c0fe44dd2aea4d5c6af04fbfe8a1c562.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16

Set 7 Bivariate distribution Chi-square test of independence

Bivariate Categorical & Discrete Data n Example 1 w X = Smoking habit w Y = On-the-job-accident w Are smoking and accident occurrence independent? n Example 2 w X = Number of rooms in a house w Y = Number of bathrooms in a house w Are the two variables independent? n Example 3 w X = Number of children in a household w Y = Attitude toward a local proposition w Are the two variables independent? 2 Dr. E. S. Soofi
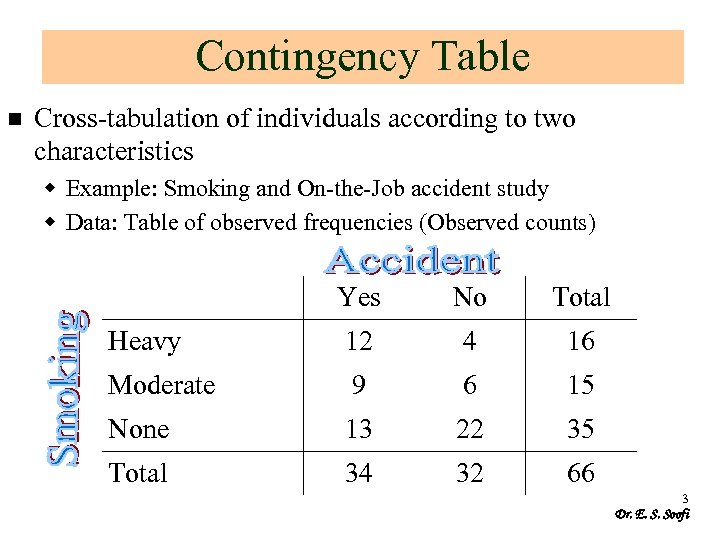
Contingency Table n Cross-tabulation of individuals according to two characteristics w Example: Smoking and On-the-Job accident study w Data: Table of observed frequencies (Observed counts) Yes No Total Heavy 12 4 16 Moderate 9 6 15 None 13 22 35 Total 34 32 66 3 Dr. E. S. Soofi
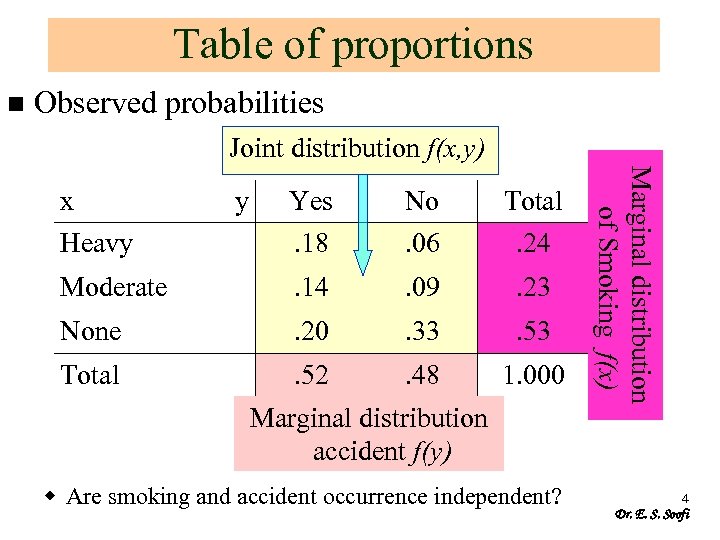
