e08d16c9d9e7165de55277628f4b7fae.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25

Session II Supply-use tables as a framework for annual and quarterly accounts Workshop on national accounts for Asian member countries of the organization of Islamic Conference Ankara, Turkey 1 -2 December 2008 by Devi Manraj IMF Regional statistics advisor devimanraj@gmail. com
Why use the SUT framework ? u u Use of SUT framework ensures internally consistent data for each activity and product category. Data from different sources appear in a systematic and organized fashion Allows the compiler to eliminate inconsistencies and to identify and fill in data gaps Allows compilation of more reliable values for GDP than those obtained by calculating GDP from the production, expenditure or income side separately 2
Use of SUT u SUT can be used as a compilation tool because the overall framework facilitates: – data checking/reconciliation. – gap filling. u A number of countries treat SUT as central to their compilation process, not just as an irregular add-on needed to derive input-output tables. 3

The Supply Table The supply table contains Two transaction columns: u Output at basic prices u Imports c. i. f. and Three adjustment columns: u Taxes on products. u Trade and transport margins; and u C. i. f. /f. o. b. adjustments. 4

The Use Table The use table includes: u Intermediate consumption; u Final consumption; u Gross capital formation; and u Exports. These transactions are valued at purchasers’ prices; i. e. the valuation includes taxes on production and imports, as well as trade and transport margins for each individual set of numbers. 5

Valuation of Transactions Equality of supply and use – Supply at basic prices Plus – Taxes less subsidies on products (Including nondeductible VAT) Plus – Trade and transport margins Equals – Supply at purchasers’ prices Equals – Use at purchasers’ prices 6
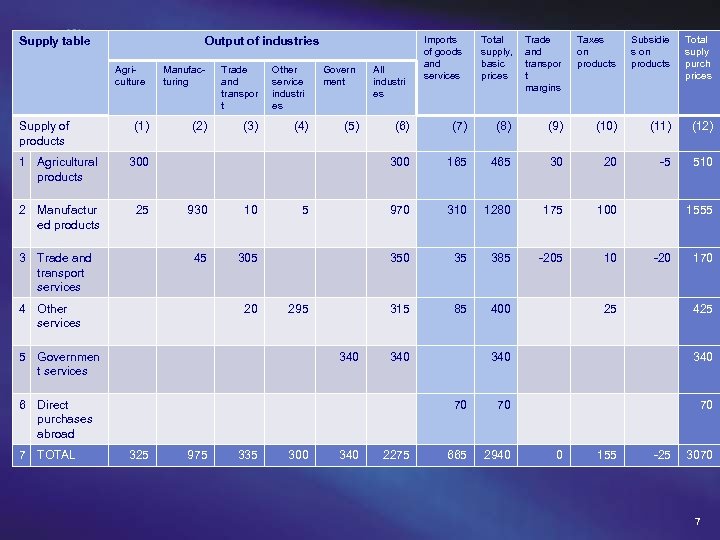
Supply table Agriculture Supply of products Imports of goods and services Total supply, basic prices Trade and transpor t margins Taxes on products Subsidie s on products Total suply purch prices (6) (7) (8) (9) (10) (11) (12) 300 165 465 30 20 -5 510 970 310 1280 175 100 35 385 -205 10 315 85 400 Output of industries (1) 1 Agricultural products 25 Trade and transpor t Other service industri es (2) (3) (4) Govern ment (5) 300 2 Manufactur ed products Manufacturing 10 45 3 Trade and transport services 930 305 4 Other services 20 5 295 5 Governmen t services 340 All industri es 340 -20 25 170 425 325 975 335 300 340 2275 340 70 6 Direct purchases abroad 7 TOTAL 1555 70 70 665 2940 0 155 -25 3070 7
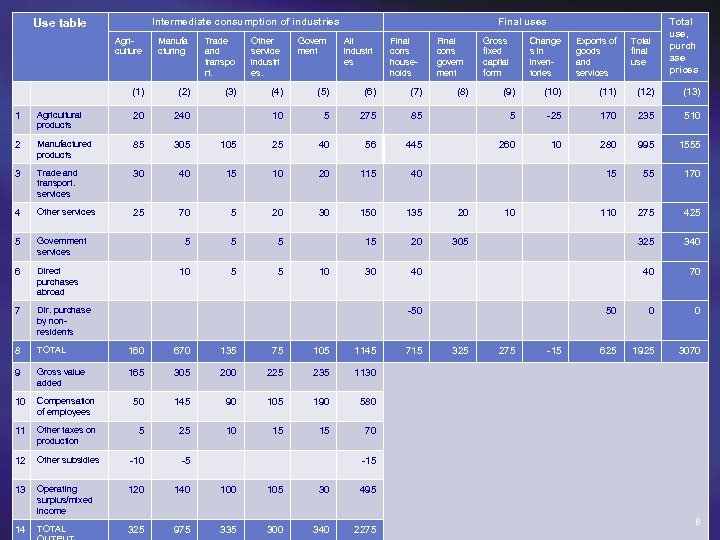
Intermediate consumption of industries Use table Final uses Agriculture Manufa cturing Trade and transpo rt. Other service industri es. Govern ment All industri es Final cons households (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7) 10 5 275 Final cons govern ment Change s in inventories Exports of goods and services Total final use (9) (10) (11) (12) (13) 85 5 -25 170 235 510 260 10 280 995 1555 15 55 170 110 275 425 340 40 70 50 0 0 625 1925 3070 (8) 1 Agricultural products 20 240 2 Manufactured products 85 305 105 25 40 56 445 3 Trade and transport. services 30 40 15 10 20 115 40 4 Other services 25 70 5 20 30 150 135 20 5 Government services 5 5 5 15 20 305 6 Direct purchases abroad 10 5 5 30 40 7 Dir. purchase by nonresidents 8 TOTAL 160 670 135 75 105 1145 9 Gross value added 165 305 200 225 235 1130 10 Compensation of employees 50 145 90 105 190 580 11 Other taxes on production 5 25 10 15 15 70 12 Other subsidies -10 -5 13 Operating surplus/mixed income 120 140 105 30 495 14 TOTAL 325 975 335 300 340 2275 Gross fixed capital form Total use, purch ase prices 10 10 -50 715 325 275 -15 8

