2b8318da2e3740d81c9e5e5ff3dac4d1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25

Service, Grid Service and Workflow Xian-He Sun Scalable Computing Software Laboratory Illinois Institute of Technology sun@iit. edu Nov. 30, 2006 Fermi Laboratory
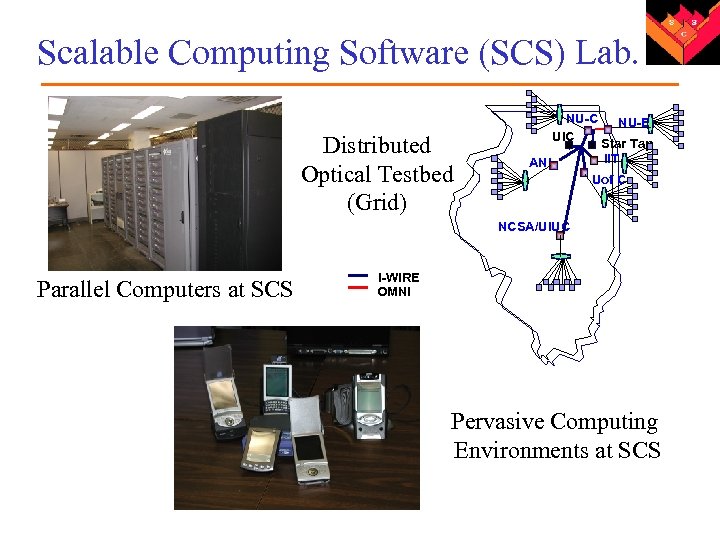
Scalable Computing Software (SCS) Lab. Distributed Optical Testbed (Grid) NU-C UIC ANL NU-E Star Tap IIT Uof C NCSA/UIUC Parallel Computers at SCS I-WIRE OMNI Pervasive Computing Environments at SCS

Grid and Utility Computing Mimic the electrical power grid Increased Efficiency Higher Quality of Service Increased Productivity Reduced Complexity & Cost Improved Resiliency
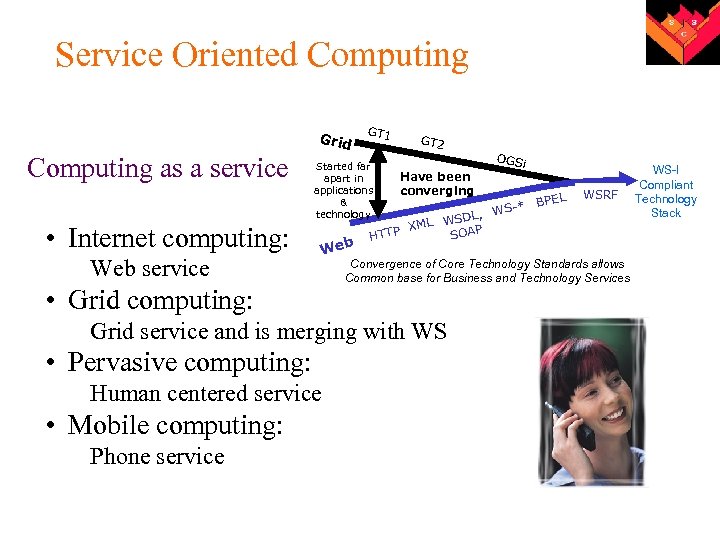
Service Oriented Computing Grid Computing as a service • Internet computing: Web service GT 1 Started far apart in applications & technology Web • Grid computing: GT 2 Have been converging Human centered service • Mobile computing: Phone service i BPEL WS-* SDL, XML W AP SO HTTP WSRF Convergence of Core Technology Standards allows Common base for Business and Technology Services Grid service and is merging with WS • Pervasive computing: OGS WS-I Compliant Technology Stack
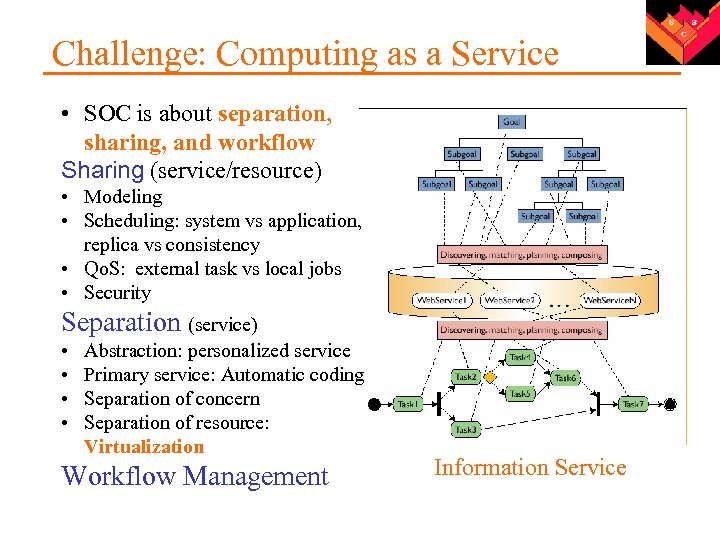
Challenge: Computing as a Service • SOC is about separation, sharing, and workflow Sharing (service/resource) • Modeling • Scheduling: system vs application, replica vs consistency • Qo. S: external task vs local jobs • Security Separation (service) • • Abstraction: personalized service Primary service: Automatic coding Separation of concern Separation of resource: Virtualization Workflow Management Information Service
Service Oriented Architecture (SOA) • SOA is the special software architecture with services are the key building blocks • SOA is basically an application development style using services • They are principles or patterns to develop application using services The concept of SOA comes from software research SOA is developed from IT experience over 30 years

