2718cb3d7150af3fbcd429e4822410de.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 43
 Session 5 Panel discussion: Standards and regulations Regional Workshop Trade and Environment Dimensions in the Food and Food Processing Industries in Asia and the Pacific Bangkok, Thailand, 16 -18 October 2006 -10 -12 1
Session 5 Panel discussion: Standards and regulations Regional Workshop Trade and Environment Dimensions in the Food and Food Processing Industries in Asia and the Pacific Bangkok, Thailand, 16 -18 October 2006 -10 -12 1
 International Organization for Standardization www. iso. org 2006 -10 -12 2
International Organization for Standardization www. iso. org 2006 -10 -12 2
 ISO The world's largest developer of standards Members 157 national standards bodies (100 member bodies 47 correspondent members 10 subscriber members( 2006 -10 -12 3
ISO The world's largest developer of standards Members 157 national standards bodies (100 member bodies 47 correspondent members 10 subscriber members( 2006 -10 -12 3
 ISO "International Organization for Standardization" "IOS" in English "OIN" in French (for Organisation internationale de normalisation( Use a word derived from the Greek meaning 2006 -10 -12 "equal" isos, 4
ISO "International Organization for Standardization" "IOS" in English "OIN" in French (for Organisation internationale de normalisation( Use a word derived from the Greek meaning 2006 -10 -12 "equal" isos, 4
 ISO Technical bodies 959 2 technical bodies (192 technical committees 541 sub-committees 2 188 working groups and 38 ad hoc study groups 649 15 International Standards ( 494 573 pages) issued 2006 -10 -12 5
ISO Technical bodies 959 2 technical bodies (192 technical committees 541 sub-committees 2 188 working groups and 38 ad hoc study groups 649 15 International Standards ( 494 573 pages) issued 2006 -10 -12 5
 Why? And Why? Why do we need international standards? Why should we support the work at international level? Why do we need to prepare ourselves to participate actively in the work? 2006 -10 -12 6
Why? And Why? Why do we need international standards? Why should we support the work at international level? Why do we need to prepare ourselves to participate actively in the work? 2006 -10 -12 6
 International Standards Making the development, manufacturing and supply of products and services more efficient, safer and cleaner. Trade between countries easier and fairer. Provide governments with a technical base for health, safety and environmental legislation. Transferring technology to developing countries. ISO standards also serve to safeguard consumers, and users in general, of products and services - as well as to make their lives simpler 2006 -10 -12 7
