572737987361e4460cc23e8a6da241e7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 Session 5 a Key and PIN Management Gareth Ellis Senior Solutions Consultant
Session 5 a Key and PIN Management Gareth Ellis Senior Solutions Consultant
 Agenda • EMV Key Management - overview • EMV Key Impacts on Issuance • PIN Management 2
Agenda • EMV Key Management - overview • EMV Key Impacts on Issuance • PIN Management 2
 Key Management Overview
Key Management Overview
 EMV Security Features • EMV requires secure key management to enable the following functions – Card authentication • Offline • Online – Cardholder verification – Issuer authentication – Non-repudiation of transactions – Secure EMV script delivery – Transport of keys between domains • For this both Triple DES (symmetric) and PKI (asymmetric) are used 4
EMV Security Features • EMV requires secure key management to enable the following functions – Card authentication • Offline • Online – Cardholder verification – Issuer authentication – Non-repudiation of transactions – Secure EMV script delivery – Transport of keys between domains • For this both Triple DES (symmetric) and PKI (asymmetric) are used 4
 Symmetric keys: how does DES work? • Single key to both encrypt and decrypt • Key is generated by a mathematical process • Encryption combines data and key using a non-secret formula • Key must be kept secret: – in the chip & in HSMs/Host of issuer – not at acquirers 5
Symmetric keys: how does DES work? • Single key to both encrypt and decrypt • Key is generated by a mathematical process • Encryption combines data and key using a non-secret formula • Key must be kept secret: – in the chip & in HSMs/Host of issuer – not at acquirers 5
 EMV Triple DES keys • Online Transaction Keys - stored in secure portion of memory in the chip and on the Issuing Host – Online authentication keys – Master Key used to create a card key – Scripting keys • Transport keys - used to ensure the secure transport of sensitive data during Issuance – Card Manufacturer – Data Preparation – Bureau/Personalisation Machine 6
EMV Triple DES keys • Online Transaction Keys - stored in secure portion of memory in the chip and on the Issuing Host – Online authentication keys – Master Key used to create a card key – Scripting keys • Transport keys - used to ensure the secure transport of sensitive data during Issuance – Card Manufacturer – Data Preparation – Bureau/Personalisation Machine 6
