088fa4410d0b2de67361919701bbebf0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37

 Session id: 36993 Effectively Validate Query/Report: Strategy and Tool Steven Luo Sr. System Analyst Barnes & Noble
Session id: 36993 Effectively Validate Query/Report: Strategy and Tool Steven Luo Sr. System Analyst Barnes & Noble
 Agenda Ÿ PART I: Introduction – Why, when, and how to validate Ÿ PART II: Strategy – – Basic strategy Advanced strategy Ÿ PART III: Tool – – Test script Engine - sql. Unit Ÿ PART IV: Conclusion
Agenda Ÿ PART I: Introduction – Why, when, and how to validate Ÿ PART II: Strategy – – Basic strategy Advanced strategy Ÿ PART III: Tool – – Test script Engine - sql. Unit Ÿ PART IV: Conclusion
 Why to Validate? Ÿ Assure Data Accuracy – – Managers need accurate data to make strategic decisions A company’s sales team needs accurate data to launch market campaign Ÿ Assure ETL (Extraction, Transformation, and Loading) Process Correctness – – ETL tools SQL scripts
Why to Validate? Ÿ Assure Data Accuracy – – Managers need accurate data to make strategic decisions A company’s sales team needs accurate data to launch market campaign Ÿ Assure ETL (Extraction, Transformation, and Loading) Process Correctness – – ETL tools SQL scripts
 When to Validate? Ÿ Any of the following types of testing needs validation: – – – Unit testing Integration testing System testing Acceptance testing Maintenance & regression testing
When to Validate? Ÿ Any of the following types of testing needs validation: – – – Unit testing Integration testing System testing Acceptance testing Maintenance & regression testing
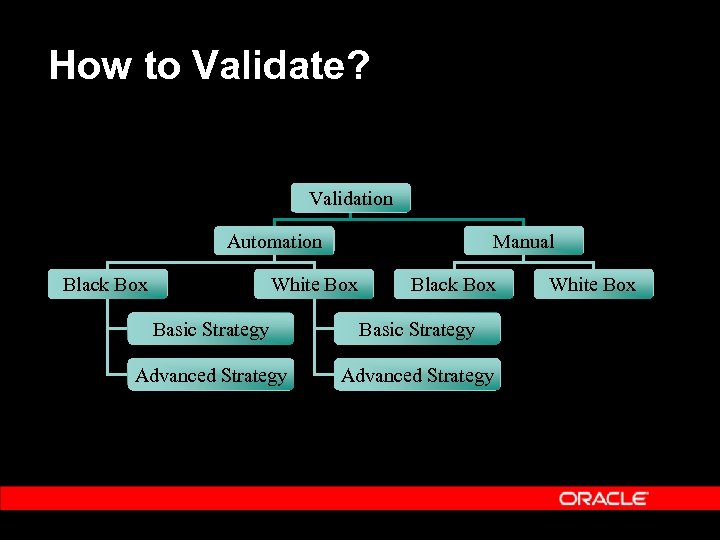 How to Validate? Validation Automation Black Box Manual White Box Black Box Basic Strategy Advanced Strategy White Box
How to Validate? Validation Automation Black Box Manual White Box Black Box Basic Strategy Advanced Strategy White Box
 Agenda Ÿ PART I: Introduction – Why, when, and how to validate? PART II : Strategy – – Basic strategy Advanced strategy Ÿ PART III: Tool – Test script – Engine - sql. Unit Ÿ PART IV: Conclusion
Agenda Ÿ PART I: Introduction – Why, when, and how to validate? PART II : Strategy – – Basic strategy Advanced strategy Ÿ PART III: Tool – Test script – Engine - sql. Unit Ÿ PART IV: Conclusion
