cfb9800298ac742df4685dc40a541aa4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29
 Session 15 – ERP Security 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Objectives Oracle ERP Overview Oracle ERP Security Oracle Workflow and Security How to Secure Oracle Applications Security and Controls Considerations by Business Cycle 7. Segregation of Duties Slide 1
Session 15 – ERP Security 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Objectives Oracle ERP Overview Oracle ERP Security Oracle Workflow and Security How to Secure Oracle Applications Security and Controls Considerations by Business Cycle 7. Segregation of Duties Slide 1
 1. Objectives • Become familiar with Oracle terminology and concepts • Understand security and control features within Oracle Applications • Discuss leading practices to secure Oracle Applications • Realize importance of segregation of duties Slide 2
1. Objectives • Become familiar with Oracle terminology and concepts • Understand security and control features within Oracle Applications • Discuss leading practices to secure Oracle Applications • Realize importance of segregation of duties Slide 2
 Agenda 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Objectives Oracle ERP Overview Oracle ERP Security Oracle Workflow and Security How to Secure Oracle Applications Security and Controls Considerations by Business Cycle 7. Segregation of Duties Slide 3
Agenda 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Objectives Oracle ERP Overview Oracle ERP Security Oracle Workflow and Security How to Secure Oracle Applications Security and Controls Considerations by Business Cycle 7. Segregation of Duties Slide 3
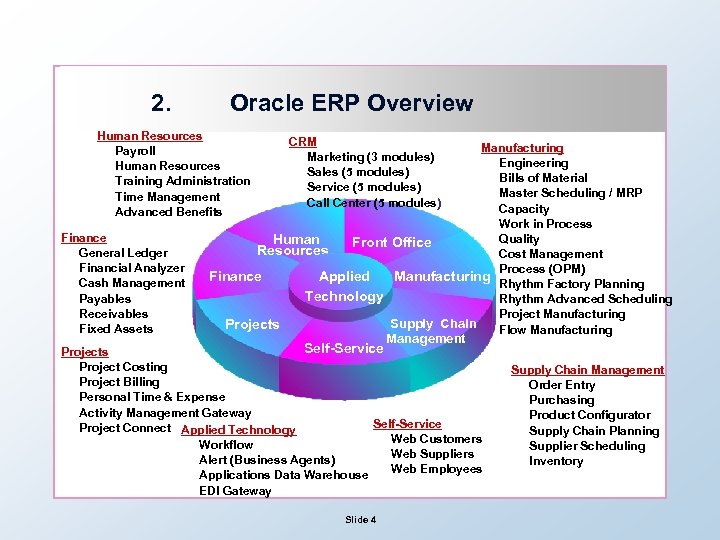 2. Oracle ERP Overview Human Resources Payroll Human Resources Training Administration Time Management Advanced Benefits Finance General Ledger Financial Analyzer Cash Management Payables Receivables Fixed Assets CRM Marketing (3 modules) Sales (5 modules) Service (5 modules) Call Center (5 modules) Manufacturing Engineering Bills of Material Master Scheduling / MRP Capacity Work in Process Quality Human Front Office Resources Cost Management Process (OPM) Finance Manufacturing Applied Rhythm Factory Planning Technology Rhythm Advanced Scheduling Project Manufacturing Supply Chain Projects Flow Manufacturing Self-Service Management Projects Project Costing Project Billing Personal Time & Expense Activity Management Gateway Self-Service Project Connect Applied Technology Web Customers Workflow Web Suppliers Alert (Business Agents) Web Employees Applications Data Warehouse EDI Gateway Slide 4 Supply Chain Management Order Entry Purchasing Product Configurator Supply Chain Planning Supplier Scheduling Inventory
2. Oracle ERP Overview Human Resources Payroll Human Resources Training Administration Time Management Advanced Benefits Finance General Ledger Financial Analyzer Cash Management Payables Receivables Fixed Assets CRM Marketing (3 modules) Sales (5 modules) Service (5 modules) Call Center (5 modules) Manufacturing Engineering Bills of Material Master Scheduling / MRP Capacity Work in Process Quality Human Front Office Resources Cost Management Process (OPM) Finance Manufacturing Applied Rhythm Factory Planning Technology Rhythm Advanced Scheduling Project Manufacturing Supply Chain Projects Flow Manufacturing Self-Service Management Projects Project Costing Project Billing Personal Time & Expense Activity Management Gateway Self-Service Project Connect Applied Technology Web Customers Workflow Web Suppliers Alert (Business Agents) Web Employees Applications Data Warehouse EDI Gateway Slide 4 Supply Chain Management Order Entry Purchasing Product Configurator Supply Chain Planning Supplier Scheduling Inventory
