a08e4b4e5267dfa55536447a9276be39.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37
 Session 702 - I'm a Vist. A Imaging Coordinator with a New System. Now What ? Presented by Jeannie Jernigan, Vist. A Imaging PACS Administrator, OI&T VAMC Fayetteville, NC 1
Session 702 - I'm a Vist. A Imaging Coordinator with a New System. Now What ? Presented by Jeannie Jernigan, Vist. A Imaging PACS Administrator, OI&T VAMC Fayetteville, NC 1
 Session Outline – Terms - Contingency Plans – Configurations - Implementation Workgroup – DICOM Basics - Getting Support – DICOM Gateways - Troubleshooting – Image Quality - Patches and Testing – Adding New Devices – Preventive Maintenance 2
Session Outline – Terms - Contingency Plans – Configurations - Implementation Workgroup – DICOM Basics - Getting Support – DICOM Gateways - Troubleshooting – Image Quality - Patches and Testing – Adding New Devices – Preventive Maintenance 2
 TERMS • Vist. A – Veterans Information System and Technology Architecture. – Primary system for storing and maintaining the patient electronic medical record. Text based – Not designed for Images • Imaging – Parallel system linked with Vist. A • Storage and Archive, Terabytes of Storage! • Management of captured data (corrections, deletions) • Retrieval • Allows the images to be linked with various parts of the patient record in Vist. A. • Both systems use program code written in Mumps and run in the Cache’ Database environment. 3
TERMS • Vist. A – Veterans Information System and Technology Architecture. – Primary system for storing and maintaining the patient electronic medical record. Text based – Not designed for Images • Imaging – Parallel system linked with Vist. A • Storage and Archive, Terabytes of Storage! • Management of captured data (corrections, deletions) • Retrieval • Allows the images to be linked with various parts of the patient record in Vist. A. • Both systems use program code written in Mumps and run in the Cache’ Database environment. 3
 TERMS (continued) • PACS - Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) are computer systems dedicated to the storage, retrieval, distribution and presentation of images. • HL 7 – Health Level 7 (HL 7) is standard based electronic message format supporting administrative, logistical, financial as well as clinical processes. • DICOM - Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) is a standard for handling, storing, printing, and transmitting information in medical imaging. • CPRS – Computerized Patient Record System. • Clinical Workstation – Software installed on workstations without any additional enhanced viewing software or monitors. • Diagnostic Workstation – Specialized workstation that allows Radiologists to interpret radiology images without film (calibratible monitors). 4
TERMS (continued) • PACS - Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) are computer systems dedicated to the storage, retrieval, distribution and presentation of images. • HL 7 – Health Level 7 (HL 7) is standard based electronic message format supporting administrative, logistical, financial as well as clinical processes. • DICOM - Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) is a standard for handling, storing, printing, and transmitting information in medical imaging. • CPRS – Computerized Patient Record System. • Clinical Workstation – Software installed on workstations without any additional enhanced viewing software or monitors. • Diagnostic Workstation – Specialized workstation that allows Radiologists to interpret radiology images without film (calibratible monitors). 4
 WHAT’S IN IMAGING? Scanned Documents Rich Text Reports ECG Waveforms Patient Photo X-Rays CT’s MRI’s Ultrasounds Dental Images Ophthalmic images Pathology Images Digital Camera Diagram Annotations Dermatology images And more… 5
WHAT’S IN IMAGING? Scanned Documents Rich Text Reports ECG Waveforms Patient Photo X-Rays CT’s MRI’s Ultrasounds Dental Images Ophthalmic images Pathology Images Digital Camera Diagram Annotations Dermatology images And more… 5
 6
6
 7
7
 VISTA IMAGING CONFIGURATIONS Vist. A Imaging can be installed in several levels 1. Basic Configuration - Storage only with Capture Workstation. Used for document scanning and Clinical Procedure reports image capture and re-display (includes Tele Retinal and Tele Derm images) 2. DICOM Configuration - Basic plus DICOM Gateways to handle DICOM modalities 3. Vist. ARad – DICOM configuration plus Vist. ARad running on Diagnostic Workstations 4. Image Routing – Vist. ARad configuration using Image Routing for remote viewing. 5. DICOM Configuration with Commercial PACS – DICOM Configuration plus Commercial Radiology PACS 8
