81dbf2cb543e83cd309f75571f5b0f85.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 56
 SESSION 6 Wednesday 14. 00 – 15. 30 Key issues for Swaziland during the procurement phase
SESSION 6 Wednesday 14. 00 – 15. 30 Key issues for Swaziland during the procurement phase
 Preparation for procurement ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Preparation for procurement ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 Step 1: Prepare the Draft RFP and get Approval The MDA must write the draft RFP, based on its feasibility study The draft RFP must be the MDA’s version of a final RFP and must include a draft PPP agreement It can highlight the areas on which bidders are being requested to provide input The draft RFP and its attachments, including the draft PPP agreement, must be submitted to the approval body before being issued to the prequalified bidders ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Step 1: Prepare the Draft RFP and get Approval The MDA must write the draft RFP, based on its feasibility study The draft RFP must be the MDA’s version of a final RFP and must include a draft PPP agreement It can highlight the areas on which bidders are being requested to provide input The draft RFP and its attachments, including the draft PPP agreement, must be submitted to the approval body before being issued to the prequalified bidders ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 Contents of the RFP Document 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. General information to bidders Essential minimum requirements Service specifications Standard specifications Payment mechanism and penalty regime Legal requirements and draft PPP agreement Commitments required from bidders Evaluation criteria Bid formalities ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Contents of the RFP Document 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. General information to bidders Essential minimum requirements Service specifications Standard specifications Payment mechanism and penalty regime Legal requirements and draft PPP agreement Commitments required from bidders Evaluation criteria Bid formalities ©David I H Wright Ltd.
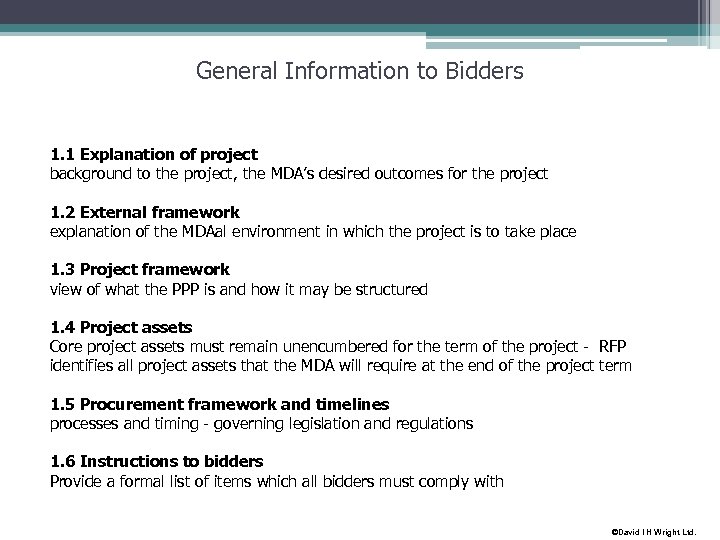 General Information to Bidders 1. 1 Explanation of project background to the project, the MDA’s desired outcomes for the project 1. 2 External framework explanation of the MDAal environment in which the project is to take place 1. 3 Project framework view of what the PPP is and how it may be structured 1. 4 Project assets Core project assets must remain unencumbered for the term of the project - RFP identifies all project assets that the MDA will require at the end of the project term 1. 5 Procurement framework and timelines processes and timing - governing legislation and regulations 1. 6 Instructions to bidders Provide a formal list of items which all bidders must comply with ©David I H Wright Ltd.
General Information to Bidders 1. 1 Explanation of project background to the project, the MDA’s desired outcomes for the project 1. 2 External framework explanation of the MDAal environment in which the project is to take place 1. 3 Project framework view of what the PPP is and how it may be structured 1. 4 Project assets Core project assets must remain unencumbered for the term of the project - RFP identifies all project assets that the MDA will require at the end of the project term 1. 5 Procurement framework and timelines processes and timing - governing legislation and regulations 1. 6 Instructions to bidders Provide a formal list of items which all bidders must comply with ©David I H Wright Ltd.
