d14ccff18583f2d5b50d1c4620bd6366.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 48

Session 11 Broadband Management MJ 11/0704 Adapted from Network Management: Principles and Practice © Mani Subramanian 2000 and solely used for Network Management course at Universitas Bina Nusantara 1
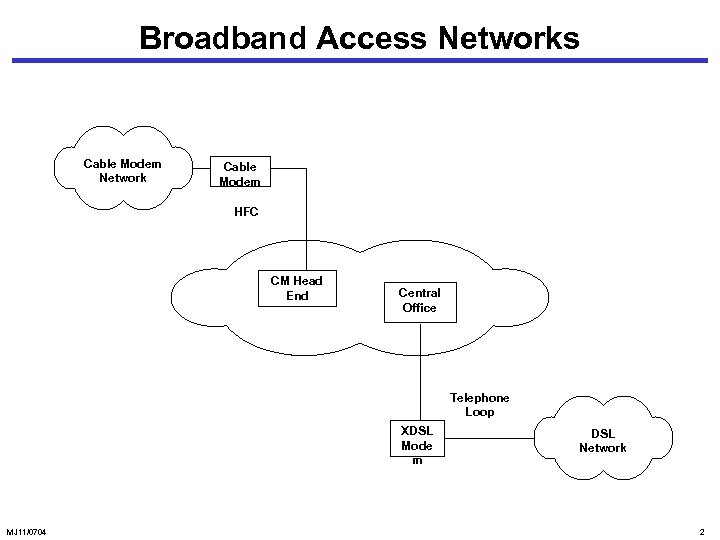
Broadband Access Networks Cable Modem Network Cable Modem HFC CM Head End Central Office Telephone Loop XDSL Mode m MJ 11/0704 DSL Network 2
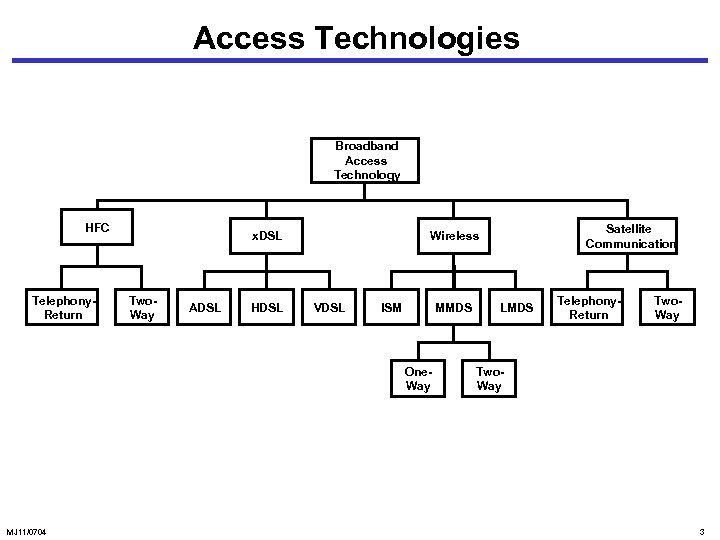
Access Technologies Broadband Access Technology HFC Telephony. Return x. DSL Two. Way ADSL HDSL VDSL ISM MMDS One. Way MJ 11/0704 Satellite Communication Wireless LMDS Telephony. Return Two. Way 3
Access Technologies • Hybrid fiber coaxial technology plant / cable modem at customer premises • Telephony return is one-way, downstream (forward direction) cable, upstream (reverse direction) telephone • Two-way downstream at high frequency band upstream at low frequency band • Carries voice, video and data • Upstream bandwidth requirements less compared to downstream bandwidth MJ 11/0704 4

Access Technologies • x. DSL: Digital subscriber line technology • Asymmetric DSL (ADSL) • High-speed DSL (HDSL) • Very-high speed DSL (VDSL) • Uses existing local loop telephone facilities MJ 11/0704 5
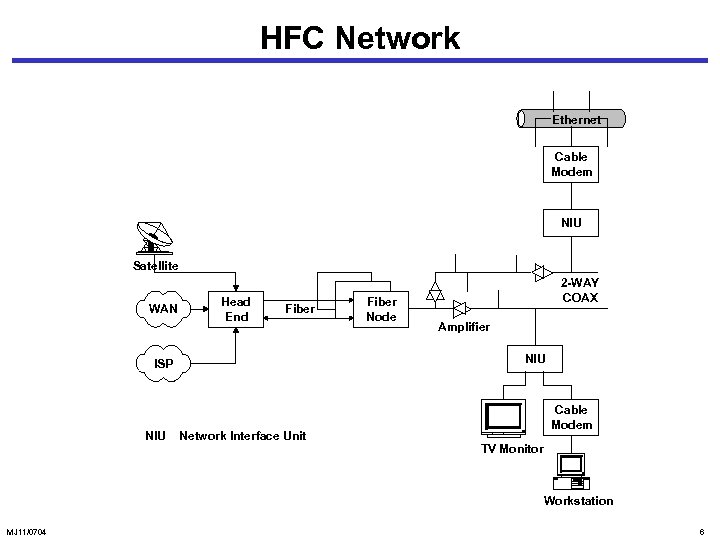
HFC Network Ethernet Cable Modem NIU Satellite WAN Head End Fiber Amplifier NIU ISP NIU Fiber Node 2 -WAY COAX Network Interface Unit Cable Modem TV Monitor Workstation MJ 11/0704 6
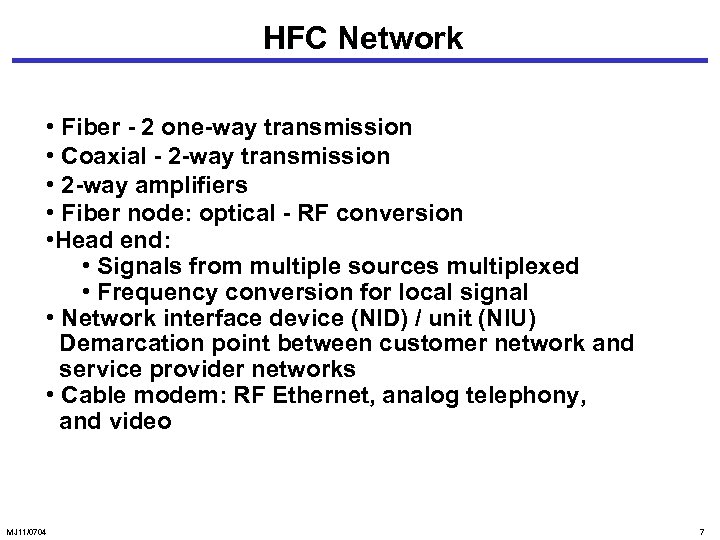
HFC Network • Fiber - 2 one-way transmission • Coaxial - 2 -way transmission • 2 -way amplifiers • Fiber node: optical - RF conversion • Head end: • Signals from multiple sources multiplexed • Frequency conversion for local signal • Network interface device (NID) / unit (NIU) Demarcation point between customer network and service provider networks • Cable modem: RF Ethernet, analog telephony, and video MJ 11/0704 7
HFC Technology • Broadband LAN • Asymmetric bandwidth allocation for 2 -way communication • RF spread-spectrum that carries multiple signals over HFC • RF spectrum allocation to carry multimedia services - voice, video and data MJ 11/0704 10 -12 8
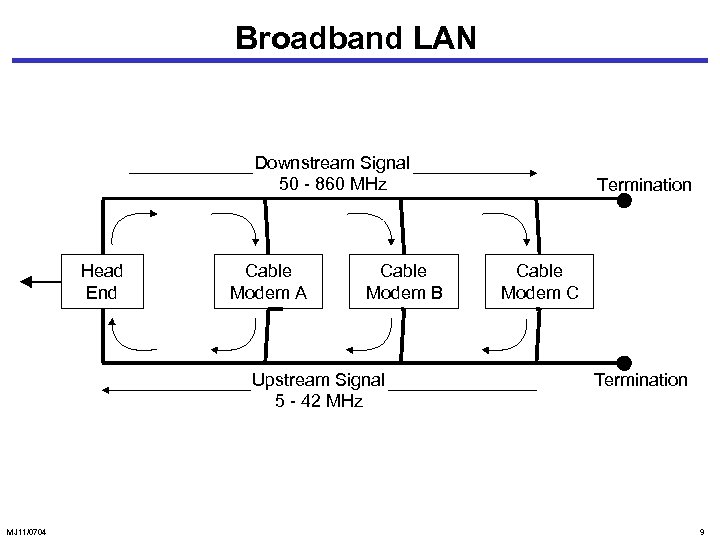
Broadband LAN Downstream Signal 50 - 860 MHz Head End Cable Modem A Cable Modem B Upstream Signal 5 - 42 MHz MJ 11/0704 Termination Cable Modem C Termination 9
Cable Modem • HFC uses tree topology • Downstream in broadcast mode • Upstream transmission by cable modem coordinated by head end • Data over cable service specifications (DOCSIS) for cable modem ensures interoperability • One-way cable modem uses telco-return MJ 11/0704 10