 Validating Report/Query Ÿ A Query or Report is actually a result set, so validating needs to answer two questions: Ÿ Are you getting the result set right? – right data in each cell Ÿ Are you getting the right result set? – exact number of records
Validating Report/Query Ÿ A Query or Report is actually a result set, so validating needs to answer two questions: Ÿ Are you getting the result set right? – right data in each cell Ÿ Are you getting the right result set? – exact number of records
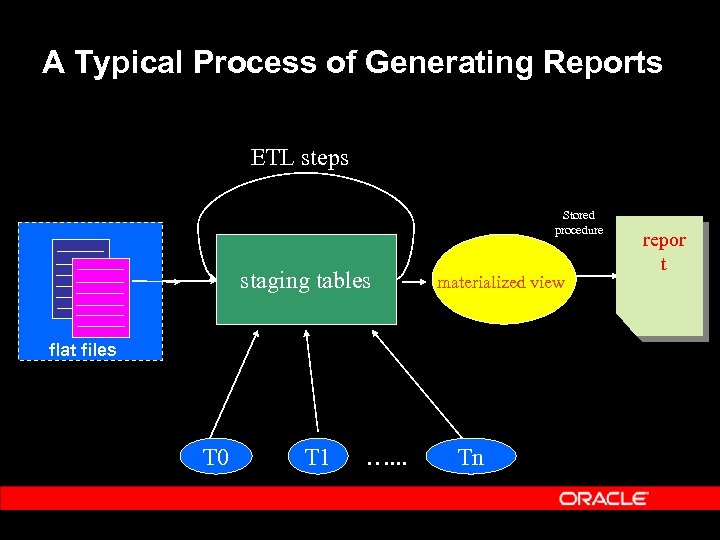 A Typical Process of Generating Reports ETL steps Stored procedure staging tables materialized view flat files T 0 T 1 …. . . Tn repor t
A Typical Process of Generating Reports ETL steps Stored procedure staging tables materialized view flat files T 0 T 1 …. . . Tn repor t
 Basic Strategy Ÿ Assert that each (cell) in the result set matches the data in the source table – – Number String Date Result Set, etc. Ÿ Sampling should be used if a result set is big Ÿ Assert the right number of records in the result set Ÿ Check duplicated…
Basic Strategy Ÿ Assert that each (cell) in the result set matches the data in the source table – – Number String Date Result Set, etc. Ÿ Sampling should be used if a result set is big Ÿ Assert the right number of records in the result set Ÿ Check duplicated…
 Advanced Strategy Ÿ Try to uncover invalid data item – Boundary Validation Ÿ Count, sum, max, min, x not in table, “between. . and” on whole resultset or certain partitions. – Special Value (constraints) Validation Ÿ is. XXX() and not. XXX() Ÿ e. g. Is. Null, not. Negative, not. Zero – Business Rule Validation Ÿ dept 1. sale> dept 2. sale
Advanced Strategy Ÿ Try to uncover invalid data item – Boundary Validation Ÿ Count, sum, max, min, x not in table, “between. . and” on whole resultset or certain partitions. – Special Value (constraints) Validation Ÿ is. XXX() and not. XXX() Ÿ e. g. Is. Null, not. Negative, not. Zero – Business Rule Validation Ÿ dept 1. sale> dept 2. sale
 Agenda Ÿ PART I: Introduction – Why, when, and how to validate ? Ÿ PART II : Strategy – – Basic Strategy Advanced Strategy PART III: Tool – – Test Script Engine - sql. Unit Ÿ PART IV: Conclusion
Agenda Ÿ PART I: Introduction – Why, when, and how to validate ? Ÿ PART II : Strategy – – Basic Strategy Advanced Strategy PART III: Tool – – Test Script Engine - sql. Unit Ÿ PART IV: Conclusion
