b150f4a4cb1cb9e06253c29964c81db4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 46
 Server Consolidation Eric D. Ho Advisory Software Consultant BMC Software, Inc. March 20, 2002 © 202 BMC Software, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Server Consolidation Eric D. Ho Advisory Software Consultant BMC Software, Inc. March 20, 2002 © 202 BMC Software, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
 Objective u This presentation is designed to show the methodology by which server consolidation study can be achieved using PATROL Perform and Predict. 2
Objective u This presentation is designed to show the methodology by which server consolidation study can be achieved using PATROL Perform and Predict. 2
 Server Consolidation Advantages Reduced total cost of ownership u Lower license cost for software u Improved system manageability l l l System backup and recovery Software distribution Reduce manpower requirements u Improve l l 3 infrastructure technology Replace older servers with newer technology Faster processors will reduce workload response times and memory requirements
Server Consolidation Advantages Reduced total cost of ownership u Lower license cost for software u Improved system manageability l l l System backup and recovery Software distribution Reduce manpower requirements u Improve l l 3 infrastructure technology Replace older servers with newer technology Faster processors will reduce workload response times and memory requirements
 Server Consolidation Challenges Need to: u Measure current usage accurately u Capture the configuration details u Characterize workloads u Understand usage patterns u Predict the consolidation effect u Evaluate alternatives u Project growth 4
Server Consolidation Challenges Need to: u Measure current usage accurately u Capture the configuration details u Characterize workloads u Understand usage patterns u Predict the consolidation effect u Evaluate alternatives u Project growth 4