VISTA IMAGING CONFIGURATIONS Vist. A Imaging can be installed in several levels 1. Basic Configuration - Storage only with Capture Workstation. Used for document scanning and Clinical Procedure reports image capture and re-display (includes Tele Retinal and Tele Derm images) 2. DICOM Configuration - Basic plus DICOM Gateways to handle DICOM modalities 3. Vist. ARad – DICOM configuration plus Vist. ARad running on Diagnostic Workstations 4. Image Routing – Vist. ARad configuration using Image Routing for remote viewing. 5. DICOM Configuration with Commercial PACS – DICOM Configuration plus Commercial Radiology PACS 8
 BASIC CONFIGURATION • Per VA requirement each facility must have Vist. A Imaging storage in place to handle scanned documents, Clinical Procedure reports, and PACS Archive. This is the minimum configuration. – RAID Storage - Holds Images (short term). Images are purged after a prescribed time period. – Optical Jukebox – Holds Images (Long Term/Archive) Could be centralized. – Background Processor (manages transfers to and from Jukebox, as well as other activities) – Clinical Display installed as needed – Clinical Capture installed as needed, OR interface to an approved commercial document capture system. – http: //vaww. va. gov/imaging/Img. Mandate 12001045. pdf 9
BASIC CONFIGURATION • Per VA requirement each facility must have Vist. A Imaging storage in place to handle scanned documents, Clinical Procedure reports, and PACS Archive. This is the minimum configuration. – RAID Storage - Holds Images (short term). Images are purged after a prescribed time period. – Optical Jukebox – Holds Images (Long Term/Archive) Could be centralized. – Background Processor (manages transfers to and from Jukebox, as well as other activities) – Clinical Display installed as needed – Clinical Capture installed as needed, OR interface to an approved commercial document capture system. – http: //vaww. va. gov/imaging/Img. Mandate 12001045. pdf 9
 DICOM CONFIGURATION • Adds DICOM processing to the Basic Configuration • Allows text information (worklist) transfer to and image storage from DICOM modalities. • Applications include – Computed Radiography – Dental Image capture – Ophthalmology Image Capture – Dermatology Image Capture – Transferring DICOM images to other modalities, such as DICOM Printers (via DICOM Store) – Encapsulated PDF’s 10
DICOM CONFIGURATION • Adds DICOM processing to the Basic Configuration • Allows text information (worklist) transfer to and image storage from DICOM modalities. • Applications include – Computed Radiography – Dental Image capture – Ophthalmology Image Capture – Dermatology Image Capture – Transferring DICOM images to other modalities, such as DICOM Printers (via DICOM Store) – Encapsulated PDF’s 10
 MORE DEFINITIONS • SCU (Service Class User) – Device taking a client role (example: device that sends print jobs) • SCP (Service Class Provider) – Device that takes a host role (Example: DICOM print server). • DICOM Images are a Composite Format – Image Data for the actual picture – A “Header” area at the beginning of the file that contains the “DICOM Header”. This area is for text data associated with the image, containing • Patient Identifying information • Exam information (date of exam, accession number, case number) • Information about acquisition modality (manufacturer, model) • Image information (geometry, attributes) • And lots of other stuff… 11
MORE DEFINITIONS • SCU (Service Class User) – Device taking a client role (example: device that sends print jobs) • SCP (Service Class Provider) – Device that takes a host role (Example: DICOM print server). • DICOM Images are a Composite Format – Image Data for the actual picture – A “Header” area at the beginning of the file that contains the “DICOM Header”. This area is for text data associated with the image, containing • Patient Identifying information • Exam information (date of exam, accession number, case number) • Information about acquisition modality (manufacturer, model) • Image information (geometry, attributes) • And lots of other stuff… 11
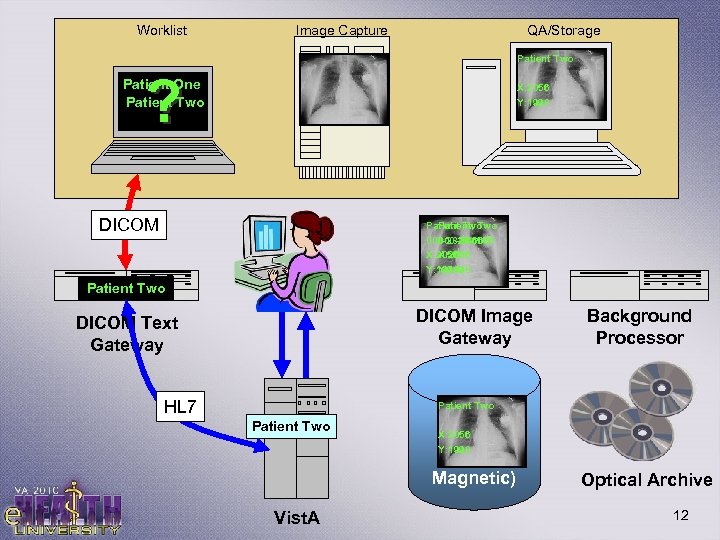 Worklist Image Capture QA/Storage Patient Two ? Patient One Patient Two X: 2056 Y: 1998 DICOM Patient Two Patient, Two 000 -28 -1665 X: 2056 Y: 1998 Patient Two DICOM Image Gateway DICOM Text Gateway HL 7 Background Processor Patient Two Vist. A Image X: 2056 Storage Y: 1998 (RAID Magnetic) Optical Archive 12
Worklist Image Capture QA/Storage Patient Two ? Patient One Patient Two X: 2056 Y: 1998 DICOM Patient Two Patient, Two 000 -28 -1665 X: 2056 Y: 1998 Patient Two DICOM Image Gateway DICOM Text Gateway HL 7 Background Processor Patient Two Vist. A Image X: 2056 Storage Y: 1998 (RAID Magnetic) Optical Archive 12
 Configuration 3: DICOM with Vist. ARad • Adds Vist. ARad diagnostic workstations to the DICOM configuration • Allows radiologists to interpret radiology images on computer (soft-copy interpretation) • Vist. ARad is simply Image viewing software with tools helpful to a radiologist – Runs on select workstations equipped with Diagnostic monitors – Communicates with Vist. A to update exam status when interpreted – Currently Patch 101 – Free software 13
