d695ddb9c0fd03ef21a36999f57e26bc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 Session 1: Day 3: CLIMATE EXTREME AND DISASTER MANAGEMENT Linking Disaster Risk Reduction and Climate Change Adaptation: Best practices of the Red Cross Red Crescent societies in delivering its assistance to support the flood prone areas in Indonesia Febi Dwirahmadi 2010 International Climate Change Adaptation Conference, Gold Coast, Queensland, Australia
Session 1: Day 3: CLIMATE EXTREME AND DISASTER MANAGEMENT Linking Disaster Risk Reduction and Climate Change Adaptation: Best practices of the Red Cross Red Crescent societies in delivering its assistance to support the flood prone areas in Indonesia Febi Dwirahmadi 2010 International Climate Change Adaptation Conference, Gold Coast, Queensland, Australia
 Structure of presentation § Disaster and climate change from global context § Disasters and climate change risks in Indonesia § DRR and CCA concepts § How RCRC deal with it? § Develop the linkages
Structure of presentation § Disaster and climate change from global context § Disasters and climate change risks in Indonesia § DRR and CCA concepts § How RCRC deal with it? § Develop the linkages
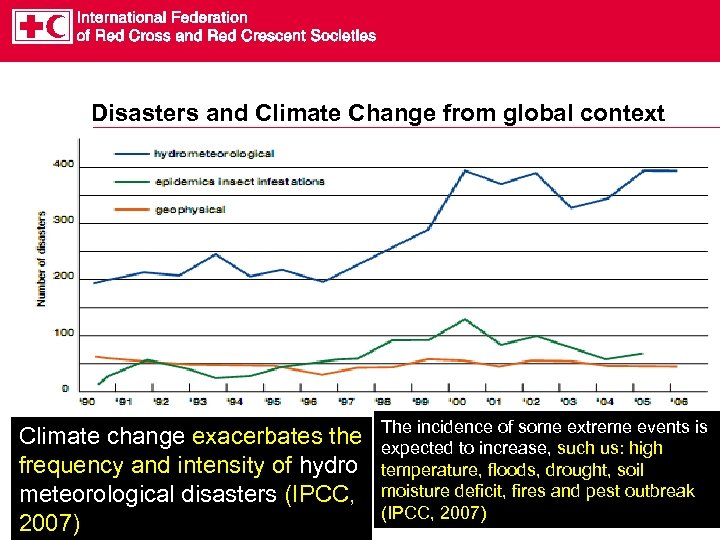 Disasters and Climate Change from global context Climate change exacerbates the frequency and intensity of hydro meteorological disasters (IPCC, 2007) The incidence of some extreme events is expected to increase, such us: high temperature, floods, drought, soil moisture deficit, fires and pest outbreak (IPCC, 2007)
Disasters and Climate Change from global context Climate change exacerbates the frequency and intensity of hydro meteorological disasters (IPCC, 2007) The incidence of some extreme events is expected to increase, such us: high temperature, floods, drought, soil moisture deficit, fires and pest outbreak (IPCC, 2007)
 Disasters and climate change in Indonesia Hydro meteorological disasters are the most common disaster in Indonesia (BNPB, 2010)
Disasters and climate change in Indonesia Hydro meteorological disasters are the most common disaster in Indonesia (BNPB, 2010)
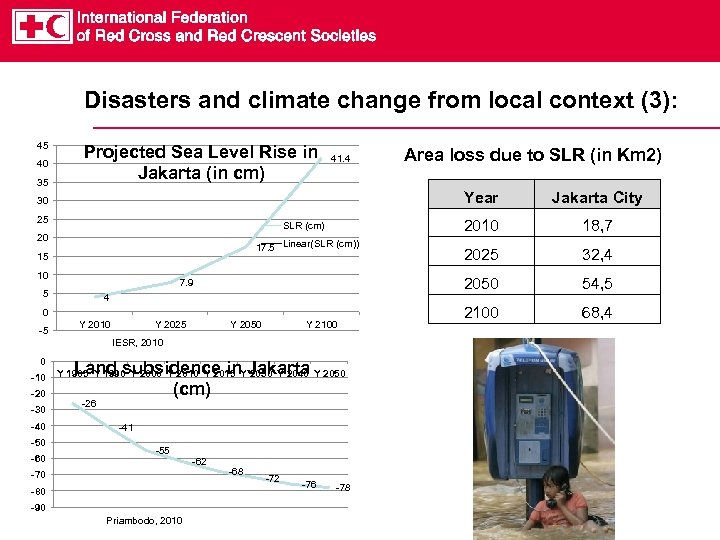 Disasters and climate change from local context (3): 45 40 35 Projected Sea Level Rise in Jakarta (in cm) 41. 4 Year SLR (cm) 20 17. 5 Linear(SLR (cm)) 15 10 7. 9 5 4 0 Y 2010 Y 2025 Y 2050 Y 2100 IESR, 2010 0 -10 -20 -30 -40 -50 -60 Land subsidence in Jakarta (cm) Y 1985 Y 1990 Y 2000 Y 2015 Y 2030 Y 2040 Y 2050 -26 -41 -55 -62 -70 -80 -90 Priambodo, 2010 -68 -72 -76 -78 18, 7 2025 32, 4 2050 25 Jakarta City 2010 30 -5 Area loss due to SLR (in Km 2) 54, 5 2100 68, 4