Cable Modem Termination System • Equipment at the head end • All cable modems terminated on the head end • Gateway to the external network • Multiplexes and demultiplexes signals • Frequency converts upstream to downstream signals • Can be designed either as a bridge or router MJ 11/0704 11
HFC Plant • Multiple fiber pairs run from head end to fiber node; each pair carries 2 one-way signals • Head end converts all (telephony, digital video, data, and analog video) signals to optical carrier to transmit on the fiber • Houses are connected from fiber node via coaxial cables • Coaxial cable are in tree topology and carries 2 -way signal • Amplifiers on the coaxial cable have 2 -way amplifiers that amplify the signals in both directions • “Drop from coaxial cable to NID (also called NIU) - called “Tap-to-TV” in CATV MJ 11/0704 12
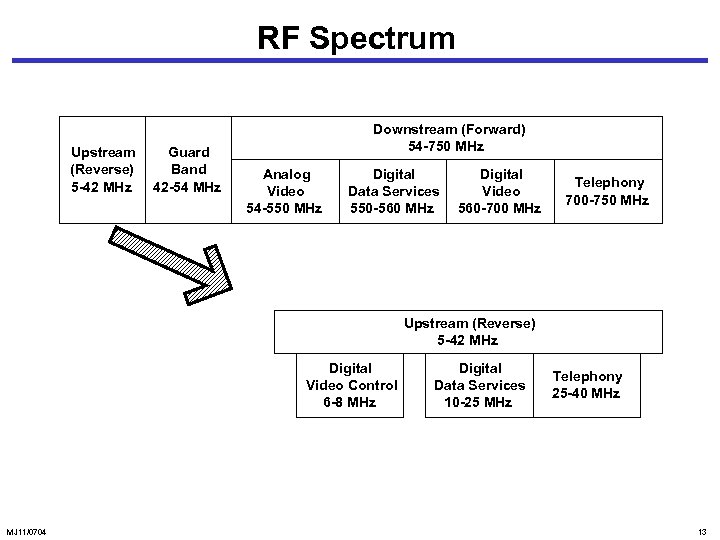
RF Spectrum Upstream (Reverse) 5 -42 MHz Guard Band 42 -54 MHz Downstream (Forward) 54 -750 MHz Analog Video 54 -550 MHz Digital Data Services 550 -560 MHz Digital Video 560 -700 MHz Telephony 700 -750 MHz Upstream (Reverse) 5 -42 MHz Digital Video Control 6 -8 MHz MJ 11/0704 Digital Data Services 10 -25 MHz Telephony 25 -40 MHz 13
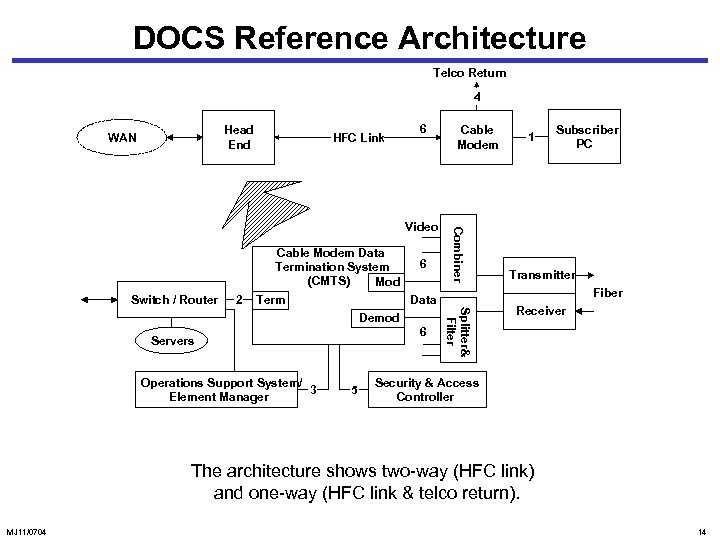
DOCS Reference Architecture Telco Return 4 Head End WAN HFC Link 6 Cable Modem Data Termination System (CMTS) Mod Switch / Router 2 Term 6 5 Splitter& Filter 6 Servers 1 Subscriber PC Transmitter Fiber Data Demod Operations Support System/ 3 Element Manager Combiner Video Cable Modem Receiver Security & Access Controller The architecture shows two-way (HFC link) and one-way (HFC link & telco return). MJ 11/0704 14
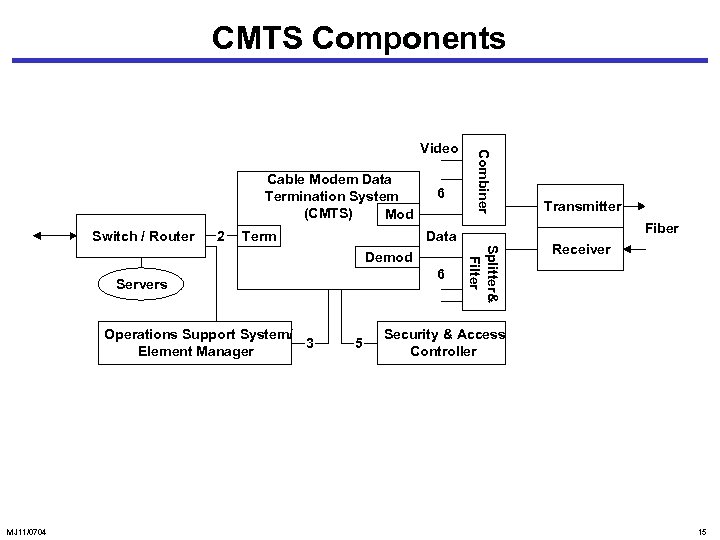
CMTS Components Cable Modem Data Termination System (CMTS) Mod Switch / Router 2 Term 6 MJ 11/0704 5 Splitter& Filter 6 Servers Transmitter Fiber Data Demod Operations Support System/ 3 Element Manager Combiner Video Receiver Security & Access Controller 15
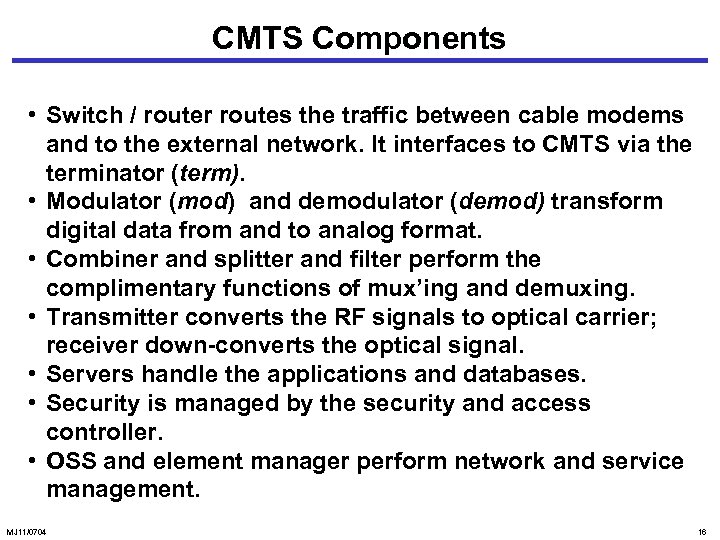
CMTS Components • Switch / router routes the traffic between cable modems and to the external network. It interfaces to CMTS via the terminator (term). • Modulator (mod) and demodulator (demod) transform digital data from and to analog format. • Combiner and splitter and filter perform the complimentary functions of mux’ing and demuxing. • Transmitter converts the RF signals to optical carrier; receiver down-converts the optical signal. • Servers handle the applications and databases. • Security is managed by the security and access controller. • OSS and element manager perform network and service management. MJ 11/0704 16
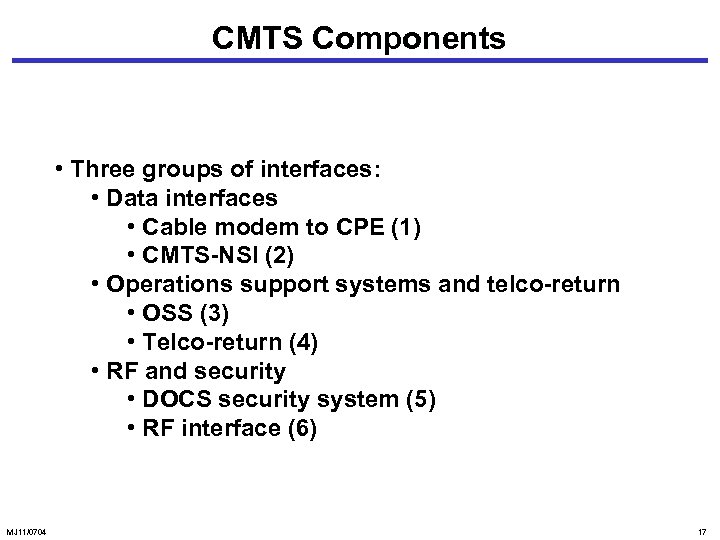