Configuration 3: DICOM with Vist. ARad • Adds Vist. ARad diagnostic workstations to the DICOM configuration • Allows radiologists to interpret radiology images on computer (soft-copy interpretation) • Vist. ARad is simply Image viewing software with tools helpful to a radiologist – Runs on select workstations equipped with Diagnostic monitors – Communicates with Vist. A to update exam status when interpreted – Currently Patch 101 – Free software 13
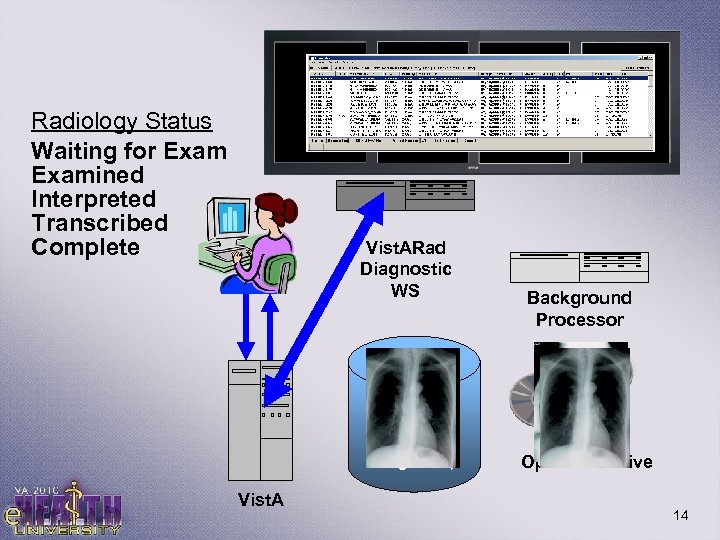 Radiology Status Waiting for Examined Interpreted Transcribed Complete Vist. ARad Diagnostic WS Image Storage (RAID Magnetic) Vist. A Background Processor Optical Archive 14
Radiology Status Waiting for Examined Interpreted Transcribed Complete Vist. ARad Diagnostic WS Image Storage (RAID Magnetic) Vist. A Background Processor Optical Archive 14
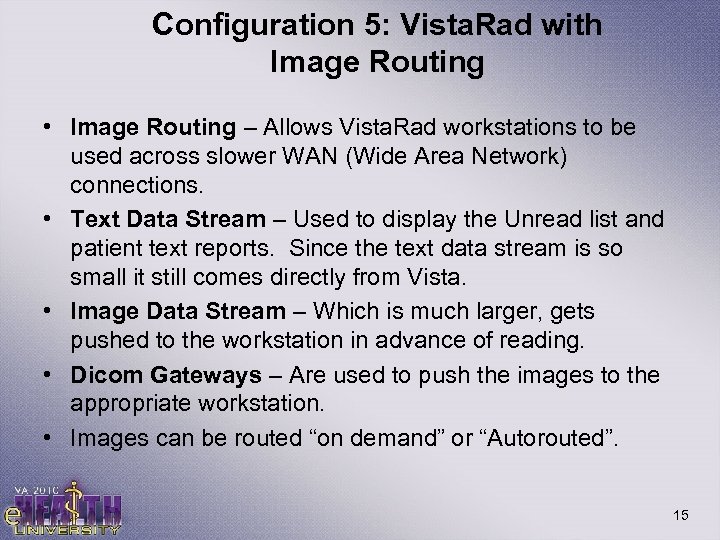 Configuration 5: Vista. Rad with Image Routing • Image Routing – Allows Vista. Rad workstations to be used across slower WAN (Wide Area Network) connections. • Text Data Stream – Used to display the Unread list and patient text reports. Since the text data stream is so small it still comes directly from Vista. • Image Data Stream – Which is much larger, gets pushed to the workstation in advance of reading. • Dicom Gateways – Are used to push the images to the appropriate workstation. • Images can be routed “on demand” or “Autorouted”. 15
Configuration 5: Vista. Rad with Image Routing • Image Routing – Allows Vista. Rad workstations to be used across slower WAN (Wide Area Network) connections. • Text Data Stream – Used to display the Unread list and patient text reports. Since the text data stream is so small it still comes directly from Vista. • Image Data Stream – Which is much larger, gets pushed to the workstation in advance of reading. • Dicom Gateways – Are used to push the images to the appropriate workstation. • Images can be routed “on demand” or “Autorouted”. 15
 Configuration 6: DICOM with Commercial PACS • PACS – Picture Archival and Communication System – Self contained patient management system for radiology – Includes separate • Patient Management and Worklist • Image Acquisition and QA • Storage • Diagnostic Interpretation • Vist. A Imaging sees a PACS simply as a modality • Sends it DICOM worklist and receives images • Required to store PACS images simultaneously in Vist. A Imaging - Portability 16
Configuration 6: DICOM with Commercial PACS • PACS – Picture Archival and Communication System – Self contained patient management system for radiology – Includes separate • Patient Management and Worklist • Image Acquisition and QA • Storage • Diagnostic Interpretation • Vist. A Imaging sees a PACS simply as a modality • Sends it DICOM worklist and receives images • Required to store PACS images simultaneously in Vist. A Imaging - Portability 16
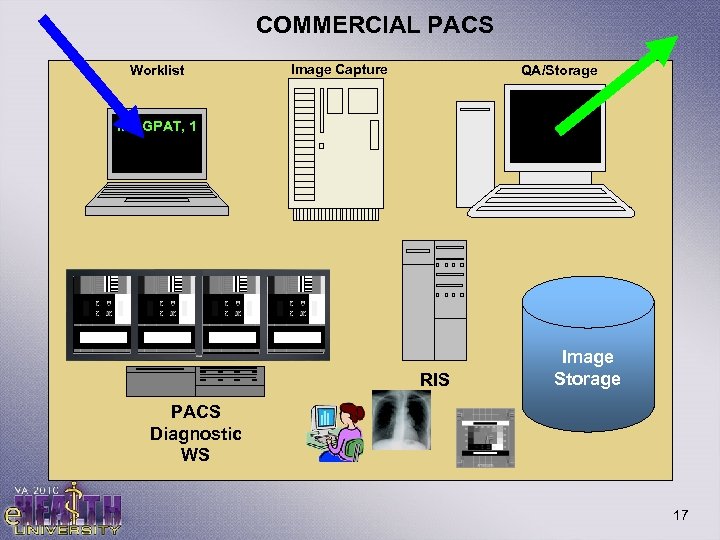 COMMERCIAL PACS Worklist Image Capture QA/Storage IMAGPAT, 1 RIS Image Storage PACS Diagnostic WS 17
COMMERCIAL PACS Worklist Image Capture QA/Storage IMAGPAT, 1 RIS Image Storage PACS Diagnostic WS 17
 Commercial PACS Continued Pros Self Contained – not solely dependent on Vist. A or other external systems. Robust Feature Set – Watch for dependencies Cons Self Contained – If integrated with another system like Vista or other HIS, data must be kept synchronized, and QA’d on both systems. Expensive to Buy and Maintain Data Stored in Proprietary Format 18
Commercial PACS Continued Pros Self Contained – not solely dependent on Vist. A or other external systems. Robust Feature Set – Watch for dependencies Cons Self Contained – If integrated with another system like Vista or other HIS, data must be kept synchronized, and QA’d on both systems. Expensive to Buy and Maintain Data Stored in Proprietary Format 18
 DICOM Text Gateway • Used to run Micronetics Mumps (MSM) on Windows 2000/XP, now run on Cache instead of MSM, and Windows 2003 Server instead of 2000/XP • Is a Worklist SCP Modality (since it responds to query requests from clients) • Queries HL 7 messages from Vist. A to fetch data – Vista builds HL 7 messages from exam orders into a global called MAGDHL 7. The text Gateway pulls the messages from that global and stores in it’s internal database. • Converts data to DICOM and sends to the requesting modality. 19
DICOM Text Gateway • Used to run Micronetics Mumps (MSM) on Windows 2000/XP, now run on Cache instead of MSM, and Windows 2003 Server instead of 2000/XP • Is a Worklist SCP Modality (since it responds to query requests from clients) • Queries HL 7 messages from Vist. A to fetch data – Vista builds HL 7 messages from exam orders into a global called MAGDHL 7. The text Gateway pulls the messages from that global and stores in it’s internal database. • Converts data to DICOM and sends to the requesting modality. 19