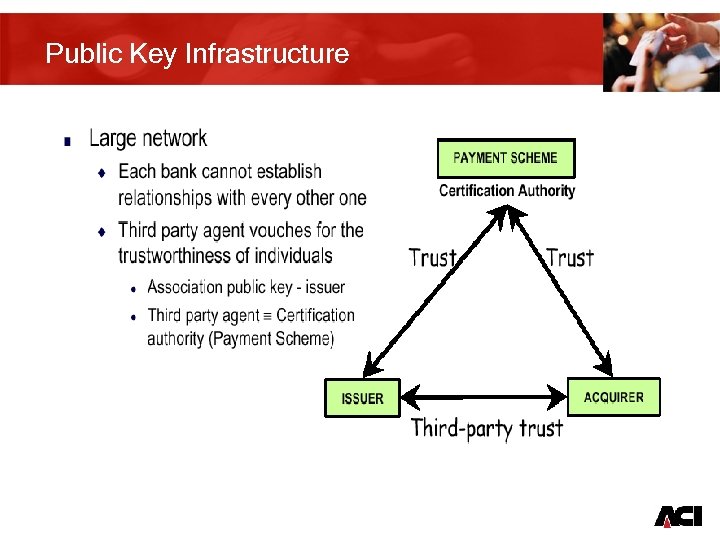 Public Key Infrastructure 7
Public Key Infrastructure 7
 Asymmetric keys: how does PKI work? • Related pairs of keys – public and private • Keys are generated by a complex mathematical process • Encryption combines data and key using a non-secret formula • Decryption is only possible using the other key of the same pair – one key must be kept secret, the other one can be public 8
Asymmetric keys: how does PKI work? • Related pairs of keys – public and private • Keys are generated by a complex mathematical process • Encryption combines data and key using a non-secret formula • Decryption is only possible using the other key of the same pair – one key must be kept secret, the other one can be public 8
 How to use of PKI keys in EMV • Offline Data Authentication Example: 1. Load Master. Card EMV Public key on every terminal 2. Send card data to Master. Card and they encrypt card data using the Master. Card EMV Private key 3. During a transaction, card sends encrypted card data to the terminal 4. Terminal uses Master. Card public key to decrypt encrypted data 5. Terminal determines the unencrypted card data 6. Card passes same card data to terminal 7. Terminal compares card data – only Master. Card could have put that data on the card 9
How to use of PKI keys in EMV • Offline Data Authentication Example: 1. Load Master. Card EMV Public key on every terminal 2. Send card data to Master. Card and they encrypt card data using the Master. Card EMV Private key 3. During a transaction, card sends encrypted card data to the terminal 4. Terminal uses Master. Card public key to decrypt encrypted data 5. Terminal determines the unencrypted card data 6. Card passes same card data to terminal 7. Terminal compares card data – only Master. Card could have put that data on the card 9
 Certification Process for Static Data Authentication • Use Data prep device to generate Issuer Key pair • Send the Issuer public key to the card scheme • Scheme returns issuer public key signed with the scheme private key (Issuer Certificate) • These are input into the data prep device and validated • The issuer certificate is personalised onto each card 10
Certification Process for Static Data Authentication • Use Data prep device to generate Issuer Key pair • Send the Issuer public key to the card scheme • Scheme returns issuer public key signed with the scheme private key (Issuer Certificate) • These are input into the data prep device and validated • The issuer certificate is personalised onto each card 10