Table of proportions n Observed probabilities Joint distribution f(x, y) y Yes. 18 No. 06 Total. 24 Moderate . 14 . 09 . 23 None . 20 . 33 . 53 Total . 52 . 48 1. 000 Marginal distribution accident f(y) w Are smoking and accident occurrence independent? Marginal distribution of Smoking f(x) x Heavy 4 Dr. E. S. Soofi
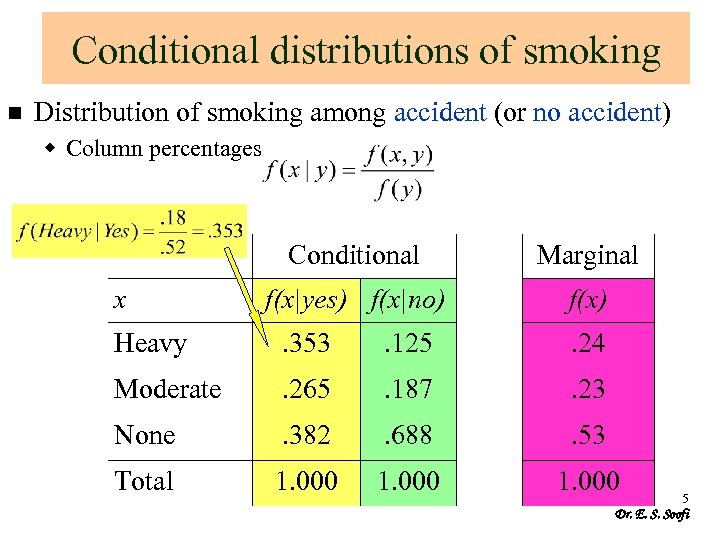
Conditional distributions of smoking n Distribution of smoking among accident (or no accident) w Column percentages Conditional x Marginal f(x|yes) f(x|no) f(x) Heavy . 353 . 125 . 24 Moderate . 265 . 187 . 23 None . 382 . 688 . 53 Total 1. 000 5 Dr. E. S. Soofi
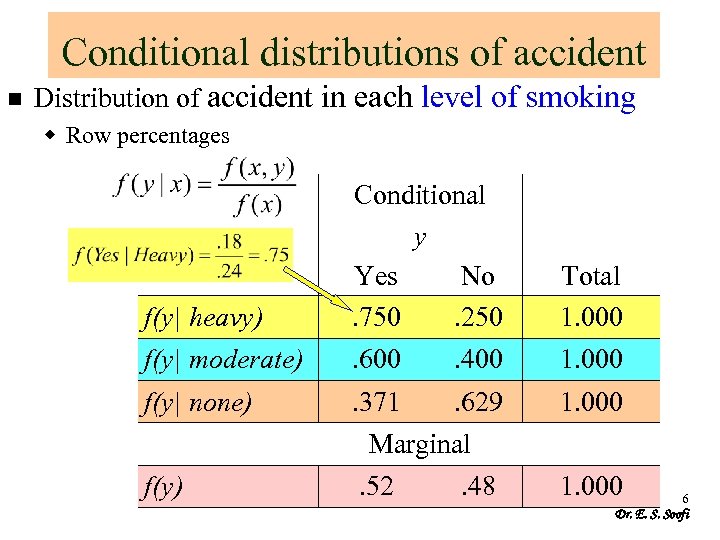
Conditional distributions of accident n Distribution of accident in each level of smoking w Row percentages f(y| heavy) Conditional y Yes No. 750. 250 Total 1. 000 f(y| moderate) . 600 . 400 1. 000 f(y| none) . 371 . 629 1. 000 Marginal f(y) . 52 . 48 1. 000 6 Dr. E. S. Soofi

