 Service Supply Relationships MD 254 Service Operations Professor Joy Field
Service Supply Relationships MD 254 Service Operations Professor Joy Field
 Service Supply Chain Characteristics n n There is a customer-supplier duality due to the co-production nature of services. The service provider typically acts as an agent for the customer when dealing with outside suppliers. Service capacity is analogous to inventory. Customer supplied inputs can vary in quality.
Service Supply Chain Characteristics n n There is a customer-supplier duality due to the co-production nature of services. The service provider typically acts as an agent for the customer when dealing with outside suppliers. Service capacity is analogous to inventory. Customer supplied inputs can vary in quality.
 Sources of Value in Service Supply Relationships n n Bi-directional optimization Managing Productive Capacity q q q n Transfer: make knowledge available (e. g. FAQ page) Replacement: substitute technology for server (e. g. digital blood pressure device, self-healing technologies) Embellishment: enable self-service and value-capture by teaching (e. g. simple maintenance, facilitating customers extracting full value from products or services) Management of perishability
Sources of Value in Service Supply Relationships n n Bi-directional optimization Managing Productive Capacity q q q n Transfer: make knowledge available (e. g. FAQ page) Replacement: substitute technology for server (e. g. digital blood pressure device, self-healing technologies) Embellishment: enable self-service and value-capture by teaching (e. g. simple maintenance, facilitating customers extracting full value from products or services) Management of perishability
 Outsourcing Services Benefits n n Allows the firm to focus on its core competences Service is cheaper to outsource than perform in-house if the ability to create and capture customer value is low Provides access to latest technology Leverage benefits of supplier economies of scale
Outsourcing Services Benefits n n Allows the firm to focus on its core competences Service is cheaper to outsource than perform in-house if the ability to create and capture customer value is low Provides access to latest technology Leverage benefits of supplier economies of scale
 Outsourcing Services Risks n n n Loss of direct control of quality Jeopardizes employee loyalty Exposure to data security and customer privacy issues Dependence on one supplier compromises future negotiation leverage Additional coordination expense and delays (i. e. , hidden costs) Atrophy of in-house capability to perform service
Outsourcing Services Risks n n n Loss of direct control of quality Jeopardizes employee loyalty Exposure to data security and customer privacy issues Dependence on one supplier compromises future negotiation leverage Additional coordination expense and delays (i. e. , hidden costs) Atrophy of in-house capability to perform service
 Managing Services Outsourcing Risks n n n Codify work Monitor work Develop metrics to measure process quality Establish price lock-in contracts Have multiple vendors
Managing Services Outsourcing Risks n n n Codify work Monitor work Develop metrics to measure process quality Establish price lock-in contracts Have multiple vendors
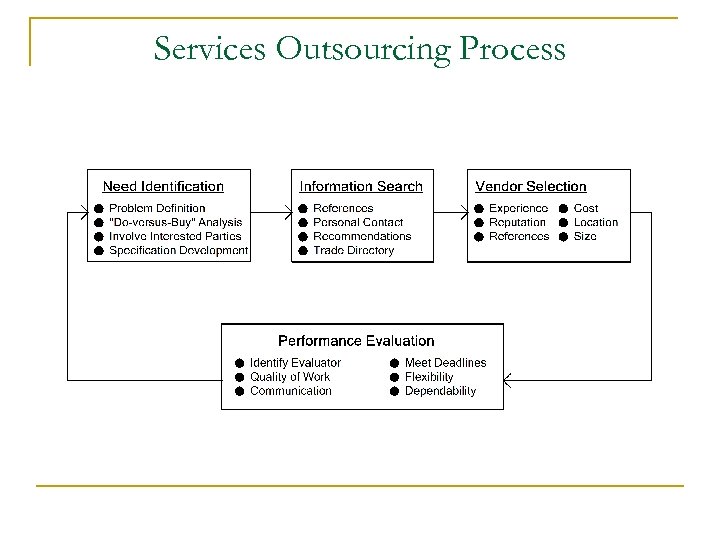 Services Outsourcing Process
Services Outsourcing Process