6b98d5e6952bcd7dc12f08e4a3113a2c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 56
 Session S 317113: What do I really need to know when upgrading Thomas Kyte http: //asktom. oracle. com/ 1
Session S 317113: What do I really need to know when upgrading Thomas Kyte http: //asktom. oracle. com/ 1
 So … What Does Oracle Database 11 g Mean To Me? Change 2
So … What Does Oracle Database 11 g Mean To Me? Change 2
 Small Change – but think about it… Let’s Go Green 3
Small Change – but think about it… Let’s Go Green 3
 Small Change – but think about it… ops$tkyte%ORA 11 GR 2> create table t 2 as 3 select substr(object_name, 1, 1 ) str, all_objects. * 4 from all_objects 5 order by dbms_random; Table created. ops$tkyte%ORA 11 GR 2> create index t_idx on t(str, object_name); Index created. ops$tkyte%ORA 11 GR 2> begin 2 dbms_stats. gather_table_stats 3 ( user, 'T', 4 method_opt => 'for all indexed columns size 254', 5 estimate_percent=>100 ); 6 end; 7 / PL/SQL procedure successfully completed. 4
Small Change – but think about it… ops$tkyte%ORA 11 GR 2> create table t 2 as 3 select substr(object_name, 1, 1 ) str, all_objects. * 4 from all_objects 5 order by dbms_random; Table created. ops$tkyte%ORA 11 GR 2> create index t_idx on t(str, object_name); Index created. ops$tkyte%ORA 11 GR 2> begin 2 dbms_stats. gather_table_stats 3 ( user, 'T', 4 method_opt => 'for all indexed columns size 254', 5 estimate_percent=>100 ); 6 end; 7 / PL/SQL procedure successfully completed. 4
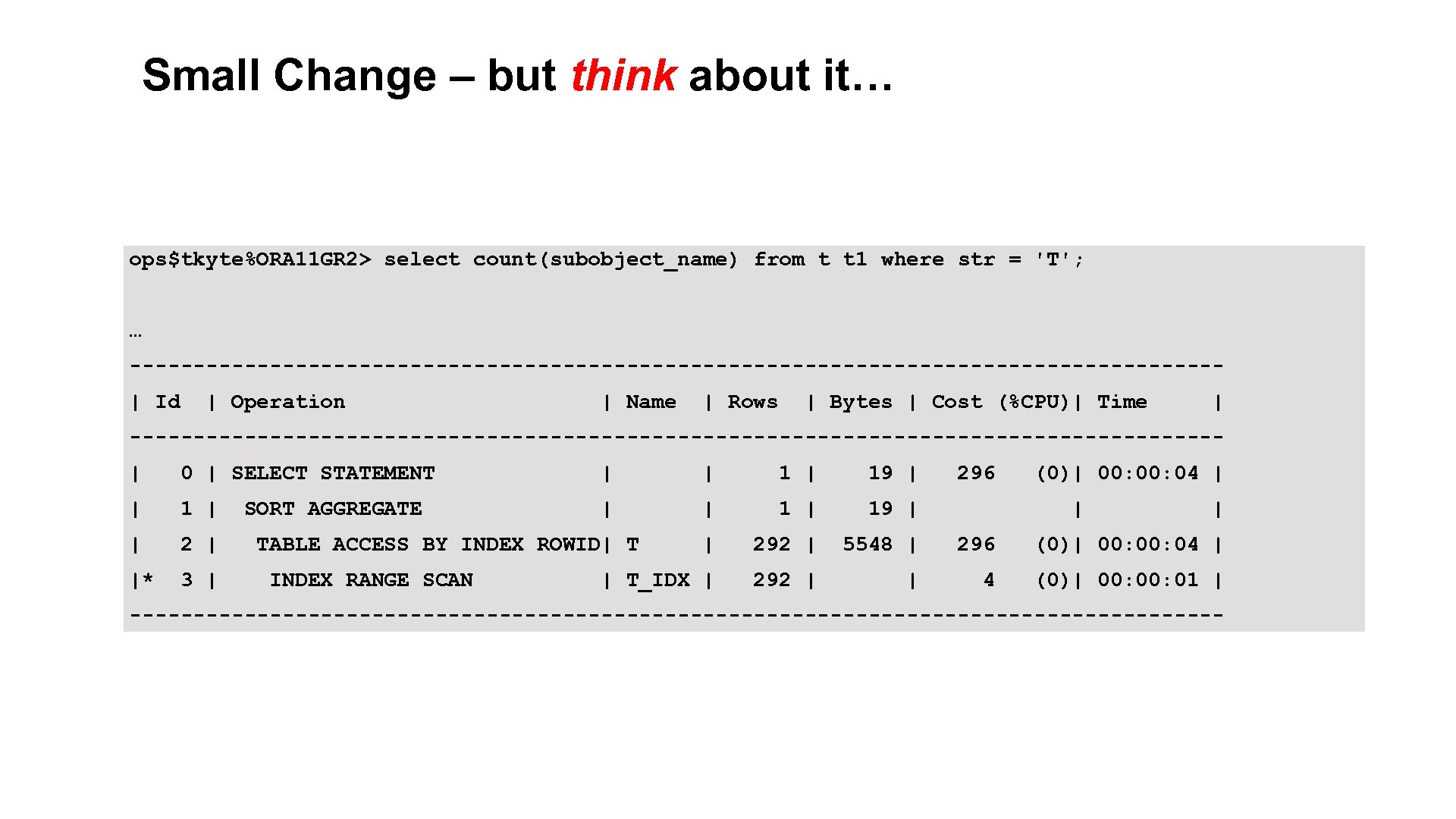 Small Change – but think about it… ops$tkyte%ORA 11 GR 2> select count(subobject_name) from t t 1 where str = 'T'; … -------------------------------------------| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time | -------------------------------------------| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 19 | | 1 | 19 | | 292 | 5548 | 296 (0)| 00: 04 | |* 3 | | T_IDX | 292 | | 4 (0)| 00: 01 | SORT AGGREGATE TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| T INDEX RANGE SCAN 296 (0)| 00: 04 | | | ------------------------------------------- 5
Small Change – but think about it… ops$tkyte%ORA 11 GR 2> select count(subobject_name) from t t 1 where str = 'T'; … -------------------------------------------| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time | -------------------------------------------| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 19 | | 1 | 19 | | 292 | 5548 | 296 (0)| 00: 04 | |* 3 | | T_IDX | 292 | | 4 (0)| 00: 01 | SORT AGGREGATE TABLE ACCESS BY INDEX ROWID| T INDEX RANGE SCAN 296 (0)| 00: 04 | | | ------------------------------------------- 5
 Small Change – but think about it… ops$tkyte%ORA 11 GR 2> insert into t 2 select 'T', all_objects. * 3 from all_objects 4 where rownum <= 1; 1 row created. ops$tkyte%ORA 11 GR 2> begin 2 dbms_stats. gather_table_stats 3 ( user, 'T', 4 method_opt => 'for all indexed columns size 254', 5 estimate_percent=>100 ); 6 end; 7 / PL/SQL procedure successfully completed. 6
Small Change – but think about it… ops$tkyte%ORA 11 GR 2> insert into t 2 select 'T', all_objects. * 3 from all_objects 4 where rownum <= 1; 1 row created. ops$tkyte%ORA 11 GR 2> begin 2 dbms_stats. gather_table_stats 3 ( user, 'T', 4 method_opt => 'for all indexed columns size 254', 5 estimate_percent=>100 ); 6 end; 7 / PL/SQL procedure successfully completed. 6
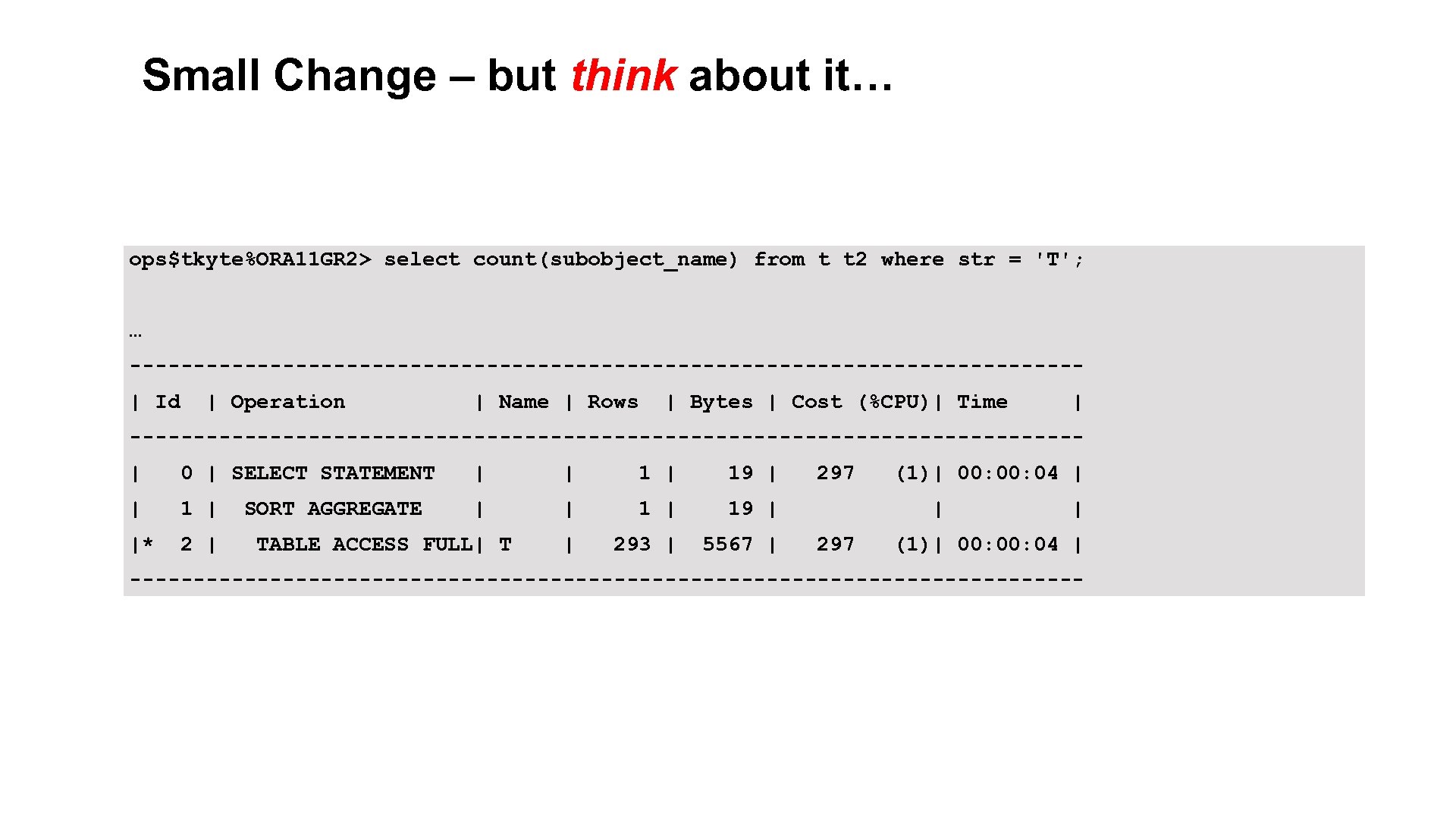 Small Change – but think about it… ops$tkyte%ORA 11 GR 2> select count(subobject_name) from t t 2 where str = 'T'; … -------------------------------------| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time | -------------------------------------| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 19 | | 1 | 19 | |* 2 | | 293 | 5567 | SORT AGGREGATE TABLE ACCESS FULL| T 297 (1)| 00: 04 | | 297 | (1)| 00: 04 | -------------------------------------- 7
Small Change – but think about it… ops$tkyte%ORA 11 GR 2> select count(subobject_name) from t t 2 where str = 'T'; … -------------------------------------| Id | Operation | Name | Rows | Bytes | Cost (%CPU)| Time | -------------------------------------| 0 | SELECT STATEMENT | | 19 | | 1 | 19 | |* 2 | | 293 | 5567 | SORT AGGREGATE TABLE ACCESS FULL| T 297 (1)| 00: 04 | | 297 | (1)| 00: 04 | -------------------------------------- 7
 ““The Law of unintended consequences holds that almost all human actions have at least one unintended consequence. Unintended consequences are a common phenomenon, due to the complexity of the world and human over-confidence. ” 8