 Server Consolidation Risks You don’t know where to start !! u Methodology, Process, Tools Wrong Size - It does not fit !! u Oops! Career change? It fits! But. . Performance stinks u Buy more…. Spend more! It will take a long time !! u By the time you are done, the solution is obsolete. 5
Server Consolidation Risks You don’t know where to start !! u Methodology, Process, Tools Wrong Size - It does not fit !! u Oops! Career change? It fits! But. . Performance stinks u Buy more…. Spend more! It will take a long time !! u By the time you are done, the solution is obsolete. 5
 Server Consolidation Methodology Six steps to Success u 1. Baseline current performance Collect detailed performance data u 2. Characterize workload l System, utility, application, database, etc. l u 3. Analyze resource usage level l u Time Series Graphical Analysis Peaks, batch windows, trends, growth pattern Workloads profiles 4. Combine systems for sizing Server and Workload stacking u 5. Consolidation modeling l Resource contention analysis l Response time degradation analysis l Growth sensitivity analysis l 6 u 6. Validate recommendation
Server Consolidation Methodology Six steps to Success u 1. Baseline current performance Collect detailed performance data u 2. Characterize workload l System, utility, application, database, etc. l u 3. Analyze resource usage level l u Time Series Graphical Analysis Peaks, batch windows, trends, growth pattern Workloads profiles 4. Combine systems for sizing Server and Workload stacking u 5. Consolidation modeling l Resource contention analysis l Response time degradation analysis l Growth sensitivity analysis l 6 u 6. Validate recommendation
 1 - Baseline Current Performance Collect detailed performance metrics u System, IO, memory, process, user u 24 x 7 u Data collected every 10 seconds u Data logged every 15 minutes l l 7 96 data records per day per server Servers: as 10, db 02, db 14, db 15, and db 25
