d9bd815d62b95c8e65f51c464dcfa2fe.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21

Services Marketing MBA-SEM-III TERM-01 -2012 MODULE-03

Learning Objectives ► To understand that effective pricing is central to financial success ► To understand the relationship between price and customer costs ► To understand value strategies for services pricing ► To understand the principle of revenue management
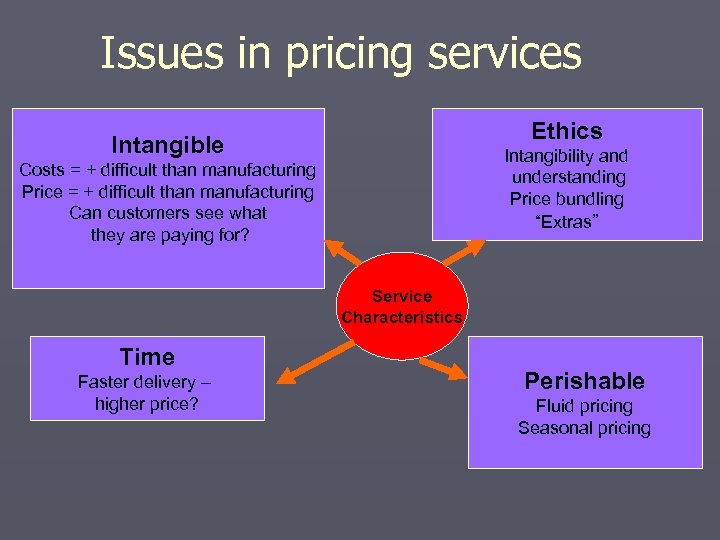
Issues in pricing services Ethics Intangible Intangibility and understanding Price bundling “Extras” Costs = + difficult than manufacturing Price = + difficult than manufacturing Can customers see what they are paying for? Service Characteristics Time Faster delivery – higher price? Perishable Fluid pricing Seasonal pricing

What Makes Service Pricing Strategy Different (and Difficult)? ► No ownership of services--hard for firms to calculate ► Intangibility of services makes it hard for customers to evaluate--what are they getting in return financial costs of creating an intangible performance ► Variability of inputs and outputs--how can firms define a “unit of service” and establish basis for pricing? for their money? ► Importance of time factor--same service may have ► Delivery through physical or electronic channels-- more value to customers when delivered faster ► Service performance are ephemeral - demands fluctuation may create differences in perceived value

Objectives of Pricing Strategies ► Revenue and profit objectives § Seek profit § Cover costs ► Patronage and user base-related objectives § Build demand § Build a user base
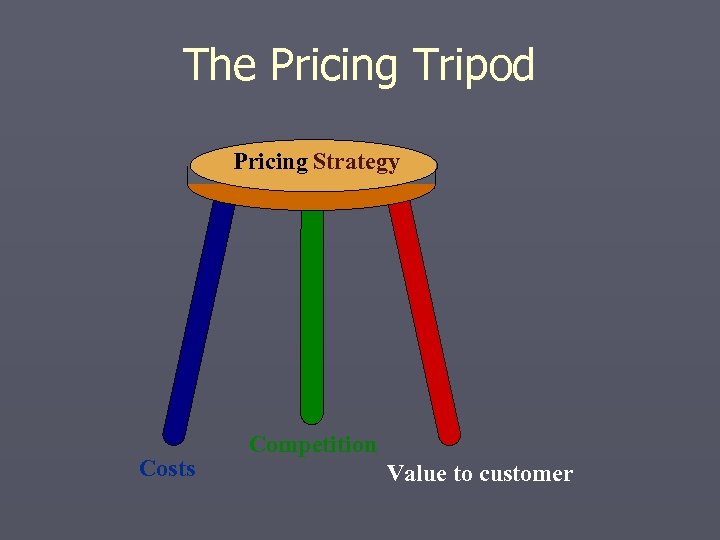
The Pricing Tripod Pricing Strategy Costs Competition Value to customer

Three Main Approaches to Pricing ► Cost-Based Pricing § Set prices relative to financial costs- (problem: defining costs) Link resource expenses to: ► variety of products produced ► complexity of products ► demands made by individual customers ► Competition-Based Pricing § Monitor competitors’ pricing strategy-especially if service lacks differentiation § Who is the price leader? (one firm sets the pace) ► Value-Based § Relate price to value perceived by customer

How do you define VALUE?