““The Law of unintended consequences holds that almost all human actions have at least one unintended consequence. Unintended consequences are a common phenomenon, due to the complexity of the world and human over-confidence. ” 8
 What do you have from the past… • Online Parameter Changes • Online Major Memory Changes • Online Schema Evolution • Online Index Creates • Quiesce • Rolling Upgrades • Online Disk reconfiguration (ASM) • Online Cross Platform Tablespace Transport • Full Database Transports • And more…. 9
What do you have from the past… • Online Parameter Changes • Online Major Memory Changes • Online Schema Evolution • Online Index Creates • Quiesce • Rolling Upgrades • Online Disk reconfiguration (ASM) • Online Cross Platform Tablespace Transport • Full Database Transports • And more…. 9
 What do you need to know? Test To Scale The ability to forget and let it go SQL Plan Management Never Stopping Planning Ahead 10
What do you need to know? Test To Scale The ability to forget and let it go SQL Plan Management Never Stopping Planning Ahead 10
 First – what do we need to do? © 2010 Oracle Corporation 11 11
First – what do we need to do? © 2010 Oracle Corporation 11 11
 Database Upgrade Process: Steps 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Analyze & gather information about environment Determine the upgrade path and choose upgrade method Prepare backup / recovery strategy and clone database to test Establish performance baseline/metrics before upgrade Develop a test plan for database, applications, and reports Test upgraded database with applications and reports Ensure adequate performance by comparing metrics gathered before and after upgrade 8. Remediate regressions, e. g, tune queries, update database parameters, call Support, etc. 9. Go Live! Planning Ahead Forget and let it go ASH and AWR Test To Scale Never Stopping SQL Plan Management 12
Database Upgrade Process: Steps 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Analyze & gather information about environment Determine the upgrade path and choose upgrade method Prepare backup / recovery strategy and clone database to test Establish performance baseline/metrics before upgrade Develop a test plan for database, applications, and reports Test upgraded database with applications and reports Ensure adequate performance by comparing metrics gathered before and after upgrade 8. Remediate regressions, e. g, tune queries, update database parameters, call Support, etc. 9. Go Live! Planning Ahead Forget and let it go ASH and AWR Test To Scale Never Stopping SQL Plan Management 12
 SQL Plan Management © 2010 Oracle Corporation 13 13
SQL Plan Management © 2010 Oracle Corporation 13 13
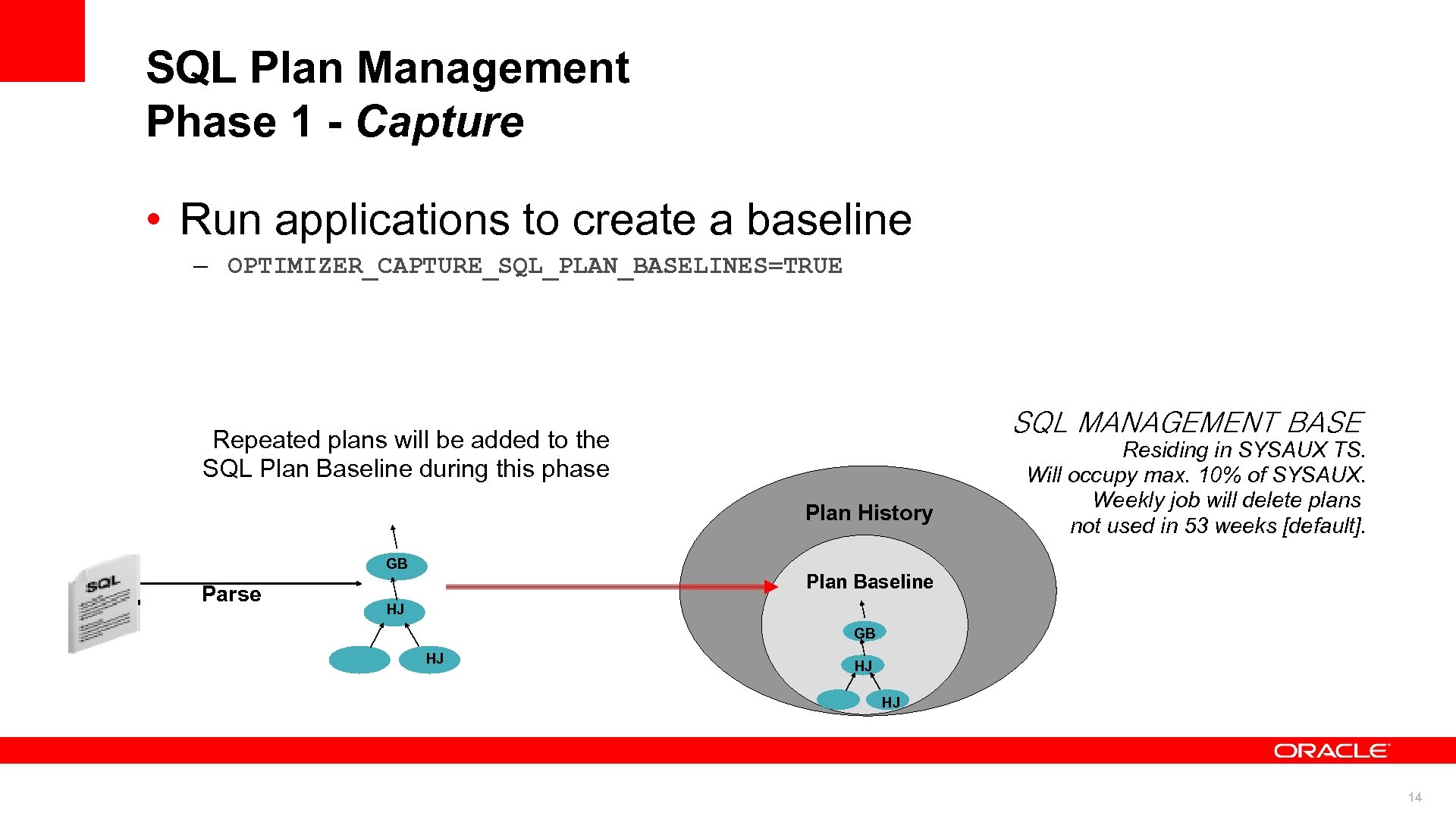 SQL Plan Management Phase 1 - Capture • Run applications to create a baseline – OPTIMIZER_CAPTURE_SQL_PLAN_BASELINES=TRUE SQL MANAGEMENT BASE Repeated plans will be added to the SQL Plan Baseline during this phase Plan History GB Parse Residing in SYSAUX TS. Will occupy max. 10% of SYSAUX. Weekly job will delete plans not used in 53 weeks [default]. Plan Baseline HJ GB HJ HJ HJ 14
SQL Plan Management Phase 1 - Capture • Run applications to create a baseline – OPTIMIZER_CAPTURE_SQL_PLAN_BASELINES=TRUE SQL MANAGEMENT BASE Repeated plans will be added to the SQL Plan Baseline during this phase Plan History GB Parse Residing in SYSAUX TS. Will occupy max. 10% of SYSAUX. Weekly job will delete plans not used in 53 weeks [default]. Plan Baseline HJ GB HJ HJ HJ 14
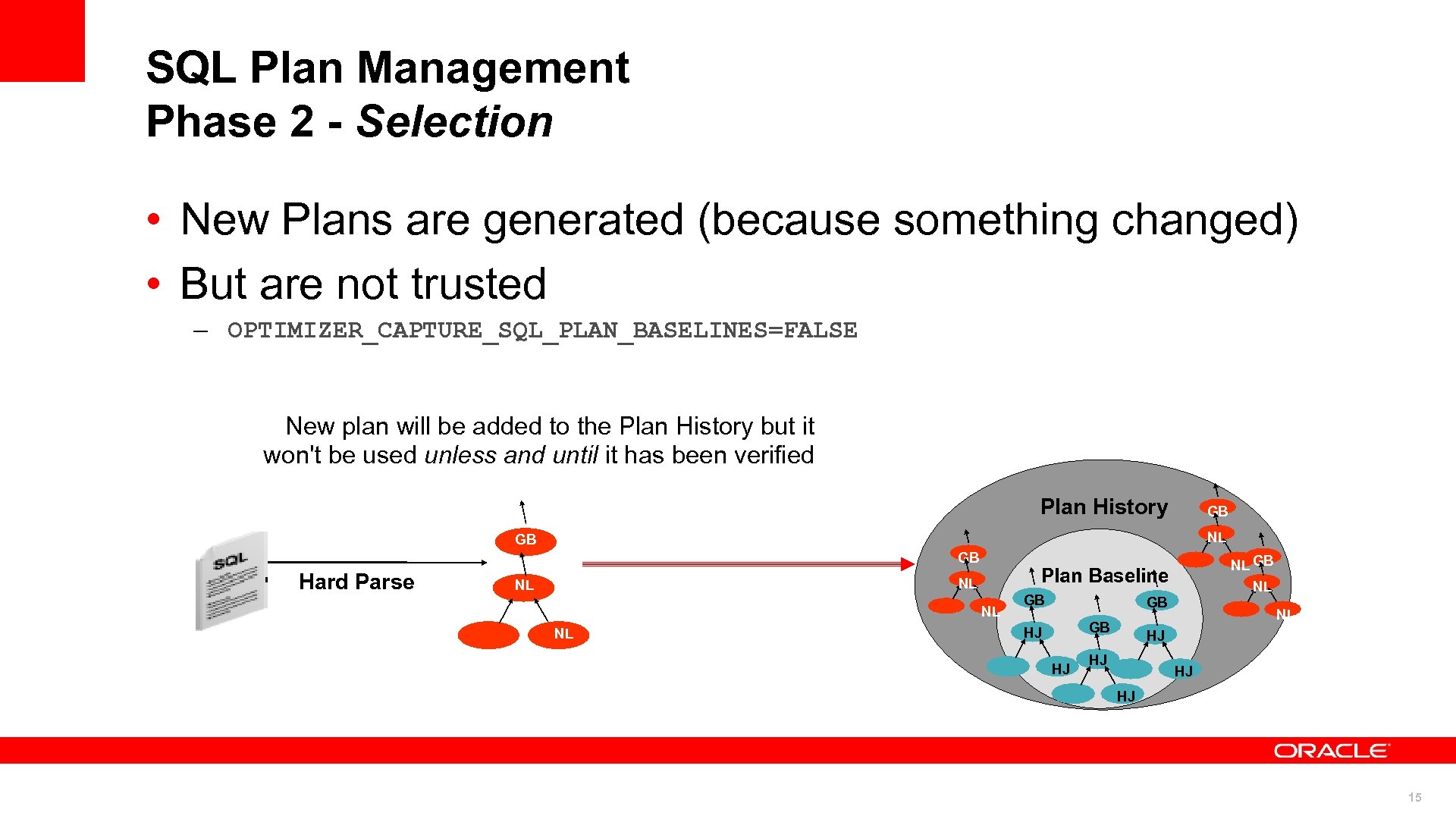 SQL Plan Management Phase 2 - Selection • New Plans are generated (because something changed) • But are not trusted – OPTIMIZER_CAPTURE_SQL_PLAN_BASELINES=FALSE New plan will be added to the Plan History but it won't be used unless and until it has been verified Plan History GB NL GB GB Hard Parse Plan Baseline NL NL NL GB GB GB HJ HJ NL HJ HJ 15
SQL Plan Management Phase 2 - Selection • New Plans are generated (because something changed) • But are not trusted – OPTIMIZER_CAPTURE_SQL_PLAN_BASELINES=FALSE New plan will be added to the Plan History but it won't be used unless and until it has been verified Plan History GB NL GB GB Hard Parse Plan Baseline NL NL NL GB GB GB HJ HJ NL HJ HJ 15