International Standards Making the development, manufacturing and supply of products and services more efficient, safer and cleaner. Trade between countries easier and fairer. Provide governments with a technical base for health, safety and environmental legislation. Transferring technology to developing countries. ISO standards also serve to safeguard consumers, and users in general, of products and services - as well as to make their lives simpler 2006 -10 -12 7
 Making a positive difference!! ISO standards, not just to engineers and manufacturers for whom they solve basic problems in production and distribution, but to society as a whole Social Responsibility, Societal Security etc. 2006 -10 -12 8
Making a positive difference!! ISO standards, not just to engineers and manufacturers for whom they solve basic problems in production and distribution, but to society as a whole Social Responsibility, Societal Security etc. 2006 -10 -12 8
 ISO and Food Industry ƀProcesses in Food Industry ƀGeneral methods of tests and analysis for food products ƀFood 2006 -10 -12 products in general 9
ISO and Food Industry ƀProcesses in Food Industry ƀGeneral methods of tests and analysis for food products ƀFood 2006 -10 -12 products in general 9
 ISO/ TC 34 Food products Scope: Standardization in the field of human and animal foodstuffs as well as animal and vegetable propagation materials, in particular terminology, sampling, methods of test and analysis, product specifications and requirements for packaging, storage and transportation. Excluded : products covered by ISO/TC 54 Essential oils and ISO/TC 93 Starch (including derivatives and by-products. ( 2006 -10 -12 10
ISO/ TC 34 Food products Scope: Standardization in the field of human and animal foodstuffs as well as animal and vegetable propagation materials, in particular terminology, sampling, methods of test and analysis, product specifications and requirements for packaging, storage and transportation. Excluded : products covered by ISO/TC 54 Essential oils and ISO/TC 93 Starch (including derivatives and by-products. ( 2006 -10 -12 10
 ISO/ TC 34 Food products ISO standards under the direct responsibility : 21 ISO standards related to the TC and its SCs: 700 Other ISO and IEC committees in liaison: ISO TC 47, TC 54, TC 93, TC 176/SC 2, CASCO International organizations in liaison: AOAC, COPA-COGECA, EAAP, EC - Commission, IDF, IH&RA, IUPAC, NMKL, OIML, OIV, UN/ECE, UNIDO, WHO 2006 -10 -12 11
ISO/ TC 34 Food products ISO standards under the direct responsibility : 21 ISO standards related to the TC and its SCs: 700 Other ISO and IEC committees in liaison: ISO TC 47, TC 54, TC 93, TC 176/SC 2, CASCO International organizations in liaison: AOAC, COPA-COGECA, EAAP, EC - Commission, IDF, IH&RA, IUPAC, NMKL, OIML, OIV, UN/ECE, UNIDO, WHO 2006 -10 -12 11