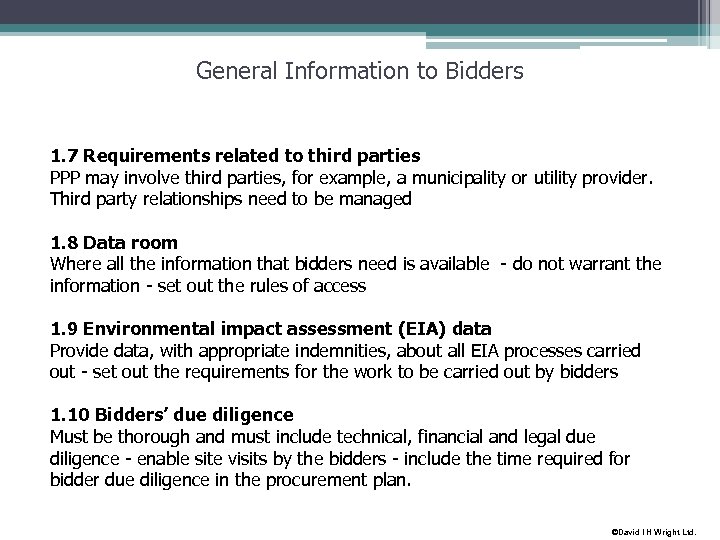 General Information to Bidders 1. 7 Requirements related to third parties PPP may involve third parties, for example, a municipality or utility provider. Third party relationships need to be managed 1. 8 Data room Where all the information that bidders need is available - do not warrant the information - set out the rules of access 1. 9 Environmental impact assessment (EIA) data Provide data, with appropriate indemnities, about all EIA processes carried out - set out the requirements for the work to be carried out by bidders 1. 10 Bidders’ due diligence Must be thorough and must include technical, financial and legal due diligence - enable site visits by the bidders - include the time required for bidder due diligence in the procurement plan. ©David I H Wright Ltd.
General Information to Bidders 1. 7 Requirements related to third parties PPP may involve third parties, for example, a municipality or utility provider. Third party relationships need to be managed 1. 8 Data room Where all the information that bidders need is available - do not warrant the information - set out the rules of access 1. 9 Environmental impact assessment (EIA) data Provide data, with appropriate indemnities, about all EIA processes carried out - set out the requirements for the work to be carried out by bidders 1. 10 Bidders’ due diligence Must be thorough and must include technical, financial and legal due diligence - enable site visits by the bidders - include the time required for bidder due diligence in the procurement plan. ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 General Information to Bidders 1. 11 Quality management system MDA must require the bidders to propose a quality management system that includes compliance reporting during both the development and operations phases. The MDA should also reserve the right to audit or check the private party’s compliance with its own quality assurance and control systems. Mechanisms for such audits or checks should be established before the signing of the PPP agreement and be included in the PPP agreement management plan. 1. 12 Important definitions The RFP must clearly list all the definitions used throughout the documents. This is to ensure clarity and to set clearly defined benchmarks. The definitions must be the same as those used in the draft PPP agreement. ©David I H Wright Ltd.
General Information to Bidders 1. 11 Quality management system MDA must require the bidders to propose a quality management system that includes compliance reporting during both the development and operations phases. The MDA should also reserve the right to audit or check the private party’s compliance with its own quality assurance and control systems. Mechanisms for such audits or checks should be established before the signing of the PPP agreement and be included in the PPP agreement management plan. 1. 12 Important definitions The RFP must clearly list all the definitions used throughout the documents. This is to ensure clarity and to set clearly defined benchmarks. The definitions must be the same as those used in the draft PPP agreement. ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 Essential Minimum Requirements What is the minimum that can be expected from a bid for it to meet the pre-defined project objectives established in the feasibility study? There will be minimum requirements for at least the following: • Financial (for example, demonstration of affordability, risk assumption, funding by private party, term sheets, and minimum insurance requirements) • Legal (for example, any MDA requirements for the types of participant in the consortium, bidder details, term sheets or draft first-tier subcontracts, and a mark up of the PPP agreement to indicate deviations from the proposed PPP agreement and to explain in their bid documents the reason for the deviation. ) • Technical (for example, essential components making up the life cycle of the service and additional operational minimum requirements) • Additional mandatory requirements (for example, tax clearance certificates for all consortium members). These minimum requirements will establish what constitutes a compliant bid. Bids which do not meet them should be rejected in the evaluation process. However, the requirements must not stifle innovation or be so onerous that otherwise solid bids are knocked out unnecessarily early. ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Essential Minimum Requirements What is the minimum that can be expected from a bid for it to meet the pre-defined project objectives established in the feasibility study? There will be minimum requirements for at least the following: • Financial (for example, demonstration of affordability, risk assumption, funding by private party, term sheets, and minimum insurance requirements) • Legal (for example, any MDA requirements for the types of participant in the consortium, bidder details, term sheets or draft first-tier subcontracts, and a mark up of the PPP agreement to indicate deviations from the proposed PPP agreement and to explain in their bid documents the reason for the deviation. ) • Technical (for example, essential components making up the life cycle of the service and additional operational minimum requirements) • Additional mandatory requirements (for example, tax clearance certificates for all consortium members). These minimum requirements will establish what constitutes a compliant bid. Bids which do not meet them should be rejected in the evaluation process. However, the requirements must not stifle innovation or be so onerous that otherwise solid bids are knocked out unnecessarily early. ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 Service Specifications There at least four ways to specify the PPP services and facilities. 1. Expressed as outputs - Services and facilities specifications are generally expressed as outputs by changing what must be done and how it is done to the required service outcome. 2. Specific outputs not directly related to the overall service - MDA may require the creation of a facility not related to the direct provision of a service, for example, a clinic to be constructed on the hospital grounds which is to be operated by another party. Construction outputs need to be defined. 3. Input specifications - Must be kept to a minimum as they may affect operational efficiency or impact excessively on the design of the facility. 