 DICOM Image Gateway Up Close • • • Like the Text Gateway, also runs MSM on Windows 2000/XP, now on Cache instead of MSM, and Windows 2003 Server instead of 2000/XP Storage SCP Modality (among others!) Receives DICOM Images from modalities and… 1. Examines Patient and exam information in the DICOM Header 2. Queries Vist. A to verify a match on Name, SSN, and Accession Number. 3. If no match, image is held and flagged for correction 4. If matched, the Image Gateway i. Queries Vist. A for an IEN (Internal Entry Number) ii. Splits the DICOM file appropriately iii. Stores/copies the image(s) to the RAID iv. Notifies Vist. A of the file locations on RAID for later retrieval v. Queues a BGP entry for copy to Jukebox 20
DICOM Image Gateway Up Close • • • Like the Text Gateway, also runs MSM on Windows 2000/XP, now on Cache instead of MSM, and Windows 2003 Server instead of 2000/XP Storage SCP Modality (among others!) Receives DICOM Images from modalities and… 1. Examines Patient and exam information in the DICOM Header 2. Queries Vist. A to verify a match on Name, SSN, and Accession Number. 3. If no match, image is held and flagged for correction 4. If matched, the Image Gateway i. Queries Vist. A for an IEN (Internal Entry Number) ii. Splits the DICOM file appropriately iii. Stores/copies the image(s) to the RAID iv. Notifies Vist. A of the file locations on RAID for later retrieval v. Queues a BGP entry for copy to Jukebox 20
 DICOM Image Gateway Up Close Saving DICOM Files as TGA • • • Targa conversion is a legacy method of converting the DICOM image data to Targa format. The conversion involves splitting the DICOM image file as follows… – BIG File – An exact TGA version of the Image data in larger DICOM files (such as X-Rays). Non-existent for smaller images. – TGA File – A second version of the TGA file. • For large images like X-Rays, this is generally 1: 8 reduced. • For smaller images (CT slices, ultrasounds) this is the whole Image. – TXT File – Contents of DICOM Header – ABS File – Abstract Image or thumbnail of the image. Once beneficial, now being replaced by native DICOM Storage. Native DICOM storage simply copies the DCM (DICOM) file into storage with it’s associated TXT and ABS file. 21
DICOM Image Gateway Up Close Saving DICOM Files as TGA • • • Targa conversion is a legacy method of converting the DICOM image data to Targa format. The conversion involves splitting the DICOM image file as follows… – BIG File – An exact TGA version of the Image data in larger DICOM files (such as X-Rays). Non-existent for smaller images. – TGA File – A second version of the TGA file. • For large images like X-Rays, this is generally 1: 8 reduced. • For smaller images (CT slices, ultrasounds) this is the whole Image. – TXT File – Contents of DICOM Header – ABS File – Abstract Image or thumbnail of the image. Once beneficial, now being replaced by native DICOM Storage. Native DICOM storage simply copies the DCM (DICOM) file into storage with it’s associated TXT and ABS file. 21
 Vist. A RAD • • • Terms of Use of the Vist. ARad diagnostic workstation is subject to the following provisions: Caution: Federal law restricts this device to use by or on the order of either a licensed practitioner or persons lawfully engaged in the manufacture or distribution of the product. No modifications may be made to this software without the express written consent of the Vist. A Imaging National Project Manager. The Food and Drug Administration classifies the Vist. ARad software as a medical device. Modifications to the Vist. ARad diagnostic workstation, such as the installation of unapproved software, will adulterate the medical device. The use of an adulterated medical device violates US federal law (21 CFR 820). Image presentation quality depends on monitor resolution, and on regular monitor testing and calibration to correct for display degradation over time. It is the responsibility of the clinical practitioner to determine if images presented on a Vist. ARad workstation are of sufficient quality for clinical interpretation. Any concerns regarding monitor resolution or calibration should be reported immediately to the Imaging Coordinator before interpretation is performed. 22
Vist. A RAD • • • Terms of Use of the Vist. ARad diagnostic workstation is subject to the following provisions: Caution: Federal law restricts this device to use by or on the order of either a licensed practitioner or persons lawfully engaged in the manufacture or distribution of the product. No modifications may be made to this software without the express written consent of the Vist. A Imaging National Project Manager. The Food and Drug Administration classifies the Vist. ARad software as a medical device. Modifications to the Vist. ARad diagnostic workstation, such as the installation of unapproved software, will adulterate the medical device. The use of an adulterated medical device violates US federal law (21 CFR 820). Image presentation quality depends on monitor resolution, and on regular monitor testing and calibration to correct for display degradation over time. It is the responsibility of the clinical practitioner to determine if images presented on a Vist. ARad workstation are of sufficient quality for clinical interpretation. Any concerns regarding monitor resolution or calibration should be reported immediately to the Imaging Coordinator before interpretation is performed. 22