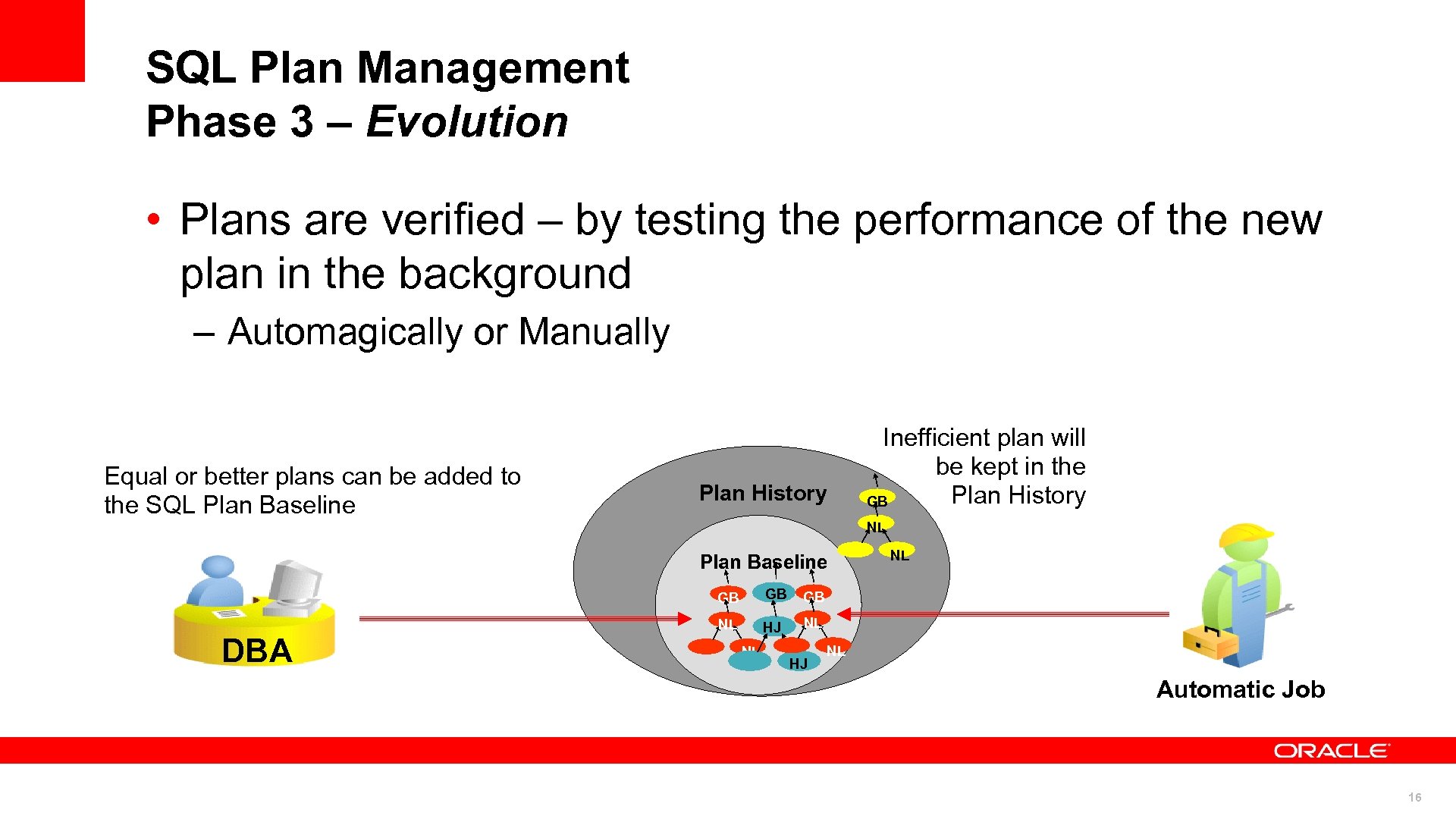 SQL Plan Management Phase 3 – Evolution • Plans are verified – by testing the performance of the new plan in the background – Automagically or Manually Equal or better plans can be added to the SQL Plan Baseline Plan History Inefficient plan will be kept in the Plan History GB NL Plan Baseline GB DBA GB GB NL HJ NL NL NL HJ NL Automatic Job 16
SQL Plan Management Phase 3 – Evolution • Plans are verified – by testing the performance of the new plan in the background – Automagically or Manually Equal or better plans can be added to the SQL Plan Baseline Plan History Inefficient plan will be kept in the Plan History GB NL Plan Baseline GB DBA GB GB NL HJ NL NL NL HJ NL Automatic Job 16
 Upgrade Scenario • Your 9 i application is already in 11 g for whatever reason • You’d like to have ‘query plan stability’ – Coupled with the opportunity to use better plans – do not want to be frozen • The steps would be…. 17
Upgrade Scenario • Your 9 i application is already in 11 g for whatever reason • You’d like to have ‘query plan stability’ – Coupled with the opportunity to use better plans – do not want to be frozen • The steps would be…. 17
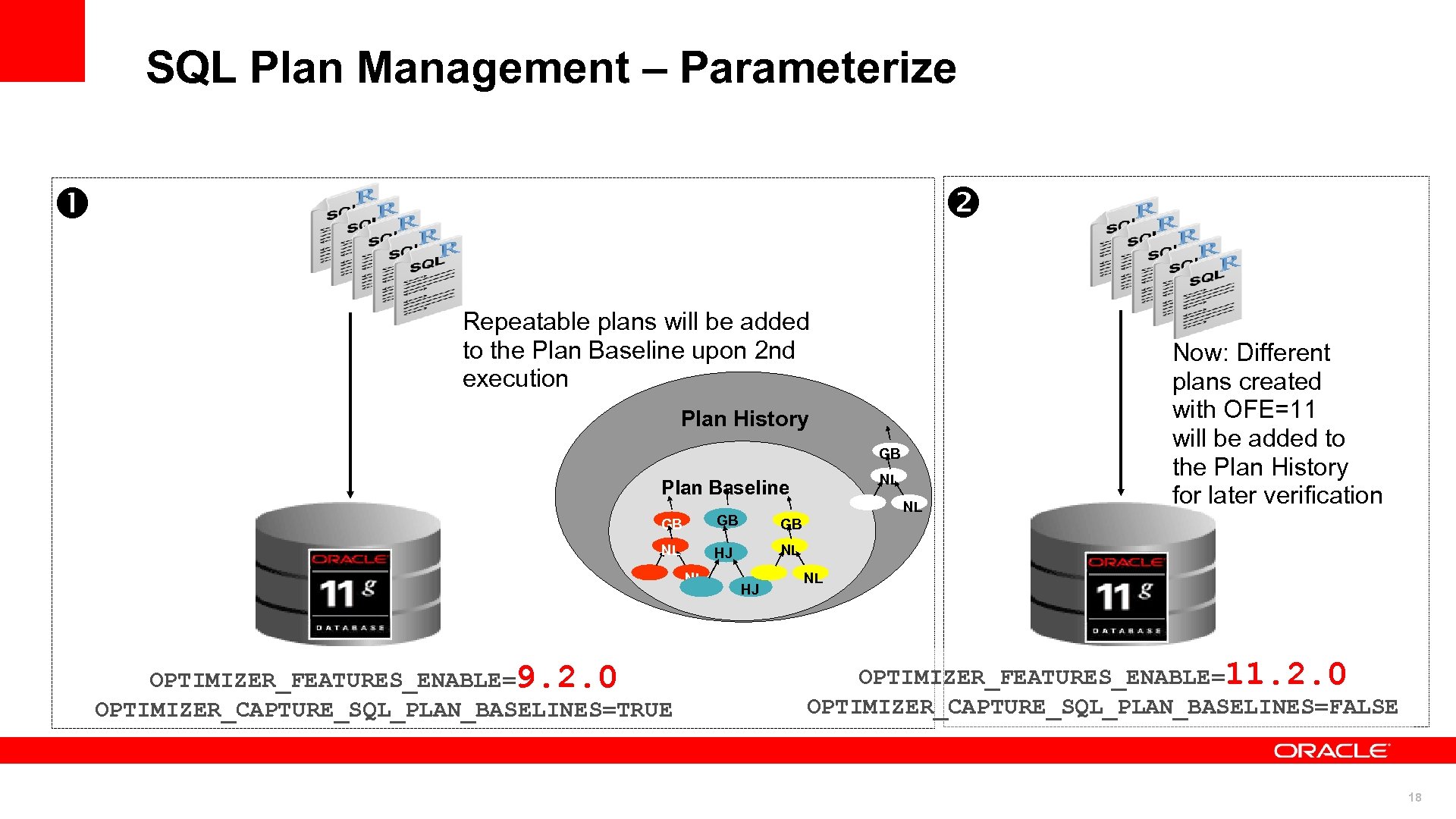 SQL Plan Management – Parameterize STS Repeatable plans will be added to the Plan Baseline upon 2 nd execution Plan History GB NL Plan Baseline GB GB GB NL HJ NL Now: Different plans created with OFE=11 will be added to the Plan History for later verification NL NL OPTIMIZER_FEATURES_ENABLE=9. 2. 0 OPTIMIZER_CAPTURE_SQL_PLAN_BASELINES=TRUE HJ NL OPTIMIZER_FEATURES_ENABLE=11. 2. 0 OPTIMIZER_CAPTURE_SQL_PLAN_BASELINES=FALSE 18
SQL Plan Management – Parameterize STS Repeatable plans will be added to the Plan Baseline upon 2 nd execution Plan History GB NL Plan Baseline GB GB GB NL HJ NL Now: Different plans created with OFE=11 will be added to the Plan History for later verification NL NL OPTIMIZER_FEATURES_ENABLE=9. 2. 0 OPTIMIZER_CAPTURE_SQL_PLAN_BASELINES=TRUE HJ NL OPTIMIZER_FEATURES_ENABLE=11. 2. 0 OPTIMIZER_CAPTURE_SQL_PLAN_BASELINES=FALSE 18
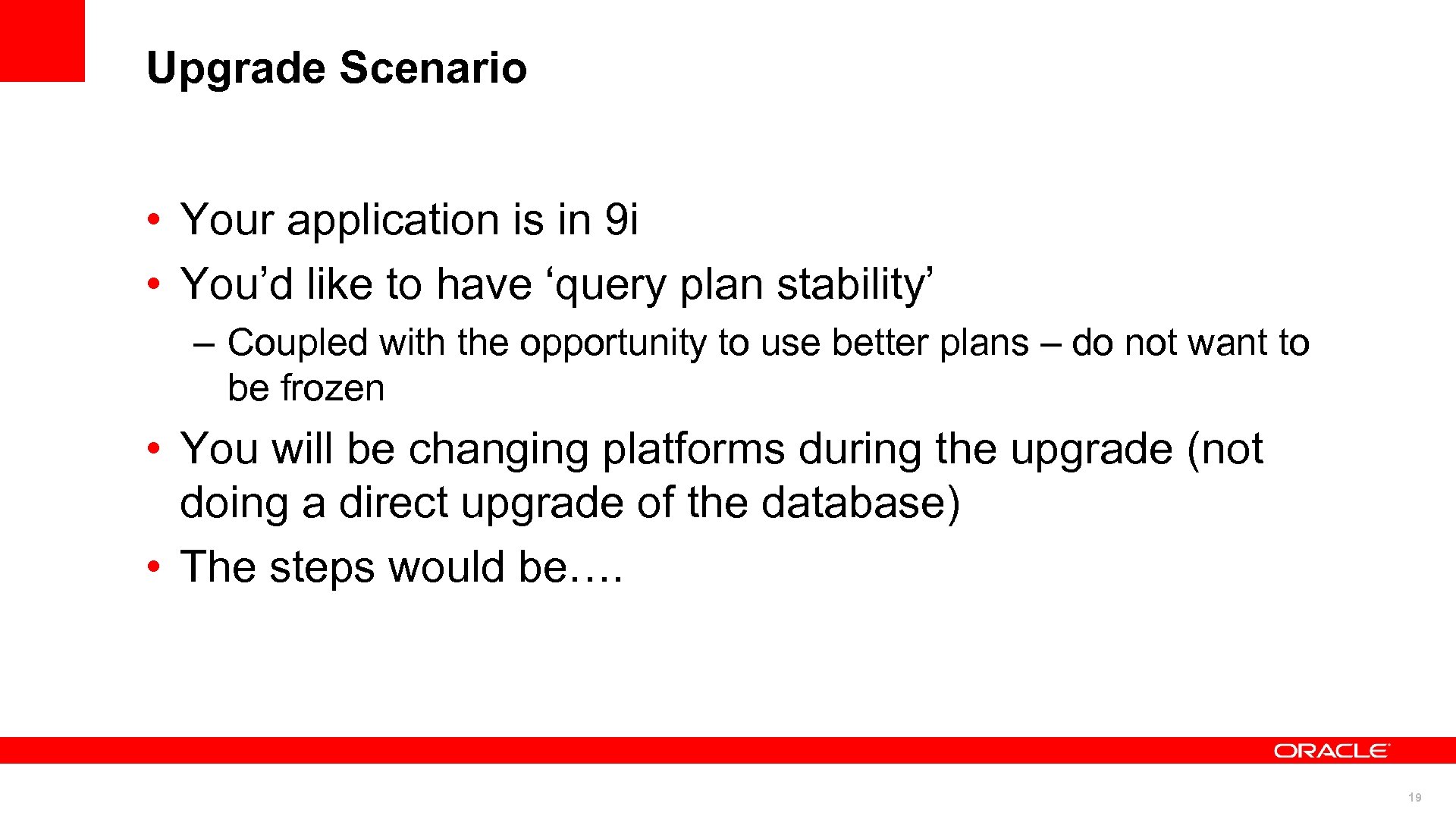 Upgrade Scenario • Your application is in 9 i • You’d like to have ‘query plan stability’ – Coupled with the opportunity to use better plans – do not want to be frozen • You will be changing platforms during the upgrade (not doing a direct upgrade of the database) • The steps would be…. 19
Upgrade Scenario • Your application is in 9 i • You’d like to have ‘query plan stability’ – Coupled with the opportunity to use better plans – do not want to be frozen • You will be changing platforms during the upgrade (not doing a direct upgrade of the database) • The steps would be…. 19
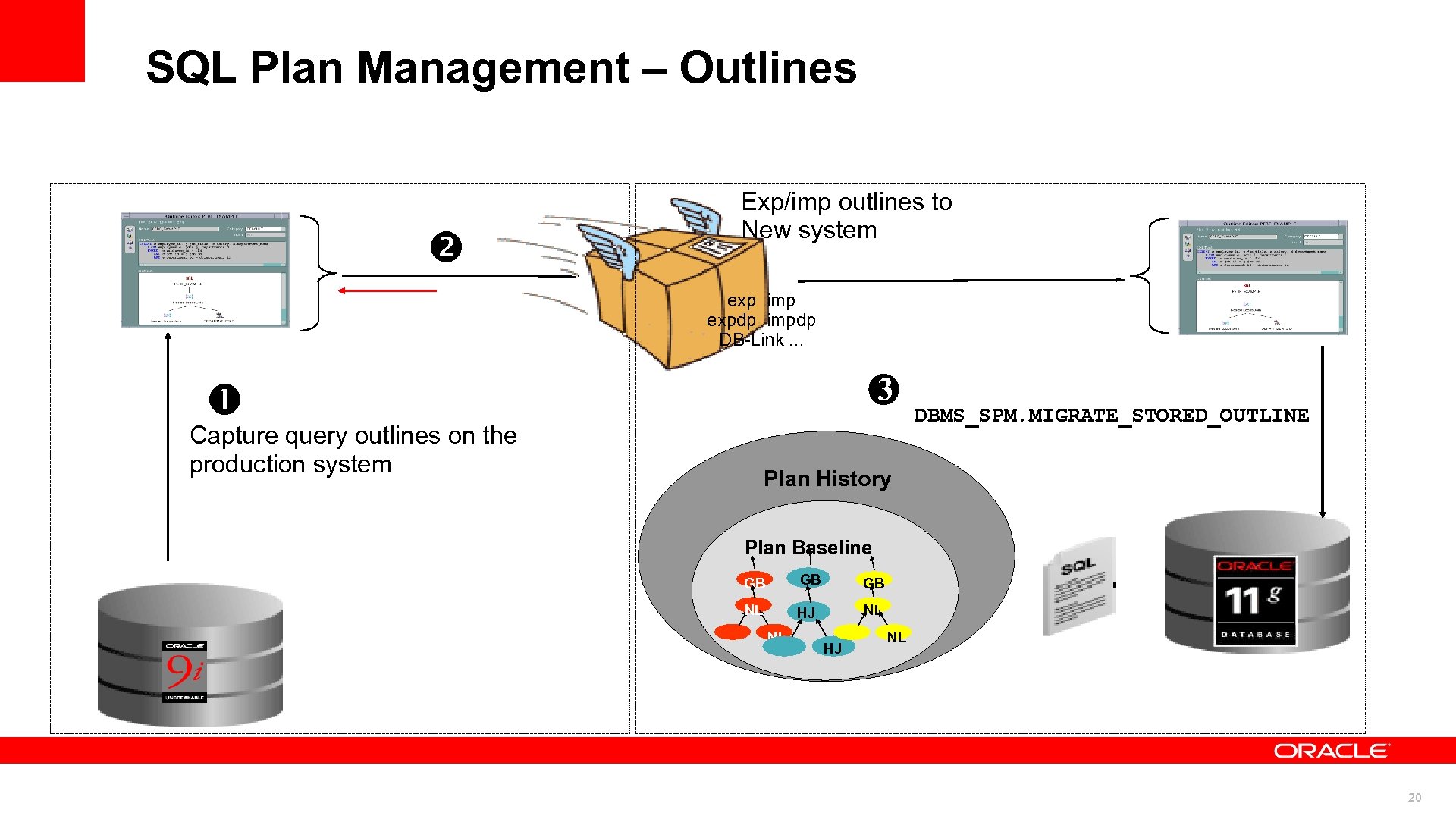 SQL Plan Management – Outlines STS Exp/imp outlines to New system SS exp imp expdp impdp DB-Link. . . 3 Capture query outlines on the production system DBMS_SPM. MIGRATE_STORED_OUTLINE Plan History Plan Baseline GB GB GB NL HJ NL 20
SQL Plan Management – Outlines STS Exp/imp outlines to New system SS exp imp expdp impdp DB-Link. . . 3 Capture query outlines on the production system DBMS_SPM. MIGRATE_STORED_OUTLINE Plan History Plan Baseline GB GB GB NL HJ NL 20
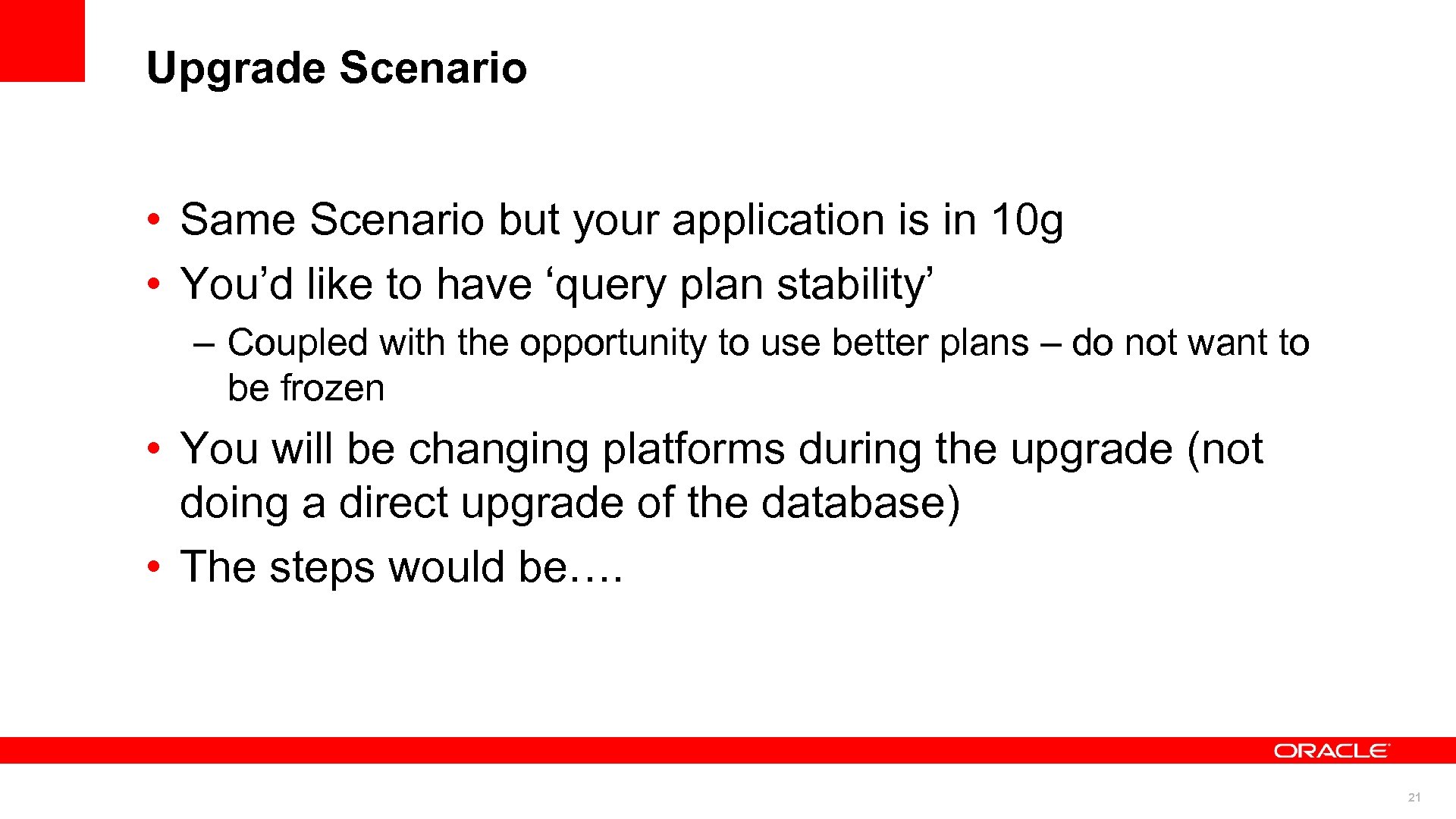 Upgrade Scenario • Same Scenario but your application is in 10 g • You’d like to have ‘query plan stability’ – Coupled with the opportunity to use better plans – do not want to be frozen • You will be changing platforms during the upgrade (not doing a direct upgrade of the database) • The steps would be…. 21
Upgrade Scenario • Same Scenario but your application is in 10 g • You’d like to have ‘query plan stability’ – Coupled with the opportunity to use better plans – do not want to be frozen • You will be changing platforms during the upgrade (not doing a direct upgrade of the database) • The steps would be…. 21
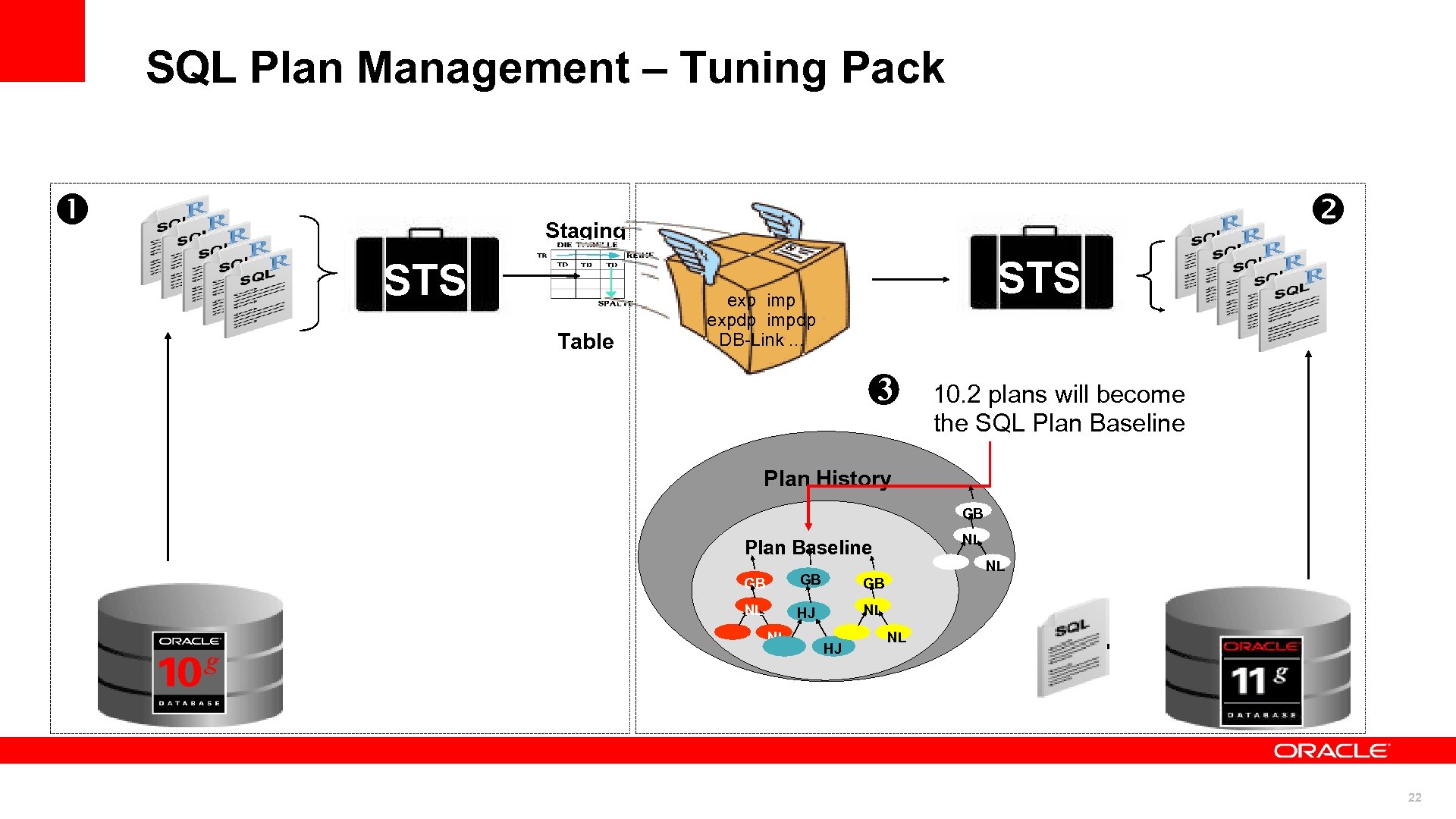 SQL Plan Management – Tuning Pack Staging STS Table STS exp imp expdp impdp DB-Link. . . 3 10. 2 plans will become the SQL Plan Baseline Plan History GB NL Plan Baseline GB GB GB NL HJ NL NL NL HJ NL 22
SQL Plan Management – Tuning Pack Staging STS Table STS exp imp expdp impdp DB-Link. . . 3 10. 2 plans will become the SQL Plan Baseline Plan History GB NL Plan Baseline GB GB GB NL HJ NL NL NL HJ NL 22
 Upgrade Scenario • You would like to deploy from development to production. . • You would like to deploy at a customer site… • And you want to start with a stable set of plans – Using better plans only after they have been verified • The steps would be…. 23