CMTS Components • Three groups of interfaces: • Data interfaces • Cable modem to CPE (1) • CMTS-NSI (2) • Operations support systems and telco-return • OSS (3) • Telco-return (4) • RF and security • DOCS security system (5) • RF interface (6) MJ 11/0704 17

HFC Management Challenges • More complex than either computer network or telecommunication network • Involves both physical and data layers • Multiple physical facilities • Legacy cable system • Multimedia service • RF spectrum management • Service and business management important for MSOs and customer • Shared media impacts security and bandwidth • Security and privacy of home network MJ 11/0704 18
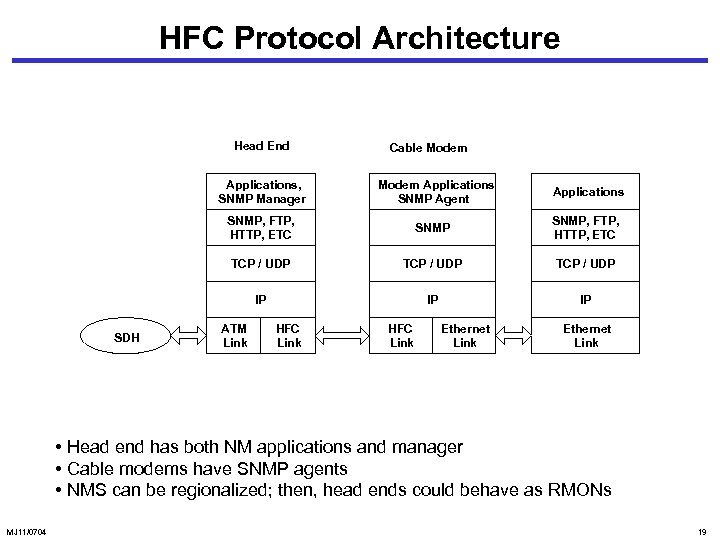
HFC Protocol Architecture Head End Applications, SNMP Manager Cable Modem Applications SNMP Agent Applications SNMP, FTP, HTTP, ETC TCP / UDP IP SDH SNMP IP IP ATM Link HFC Link Ethernet Link • Head end has both NM applications and manager • Cable modems have SNMP agents • NMS can be regionalized; then, head ends could behave as RMONs MJ 11/0704 19
HFC / CM Management • Cable modem management • CMTS management • HFC link management • RF spectrum management MJ 11/0704 20
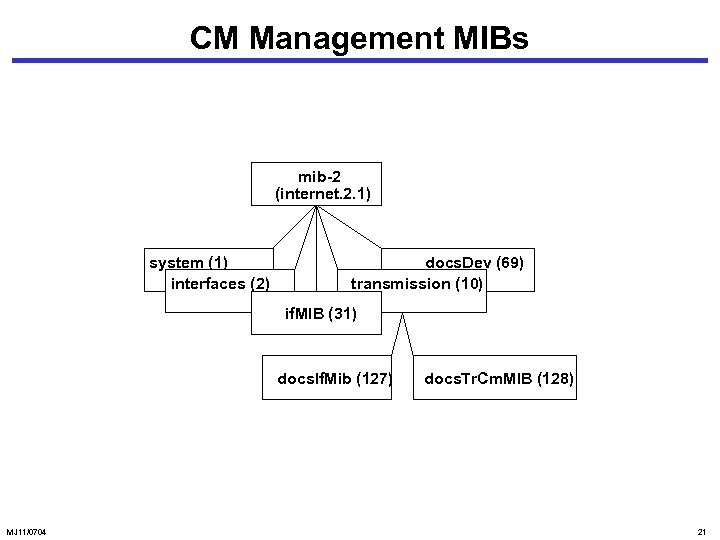
CM Management MIBs mib-2 (internet. 2. 1) system (1) interfaces (2) docs. Dev (69) transmission (10) if. MIB (31) docs. If. Mib (127) MJ 11/0704 docs. Tr. Cm. MIB (128) 21
CM Management MIBs • Three categories of MIBs • Standard MIBs: • system, interfaces, if. MIB • CM and CMTS interfaces • doc. If. MIB. . RF Interfaces in CM and CMTS, base line privacy and Qo. S • docs. Tr. Cm. MIB. . telephony-return interface • CM and CMTS objects • docs. Dev. MIB MJ 11/0704 22
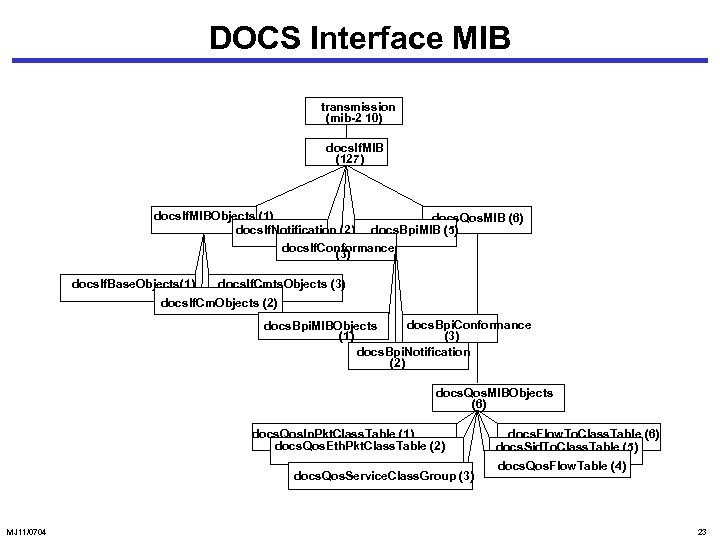
DOCS Interface MIB transmission (mib-2 10) docs. If. MIB (127) docs. If. MIBObjects (1) docs. Qos. MIB (6) docs. If. Notification (2) docs. Bpi. MIB (5) docs. If. Conformance (3) docs. If. Base. Objects(1) docs. If. Cmts. Objects (3) docs. If. Cm. Objects (2) docs. Bpi. Conformance docs. Bpi. MIBObjects (1) (3) docs. Bpi. Notification (2) docs. Qos. MIBObjects (6) docs. Qos. Ip. Pkt. Class. Table (1) docs. Qos. Eth. Pkt. Class. Table (2) docs. Qos. Service. Class. Group (3) MJ 11/0704 docs. Flow. To. Class. Table (6) docs. Sid. To. Class. Table (5) docs. Qos. Flow. Table (4) 23
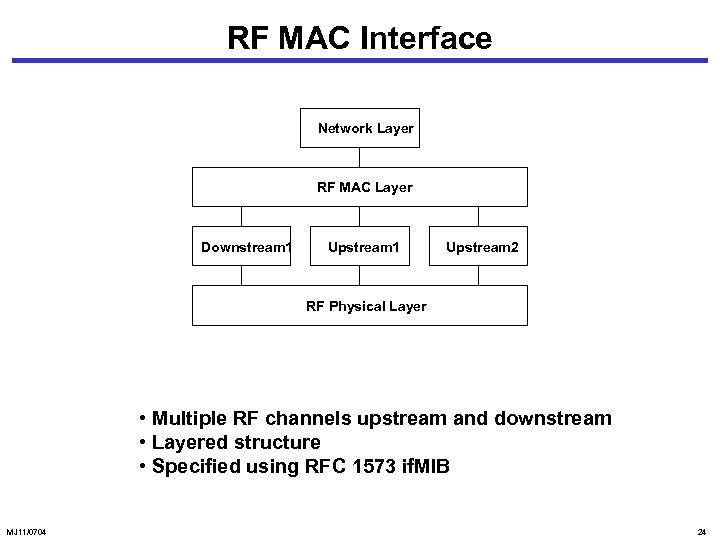
RF MAC Interface Network Layer RF MAC Layer Downstream 1 Upstream 2 RF Physical Layer • Multiple RF channels upstream and downstream • Layered structure • Specified using RFC 1573 if. MIB MJ 11/0704 24
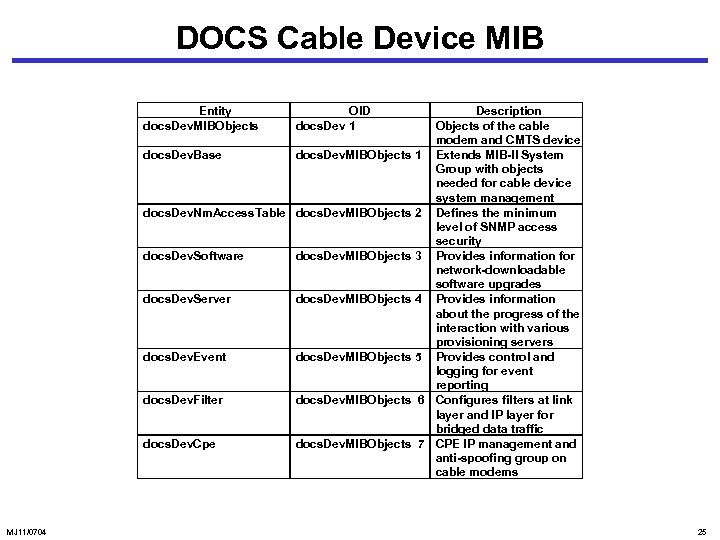