1 - Baseline Current Performance Collect detailed performance metrics u System, IO, memory, process, user u 24 x 7 u Data collected every 10 seconds u Data logged every 15 minutes l l 7 96 data records per day per server Servers: as 10, db 02, db 14, db 15, and db 25
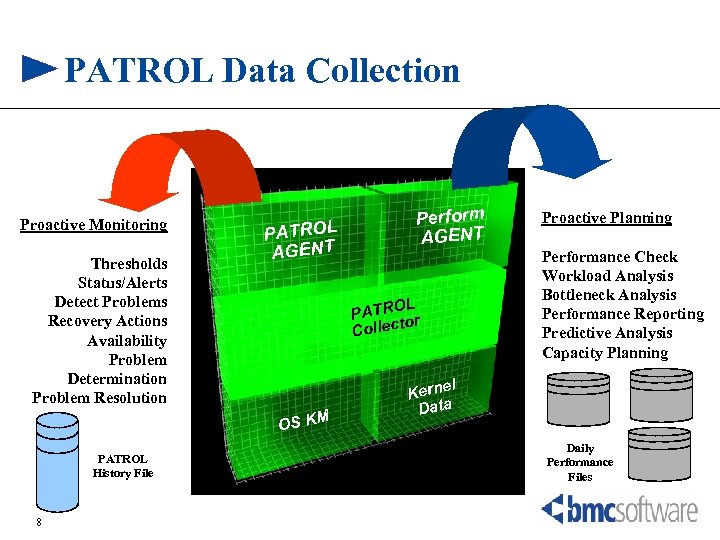 PATROL Data Collection Proactive Monitoring Thresholds Status/Alerts Detect Problems Recovery Actions Availability Problem Determination Problem Resolution PATROL AGENT L PATRO r to Collec M OS K PATROL History File 8 Perform AGENT Proactive Planning Performance Check Workload Analysis Bottleneck Analysis Performance Reporting Predictive Analysis Capacity Planning l Kerne Data Daily Performance Files
PATROL Data Collection Proactive Monitoring Thresholds Status/Alerts Detect Problems Recovery Actions Availability Problem Determination Problem Resolution PATROL AGENT L PATRO r to Collec M OS K PATROL History File 8 Perform AGENT Proactive Planning Performance Check Workload Analysis Bottleneck Analysis Performance Reporting Predictive Analysis Capacity Planning l Kerne Data Daily Performance Files
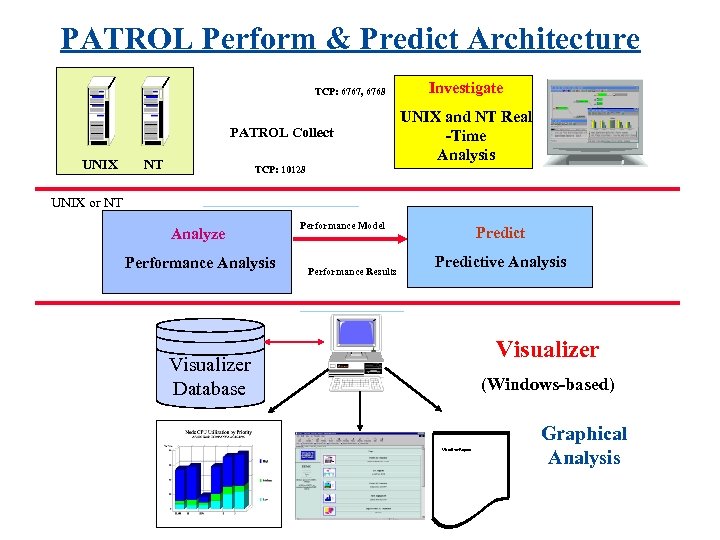 PATROL Perform & Predict Architecture TCP: 6767, 6768 PATROL Collect UNIX NT Investigate UNIX and NT Real -Time Analysis TCP: 10128 UNIX or NT Analyze Performance Analysis Performance Model Performance Results Predictive Analysis Visualizer Database (Windows-based) Visualizer Reports Graphical Analysis
PATROL Perform & Predict Architecture TCP: 6767, 6768 PATROL Collect UNIX NT Investigate UNIX and NT Real -Time Analysis TCP: 10128 UNIX or NT Analyze Performance Analysis Performance Model Performance Results Predictive Analysis Visualizer Database (Windows-based) Visualizer Reports Graphical Analysis
 10
10
 11
11
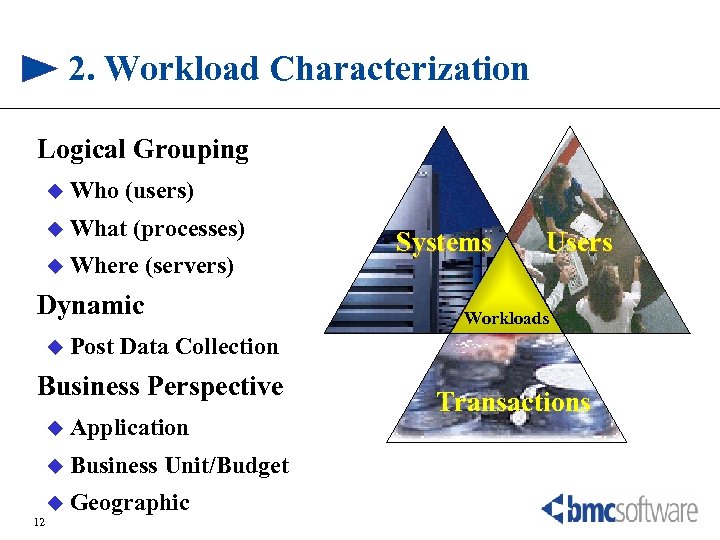 2. Workload Characterization Logical Grouping u Who (users) u What (processes) u Where (servers) Dynamic u Post Users Workloads Data Collection Business Perspective u Application u Business Unit/Budget u Geographic 12 Systems Transactions