Upgrade Scenario • You would like to deploy from development to production. . • You would like to deploy at a customer site… • And you want to start with a stable set of plans – Using better plans only after they have been verified • The steps would be…. 23
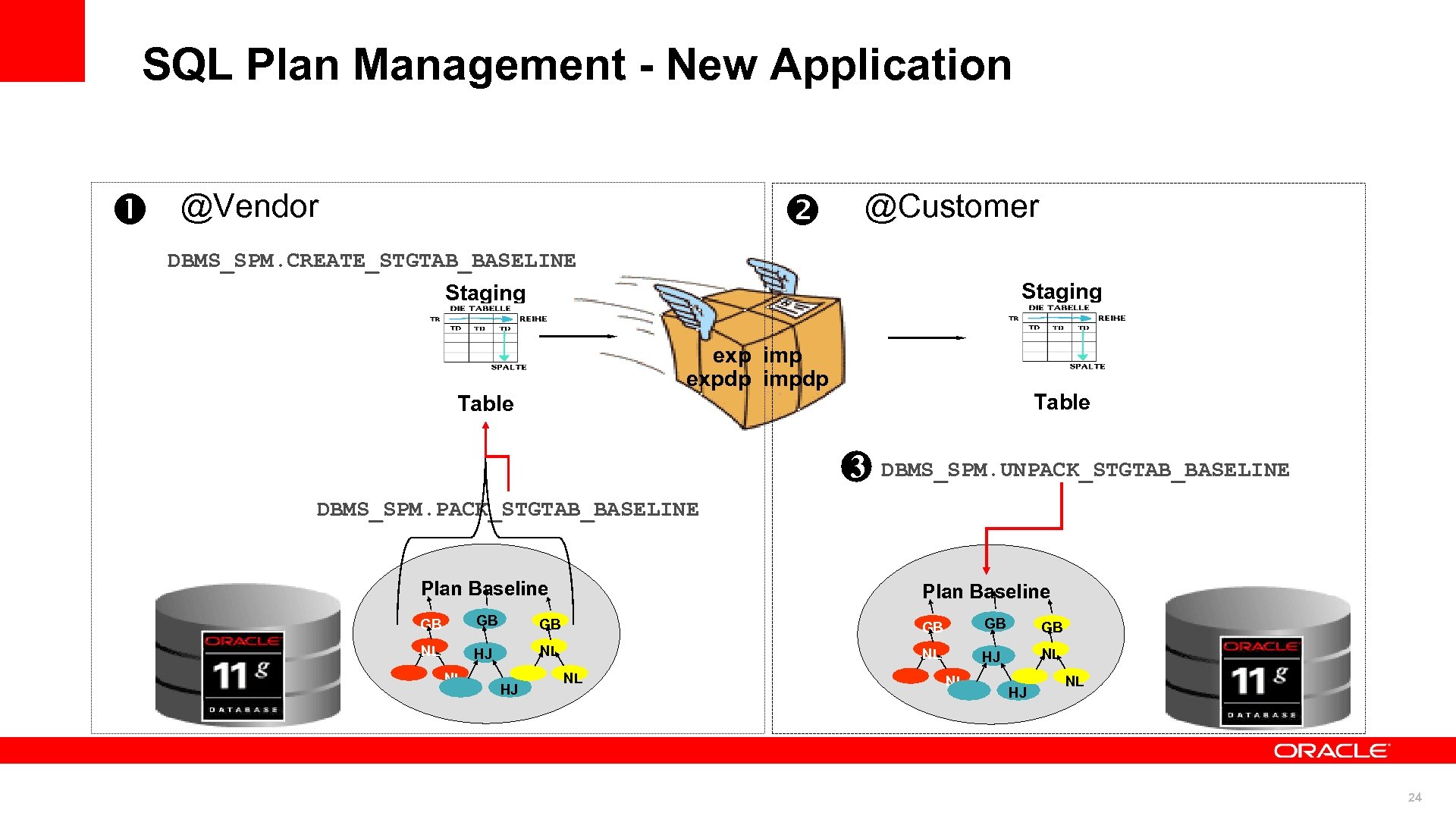 SQL Plan Management - New Application @Vendor @Customer DBMS_SPM. CREATE_STGTAB_BASELINE Staging exp imp expdp impdp Table 3 DBMS_SPM. UNPACK_STGTAB_BASELINE DBMS_SPM. PACK_STGTAB_BASELINE Plan Baseline GB GB GB NL HJ NL 24
SQL Plan Management - New Application @Vendor @Customer DBMS_SPM. CREATE_STGTAB_BASELINE Staging exp imp expdp impdp Table 3 DBMS_SPM. UNPACK_STGTAB_BASELINE DBMS_SPM. PACK_STGTAB_BASELINE Plan Baseline GB GB GB NL HJ NL 24
 Test to Scale © 2010 Oracle Corporation 25 25
Test to Scale © 2010 Oracle Corporation 25 25
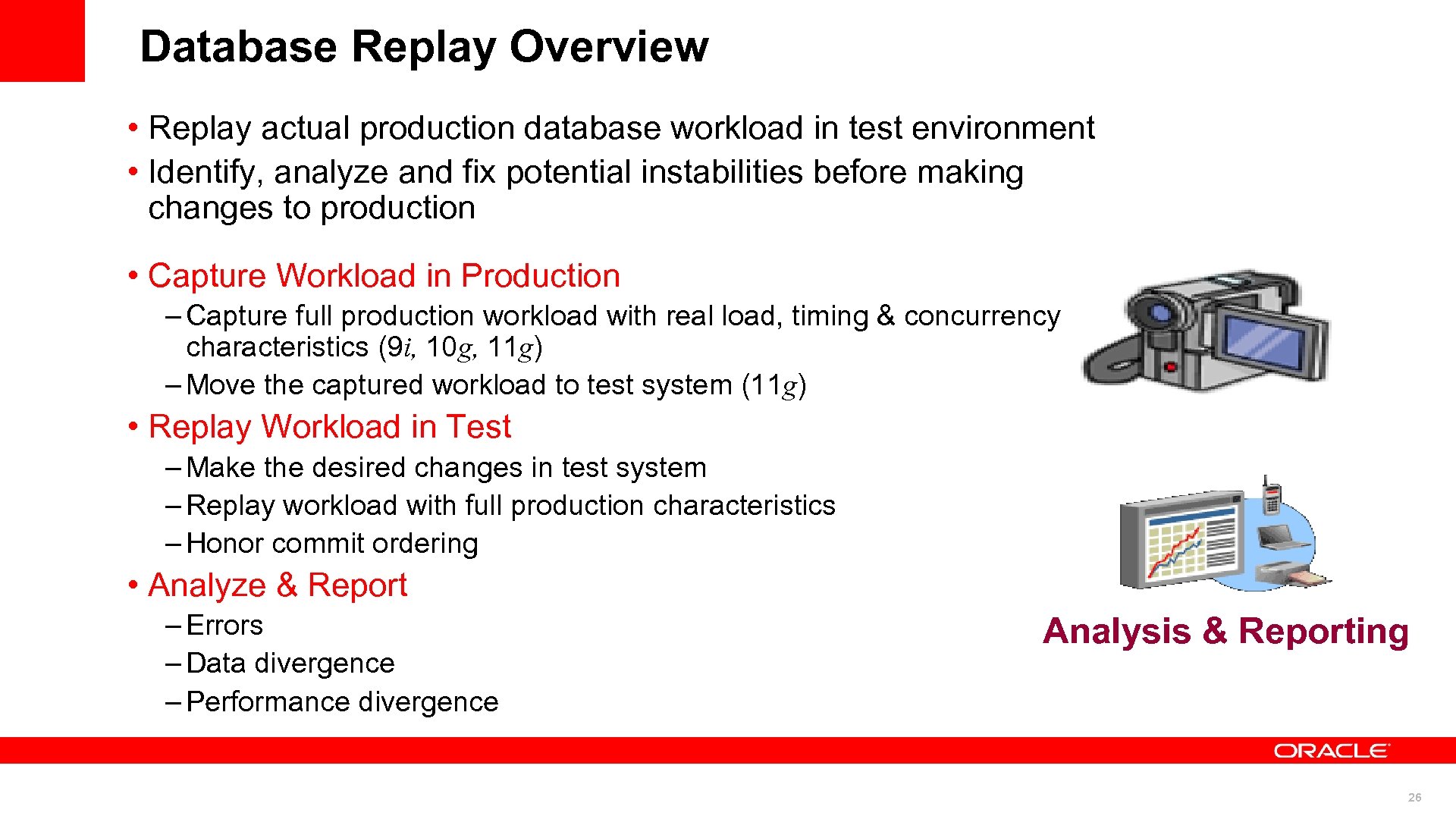 Database Replay Overview • Replay actual production database workload in test environment • Identify, analyze and fix potential instabilities before making changes to production • Capture Workload in Production – Capture full production workload with real load, timing & concurrency characteristics (9 i, 10 g, 11 g) – Move the captured workload to test system (11 g) • Replay Workload in Test – Make the desired changes in test system – Replay workload with full production characteristics – Honor commit ordering • Analyze & Report – Errors – Data divergence – Performance divergence Analysis & Reporting 26
Database Replay Overview • Replay actual production database workload in test environment • Identify, analyze and fix potential instabilities before making changes to production • Capture Workload in Production – Capture full production workload with real load, timing & concurrency characteristics (9 i, 10 g, 11 g) – Move the captured workload to test system (11 g) • Replay Workload in Test – Make the desired changes in test system – Replay workload with full production characteristics – Honor commit ordering • Analyze & Report – Errors – Data divergence – Performance divergence Analysis & Reporting 26
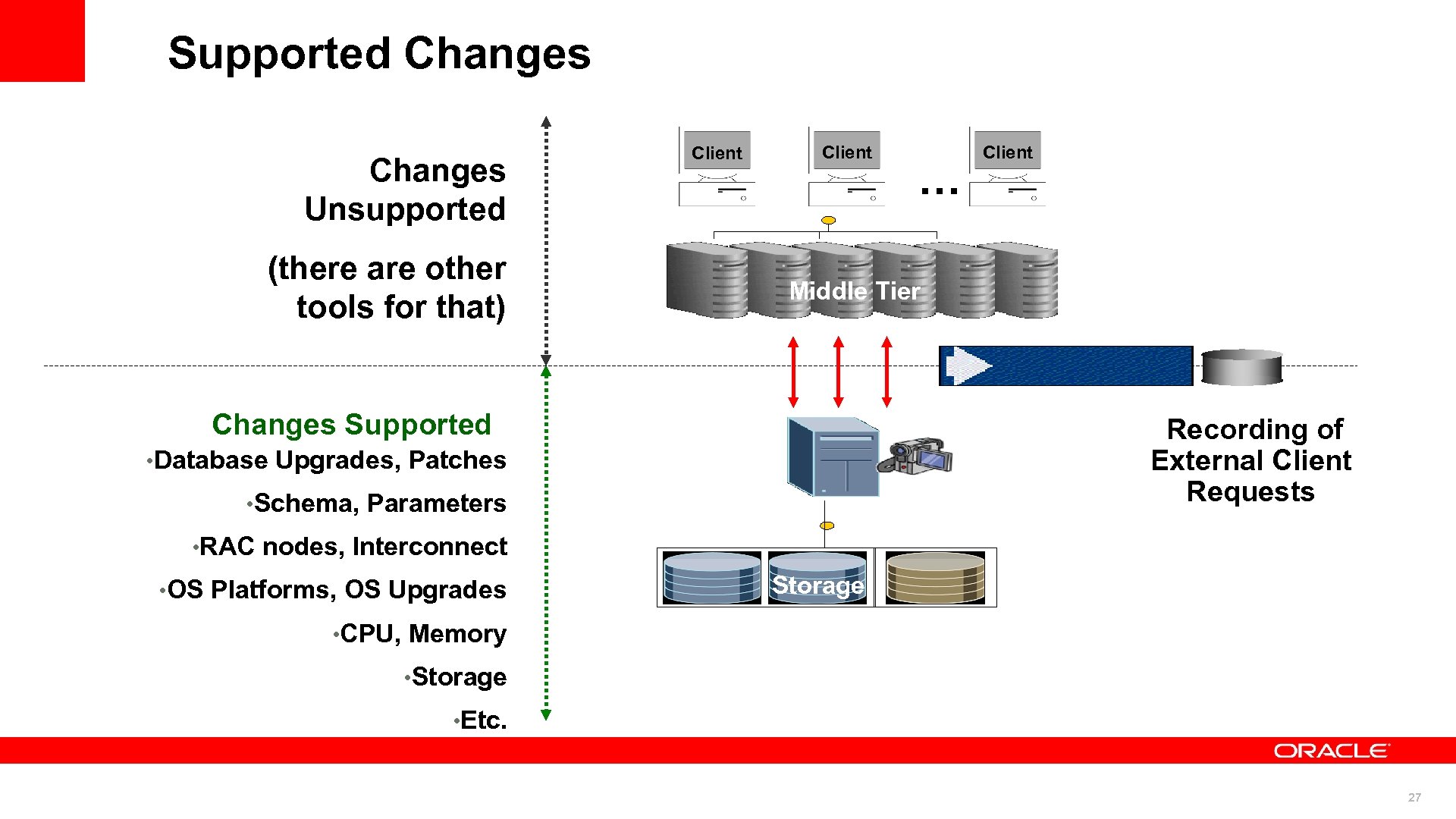 Supported Changes Unsupported (there are other tools for that) Client … Client Middle Tier Changes Supported Recording of External Client Requests • Database Upgrades, Patches • Schema, Parameters • RAC nodes, Interconnect • OS Platforms, OS Upgrades Storage • CPU, Memory • Storage • Etc. 27
Supported Changes Unsupported (there are other tools for that) Client … Client Middle Tier Changes Supported Recording of External Client Requests • Database Upgrades, Patches • Schema, Parameters • RAC nodes, Interconnect • OS Platforms, OS Upgrades Storage • CPU, Memory • Storage • Etc. 27
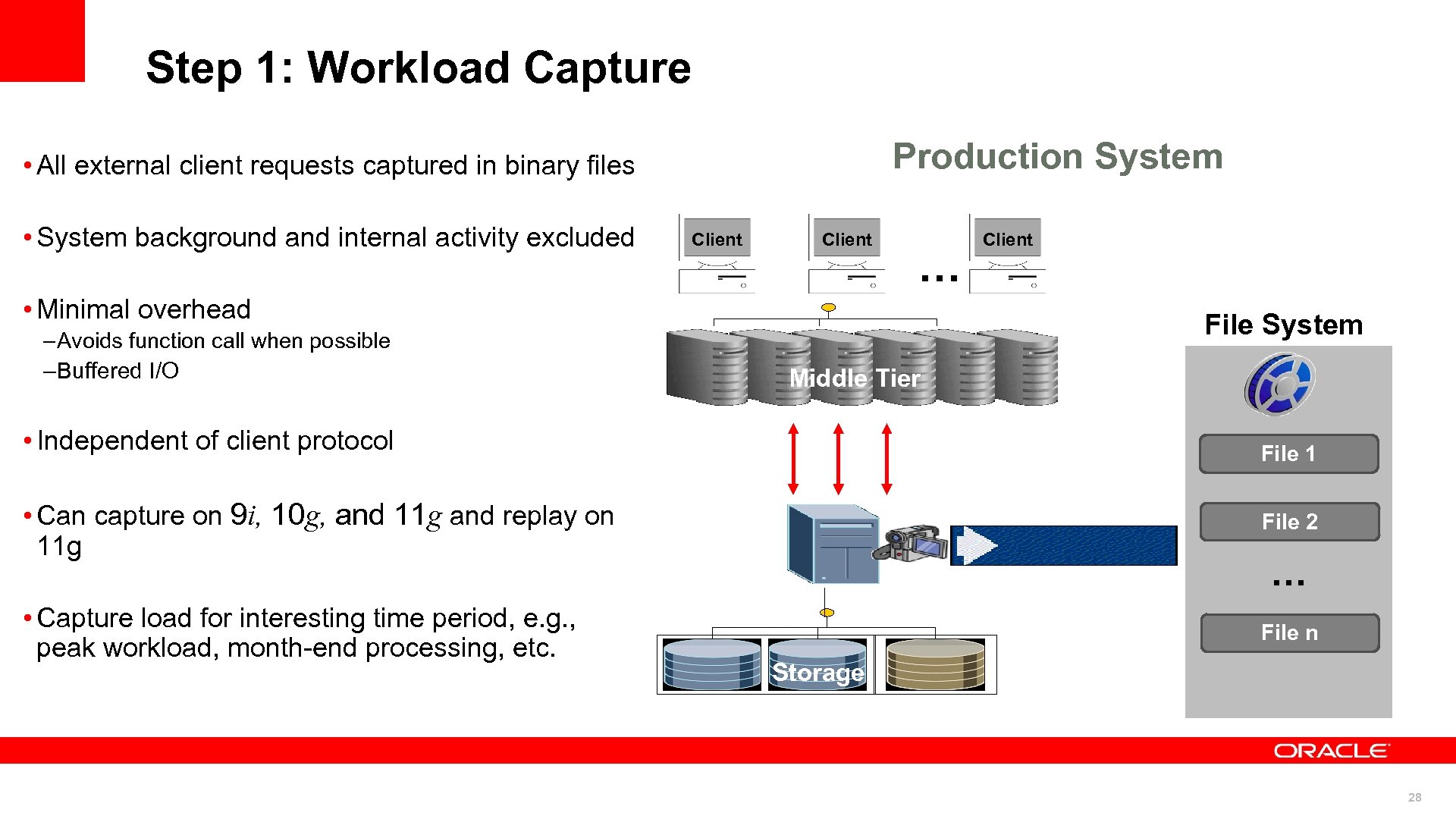 Step 1: Workload Capture Production System • All external client requests captured in binary files • System background and internal activity excluded Client … • Minimal overhead – Avoids function call when possible – Buffered I/O Client File System Middle Tier • Independent of client protocol File 1 • Can capture on 9 i, 10 g, and 11 g and replay on 11 g File 2 • Capture load for interesting time period, e. g. , peak workload, month-end processing, etc. File n … Storage 28
Step 1: Workload Capture Production System • All external client requests captured in binary files • System background and internal activity excluded Client … • Minimal overhead – Avoids function call when possible – Buffered I/O Client File System Middle Tier • Independent of client protocol File 1 • Can capture on 9 i, 10 g, and 11 g and replay on 11 g File 2 • Capture load for interesting time period, e. g. , peak workload, month-end processing, etc. File n … Storage 28
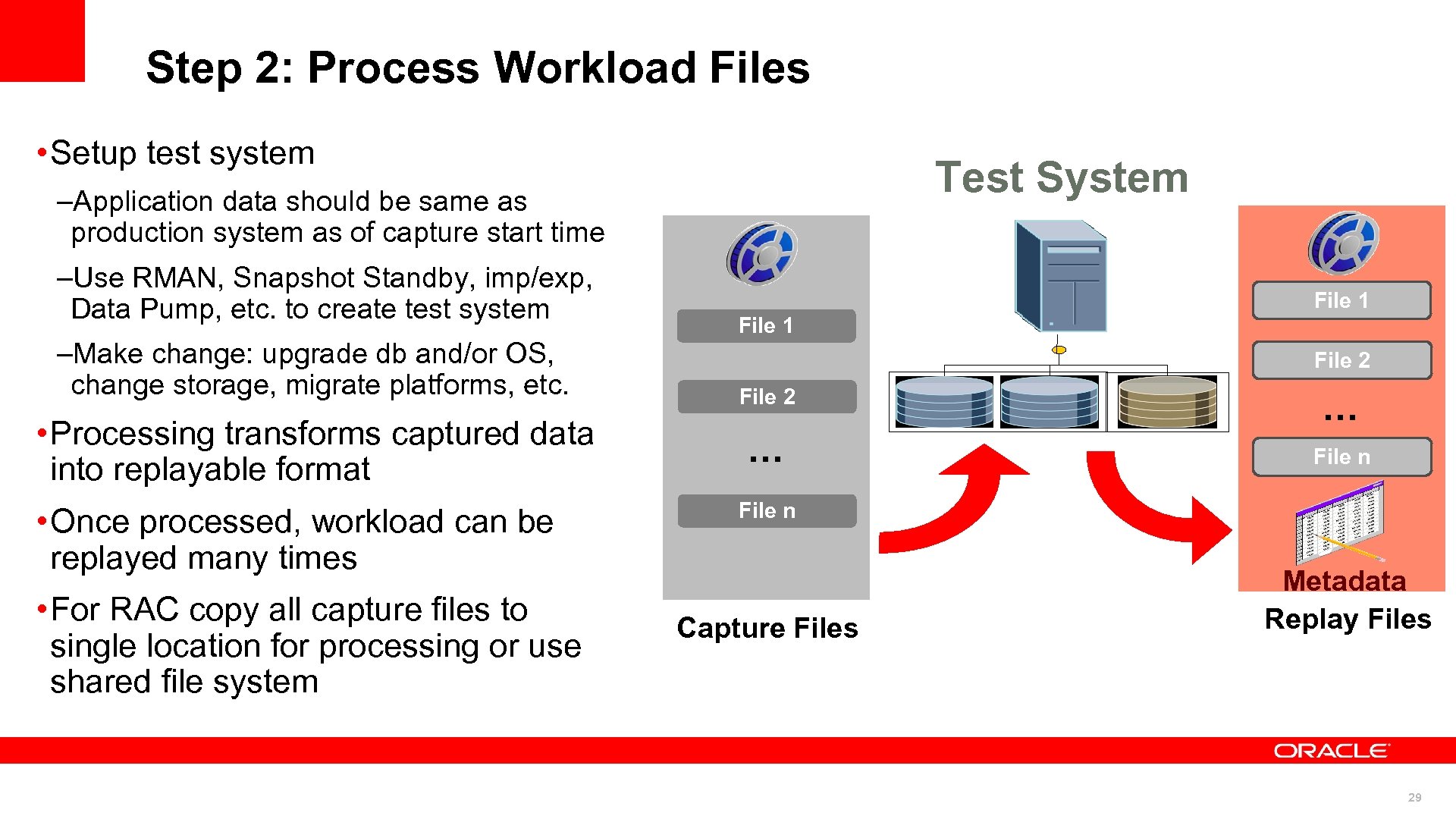 Step 2: Process Workload Files • Setup test system Test System –Application data should be same as production system as of capture start time –Use RMAN, Snapshot Standby, imp/exp, Data Pump, etc. to create test system –Make change: upgrade db and/or OS, change storage, migrate platforms, etc. • Processing transforms captured data into replayable format • Once processed, workload can be replayed many times • For RAC copy all capture files to single location for processing or use shared file system File 1 File 2 … … File n Capture Files Metadata Replay Files 29