Are the Two Variables Independent? n Example 1 w X = Smoking habit w Y = On-the-job-accident w Are smoking and accident occurrence independent? n X and Y independent when: w f(y|x) = f(y) for all values of x and y w f(x|y) = f(x) for all values of x and y w f(x, y) = f(x) f(y) for all values of x and y 7 Dr. E. S. Soofi
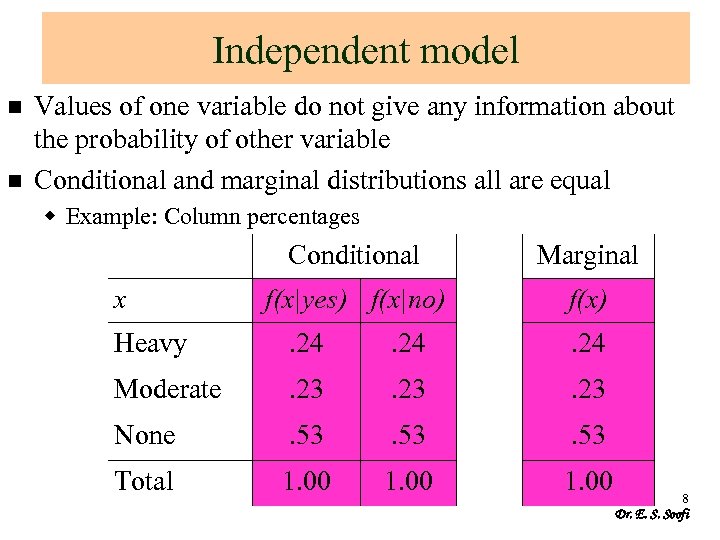
Independent model n n Values of one variable do not give any information about the probability of other variable Conditional and marginal distributions all are equal w Example: Column percentages Conditional x Marginal f(x|yes) f(x|no) f(x) Heavy . 24 Moderate . 23 None . 53 Total 1. 00 8 Dr. E. S. Soofi
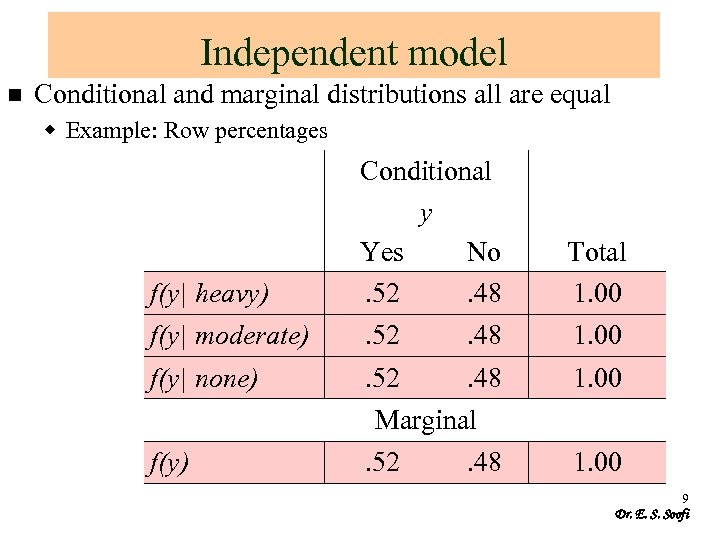
Independent model n Conditional and marginal distributions all are equal w Example: Row percentages f(y| heavy) Conditional y Yes No. 52. 48 Total 1. 00 f(y| moderate) . 52 . 48 1. 00 f(y| none) . 52 . 48 1. 00 Marginal f(y) . 52 . 48 1. 00 9 Dr. E. S. Soofi
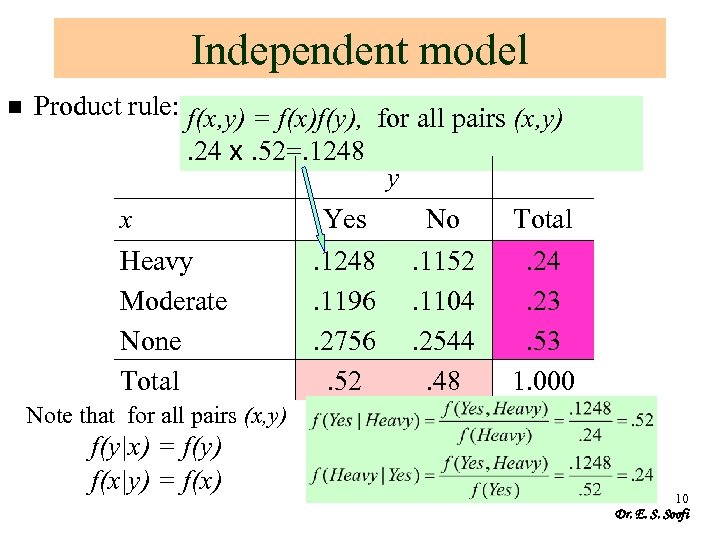
