35d356b6907f5abafef130a27159a667.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 54
 Service Location Protocol and Net. Ware® Joe R. Doupnik, Professor of ECE jrd@cc. usu. edu Utah State University
Service Location Protocol and Net. Ware® Joe R. Doupnik, Professor of ECE jrd@cc. usu. edu Utah State University
 The Big Picture • “Finding things” on the Internet, pure IP, is a big tough problem • Search engines help find document content, but not services • Service Location Protocol (SLP) is an Internet standard to find services offered by devices on the network
The Big Picture • “Finding things” on the Internet, pure IP, is a big tough problem • Search engines help find document content, but not services • Service Location Protocol (SLP) is an Internet standard to find services offered by devices on the network
 The Players • Domain Name System (DNS) • Tables to relate IP names to numbers • Has a few other record types (MX for mail…) • Data types largely fixed by enormous installed base (no Internet without it) • Callers get limited information about a chosen machine, but which machine to ask about? • Global tree, servers can walk tree
The Players • Domain Name System (DNS) • Tables to relate IP names to numbers • Has a few other record types (MX for mail…) • Data types largely fixed by enormous installed base (no Internet without it) • Callers get limited information about a chosen machine, but which machine to ask about? • Global tree, servers can walk tree
 The Players (cont. ) • Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) • Has tables of many properties of machines, including SLP info • Has only local information • We obtain information about only our own machine and subnet • Data is extensible and flexible • Can couple to DNS for Dynamic DNS (address pools, etc. )
The Players (cont. ) • Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) • Has tables of many properties of machines, including SLP info • Has only local information • We obtain information about only our own machine and subnet • Data is extensible and flexible • Can couple to DNS for Dynamic DNS (address pools, etc. )
 The Players (cont. ) • Service Location Protocol (SLP) • Collects information from service devices • Automatic service discovery • Tells callers (User Agents) where to find the service and some detail about it • Acts as an information booth to direct callers to the right service upon demand • Does not spam the network with service announcements the way IPX™ SAPs do • But there are small advertisements • Language and character set sensitive