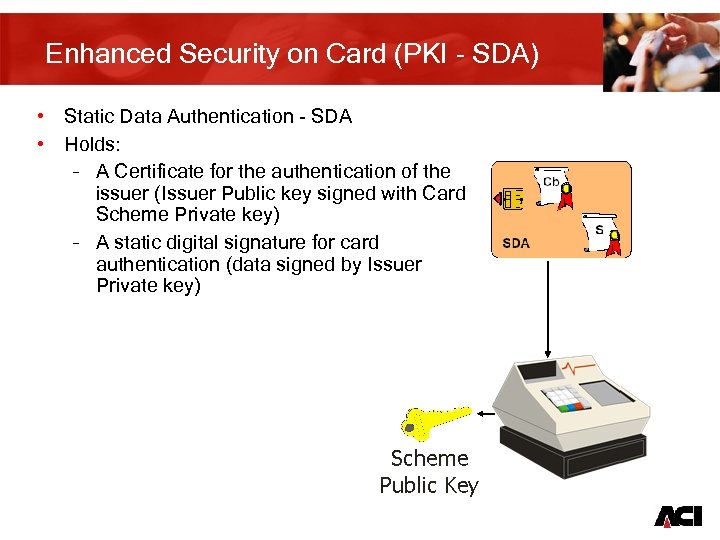 Enhanced Security on Card (PKI - SDA) • Static Data Authentication - SDA • Holds: – A Certificate for the authentication of the issuer (Issuer Public key signed with Card Scheme Private key) – A static digital signature for card authentication (data signed by Issuer Private key) 11
Enhanced Security on Card (PKI - SDA) • Static Data Authentication - SDA • Holds: – A Certificate for the authentication of the issuer (Issuer Public key signed with Card Scheme Private key) – A static digital signature for card authentication (data signed by Issuer Private key) 11
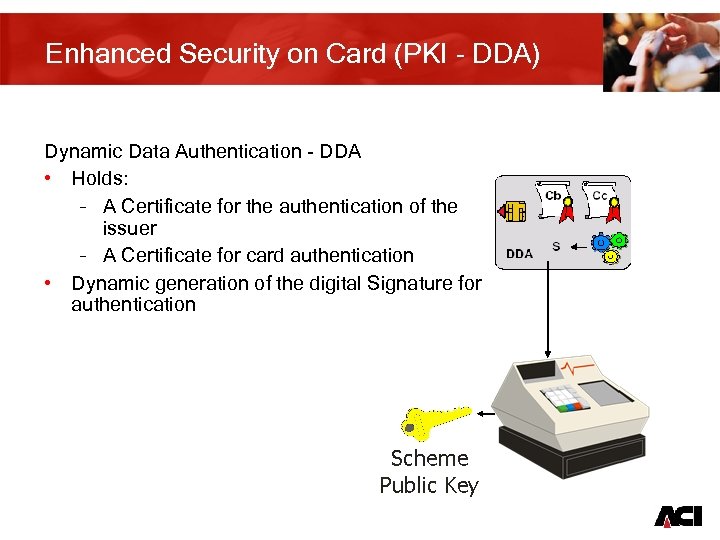 Enhanced Security on Card (PKI - DDA) Dynamic Data Authentication - DDA • Holds: – A Certificate for the authentication of the issuer – A Certificate for card authentication • Dynamic generation of the digital Signature for authentication 12
Enhanced Security on Card (PKI - DDA) Dynamic Data Authentication - DDA • Holds: – A Certificate for the authentication of the issuer – A Certificate for card authentication • Dynamic generation of the digital Signature for authentication 12
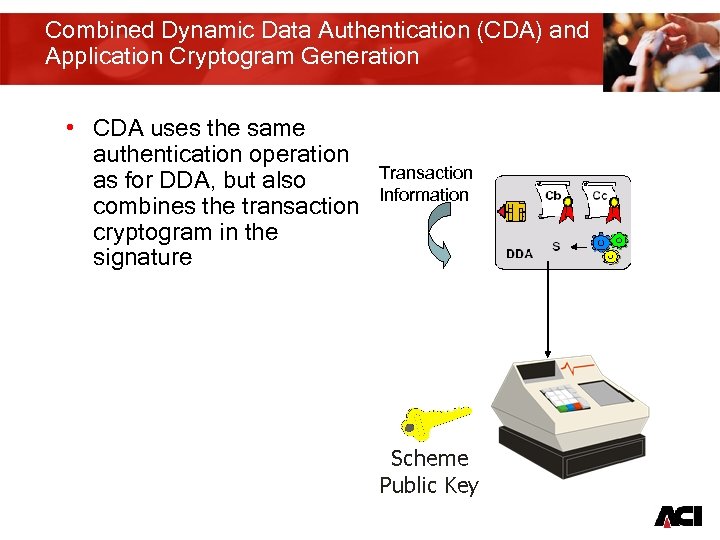 Combined Dynamic Data Authentication (CDA) and Application Cryptogram Generation • CDA uses the same authentication operation as for DDA, but also combines the transaction cryptogram in the signature Transaction Information 13
Combined Dynamic Data Authentication (CDA) and Application Cryptogram Generation • CDA uses the same authentication operation as for DDA, but also combines the transaction cryptogram in the signature Transaction Information 13
 EMV Key Impacts on Issuance
EMV Key Impacts on Issuance
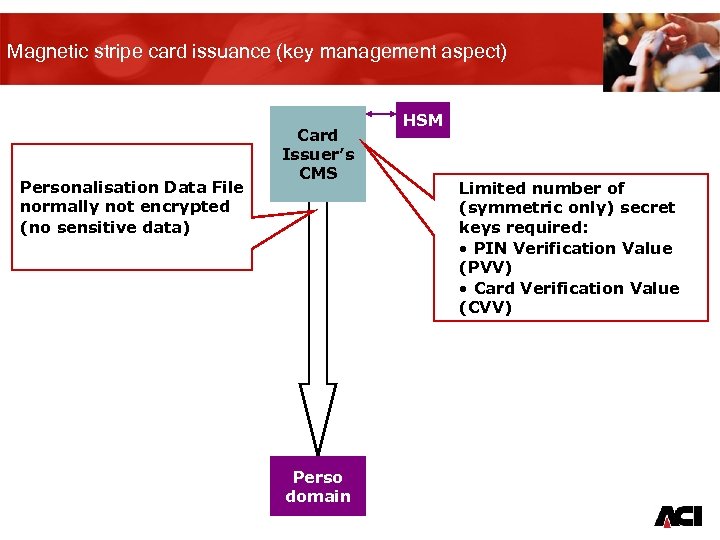 Magnetic stripe card issuance (key management aspect) Personalisation Data File normally not encrypted (no sensitive data) Card Issuer’s CMS HSM Limited number of (symmetric only) secret keys required: • PIN Verification Value (PVV) • Card Verification Value (CVV) Perso domain 15
Magnetic stripe card issuance (key management aspect) Personalisation Data File normally not encrypted (no sensitive data) Card Issuer’s CMS HSM Limited number of (symmetric only) secret keys required: • PIN Verification Value (PVV) • Card Verification Value (CVV) Perso domain 15