Independent model n Product rule: f(x, y) = f(x)f(y), for all pairs (x, y). 24 x. 52=. 1248 y x Yes No Total Heavy Moderate None Total . 1248. 1196. 2756. 52 . 1152. 1104. 2544. 48 . 24. 23. 53 1. 000 Note that for all pairs (x, y) f(y|x) = f(y) f(x|y) = f(x) 10 Dr. E. S. Soofi
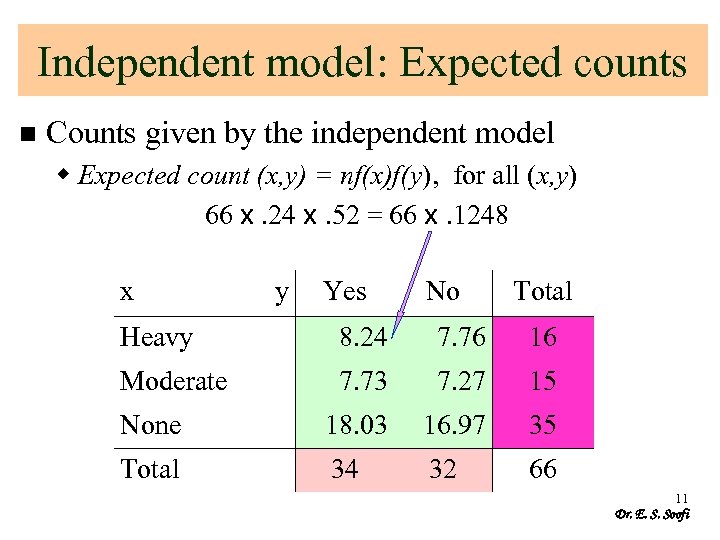
Independent model: Expected counts n Counts given by the independent model w Expected count (x, y) = nf(x)f(y), for all (x, y) 66 x. 24 x. 52 = 66 x. 1248 x y Yes No Total Heavy 8. 24 7. 76 16 Moderate 7. 73 7. 27 15 None 18. 03 16. 97 35 Total 34 32 66 11 Dr. E. S. Soofi
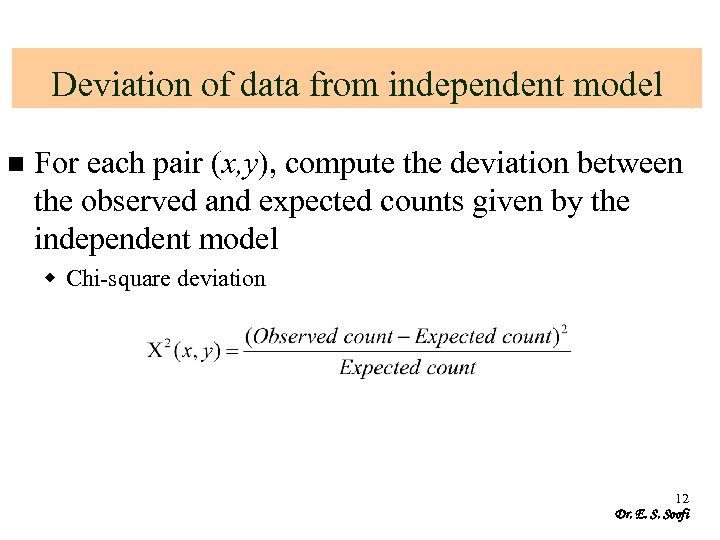
Deviation of data from independent model n For each pair (x, y), compute the deviation between the observed and expected counts given by the independent model w Chi-square deviation 12 Dr. E. S. Soofi
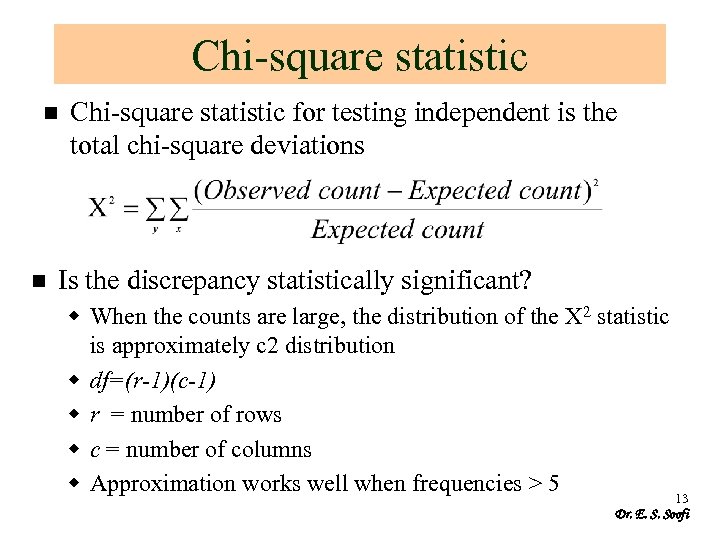
Chi-square statistic n n Chi-square statistic for testing independent is the total chi-square deviations Is the discrepancy statistically significant? w When the counts are large, the distribution of the X 2 statistic is