The Players (cont. ) • Service Location Protocol (SLP) • Collects information from service devices • Automatic service discovery • Tells callers (User Agents) where to find the service and some detail about it • Acts as an information booth to direct callers to the right service upon demand • Does not spam the network with service announcements the way IPX™ SAPs do • But there are small advertisements • Language and character set sensitive
 SLP Components • Service Agents (SA) encapsulate the name, address, and properties of services into SLP style packets • Directory Agents (DA) collect summary information from SAs and deal with clients. DAs are optional but useful holders of addresses etc. • User Agents (UA) help the user talk to SAs and DAs
SLP Components • Service Agents (SA) encapsulate the name, address, and properties of services into SLP style packets • Directory Agents (DA) collect summary information from SAs and deal with clients. DAs are optional but useful holders of addresses etc. • User Agents (UA) help the user talk to SAs and DAs
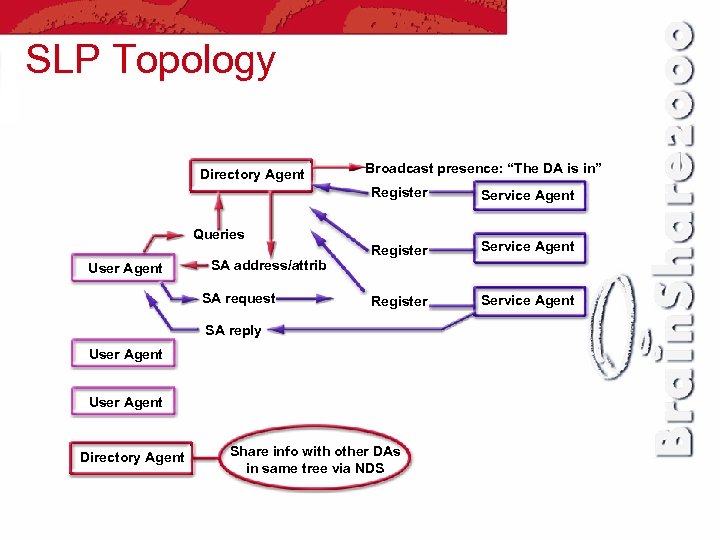 SLP Topology Directory Agent Broadcast presence: “The DA is in” Register Service Agent Queries User Agent SA address/attrib SA request SA reply User Agent Directory Agent Share info with other DAs in same tree via NDS
SLP Topology Directory Agent Broadcast presence: “The DA is in” Register Service Agent Queries User Agent SA address/attrib SA request SA reply User Agent Directory Agent Share info with other DAs in same tree via NDS
 SLP Components • SLP material is stored in Novell Directory Services® (NDS) • In NDS® create an SLP Directory Agent object, with optional SLP “Scope” objects • Net. Ware 5 servers activate a DA by loading SLPDA. NLM • Little to no configuration is necessary, but file SYS: ETCSLP. CFG can help in some cases • Scope info is similar to IPX SAP tables
SLP Components • SLP material is stored in Novell Directory Services® (NDS) • In NDS® create an SLP Directory Agent object, with optional SLP “Scope” objects • Net. Ware 5 servers activate a DA by loading SLPDA. NLM • Little to no configuration is necessary, but file SYS: ETCSLP. CFG can help in some cases • Scope info is similar to IPX SAP tables
 NWAdmn 32: DA, Scope Creation Create new object SLP object classes
