2dcd503c31e53f2a1e665650d7d2dbd3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28

Session 1 Background and Legislative Requirements 1

Clinical. Trials. gov Background Dr. Deborah A. Zarin 2

Clinical. Trials. gov Team Jerry Sheehan Director • Deborah Zarin Project Leads • Annice Bergeris • Nicholas Ide • Alison Robbins • Tony Tse • Rebecca Williams Quality Assurance • John Frye • Cherryl Macalintal • Alex Valentine Betsy Humphreys Systems Development • Jane Fun • John Gillen • Alex Kostyukovsky • Russell Loane • Allison Yu Domain Expert • William Harlan Administration • Tamia Whitfield 3

Ethical and Scientific Rationale for Increased Clinical Trial Transparency • Subjects put themselves at risk • Subject’s right to be informed – All available options, including ongoing trials – Previous research, including completed trials • Avoid redundant trials • Support Evidenced-Based Medicine (EBM) • Detect reporting problems – Lack of publication – Unexplained changes to protocol 4

Recent Events: Lack of Transparency in Clinical Research 5
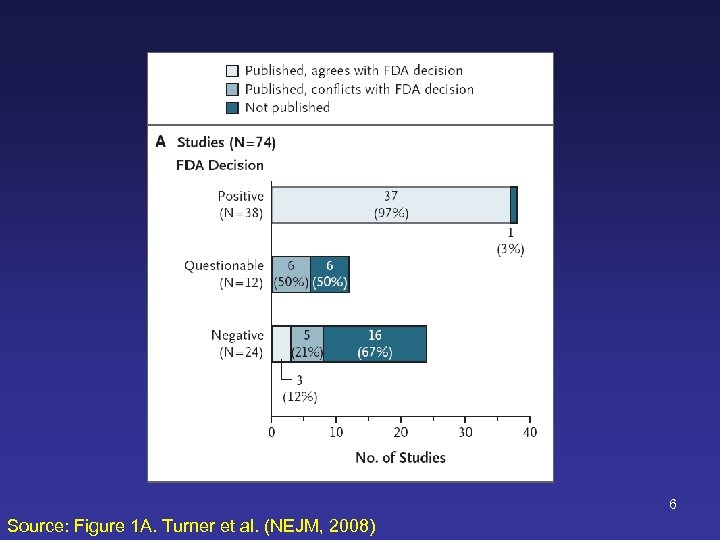
6 Source: Figure 1 A. Turner et al. (NEJM, 2008)

The investigation was launched following concerns… • …although the ENHANCE trial ended in April 2006, the data had not yet been released. • …[the sponsors] did not register the clinical trial in a timely manner. • …[the sponsors] attempted to change the study endpoints, and thus the study results, prior to the public release of the results. 7

8 Source: Silverstein FE et al. JAMA. 2000 Sep 13; 284(10): 1247 -55.
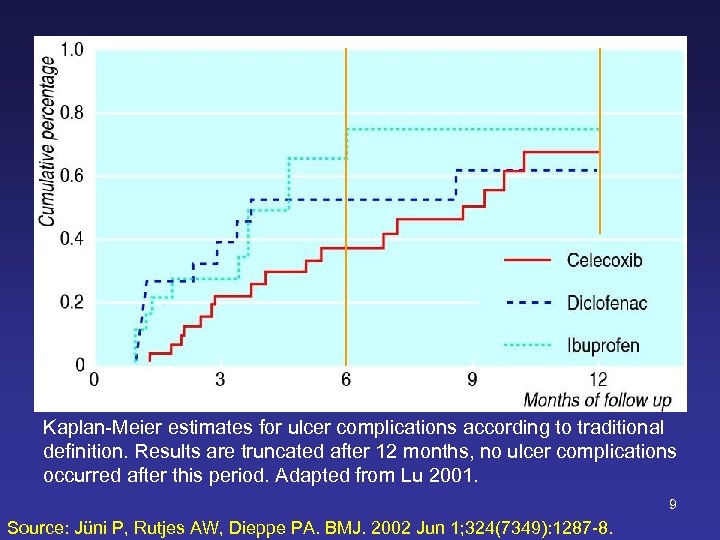
Kaplan-Meier estimates for ulcer complications according to traditional definition. Results are truncated after 12 months, no ulcer complications occurred after this period. Adapted from Lu 2001. 9 Source: Jüni P, Rutjes AW, Dieppe PA. BMJ. 2002 Jun 1; 324(7349): 1287 -8.