Disasters and climate change from local context (3): 45 40 35 Projected Sea Level Rise in Jakarta (in cm) 41. 4 Year SLR (cm) 20 17. 5 Linear(SLR (cm)) 15 10 7. 9 5 4 0 Y 2010 Y 2025 Y 2050 Y 2100 IESR, 2010 0 -10 -20 -30 -40 -50 -60 Land subsidence in Jakarta (cm) Y 1985 Y 1990 Y 2000 Y 2015 Y 2030 Y 2040 Y 2050 -26 -41 -55 -62 -70 -80 -90 Priambodo, 2010 -68 -72 -76 -78 18, 7 2025 32, 4 2050 25 Jakarta City 2010 30 -5 Area loss due to SLR (in Km 2) 54, 5 2100 68, 4
 Disaster and climate change in Indonesia (2) Jakarta is sinking !
Disaster and climate change in Indonesia (2) Jakarta is sinking !
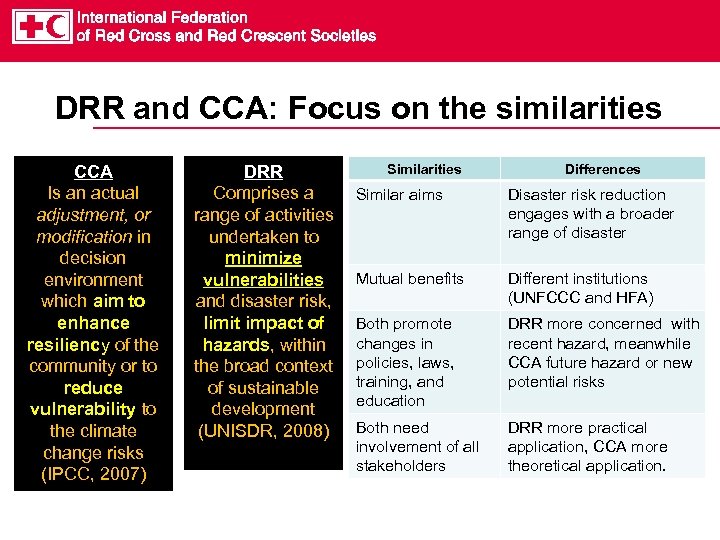 DRR and CCA: Focus on the similarities CCA Is an actual adjustment, or modification in decision environment which aim to enhance resiliency of the community or to reduce vulnerability to the climate change risks (IPCC, 2007) DRR Comprises a range of activities undertaken to minimize vulnerabilities and disaster risk, limit impact of hazards, within the broad context of sustainable development (UNISDR, 2008) Similarities Differences Similar aims Disaster risk reduction engages with a broader range of disaster Mutual benefits Different institutions (UNFCCC and HFA) Both promote changes in policies, laws, training, and education DRR more concerned with recent hazard, meanwhile CCA future hazard or new potential risks Both need involvement of all stakeholders DRR more practical application, CCA more theoretical application.
DRR and CCA: Focus on the similarities CCA Is an actual adjustment, or modification in decision environment which aim to enhance resiliency of the community or to reduce vulnerability to the climate change risks (IPCC, 2007) DRR Comprises a range of activities undertaken to minimize vulnerabilities and disaster risk, limit impact of hazards, within the broad context of sustainable development (UNISDR, 2008) Similarities Differences Similar aims Disaster risk reduction engages with a broader range of disaster Mutual benefits Different institutions (UNFCCC and HFA) Both promote changes in policies, laws, training, and education DRR more concerned with recent hazard, meanwhile CCA future hazard or new potential risks Both need involvement of all stakeholders DRR more practical application, CCA more theoretical application.
 So how we deal with it?
So how we deal with it?