 Agenda 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Objectives Oracle ERP Overview Oracle ERP Security Oracle Workflow and Security How to Secure Oracle Applications Security and Controls Considerations by Business Cycle 7. Segregation of Duties Slide 5
Agenda 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Objectives Oracle ERP Overview Oracle ERP Security Oracle Workflow and Security How to Secure Oracle Applications Security and Controls Considerations by Business Cycle 7. Segregation of Duties Slide 5
 Oracle ERP Security Issues • Oracle Applications is huge and complex – – – • Acquisition of other major ERPs – • More than 100 modules Millions of lines of coding Hundreds of configurations (settings) People. Soft, JDE, Siebel, etc…… Multiple Technologies involved – Multiple technologies like Networks, OS, Web server, Application Server, Database, Reporting, etc. . Slide 6
Oracle ERP Security Issues • Oracle Applications is huge and complex – – – • Acquisition of other major ERPs – • More than 100 modules Millions of lines of coding Hundreds of configurations (settings) People. Soft, JDE, Siebel, etc…… Multiple Technologies involved – Multiple technologies like Networks, OS, Web server, Application Server, Database, Reporting, etc. . Slide 6
 Oracle ERP Security Issues (cont’d) • Many seeded account passwords and seeded configuration settings that are not secure • Multiple access avenues: – – Applications - any account with Sysadmin responsibility Process Tab – ANZ Menus Database – system, sys, applsys UNIX - root, oracle, applmgr Slide 7
Oracle ERP Security Issues (cont’d) • Many seeded account passwords and seeded configuration settings that are not secure • Multiple access avenues: – – Applications - any account with Sysadmin responsibility Process Tab – ANZ Menus Database – system, sys, applsys UNIX - root, oracle, applmgr Slide 7
 Oracle ERP Security Issues (cont’d) • Complex regulatory environment • Customization and Extensions to Oracle Applications • Security and Controls should be on the “critical path” during implementations Slide 8
Oracle ERP Security Issues (cont’d) • Complex regulatory environment • Customization and Extensions to Oracle Applications • Security and Controls should be on the “critical path” during implementations Slide 8
 Agenda 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Objectives Oracle ERP Overview Oracle ERP Security Oracle Workflow and Security How to Secure Oracle Applications Security and Controls Considerations by Business Cycle 7. Segregation of Duties Slide 9
Agenda 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Objectives Oracle ERP Overview Oracle ERP Security Oracle Workflow and Security How to Secure Oracle Applications Security and Controls Considerations by Business Cycle 7. Segregation of Duties Slide 9
 Oracle Workflow and Security What does it Do? • Oracle Workflow automates standard business processes, allowing for transparency and a recorded history of process transactions • Oracle Workflow is highly customizable and is used to drive processes through the system from start to finish. Who uses it? • Workflow Specialist configures workflow during install • End Users • Workflow Administrator Slide 10