NWAdmn 32: DA, Scope Creation Create new object SLP object classes
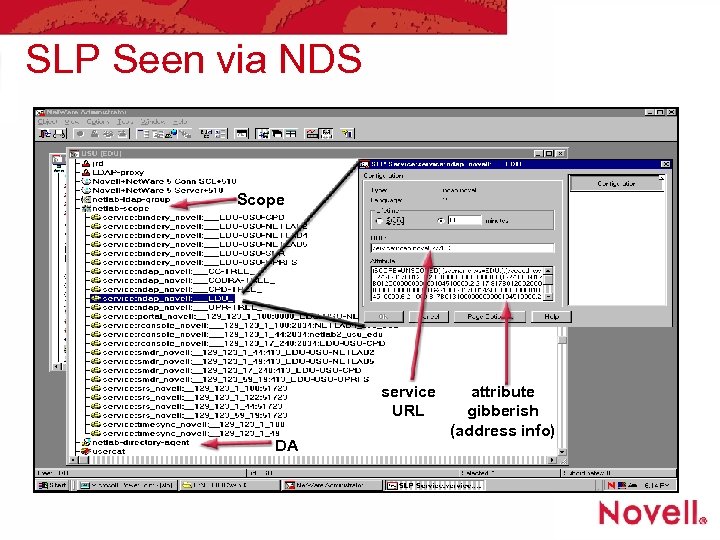 SLP Seen via NDS Scope service URL DA attribute gibberish (address info)
SLP Seen via NDS Scope service URL DA attribute gibberish (address info)
 How a Directory Agent Works • DA periodically advertises its own presence so that Service Agents can discover and register with it • A DA listens to the wire for unicast, multicast, and broadcast SLP messages carried in TCP or UDP over IP packets • DAs can discover other DAs via NDS (not in the RFCs) • It’s a DA union at work here
How a Directory Agent Works • DA periodically advertises its own presence so that Service Agents can discover and register with it • A DA listens to the wire for unicast, multicast, and broadcast SLP messages carried in TCP or UDP over IP packets • DAs can discover other DAs via NDS (not in the RFCs) • It’s a DA union at work here
 How DAs Work (cont’d) • Clients find DAs and ask for address and attributes of services • DA transactions can use security authenticators to limit access • DA advertising interval is once per minute • Use of broadcast and multicast will be a problem on large nets, must be dealt with
How DAs Work (cont’d) • Clients find DAs and ask for address and attributes of services • DA transactions can use security authenticators to limit access • DA advertising interval is once per minute • Use of broadcast and multicast will be a problem on large nets, must be dealt with
 SLP Scopes • “Scopes” are introduced to attempt localizing information on large sites • Scopes are name strings which UAs, DAs and SAs use to partition information • DAs pay attention to SAs in their list of Scopes, can attend to many scopes • Default scope is UNSCOPED (“”) • Unscoped DAs also hold info from scoped SAs • Scopes names are created by system manager
SLP Scopes • “Scopes” are introduced to attempt localizing information on large sites • Scopes are name strings which UAs, DAs and SAs use to partition information • DAs pay attention to SAs in their list of Scopes, can attend to many scopes • Default scope is UNSCOPED (“”) • Unscoped DAs also hold info from scoped SAs • Scopes names are created by system manager
 Client Configuration • Clients can be hard coded with the IP address (or name) of a DA, and with Scopes to use Client 32™ properties tables • Clients can be told the same information via DHCP—use DHCP tag types • 78, Directory Agent IP number • 79, Service Scope name • NCP queries to NDS yield the same info