DOCS Cable Device MIB Entity docs. Dev. MIBObjects Description Objects of the cable modem and CMTS device docs. Dev. Base docs. Dev. MIBObjects 1 Extends MIB-II System Group with objects needed for cable device system management docs. Dev. Nm. Access. Table docs. Dev. MIBObjects 2 Defines the minimum level of SNMP access security docs. Dev. Software docs. Dev. MIBObjects 3 Provides information for network-downloadable software upgrades docs. Dev. Server docs. Dev. MIBObjects 4 Provides information about the progress of the interaction with various provisioning servers docs. Dev. Event docs. Dev. MIBObjects 5 Provides control and logging for event reporting docs. Dev. Filter docs. Dev. MIBObjects 6 Configures filters at link layer and IP layer for bridged data traffic docs. Dev. Cpe docs. Dev. MIBObjects 7 CPE IP management and anti-spoofing group on cable modems MJ 11/0704 OID docs. Dev 1 25
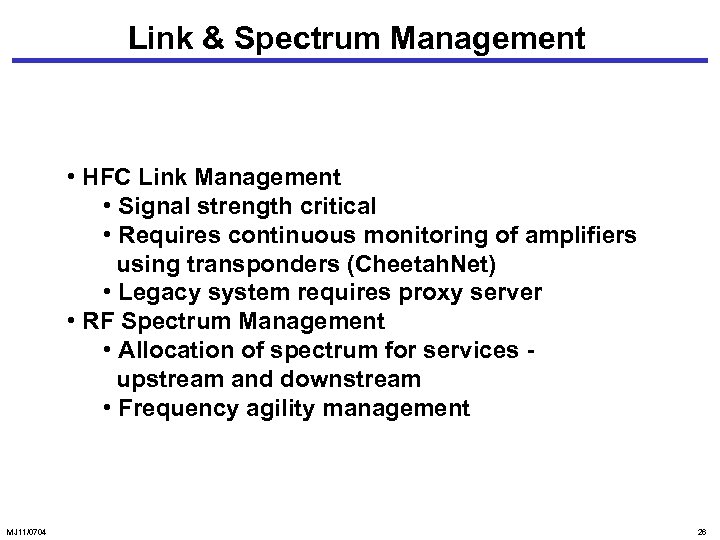
Link & Spectrum Management • HFC Link Management • Signal strength critical • Requires continuous monitoring of amplifiers using transponders (Cheetah. Net) • Legacy system requires proxy server • RF Spectrum Management • Allocation of spectrum for services upstream and downstream • Frequency agility management MJ 11/0704 26
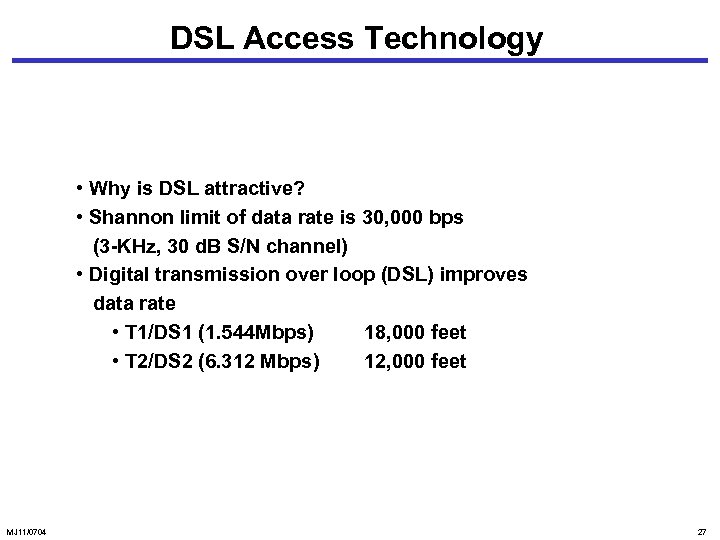
DSL Access Technology • Why is DSL attractive? • Shannon limit of data rate is 30, 000 bps (3 -KHz, 30 d. B S/N channel) • Digital transmission over loop (DSL) improves data rate • T 1/DS 1 (1. 544 Mbps) 18, 000 feet • T 2/DS 2 (6. 312 Mbps) 12, 000 feet MJ 11/0704 27

DSL Limitations • Loop conditions with no direct copper to the house • Loaded coils in loop (used to increase analog distance) cannot carry digital signal • Modern subdivisions have fiber to the neighborhood or curb with digital mux • Operating company inventory dated (administrative issue) MJ 11/0704 28
![x. DSL Technologies Copper Access Transmission Technologies [ADSL Forum] Name Meaning Modem Voice Band x. DSL Technologies Copper Access Transmission Technologies [ADSL Forum] Name Meaning Modem Voice Band](https://present5.com/presentation/d14ccff18583f2d5b50d1c4620bd6366/image-29.jpg)
x. DSL Technologies Copper Access Transmission Technologies [ADSL Forum] Name Meaning Modem Voice Band Modems ISDN Data rate 1200 bps to 28, 800 bps Mode Cable Duplex 2 -pair Integrated 160 kbps Services Digital Network High data rate 1. 544 Mbps Digital 2. 048 Mbps Subscriber Line Duplex SDSL Single line 1. 544 Mbps Digital 2. 048 Mbps Subscriber Line Duplex 1 -pair Duplex ADSL Asymmetric 1. 5 to 9 Mbps Down Digital 16 to 640 kbps Up Subscriber Line 1 -pair VDSL Very high data 13 to 52 Mbps rate Digital 1. 5 to 2. 3 Subscriber Line Mbps 2 -pair HDSL MJ 11/0704 Duplex 2 -pair Duplex Down Up Applications Low data rate data communications ISDN service Voice and data communications T 1/E 1 service Feeder plant, WAN, LAN access, server access Same as HDSL plus premises access for symmetric services Internet access, video demand, simplex video, LAN access, interactive multimedia Same as ADSL plus HDTV 29
