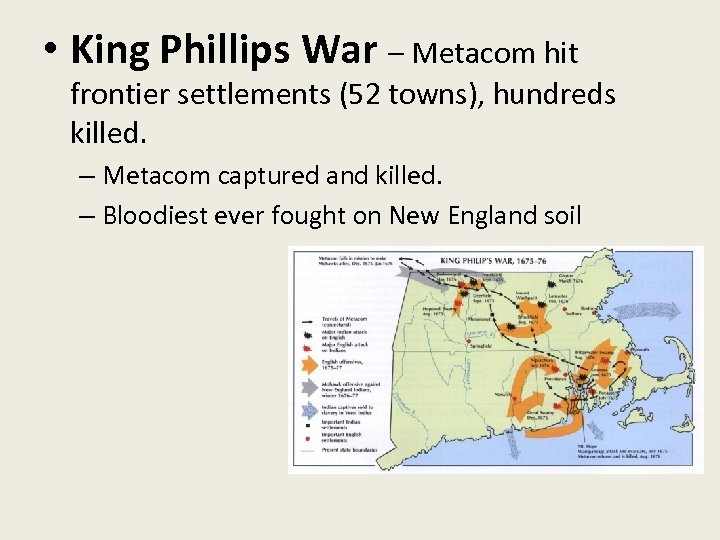 • King Phillips War – Metacom hit frontier settlements (52 towns), hundreds killed. – Metacom captured and killed. – Bloodiest ever fought on New England soil
• King Phillips War – Metacom hit frontier settlements (52 towns), hundreds killed. – Metacom captured and killed. – Bloodiest ever fought on New England soil
 Expansion and Native Americans • New diseases • Fur trade – depleted beavers/other furbearing animals • Ecosystem – no deer, wild plants could not grow • Flooding • Domestic animals • Alcohol • Converted to Christianity
Expansion and Native Americans • New diseases • Fur trade – depleted beavers/other furbearing animals • Ecosystem – no deer, wild plants could not grow • Flooding • Domestic animals • Alcohol • Converted to Christianity
 Seeds of Colonial Unity and Independence • Charles II/James II – disliked rep govt, wanted direct political control in North America • Control trade through the Navigation Acts – Colonies could not export “enumerated goods” to any country except England, couldn’t export in non-English ships, tax if they wanted to sell to anyone else, could enforce • MA ignored royal orders • Crown – carved out NH, revoked MA’s charter
Seeds of Colonial Unity and Independence • Charles II/James II – disliked rep govt, wanted direct political control in North America • Control trade through the Navigation Acts – Colonies could not export “enumerated goods” to any country except England, couldn’t export in non-English ships, tax if they wanted to sell to anyone else, could enforce • MA ignored royal orders • Crown – carved out NH, revoked MA’s charter
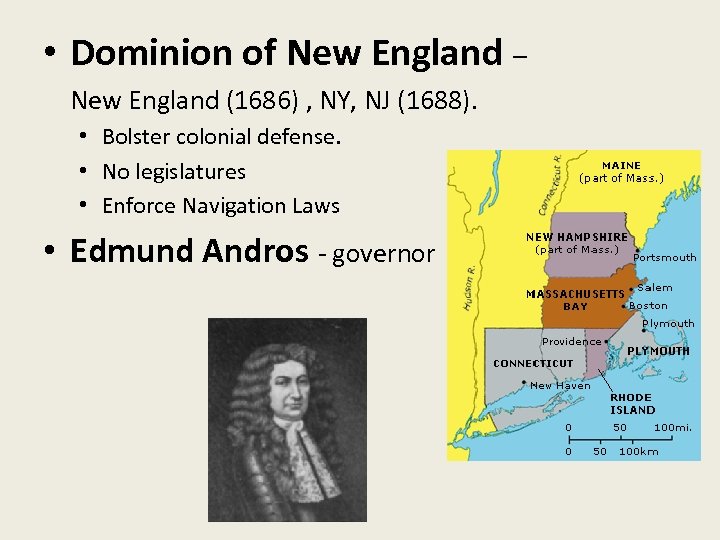 • Dominion of New England – New England (1686) , NY, NJ (1688). • Bolster colonial defense. • No legislatures • Enforce Navigation Laws • Edmund Andros - governor
• Dominion of New England – New England (1686) , NY, NJ (1688). • Bolster colonial defense. • No legislatures • Enforce Navigation Laws • Edmund Andros - governor
 • Andros –very harsh – supported the Catholic Church, no town meetings, heavy taxes Glorious Revolution – William and Mary (daughter of James II) took the throne. Colonists chased Andros out!
