c886b470b5b9ca946c1c6e08357d5bcf.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17

Serving Older Adults and Individuals with Disabilities through No Wrong Door Aging and Disability I&R Professionals – NASUAD January 21, 2015
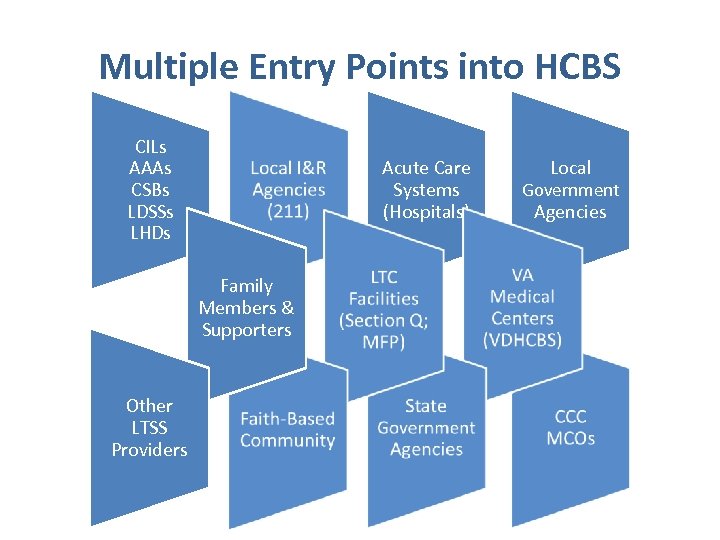
Multiple Entry Points into HCBS CILs AAAs CSBs LDSSs LHDs Acute Care Systems (Hospitals) Family Members & Supporters Other LTSS Providers Local Government Agencies

Challenges to Multiple Entry Points § People fall through the cracks between the referral point and the access/enrollment into a service § People must provide same information to each provider (often details are left out) § Duplication of information collected § Referrals are often based on Coordinator’s knowledge, not on individual choice § No common community record to track what supports an individual may have § Most providers have their own Case Management system
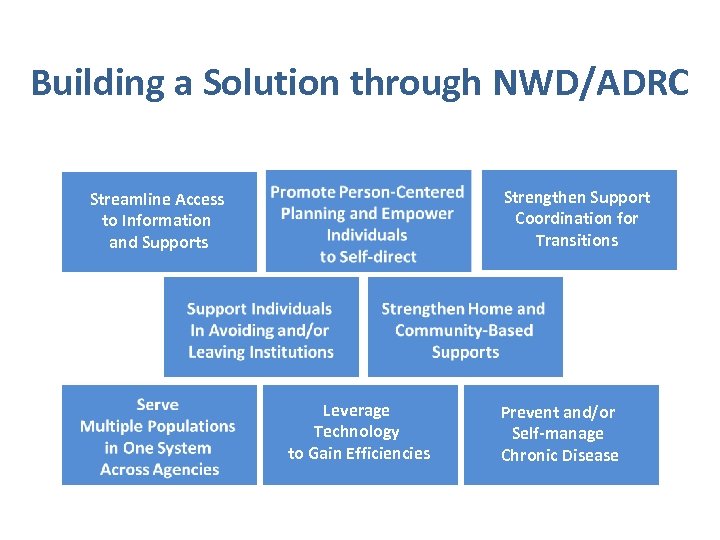
Building a Solution through NWD/ADRC Strengthen Support Coordination for Transitions Streamline Access to Information and Supports Leverage Technology to Gain Efficiencies Prevent and/or Self-manage Chronic Disease

Virtual Single Point of Entry for Accessing HCBS across Virginia § Older Adults § Individuals with Disabilities § Family Caregivers § Public and Private § Statewide Initiative

No Wrong Door Network A virtual statewide network of long-term care providers, connected by a web-based system that enables partners to: 1. Share client data in a secure web-based system 2. Make electronic automated referrals between providers 3. Track individual progress 4. Access reports related to referrals