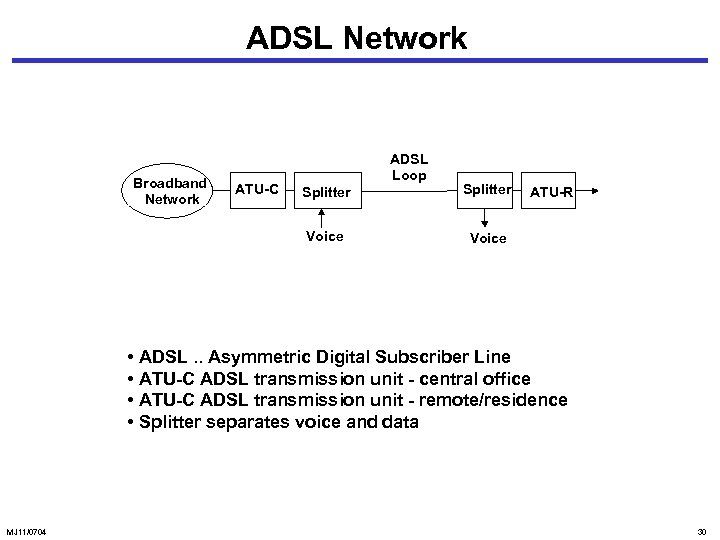
ADSL Network Broadband Network ATU-C ADSL Loop Splitter Voice ATU-R • ADSL. . Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line • ATU-C ADSL transmission unit - central office • ATU-C ADSL transmission unit - remote/residence • Splitter separates voice and data MJ 11/0704 30
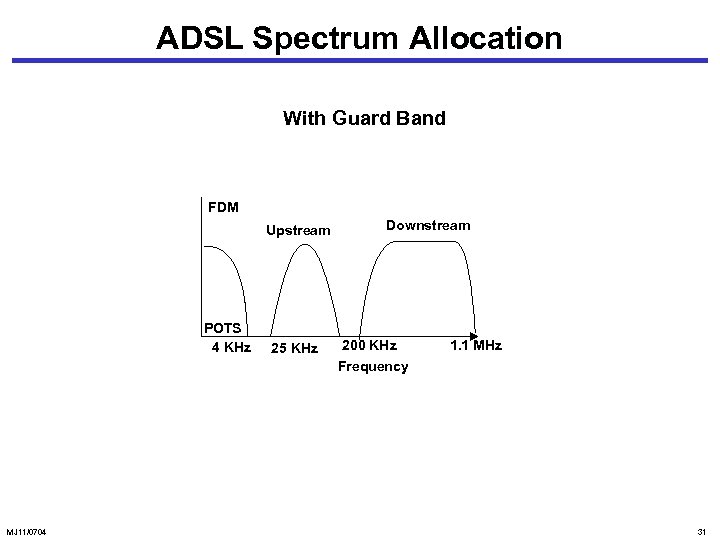
ADSL Spectrum Allocation With Guard Band FDM Upstream POTS 4 KHz MJ 11/0704 25 KHz Downstream 200 KHz Frequency 1. 1 MHz 31
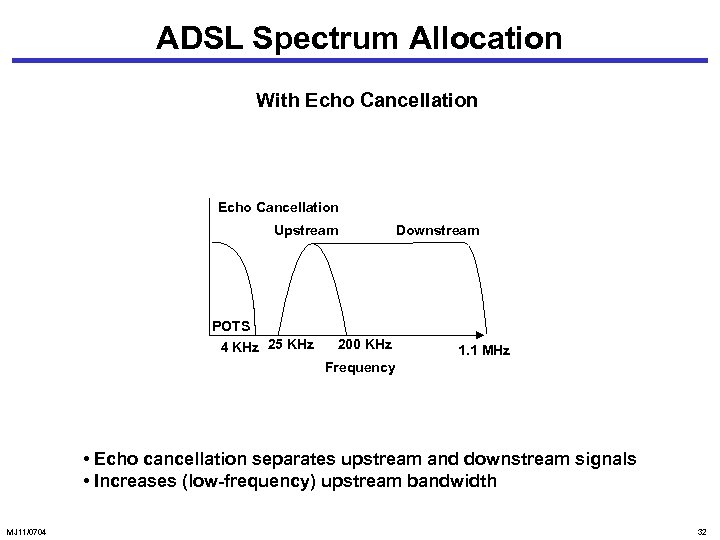
ADSL Spectrum Allocation With Echo Cancellation Upstream POTS 4 KHz 25 KHz 200 KHz Downstream 1. 1 MHz Frequency • Echo cancellation separates upstream and downstream signals • Increases (low-frequency) upstream bandwidth MJ 11/0704 32
Modulation Schemes • Carrierless amplitude phase (CAP) modulation • Discrete multi. Tone modulation (DMT): 4 k. Hz tones • Both CAP and DMT are QAM-based • DMT outperforms CAP • 4 -to-1 downstream throughput • 10 -to-1 upstream throughput • Rate adaptive • On-going active monitoring • Maximum loop variation coverage • Standard and hence interoperability MJ 11/0704 33
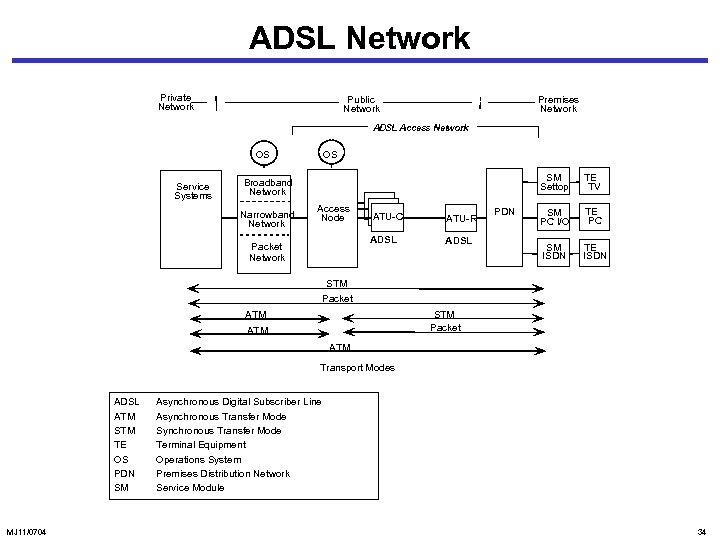
ADSL Network Private Network Public Network Premises Network ADSL Access Network OS Service Systems OS SM Settop Broadband Network Narrowband Network Access Node ATU-R ADSL Packet Network ATU-C ADSL PDN TE TV SM PC I/O TE PC SM ISDN TE ISDN STM Packet ATM ATM Transport Modes ADSL ATM STM TE OS PDN SM MJ 11/0704 Asynchronous Digital Subscriber Line Asynchronous Transfer Mode Synchronous Transfer Mode Terminal Equipment Operations System Premises Distribution Network Service Module 34
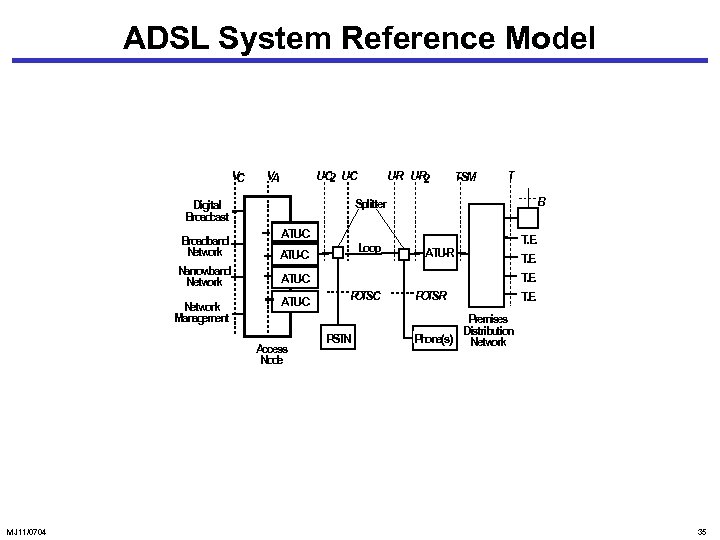
ADSL System Reference Model V C U 2 U -C -C V A TM -S T B Splitter Digital Broadcast ATU-C Broadband Netw ork ATU-C Narrow band Netw ork ATU-C Network M anagem ent ATU-C Access Node MJ 11/0704 U U 2 -R -R Loop ATU-R T. . E P T -C OS PSTN P T -R OS T. . E Prem ises Distribution Phone(s) Netw ork 35
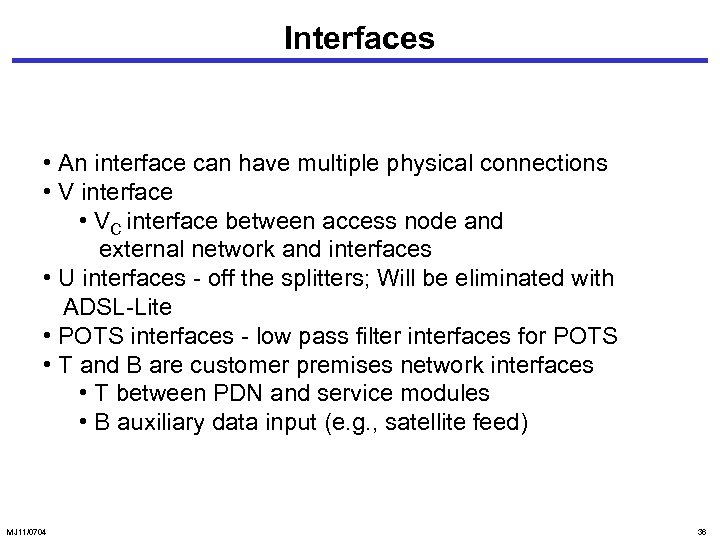
Interfaces • An interface can have multiple physical connections • V interface • VC interface between access node and external network and interfaces • U interfaces - off the splitters; Will be eliminated with ADSL-Lite • POTS interfaces - low pass filter interfaces for POTS • T and B are customer premises network interfaces • T between PDN and service modules • B auxiliary data input (e. g. , satellite feed) MJ 11/0704 36