 Image Quality Basics • Image Quality is Everything • Good, Working, Appropriate Equipment • Appropriate Resolution (aka Image Matrix) – 1: 1 Pixel Ratio – The Ideal Scenario – Image Type Requirements – Larger display matrices are in “Megapixels”, ie 5 mp is 2500 x 2000 pixels. – Intended Use (Clinical Review vs. Diagnostic Review) • Proper Grayscale – 0 to 100 in 1/60 of a Second – What Affects Perceived Grayscale? • Hardware Limitations, Setup, Environment • Appropriate and Calibrated Resolution/Grayscale is at the Heart of a Diagnostic Display System 23
Image Quality Basics • Image Quality is Everything • Good, Working, Appropriate Equipment • Appropriate Resolution (aka Image Matrix) – 1: 1 Pixel Ratio – The Ideal Scenario – Image Type Requirements – Larger display matrices are in “Megapixels”, ie 5 mp is 2500 x 2000 pixels. – Intended Use (Clinical Review vs. Diagnostic Review) • Proper Grayscale – 0 to 100 in 1/60 of a Second – What Affects Perceived Grayscale? • Hardware Limitations, Setup, Environment • Appropriate and Calibrated Resolution/Grayscale is at the Heart of a Diagnostic Display System 23
 Image Quality and Grayscale Calibration Producing a Good Curve 24
Image Quality and Grayscale Calibration Producing a Good Curve 24
 Adding New DICOM Modalities Tools to Help Ensure Successful Interface – DICOM Conformance Statement – Should be required BEFORE procurement. – Vendor Survey – Required component of Directive 6550 • Networking/Security specifics (no external modems required, etc) • Users do not require administrative privilege to function • Physical characteristics (electrical, floor loading, environmental) • Any items you wish you knew from prior procurements – Contact Silver Spring (VHA VI DICOM Validation mail group) to verify that the device is approved for interface if not on the approved list on the web site (yes it MUST be approved). – If the device is not approved instruct the vendor to contact Silver Spring for validation. Do not back down on this! Approved list http: //vaww. va. gov/imaging/Vist. A_Imaging_DICOM_Modality_Interfaces. pdf 25
Adding New DICOM Modalities Tools to Help Ensure Successful Interface – DICOM Conformance Statement – Should be required BEFORE procurement. – Vendor Survey – Required component of Directive 6550 • Networking/Security specifics (no external modems required, etc) • Users do not require administrative privilege to function • Physical characteristics (electrical, floor loading, environmental) • Any items you wish you knew from prior procurements – Contact Silver Spring (VHA VI DICOM Validation mail group) to verify that the device is approved for interface if not on the approved list on the web site (yes it MUST be approved). – If the device is not approved instruct the vendor to contact Silver Spring for validation. Do not back down on this! Approved list http: //vaww. va. gov/imaging/Vist. A_Imaging_DICOM_Modality_Interfaces. pdf 25
 Documentation • Image Acquisition Technical Data Sheets – 2 Different forms – DICOM and Clinical Capture – Need to submit a form for each new modality and/or Clinical Capture device • Image Quality Certification Form – Submitted after interface is in use – Completed by end user • Latest forms on Imaging/Clinical Procedures Web Site – http: //vaww 4. va. gov/imaging/IMGplanproc. htm – http: //vista. med. va. gov/Clinical. Specialties/clinproc/ 26
Documentation • Image Acquisition Technical Data Sheets – 2 Different forms – DICOM and Clinical Capture – Need to submit a form for each new modality and/or Clinical Capture device • Image Quality Certification Form – Submitted after interface is in use – Completed by end user • Latest forms on Imaging/Clinical Procedures Web Site – http: //vaww 4. va. gov/imaging/IMGplanproc. htm – http: //vista. med. va. gov/Clinical. Specialties/clinproc/ 26
 Preventive Maintenance Not official OR comprehensive! • Each Morning – Review basic operation, DICOM Gateways, BGP, Jukebox, etc. – Review System logs for events – Review Vist. A error trap – Review prior night’s Backups – Remove any completed Jukebox copy media to secure location – Walk through key areas as time permits – Keep a log of any anomalies • Monthly – Monthly backup operations (remove media to offsite, etc) – Purge DICOM Gateways – Check RAID free space 27