Communication, Referral, Information, and Assistance (CRIA) CRIA HCBS 7
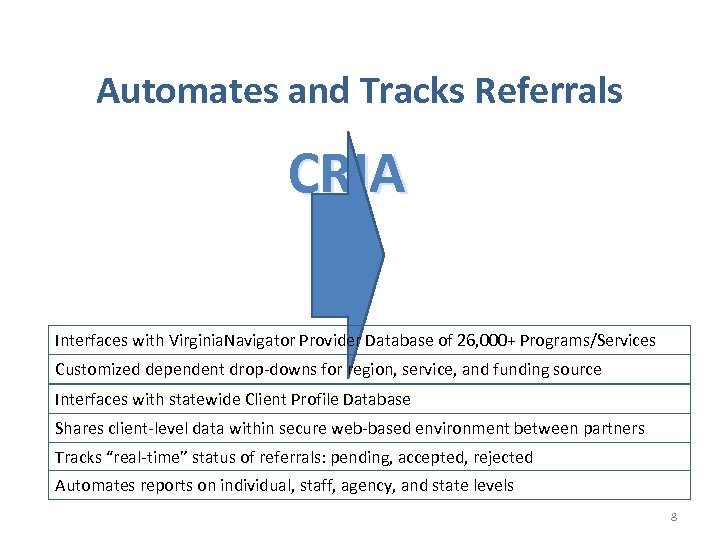
Automates and Tracks Referrals CRIA Interfaces with Virginia. Navigator Provider Database of 26, 000+ Programs/Services Customized dependent drop-downs for region, service, and funding source Interfaces with statewide Client Profile Database Shares client-level data within secure web-based environment between partners Tracks “real-time” status of referrals: pending, accepted, rejected Automates reports on individual, staff, agency, and state levels 8
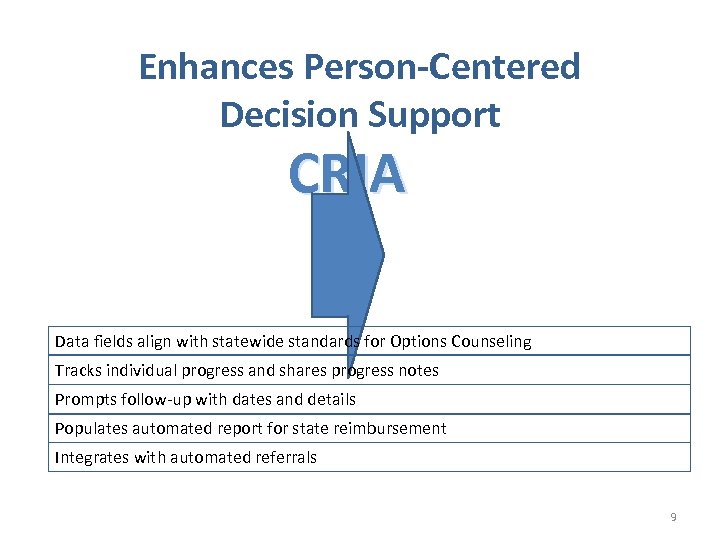
Enhances Person-Centered Decision Support CRIA Data fields align with statewide standards for Options Counseling Tracks individual progress and shares progress notes Prompts follow-up with dates and details Populates automated report for state reimbursement Integrates with automated referrals 9
Supports Transitions CRIA Integrates with Care Transition Module Automates reports for CMS Reimbursement Tracks quality assurance measures related to readmission Tracks Section Q protocol and response rates Integrates with automated referrals to MFP Transition Coordination Providers (TCPs) 10
Provides Universal Assessment CRIA Integrates with Virginia’s Uniform Assessment Instrument Expedites eligibility process Can be downloaded to laptops and used in remote areas of the state Assessment areas include: Current formal services; Financial resources; Physical environment; ADLs/IADLs; Medical Admissions; Diagnoses; Medications List; Sensory functions; Nutrition; Cognitive Function; Behavior Patterns and Emotional Status 11
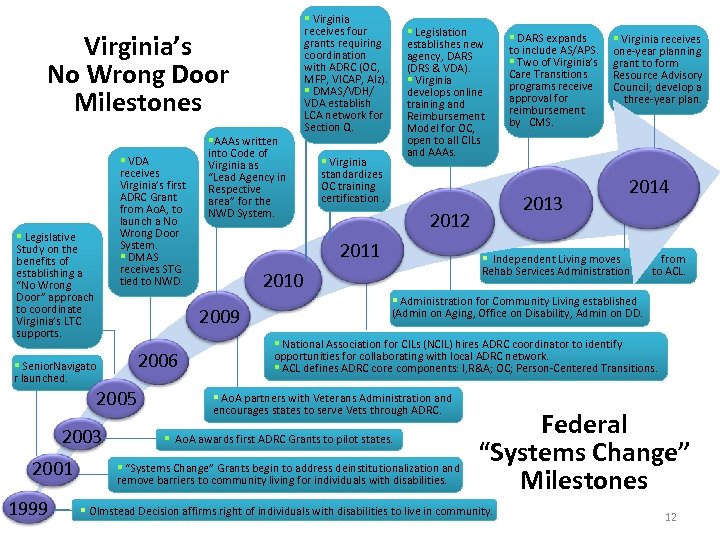