Derivation of Supply Table at basic prices Market output = Sales u + Change in inventories (FG and WIP) u Non-market output (= Cost of production) = Intermediate consumption + + + Compensation of employees Other Taxes less subsidies on production Consumption of fixed capital 9

Derivation of Supply. Table at basic prices Intermediate consumption = Purchases - Change in inventories (materials) u Value added = Output - Intermediate consumption u Operating surplus = Value added - Compensation of employees - Taxes less subsidies on production - Consumption of fixed capital u 10

Transport Margins u When is the cost of transportation to be treated as a transport margin? u Transport margins consist of transport charges paid separately by the purchaser to take delivery at a required time and place (SNA 15. 28) u If not paid separately, the transport cost could be included as part of the basic price of the good, part of the wholesale or retail margin, or as an expense of the purchaser. 11

Trade Margins u A trade margin (wholesale or retail trade) applies only when there is a distribution service provided by the trader through buying and reselling a product. u A trade margin does not apply to direct sales by a producer, even when the sales are to households. 12

Trade Margins u Trade margin is defined as the difference between the selling price of the good for resale and the price that would have to be paid by the distributor to replace the good at the time it is sold. u The trade margin is the output of the distributor. As with other producers, value added is obtained by subtracting intermediate consumption. 13

Trade Margins u Broadly, the trade margin is calculated as: – Sales – less purchases of goods for resale – plus change in inventories for resale – Note: purchases of goods for resale should exclude any transport charges invoiced separately to the distributor; such transport charges are to be shown as intermediate consumption of the distributor. (SNA 6. 112) u The trade margin is part of the difference between the basic price of a good and its purchasers’ price. 14

Trade Margins u Data sources for trade margins: – – Total margin earned from establishment data. Margins for broad commodity groups. Markup rates for particular kinds of goods Supply/use of the goods subject to the margin. u u u Balancing process to fit available, but incomplete, data. Much prorating in practice. Separate margin calculations for wholesale, retail, and other? Yes, if different usage patterns and data available to do so. 15

Treatment of Imports u Consistent with the Balance of Payments Manual in valuing imports of goods in total on a f. o. b. basis, and to show international transportation as a service. u However, in the Supply/Use framework, imports at the commodity level are valued on a c. i. f. basis (including international transportation). u A c. i. f. /f. o. b. adjustment is made in the Supply table to accommodate these two valuation bases, and to ensure that domestic carriage of imports is not double counted. 16

Treatment of Imports u Example of c. i. f. /f. o. b. adjustment: – Assume imports c. i. f. = 1, 000 f. o. b. = 900 – International transportation = 100 – Domestic carriers = 20 – Foreign carriers = 80 – Assume domestic transportation to the user = 30 17

Treatment of Imports u Therefore, – imports of goods f. o. b. = 900 – imports of services = 80 – Domestic services = 20 + 30 = 50 – Supply at purchasers’ prices = 1, 030 u The c. i. f. /f. o. b. adjustment ensures that these values are reflected in the Supply table. 18