2. Workload Characterization Logical Grouping u Who (users) u What (processes) u Where (servers) Dynamic u Post Users Workloads Data Collection Business Perspective u Application u Business Unit/Budget u Geographic 12 Systems Transactions
 Sample Workloads Characterize workloads u Oracle 13 (1 process = 1 transaction) u axciom (Oracle Instance MEMPWD) u f 45 (Oracle Financials Form 45) u f 60 (Oracle Financials Form 60) u ar 25 run u RGRAGR u PMSERVER u GL u tools (BMC, HP, etc. ) u system u zzz (the rest of processes)
Sample Workloads Characterize workloads u Oracle 13 (1 process = 1 transaction) u axciom (Oracle Instance MEMPWD) u f 45 (Oracle Financials Form 45) u f 60 (Oracle Financials Form 60) u ar 25 run u RGRAGR u PMSERVER u GL u tools (BMC, HP, etc. ) u system u zzz (the rest of processes)
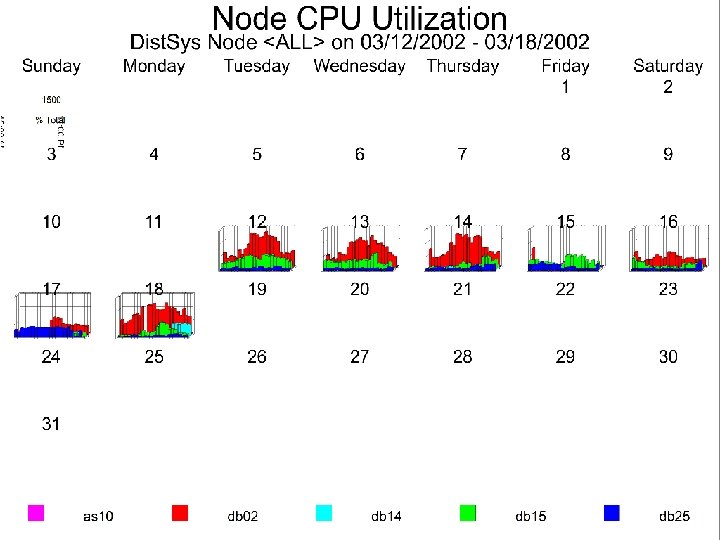
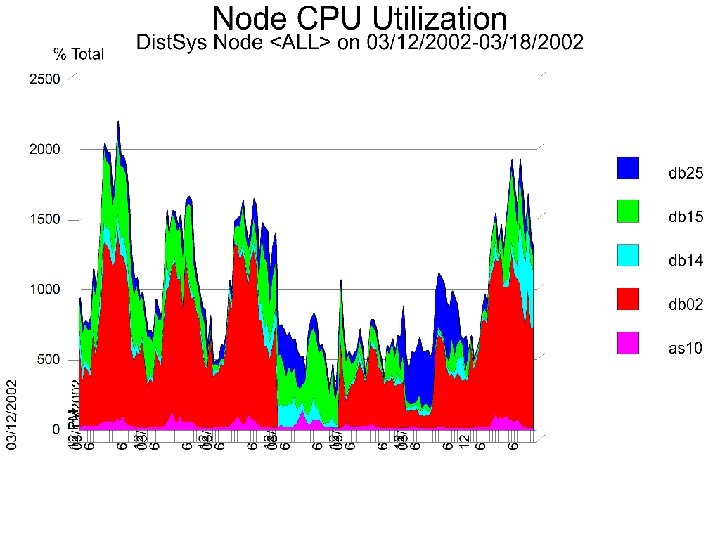
 3 - Analyze Resource Usage Level u (A) Time Series Graphical Analysis l Peaks l Batch windows l Trends l Growth pattern u (B) 14 Workload Analysis
3 - Analyze Resource Usage Level u (A) Time Series Graphical Analysis l Peaks l Batch windows l Trends l Growth pattern u (B) 14 Workload Analysis
 15
15
 16
16
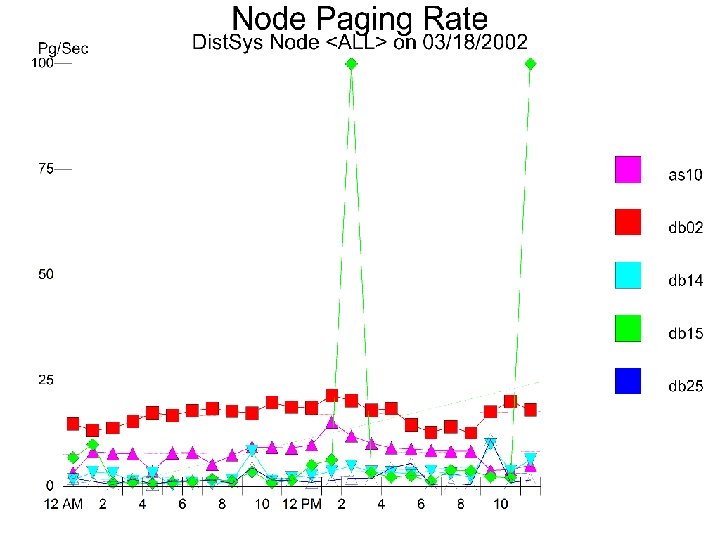 17
17
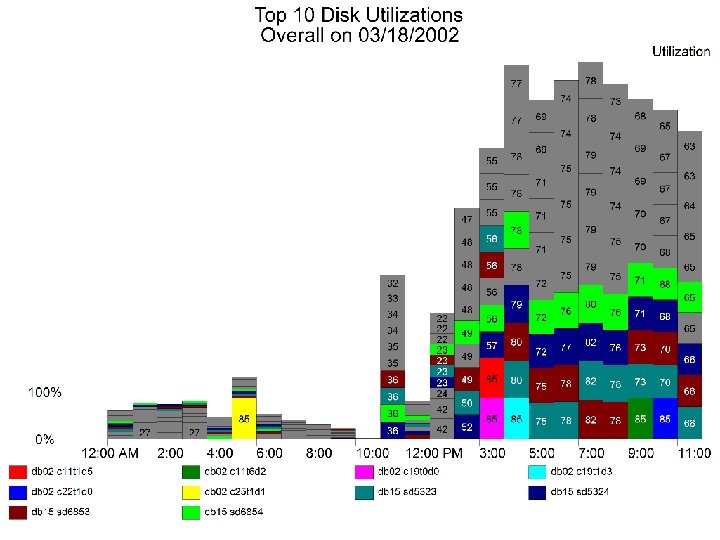 18
18
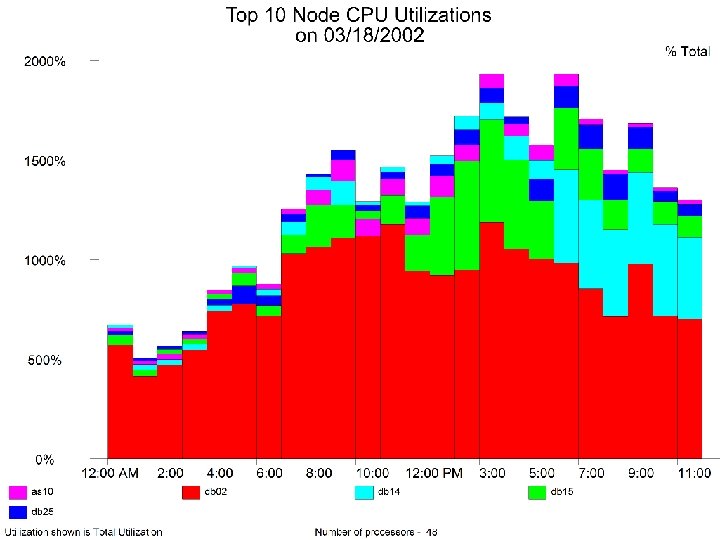
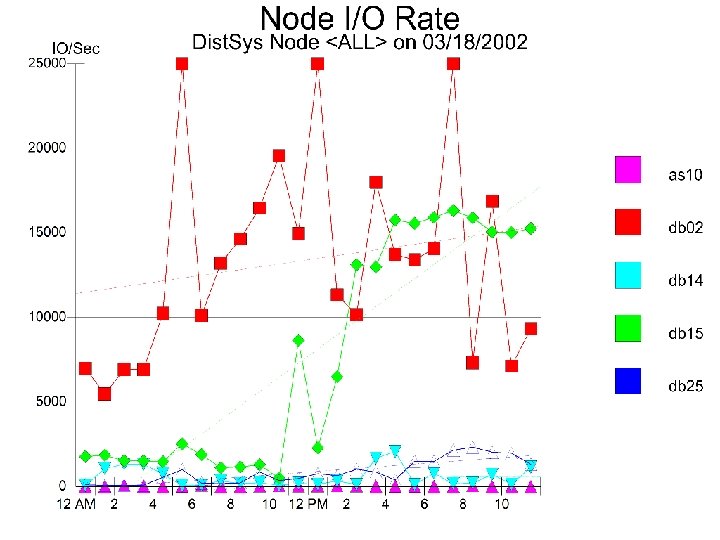
 3 - Analyze Resource Usage Level u (A) Time Series Graphical Analysis l Peaks l Batch windows l Trends l Growth pattern u (B) 19 Workload Analysis
3 - Analyze Resource Usage Level u (A) Time Series Graphical Analysis l Peaks l Batch windows l Trends l Growth pattern u (B) 19 Workload Analysis
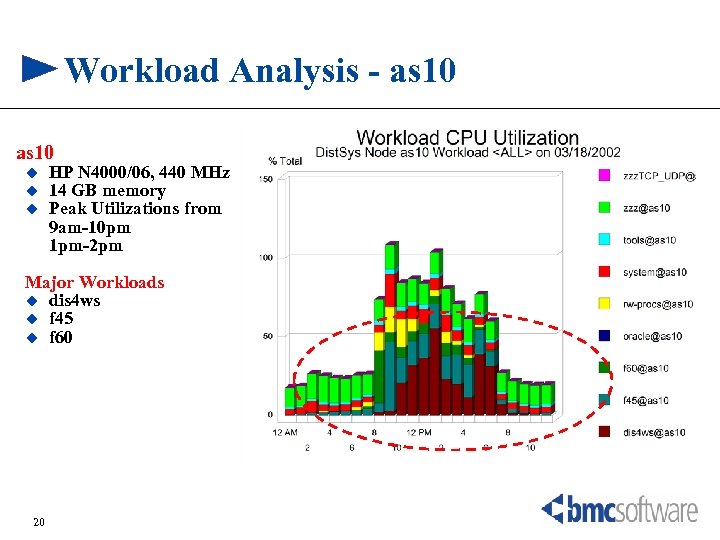 Workload Analysis - as 10 u u u HP N 4000/06, 440 MHz 14 GB memory Peak Utilizations from 9 am-10 pm 1 pm-2 pm Major Workloads u dis 4 ws u f 45 u f 60 20