 Participation in the work of ISO/TC 34 Participating countries: 51 Observer countries: 50 2006 -10 -12 12
Participation in the work of ISO/TC 34 Participating countries: 51 Observer countries: 50 2006 -10 -12 12
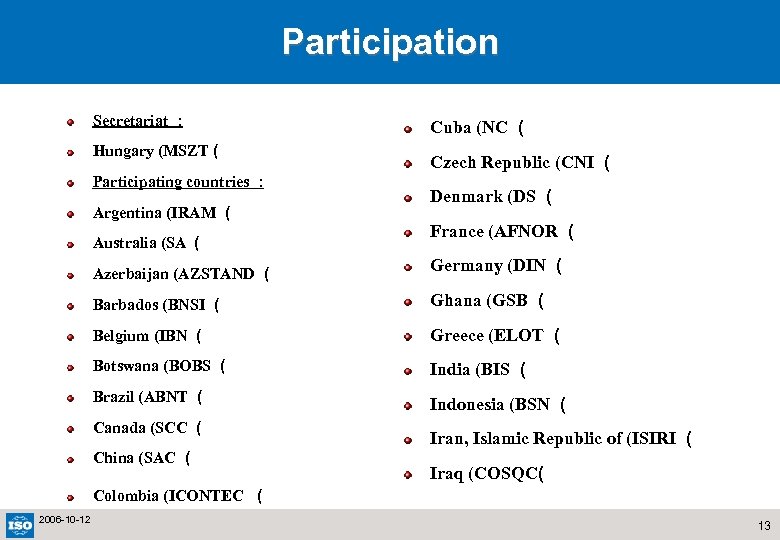 Participation Secretariat : Hungary (MSZT ( Participating countries : Argentina (IRAM ( Australia (SA ( Cuba (NC ( Czech Republic (CNI ( Denmark (DS ( France (AFNOR ( Azerbaijan (AZSTAND ( Germany (DIN ( Barbados (BNSI ( Ghana (GSB ( Belgium (IBN ( Greece (ELOT ( Botswana (BOBS ( India (BIS ( Brazil (ABNT ( Indonesia (BSN ( Canada (SCC ( China (SAC ( Iran, Islamic Republic of (ISIRI ( Iraq (COSQC( Colombia (ICONTEC ( 2006 -10 -12 13
Participation Secretariat : Hungary (MSZT ( Participating countries : Argentina (IRAM ( Australia (SA ( Cuba (NC ( Czech Republic (CNI ( Denmark (DS ( France (AFNOR ( Azerbaijan (AZSTAND ( Germany (DIN ( Barbados (BNSI ( Ghana (GSB ( Belgium (IBN ( Greece (ELOT ( Botswana (BOBS ( India (BIS ( Brazil (ABNT ( Indonesia (BSN ( Canada (SCC ( China (SAC ( Iran, Islamic Republic of (ISIRI ( Iraq (COSQC( Colombia (ICONTEC ( 2006 -10 -12 13
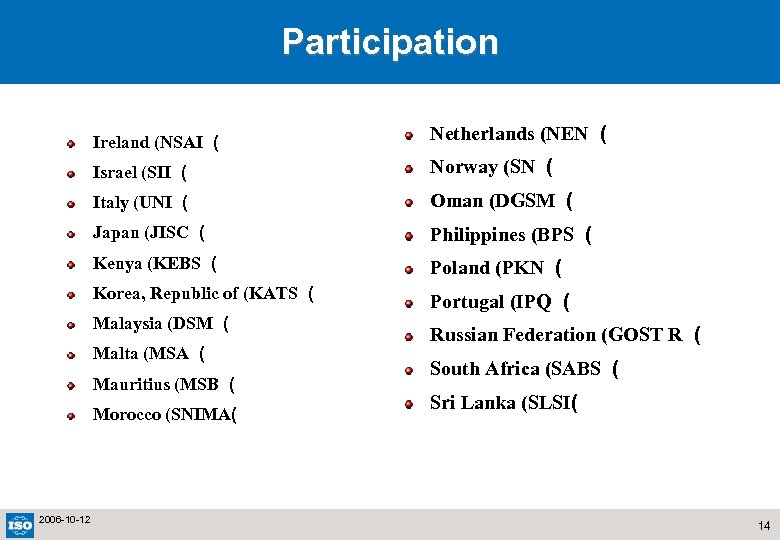 Participation Ireland (NSAI ( Netherlands (NEN ( Israel (SII ( Norway (SN ( Italy (UNI ( Oman (DGSM ( Japan (JISC ( Philippines (BPS ( Kenya (KEBS ( Poland (PKN ( Korea, Republic of (KATS ( Portugal (IPQ ( Malaysia (DSM ( Malta (MSA ( Mauritius (MSB ( Morocco (SNIMA( 2006 -10 -12 Russian Federation (GOST R ( South Africa (SABS ( Sri Lanka (SLSI( 14
Participation Ireland (NSAI ( Netherlands (NEN ( Israel (SII ( Norway (SN ( Italy (UNI ( Oman (DGSM ( Japan (JISC ( Philippines (BPS ( Kenya (KEBS ( Poland (PKN ( Korea, Republic of (KATS ( Portugal (IPQ ( Malaysia (DSM ( Malta (MSA ( Mauritius (MSB ( Morocco (SNIMA( 2006 -10 -12 Russian Federation (GOST R ( South Africa (SABS ( Sri Lanka (SLSI( 14
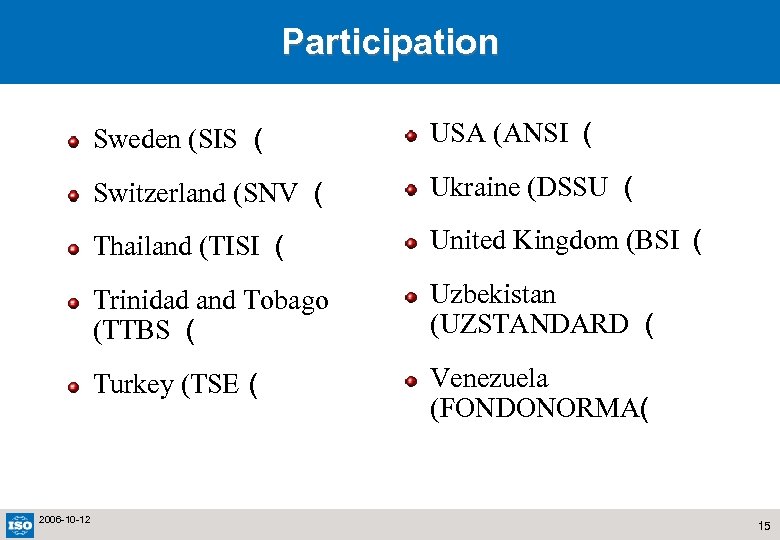 Participation Sweden (SIS ( Switzerland (SNV ( Ukraine (DSSU ( Thailand (TISI ( United Kingdom (BSI ( Trinidad and Tobago (TTBS ( Uzbekistan (UZSTANDARD ( Turkey (TSE ( 2006 -10 -12 USA (ANSI ( Venezuela (FONDONORMA( 15
Participation Sweden (SIS ( Switzerland (SNV ( Ukraine (DSSU ( Thailand (TISI ( United Kingdom (BSI ( Trinidad and Tobago (TTBS ( Uzbekistan (UZSTANDARD ( Turkey (TSE ( 2006 -10 -12 USA (ANSI ( Venezuela (FONDONORMA( 15
 Choices for developing countries Wait and see!! Be a “standards taker” Get actively involved!! Be a “standards setter” Consider “Twinning Arrangements” 2006 -10 -12 16
Choices for developing countries Wait and see!! Be a “standards taker” Get actively involved!! Be a “standards setter” Consider “Twinning Arrangements” 2006 -10 -12 16