Oracle Workflow and Security What does it Do? • Oracle Workflow automates standard business processes, allowing for transparency and a recorded history of process transactions • Oracle Workflow is highly customizable and is used to drive processes through the system from start to finish. Who uses it? • Workflow Specialist configures workflow during install • End Users • Workflow Administrator Slide 10
 Oracle Workflow and Security (cont’d) Most Commonly Used Seeded Workflows General Ledger Order Management Journal Entry Approval Order and Return Processing i. Expense Report Approvals Schedule, ship and pack delivery Purchasing Terminated Employees Requisition and PO Document Approval Accounts Payable Auto Document Creation Invoice Approval Receipt Confirmation Process Pay (Positive Pay) Message Exceeding of Price/Receipt Tolerances Receivables Projects Credit Memo Approvals Projects Approval Credit Application Approval Project Accounting i. Timecard Approval Slide 11
Oracle Workflow and Security (cont’d) Most Commonly Used Seeded Workflows General Ledger Order Management Journal Entry Approval Order and Return Processing i. Expense Report Approvals Schedule, ship and pack delivery Purchasing Terminated Employees Requisition and PO Document Approval Accounts Payable Auto Document Creation Invoice Approval Receipt Confirmation Process Pay (Positive Pay) Message Exceeding of Price/Receipt Tolerances Receivables Projects Credit Memo Approvals Projects Approval Credit Application Approval Project Accounting i. Timecard Approval Slide 11
 Agenda 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Objectives Oracle ERP Overview Oracle ERP Security Oracle Workflow and Security How to Secure Oracle Applications Security and Controls Considerations by Business Cycle 7. Segregation of Duties 8. Configurable Controls Slide 12
Agenda 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Objectives Oracle ERP Overview Oracle ERP Security Oracle Workflow and Security How to Secure Oracle Applications Security and Controls Considerations by Business Cycle 7. Segregation of Duties 8. Configurable Controls Slide 12
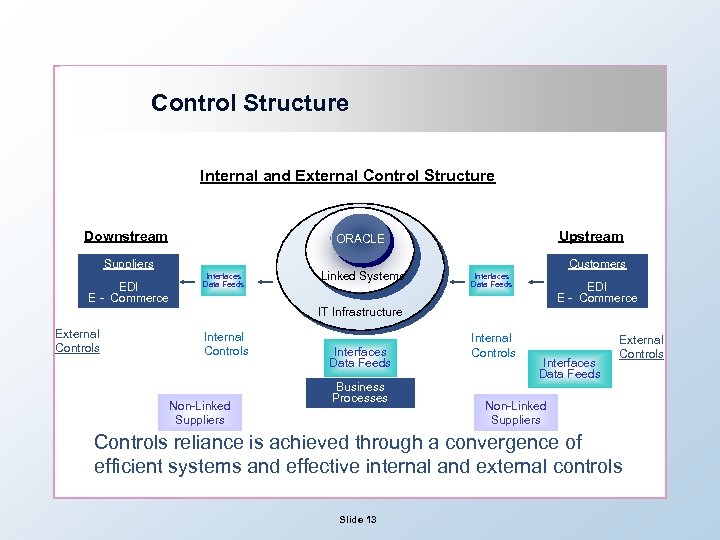 Control Structure Internal and External Control Structure Downstream Suppliers EDI E - Commerce Upstream ORACLE Interfaces Data Feeds Linked Systems Customers Interfaces Data Feeds EDI E - Commerce IT Infrastructure External Controls Internal Controls Non-Linked Suppliers Interfaces Data Feeds Business Processes Internal Controls Interfaces Data Feeds External Controls Non-Linked Suppliers Controls reliance is achieved through a convergence of efficient systems and effective internal and external controls Slide 13
Control Structure Internal and External Control Structure Downstream Suppliers EDI E - Commerce Upstream ORACLE Interfaces Data Feeds Linked Systems Customers Interfaces Data Feeds EDI E - Commerce IT Infrastructure External Controls Internal Controls Non-Linked Suppliers Interfaces Data Feeds Business Processes Internal Controls Interfaces Data Feeds External Controls Non-Linked Suppliers Controls reliance is achieved through a convergence of efficient systems and effective internal and external controls Slide 13