Preventive Maintenance Not official OR comprehensive! • Each Morning – Review basic operation, DICOM Gateways, BGP, Jukebox, etc. – Review System logs for events – Review Vist. A error trap – Review prior night’s Backups – Remove any completed Jukebox copy media to secure location – Walk through key areas as time permits – Keep a log of any anomalies • Monthly – Monthly backup operations (remove media to offsite, etc) – Purge DICOM Gateways – Check RAID free space 27
 Disaster/Contingency Plans • • PLAN for Disasters – Make a point to make your disaster guide easy to follow in urgent situations – Label key information on critical equipment for quick access (where appropriate. Be discrete with public equipment) Document Formula (Again, NOT Official) Consult with your ISO – Accurate Table of Contents – Emergency Contacts – System overview with good diagrams – Key information for each piece of equipment. Give complex devices (Imaging SAN) an overview section AND component sections • Function • Effect of Outage • Startup/Shutdown procedure • Contingency Plan • Notes 28
Disaster/Contingency Plans • • PLAN for Disasters – Make a point to make your disaster guide easy to follow in urgent situations – Label key information on critical equipment for quick access (where appropriate. Be discrete with public equipment) Document Formula (Again, NOT Official) Consult with your ISO – Accurate Table of Contents – Emergency Contacts – System overview with good diagrams – Key information for each piece of equipment. Give complex devices (Imaging SAN) an overview section AND component sections • Function • Effect of Outage • Startup/Shutdown procedure • Contingency Plan • Notes 28
 Implementation Workgroup • Group comprised of key individuals representing key disciplines (Required by Directive 6550) – Integrating Service (Radiology, Cardiology, etc) – Imaging Coordinator (YOU!) – IRM – Biomedical Engineering – Procurement (If considering major purchases) – Your Implementation Manager for larger projects • Helps keep the Devil OUT of the details • Should be involved on EVERY medical device purchase that hopes to integrate with VA network. 29
Implementation Workgroup • Group comprised of key individuals representing key disciplines (Required by Directive 6550) – Integrating Service (Radiology, Cardiology, etc) – Imaging Coordinator (YOU!) – IRM – Biomedical Engineering – Procurement (If considering major purchases) – Your Implementation Manager for larger projects • Helps keep the Devil OUT of the details • Should be involved on EVERY medical device purchase that hopes to integrate with VA network. 29
 Getting Support • National Helpdesk 888 -596 -4357 – Will help you identify who to contact – Will page support personnel and enter Remedy tickets for urgent issues • Remedy for VA Package Issues (Vist. A Imaging) – Use Remedy to track the status of your support calls and update support staff • HP Expertise Center – 800 -299 -7282 – Will help with server hardware issues 30
Getting Support • National Helpdesk 888 -596 -4357 – Will help you identify who to contact – Will page support personnel and enter Remedy tickets for urgent issues • Remedy for VA Package Issues (Vist. A Imaging) – Use Remedy to track the status of your support calls and update support staff • HP Expertise Center – 800 -299 -7282 – Will help with server hardware issues 30
 • Weekly Imaging Conference Call – Held each Thursday from 12: 00 – 1: 00 PM Eastern Time – Forum for announcing new developments – Forum for addressing the group on issues your site/VISN may be experiencing – Call in number – 800 -767 -1750, code - 18449 • Monthly HP Imaging Conference Call – Held 3 rd Tuesday of the month from 2: 00 – 3: 00 PM Eastern Time (1 -877 -675 -4345, Passcode: 2102543262) – Forum for hardware issues • Get on the List. Serve to receive critical updates and requests. 31
• Weekly Imaging Conference Call – Held each Thursday from 12: 00 – 1: 00 PM Eastern Time – Forum for announcing new developments – Forum for addressing the group on issues your site/VISN may be experiencing – Call in number – 800 -767 -1750, code - 18449 • Monthly HP Imaging Conference Call – Held 3 rd Tuesday of the month from 2: 00 – 3: 00 PM Eastern Time (1 -877 -675 -4345, Passcode: 2102543262) – Forum for hardware issues • Get on the List. Serve to receive critical updates and requests. 31
 TROUBLESHOOTING • I’m still getting an “ID Mismatch” Why? Answer: If BOTH the ICN and the SSN have been changed, the images will be nonviewable. • No images on a patient, but the case says it’s complete. a. Did the images really get sent from the modality/device? b. Are they a DICOM correct? • Image is there but non-viewable. Answer: Patch 93 introduced the TIU Business rule association. If an image is associated to a progress note that is non-viewable, you will no longer be able to view that image. 32