Workload Analysis - as 10 u u u HP N 4000/06, 440 MHz 14 GB memory Peak Utilizations from 9 am-10 pm 1 pm-2 pm Major Workloads u dis 4 ws u f 45 u f 60 20
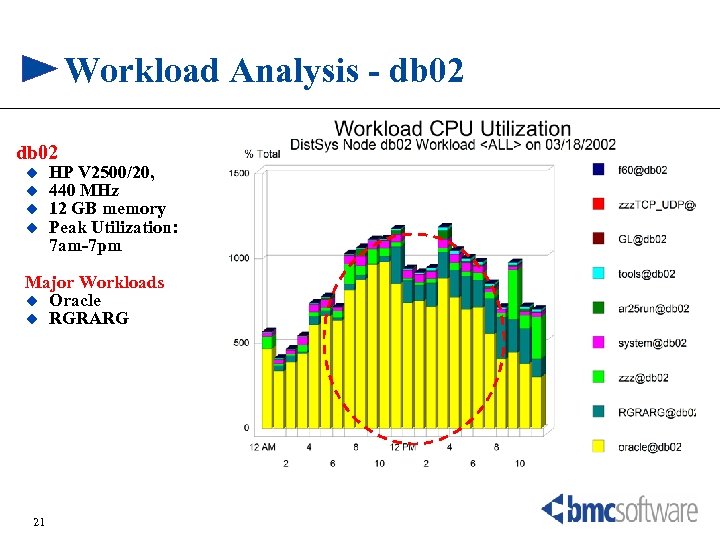 Workload Analysis - db 02 u u HP V 2500/20, 440 MHz 12 GB memory Peak Utilization: 7 am-7 pm Major Workloads u Oracle u RGRARG 21
Workload Analysis - db 02 u u HP V 2500/20, 440 MHz 12 GB memory Peak Utilization: 7 am-7 pm Major Workloads u Oracle u RGRARG 21
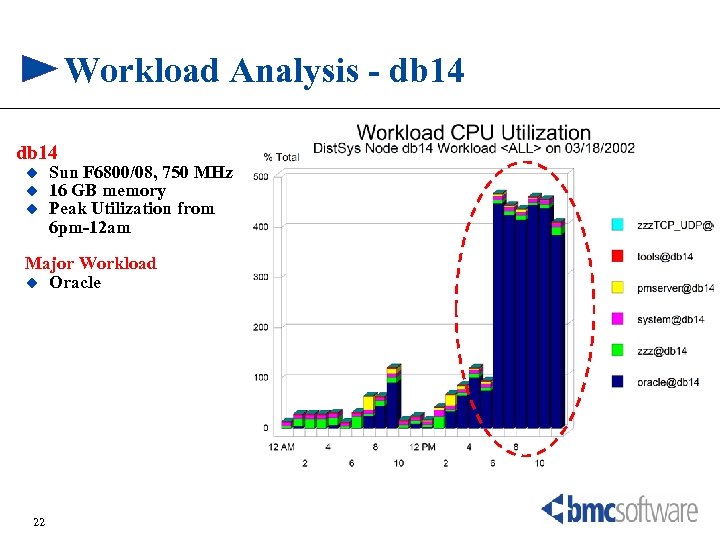 Workload Analysis - db 14 u u u Sun F 6800/08, 750 MHz 16 GB memory Peak Utilization from 6 pm-12 am Major Workload u Oracle 22
Workload Analysis - db 14 u u u Sun F 6800/08, 750 MHz 16 GB memory Peak Utilization from 6 pm-12 am Major Workload u Oracle 22
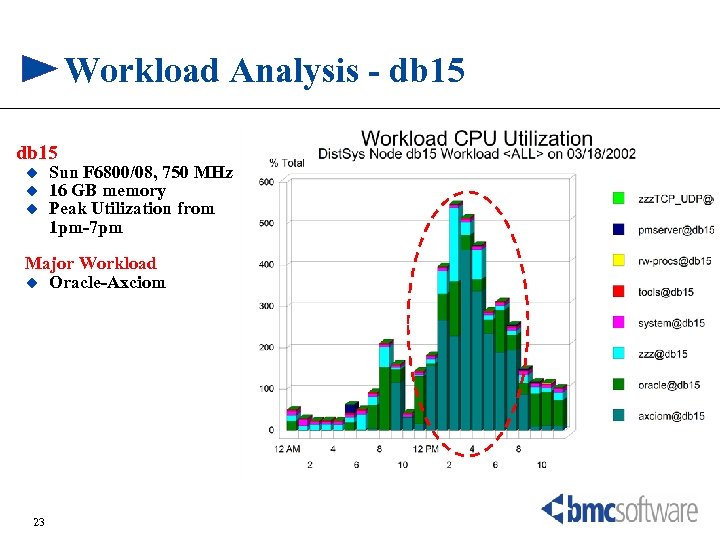 Workload Analysis - db 15 u u u Sun F 6800/08, 750 MHz 16 GB memory Peak Utilization from 1 pm-7 pm Major Workload u Oracle-Axciom 23
Workload Analysis - db 15 u u u Sun F 6800/08, 750 MHz 16 GB memory Peak Utilization from 1 pm-7 pm Major Workload u Oracle-Axciom 23
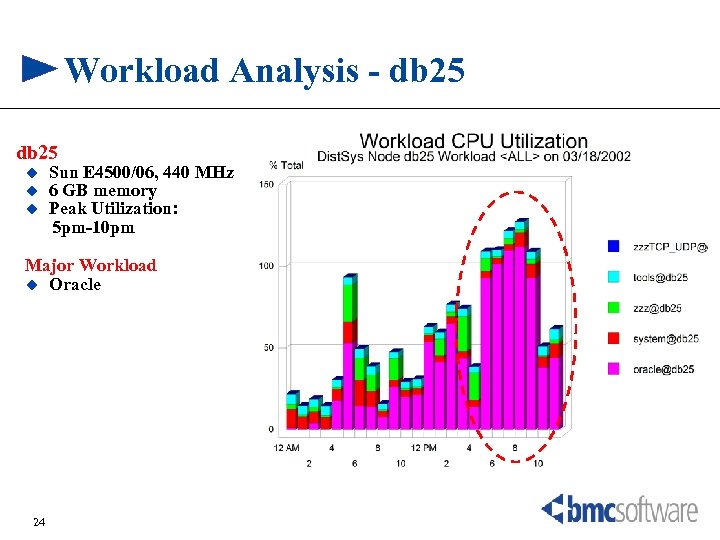 Workload Analysis - db 25 u u u Sun E 4500/06, 440 MHz 6 GB memory Peak Utilization: 5 pm-10 pm Major Workload u Oracle 24
Workload Analysis - db 25 u u u Sun E 4500/06, 440 MHz 6 GB memory Peak Utilization: 5 pm-10 pm Major Workload u Oracle 24
 4 - Combine Systems for Sizing u Server l Combined as 10 and db 02 into 1 server u l stacking Change db 02 from HP to Sun F 6800 Combined 2 database servers (db 14 and db 25) into 1 server u Workload l stacking Stack up all Oracle Instances u Check total capacity requirement u Use graphical visualization for quick check! 25
4 - Combine Systems for Sizing u Server l Combined as 10 and db 02 into 1 server u l stacking Change db 02 from HP to Sun F 6800 Combined 2 database servers (db 14 and db 25) into 1 server u Workload l stacking Stack up all Oracle Instances u Check total capacity requirement u Use graphical visualization for quick check! 25