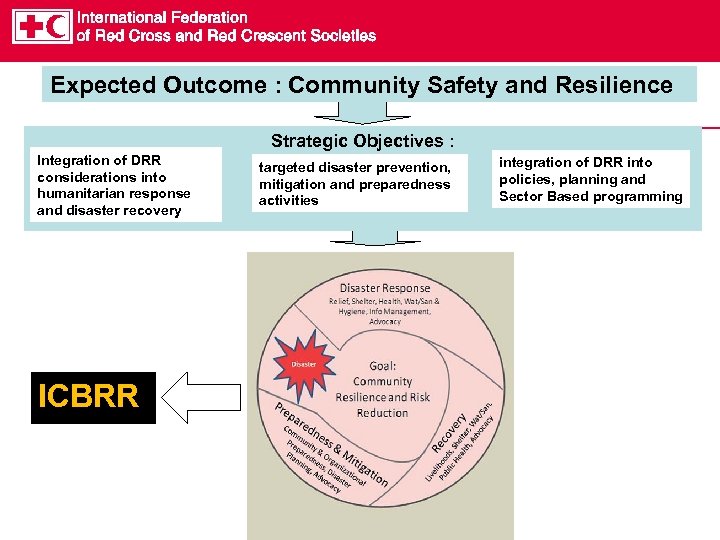 Expected Outcome : Community Safety and Resilience Strategic Objectives : Integration of DRR considerations into humanitarian response and disaster recovery ICBRR targeted disaster prevention, mitigation and preparedness activities integration of DRR into policies, planning and Sector Based programming
Expected Outcome : Community Safety and Resilience Strategic Objectives : Integration of DRR considerations into humanitarian response and disaster recovery ICBRR targeted disaster prevention, mitigation and preparedness activities integration of DRR into policies, planning and Sector Based programming
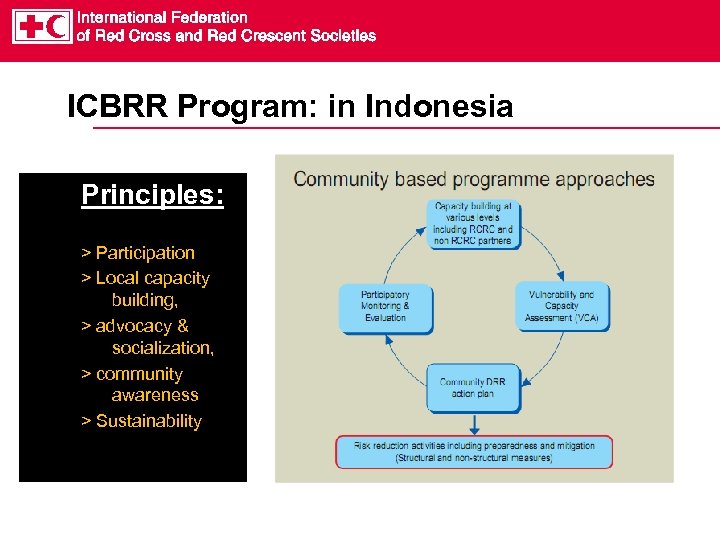 ICBRR Program: in Indonesia Principles: > Participation > Local capacity building, > advocacy & socialization, > community awareness > Sustainability
ICBRR Program: in Indonesia Principles: > Participation > Local capacity building, > advocacy & socialization, > community awareness > Sustainability
 Best practices from ICBRR in Jakarta LESS resilience and MORE vulnerable MORE resilience and LESS vulnerable
Best practices from ICBRR in Jakarta LESS resilience and MORE vulnerable MORE resilience and LESS vulnerable
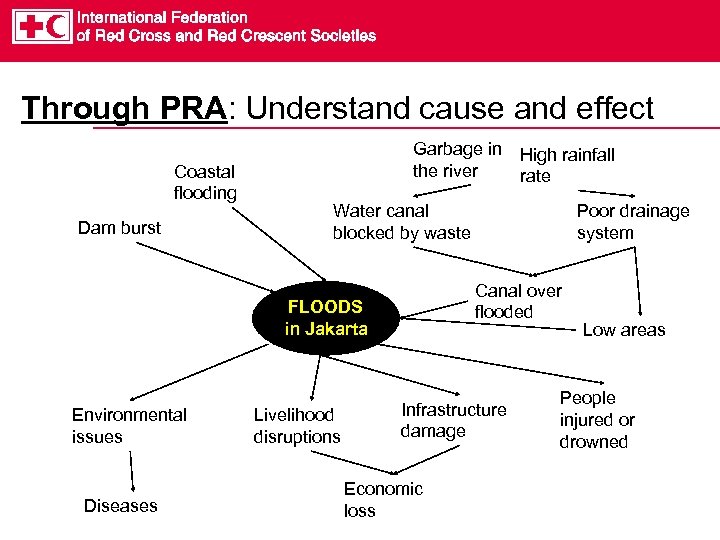 Through PRA: Understand cause and effect Coastal flooding Dam burst Garbage in the river Water canal blocked by waste Diseases Livelihood disruptions Poor drainage system Canal over flooded FLOODS in Jakarta Environmental issues High rainfall rate Infrastructure damage Economic loss Low areas People injured or drowned
Through PRA: Understand cause and effect Coastal flooding Dam burst Garbage in the river Water canal blocked by waste Diseases Livelihood disruptions Poor drainage system Canal over flooded FLOODS in Jakarta Environmental issues High rainfall rate Infrastructure damage Economic loss Low areas People injured or drowned
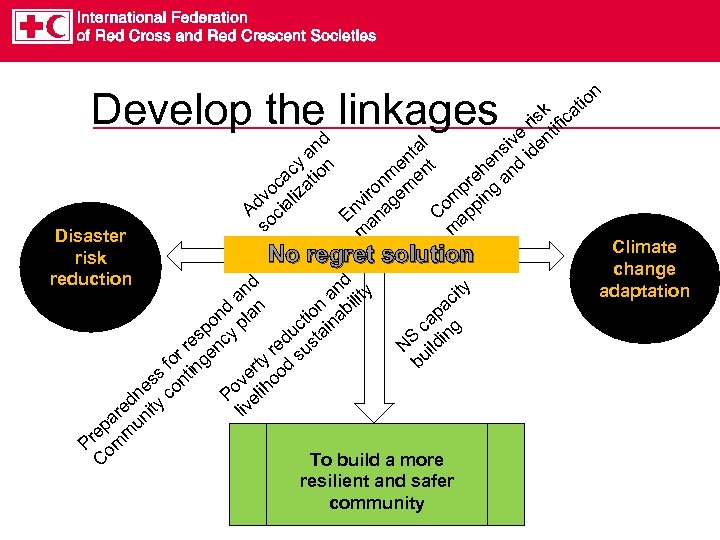 Develop the linkages Disaster risk reduction k ris tific e d l iv den a an ns d i nt t e y n e m en ac tio eh an n pr ng oc liza ro gem i dv ia om ppi nv na A c C a E a so m m No regret solution nd ity nd ty a il a ci n a nd lan io nab t i ap g o p c uc ta sp cy S ldin d s e n N ui re su r r ge y d o n b t f s nti er oo s ov lih ne co P e ed ity liv r n a ep mu Pr om To build a more C resilient and safer community n io at Climate change adaptation