• Andros –very harsh – supported the Catholic Church, no town meetings, heavy taxes Glorious Revolution – William and Mary (daughter of James II) took the throne. Colonists chased Andros out!
 • Salutary Neglect – Navigation Acts were weakly enforced. **** Colonies were more prosperous when left alone****
• Salutary Neglect – Navigation Acts were weakly enforced. **** Colonies were more prosperous when left alone****
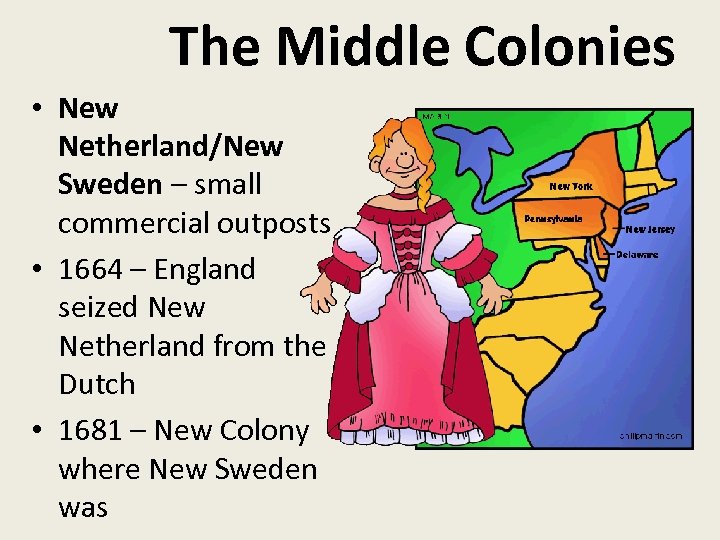 The Middle Colonies • New Netherland/New Sweden – small commercial outposts • 1664 – England seized New Netherland from the Dutch • 1681 – New Colony where New Sweden was
The Middle Colonies • New Netherland/New Sweden – small commercial outposts • 1664 – England seized New Netherland from the Dutch • 1681 – New Colony where New Sweden was
 New Netherland • • • First multi-ethnic society Little religion Fur trading Took over New Sweden Becomes New York (Duke of York) and New Jersey (proprietors)
New Netherland • • • First multi-ethnic society Little religion Fur trading Took over New Sweden Becomes New York (Duke of York) and New Jersey (proprietors)
 Penn’s “Holy Experiment” • William Penn • Quaker Characteristics – no taxes to church, no paid clergy, spoke in church when moved, kept hats on, “thee, ” “thou, ” no oaths, refused military service • Pennsylvania - Practiced religious tolerance, …rich mix of ethnic groups • Philadelphia • No starving time • Exported – grain and other foodstuffs
Penn’s “Holy Experiment” • William Penn • Quaker Characteristics – no taxes to church, no paid clergy, spoke in church when moved, kept hats on, “thee, ” “thou, ” no oaths, refused military service • Pennsylvania - Practiced religious tolerance, …rich mix of ethnic groups • Philadelphia • No starving time • Exported – grain and other foodstuffs
 Questions • 1. Compare and contrast the New England middle colonies in terms of motives for founding, religious and social composition, and political development. • 2. What efforts were made to strengthen English control over the colonies in the 17 th century, and why did they generally fail?
Questions • 1. Compare and contrast the New England middle colonies in terms of motives for founding, religious and social composition, and political development. • 2. What efforts were made to strengthen English control over the colonies in the 17 th century, and why did they generally fail?