Customers’ definition of value Zeithaml (1988) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Value is low price Value is whatever I want in a product Value is the quality I get for the price I pay Value is what I get for what I give Net value = Benefits - cost

Enhancing Gross Value ► Pricing Strategies to Reduce Uncertainty § service guarantees § benefit-driven (pricing that aspect of service that creates value) § flat rate (quoting a fixed price in advance) ► Relationship Pricing § non-price incentives § discounts for volume purchases § discounts for purchasing multiple services ► Low-cost Leadership § Convince customers not to equate price with quality § Must keep economic costs low to ensure profitability at low price
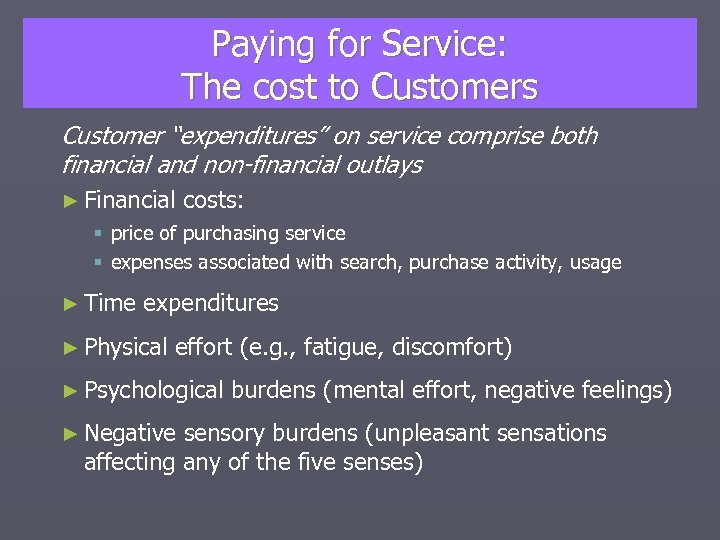
Paying for Service: The cost to Customers Customer “expenditures” on service comprise both financial and non-financial outlays ► Financial costs: § price of purchasing service § expenses associated with search, purchase activity, usage ► Time expenditures ► Physical effort (e. g. , fatigue, discomfort) ► Psychological ► Negative burdens (mental effort, negative feelings) sensory burdens (unpleasant sensations affecting any of the five senses)

Trading off monetary and nonmonetary costs Which clinic would you patronize if you needed a chest x-ray (assuming all three clinics offer good quality) ? Clinic A Clinic B Clinic C = Price $45 = Located 1 hour away by car or transit = Next available appointment is in 3 weeks = Hours: Monday – Friday, 9 am – 5 pm = Estimated wait at clinic is about 2 hours = Price $85 = Located 15 min away by car or transit = Next available appointment is in 1 week = Hours: Monday – Friday, 8 am – 10 pm = Estimated wait at clinic is about 30 45 minutes = Price $125 = Located next to your office or college = Next appointment is in 1 day = Hours: Mo –Sat, 8 am – 10 pm = By appointment estimated wait at clinic is about 0 to 15 minutes

Increasing Net Value by Reducing Non-financial Costs of Service ► Reduce time costs of service at each stage ► Minimize unwanted psychological costs of service ► Eliminate unwanted physical costs of service ► Decrease unpleasant sensory costs of service