Virginia’s No Wrong Door Milestones § VDA receives Virginia’s first ADRC Grant from Ao. A, to launch a No Wrong Door System. § DMAS receives STG tied to NWD. § Legislative Study on the benefits of establishing a “No Wrong Door” approach to coordinate Virginia’s LTC supports. 2006 2005 2003 1999 § Legislation establishes new agency, DARS (DRS & VDA). § Virginia develops online training and Reimbursement Model for OC, open to all CILs and AAAs. § Virginia standardizes OC training certification. § DARS expands to include AS/APS. § Two of Virginia’s Care Transitions programs receive approval for reimbursement by CMS. 2013 2012 2011 § Virginia receives one-year planning grant to form Resource Advisory Council; develop a three-year plan. 2014 § Independent Living moves Rehab Services Administration 2010 2009 § Senior. Navigato r launched. 2001 §AAAs written into Code of Virginia as “Lead Agency in Respective area” for the NWD System. § Virginia receives four grants requiring coordination with ADRC (OC, MFP, VICAP, Alz). § DMAS/VDH/ VDA establish LCA network for Section Q. from to ACL. § Administration for Community Living established (Admin on Aging, Office on Disability, Admin on DD. § National Association for CILs (NCIL) hires ADRC coordinator to identify opportunities for collaborating with local ADRC network. § ACL defines ADRC core components: I, R&A; OC; Person-Centered Transitions. § Ao. A partners with Veterans Administration and encourages states to serve Vets through ADRC. § Ao. A awards first ADRC Grants to pilot states. § “Systems Change” Grants begin to address deinstitutionalization and remove barriers to community living for individuals with disabilities. Federal “Systems Change” Milestones § Olmstead Decision affirms right of individuals with disabilities to live in community. 12
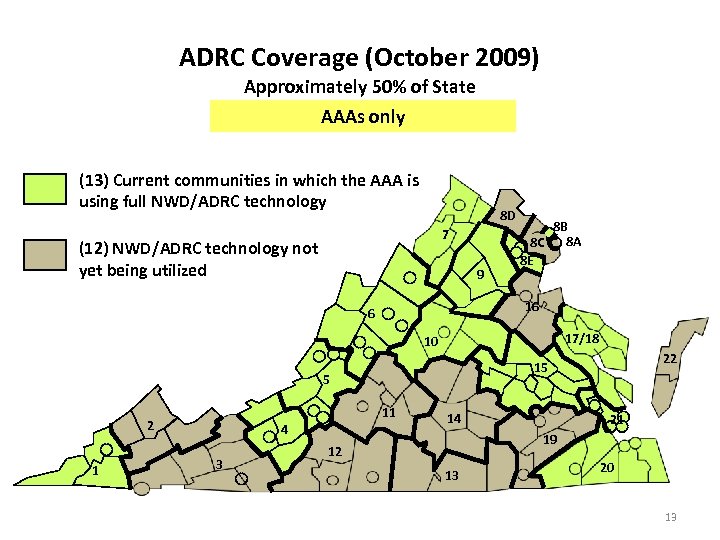
ADRC Coverage (October 2009) Approximately 50% of State AAAs only (13) Current communities in which the AAA is using full NWD/ADRC technology 8 D 7 (12) NWD/ADRC technology not yet being utilized 9 8 B 8 A 8 C 8 E 16 6 17/18 10 5 2 1 11 4 3 22 15 14 21 19 12 13 20 13
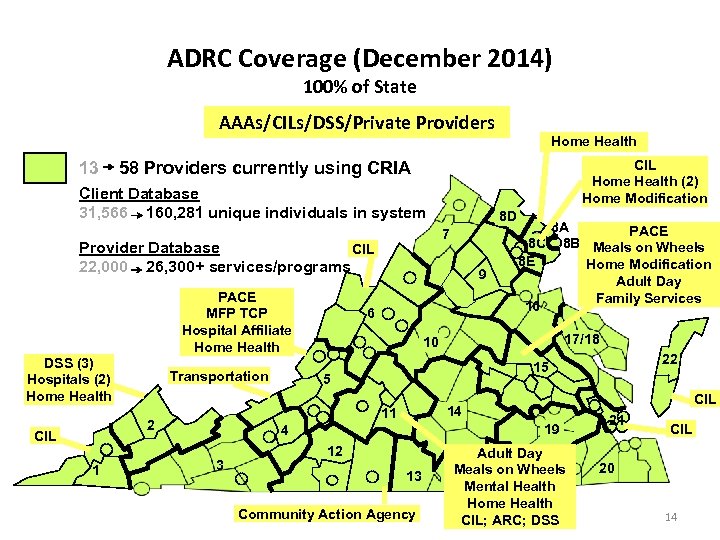