 Why Use a Validation Tool? Ÿ Automate the validating process – Reduces the cost, time and effort Ÿ Reuse the procedures – Write once, run many times on QA box and/or production box. Ÿ Re-factor SQL Ÿ Share by group (save to PVCS)
Why Use a Validation Tool? Ÿ Automate the validating process – Reduces the cost, time and effort Ÿ Reuse the procedures – Write once, run many times on QA box and/or production box. Ÿ Re-factor SQL Ÿ Share by group (save to PVCS)
 Tool Ÿ Open Source – – j. Unit, etc. Steven Feuerstein’s ut. PL/SQL Ÿ My tool -- sql. Unit
Tool Ÿ Open Source – – j. Unit, etc. Steven Feuerstein’s ut. PL/SQL Ÿ My tool -- sql. Unit
 sql. Unit Overview Ÿ The framework consists of two major parts – – test scripts test engine Ÿ implemented in java stored procedure with PL/SQL interface Ÿ Implement 2 types of strategy – – basic strategy advanced strategy Ÿ Record the validating results Ÿ Monitor long-running validation process
sql. Unit Overview Ÿ The framework consists of two major parts – – test scripts test engine Ÿ implemented in java stored procedure with PL/SQL interface Ÿ Implement 2 types of strategy – – basic strategy advanced strategy Ÿ Record the validating results Ÿ Monitor long-running validation process
 sql. Unit Overview (2) Ÿ From the Engine Perspective – run all your test cases defined in your PL/SQL package Ÿ From the User Perspective – – write all test scripts start the Engine
sql. Unit Overview (2) Ÿ From the Engine Perspective – run all your test cases defined in your PL/SQL package Ÿ From the User Perspective – – write all test scripts start the Engine
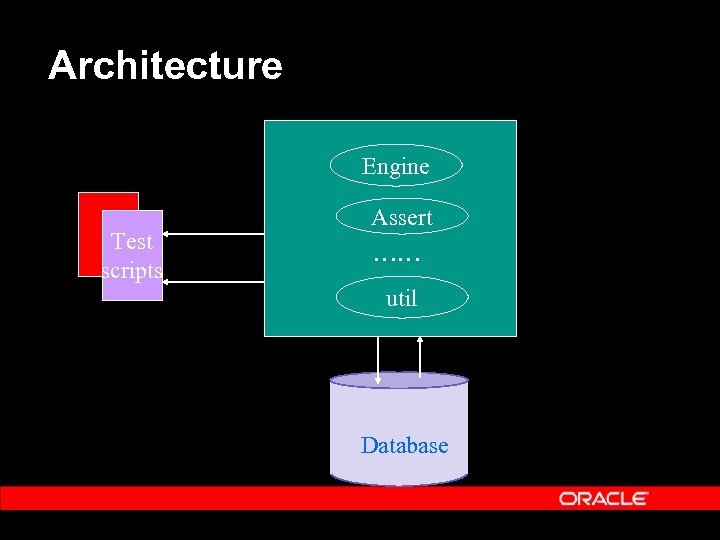 Architecture Engine Test scripts Assert …… util Database
Architecture Engine Test scripts Assert …… util Database
 Test Script (1) Ÿ Ÿ Write Test script in PL/SQL Define test package Call APIs Define test procedures – – – Test procedure MUST begin with ‘test’ Setup() : Teardown(): clean up
Test Script (1) Ÿ Ÿ Write Test script in PL/SQL Define test package Call APIs Define test procedures – – – Test procedure MUST begin with ‘test’ Setup() : Teardown(): clean up
 Test Script (2) Ÿ Use your business knowledge to get expected data and actual data – Get raw or original data from source table Ÿ such as POS, Daily Sales, etc. – Get data from a report Ÿ call API fetch. Cursor. Data(…), or Ÿ using cursor directly, e. g. cc : = my_test_pkg. get_ref_cursor('SCOTT'); loop fetch cc into value 1, value 2, . . . , valuek; exit when cc%notfound ; if(. . . ) then sqlunit. assert(‘desc’, value 1, 100); end if; end loop;