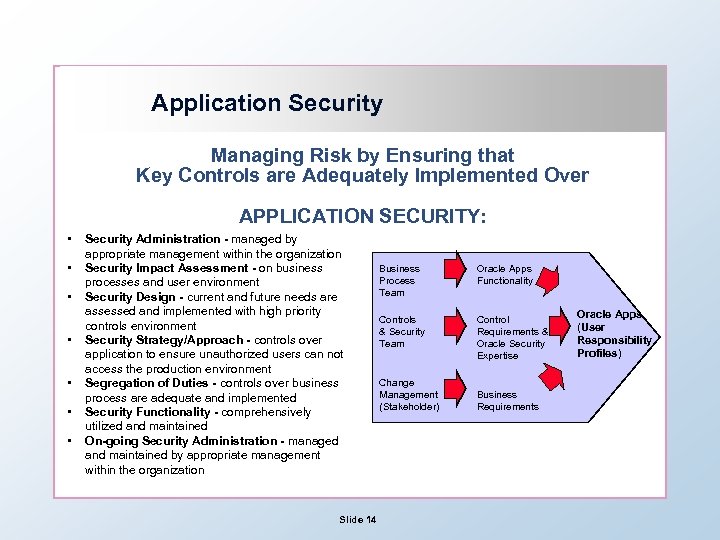 Application Security Managing Risk by Ensuring that Key Controls are Adequately Implemented Over APPLICATION SECURITY: • • Security Administration - managed by appropriate management within the organization Security Impact Assessment - on business processes and user environment Security Design - current and future needs are assessed and implemented with high priority controls environment Security Strategy/Approach - controls over application to ensure unauthorized users can not access the production environment Segregation of Duties - controls over business process are adequate and implemented Security Functionality - comprehensively utilized and maintained On-going Security Administration - managed and maintained by appropriate management within the organization Slide 14 Business Process Team Oracle Apps Functionality Controls & Security Team Control Requirements & Oracle Security Expertise Change Management (Stakeholder) Business Requirements Oracle Apps (User Responsibility Profiles)
Application Security Managing Risk by Ensuring that Key Controls are Adequately Implemented Over APPLICATION SECURITY: • • Security Administration - managed by appropriate management within the organization Security Impact Assessment - on business processes and user environment Security Design - current and future needs are assessed and implemented with high priority controls environment Security Strategy/Approach - controls over application to ensure unauthorized users can not access the production environment Segregation of Duties - controls over business process are adequate and implemented Security Functionality - comprehensively utilized and maintained On-going Security Administration - managed and maintained by appropriate management within the organization Slide 14 Business Process Team Oracle Apps Functionality Controls & Security Team Control Requirements & Oracle Security Expertise Change Management (Stakeholder) Business Requirements Oracle Apps (User Responsibility Profiles)
 Some Leading Practices to Secure Oracle (Cont’d) • Restrict ‘Back-end’ access to the Database • Review of standard reports to access signon, unsuccessful signon, responsibility usage, form usage and concurrent request usage. • Enabling Auditing on certain Tables • Oracle Alerts Slide 15
Some Leading Practices to Secure Oracle (Cont’d) • Restrict ‘Back-end’ access to the Database • Review of standard reports to access signon, unsuccessful signon, responsibility usage, form usage and concurrent request usage. • Enabling Auditing on certain Tables • Oracle Alerts Slide 15
 Some Leading Practices to Secure Oracle (Cont’d) Profile Options – Signon / Suggested settings • Signon Password No Reuse – “ 180” • Signon Password Length – “ 6 -8” • Signon Password Hard to Guess – “Y” • Signon Password Failure Limit – “ 3” Slide 16
Some Leading Practices to Secure Oracle (Cont’d) Profile Options – Signon / Suggested settings • Signon Password No Reuse – “ 180” • Signon Password Length – “ 6 -8” • Signon Password Hard to Guess – “Y” • Signon Password Failure Limit – “ 3” Slide 16
 Agenda 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Objectives Oracle ERP Overview Oracle ERP Security Oracle Workflow and Security How to Secure Oracle Applications Security and Controls Considerations by Business Cycle 7. Segregation of Duties Slide 17
Agenda 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Objectives Oracle ERP Overview Oracle ERP Security Oracle Workflow and Security How to Secure Oracle Applications Security and Controls Considerations by Business Cycle 7. Segregation of Duties Slide 17
 Security and Controls Considerations by Business Cycle A ‘configurable control’ is • Any setting in Oracle Apps that can be modified, and which can affect the operation of a function in Oracle Apps – Profile options – Transaction type settings – Financial options – Payment options – Invoice options • Different from ‘inherent’ controls, which are preprogrammed settings that are generally not overrideable or modifiable (e. g. quantity values not allowing non-numeric characters) Slide 18