Client Configuration • Clients can be hard coded with the IP address (or name) of a DA, and with Scopes to use Client 32™ properties tables • Clients can be told the same information via DHCP—use DHCP tag types • 78, Directory Agent IP number • 79, Service Scope name • NCP queries to NDS yield the same info
 Client Startup • The first thing Client 32 does is try to find a DA, and ask it about the address of a server offering NDS tree, context, and desired server • Only later does the login panel pop up • Several methods are available to locate this information
Client Startup • The first thing Client 32 does is try to find a DA, and ask it about the address of a server offering NDS tree, context, and desired server • Only later does the login panel pop up • Several methods are available to locate this information
 Client: Order of Query Mechanisms This order
Client: Order of Query Mechanisms This order
 Client: Specifying Scope Empty = “UNSCOPED”
Client: Specifying Scope Empty = “UNSCOPED”
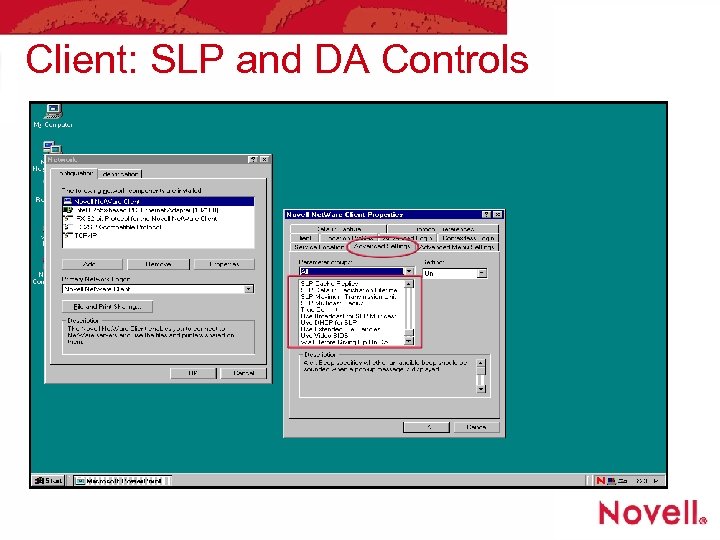 Client: SLP and DA Controls
Client: SLP and DA Controls
 Cheat Sheet for Packet Details • DCHP query, get reply of standard IP info • DHCP INFORM, get reply: IP of Directory Agent (DA) and Scope etc, slow with two second repeat delay • Multicast for any DA, get reply • Unicast to that DA for desired server, get reply: IP address
Cheat Sheet for Packet Details • DCHP query, get reply of standard IP info • DHCP INFORM, get reply: IP of Directory Agent (DA) and Scope etc, slow with two second repeat delay • Multicast for any DA, get reply • Unicast to that DA for desired server, get reply: IP address
 Cheat Sheet for Packet Details • If mixed IP/IPX client then do IPX SAP “query nearest file server” in case server speaks only IPX • Unicast again to that DA for selected server’s SLP attributes, get reply with IP address and port • DNS query for Tree. IP-domainname (but why? ) • Start connection to target server
Cheat Sheet for Packet Details • If mixed IP/IPX client then do IPX SAP “query nearest file server” in case server speaks only IPX • Unicast again to that DA for selected server’s SLP attributes, get reply with IP address and port • DNS query for Tree. IP-domainname (but why? ) • Start connection to target server
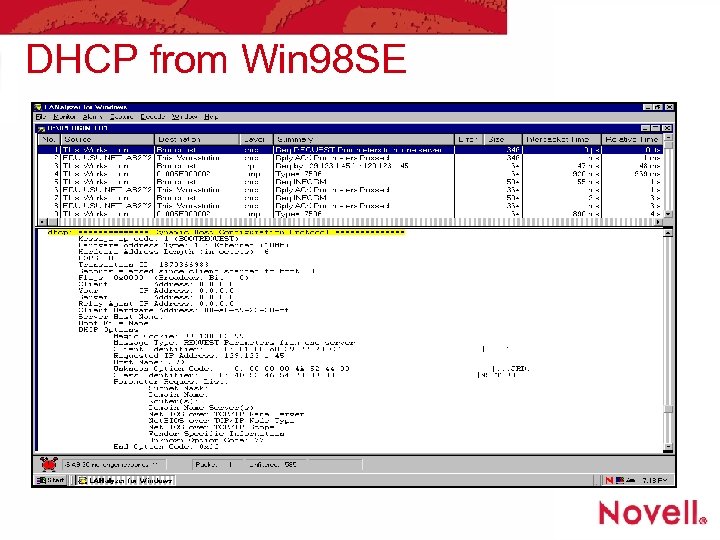 DHCP from Win 98 SE
DHCP from Win 98 SE