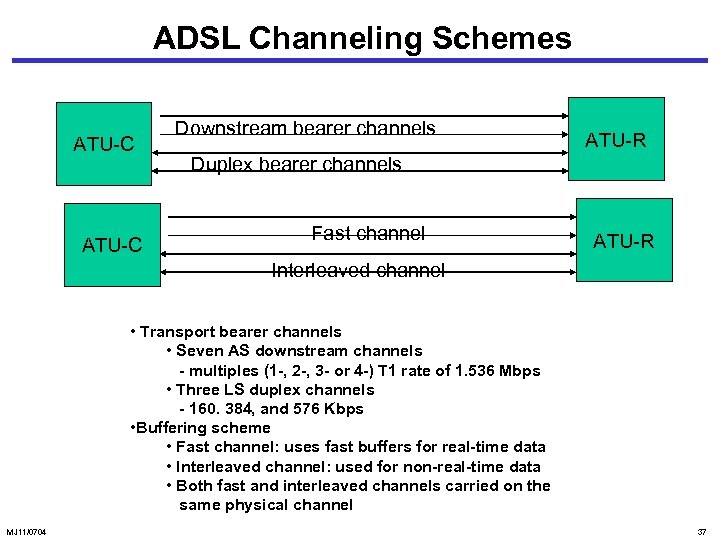
ADSL Channeling Schemes ATU-C Downstream bearer channels ATU-R Duplex bearer channels Fast channel ATU-R Interleaved channel • Transport bearer channels • Seven AS downstream channels - multiples (1 -, 2 -, 3 - or 4 -) T 1 rate of 1. 536 Mbps • Three LS duplex channels - 160. 384, and 576 Kbps • Buffering scheme • Fast channel: uses fast buffers for real-time data • Interleaved channel: used for non-real-time data • Both fast and interleaved channels carried on the same physical channel MJ 11/0704 37
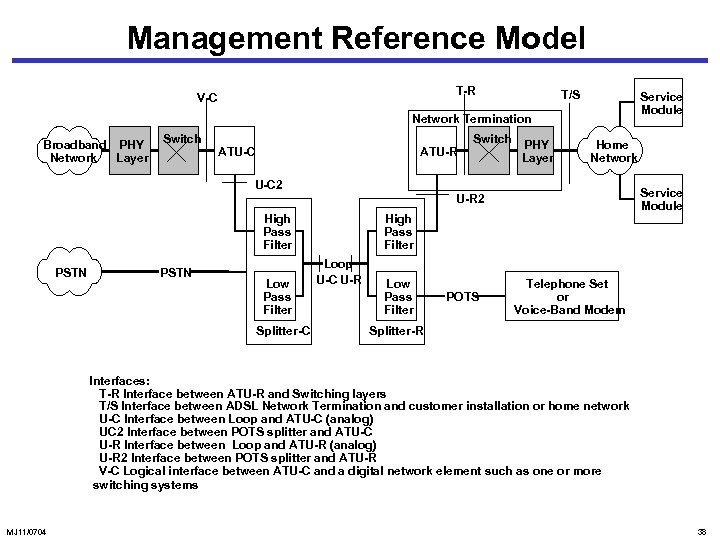
Management Reference Model T-R V-C T/S Service Module Network Termination Broadband PHY Network Layer Switch ATU-C ATU-R Switch PHY Layer Home Network U-C 2 Service Module U-R 2 High Pass Filter PSTN Low Pass Filter Splitter-C High Pass Filter Loop U-C U-R Low Pass Filter POTS Telephone Set or Voice-Band Modem Splitter-R Interfaces: T-R Interface between ATU-R and Switching layers T/S Interface between ADSL Network Termination and customer installation or home network U-C Interface between Loop and ATU-C (analog) UC 2 Interface between POTS splitter and ATU-C U-R Interface between Loop and ATU-R (analog) U-R 2 Interface between POTS splitter and ATU-R V-C Logical interface between ATU-C and a digital network element such as one or more switching systems MJ 11/0704 38
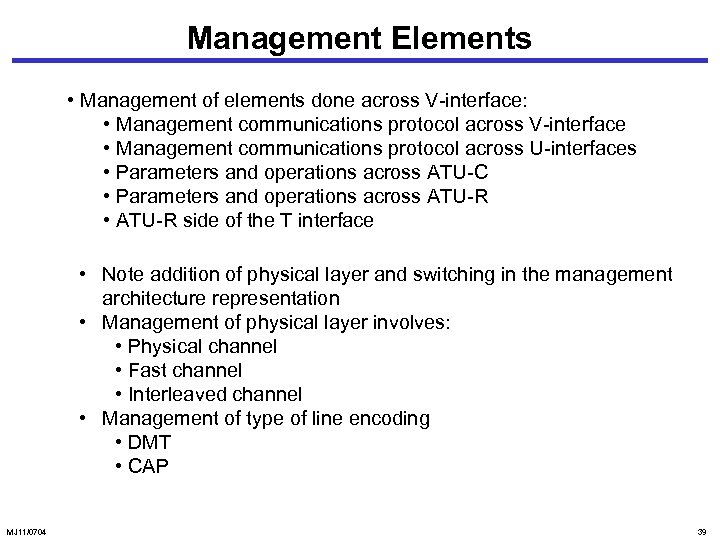
Management Elements • Management of elements done across V-interface: • Management communications protocol across V-interface • Management communications protocol across U-interfaces • Parameters and operations across ATU-C • Parameters and operations across ATU-R • ATU-R side of the T interface • Note addition of physical layer and switching in the management architecture representation • Management of physical layer involves: • Physical channel • Fast channel • Interleaved channel • Management of type of line encoding • DMT • CAP MJ 11/0704 39
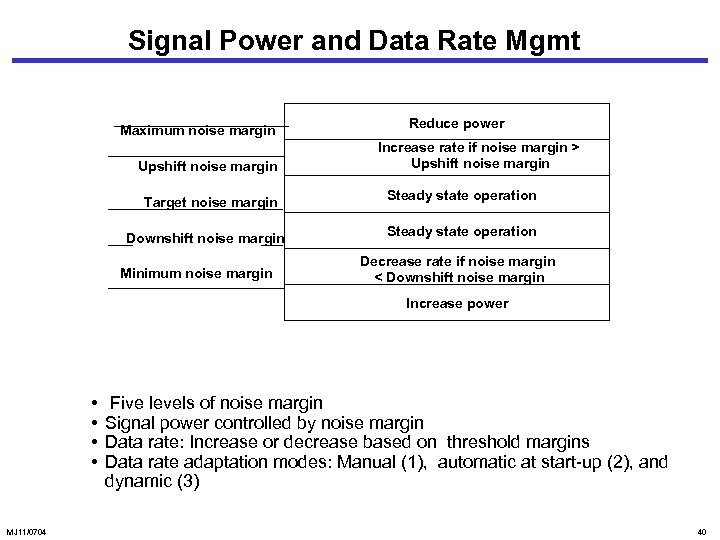
Signal Power and Data Rate Mgmt Maximum noise margin Upshift noise margin Target noise margin Downshift noise margin Minimum noise margin Reduce power Increase rate if noise margin > Upshift noise margin Steady state operation Decrease rate if noise margin < Downshift noise margin Increase power • • MJ 11/0704 Five levels of noise margin Signal power controlled by noise margin Data rate: Increase or decrease based on threshold margins Data rate adaptation modes: Manual (1), automatic at start-up (2), and dynamic (3) 40
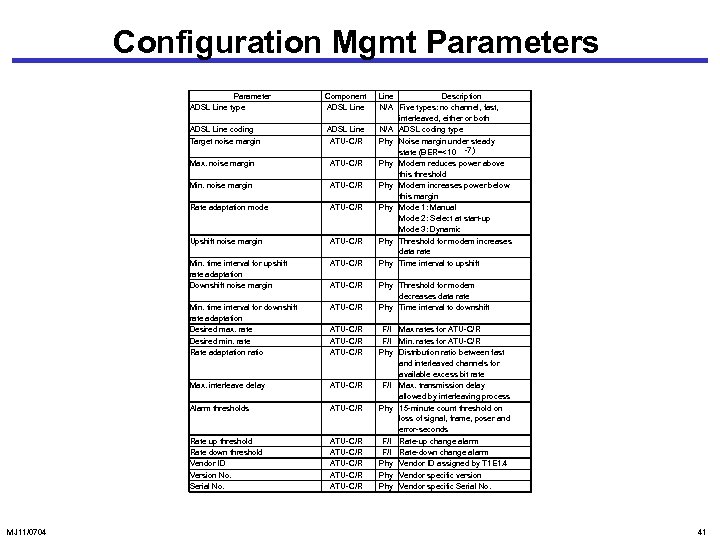