4. Conditions-of-asset-specifications - Where the assets revert to the MDA they must be in a specified condition, which dictates replacement and maintenance cycles as well as financial assumptions such as residual value and depreciation. The condition is always expressed as a remaining life or already-utilised life, as determined by industry norms or as agreed between the MDA and the private party in the PPP agreement. ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Service Specifications There at least four ways to specify the PPP services and facilities. 1. Expressed as outputs - Services and facilities specifications are generally expressed as outputs by changing what must be done and how it is done to the required service outcome. 2. Specific outputs not directly related to the overall service - MDA may require the creation of a facility not related to the direct provision of a service, for example, a clinic to be constructed on the hospital grounds which is to be operated by another party. Construction outputs need to be defined. 3. Input specifications - Must be kept to a minimum as they may affect operational efficiency or impact excessively on the design of the facility. 4. Conditions-of-asset-specifications - Where the assets revert to the MDA they must be in a specified condition, which dictates replacement and maintenance cycles as well as financial assumptions such as residual value and depreciation. The condition is always expressed as a remaining life or already-utilised life, as determined by industry norms or as agreed between the MDA and the private party in the PPP agreement. ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 Standard Specifications The RFP must apply objective standards, which are measurable and consistent with best practice. Make extensive use of specifications applicable to all standard components of the project. These could be construction specifications and standard operational requirements (SABS and ISO are prime examples). Select appropriate standards with care: How applicable are they to the project? How are they used in the industry? Are they appropriate? ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Standard Specifications The RFP must apply objective standards, which are measurable and consistent with best practice. Make extensive use of specifications applicable to all standard components of the project. These could be construction specifications and standard operational requirements (SABS and ISO are prime examples). Select appropriate standards with care: How applicable are they to the project? How are they used in the industry? Are they appropriate? ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 Payment Mechanism and Penalty Regime The RFP must not be issued without a payment mechanism, which includes at least the following in a unitary payment arrangement: • a single, indivisible unitary payment for full availability and performance of the services • an appropriate indexation (CPIX, unless the feasibility study demonstrates an alternative indexation as providing value for money) • a mechanism for penalising partial or complete failure of the availability and performance of the service, by means of penalty deductions • no limit to deductions for non-availability • a mechanism for dealing with changes to service requirements. ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Payment Mechanism and Penalty Regime The RFP must not be issued without a payment mechanism, which includes at least the following in a unitary payment arrangement: • a single, indivisible unitary payment for full availability and performance of the services • an appropriate indexation (CPIX, unless the feasibility study demonstrates an alternative indexation as providing value for money) • a mechanism for penalising partial or complete failure of the availability and performance of the service, by means of penalty deductions • no limit to deductions for non-availability • a mechanism for dealing with changes to service requirements. ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 Legal Requirements and Draft PPP Agreement These are all the key commercial and performance requirements necessary to sign off that the consortium has the legal status and capacity to fulfil the requirements of the PPP agreement, including: • shareholding agreements • corporate governance requirements • full disclosure of the consortium makeup, including lenders, sponsors, and parent companies. The RFP must include a draft PPP agreement that allows for highly structured bidder input. ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Legal Requirements and Draft PPP Agreement These are all the key commercial and performance requirements necessary to sign off that the consortium has the legal status and capacity to fulfil the requirements of the PPP agreement, including: • shareholding agreements • corporate governance requirements • full disclosure of the consortium makeup, including lenders, sponsors, and parent companies. The RFP must include a draft PPP agreement that allows for highly structured bidder input. ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 Commitments Required from Bidders Crucial part of RFP - sets out what information is required from bidders Bidders must provide information on at least the following aspects of their bid: All technical aspects, including all relevant service details • Bidders should prepare the components of the service level agreements (SLAs) that will be part of the PPP agreement • Where the MDA has not specified these as essential minimum requirements, they must respond to the service and standard specifications in the RFP • SLAs should be in schedules to the draft PPP agreement as well as in the main body of the bidders’ proposals Bidder’s quality management system ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Commitments Required from Bidders Crucial part of RFP - sets out what information is required from bidders Bidders must provide information on at least the following aspects of their bid: All technical aspects, including all relevant service details • Bidders should prepare the components of the service level agreements (SLAs) that will be part of the PPP agreement • Where the MDA has not specified these as essential minimum requirements, they must respond to the service and standard specifications in the RFP • SLAs should be in schedules to the draft PPP agreement as well as in the main body of the bidders’ proposals Bidder’s quality management system ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 Commitments Required from Bidders Security requirements The MDA should clearly stipulate the type as well as the amount of any security that it will require from the private party, and request that each bidder cost for this security as a separate component of its total bid price, as this will aid in the evaluation process This should include security against late service commencement and for final maintenance obligations. Usually in standard conditions Liquidated damages If liquidated damages will not impact severely on vfm, the MDA should specify the level of liquidated damages (including any cap) in the RFP so that bidders can properly price for these damages This will also help the MDA’s evaluation team in exposing the ‘real’ costs of the bid and improve competitiveness in the selection of the bids ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Commitments Required from Bidders Security requirements The MDA should clearly stipulate the type as well as the amount of any security that it will require from the private party, and request that each bidder cost for this security as a separate component of its total bid price, as this will aid in the evaluation process This should include security against late service commencement and for final maintenance obligations. Usually in standard conditions Liquidated damages If liquidated damages will not impact severely on vfm, the MDA should specify the level of liquidated damages (including any cap) in the RFP so that bidders can properly price for these damages This will also help the MDA’s evaluation team in exposing the ‘real’ costs of the bid and improve competitiveness in the selection of the bids ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 Commitments Required from Bidders Contents of the financial models Critical information is contained in bidders’ financial models, and the RFP should specify the format in which this information is to be shown in the bids in order to allow the MDA to compare a bidder’s model with the MDA’s feasibility study models and with other bidders’ models. The checklist below needs to be carefully refined for each project. See pages 35 -37 of SA Module 5 ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Commitments Required from Bidders Contents of the financial models Critical information is contained in bidders’ financial models, and the RFP should specify the format in which this information is to be shown in the bids in order to allow the MDA to compare a bidder’s model with the MDA’s feasibility study models and with other bidders’ models. The checklist below needs to be carefully refined for each project. See pages 35 -37 of SA Module 5 ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 Evaluation criteria Give broad categories of evaluation, but in sufficient detail to focus bidders’ attention on the value-for-money areas of the RFP Point allocations should not be given, as this leads to proposals being tailored to the evaluation and not to the best value for the project The number of points allocated to each category or sub-category should not be disclosed in the RFP The process and evaluation methodology should be set out so that bidders take comfort from an auditable process with checks and balances The RFP should specify that technical and price elements of the bid will each be scored out of 100 points. The scores achieved will be calculated into the bidder’s overall score, using the following formula: ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Evaluation criteria Give broad categories of evaluation, but in sufficient detail to focus bidders’ attention on the value-for-money areas of the RFP Point allocations should not be given, as this leads to proposals being tailored to the evaluation and not to the best value for the project The number of points allocated to each category or sub-category should not be disclosed in the RFP The process and evaluation methodology should be set out so that bidders take comfort from an auditable process with checks and balances The RFP should specify that technical and price elements of the bid will each be scored out of 100 points. The scores achieved will be calculated into the bidder’s overall score, using the following formula: ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 Bid Formalities Bid formalities • the time, place and manner of bid submission (proposals for large projects may take up substantial space and separate secure facilities may be required for submitting bids) • how proposals will be opened • bid bonds • period required for bid validity • formal requirements for filling out bid forms • formal processes for communication with bidders • the MDA’s reservation of the right to terminate the process, including the right to terminate negotiation with the preferred bidder if it is unlikely that an agreement will be concluded, in which case negotiations with other bidders may begin. In addition the MDA should state that it is not bound to enter into a contract with any bidder • a discretion to be exercised by the bid evaluation panel in the event of noncompliance in any of the bids • reservation of the MDA’s right to conduct a BAFO process. ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Bid Formalities Bid formalities • the time, place and manner of bid submission (proposals for large projects may take up substantial space and separate secure facilities may be required for submitting bids) • how proposals will be opened • bid bonds • period required for bid validity • formal requirements for filling out bid forms • formal processes for communication with bidders • the MDA’s reservation of the right to terminate the process, including the right to terminate negotiation with the preferred bidder if it is unlikely that an agreement will be concluded, in which case negotiations with other bidders may begin. In addition the MDA should state that it is not bound to enter into a contract with any bidder • a discretion to be exercised by the bid evaluation panel in the event of noncompliance in any of the bids • reservation of the MDA’s right to conduct a BAFO process. ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 SESSION 1 The Request for Proposals
SESSION 1 The Request for Proposals
 The RFP Stage 1. Prepare the draft RFP document 2. Get feedback from bidders 3. Prepare the RFP document ©David I H Wright Ltd.