 Working area of ISO/TC 34/WG 7 Genetically modified organisms and derived products TC 34/WG 8 Food safety management systems TC 34/WG 9 Traceability system in the agriculture food chain - General principles for design and development TC 34/WG 10 Food irradiation 2006 -10 -12 17
Working area of ISO/TC 34/WG 7 Genetically modified organisms and derived products TC 34/WG 8 Food safety management systems TC 34/WG 9 Traceability system in the agriculture food chain - General principles for design and development TC 34/WG 10 Food irradiation 2006 -10 -12 17
 Working area of ISO/TC 34 Joint CASCO - TC 34 WG: Requirements for bodies providing audit and certification of food safety management systems TC 34/WG 12 Application of ISO 9001: 2000 in the agriculture TC 34/SC 2 Oleaginous seeds and fruits and oilseed meals TC 34/SC 3 Fruit and vegetable products TC 34/SC 4 Cereals and pulses TC 34/SC 5 Milk and milk products 2006 -10 -12 18
Working area of ISO/TC 34 Joint CASCO - TC 34 WG: Requirements for bodies providing audit and certification of food safety management systems TC 34/WG 12 Application of ISO 9001: 2000 in the agriculture TC 34/SC 2 Oleaginous seeds and fruits and oilseed meals TC 34/SC 3 Fruit and vegetable products TC 34/SC 4 Cereals and pulses TC 34/SC 5 Milk and milk products 2006 -10 -12 18
 Working area of ISO/TC 34/SC 6 Meat, poultry, fish, eggs and their products TC 34/SC 7 Spices, culinary herbs and condiments TC 34/SC 8 Tea TC 34/SC 9 Microbiology TC 34/SC 10 Animal feeding stuffs 2006 -10 -12 19
Working area of ISO/TC 34/SC 6 Meat, poultry, fish, eggs and their products TC 34/SC 7 Spices, culinary herbs and condiments TC 34/SC 8 Tea TC 34/SC 9 Microbiology TC 34/SC 10 Animal feeding stuffs 2006 -10 -12 19
 Working area of ISO/TC 34/SC 11 Animal and vegetable fats and oils TC 34/SC 12 Sensory analysis TC 34/SC 14 Fresh, dry and dried fruits and vegetables TC 34/SC 15 Coffee 2006 -10 -12 20
Working area of ISO/TC 34/SC 11 Animal and vegetable fats and oils TC 34/SC 12 Sensory analysis TC 34/SC 14 Fresh, dry and dried fruits and vegetables TC 34/SC 15 Coffee 2006 -10 -12 20
 Processes in Food Industry ISO 22000: 2005 Food safety management systems-Requirements for any organization in the food chain ISO/TS 22005: 2005 Food safety management systems- Guidance on the application of ISO 22000: 2005 2006 -10 -12 21
Processes in Food Industry ISO 22000: 2005 Food safety management systems-Requirements for any organization in the food chain ISO/TS 22005: 2005 Food safety management systems- Guidance on the application of ISO 22000: 2005 2006 -10 -12 21
 Benefits from implementation of ISO 22000 For businesses, ISO 22000 widely accepted in food sector; Businesses implementing ISO 22000 can compete on many more markets around the world 2006 -10 -12 22