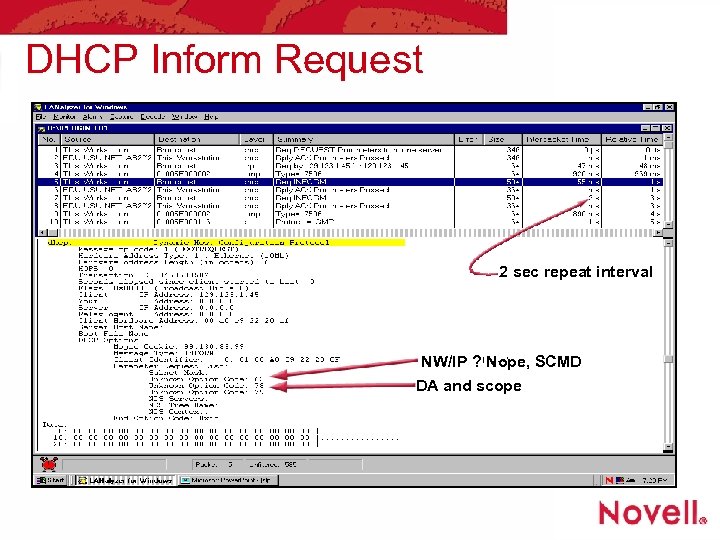 DHCP Inform Request 2 sec repeat interval NW/IP ? Nope, SCMD DA and scope
DHCP Inform Request 2 sec repeat interval NW/IP ? Nope, SCMD DA and scope
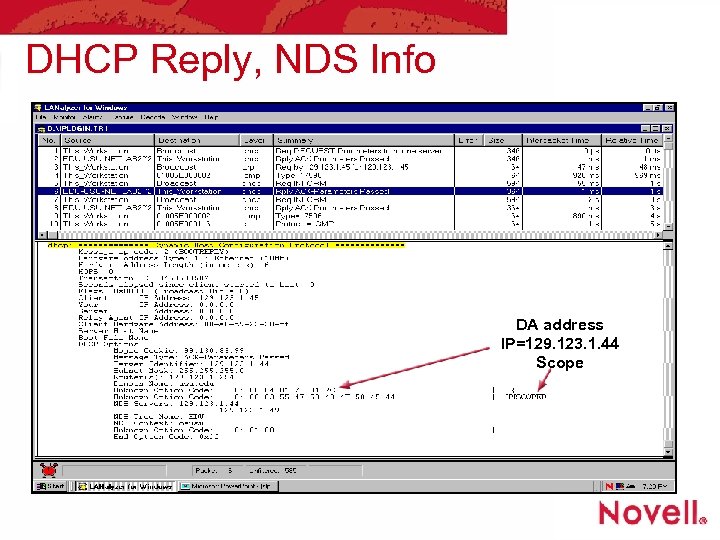 DHCP Reply, NDS Info DA address IP=129. 123. 1. 44 Scope
DHCP Reply, NDS Info DA address IP=129. 123. 1. 44 Scope
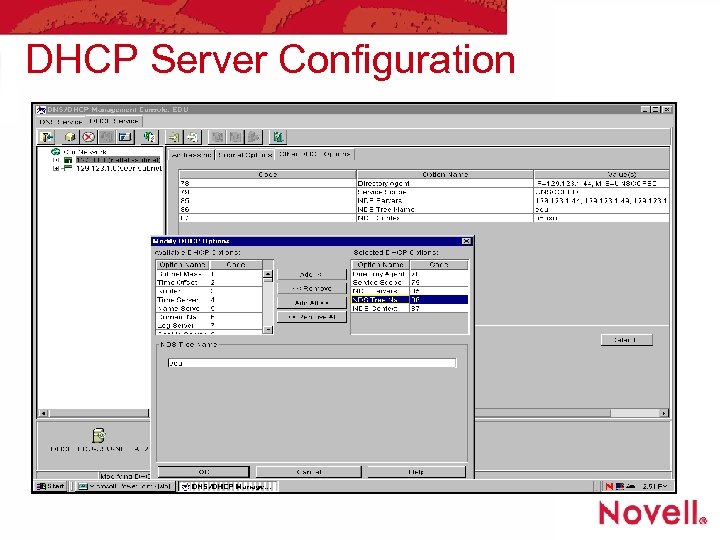 DHCP Server Configuration
DHCP Server Configuration
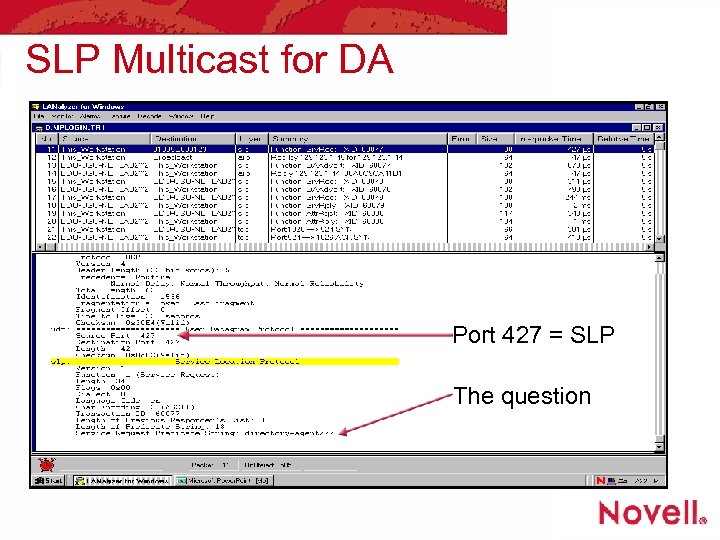 SLP Multicast for DA Port 427 = SLP The question
SLP Multicast for DA Port 427 = SLP The question
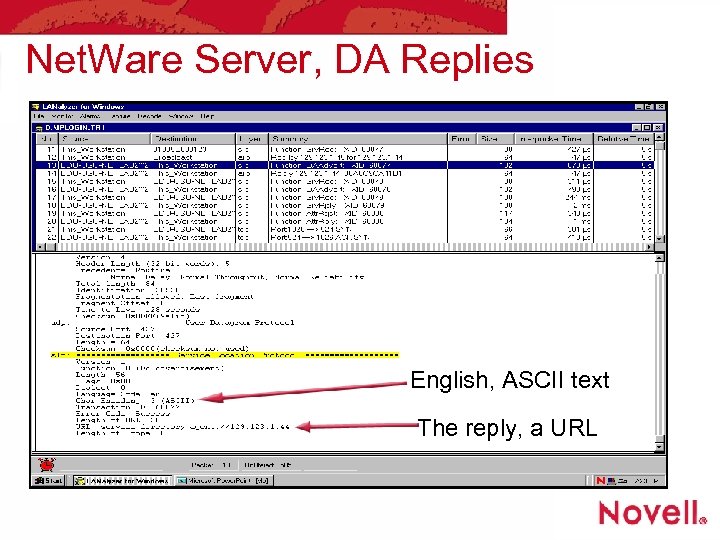 Net. Ware Server, DA Replies English, ASCII text The reply, a URL
Net. Ware Server, DA Replies English, ASCII text The reply, a URL
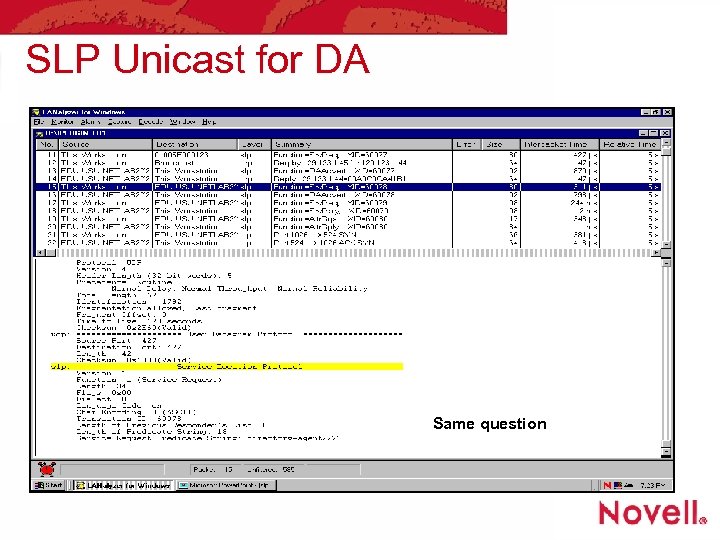 SLP Unicast for DA Same question
SLP Unicast for DA Same question
 Net. Ware Server DA Replies Same reply
Net. Ware Server DA Replies Same reply
 SLP Service Request IPX name of preferred server
SLP Service Request IPX name of preferred server
 SLP Service Reply Get that IPX style name
SLP Service Reply Get that IPX style name
 SLP Service Attributes Request Address of that server
SLP Service Attributes Request Address of that server
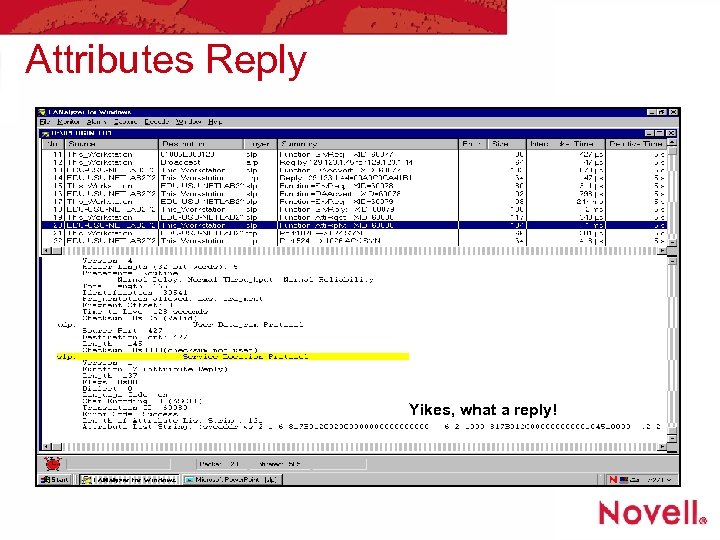 Attributes Reply Yikes, what a reply!
Attributes Reply Yikes, what a reply!
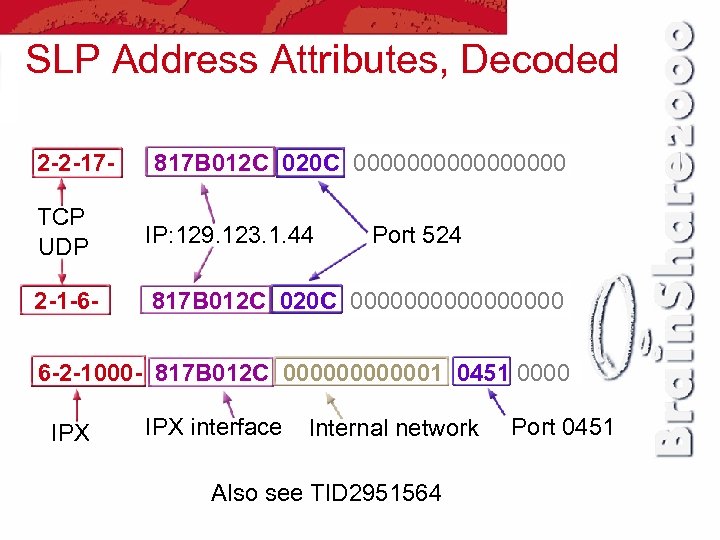 SLP Address Attributes, Decoded 2 -2 -17 - 817 B 012 C 020 C 00000000 TCP UDP IP: 129. 123. 1. 44 2 -1 -6 - 817 B 012 C 020 C 00000000 Port 524 6 -2 -1000 - 817 B 012 C 0000001 0451 0000 IPX interface Internal network Also see TID 2951564 Port 0451
SLP Address Attributes, Decoded 2 -2 -17 - 817 B 012 C 020 C 00000000 TCP UDP IP: 129. 123. 1. 44 2 -1 -6 - 817 B 012 C 020 C 00000000 Port 524 6 -2 -1000 - 817 B 012 C 0000001 0451 0000 IPX interface Internal network Also see TID 2951564 Port 0451
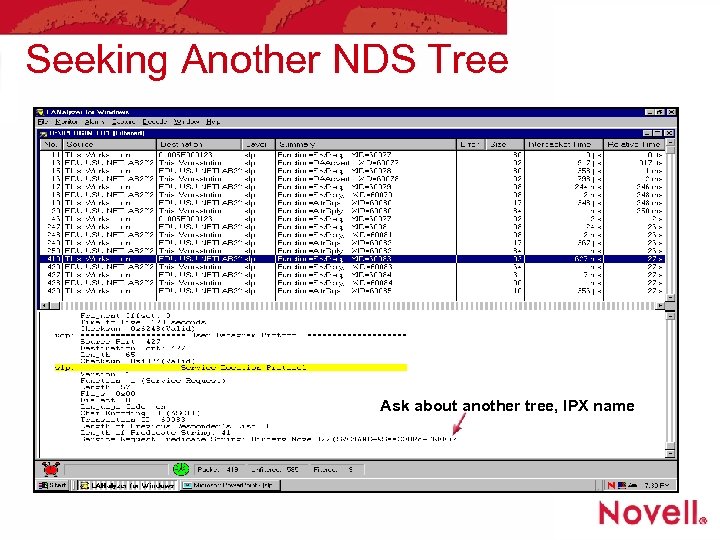 Seeking Another NDS Tree Ask about another tree, IPX name
Seeking Another NDS Tree Ask about another tree, IPX name
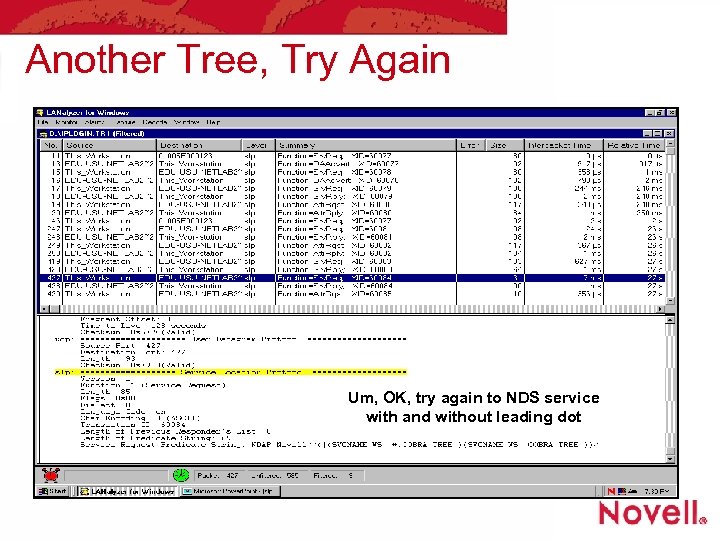 Another Tree, Try Again Um, OK, try again to NDS service with and without leading dot
Another Tree, Try Again Um, OK, try again to NDS service with and without leading dot
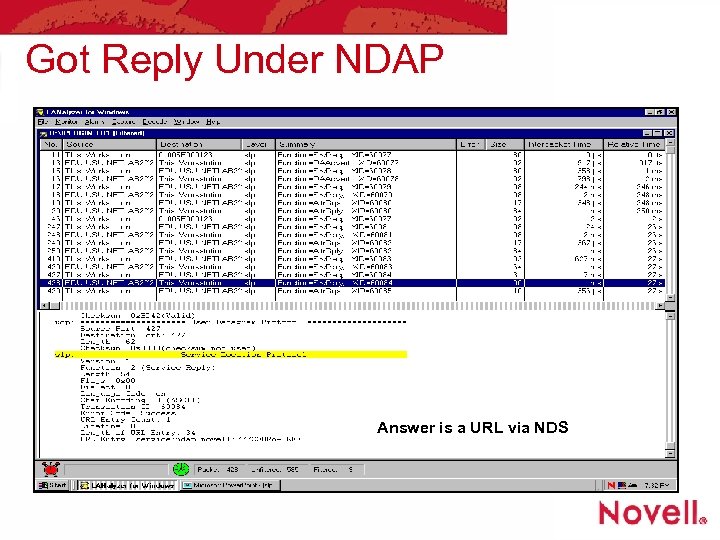 Got Reply Under NDAP Answer is a URL via NDS
Got Reply Under NDAP Answer is a URL via NDS
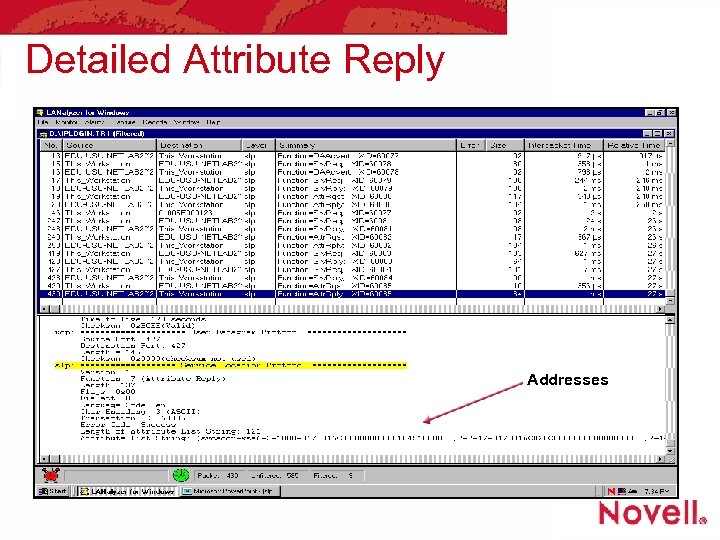 Detailed Attribute Reply Addresses
Detailed Attribute Reply Addresses