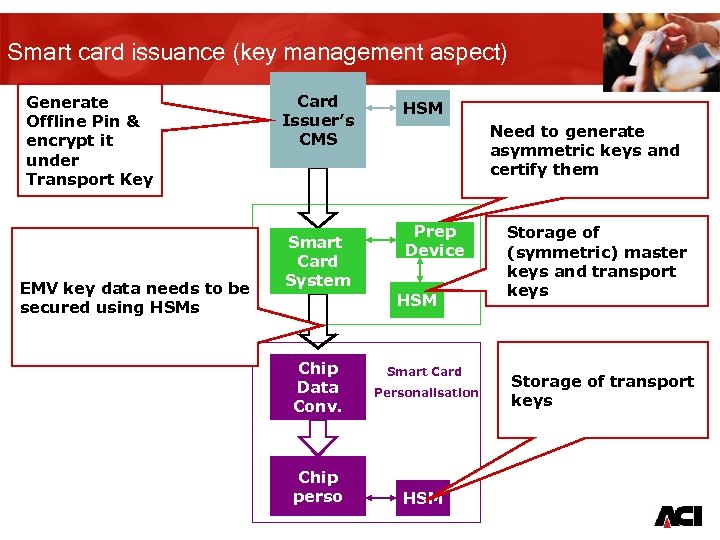 Smart card issuance (key management aspect) Generate Offline Pin & encrypt it under Transport Key EMV key data needs to be secured using HSMs Card Issuer’s CMS Smart Card System HSM Need to generate asymmetric keys and certify them Prep Device HSM Chip Data Conv. Chip perso Smart Card Personalisation Storage of (symmetric) master keys and transport keys Storage of transport keys HSM 16
Smart card issuance (key management aspect) Generate Offline Pin & encrypt it under Transport Key EMV key data needs to be secured using HSMs Card Issuer’s CMS Smart Card System HSM Need to generate asymmetric keys and certify them Prep Device HSM Chip Data Conv. Chip perso Smart Card Personalisation Storage of (symmetric) master keys and transport keys Storage of transport keys HSM 16
 How to add EMV (crypto) data to Cards? • Data preparation phase, you can use – Smart Card Management systems – data prep devices or • These systems – Generate, store and manage keys for each application – Send Public keys to Certificate Authorities – Stores the certificates returned from CAs in a database – Adds the smart card data for each card to Embossing File • Personalisation – writing EMV data to the card – Can use Smart Card Management Systems or software from Printer vendors – Need to decrypt secret data from Data Prep and re-encrypt it to send it to the card – Need to use issuer keys to ‘open’ each card to write to the chip 17
How to add EMV (crypto) data to Cards? • Data preparation phase, you can use – Smart Card Management systems – data prep devices or • These systems – Generate, store and manage keys for each application – Send Public keys to Certificate Authorities – Stores the certificates returned from CAs in a database – Adds the smart card data for each card to Embossing File • Personalisation – writing EMV data to the card – Can use Smart Card Management Systems or software from Printer vendors – Need to decrypt secret data from Data Prep and re-encrypt it to send it to the card – Need to use issuer keys to ‘open’ each card to write to the chip 17
 EMV Impacts to PIN Management
EMV Impacts to PIN Management
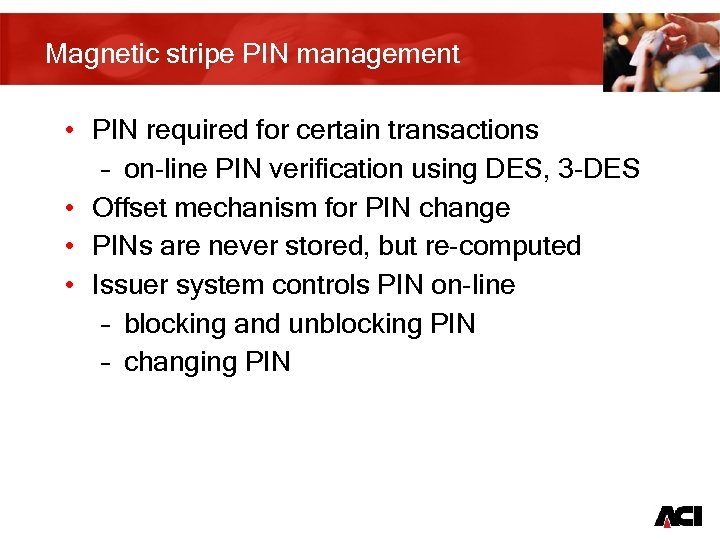 Magnetic stripe PIN management • PIN required for certain transactions – on-line PIN verification using DES, 3 -DES • Offset mechanism for PIN change • PINs are never stored, but re-computed • Issuer system controls PIN on-line – blocking and unblocking PIN – changing PIN 19