Benefits from implementation of ISO 22000 For businesses, ISO 22000 widely accepted in food sector; Businesses implementing ISO 22000 can compete on many more markets around the world 2006 -10 -12 22
 Benefits from implementation of ISO 22000 For consumers: ISO 22000 provides assurance for: -quality -safety -reliability 2006 -10 -12 23
Benefits from implementation of ISO 22000 For consumers: ISO 22000 provides assurance for: -quality -safety -reliability 2006 -10 -12 23
 Benefits from implementation of ISO 22000 For trade officials negotiating agreements in food sector, International Standards, like ISO 22000, are the technical means by which political trade agreements can be put into practice/ reached 2006 -10 -12 24
Benefits from implementation of ISO 22000 For trade officials negotiating agreements in food sector, International Standards, like ISO 22000, are the technical means by which political trade agreements can be put into practice/ reached 2006 -10 -12 24
 Benefits from implementation of ISO 22000 For developing countries, ISO 22000 represents an international consensus and constitute an important source of technological know-how; It gives developing countries a basis for making the right decisions when investing their scarce resources 2006 -10 -12 25
Benefits from implementation of ISO 22000 For developing countries, ISO 22000 represents an international consensus and constitute an important source of technological know-how; It gives developing countries a basis for making the right decisions when investing their scarce resources 2006 -10 -12 25
 Benefits from implementation of ISO 22000 can contribute to the quality of life in general by: -ensuring safe food -reducing food-related diseases -better quality and safer jobs in the food industry -better utilization of resources -more efficient validation and documentation of techniques, methods and procedures -increased profits -increased potential for economic growth and development 2006 -10 -12 26
Benefits from implementation of ISO 22000 can contribute to the quality of life in general by: -ensuring safe food -reducing food-related diseases -better quality and safer jobs in the food industry -better utilization of resources -more efficient validation and documentation of techniques, methods and procedures -increased profits -increased potential for economic growth and development 2006 -10 -12 26
 Benefits from implementation of ISO 22000 For governments, -bases for developing health, safety and environmental legislation -education of food regulatory personnel 2006 -10 -12 27
Benefits from implementation of ISO 22000 For governments, -bases for developing health, safety and environmental legislation -education of food regulatory personnel 2006 -10 -12 27