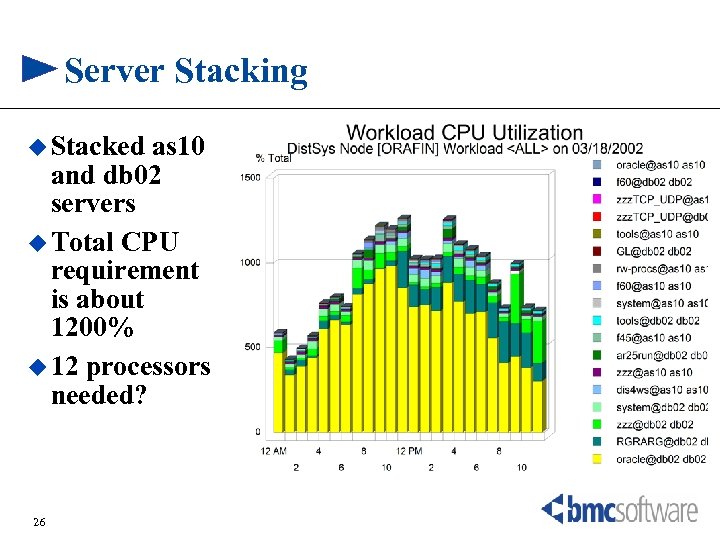 Server Stacking u Stacked as 10 and db 02 servers u Total CPU requirement is about 1200% u 12 processors needed? 26
Server Stacking u Stacked as 10 and db 02 servers u Total CPU requirement is about 1200% u 12 processors needed? 26
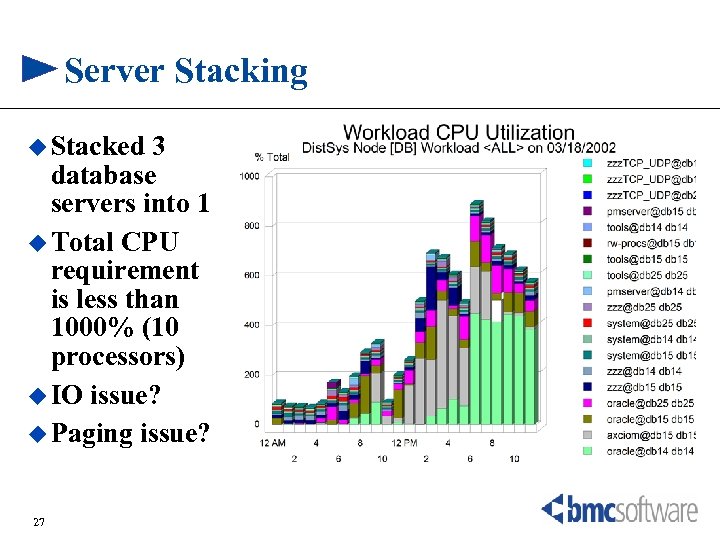 Server Stacking u Stacked 3 database servers into 1 u Total CPU requirement is less than 1000% (10 processors) u IO issue? u Paging issue? 27
Server Stacking u Stacked 3 database servers into 1 u Total CPU requirement is less than 1000% (10 processors) u IO issue? u Paging issue? 27
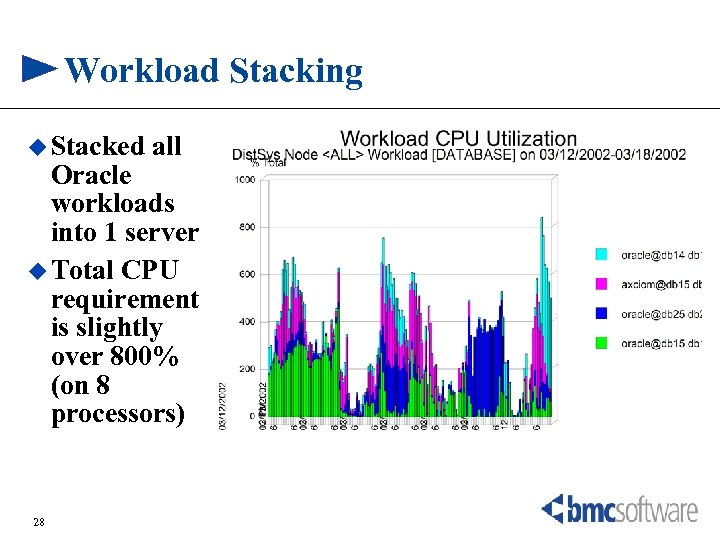 Workload Stacking u Stacked all Oracle workloads into 1 server u Total CPU requirement is slightly over 800% (on 8 processors) 28
Workload Stacking u Stacked all Oracle workloads into 1 server u Total CPU requirement is slightly over 800% (on 8 processors) 28
 5 - Consolidation Modeling u Resource l Combined as 10 and db 02 into 1 server u l contention analysis Change db 02 from HP to Sun F 6800/16 @750 MHz Consolidate Workloads from db 14 and db 25 into db 14 u Response time degradation analysis u Growth sensitivity analysis l Use 3/18/2002 14: 00 to 15: 00 as baseline interval Let’s see how PATROL Predict works…. . . 29
5 - Consolidation Modeling u Resource l Combined as 10 and db 02 into 1 server u l contention analysis Change db 02 from HP to Sun F 6800/16 @750 MHz Consolidate Workloads from db 14 and db 25 into db 14 u Response time degradation analysis u Growth sensitivity analysis l Use 3/18/2002 14: 00 to 15: 00 as baseline interval Let’s see how PATROL Predict works…. . . 29
 Baseline Model: Mar-18 -2002, 14: 00 Prepare the baseline model u u 30 Build a model for all nodes at peak utilization Calibrate the models to ensure measured and calculated values are accurate.
Baseline Model: Mar-18 -2002, 14: 00 Prepare the baseline model u u 30 Build a model for all nodes at peak utilization Calibrate the models to ensure measured and calculated values are accurate.