Develop the linkages Disaster risk reduction k ris tific e d l iv den a an ns d i nt t e y n e m en ac tio eh an n pr ng oc liza ro gem i dv ia om ppi nv na A c C a E a so m m No regret solution nd ity nd ty a il a ci n a nd lan io nab t i ap g o p c uc ta sp cy S ldin d s e n N ui re su r r ge y d o n b t f s nti er oo s ov lih ne co P e ed ity liv r n a ep mu Pr om To build a more C resilient and safer community n io at Climate change adaptation
 What have been done: the linkages (1) 1. Preparedness for response and community contigency plan: § Water rescue training § Disaster preparedness in school § CB early warning system § Safety evacuation route, drills and simulation 2. Environmental Management § Green and clean promotion § Waste management (3 R), compost making
What have been done: the linkages (1) 1. Preparedness for response and community contigency plan: § Water rescue training § Disaster preparedness in school § CB early warning system § Safety evacuation route, drills and simulation 2. Environmental Management § Green and clean promotion § Waste management (3 R), compost making
 What have been done: the linkages (2) 3. Comprehensive risk mapping and assessment § Include climate risk into HVCA 4. Advocacy and socialization § Endorsement by local authority and other key stakeholders § Campaign 5. NS Capacity building § Well-prepared National Society: technical ability, volunteer mobilization, good governance, sound financial system
What have been done: the linkages (2) 3. Comprehensive risk mapping and assessment § Include climate risk into HVCA 4. Advocacy and socialization § Endorsement by local authority and other key stakeholders § Campaign 5. NS Capacity building § Well-prepared National Society: technical ability, volunteer mobilization, good governance, sound financial system
 What have been done: the linkages (3) 6. Poverty reduction and livelihood sustainability § Microfinance: Establishment of saving and loan cooperation (transfer risk and protect livelihoods) § Community training on business planning and business plan writing § Community life skill training: small enterprises using used materials.
What have been done: the linkages (3) 6. Poverty reduction and livelihood sustainability § Microfinance: Establishment of saving and loan cooperation (transfer risk and protect livelihoods) § Community training on business planning and business plan writing § Community life skill training: small enterprises using used materials.
 Thanks – terima kasih www. ifrc. org
Thanks – terima kasih www. ifrc. org