 Filling a gap between ISO 9001: 2000 and HACCP Contributes to a better understanding and further development of Codex HACCP; Auditable standards with clear requirements; System approach rather than product approach; Suitable for regulators 2006 -10 -12 28
Filling a gap between ISO 9001: 2000 and HACCP Contributes to a better understanding and further development of Codex HACCP; Auditable standards with clear requirements; System approach rather than product approach; Suitable for regulators 2006 -10 -12 28
 Good scientific sense!! ISO 22000 makes good scientific sense for those who are involved in food processing, manufacturing, storage, distribution of food and food products ISO 22000 provides food safety and security; ISO 22000 can be applied on its own or in combination with other management system standards such as ISO 9001: 2000 2006 -10 -12 29
Good scientific sense!! ISO 22000 makes good scientific sense for those who are involved in food processing, manufacturing, storage, distribution of food and food products ISO 22000 provides food safety and security; ISO 22000 can be applied on its own or in combination with other management system standards such as ISO 9001: 2000 2006 -10 -12 29
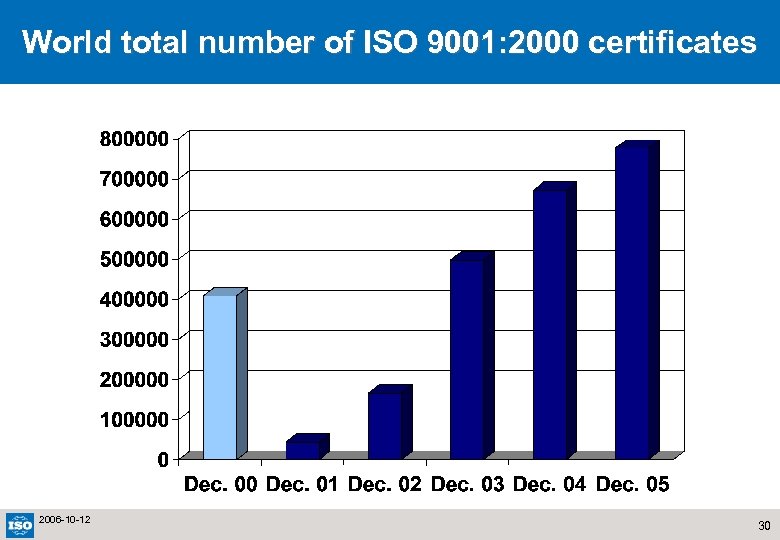 World total number of ISO 9001: 2000 certificates 2006 -10 -12 30
World total number of ISO 9001: 2000 certificates 2006 -10 -12 30
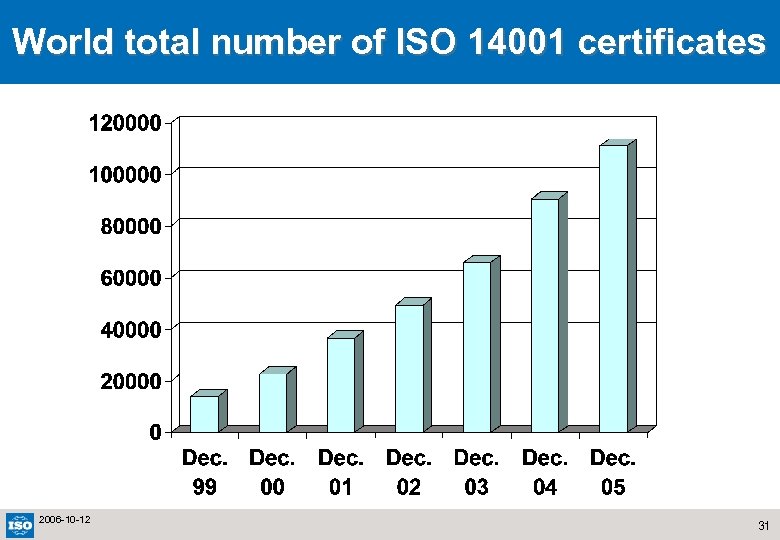 World total number of ISO 14001 certificates 2006 -10 -12 31
World total number of ISO 14001 certificates 2006 -10 -12 31
 ISO Survey of Certifications (2005) Food products, beverages and tobacco ISO 9001: 2000 Certificates by industrial sector 25737 ISO 14001 Certificates by industrial sector 3099 ISO 22000? Will see!! 2006 -10 -12 32
ISO Survey of Certifications (2005) Food products, beverages and tobacco ISO 9001: 2000 Certificates by industrial sector 25737 ISO 14001 Certificates by industrial sector 3099 ISO 22000? Will see!! 2006 -10 -12 32
 ISO 26000 Social Responsibility This standard is not a management system standard and is not suitable for conformity assessment or certification purposes 2006 -10 -12 33
ISO 26000 Social Responsibility This standard is not a management system standard and is not suitable for conformity assessment or certification purposes 2006 -10 -12 33
 Core issues Organizational governance Environment Human rights Labour practices Fair operating practices Consumer issues Community involvement/society development 2006 -10 -12 34
Core issues Organizational governance Environment Human rights Labour practices Fair operating practices Consumer issues Community involvement/society development 2006 -10 -12 34