The RFP Stage 1. Prepare the draft RFP document 2. Get feedback from bidders 3. Prepare the RFP document ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 Prepare the draft RFP document Get pre-qualified bidders to participate in the preparation of the final RFP if project is large, complex or innovative Business case will have tested the market to some extent, but useful to test in detail with parties who have shown their knowledge and capacity ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Prepare the draft RFP document Get pre-qualified bidders to participate in the preparation of the final RFP if project is large, complex or innovative Business case will have tested the market to some extent, but useful to test in detail with parties who have shown their knowledge and capacity ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 Get feedback from bidders Must be structured and not compromise procedural fairness Bidders’ conference plus 1 -to-1 meetings Common feedback more valuable than isolated feedback Feedback from a consortium more valuable ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Get feedback from bidders Must be structured and not compromise procedural fairness Bidders’ conference plus 1 -to-1 meetings Common feedback more valuable than isolated feedback Feedback from a consortium more valuable ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 Prepare the final RFP document General information Essential minimum requirements Service specifications Standard specifications Payment mechanism and penalty regime Legal requirements and draft PPP agreement Commitments required from bidders Evaluation criteria Bid formalities ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Prepare the final RFP document General information Essential minimum requirements Service specifications Standard specifications Payment mechanism and penalty regime Legal requirements and draft PPP agreement Commitments required from bidders Evaluation criteria Bid formalities ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 General information to bidders Explanation of the project External framework Project assets – must be unencumbered – state what assets are needed at the end of the project term Procurement framework and timelines ©David I H Wright Ltd.
General information to bidders Explanation of the project External framework Project assets – must be unencumbered – state what assets are needed at the end of the project term Procurement framework and timelines ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 General information to bidders Instructions to bidders Requirements relating to third parties Data room EIA data Bidders’ due diligence Quality management system Important definitions ©David I H Wright Ltd.
General information to bidders Instructions to bidders Requirements relating to third parties Data room EIA data Bidders’ due diligence Quality management system Important definitions ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 Essential minimum requirements Financial Legal Technical Additional mandatory requirements ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Essential minimum requirements Financial Legal Technical Additional mandatory requirements ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 Service specifications Expressed as outputs Input specifications Conditions of asset specifications ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Service specifications Expressed as outputs Input specifications Conditions of asset specifications ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 Service specifications Standard specifications Payment mechanism and penalty regime Legal requirements and draft PPP agreement Commitments required from bidders Evaluation criteria Bid formalities ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Service specifications Standard specifications Payment mechanism and penalty regime Legal requirements and draft PPP agreement Commitments required from bidders Evaluation criteria Bid formalities ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 Legal requirements and draft PPP agreement Key requirements necessary to ensure consortium has legal status and capacity Draft PPP agreement should use standard provisions where possible But there will be project specific schedules ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Legal requirements and draft PPP agreement Key requirements necessary to ensure consortium has legal status and capacity Draft PPP agreement should use standard provisions where possible But there will be project specific schedules ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 Commitments needed from bidders Technical aspects including relevant service details Quality management system Level of funding commitment Financial and project structure Security requirements Liquidated damages Contents of the financial models (section 7. 10 of Module 5 of South African Guidance) Evaluation criteria Price Overall integrated solution ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Commitments needed from bidders Technical aspects including relevant service details Quality management system Level of funding commitment Financial and project structure Security requirements Liquidated damages Contents of the financial models (section 7. 10 of Module 5 of South African Guidance) Evaluation criteria Price Overall integrated solution ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 Evaluation criteria ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Evaluation criteria ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 Evaluation criteria – Technical Solution Development phase • Extent, quality, safety, cost effectiveness, functionality and innovation of design • Impact on social and biophysical environment • Deliverability and time schedules • Integration of design, development and operations with clear commissioning schedule • Quality management systems ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Evaluation criteria – Technical Solution Development phase • Extent, quality, safety, cost effectiveness, functionality and innovation of design • Impact on social and biophysical environment • Deliverability and time schedules • Integration of design, development and operations with clear commissioning schedule • Quality management systems ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 Evaluation criteria – Technical Solution Delivery Phase • Extent to which proposed performance targets exceed minimum specifications • Operating methodology • Quality and type of proposed services to end users • Quality of proposed management structure, staffing, systems and practices • Quality of safety plans • Quality management system ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Evaluation criteria – Technical Solution Delivery Phase • Extent to which proposed performance targets exceed minimum specifications • Operating methodology • Quality and type of proposed services to end users • Quality of proposed management structure, staffing, systems and practices • Quality of safety plans • Quality management system ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 Evaluation criteria – Legal Solution SPV