Test Script (2) Ÿ Use your business knowledge to get expected data and actual data – Get raw or original data from source table Ÿ such as POS, Daily Sales, etc. – Get data from a report Ÿ call API fetch. Cursor. Data(…), or Ÿ using cursor directly, e. g. cc : = my_test_pkg. get_ref_cursor('SCOTT'); loop fetch cc into value 1, value 2, . . . , valuek; exit when cc%notfound ; if(. . . ) then sqlunit. assert(‘desc’, value 1, 100); end if; end loop;
 APIs for Basic Strategy procedure run. Test. Cases(test. Package. Name varchar 2) procedure assert(description varchar 2, num 1 number, num 2 number) procedure assert(description varchar 2, str 1 varchar 2, str 2 varchar 2) procedure assert(description varchar 2, a 1 STRING_ARRAY, a 2 STRING_ARRAY) procedure assert(description STRING_ARRAY, a 1 STRING_ARRAY, a 2 STRING_ARRAY) procedure assert. Query(description varchar 2, query 1 varchar 2, query 2 varchar 2) procedure fetch. Ref. Cursor. Into(pname in varchar 2, parameters in STRING_ARRAY, fetchfields in out STRING_ARRAY, uniq. Field in varchar 2, uniq. Value in varchar 2 ) function get. Count. For. Query(sqlstr varchar 2) return number function get. Count. For. Procedure(sqlstr varchar 2) return number
APIs for Basic Strategy procedure run. Test. Cases(test. Package. Name varchar 2) procedure assert(description varchar 2, num 1 number, num 2 number) procedure assert(description varchar 2, str 1 varchar 2, str 2 varchar 2) procedure assert(description varchar 2, a 1 STRING_ARRAY, a 2 STRING_ARRAY) procedure assert(description STRING_ARRAY, a 1 STRING_ARRAY, a 2 STRING_ARRAY) procedure assert. Query(description varchar 2, query 1 varchar 2, query 2 varchar 2) procedure fetch. Ref. Cursor. Into(pname in varchar 2, parameters in STRING_ARRAY, fetchfields in out STRING_ARRAY, uniq. Field in varchar 2, uniq. Value in varchar 2 ) function get. Count. For. Query(sqlstr varchar 2) return number function get. Count. For. Procedure(sqlstr varchar 2) return number
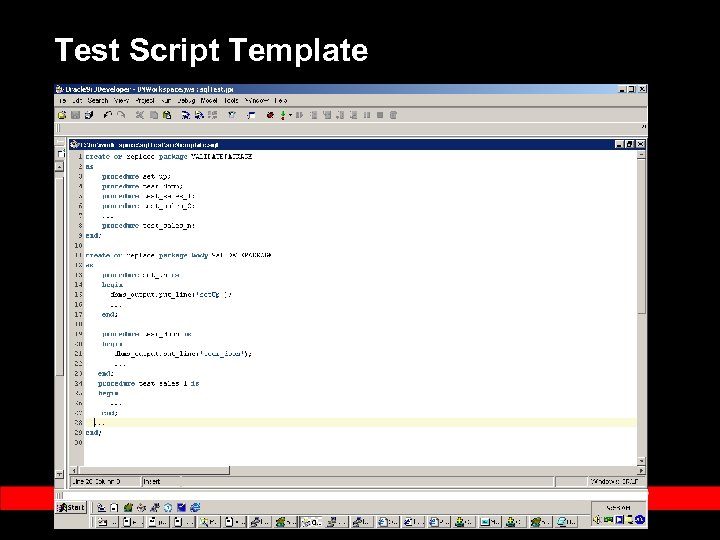 Test Script Template
Test Script Template
 Apply Basic Strategy Ÿ A tool should pick up: – m column(s) in a row of a result set Ÿ m: between 1 and number of columns – m column(s) in n rows of a result set Ÿ m: between 1 and number of columns Ÿ n: between 2 and number of rows Ÿ Cells to be validated: – cells: between 1 and m*n