approximately c 2 distribution w df=(r-1)(c-1) w r = number of rows w c = number of columns w Approximation works well when frequencies > 5 13 Dr. E. S. Soofi

Test of independence n Is the discrepancy statistically significant? w Is above a threshold? n Select an upper tail probability threshold a w a =. 10, . 05, . 01 w a is called the significance level w Find the chi-square threshold from the table w Reject the independent model at a level when X 2 > the threshold 14 Dr. E. S. Soofi
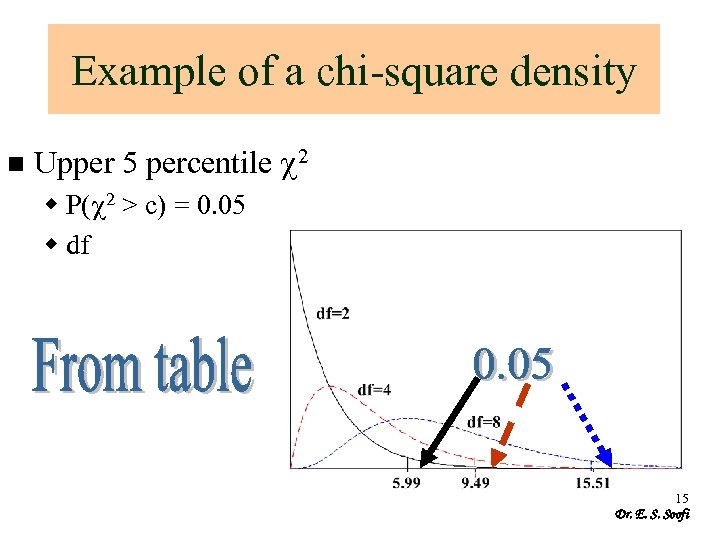
Example of a chi-square density n Upper 5 percentile c 2 w P(c 2 > c) = 0. 05 w df 15 Dr. E. S. Soofi
MINITAB computation n Frequency table in worksheet w Stat >> Tables >> Chi-square Test n Individual data in worksheet (coded) w Stat >> Tables >> Cross tabulation and Chi-square • Row • Column • Chi-square – Chi-square analysis – Expected cell counts – Each cell’s contribution to the Chi-square statistic 16 Dr. E. S. Soofi
c0fe44dd2aea4d5c6af04fbfe8a1c562.ppt