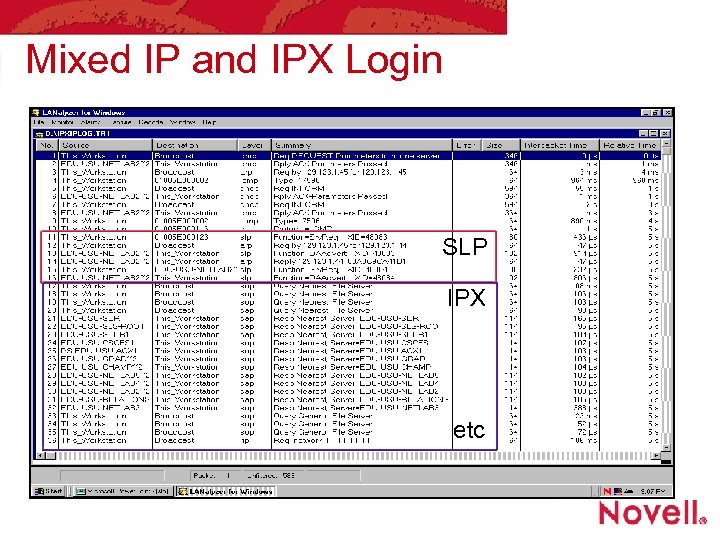 Mixed IP and IPX Login SLP IPX etc
Mixed IP and IPX Login SLP IPX etc
 Novell SLP service names, so far • Form of • • service. xxxx. novell bindery. novell = NW server SAP Type 4 mgw. novell = SCMD gateway ndap. novell = NDS server (partition. tree) portal. novell = Portal server (NW 5. 1) rconsole. novell = Rconj (Java rconsole) sapsrv. novell = IPX sap server srs. novell = SMS backup timesync. novell = timesync. nlm (NTP)
Novell SLP service names, so far • Form of • • service. xxxx. novell bindery. novell = NW server SAP Type 4 mgw. novell = SCMD gateway ndap. novell = NDS server (partition. tree) portal. novell = Portal server (NW 5. 1) rconsole. novell = Rconj (Java rconsole) sapsrv. novell = IPX sap server srs. novell = SMS backup timesync. novell = timesync. nlm (NTP)
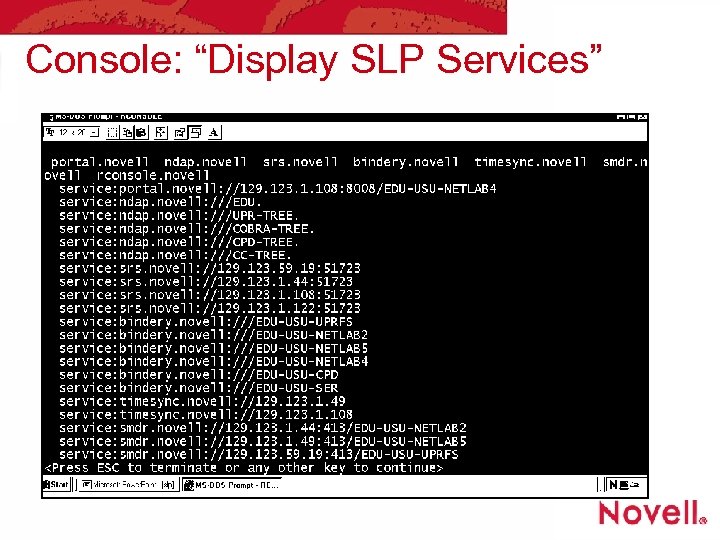 Console: “Display SLP Services”
Console: “Display SLP Services”
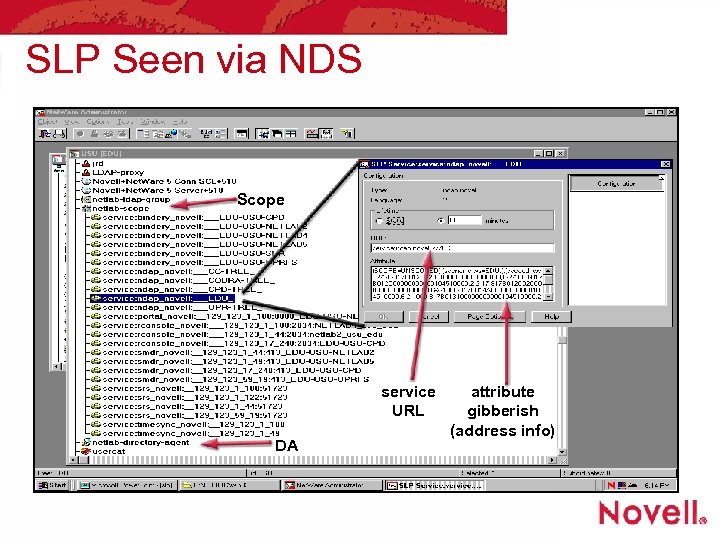 SLP Seen via NDS Scope service URL DA attribute gibberish (address info)
SLP Seen via NDS Scope service URL DA attribute gibberish (address info)
 Sys: etcslp. cfg, DA Part • • • • ; ; ; ; This is a sample of the slp configuration file. Two types of entries can be made: 1) DA entries, 2) SA Register Filters. The DA entry allows static configuration of a know DA. This would be used when the DA was out of multicast range and DHCP was not being used to configure the DA. The static DA configuration format is as follows 'DA
Sys: etcslp. cfg, DA Part • • • • ; ; ; ; This is a sample of the slp configuration file. Two types of entries can be made: 1) DA entries, 2) SA Register Filters. The DA entry allows static configuration of a know DA. This would be used when the DA was out of multicast range and DHCP was not being used to configure the DA. The static DA configuration format is as follows 'DA
 Sys: etcslp. cfg SA Part • • • ; ; ; The SA Register Filter would be used when the administrator wanted all services of a specific service type being mapped to a single scope. For example, the administrator wanted all "lpr" printers being registered to scope "printer". The format is as follows: 'REGISTER TYPE "
Sys: etcslp. cfg SA Part • • • ; ; ; The SA Register Filter would be used when the administrator wanted all services of a specific service type being mapped to a single scope. For example, the administrator wanted all "lpr" printers being registered to scope "printer". The format is as follows: 'REGISTER TYPE "