Clinical. Trials. gov • Prospective registry • Interventional and observational “trials” – Approved by IRB (or equivalent) – Conform to regulations of national health authorities • All sponsor types • All intervention types • Summary of key protocol items – Consistent with ICMJE and WHO • Links to publications, other info • Does not include unpublished results 10
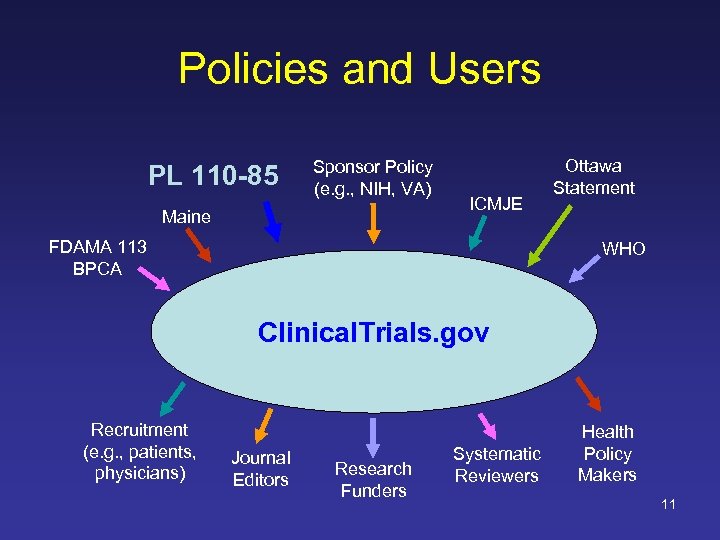
Policies and Users PL 110 -85 Sponsor Policy (e. g. , NIH, VA) Maine ICMJE FDAMA 113 BPCA Ottawa Statement WHO Clinical. Trials. gov Recruitment (e. g. , patients, physicians) Journal Editors Research Funders Systematic Reviewers Health Policy Makers 11

International Registries and Number of Trials (as of 2/4/08) Clinical. Trials. gov 50, 564 ISRCTN (UK) 6, 514 Australian New Zealand Clinical Trial Registry (ANZCTR) Netherlands Trial Registry 1, 973 UMIN Clinical Trials Registry (Japan) 943 1, 111 Chinese Clinical Trial Register (Chi. CTR) 34 Clinical Trials Registry – India (CTRI) 16 12

Characteristics of Clinical. Trials. gov • Web-based registration system (PRS) • Register through organizational accounts – Key part of validation • XML data upload (<20% records) • Data are dynamic—”data provider” can modify data at any time – Changes are tracked 13

Homepage - Clinical. Trials. gov 14
15
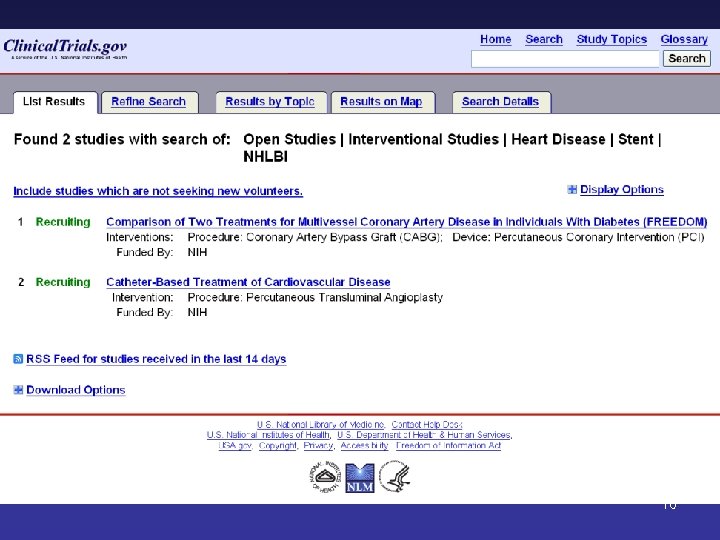
16