Step 2: Process Workload Files • Setup test system Test System –Application data should be same as production system as of capture start time –Use RMAN, Snapshot Standby, imp/exp, Data Pump, etc. to create test system –Make change: upgrade db and/or OS, change storage, migrate platforms, etc. • Processing transforms captured data into replayable format • Once processed, workload can be replayed many times • For RAC copy all capture files to single location for processing or use shared file system File 1 File 2 … … File n Capture Files Metadata Replay Files 29
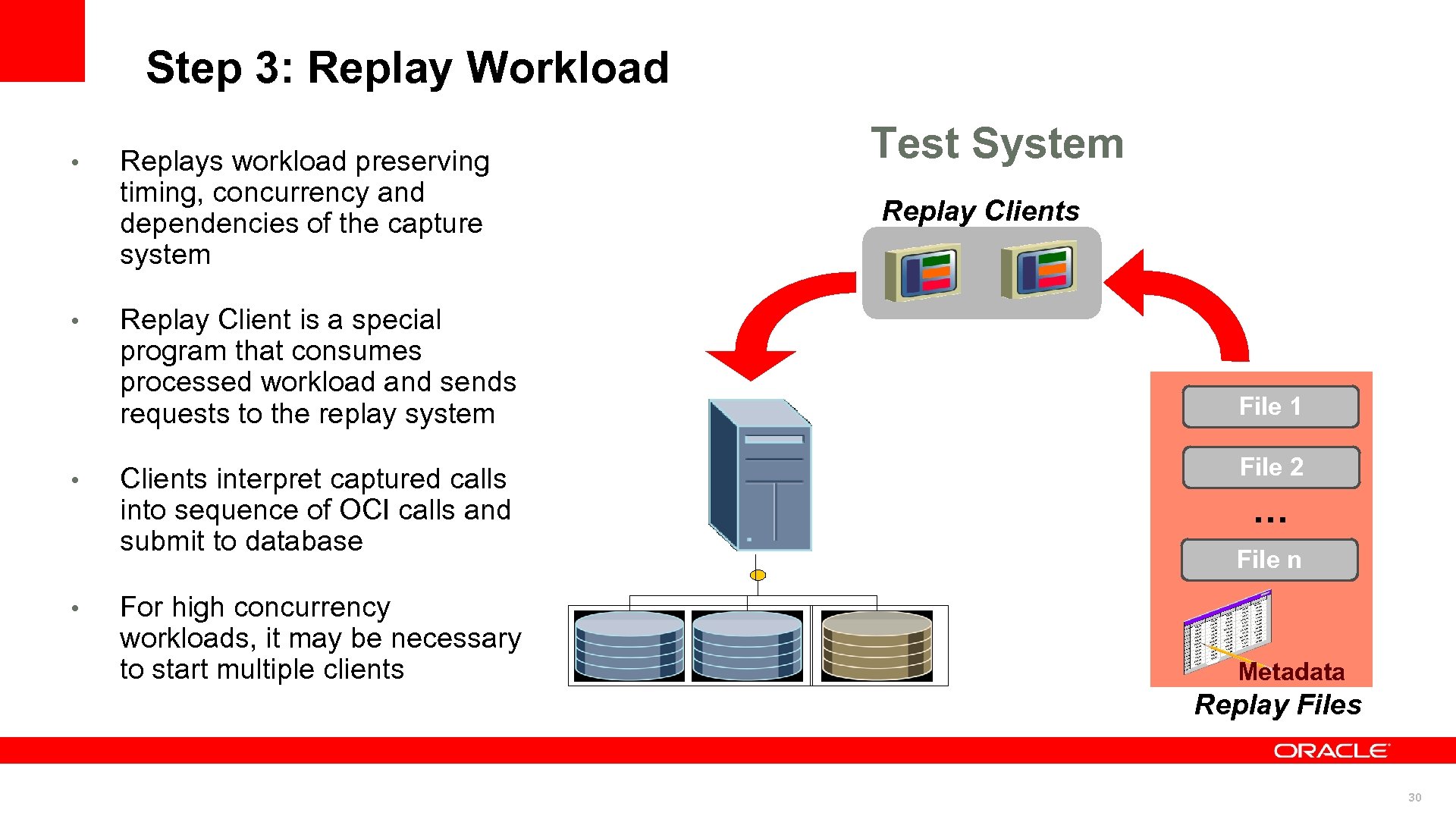 Step 3: Replay Workload • • Replays workload preserving timing, concurrency and dependencies of the capture system Replay Client is a special program that consumes processed workload and sends requests to the replay system Clients interpret captured calls into sequence of OCI calls and submit to database For high concurrency workloads, it may be necessary to start multiple clients Test System Replay Clients File 1 File 2 … File n Metadata Replay Files 30
Step 3: Replay Workload • • Replays workload preserving timing, concurrency and dependencies of the capture system Replay Client is a special program that consumes processed workload and sends requests to the replay system Clients interpret captured calls into sequence of OCI calls and submit to database For high concurrency workloads, it may be necessary to start multiple clients Test System Replay Clients File 1 File 2 … File n Metadata Replay Files 30
 Analysis & Reporting • Error Divergence: For each call error divergence is reported –New: Error encountered during replay not seen during capture –Not Found: Error encountered during capture not seen during replay –Mutated: Different error produced in replay than during capture • Data Divergence –Replay: Number of rows returned by each call are compared and divergences reported –User: Application level validation scripts • Performance Reporting –Capture and Replay Report: Provides high-level performance information –ADDM Report: Provides in-depth performance analysis –AWR, ASH Report: Facilitates comparative or skew analysis 31
Analysis & Reporting • Error Divergence: For each call error divergence is reported –New: Error encountered during replay not seen during capture –Not Found: Error encountered during capture not seen during replay –Mutated: Different error produced in replay than during capture • Data Divergence –Replay: Number of rows returned by each call are compared and divergences reported –User: Application level validation scripts • Performance Reporting –Capture and Replay Report: Provides high-level performance information –ADDM Report: Provides in-depth performance analysis –AWR, ASH Report: Facilitates comparative or skew analysis 31
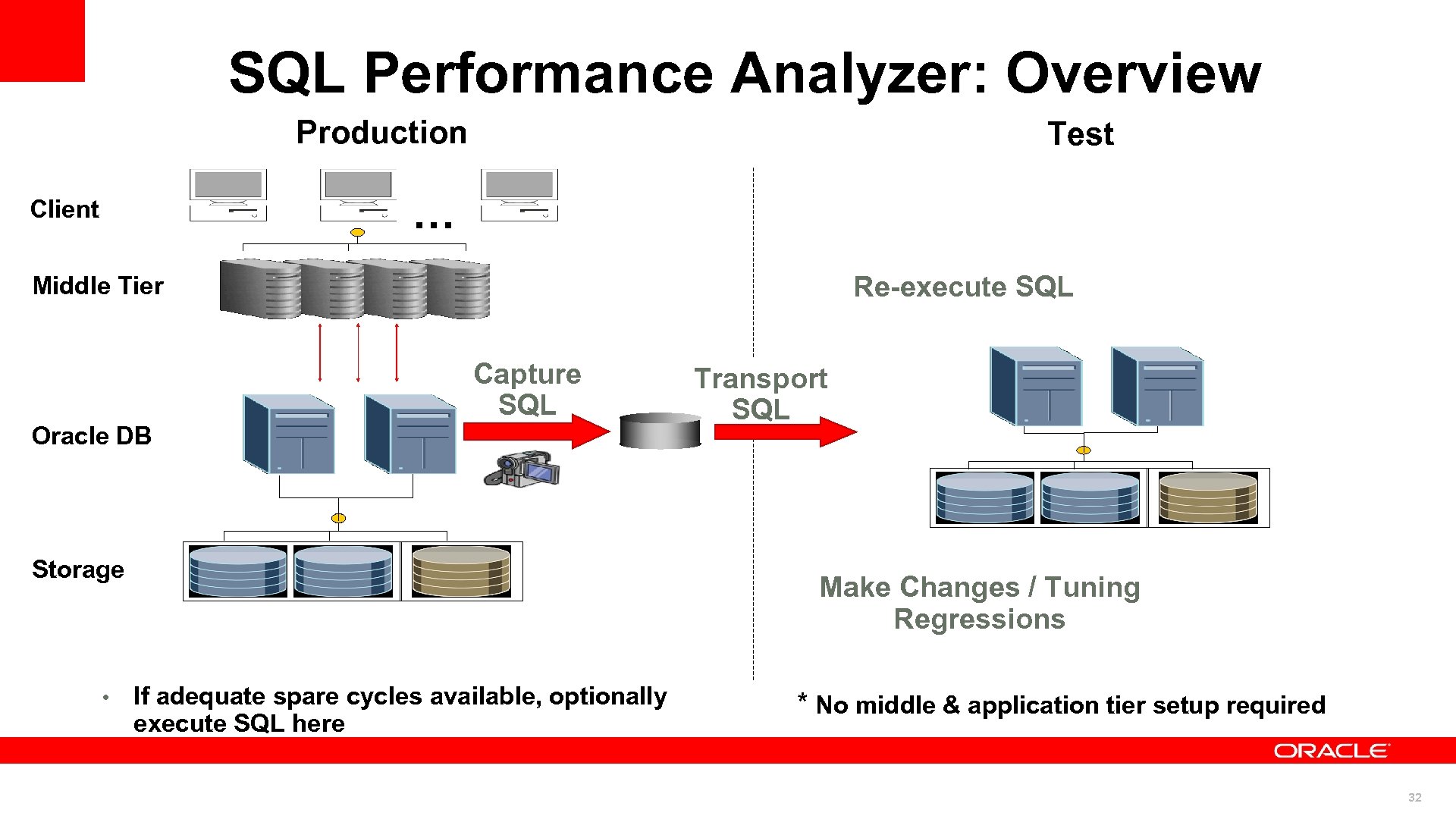 SQL Performance Analyzer: Overview Production Test … Client Re-execute SQL Middle Tier Capture SQL Oracle DB Storage • Transport SQL … … Make Changes / Tuning Regressions If adequate spare cycles available, optionally execute SQL here * No middle & application tier setup required 32
SQL Performance Analyzer: Overview Production Test … Client Re-execute SQL Middle Tier Capture SQL Oracle DB Storage • Transport SQL … … Make Changes / Tuning Regressions If adequate spare cycles available, optionally execute SQL here * No middle & application tier setup required 32
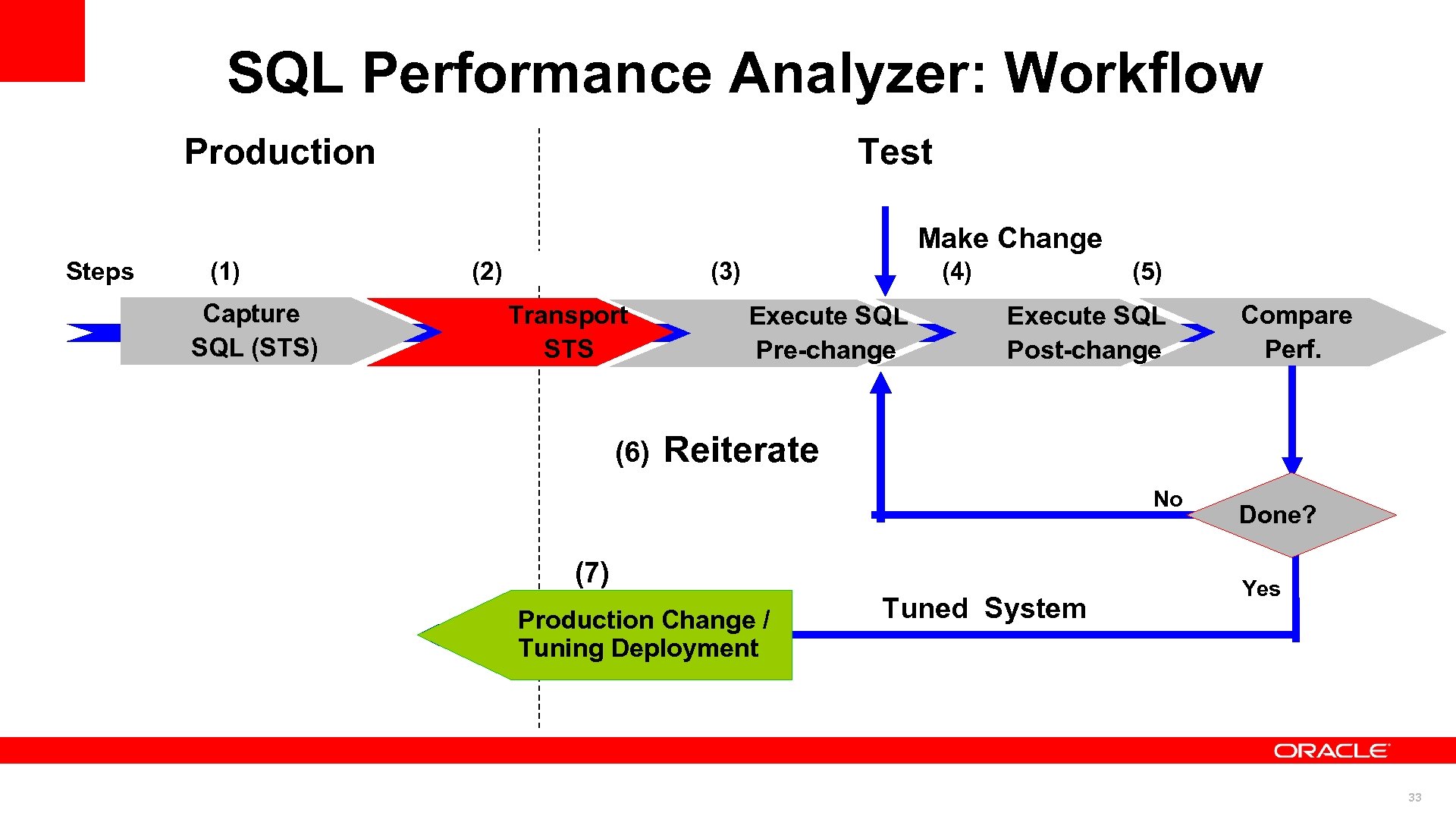 SQL Performance Analyzer: Workflow Production Test Make Change Steps (1) Capture SQL (STS) (2) (3) Transport STS (6) (4) Execute SQL Pre-change (5) Execute SQL Post-change Compare Perf. Reiterate No (7) Production Change / (7) Deployment Tuning Tuned System Done? Yes 33
SQL Performance Analyzer: Workflow Production Test Make Change Steps (1) Capture SQL (STS) (2) (3) Transport STS (6) (4) Execute SQL Pre-change (5) Execute SQL Post-change Compare Perf. Reiterate No (7) Production Change / (7) Deployment Tuning Tuned System Done? Yes 33
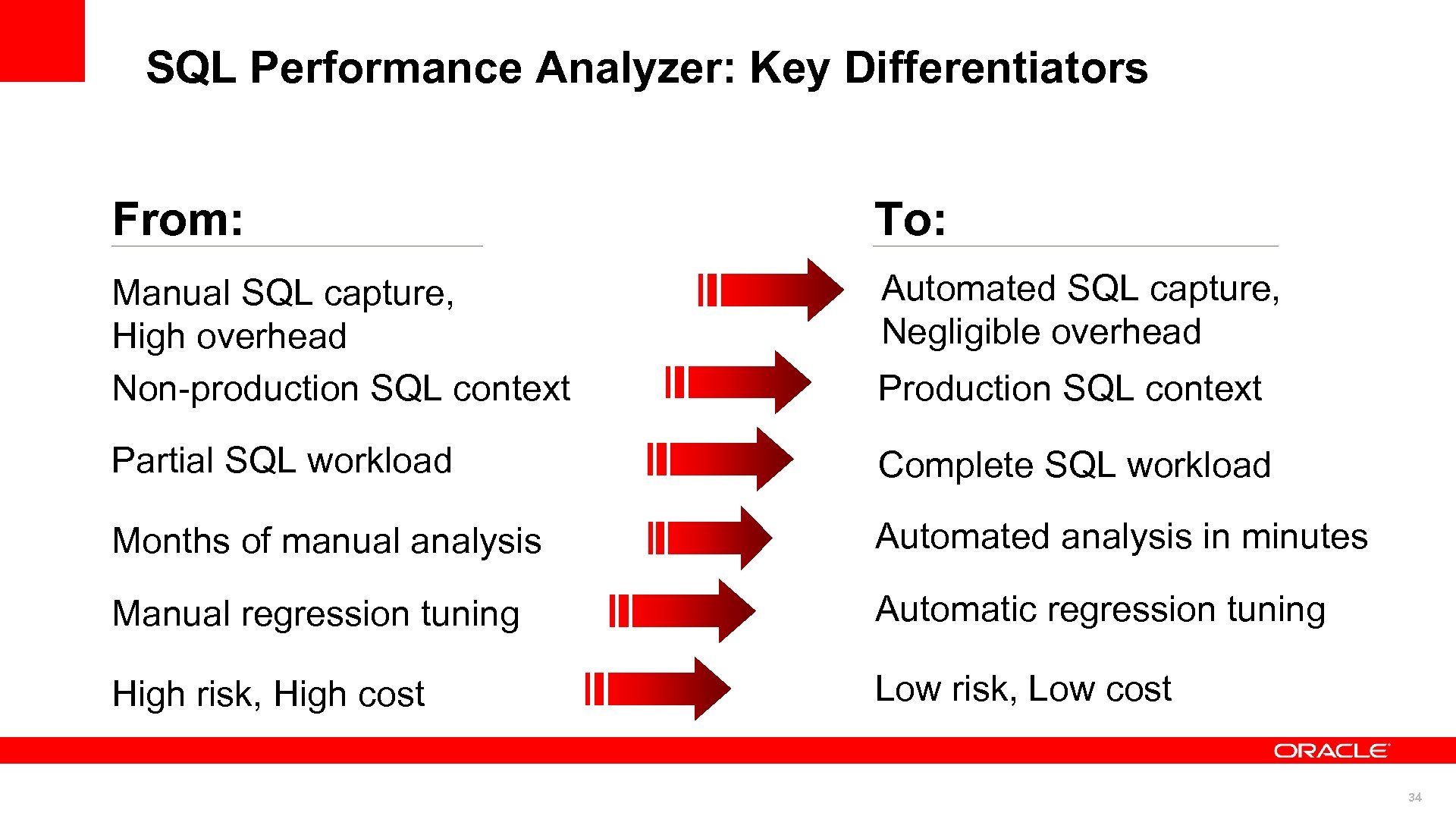 SQL Performance Analyzer: Key Differentiators From: To: Manual SQL capture, High overhead Non-production SQL context Automated SQL capture, Negligible overhead Production SQL context Partial SQL workload Complete SQL workload Months of manual analysis Automated analysis in minutes Manual regression tuning Automatic regression tuning High risk, High cost Low risk, Low cost 34
SQL Performance Analyzer: Key Differentiators From: To: Manual SQL capture, High overhead Non-production SQL context Automated SQL capture, Negligible overhead Production SQL context Partial SQL workload Complete SQL workload Months of manual analysis Automated analysis in minutes Manual regression tuning Automatic regression tuning High risk, High cost Low risk, Low cost 34