 Console, SLP Controls
Console, SLP Controls
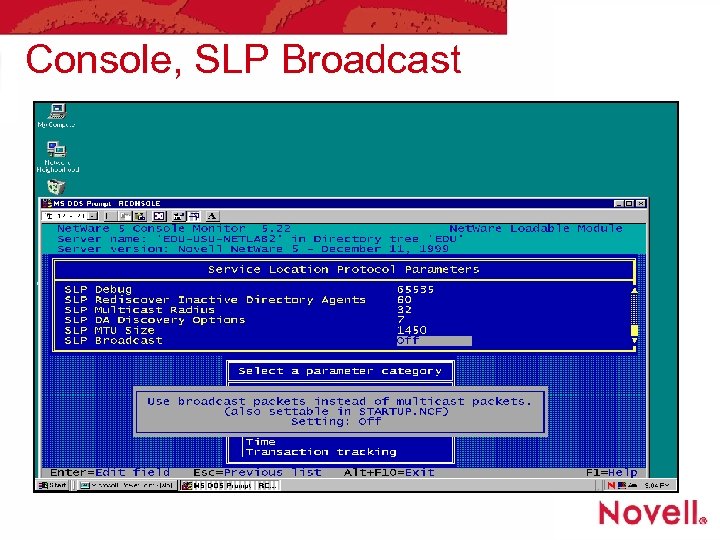 Console, SLP Broadcast
Console, SLP Broadcast
 Where to “Read More About It” • SLP is documented as follows • • • RFC 2165 SLP version 1 (in Net. Ware today) RFC 2608 SLP version 2 (current) RFC 2609 SLP templates and schemes RFC 2614 SLP API suggestion Plus draft RFCs, in progress Novell TIDs, for Novell’s implementation • See also • http: //www. svrloc. org/ and http: //www. ietf. org/
Where to “Read More About It” • SLP is documented as follows • • • RFC 2165 SLP version 1 (in Net. Ware today) RFC 2608 SLP version 2 (current) RFC 2609 SLP templates and schemes RFC 2614 SLP API suggestion Plus draft RFCs, in progress Novell TIDs, for Novell’s implementation • See also • http: //www. svrloc. org/ and http: //www. ietf. org/
 Recommendations for the Future, a Personal View • What follows is the way I would have designed SLP communications • With the help of my grad students it may reach the RFC level • Scale to Internet, cut traffic, don’t be naïve, bring topology under control • These are not statements by Novell
Recommendations for the Future, a Personal View • What follows is the way I would have designed SLP communications • With the help of my grad students it may reach the RFC level • Scale to Internet, cut traffic, don’t be naïve, bring topology under control • These are not statements by Novell
 Recommendations for the Future, a Personal View (cont. ) • Eliminate multicast and broadcast • Both require listeners to believe what they hear (naïve at best) • Both bother stations • Multicast leaks to the Internet • Replace with unicast, informed by DHCP giving address of a DA • Eliminate periodic probes and adverts
Recommendations for the Future, a Personal View (cont. ) • Eliminate multicast and broadcast • Both require listeners to believe what they hear (naïve at best) • Both bother stations • Multicast leaks to the Internet • Replace with unicast, informed by DHCP giving address of a DA • Eliminate periodic probes and adverts
 Recommendations for the Future, a Personal View • Scale to the world • Use DNS system to carry IP numbers of DAs to contact at a site, like email MX records. The tree already exists. • Use DNS to walk tree to the site or to other places at same site • Eliminate concept of “scopes” • Use credentials to access services (done partly now, do better later)