http: //Clinical. Trials. gov/archive 17

18

Clinical. Trials. gov General Statistics 19
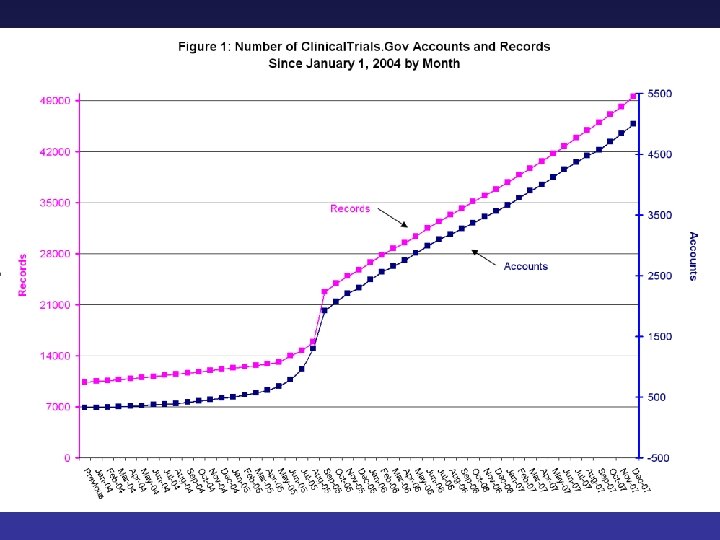
20
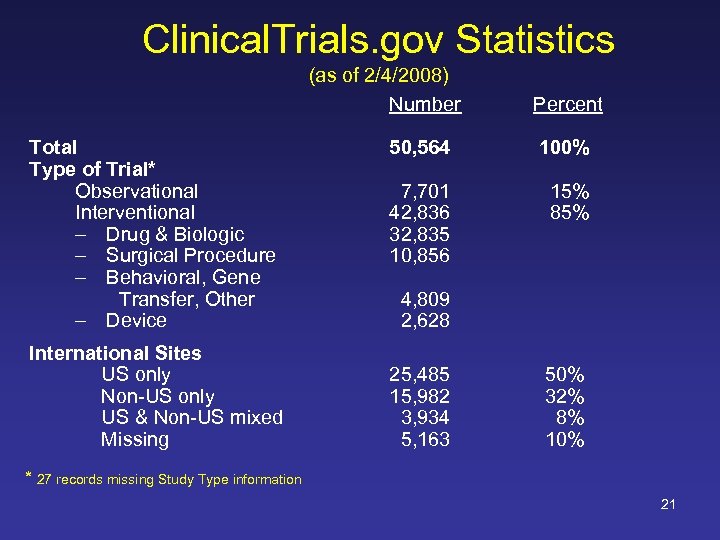
Clinical. Trials. gov Statistics (as of 2/4/2008) Number Total Type of Trial* Observational Interventional – Drug & Biologic – Surgical Procedure – Behavioral, Gene Transfer, Other – Device International Sites US only Non-US only US & Non-US mixed Missing Percent 50, 564 7, 701 42, 836 32, 835 10, 856 100% 15% 85% 4, 809 2, 628 25, 485 15, 982 3, 934 5, 163 50% 32% 8% 10% * 27 records missing Study Type information 21
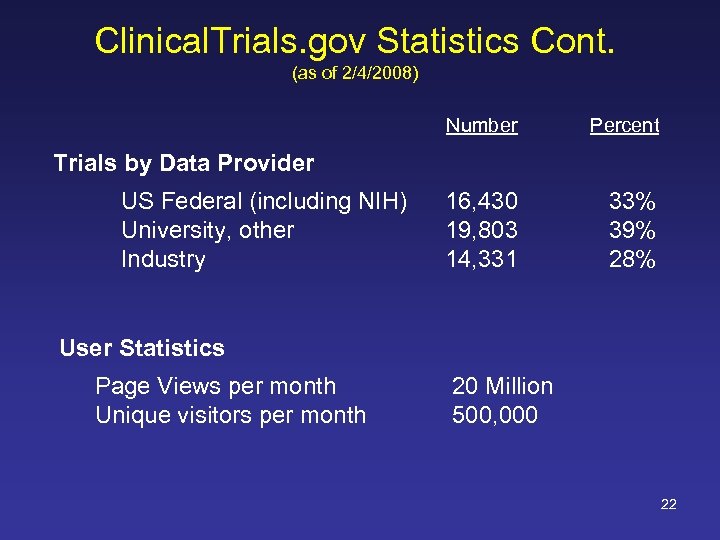
Clinical. Trials. gov Statistics Cont. (as of 2/4/2008) Number Percent 16, 430 19, 803 14, 331 33% 39% 28% Trials by Data Provider US Federal (including NIH) University, other Industry User Statistics Page Views per month Unique visitors per month 20 Million 500, 000 22