structure Robustness of bidder’s structure – are proposals reflected in structure and shareholder agreements – level of commitment of each consortium member – equity participation of each member Mark up of draft PPP agreement and its impact on risk ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Evaluation criteria – Legal Solution SPV structure Robustness of bidder’s structure – are proposals reflected in structure and shareholder agreements – level of commitment of each consortium member – equity participation of each member Mark up of draft PPP agreement and its impact on risk ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 Evaluation criteria – Financial Solution 1 Total project cost cf. affordability constraints Realism of operating and capital expenditure including assessment of whether QM systems have been costed Robustness of proposals including sensitivity to changes in operating and maintenance costs, currency fluctuations, inflation and interest rates Level and nature of equity Level of commitment of debt and equity providers ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Evaluation criteria – Financial Solution 1 Total project cost cf. affordability constraints Realism of operating and capital expenditure including assessment of whether QM systems have been costed Robustness of proposals including sensitivity to changes in operating and maintenance costs, currency fluctuations, inflation and interest rates Level and nature of equity Level of commitment of debt and equity providers ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 Evaluation criteria – Financial Solution 2 Level of risk assumed and deviation from terms of tender documentation Cost, level and nature of insurance proposed Risk allocation: proposed risk profile tested vs • Nature and extent of risk • Likelihood of risk • Passing down of risk and obligations to other key contractors Consistency between financing arrangements and the draft PPP agreement – acceptance by financiers Percentage of total debt outstanding to be repaid on private party default ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Evaluation criteria – Financial Solution 2 Level of risk assumed and deviation from terms of tender documentation Cost, level and nature of insurance proposed Risk allocation: proposed risk profile tested vs • Nature and extent of risk • Likelihood of risk • Passing down of risk and obligations to other key contractors Consistency between financing arrangements and the draft PPP agreement – acceptance by financiers Percentage of total debt outstanding to be repaid on private party default ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 Bid formalities Time, place and management of bid submission How proposals will be opened Bid bonds Period of bid validity Formal requirements for filling out bid forms Processes for communication Reservation of right to terminate process at any stage Not bound to enter into a contract with any bidder Discretion to be exercised by the bid evaluation panel in event of non-compliance in any bid Reservation of right to conduct a BAFO process ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Bid formalities Time, place and management of bid submission How proposals will be opened Bid bonds Period of bid validity Formal requirements for filling out bid forms Processes for communication Reservation of right to terminate process at any stage Not bound to enter into a contract with any bidder Discretion to be exercised by the bid evaluation panel in event of non-compliance in any bid Reservation of right to conduct a BAFO process ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 SESSION 2 Choosing the Preferred Bidder
SESSION 2 Choosing the Preferred Bidder
 Critical Success Factors 1. Experienced bid managers and competent officials 2. Anti-corruption practices 3. Secure environment 4. Ability to have clarification meetings 5. Formal recording of correspondence 6. Acceptance of consortium changes 7. Bidders’ due diligence ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Critical Success Factors 1. Experienced bid managers and competent officials 2. Anti-corruption practices 3. Secure environment 4. Ability to have clarification meetings 5. Formal recording of correspondence 6. Acceptance of consortium changes 7. Bidders’ due diligence ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 Compliance with procurement rules and good international practice Accounting officer/authority must ensure that: • Evaluation process in compliance with procedural fairness provisions • Evaluation criteria and processes established before submission of proposals • Evaluation teams and committees appointed in writing – all declarations and codes of conduct signed ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Compliance with procurement rules and good international practice Accounting officer/authority must ensure that: • Evaluation process in compliance with procedural fairness provisions • Evaluation criteria and processes established before submission of proposals • Evaluation teams and committees appointed in writing – all declarations and codes of conduct signed ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 Levels of evaluation 1. Technical evaluation teams (TETs) 2. Evaluation co-ordination committee (ECC) 3. Project evaluation committee (PEC) Each level has its own built-in checks and balances ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Levels of evaluation 1. Technical evaluation teams (TETs) 2. Evaluation co-ordination committee (ECC) 3. Project evaluation committee (PEC) Each level has its own built-in checks and balances ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 Evaluate the bids 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. TETs ECC PEC Clarification Evaluate variant bids Choose preferred and reserve bidders ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Evaluate the bids 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. TETs ECC PEC Clarification Evaluate variant bids Choose preferred and reserve bidders ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 Technical Evaluation Teams Technical evaluation comprises a number of streams Overall integrated solution is evaluated by the ECC Communication between the TETs, and between the TETs , the ECC and the PEC is critical ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Technical Evaluation Teams Technical evaluation comprises a number of streams Overall integrated solution is evaluated by the ECC Communication between the TETs, and between the TETs , the ECC and the PEC is critical ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 Technical Evaluation Teamsprocesses Preliminary work: • Separate variant bids for separate evaluation • Check for completeness • Check for compliance Detailed analysis • Technical solution • Legal solution • Financial solution • Price Reports to ECC ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Technical Evaluation Teamsprocesses Preliminary work: • Separate variant bids for separate evaluation • Check for completeness • Check for compliance Detailed analysis • Technical solution • Legal solution • Financial solution • Price Reports to ECC ©David I H Wright Ltd.