Security and Controls Considerations by Business Cycle A ‘configurable control’ is • Any setting in Oracle Apps that can be modified, and which can affect the operation of a function in Oracle Apps – Profile options – Transaction type settings – Financial options – Payment options – Invoice options • Different from ‘inherent’ controls, which are preprogrammed settings that are generally not overrideable or modifiable (e. g. quantity values not allowing non-numeric characters) Slide 18
 Security and Controls Considerations by Business Cycle The following key cycles will be discussed in the next few slides • • • Order to Cash Procure to Pay General Ledger/Financial Close Slide 19
Security and Controls Considerations by Business Cycle The following key cycles will be discussed in the next few slides • • • Order to Cash Procure to Pay General Ledger/Financial Close Slide 19
 Security and Controls Considerations by Business Cycle 1. Order to Cash – – – OM Transactions type Setting Holds: Operational and Financial Processing Constraints Rules Payment Terms Credit Limit and Credit Check What is security implication? Slide 20
Security and Controls Considerations by Business Cycle 1. Order to Cash – – – OM Transactions type Setting Holds: Operational and Financial Processing Constraints Rules Payment Terms Credit Limit and Credit Check What is security implication? Slide 20
 Security and Controls Considerations by Business Cycle 2. Procure to Pay – – – Document Types – PO, Requisitions, etc Approval Limits and Approval Groups Tolerances Invoice Matching Banks setup What is security implication? Slide 21
Security and Controls Considerations by Business Cycle 2. Procure to Pay – – – Document Types – PO, Requisitions, etc Approval Limits and Approval Groups Tolerances Invoice Matching Banks setup What is security implication? Slide 21
 Security and Controls Considerations by Business Cycle 3. General Ledger/Financial Close – – – GL Chart of Accounts, Security rules, Cross-validation rules Journal Approval and Posting Consolidation Mapping Rules Translation and Exchange Rates Suspense Posting and Dynamic insert option What is security implication? Slide 22
Security and Controls Considerations by Business Cycle 3. General Ledger/Financial Close – – – GL Chart of Accounts, Security rules, Cross-validation rules Journal Approval and Posting Consolidation Mapping Rules Translation and Exchange Rates Suspense Posting and Dynamic insert option What is security implication? Slide 22
 Agenda 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Objectives Oracle ERP Overview Oracle ERP Security Oracle Workflow and Security How to Secure Oracle Applications Security and Controls Considerations by Business Cycle 7. Segregation of Duties Slide 23
Agenda 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Objectives Oracle ERP Overview Oracle ERP Security Oracle Workflow and Security How to Secure Oracle Applications Security and Controls Considerations by Business Cycle 7. Segregation of Duties Slide 23
 Segregation of Duties What is ‘Segregation of Duties’ (SOD)? • The principle of separating incompatible functions from an individual • Designed to prevent, rather than detect • Reduces risk, as circumventing a well designed SOD environment requires collusion • SOD includes system level segregation as well as segregation of manual processes Slide 24