Magnetic stripe PIN management • PIN required for certain transactions – on-line PIN verification using DES, 3 -DES • Offset mechanism for PIN change • PINs are never stored, but re-computed • Issuer system controls PIN on-line – blocking and unblocking PIN – changing PIN 19
 EMV PIN management • Chip contains offline PIN value for offline verification • Other applications may use same PIN • Without Offline PIN, CAP is not possible • EMV offers scripting mechanism to (un)block and change the PIN • Implicit and explicit PIN unblock 20
EMV PIN management • Chip contains offline PIN value for offline verification • Other applications may use same PIN • Without Offline PIN, CAP is not possible • EMV offers scripting mechanism to (un)block and change the PIN • Implicit and explicit PIN unblock 20
 Synchronisation issues • PIN information rests in (at least) 2 places • In authorisation system for online PIN verification • In PIN generation domain (when issuing cards) • New: in the chip • Counting failed PIN attempts • Blocking and unblocking the PINs • Changing the value of the PINs, recovering from error situations 21
Synchronisation issues • PIN information rests in (at least) 2 places • In authorisation system for online PIN verification • In PIN generation domain (when issuing cards) • New: in the chip • Counting failed PIN attempts • Blocking and unblocking the PINs • Changing the value of the PINs, recovering from error situations 21
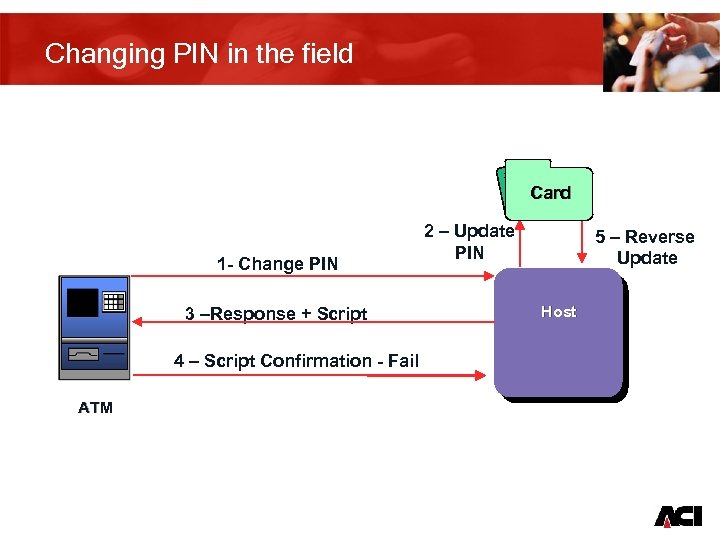 Changing PIN in the field Card 1 - Change PIN 3 –Response + Script 2 – Update PIN 5 – Reverse Update Host 4 – Script Confirmation - Fail ATM 23
Changing PIN in the field Card 1 - Change PIN 3 –Response + Script 2 – Update PIN 5 – Reverse Update Host 4 – Script Confirmation - Fail ATM 23
 PIN Management conclusions • (Offline) PIN is becoming best practice • PIN change facilities are needed to remember PINs on many cards • Implementing offline PIN touches many systems • Probably the hardest part of implementing Offline PIN is customer education! 25
PIN Management conclusions • (Offline) PIN is becoming best practice • PIN change facilities are needed to remember PINs on many cards • Implementing offline PIN touches many systems • Probably the hardest part of implementing Offline PIN is customer education! 25