ADRC Coverage (December 2014) 100% of State AAAs/CILs/DSS/Private Providers 13 CIL Home Health (2) Home Modification 58 Providers currently using CRIA Client Database 31, 566 160, 281 unique individuals in system PACE MFP TCP Hospital Affiliate Home Health DSS (3) Hospitals (2) Home Health Transportation 1 9 6 17/18 22 15 5 CIL 14 19 4 3 8 A PACE 8 C 8 B Meals on Wheels 8 E Home Modification Adult Day Family Services 16 10 11 2 8 D 7 Provider Database CIL 22, 000 26, 300+ services/programs CIL Home Health 12 13 Community Action Agency Adult Day Meals on Wheels Mental Health Home Health CIL; ARC; DSS 21 CIL 20 14
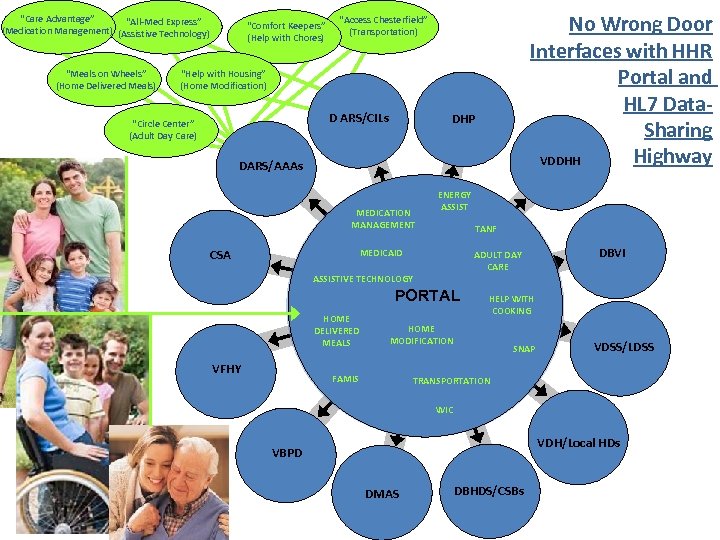
“Care Advantage” “All-Med Express” (Medication Management) (Assistive Technology) “Meals on Wheels” (Home Delivered Meals) “Comfort Keepers” (Help with Chores) No Wrong Door Interfaces with HHR Portal and HL 7 Data. Sharing Highway VDDHH “Access Chesterfield” (Transportation) “Help with Housing” (Home Modification) D ARS/CILs “Circle Center” (Adult Day Care) DHP DARS/AAAs MEDICATION MANAGEMENT CSA ENERGY ASSIST TANF MEDICAID ADULT DAY CARE ASSISTIVE TECHNOLOGY HOME DELIVERED MEALS VFHY PORTAL Portal HELP WITH COOKING HOME MODIFICATION FAMIS DBVI SNAP VDSS/LDSS TRANSPORTATION WIC VDH/Local HDs VBPD DMAS DBHDS/CSBs

NWD/ADRC: Evaluating Outcomes § Integrating evaluation into process using Technology to Document and Demonstrate § Tracking Community Tenure via Living Environment § Increase in individuals served § Increased understanding of options § Increased knowledge of caregiver supports § Documenting gaps and unmet needs in HCBS § Successfully supporting individuals in the environment of their choice

Serving Older Adults and Individuals with Disabilities through No Wrong Door Aging and Disability I&R Professionals – NASUAD January 21, 2015 Erika Yssel No Wrong Door Expansion Specialist Department for Aging and Rehabilitative Services Cell: (804) 385 -3645 Erika. Yssel@dars. virginia. gov
c886b470b5b9ca946c1c6e08357d5bcf.ppt