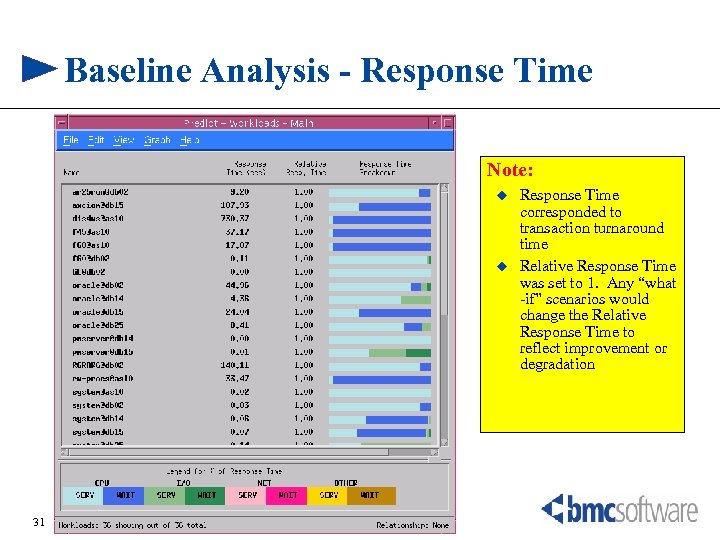 Baseline Analysis - Response Time Note: u u 31 Response Time corresponded to transaction turnaround time Relative Response Time was set to 1. Any “what -if” scenarios would change the Relative Response Time to reflect improvement or degradation
Baseline Analysis - Response Time Note: u u 31 Response Time corresponded to transaction turnaround time Relative Response Time was set to 1. Any “what -if” scenarios would change the Relative Response Time to reflect improvement or degradation
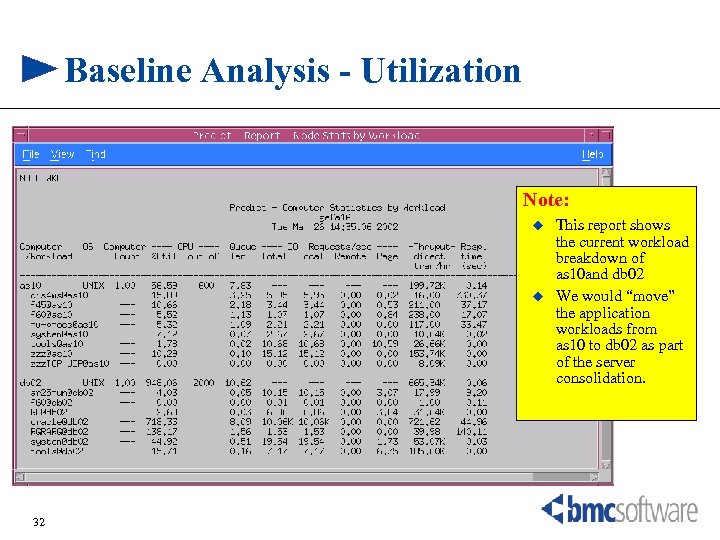 Baseline Analysis - Utilization Note: u u 32 This report shows the current workload breakdown of as 10 and db 02 We would “move” the application workloads from as 10 to db 02 as part of the server consolidation.
Baseline Analysis - Utilization Note: u u 32 This report shows the current workload breakdown of as 10 and db 02 We would “move” the application workloads from as 10 to db 02 as part of the server consolidation.
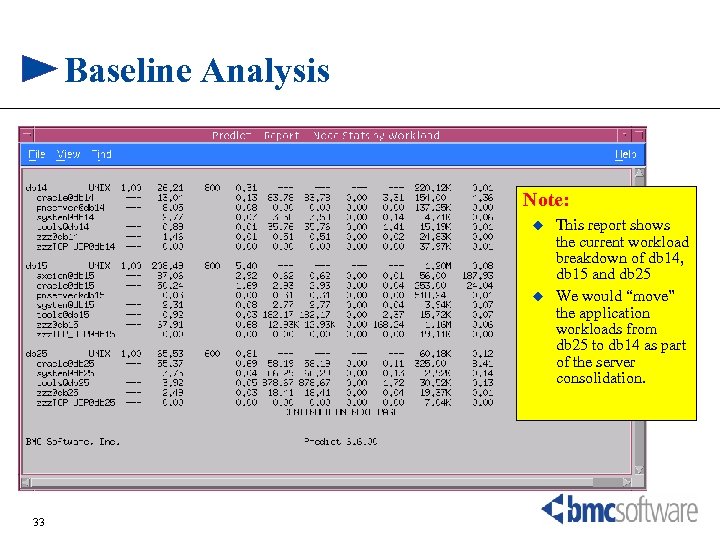 Baseline Analysis Note: u u 33 This report shows the current workload breakdown of db 14, db 15 and db 25 We would “move” the application workloads from db 25 to db 14 as part of the server consolidation.
Baseline Analysis Note: u u 33 This report shows the current workload breakdown of db 14, db 15 and db 25 We would “move” the application workloads from db 25 to db 14 as part of the server consolidation.
 What-if Analyses u Growth Sensitivity Analysis u Server Sizing l l Application Server Database Server… u Application Sizing u Disaster Planning u Hardware Purchase Planning u Capacity Planning 34
What-if Analyses u Growth Sensitivity Analysis u Server Sizing l l Application Server Database Server… u Application Sizing u Disaster Planning u Hardware Purchase Planning u Capacity Planning 34
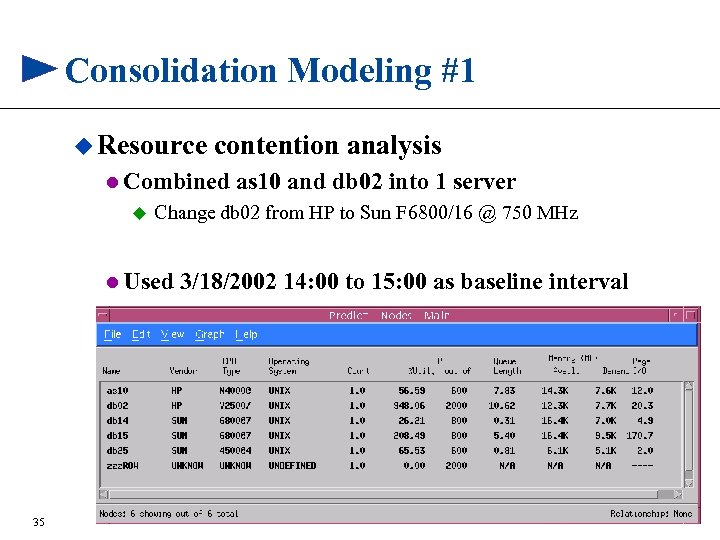 Consolidation Modeling #1 u Resource contention analysis l Combined u Change db 02 from HP to Sun F 6800/16 @ 750 MHz l Used 35 as 10 and db 02 into 1 server 3/18/2002 14: 00 to 15: 00 as baseline interval