Revenue Management: Maximizing Revenue from Available Capacity at a Given Time ► Based on price customization - charging different customers (value segments) different prices for same product ► Useful in dynamic markets where demand can be divided into different price buckets according to price sensitivity ► Requires rate fences to prevent customers in one value segment from purchasing more cheaply than willing to pay ► RM uses mathematical models to examine historical data and real time information to determine § what prices to charge within each price bucket § how many service units to allocate to each bucket
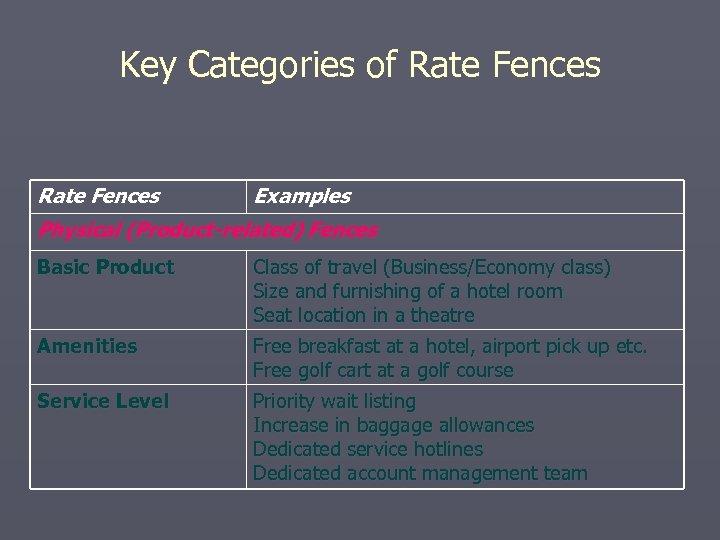
Key Categories of Rate Fences Examples Physical (Product-related) Fences Basic Product Class of travel (Business/Economy class) Size and furnishing of a hotel room Seat location in a theatre Amenities Free breakfast at a hotel, airport pick up etc. Free golf cart at a golf course Service Level Priority wait listing Increase in baggage allowances Dedicated service hotlines Dedicated account management team
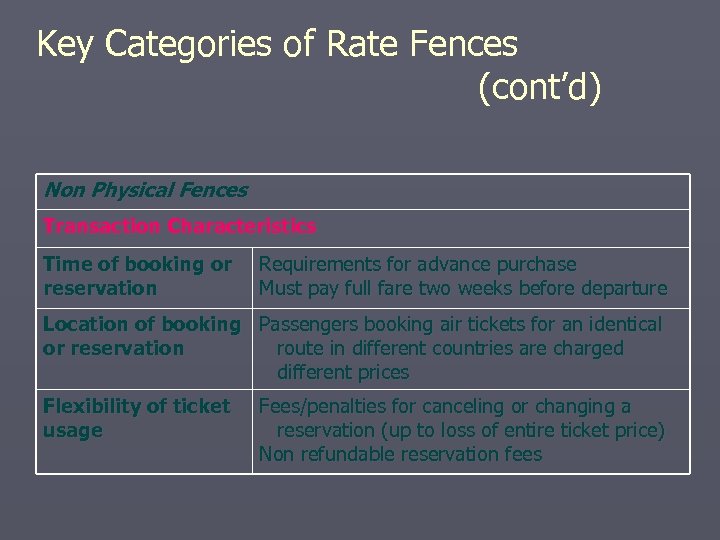
Key Categories of Rate Fences (cont’d) Non Physical Fences Transaction Characteristics Time of booking or reservation Requirements for advance purchase Must pay full fare two weeks before departure Location of booking Passengers booking air tickets for an identical or reservation route in different countries are charged different prices Flexibility of ticket usage Fees/penalties for canceling or changing a reservation (up to loss of entire ticket price) Non refundable reservation fees
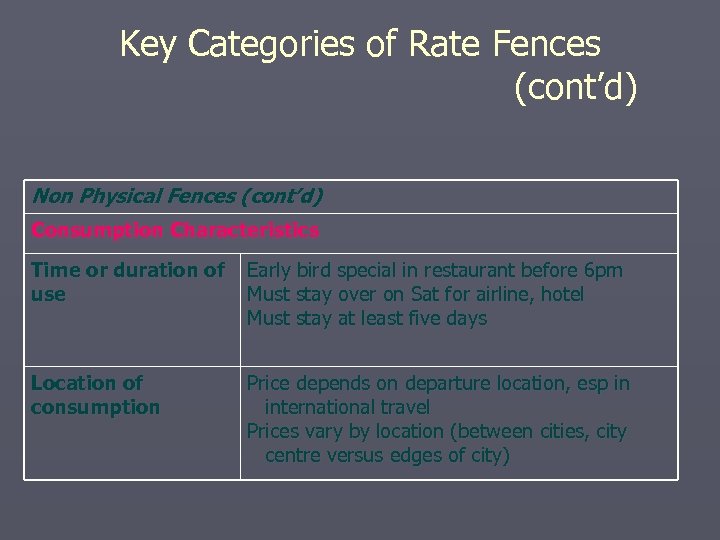