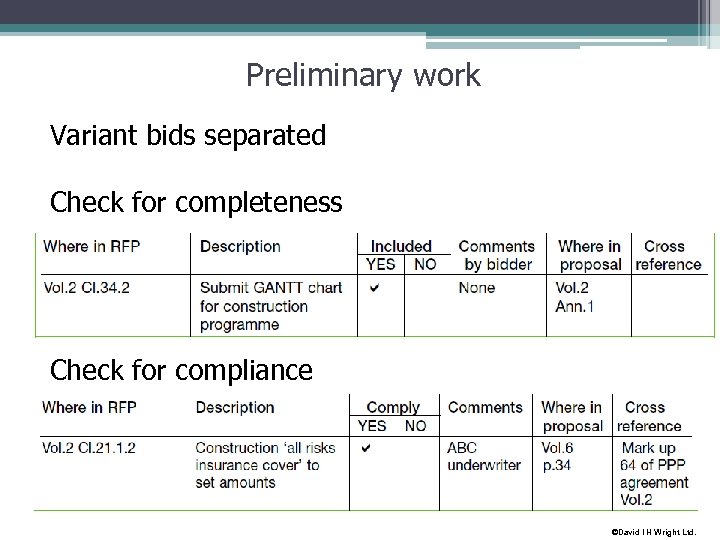 Preliminary work Variant bids separated Check for completeness Check for compliance ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Preliminary work Variant bids separated Check for completeness Check for compliance ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 Detailed analysis Technical solution • Is project deliverable? • Will outputs be delivered? • Solution due diligence • Each element must be assessed from design, development and operational perspectives – objective is to: • Confirm service specs reflect needs • Capture deficiencies/added benefits • Evaluate as inadequate, adequate/good • List of questions • Assess vfm impact ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Detailed analysis Technical solution • Is project deliverable? • Will outputs be delivered? • Solution due diligence • Each element must be assessed from design, development and operational perspectives – objective is to: • Confirm service specs reflect needs • Capture deficiencies/added benefits • Evaluate as inadequate, adequate/good • List of questions • Assess vfm impact ©David I H Wright Ltd.
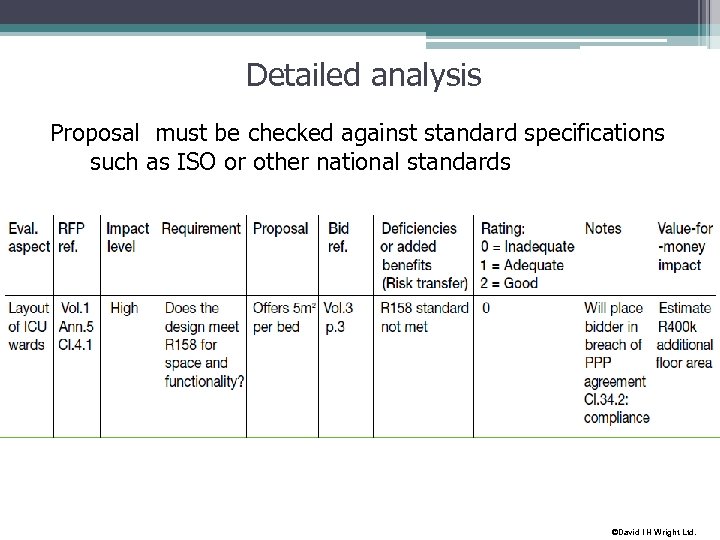 Detailed analysis Proposal must be checked against standard specifications such as ISO or other national standards ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Detailed analysis Proposal must be checked against standard specifications such as ISO or other national standards ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 Legal solution Two tasks: 1. Legal due diligence on structure and legal status of the consortium and status of individual firms 2. Evaluation of marked up draft PPP agreement • Capturing all marked-up amendments • Assessing each vs risk matrix in business case • Capturing vfm implications determined in the business case and commenting • Working with financial evaluation team to assess vfm on issues not identified in the business case Output is not a score – notes for resolution and updating of risk matrix for each team ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Legal solution Two tasks: 1. Legal due diligence on structure and legal status of the consortium and status of individual firms 2. Evaluation of marked up draft PPP agreement • Capturing all marked-up amendments • Assessing each vs risk matrix in business case • Capturing vfm implications determined in the business case and commenting • Working with financial evaluation team to assess vfm on issues not identified in the business case Output is not a score – notes for resolution and updating of risk matrix for each team ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 Financial solution Requires complete understanding of project costs over whole term, structure of consortium and its funding, and key vfm deficiencies or additions in each bid Financial team requires inputs from other teams in assessing or identifying: • Affordability • Certainty of development and operational costs • Certainty, nature and costs of funding • Project participants and structure • Omitted items from financial model • Project vfm • Project bankability Financial team must then produce a composite score and a series of note showing items for resolution ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Financial solution Requires complete understanding of project costs over whole term, structure of consortium and its funding, and key vfm deficiencies or additions in each bid Financial team requires inputs from other teams in assessing or identifying: • Affordability • Certainty of development and operational costs • Certainty, nature and costs of funding • Project participants and structure • Omitted items from financial model • Project vfm • Project bankability Financial team must then produce a composite score and a series of note showing items for resolution ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 Price and reports Price is closely linked to qualitative elements RFP describes form in which price will be presented – price offered must be scrutinised with the financial solution before price points are allocated Each TET produces its own report and score sheets and passes them to the ECC ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Price and reports Price is closely linked to qualitative elements RFP describes form in which price will be presented – price offered must be scrutinised with the financial solution before price points are allocated Each TET produces its own report and score sheets and passes them to the ECC ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 Step 2 Evaluation Co-ordination Committee Role of ECC: • Co-ordinate TETs through regular meetings with team leaders • Approve clarification communications with bidders • Pass TET reports onto PEC with a recommendation on which bidders to take forward as compliant bids • Interrogate TET reports until committee is satisfied that each report is fully substantiated ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Step 2 Evaluation Co-ordination Committee Role of ECC: • Co-ordinate TETs through regular meetings with team leaders • Approve clarification communications with bidders • Pass TET reports onto PEC with a recommendation on which bidders to take forward as compliant bids • Interrogate TET reports until committee is satisfied that each report is fully substantiated ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 Step 2 Evaluation Co-ordination Committee • • • Prepare recommendation on further processes such as BAFO Evaluate and score overall integrated solution for the project and provide resolution notes Compile total project evaluation notes and report into a single recommendation on process and outcome (preferred and reserve bidders) to pass to PEC ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Step 2 Evaluation Co-ordination Committee • • • Prepare recommendation on further processes such as BAFO Evaluate and score overall integrated solution for the project and provide resolution notes Compile total project evaluation notes and report into a single recommendation on process and outcome (preferred and reserve bidders) to pass to PEC ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 Step 3 Project Evaluation Committee PEC is the accounting officer/authority supported by individuals appointed by him or her Role is to: • Accept bids as complete and compliant • Receive and evaluate the report and recommendations from the ECC • Give a final score to the bids • Decide on a BAFO process • Select a preferred and reserved bidder ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Step 3 Project Evaluation Committee PEC is the accounting officer/authority supported by individuals appointed by him or her Role is to: • Accept bids as complete and compliant • Receive and evaluate the report and recommendations from the ECC • Give a final score to the bids • Decide on a BAFO process • Select a preferred and reserved bidder ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 Step 4 Clarification needed to ensure that evaluation reflects a full understanding of each proposal Negotiation often not permitted during the evaluation process Clarification involves written questions and responses and must not solicit any change Response vetted to ensure no change otherwise set aside ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Step 4 Clarification needed to ensure that evaluation reflects a full understanding of each proposal Negotiation often not permitted during the evaluation process Clarification involves written questions and responses and must not solicit any change Response vetted to ensure no change otherwise set aside ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 Step 5 Evaluate variant bids Takes place after compliant bids evaluated Evaluated as a stand alone proposal – in practice amend the score of the compliant bid in the specific areas of variation More complex however – variant bids impact on other elements and materially affect overall risk transfer Financial and performance impacts must be identified and evaluated Aim is to quantify change in vfm ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Step 5 Evaluate variant bids Takes place after compliant bids evaluated Evaluated as a stand alone proposal – in practice amend the score of the compliant bid in the specific areas of variation More complex however – variant bids impact on other elements and materially affect overall risk transfer Financial and performance impacts must be identified and evaluated Aim is to quantify change in vfm ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 Step 6 Choose preferred and reserve bidders Should not be announced until approval has been obtained for the value for money report ©David I H Wright Ltd.
Step 6 Choose preferred and reserve bidders Should not be announced until approval has been obtained for the value for money report ©David I H Wright Ltd.
 BAFO Process Please review pages 51 – 56 of South African Module 5 ©David I H Wright Ltd.
BAFO Process Please review pages 51 – 56 of South African Module 5 ©David I H Wright Ltd.