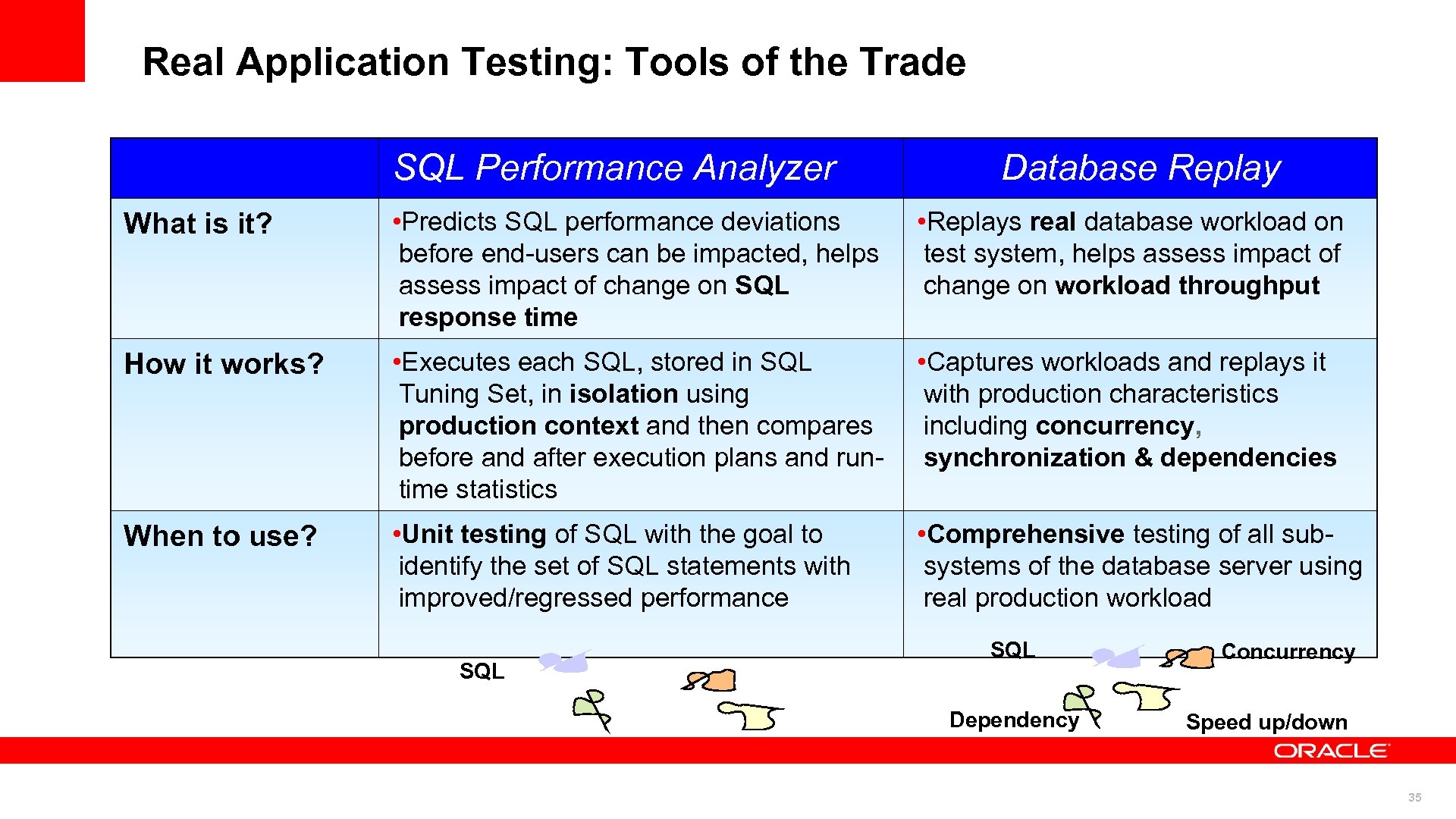 Real Application Testing: Tools of the Trade SQL Performance Analyzer Database Replay What is it? • Predicts SQL performance deviations before end-users can be impacted, helps assess impact of change on SQL response time • Replays real database workload on test system, helps assess impact of change on workload throughput How it works? • Executes each SQL, stored in SQL Tuning Set, in isolation using production context and then compares before and after execution plans and runtime statistics • Captures workloads and replays it with production characteristics including concurrency, synchronization & dependencies When to use? • Unit testing of SQL with the goal to identify the set of SQL statements with improved/regressed performance • Comprehensive testing of all subsystems of the database server using real production workload SQL Dependency Concurrency Speed up/down 35
Real Application Testing: Tools of the Trade SQL Performance Analyzer Database Replay What is it? • Predicts SQL performance deviations before end-users can be impacted, helps assess impact of change on SQL response time • Replays real database workload on test system, helps assess impact of change on workload throughput How it works? • Executes each SQL, stored in SQL Tuning Set, in isolation using production context and then compares before and after execution plans and runtime statistics • Captures workloads and replays it with production characteristics including concurrency, synchronization & dependencies When to use? • Unit testing of SQL with the goal to identify the set of SQL statements with improved/regressed performance • Comprehensive testing of all subsystems of the database server using real production workload SQL Dependency Concurrency Speed up/down 35
 More information… • Hands on Lab: S 318966 – Database and Application Testing HOL – Wed: 4. 45 -5. 45 pm – Marriott Golden Gate • SPA / Database Replay Demo grounds – Moscone West: 038/039 36
More information… • Hands on Lab: S 318966 – Database and Application Testing HOL – Wed: 4. 45 -5. 45 pm – Marriott Golden Gate • SPA / Database Replay Demo grounds – Moscone West: 038/039 36
 The Ability to forget And let it go © 2010 Oracle Corporation 37 37
The Ability to forget And let it go © 2010 Oracle Corporation 37 37
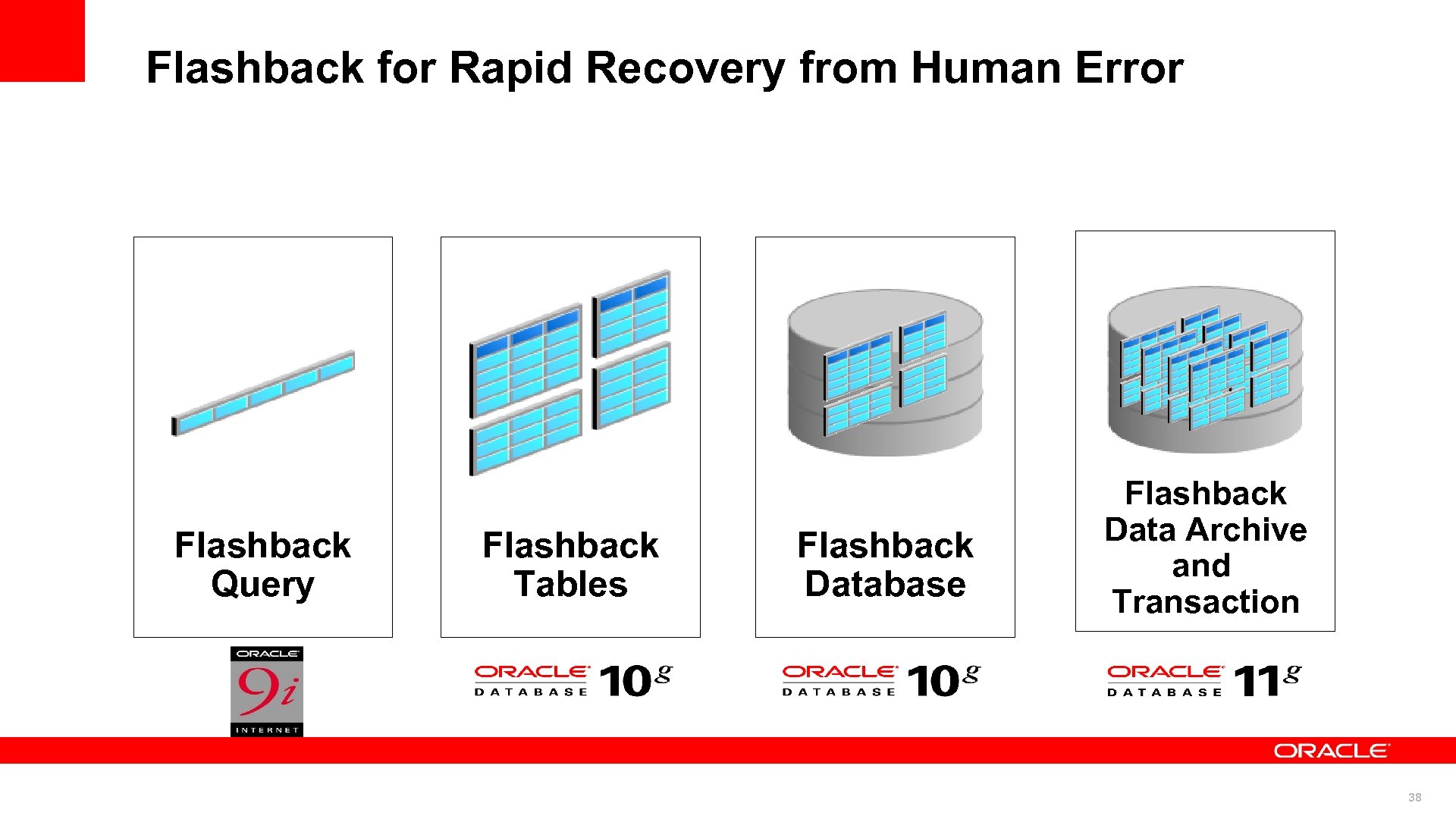 Flashback for Rapid Recovery from Human Error Flashback Query Flashback Tables Flashback Database Flashback Data Archive and Transaction 38
Flashback for Rapid Recovery from Human Error Flashback Query Flashback Tables Flashback Database Flashback Data Archive and Transaction 38
 Restore Points • Restore point – specifies a jump label –Named Restore Point • Similar to a bookmark • "Can be" - but no guarantee • Will be recorded to the control file SQL> CREATE RESTORE POINT rpt; SQL> FLASHBACK DATABASE TO RESTORE POINT rpt; –Guaranteed Restore Point • Similar to storage snapshots • Overrides the FLASHBACK_RETENTION_TARGET • Attention: A guarantee restore point can stop the whole database SQL> CREATE RESTORE POINT grpt GUARANTEE FLASHBACK DATABASE; SQL> FLASHBACK DATABASE TO RESTORE POINT grpt; 39
Restore Points • Restore point – specifies a jump label –Named Restore Point • Similar to a bookmark • "Can be" - but no guarantee • Will be recorded to the control file SQL> CREATE RESTORE POINT rpt; SQL> FLASHBACK DATABASE TO RESTORE POINT rpt; –Guaranteed Restore Point • Similar to storage snapshots • Overrides the FLASHBACK_RETENTION_TARGET • Attention: A guarantee restore point can stop the whole database SQL> CREATE RESTORE POINT grpt GUARANTEE FLASHBACK DATABASE; SQL> FLASHBACK DATABASE TO RESTORE POINT grpt; 39
 Never Stopping © 2010 Oracle Corporation 40 40
Never Stopping © 2010 Oracle Corporation 40 40
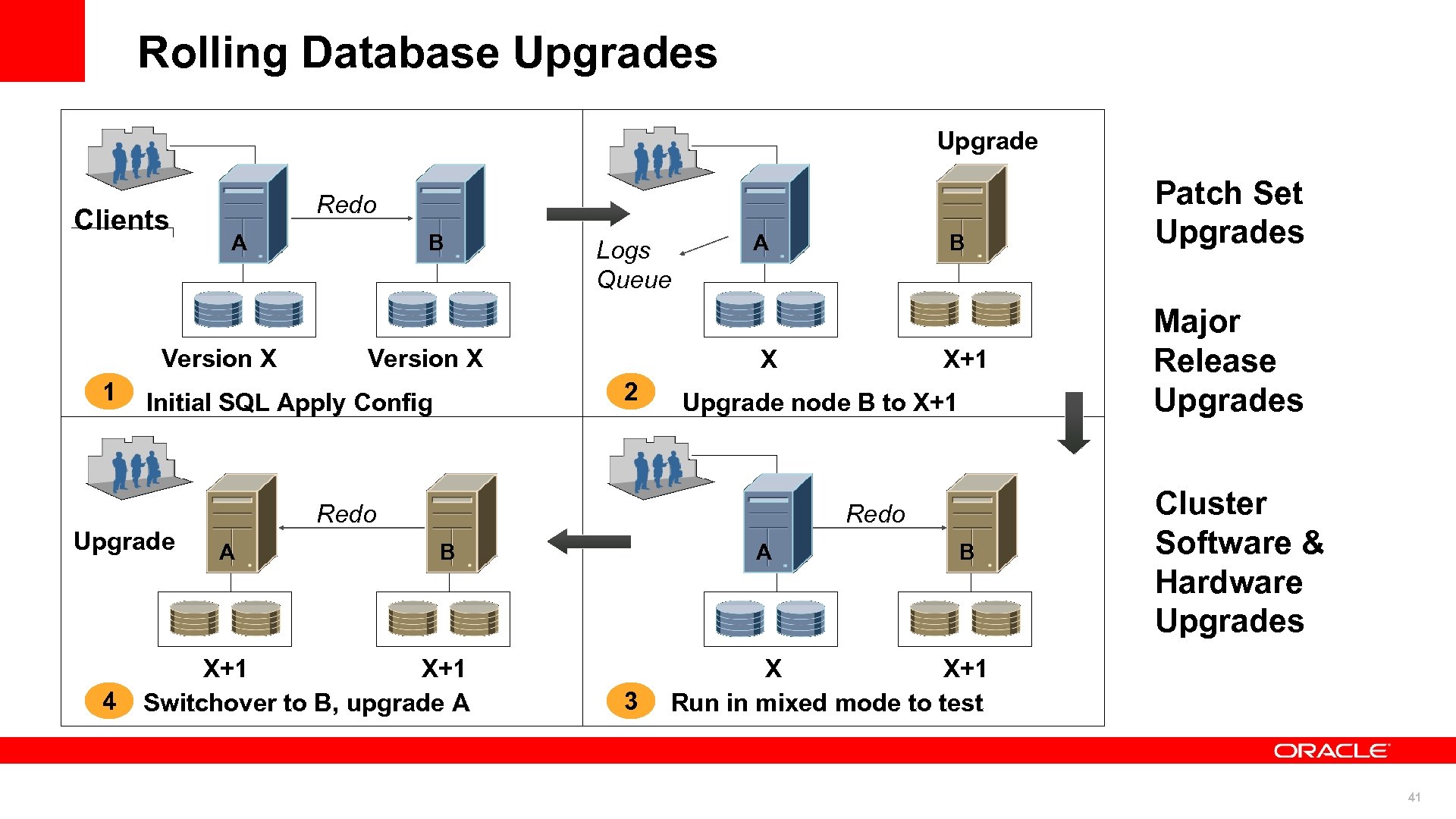 Rolling Database Upgrades Upgrade Clients Redo A Version X 1 Logs Queue Version X A X+1 Upgrade node B to X+1 Redo A B X 2 Initial SQL Apply Config Upgrade 4 B Redo B X+1 Switchover to B, upgrade A A 3 B Patch Set Upgrades Major Release Upgrades Cluster Software & Hardware Upgrades X X+1 Run in mixed mode to test 41