Segregation of Duties What is ‘Segregation of Duties’ (SOD)? • The principle of separating incompatible functions from an individual • Designed to prevent, rather than detect • Reduces risk, as circumventing a well designed SOD environment requires collusion • SOD includes system level segregation as well as segregation of manual processes Slide 24
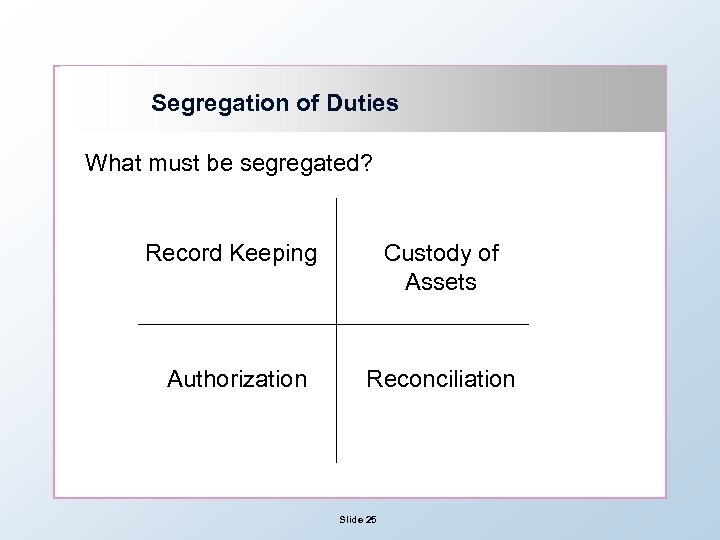 Segregation of Duties What must be segregated? Record Keeping Custody of Assets Authorization Reconciliation Slide 25
Segregation of Duties What must be segregated? Record Keeping Custody of Assets Authorization Reconciliation Slide 25
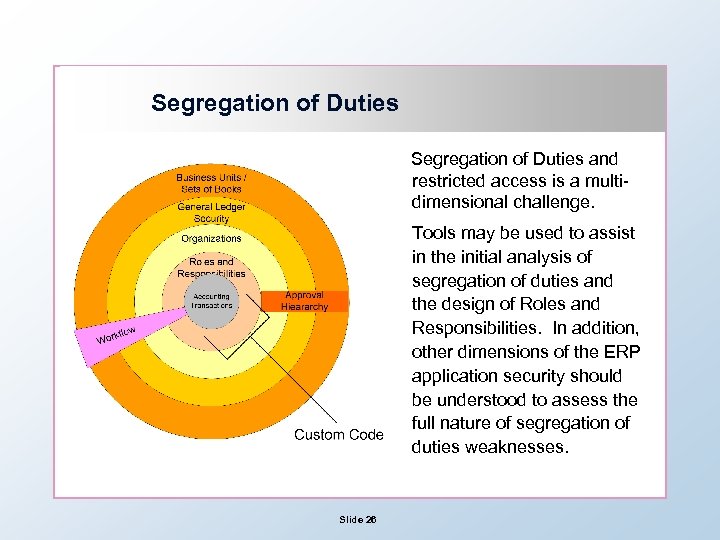 Segregation of Duties and restricted access is a multidimensional challenge. Tools may be used to assist in the initial analysis of segregation of duties and the design of Roles and Responsibilities. In addition, other dimensions of the ERP application security should be understood to assess the full nature of segregation of duties weaknesses. Slide 26
Segregation of Duties and restricted access is a multidimensional challenge. Tools may be used to assist in the initial analysis of segregation of duties and the design of Roles and Responsibilities. In addition, other dimensions of the ERP application security should be understood to assess the full nature of segregation of duties weaknesses. Slide 26
 Segregation of Duties In a practical way, SOD is enforced in Oracle through responsibilities! • A responsibility defines a set of menu options and functions that are accessible to a user and defines reports and processes which may be run • Responsibilities usually grant access to just one Oracle module, such as General Ledger or Accounts Payable • A user can be assigned more than one responsibility • Role Based Access Control (RBAC) Slide 27
Segregation of Duties In a practical way, SOD is enforced in Oracle through responsibilities! • A responsibility defines a set of menu options and functions that are accessible to a user and defines reports and processes which may be run • Responsibilities usually grant access to just one Oracle module, such as General Ledger or Accounts Payable • A user can be assigned more than one responsibility • Role Based Access Control (RBAC) Slide 27
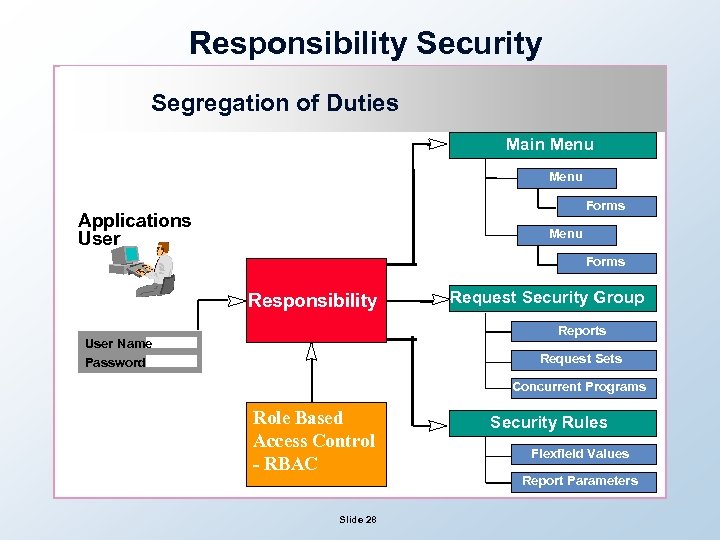 Responsibility Security Segregation of Duties Main Menu Forms Applications User Menu Forms Responsibility Request Security Group Reports User Name Password Request Sets Concurrent Programs Role Based Access Control - RBAC Slide 28 Security Rules Flexfield Values Report Parameters
Responsibility Security Segregation of Duties Main Menu Forms Applications User Menu Forms Responsibility Request Security Group Reports User Name Password Request Sets Concurrent Programs Role Based Access Control - RBAC Slide 28 Security Rules Flexfield Values Report Parameters
 Summary • Oracle automated controls include: • Configurable parameters and settings • User access controls and responsibilities • Review of Oracle configurations and access levels are always as of a ‘point-in-time’ • Segregation of Duties is critical – Requires use of right tool to perform the review – Manual review not recommended Slide 29
Summary • Oracle automated controls include: • Configurable parameters and settings • User access controls and responsibilities • Review of Oracle configurations and access levels are always as of a ‘point-in-time’ • Segregation of Duties is critical – Requires use of right tool to perform the review – Manual review not recommended Slide 29