Configuration Mgmt Parameters Parameter ADSL Line type Component ADSL Line coding Target noise margin ADSL Line ATU-C/R Max. noise margin Min. noise margin ATU-C/R Rate adaptation mode ATU-C/R Upshift noise margin ATU-C/R Min. time interval for upshift rate adaptation Downshift noise margin ATU-C/R Min. time interval for downshift rate adaptation Desired max. rate Desired min. rate Rate adaptation ratio ATU-C/R Max. interleave delay ATU-C/R Alarm thresholds ATU-C/R Rate up threshold Rate down threshold Vendor ID Version No. Serial No. MJ 11/0704 ATU-C/R ATU-C/R ATU-C/R Line Description N/A Five types: no channel, fast, interleaved, either or both N/A ADSL coding type Phy Noise margin under steady state (BER=<10 -7) Phy Modem reduces power above this threshold Phy Modem increases power below this margin Phy Mode 1: Manual Mode 2: Select at start-up Mode 3: Dynamic Phy Threshold for modem increases data rate Phy Time interval to upshift Phy Threshold for modem decreases data rate Phy Time interval to downshift F/I Max rates for ATU-C/R F/I Min. rates for ATU-C/R Phy Distribution ratio between fast and interleaved channels for available excess bit rate F/I Max. transmission delay allowed by interleaving process Phy 15 -minute count threshold on loss of signal, frame, poser and error-seconds F/I Rate-up change alarm F/I Rate-down change alarm Phy Vendor ID assigned by T 1 E 1. 4 Phy Vendor specific version Phy Vendor specific Serial No. 41
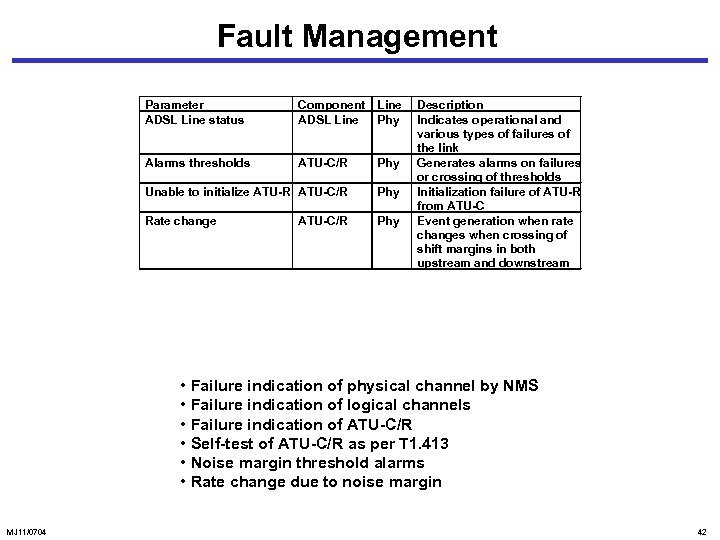
Fault Management Parameter ADSL Line status Component ADSL Line Phy Alarms thresholds ATU-C/R Phy Unable to initialize ATU-R ATU-C/R Phy Rate change Phy ATU-C/R Description Indicates operational and various types of failures of the link Generates alarms on failures or crossing of thresholds Initialization failure of ATU-R from ATU-C Event generation when rate changes when crossing of shift margins in both upstream and downstream • Failure indication of physical channel by NMS • Failure indication of logical channels • Failure indication of ATU-C/R • Self-test of ATU-C/R as per T 1. 413 • Noise margin threshold alarms • Rate change due to noise margin MJ 11/0704 42
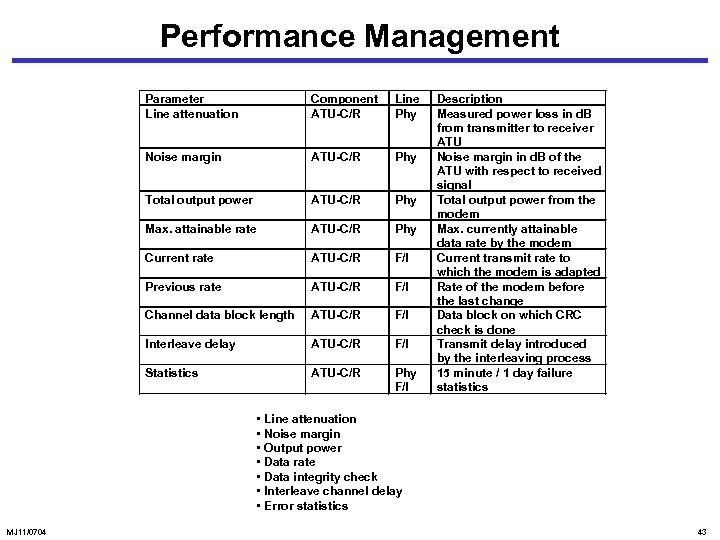
Performance Management Parameter Line attenuation Component ATU-C/R Line Phy Noise margin ATU-C/R Phy Total output power ATU-C/R Phy Max. attainable rate ATU-C/R Phy Current rate ATU-C/R F/I Previous rate ATU-C/R F/I Channel data block length ATU-C/R F/I Interleave delay ATU-C/R F/I Statistics ATU-C/R Phy F/I Description Measured power loss in d. B from transmitter to receiver ATU Noise margin in d. B of the ATU with respect to received signal Total output power from the modem Max. currently attainable data rate by the modem Current transmit rate to which the modem is adapted Rate of the modem before the last change Data block on which CRC check is done Transmit delay introduced by the interleaving process 15 minute / 1 day failure statistics • Line attenuation • Noise margin • Output power • Data rate • Data integrity check • Interleave channel delay • Error statistics MJ 11/0704 43