Rolling Database Upgrades Upgrade Clients Redo A Version X 1 Logs Queue Version X A X+1 Upgrade node B to X+1 Redo A B X 2 Initial SQL Apply Config Upgrade 4 B Redo B X+1 Switchover to B, upgrade A A 3 B Patch Set Upgrades Major Release Upgrades Cluster Software & Hardware Upgrades X X+1 Run in mixed mode to test 41
 Online Application Upgrade Edition-based redefinition • Code changes are installed in the privacy of a new edition • Data changes are made safely by writing only to new columns or new tables not seen by the old edition • An editioning view exposes a different projection of a table into each edition to allow each to see just its own columns • A crossedition trigger propagates data changes made by the old edition into the new edition’s columns, or (in hotrollover) vice-versa 42
Online Application Upgrade Edition-based redefinition • Code changes are installed in the privacy of a new edition • Data changes are made safely by writing only to new columns or new tables not seen by the old edition • An editioning view exposes a different projection of a table into each edition to allow each to see just its own columns • A crossedition trigger propagates data changes made by the old edition into the new edition’s columns, or (in hotrollover) vice-versa 42
 Editions & object visibility Object_4 Object_3 Object_2 Object_1 Pre-upgrade edition 43
Editions & object visibility Object_4 Object_3 Object_2 Object_1 Pre-upgrade edition 43
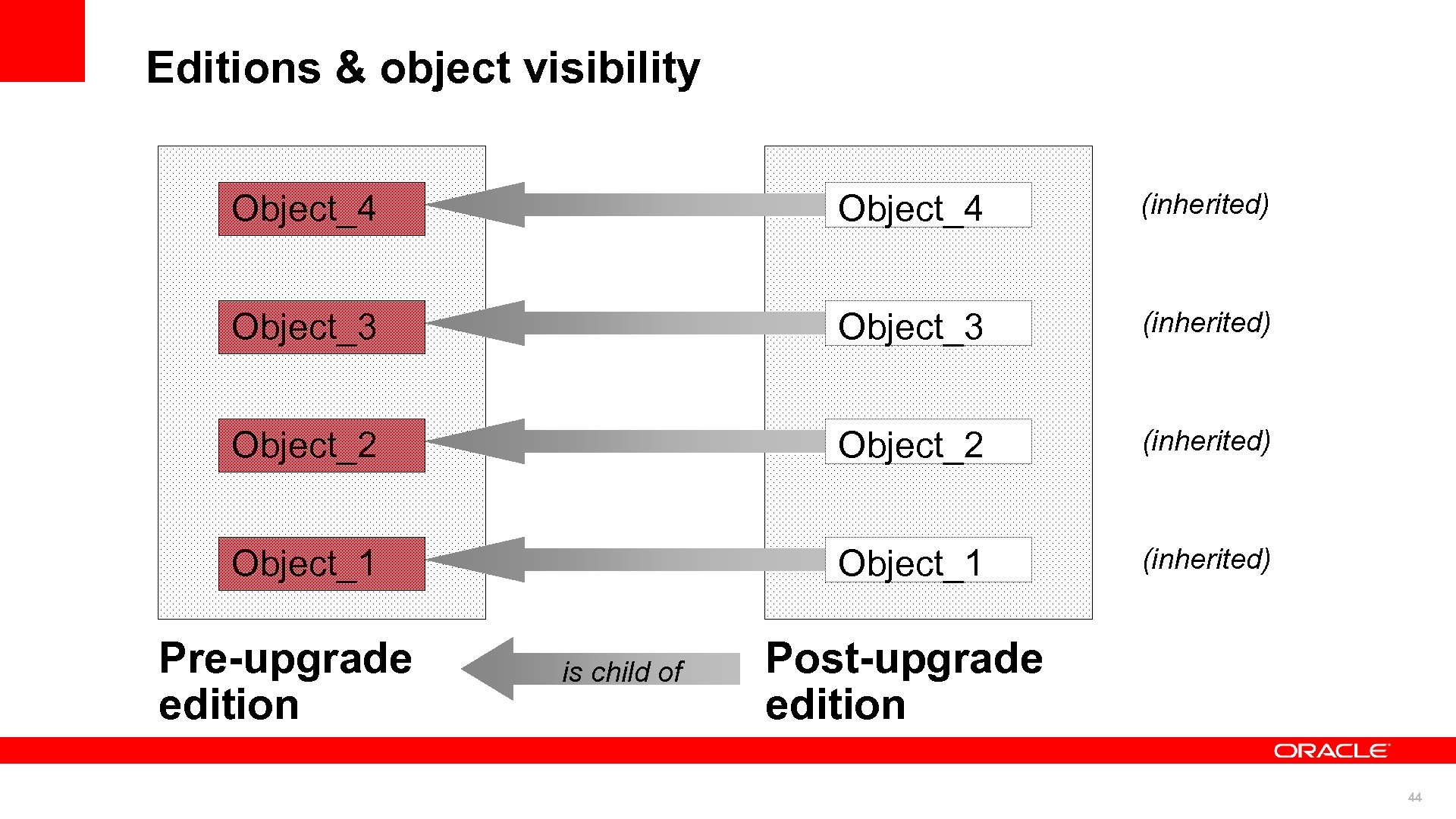 Editions & object visibility Object_4 (inherited) Object_3 (inherited) Object_2 (inherited) Object_1 (inherited) Pre-upgrade edition is child of Post-upgrade edition 44
Editions & object visibility Object_4 (inherited) Object_3 (inherited) Object_2 (inherited) Object_1 (inherited) Pre-upgrade edition is child of Post-upgrade edition 44
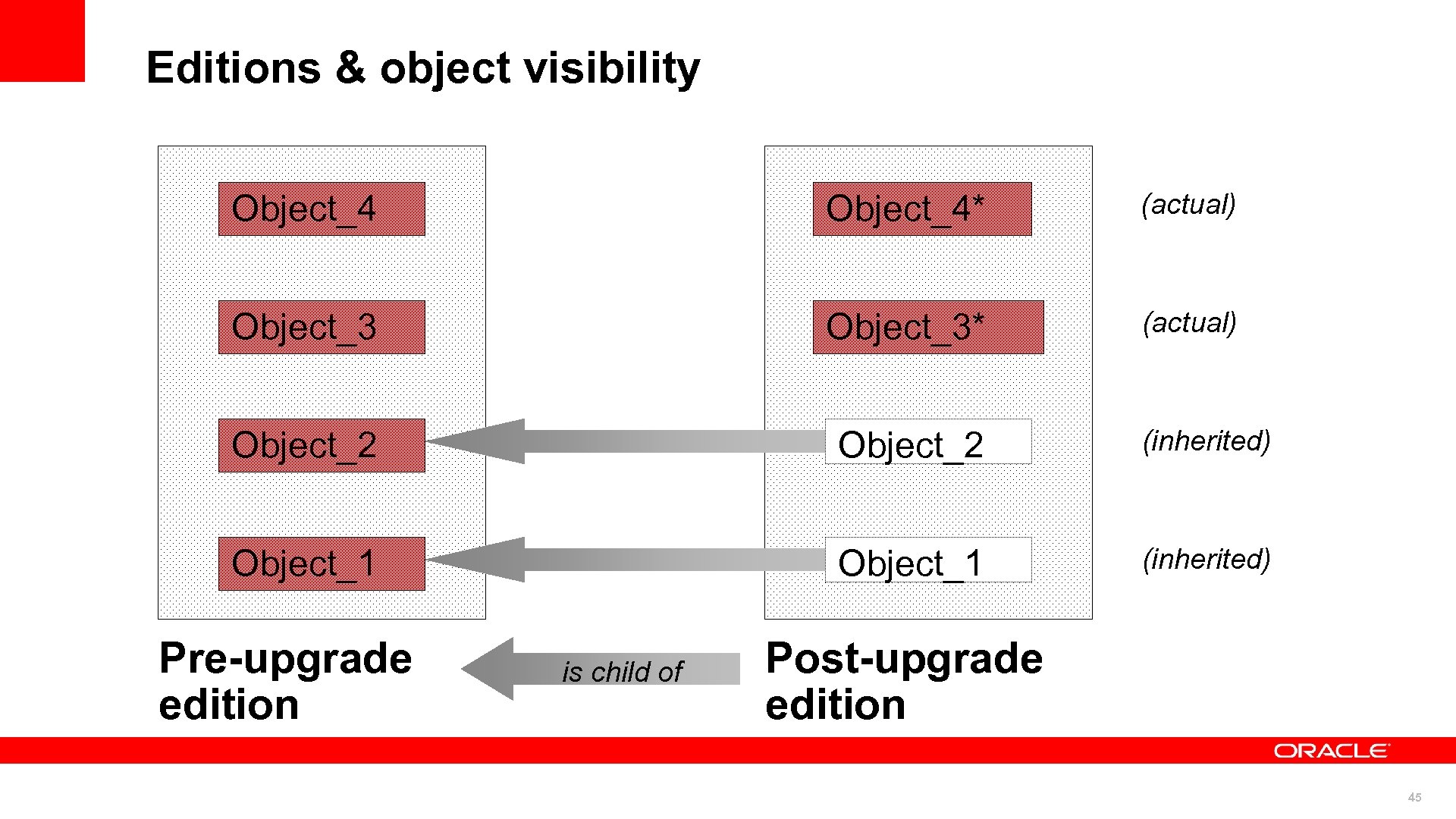 Editions & object visibility Object_4* (actual) Object_3* (actual) Object_2 (inherited) Object_1 (inherited) Pre-upgrade edition is child of Post-upgrade edition 45
Editions & object visibility Object_4* (actual) Object_3* (actual) Object_2 (inherited) Object_1 (inherited) Pre-upgrade edition is child of Post-upgrade edition 45
 Planning Ahead Upgrade Planner © 2010 Oracle Corporation 46 46
Planning Ahead Upgrade Planner © 2010 Oracle Corporation 46 46
 The following is intended to outline our general product direction. It is intended for information purposes only, and may not be incorporated into any contract. It is not a commitment to deliver any material, code, or functionality, and should not be relied upon in making purchasing decisions. The development, release, and timing of any features or functionality described for Oracle’s products remains at the sole discretion of Oracle. 47
The following is intended to outline our general product direction. It is intended for information purposes only, and may not be incorporated into any contract. It is not a commitment to deliver any material, code, or functionality, and should not be relied upon in making purchasing decisions. The development, release, and timing of any features or functionality described for Oracle’s products remains at the sole discretion of Oracle. 47
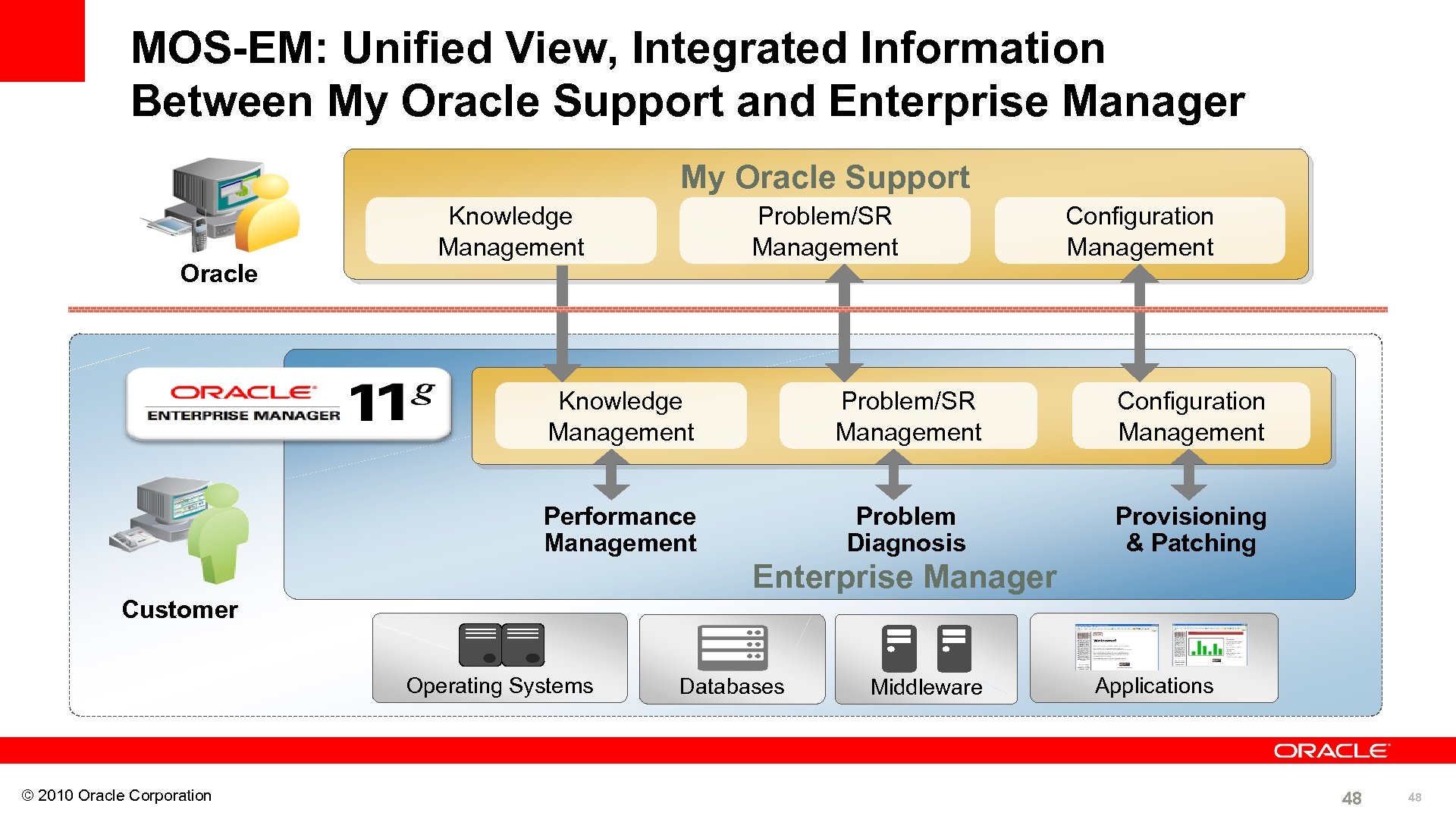 MOS-EM: Unified View, Integrated Information Between My Oracle Support and Enterprise Manager My Oracle Support Oracle Knowledge Management Problem/SR Management Configuration Management Performance Management Problem Diagnosis Provisioning & Patching Enterprise Manager Customer Operating Systems © 2010 Oracle Corporation Databases Middleware Applications 48 48
MOS-EM: Unified View, Integrated Information Between My Oracle Support and Enterprise Manager My Oracle Support Oracle Knowledge Management Problem/SR Management Configuration Management Performance Management Problem Diagnosis Provisioning & Patching Enterprise Manager Customer Operating Systems © 2010 Oracle Corporation Databases Middleware Applications 48 48
 My Oracle Support – Upgrade Planner What Are We Announcing? • New Feature in My Oracle Support – Assist customers in planning the an Upgrade of Oracle technology • Benefits – Reduced time to create, manage and execute Upgrade plan • Streamlined process to request merge patches – Greater Reliability due to Software Currency • Latest SW, Patch, and Certification information • Accuracy of recommendations based on config data (not manual) – Lower Risk • Automated analysis for missing patches and conflict checking © 2010 Oracle Corporation 49 49