Organizational Accounts Total 4, 792 – Fed accounts 71 – NIH accounts 26 – Industry 1, 783 – Other 2, 912 23

Validation of Data for Registry • Issues – Quality Assurance: Are the entries as accurate and informative as possible? – Validation (w/o access to protocols): Is the fundamental information true? • QA Process at Clinical. Trials. gov – System of automated and manual checks – Staff works with data provider to correct/improve records – Links inserted 24

25
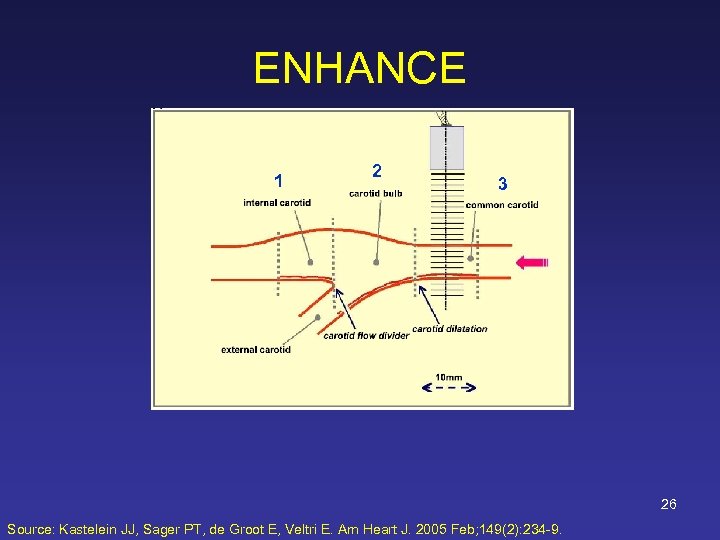
ENHANCE 1 2 3 26 Source: Kastelein JJ, Sager PT, de Groot E, Veltri E. Am Heart J. 2005 Feb; 149(2): 234 -9.
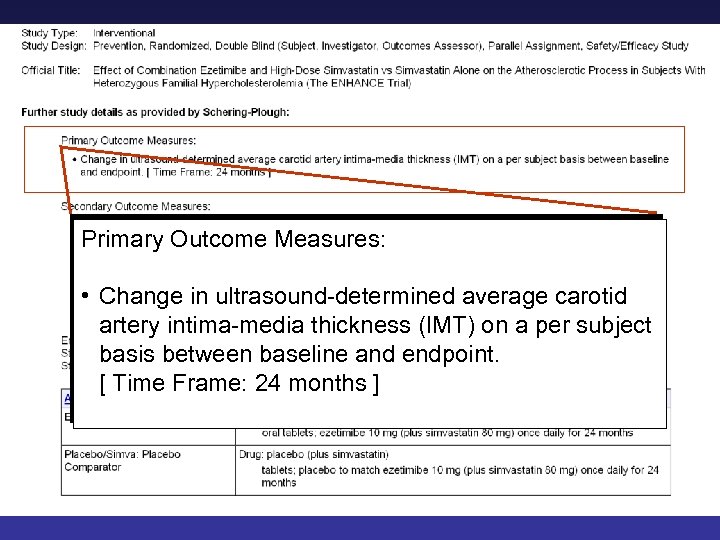
Primary Outcome Measures: • • Change in ultrasound-determined average carotid artery intima-media thickness (IMT) on a per subject basis between baseline and endpoint. [ Time Frame: 24 months ] 27

Legislative Requirements Jerry Sheehan 28
2dcd503c31e53f2a1e665650d7d2dbd3.ppt