What is SOA ? – more detail • An architecture that implements business functionality as a set of shared, reusable services • Way of designing a software system and its surrounding environment to provide services either to end-user applications, to executable business processes or to other services through published and discoverable service interfaces. • Aggregation of components for a business driver • Extended bus with shared services • service interface being defined separately from implementation and provides service encapsulation and platform/language independence.
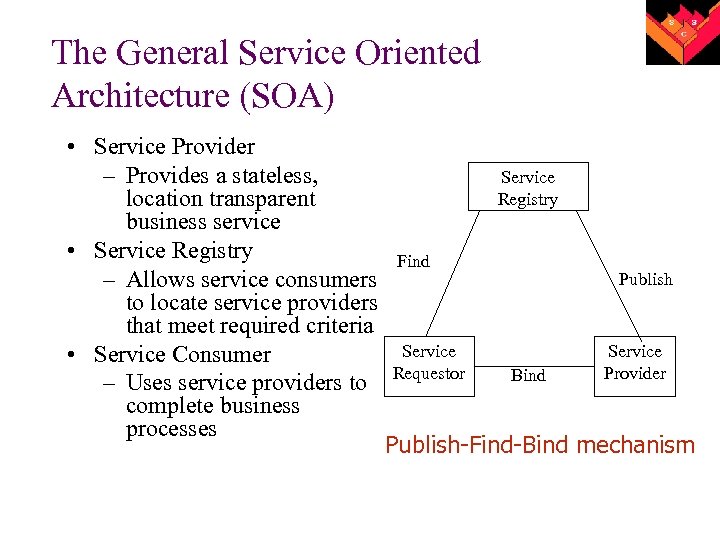
The General Service Oriented Architecture (SOA) • Service Provider – Provides a stateless, location transparent business service • Service Registry – Allows service consumers to locate service providers that meet required criteria • Service Consumer – Uses service providers to complete business processes Service Registry Find Service Requestor Publish Bind Service Provider Publish-Find-Bind mechanism

What is Web Service? • A software component • Identified by unique URI • Who can be discovered by other soft. comp • web services are a stack of emerging standards that describe a serviceoriented, componentbased architecture

Key Players • Do you know me ? ? – Describe by – WSDL • Do you want to find me ? ? – Discover in – UDDI • Do you want to communicate with me? ? – Communicate through– SOAP/XML
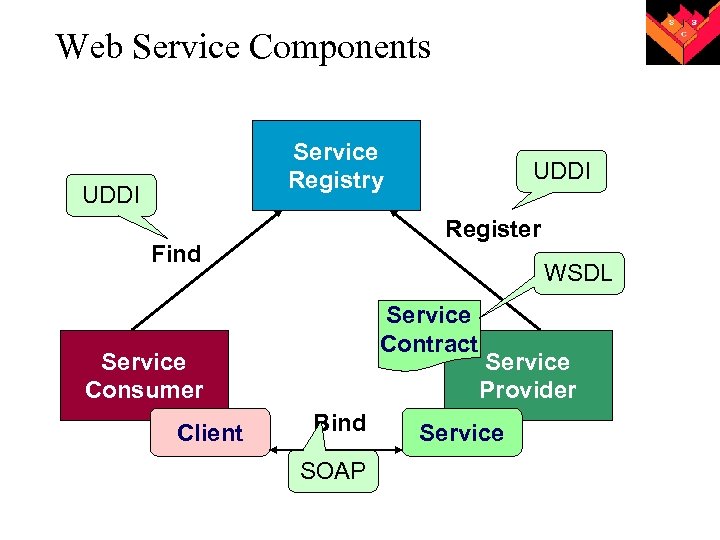
Web Service Components Service Registry UDDI Register Find WSDL Service Contract Service Consumer Client UDDI Bind SOAP Service Provider Service
The Grid Computing • Infrastructure (“middleware” & “services”) for establishing, managing, and evolving multiorganizational federations • Mechanisms for creating and managing workflow within such federations • Three key criteria – Coordinates distributed resources … – using standard, open, general-purpose protocols and interfaces … – to deliver non-trivial qualities of service.