Apply Basic Strategy Ÿ A tool should pick up: – m column(s) in a row of a result set Ÿ m: between 1 and number of columns – m column(s) in n rows of a result set Ÿ m: between 1 and number of columns Ÿ n: between 2 and number of rows Ÿ Cells to be validated: – cells: between 1 and m*n
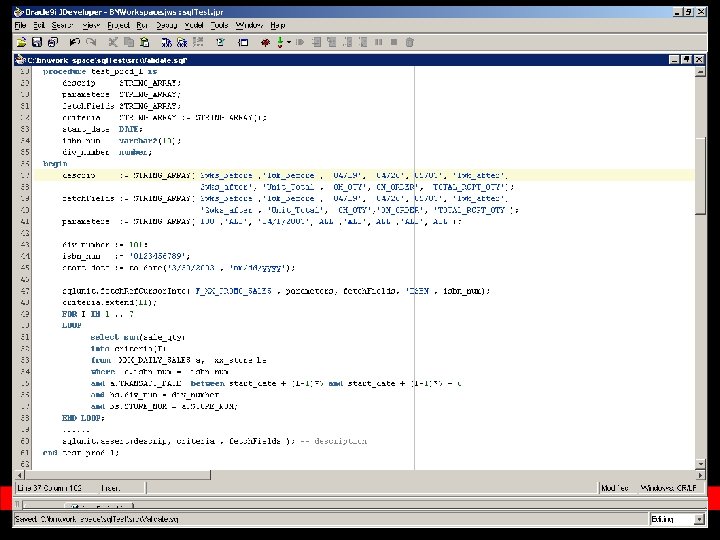
 Apply Advanced Strategy Ÿ Advanced Strategy – – – Boundary Object Special value (Constraint)Object Business Rule Object
Apply Advanced Strategy Ÿ Advanced Strategy – – – Boundary Object Special value (Constraint)Object Business Rule Object
 Test Script for Advance Strategy procedure test_adv_1 is obj sqlunit. Boundary : = sqlunit. Boundary(NULL, NULL); begin obj. set. Testing. Query('my_test_pkg. get_ref_cursor(''SCOTT'')'); obj. set. Count. Criteria(2); obj. set. Query. Criteria('c 1 is not null'); obj. set. Query. Type(1); //1 : store procedure. 0: sql query obj. check. Boundary; exception when others then dbms_output. put_line('exception! '); end test_adv_1;
Test Script for Advance Strategy procedure test_adv_1 is obj sqlunit. Boundary : = sqlunit. Boundary(NULL, NULL); begin obj. set. Testing. Query('my_test_pkg. get_ref_cursor(''SCOTT'')'); obj. set. Count. Criteria(2); obj. set. Query. Criteria('c 1 is not null'); obj. set. Query. Type(1); //1 : store procedure. 0: sql query obj. check. Boundary; exception when others then dbms_output. put_line('exception! '); end test_adv_1;
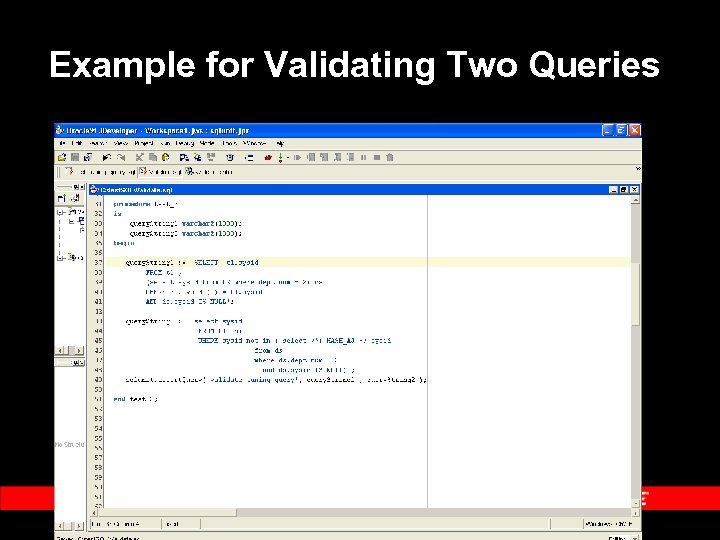 Example for Validating Two Queries
Example for Validating Two Queries
 How Engine Works Ÿ Users start the Engine by calling … exec sqlunit. runtestcases('VALIDATEPACKAGE'); Ÿ Engine calls back test scripts by calling the following: set_up; test_1; tear_down; set_up; test_2; tear_down; . . . set_up; test_n; tear_down; Ÿ Test scripts call Framework APIs …. sqlunit. assert(. . . )
How Engine Works Ÿ Users start the Engine by calling … exec sqlunit. runtestcases('VALIDATEPACKAGE'); Ÿ Engine calls back test scripts by calling the following: set_up; test_1; tear_down; set_up; test_2; tear_down; . . . set_up; test_n; tear_down; Ÿ Test scripts call Framework APIs …. sqlunit. assert(. . . )