TROUBLESHOOTING • I’m still getting an “ID Mismatch” Why? Answer: If BOTH the ICN and the SSN have been changed, the images will be nonviewable. • No images on a patient, but the case says it’s complete. a. Did the images really get sent from the modality/device? b. Are they a DICOM correct? • Image is there but non-viewable. Answer: Patch 93 introduced the TIU Business rule association. If an image is associated to a progress note that is non-viewable, you will no longer be able to view that image. 32
![Keys/Menu Options • IMAG Imaging System Manager Menu. . . [MAG SYS MENU] **> Keys/Menu Options • IMAG Imaging System Manager Menu. . . [MAG SYS MENU] **>](https://present5.com/presentation/a08e4b4e5267dfa55536447a9276be39/image-33.jpg) Keys/Menu Options • IMAG Imaging System Manager Menu. . . [MAG SYS MENU] **> Locked with MAG SYSTEM • MAG WINDOWS – MAG DELETE – MAGDISP Clin/MAGDISP Admin – MAG CAPTURE, MAGCAP TIU, MAGCAPMAGJ VISTARAD • MAGJ VISTARAD WINDOWS – WINDOWSVRAD Keys: MAGJ 33
Keys/Menu Options • IMAG Imaging System Manager Menu. . . [MAG SYS MENU] **> Locked with MAG SYSTEM • MAG WINDOWS – MAG DELETE – MAGDISP Clin/MAGDISP Admin – MAG CAPTURE, MAGCAP TIU, MAGCAPMAGJ VISTARAD • MAGJ VISTARAD WINDOWS – WINDOWSVRAD Keys: MAGJ 33
 Patches • Patch 94 Clinical Capture/Display Client • Patch 90 Vist. ARAD • Patch 83 Vist. A Imaging Exchange (VIX support • Patch 39 BGP Enhancements • 66 DICOM Query/Retrieve • Others 34
Patches • Patch 94 Clinical Capture/Display Client • Patch 90 Vist. ARAD • Patch 83 Vist. A Imaging Exchange (VIX support • Patch 39 BGP Enhancements • 66 DICOM Query/Retrieve • Others 34
 • Patch 90 is a Vist. ARad enhancement patch that also has BSE and includes remote image views in the patient exams list, the capability to remotely read/interpret studies; and provides a single sign-on to a group of selected remote sites and the local site. • Patch 83 allows remote image viewing of VA/Do. D and VA-to VA Image Sharing (using the VIX environment). It allows access to Do. D radiology images using existing Clinical Display remote image views functions. And, in conjunction with 90, allows new VA-to-VA remote image access and remote exam list monitoring for Vist. ARad (enhanced remote reading capabilities). • Patch 39 is the Background Processor Enhancement patch that allows for automatic restart of the BGP upon disconnection, PGP system monitor status failure email user notifications (set frequency intervals and recipients); and an improved GUI interface for managing the BGP settings (BGP queues, etc) in addition to improved purge options (manual purge by selected shares, purge by Date Modified, purge by Date Created). (VEHU Imaging Session 760) • Patch 66 DICOM Query/Retrieve provides the ability for DICOM to serve as a Service Class Provider (SCP) to enable current specialty workstations, PACS, and teleradiology systems to query and retrieve images stored in Vist. A Imaging. • Some other improvements in field testing include (not a complete listing): • 98 Storage Utilities (Mag. Dexter, Mag. Utility, Mag. Kat) – to backfill specific fields in Image file #2005 to address discrepancies that may appear in displaying older images; new storage mgmt utilities with GUI’s. • 99 DICOM Object Storage – Allow the option to store all currently supported DICOM modalities images in native DICOM format that would otherwise be stored in Targa formate (e. g. CR & DX modalities) WITHOUT changing or transforming the presentation. • 105 Advanced Web Image Viewer (AWIV) Development – will let Vist. AWeb users locate and display VA images associated with progress notes (supports display of images associated with Radiology reports as well) • Some others to mention that are in Development: • 34 Storing DICOM objects Phase 3 – takes patch 99 further in that it allows storage of all composite DICOM objects that are transmitted to Vist. A Imaging for currently supported and unsupported SOP class images regardless of modality. The images are retained in DICOM format without alteration. The storage of DICOM objects in DICOM format will be mandatory in Patch 34. • 106 Teledermatology – includes DICOM image capture via the Vist. A Imaging Clinical Capture/Display client; controlled use of Telereader with Thin Clients; and limited annotation when reviewing images in Telereader/display. (currently specialized software is utilized to capture Tele. Derm images). • 115 – Vist. A Rad Enhancements – Includes a process for automatically updating the Vist. ARad client software; CCOW integration, provides management functions including remove or disable a user from the settings file (e. g. residents who leave). Also provides a default profile to copy settings/hanging protocols to new users. • 117 Maintenance for Display and capture – (improve QA reporting features, ability to print multiple images, deleted image placeholder, to name a few) • There are several other maintenance and enhancement patches for Vist. ARad, Display and Capture and the gateways that are underway. 35 Each will improve the current products being used and address Remedy ticket issues that have been reported.