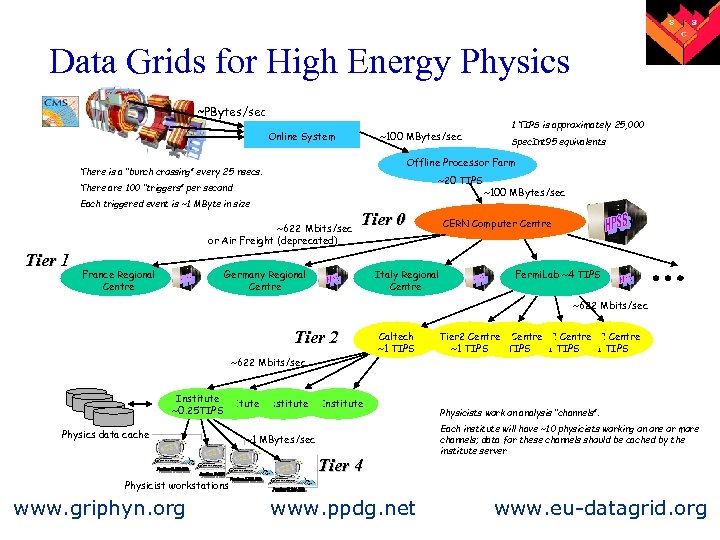
Data Grids for High Energy Physics ~PBytes/sec Online System ~100 MBytes/sec ~20 TIPS There are 100 “triggers” per second Each triggered event is ~1 MByte in size ~622 Mbits/sec or Air Freight (deprecated) France Regional Centre Spec. Int 95 equivalents Offline Processor Farm There is a “bunch crossing” every 25 nsecs. Tier 1 1 TIPS is approximately 25, 000 Tier 0 Germany Regional Centre Italy Regional Centre ~100 MBytes/sec CERN Computer Centre Fermi. Lab ~4 TIPS ~622 Mbits/sec Tier 2 ~622 Mbits/sec Institute ~0. 25 TIPS Physics data cache Caltech ~1 TIPS Institute ~1 MBytes/sec Tier 4 Tier 2 Centre Tier 2 Centre ~1 TIPS Physicists work on analysis “channels”. Each institute will have ~10 physicists working on one or more channels; data for these channels should be cached by the institute server Physicist workstations www. griphyn. org www. ppdg. net www. eu-datagrid. org
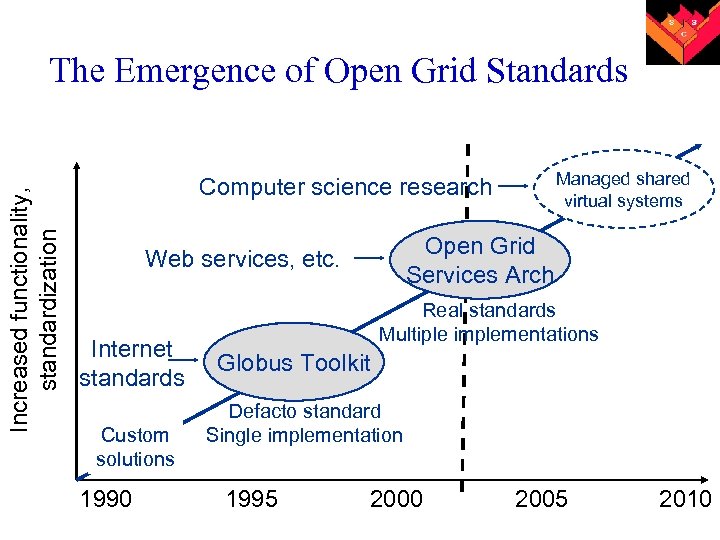
Increased functionality, standardization The Emergence of Open Grid Standards Managed shared virtual systems Computer science research Open Grid Services Arch Web services, etc. Internet standards Custom solutions 1990 Real standards Multiple implementations Globus Toolkit Defacto standard Single implementation 1995 2000 2005 2010
Open Grid Services Architecture • Everything is a service • A standard substrate: the Grid service – A Grid service is a Web service – Standard interfaces and behaviors that address key distributed system issues: naming, service state, lifetime, notification • Supports standard service specifications – Agreement, data access & integration, workflow, security, policy, diagnostics, etc. – Target of current & planned GGF efforts • Supports arbitrary application-specific services based on these & other definitions