Steps for compilation of SUT u Step 1: Design of classifications and conversion keys specific to the country. Conversions are best carried out in Access. Results are subsequently imported to Excel u Step 2: Construction of files where data from individual sources are treated u Step 3: Setting up of a computerised system for the balancing of supply and use by product category 19

Balancing supply and use transactions consists of two main steps: 1. Manual balancing: u Requires a great deal of judgment of the national accountant. u Procedure is largely a matter of trial and errors where statistical discrepancies are eliminated step by step. 2. Mechanical balancing: u Final part of the balancing exercise and requires no further judgment on the part of the national accountant. u It is not done until remaining discrepancies are so small that they are devoid of economic or analytical meaning. 20
Examples of adjustments within the manual balancing process u Evaluate input / output structures of all columns to identify data gaps, and checking potential coding and classification problems (activity or vertical dimension); u Identify anchors – i. e. identify which transactions are most reliable, and therefore least subject to change. u Analyze and gradually eliminate discrepancies between supply and use for all rows of the SUT (product or horizontal dimension); u Finalize adjustments to input / output structures by activity, and make conclusive checks of product balances. 21

Adjusting imports and exports u Importers have an incentive to underinvoice. In addition, it is very probable that some smuggling occurs. u For exports, the incentive to under-invoice is weaker. It might be relevant to increase export data as well, but usually with a smaller percentage increase. 22

Other adjustments u Identifying values for capital formation u Identifying products that serve as inputs into other product categories u Identifying purchases abroad (missing exports) u Identifying informal sector activities 23
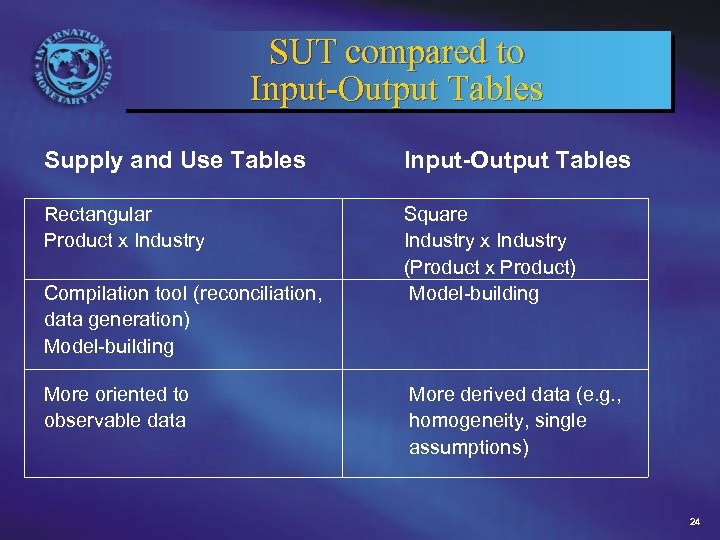
SUT compared to Input-Output Tables Supply and Use Tables Input-Output Tables Rectangular Product x Industry Square Industry x Industry (Product x Product) Model-building Compilation tool (reconciliation, data generation) Model-building More oriented to observable data More derived data (e. g. , homogeneity, single assumptions) 24
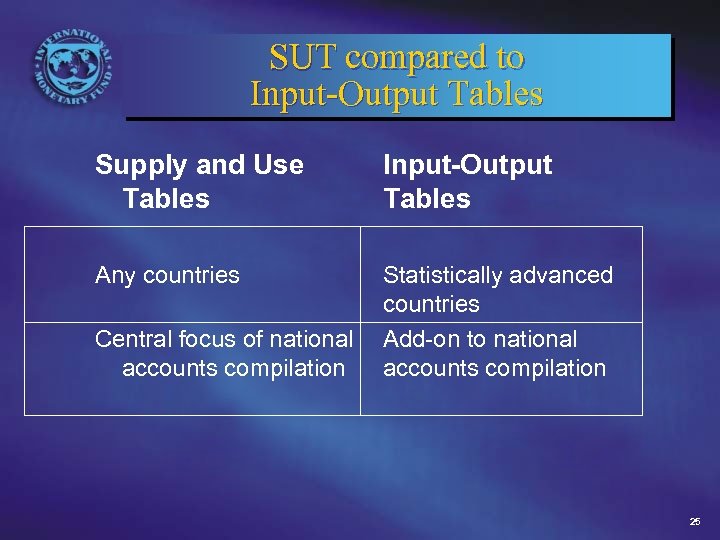
SUT compared to Input-Output Tables Supply and Use Tables Input-Output Tables Any countries Statistically advanced countries Central focus of national Add-on to national accounts compilation 25
e08d16c9d9e7165de55277628f4b7fae.ppt