• Patch 90 is a Vist. ARad enhancement patch that also has BSE and includes remote image views in the patient exams list, the capability to remotely read/interpret studies; and provides a single sign-on to a group of selected remote sites and the local site. • Patch 83 allows remote image viewing of VA/Do. D and VA-to VA Image Sharing (using the VIX environment). It allows access to Do. D radiology images using existing Clinical Display remote image views functions. And, in conjunction with 90, allows new VA-to-VA remote image access and remote exam list monitoring for Vist. ARad (enhanced remote reading capabilities). • Patch 39 is the Background Processor Enhancement patch that allows for automatic restart of the BGP upon disconnection, PGP system monitor status failure email user notifications (set frequency intervals and recipients); and an improved GUI interface for managing the BGP settings (BGP queues, etc) in addition to improved purge options (manual purge by selected shares, purge by Date Modified, purge by Date Created). (VEHU Imaging Session 760) • Patch 66 DICOM Query/Retrieve provides the ability for DICOM to serve as a Service Class Provider (SCP) to enable current specialty workstations, PACS, and teleradiology systems to query and retrieve images stored in Vist. A Imaging. • Some other improvements in field testing include (not a complete listing): • 98 Storage Utilities (Mag. Dexter, Mag. Utility, Mag. Kat) – to backfill specific fields in Image file #2005 to address discrepancies that may appear in displaying older images; new storage mgmt utilities with GUI’s. • 99 DICOM Object Storage – Allow the option to store all currently supported DICOM modalities images in native DICOM format that would otherwise be stored in Targa formate (e. g. CR & DX modalities) WITHOUT changing or transforming the presentation. • 105 Advanced Web Image Viewer (AWIV) Development – will let Vist. AWeb users locate and display VA images associated with progress notes (supports display of images associated with Radiology reports as well) • Some others to mention that are in Development: • 34 Storing DICOM objects Phase 3 – takes patch 99 further in that it allows storage of all composite DICOM objects that are transmitted to Vist. A Imaging for currently supported and unsupported SOP class images regardless of modality. The images are retained in DICOM format without alteration. The storage of DICOM objects in DICOM format will be mandatory in Patch 34. • 106 Teledermatology – includes DICOM image capture via the Vist. A Imaging Clinical Capture/Display client; controlled use of Telereader with Thin Clients; and limited annotation when reviewing images in Telereader/display. (currently specialized software is utilized to capture Tele. Derm images). • 115 – Vist. A Rad Enhancements – Includes a process for automatically updating the Vist. ARad client software; CCOW integration, provides management functions including remove or disable a user from the settings file (e. g. residents who leave). Also provides a default profile to copy settings/hanging protocols to new users. • 117 Maintenance for Display and capture – (improve QA reporting features, ability to print multiple images, deleted image placeholder, to name a few) • There are several other maintenance and enhancement patches for Vist. ARad, Display and Capture and the gateways that are underway. 35 Each will improve the current products being used and address Remedy ticket issues that have been reported.
 Becoming a Test Site – Why should I? • • Helps the project Helps your site (help shape new software) – Test Phases • • • E 3 R/NSR Concept and Development Internal Testing Alpha Testing – Design refinement and bug squashing Beta Testing – Small bug squashing Release – Test Documentation • • Testing Scenarios Site Feedback Forms 36
Becoming a Test Site – Why should I? • • Helps the project Helps your site (help shape new software) – Test Phases • • • E 3 R/NSR Concept and Development Internal Testing Alpha Testing – Design refinement and bug squashing Beta Testing – Small bug squashing Release – Test Documentation • • Testing Scenarios Site Feedback Forms 36
 Questions… 37
Questions… 37