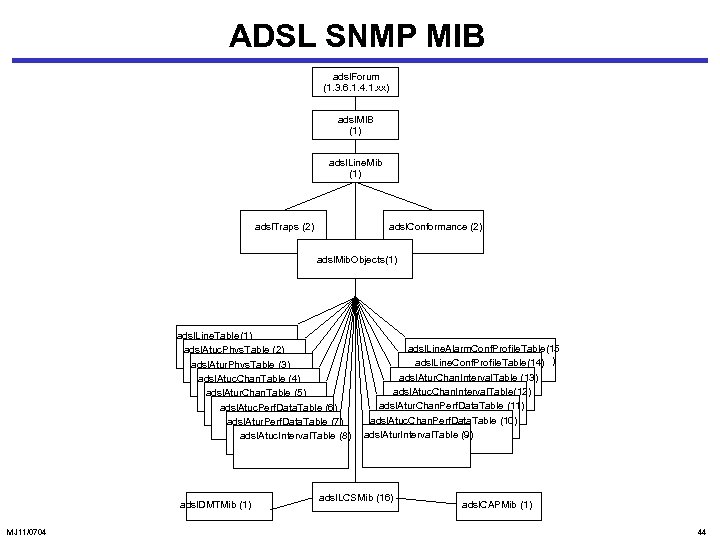
ADSL SNMP MIB adsl. Forum (1. 3. 6. 1. 4. 1. xx) adsl. MIB (1) adsl. Line. Mib (1) adsl. Traps (2) adsl. Conformance (2) adsl. Mib. Objects(1) adsl. Line. Table (1) adsl. Atuc. Phys. Table (2) adsl. Atur. Phys. Table (3) adsl. Atuc. Chan. Table (4) adsl. Atur. Chan. Table (5) adsl. Atuc. Perf. Data. Table (6) adsl. Atur. Perf. Data. Table (7) adsl. Atuc. Interval. Table (8) adsl. DMTMib (1) MJ 11/0704 adsl. Line. Alarm. Conf. Profile. Table(15 adsl. Line. Conf. Profile. Table(14) ) adsl. Atur. Chan. Interval. Table (13) adsl. Atuc. Chan. Interval. Table(12) adsl. Atur. Chan. Perf. Data. Table (11) adsl. Atuc. Chan. Perf. Data. Table (10) adsl. Atur. Interval. Table (9) adsl. LCSMib (16) adsl. CAPMib (1) 44
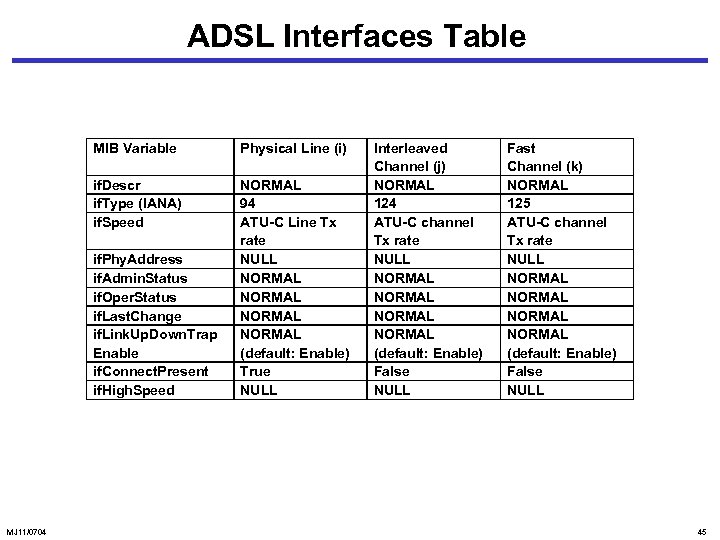
ADSL Interfaces Table MIB Variable Physical Line (i) if. Descr if. Type (IANA) if. Speed NORMAL 94 ATU-C Line Tx rate NULL NORMAL (default: Enable) True NULL if. Phy. Address if. Admin. Status if. Oper. Status if. Last. Change if. Link. Up. Down. Trap Enable if. Connect. Present if. High. Speed MJ 11/0704 Interleaved Channel (j) NORMAL 124 ATU-C channel Tx rate NULL NORMAL (default: Enable) False NULL Fast Channel (k) NORMAL 125 ATU-C channel Tx rate NULL NORMAL (default: Enable) False NULL 45
ADSL Profiles Management • Configuration profile • Performance profile • Alarm profile • Traps • Generic • Loss of frame • Loss of signal • Loss of power • Error-second threshold • Data rate change • Loss of link • ATU-C initialization failure MJ 11/0704 46
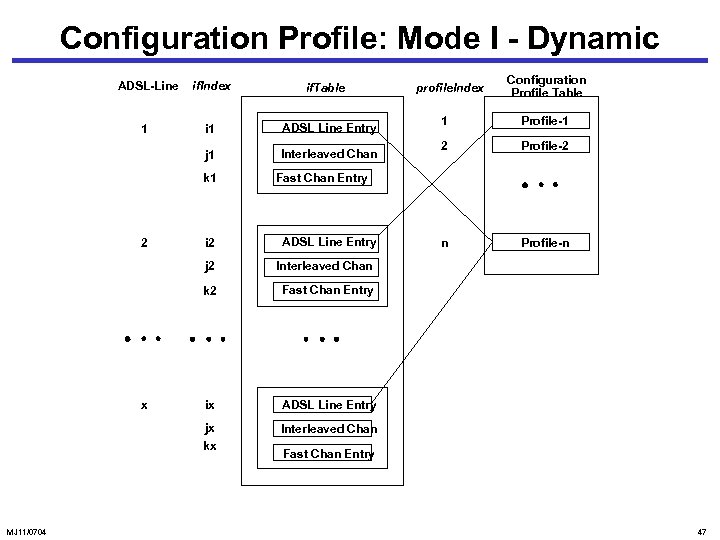
Configuration Profile: Mode I - Dynamic ADSL-Line if. Index if. Table i 1 ADSL Line Entry j 1 1 Interleaved Chan k 1 2 i 2 ADSL Line Entry 1 Profile-1 2 Profile-2 n Profile-n Interleaved Chan k 2 Fast Chan Entry ix ADSL Line Entry jx Interleaved Chan kx MJ 11/0704 Configuration Profile Table Fast Chan Entry j 2 x profile. Index Fast Chan Entry 47
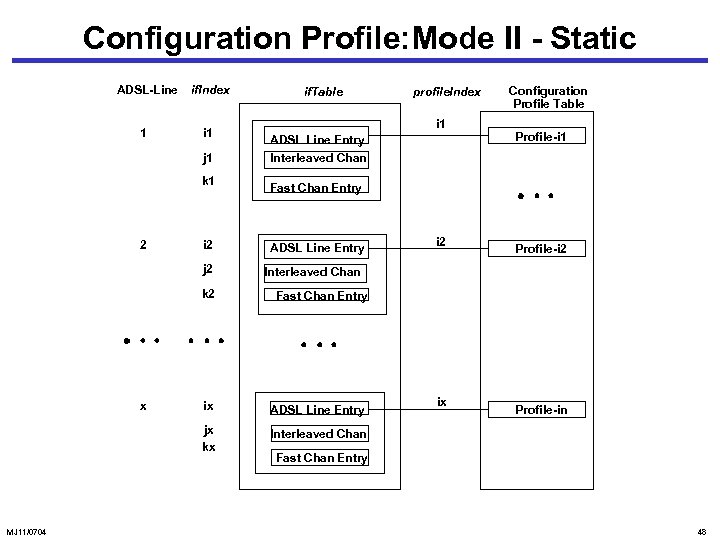
Configuration Profile: Mode II - Static ADSL-Line 1 if. Index i 1 j 1 k 1 2 i 2 j 2 if. Table i 1 ADSL Line Entry Interleaved Chan ADSL Line Entry Profile-i 1 i 2 Profile-i 2 Interleaved Chan Fast Chan Entry ix ADSL Line Entry jx kx MJ 11/0704 Configuration Profile Table Fast Chan Entry k 2 x profile. Index Interleaved Chan ix Profile-in Fast Chan Entry 48
d14ccff18583f2d5b50d1c4620bd6366.ppt