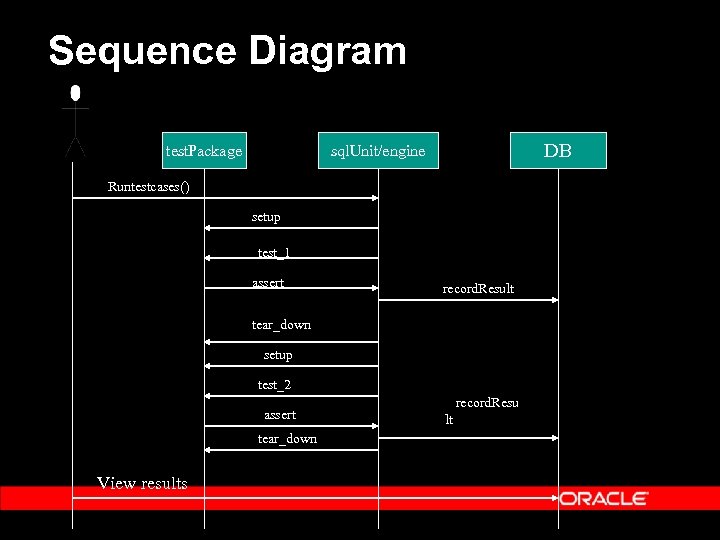 Sequence Diagram test. Package DB sql. Unit/engine Runtestcases() setup test_1 assert record. Result tear_down setup test_2 assert tear_down View results record. Resu lt
Sequence Diagram test. Package DB sql. Unit/engine Runtestcases() setup test_1 assert record. Result tear_down setup test_2 assert tear_down View results record. Resu lt
 Record the Test Result Ÿ Use package name as testing result table name.
Record the Test Result Ÿ Use package name as testing result table name.
 Monitoring Validation Process Ÿ At Engine level, by instrumentation DBMS_APPLICATION_INFO into Engine, you can monitor the progress Ÿ At test script, you can instrument DBMS_APPLICATION_INFO to test scripts too. Ÿ Get the progress information from v$session_longop in other session
Monitoring Validation Process Ÿ At Engine level, by instrumentation DBMS_APPLICATION_INFO into Engine, you can monitor the progress Ÿ At test script, you can instrument DBMS_APPLICATION_INFO to test scripts too. Ÿ Get the progress information from v$session_longop in other session
 Test Scripts Guideline Ÿ Be simple Ÿ Don’t use the same sql that generates the report Ÿ Use Business/domain knowledge
Test Scripts Guideline Ÿ Be simple Ÿ Don’t use the same sql that generates the report Ÿ Use Business/domain knowledge
 Conclusion Ÿ Data accuracy is very important Ÿ Use automated validating tool whenever possible
Conclusion Ÿ Data accuracy is very important Ÿ Use automated validating tool whenever possible
 Limitation of validation “ Program testing can be used to show the presence of bugs, but never to show their absence” --E. W. Dijkstra
Limitation of validation “ Program testing can be used to show the presence of bugs, but never to show their absence” --E. W. Dijkstra
 References Ÿ Asimkumar Munshi, Testing a Data Warehouse Application white paper http: //www. wipro. com/insights/testinga. DWApplication. htm Ÿ B. Hailpern and P. Santhanam Software debugging, testing, and verification IBM System Journal Vol. 41, No. 1, 2002 Ÿ Thomas Kyte, Expert One on One Oracle, Wrox, 2001
References Ÿ Asimkumar Munshi, Testing a Data Warehouse Application white paper http: //www. wipro. com/insights/testinga. DWApplication. htm Ÿ B. Hailpern and P. Santhanam Software debugging, testing, and verification IBM System Journal Vol. 41, No. 1, 2002 Ÿ Thomas Kyte, Expert One on One Oracle, Wrox, 2001
 Q & A QUESTIONS ANSWERS
Q & A QUESTIONS ANSWERS