SOA and Web Service • SOA mostly defined and explained with some accompanied implementations • Web services are a stack of emerging standards that describe a service-oriented, componentbased architecture • Web services are limited SOA, but they are the only available best practical solution till now • SOA and Web service are still evolving each other • Web service cannot support all the computing service in its current form

Grid and Web Service • Grid? What is the Grid? – Standard, technology, infrastructure, application – Globus or general distributed computing ? • Standard – Merging with Web service • Application – Large scientific application vs. light business application • Technology – Resource sharing vs. service sharing, resource sharing vs. pay for service, coordinate virtual organizations vs. create VOs (very hard), stateful vs. stateless
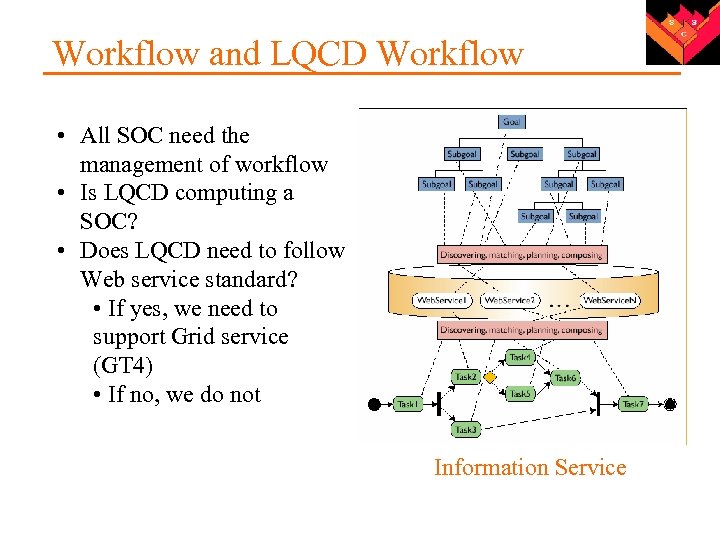
Workflow and LQCD Workflow • All SOC need the management of workflow • Is LQCD computing a SOC? • Does LQCD need to follow Web service standard? • If yes, we need to support Grid service (GT 4) • If no, we do not Information Service
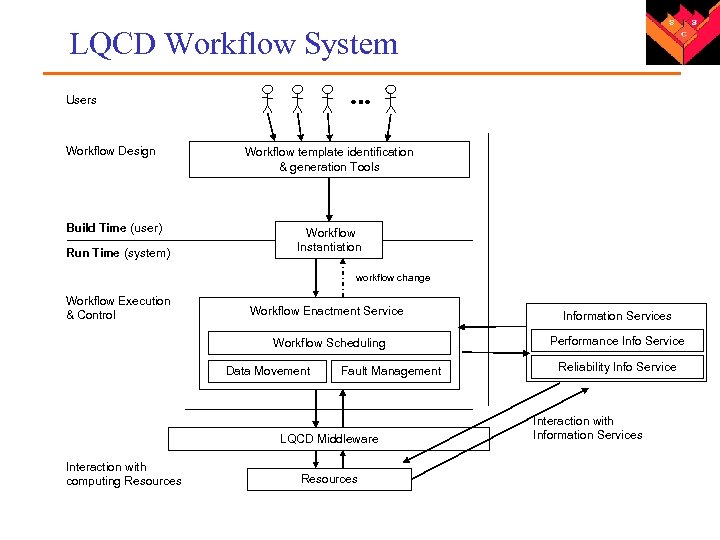
LQCD Workflow System Users Workflow Design Workflow template identification & generation Tools Build Time (user) Workflow Instantiation Run Time (system) workflow change Workflow Execution & Control Workflow Enactment Service Information Services Workflow Scheduling Performance Info Service Data Movement Fault Management LQCD Middleware Interaction with computing Resources Reliability Info Service Interaction with Information Services
Workflow Management Systems • Comparison Functionality – – – Workflow template identification & generation Tools Workflow specification Workflow scheduling & rescheduling Fault Management Data Movement Interaction with monitor system • Target Systems – Askalon – Kepler – Grid Physics Network