My Oracle Support – Upgrade Planner What Are We Announcing? • New Feature in My Oracle Support – Assist customers in planning the an Upgrade of Oracle technology • Benefits – Reduced time to create, manage and execute Upgrade plan • Streamlined process to request merge patches – Greater Reliability due to Software Currency • Latest SW, Patch, and Certification information • Accuracy of recommendations based on config data (not manual) – Lower Risk • Automated analysis for missing patches and conflict checking © 2010 Oracle Corporation 49 49
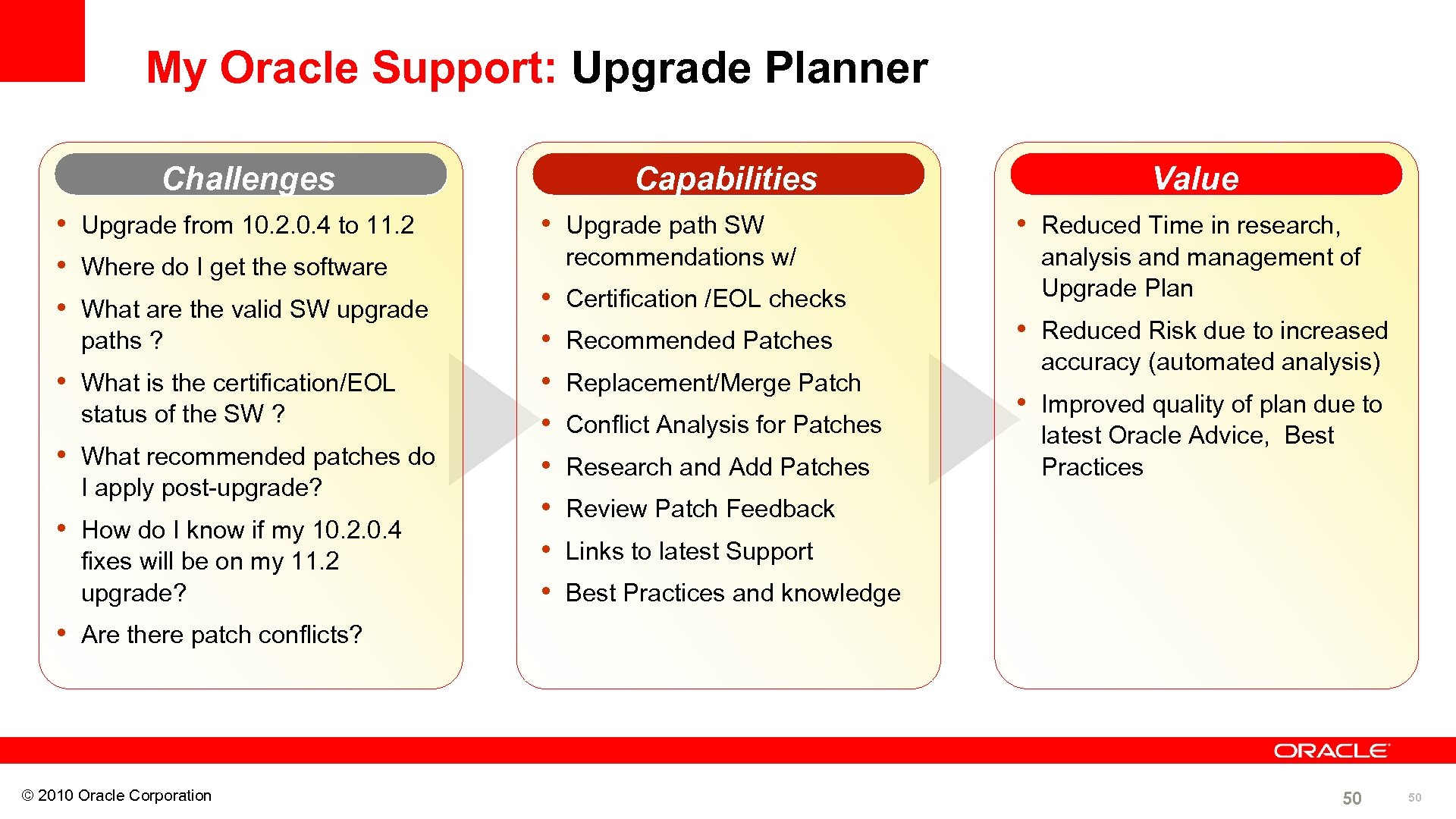 My Oracle Support: Upgrade Planner Challenges • Upgrade from 10. 2. 0. 4 to 11. 2 • Where do I get the software • What are the valid SW upgrade paths ? • What is the certification/EOL status of the SW ? • What recommended patches do I apply post-upgrade? • How do I know if my 10. 2. 0. 4 fixes will be on my 11. 2 upgrade? Capabilities • Upgrade path SW recommendations w/ • • Certification /EOL checks Recommended Patches Replacement/Merge Patch Conflict Analysis for Patches Research and Add Patches Value • Reduced Time in research, analysis and management of Upgrade Plan • Reduced Risk due to increased accuracy (automated analysis) • Improved quality of plan due to latest Oracle Advice, Best Practices Review Patch Feedback Links to latest Support Best Practices and knowledge • Are there patch conflicts? © 2010 Oracle Corporation 50 50
My Oracle Support: Upgrade Planner Challenges • Upgrade from 10. 2. 0. 4 to 11. 2 • Where do I get the software • What are the valid SW upgrade paths ? • What is the certification/EOL status of the SW ? • What recommended patches do I apply post-upgrade? • How do I know if my 10. 2. 0. 4 fixes will be on my 11. 2 upgrade? Capabilities • Upgrade path SW recommendations w/ • • Certification /EOL checks Recommended Patches Replacement/Merge Patch Conflict Analysis for Patches Research and Add Patches Value • Reduced Time in research, analysis and management of Upgrade Plan • Reduced Risk due to increased accuracy (automated analysis) • Improved quality of plan due to latest Oracle Advice, Best Practices Review Patch Feedback Links to latest Support Best Practices and knowledge • Are there patch conflicts? © 2010 Oracle Corporation 50 50
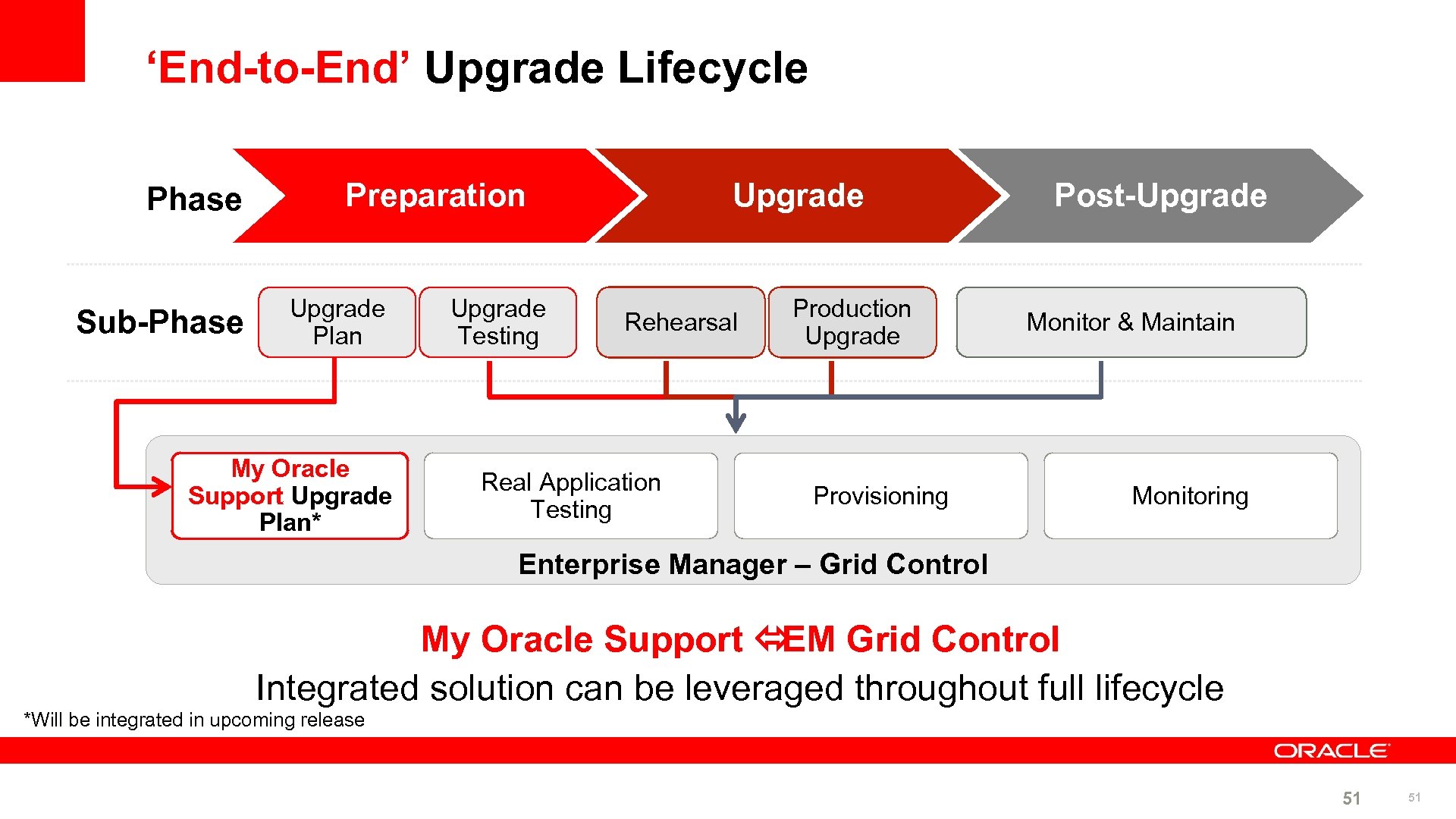 ‘End-to-End’ Upgrade Lifecycle Phase Sub-Phase Preparation Upgrade Plan My Oracle Support Upgrade Plan* Upgrade Testing Upgrade Rehearsal Real Application Testing Production Upgrade Provisioning Post-Upgrade Monitor & Maintain Monitoring Enterprise Manager – Grid Control My Oracle Support ó Grid Control EM Integrated solution can be leveraged throughout full lifecycle *Will be integrated in upcoming release 51 51
‘End-to-End’ Upgrade Lifecycle Phase Sub-Phase Preparation Upgrade Plan My Oracle Support Upgrade Plan* Upgrade Testing Upgrade Rehearsal Real Application Testing Production Upgrade Provisioning Post-Upgrade Monitor & Maintain Monitoring Enterprise Manager – Grid Control My Oracle Support ó Grid Control EM Integrated solution can be leveraged throughout full lifecycle *Will be integrated in upcoming release 51 51

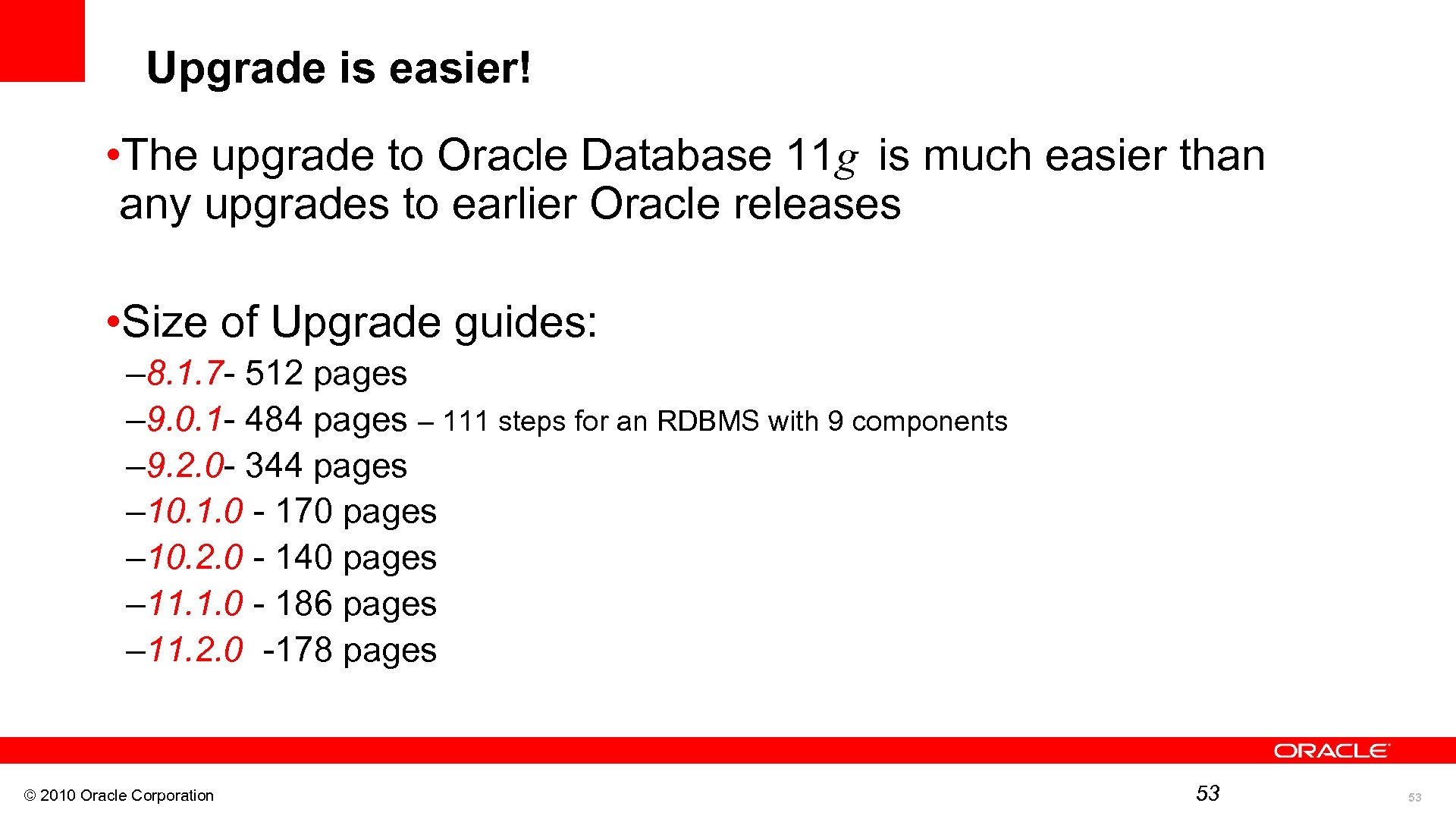 Upgrade is easier! is much easier than • The upgrade to Oracle Database 11 g any upgrades to earlier Oracle releases • Size of Upgrade guides: – 8. 1. 7 - 512 pages – 9. 0. 1 - 484 pages – 111 steps for an RDBMS with 9 components – 9. 2. 0 - 344 pages – 10. 1. 0 - 170 pages – 10. 2. 0 - 140 pages – 11. 1. 0 - 186 pages – 11. 2. 0 -178 pages © 2010 Oracle Corporation 53 53
Upgrade is easier! is much easier than • The upgrade to Oracle Database 11 g any upgrades to earlier Oracle releases • Size of Upgrade guides: – 8. 1. 7 - 512 pages – 9. 0. 1 - 484 pages – 111 steps for an RDBMS with 9 components – 9. 2. 0 - 344 pages – 10. 1. 0 - 170 pages – 10. 2. 0 - 140 pages – 11. 1. 0 - 186 pages – 11. 2. 0 -178 pages © 2010 Oracle Corporation 53 53
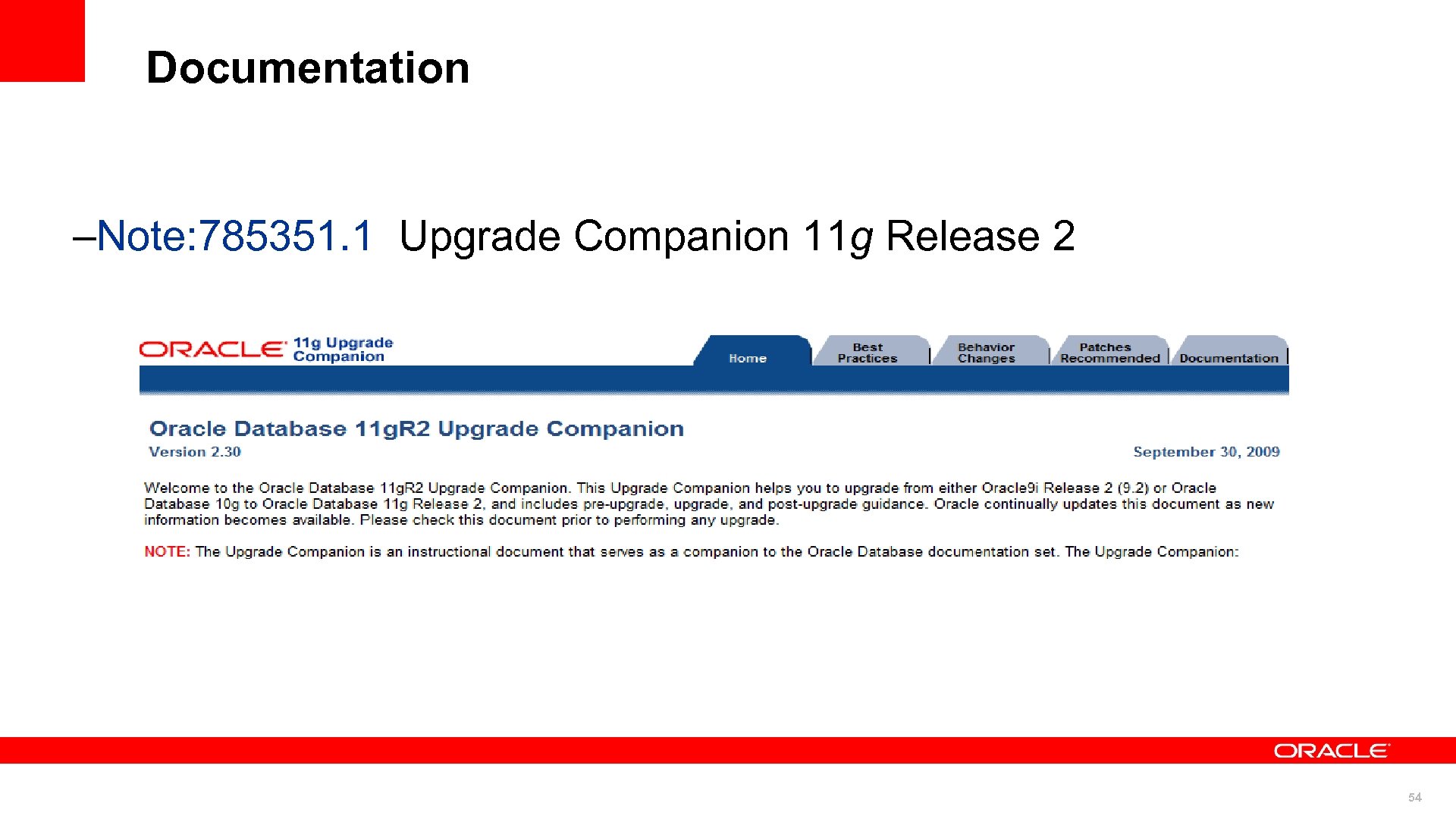 Documentation –Note: 785351. 1 Upgrade Companion 11 g Release 2 54
Documentation –Note: 785351. 1 Upgrade Companion 11 g Release 2 54
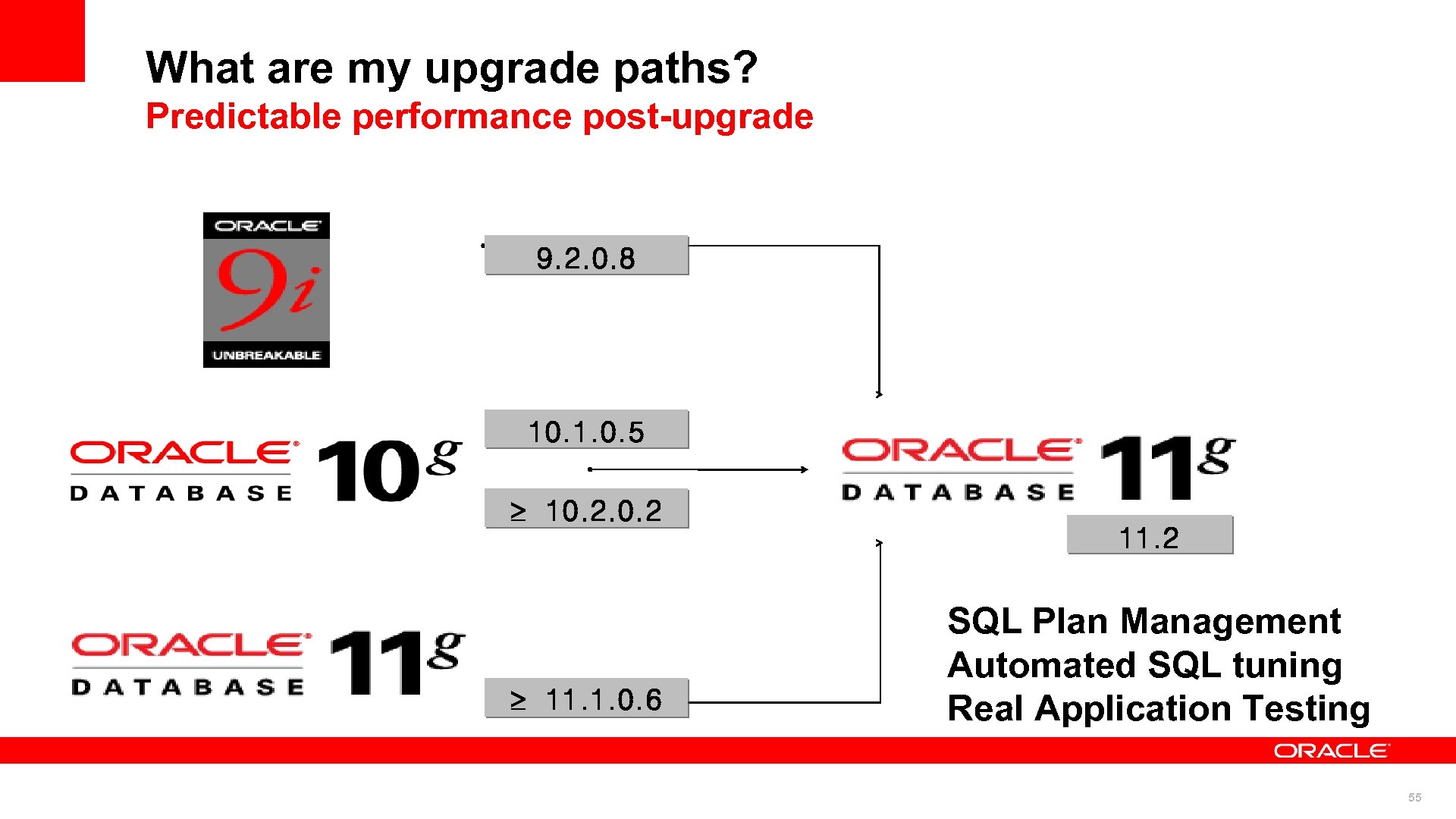 What are my upgrade paths? Predictable performance post-upgrade 9. 2. 0. 8 10. 1. 0. 5 10. 2 11. 1. 0. 6 11. 2 SQL Plan Management Automated SQL tuning Real Application Testing 55
What are my upgrade paths? Predictable performance post-upgrade 9. 2. 0. 8 10. 1. 0. 5 10. 2 11. 1. 0. 6 11. 2 SQL Plan Management Automated SQL tuning Real Application Testing 55
 56
56