Key Categories of Rate Fences (cont’d) Non Physical Fences (cont’d) Consumption Characteristics Time or duration of use Early bird special in restaurant before 6 pm Must stay over on Sat for airline, hotel Must stay at least five days Location of consumption Price depends on departure location, esp in international travel Prices vary by location (between cities, city centre versus edges of city)
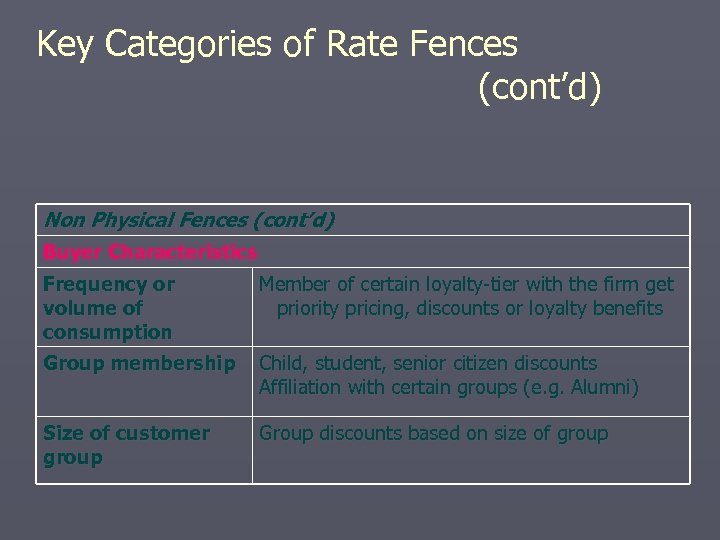
Key Categories of Rate Fences (cont’d) Non Physical Fences (cont’d) Buyer Characteristics Frequency or volume of consumption Member of certain loyalty-tier with the firm get priority pricing, discounts or loyalty benefits Group membership Child, student, senior citizen discounts Affiliation with certain groups (e. g. Alumni) Size of customer group Group discounts based on size of group
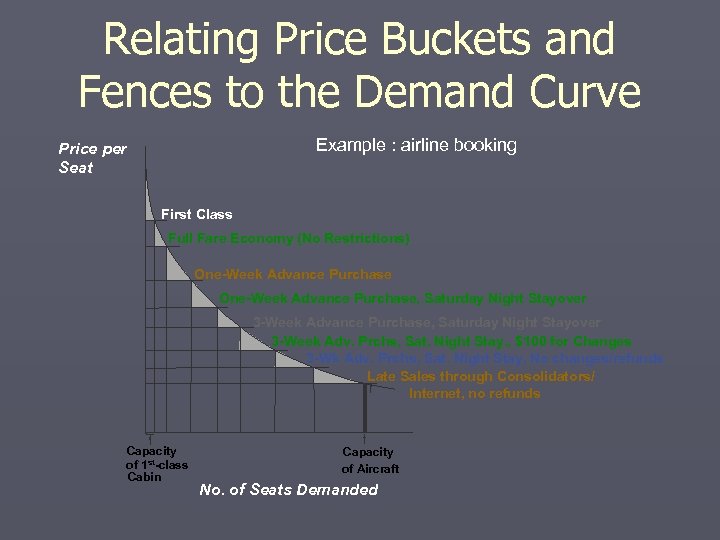
Relating Price Buckets and Fences to the Demand Curve Example : airline booking Price per Seat First Class Full Fare Economy (No Restrictions) One-Week Advance Purchase, Saturday Night Stayover 3 -Week Adv. Prchs, Sat. Night Stay. , $100 for Changes 3 -Wk Adv. Prchs, Sat. Night Stay, No changes/refunds Late Sales through Consolidators/ Internet, no refunds Capacity of 1 st-class Cabin Capacity of Aircraft No. of Seats Demanded

Seven Issues to consider for a Pricing Strategy 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. How much should be charged for this service? What should be the basis of pricing? Who should collect payment? Where should payment be made? When should payment be made? How should price be communicated to the target market?

Questions ► What The three imp factors of service pricing. ► How the customer perceives value of service. ► What are the important factors of revenue management in service Pricing. ► What are three broad categories of price fencing. ► What the seven key issues in service pricing.
d9bd815d62b95c8e65f51c464dcfa2fe.ppt