Current Result: the GHS System The GHS (Grid Harvest Service) system • GHS is a long-term, application-level performance evaluation and task scheduling system specially designed to handle the resources availability issues for solving large-scale applications. • The resource availability could be due to contention or due to fault. The two different causes require different performance modeling and prediction • Support rescheduling
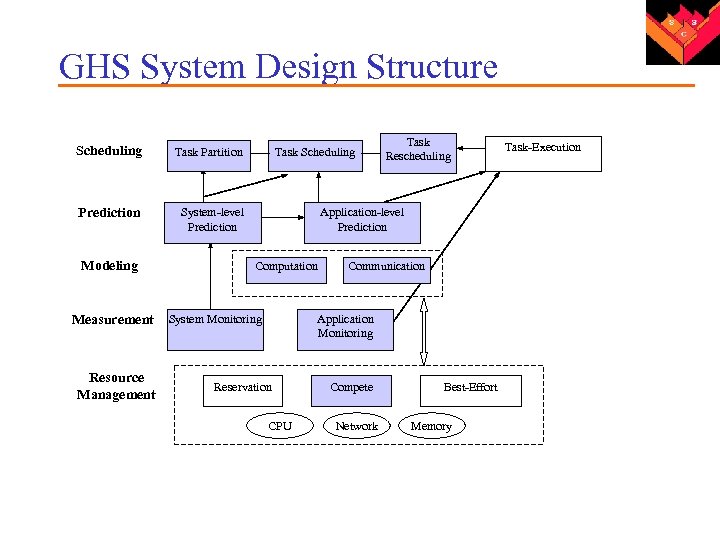
GHS System Design Structure Scheduling Task Partition Prediction System-level Prediction Modeling Measurement Resource Management Task Scheduling Task Rescheduling Application-level Prediction Computation Communication Application Monitoring System Monitoring Reservation CPU Compete Network Best-Effort Memory Task-Execution
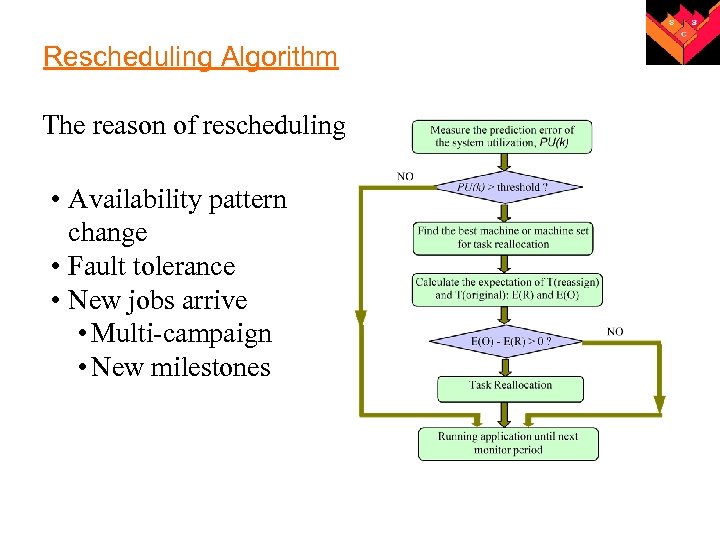
Rescheduling Algorithm The reason of rescheduling • Availability pattern change • Fault tolerance • New jobs arrive • Multi-campaign • New milestones
Automated Deployment of Meta-task • APST software – Apple. S scheduling – NWS prediction • Integrating GHS prediction and scheduling into APST – Modify the Metric. Type and Service. Type data structure in the Meta-data Bookkeeper – Add GHS server to provide information service – Add Ghs. Metatask. Sched() – Modify Xml. File parser in the Controller component

Software Released • http: //www. meta. cs. iit. edu/~ghs • GHS 1. 0 – Functionalities for performance prediction, measurement, task allocation, and task scheduling • GHS-APST 1. 0 – Integrate GHS prediction and scheduling into APST execution management – Add GHS server and GHS daemons for performance data collection and inquiry – Unchanged user interface • apstd –heuristc=ghs • Tested on Sun. OS 5. 9 and Linux 2. 4. 20 • Releases are for contention availability, fault availability is a work in progress.
2b8318da2e3740d81c9e5e5ff3dac4d1.ppt