 The environment Organizations should ensure that their activities respect, promote and advance internationally recognized environmental principles and commitments. For example, organizations should: Support a precautionary approach to environmental challenges; Undertake initiatives to promote greater environmental responsibility; Encourage the development and diffusion of environmentally beneficial technologies; and Accept the “polluter pays” principle 2006 -10 -12 35
The environment Organizations should ensure that their activities respect, promote and advance internationally recognized environmental principles and commitments. For example, organizations should: Support a precautionary approach to environmental challenges; Undertake initiatives to promote greater environmental responsibility; Encourage the development and diffusion of environmentally beneficial technologies; and Accept the “polluter pays” principle 2006 -10 -12 35
 The environment - Core issues Pollution prevention Prevention of global warming Sustainable consumption and land use Preservation and restoration of ecosystems and the natural environment Respect for future generations 2006 -10 -12 36
The environment - Core issues Pollution prevention Prevention of global warming Sustainable consumption and land use Preservation and restoration of ecosystems and the natural environment Respect for future generations 2006 -10 -12 36
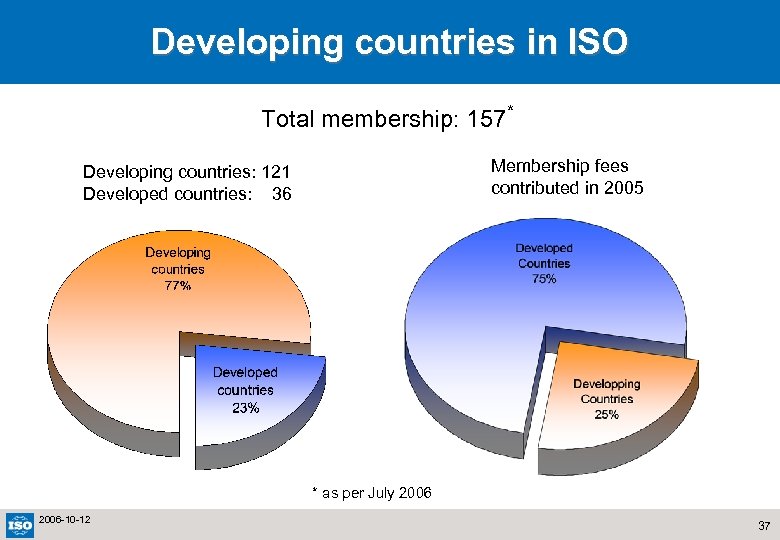 Developing countries in ISO Total membership: 157* Membership fees contributed in 2005 Developing countries: 121 Developed countries: 36 * as per July 2006 -10 -12 37
Developing countries in ISO Total membership: 157* Membership fees contributed in 2005 Developing countries: 121 Developed countries: 36 * as per July 2006 -10 -12 37
 ISO Action Plan 2005 -2010 2006 -10 -12 38
ISO Action Plan 2005 -2010 2006 -10 -12 38
 ISO Action Plan 2005 -2010 2006 -10 -12 39
ISO Action Plan 2005 -2010 2006 -10 -12 39
 ISO Action Plan 2005 -2010 2006 -10 -12 40
ISO Action Plan 2005 -2010 2006 -10 -12 40
 ISO website: http: //www. iso. org 2006 -10 -12 41
ISO website: http: //www. iso. org 2006 -10 -12 41
 Thank you note Dr. Deryck D. Pattron, Ph. D. , FDI, Ministry of Health, Port of Spain, Trinidad, West Indies Dr. Bernardo Calzadilla Sarmiento, Director Technical assistance and training services ISO Central Secretariat Sari Rajakoski, ISO/DEVCO Secretariat 2006 -10 -12 42
Thank you note Dr. Deryck D. Pattron, Ph. D. , FDI, Ministry of Health, Port of Spain, Trinidad, West Indies Dr. Bernardo Calzadilla Sarmiento, Director Technical assistance and training services ISO Central Secretariat Sari Rajakoski, ISO/DEVCO Secretariat 2006 -10 -12 42
 End of presentation Thank you 2006 -10 -12 43
End of presentation Thank you 2006 -10 -12 43