Recommendations for the Future, a Personal View • Scale to the world • Use DNS system to carry IP numbers of DAs to contact at a site, like email MX records. The tree already exists. • Use DNS to walk tree to the site or to other places at same site • Eliminate concept of “scopes” • Use credentials to access services (done partly now, do better later)
 Recommendations for the Future, a Personal View • Directory Agents: redundancy, Scopes • Statically configure each DA with a list of peer DAs (friends) • Peers can share info • No auto discovery, no advertisements • Peer list replaces Scopes • All other DAs are remote, find via DNS • Remember SA registration, but accept unreachability reports from clients • Do counting of reports before believing • If necessary probe a problem SA
Recommendations for the Future, a Personal View • Directory Agents: redundancy, Scopes • Statically configure each DA with a list of peer DAs (friends) • Peers can share info • No auto discovery, no advertisements • Peer list replaces Scopes • All other DAs are remote, find via DNS • Remember SA registration, but accept unreachability reports from clients • Do counting of reports before believing • If necessary probe a problem SA
 Recommendations for the Future, a Personal View • Service Agents • Learn about DAs via DHCP, same as all clients; register with each DA in list • Register with DAs, and deregister, but do not periodically reregister • DAs, “Remember what you have been told once until informed otherwise” • Eliminate concept of “scopes”, use static list of DA peers
Recommendations for the Future, a Personal View • Service Agents • Learn about DAs via DHCP, same as all clients; register with each DA in list • Register with DAs, and deregister, but do not periodically reregister • DAs, “Remember what you have been told once until informed otherwise” • Eliminate concept of “scopes”, use static list of DA peers
 Recommendations for the Future, a Personal View • User Agents • Acquire DA address via DHCP • This is the client’s “smarter host” • Unicast to that DA • UA is unaware of network topology • The DA performs recursive lookups on behalf of a UA • Report to DA if an SA is unreachable
Recommendations for the Future, a Personal View • User Agents • Acquire DA address via DHCP • This is the client’s “smarter host” • Unicast to that DA • UA is unaware of network topology • The DA performs recursive lookups on behalf of a UA • Report to DA if an SA is unreachable