Consolidation Modeling #1 u Resource contention analysis l Combined u Change db 02 from HP to Sun F 6800/16 @ 750 MHz l Used 35 as 10 and db 02 into 1 server 3/18/2002 14: 00 to 15: 00 as baseline interval
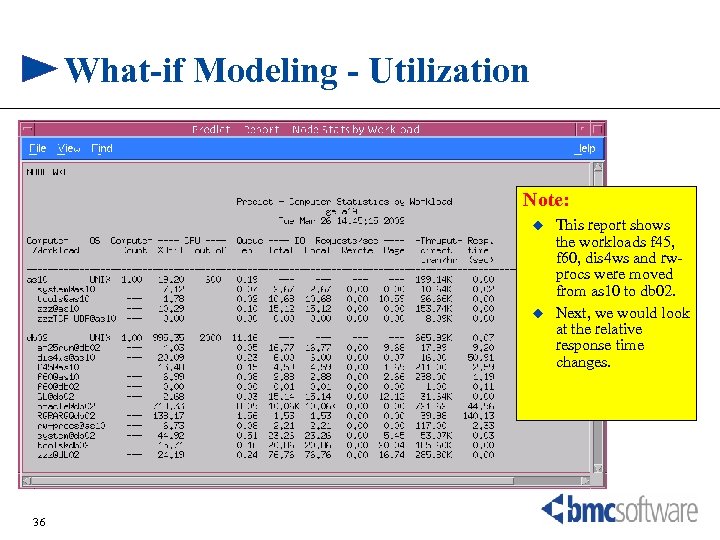 What-if Modeling - Utilization Note: u u 36 This report shows the workloads f 45, f 60, dis 4 ws and rwprocs were moved from as 10 to db 02. Next, we would look at the relative response time changes.
What-if Modeling - Utilization Note: u u 36 This report shows the workloads f 45, f 60, dis 4 ws and rwprocs were moved from as 10 to db 02. Next, we would look at the relative response time changes.
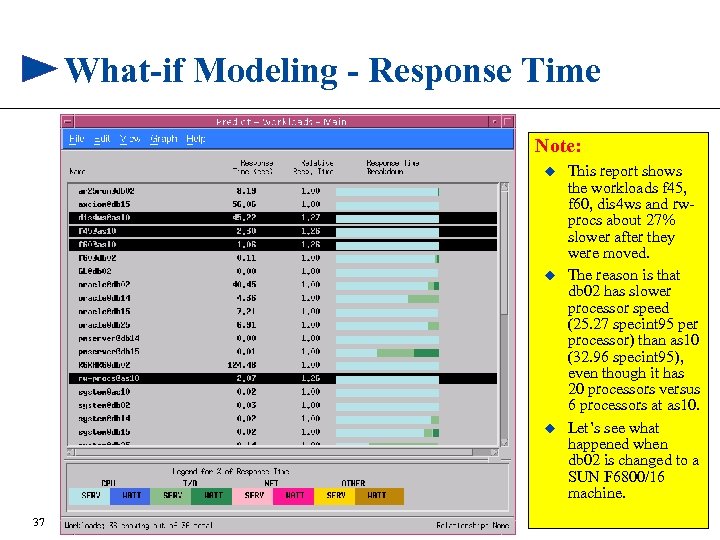 What-if Modeling - Response Time Note: u u u 37 This report shows the workloads f 45, f 60, dis 4 ws and rwprocs about 27% slower after they were moved. The reason is that db 02 has slower processor speed (25. 27 specint 95 per processor) than as 10 (32. 96 specint 95), even though it has 20 processors versus 6 processors at as 10. Let’s see what happened when db 02 is changed to a SUN F 6800/16 machine.
What-if Modeling - Response Time Note: u u u 37 This report shows the workloads f 45, f 60, dis 4 ws and rwprocs about 27% slower after they were moved. The reason is that db 02 has slower processor speed (25. 27 specint 95 per processor) than as 10 (32. 96 specint 95), even though it has 20 processors versus 6 processors at as 10. Let’s see what happened when db 02 is changed to a SUN F 6800/16 machine.
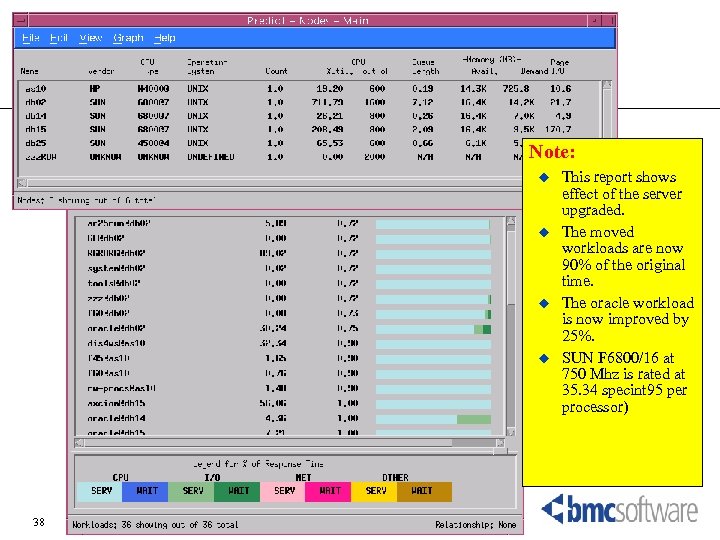 Note: u u 38 This report shows effect of the server upgraded. The moved workloads are now 90% of the original time. The oracle workload is now improved by 25%. SUN F 6800/16 at 750 Mhz is rated at 35. 34 specint 95 per processor)
Note: u u 38 This report shows effect of the server upgraded. The moved workloads are now 90% of the original time. The oracle workload is now improved by 25%. SUN F 6800/16 at 750 Mhz is rated at 35. 34 specint 95 per processor)
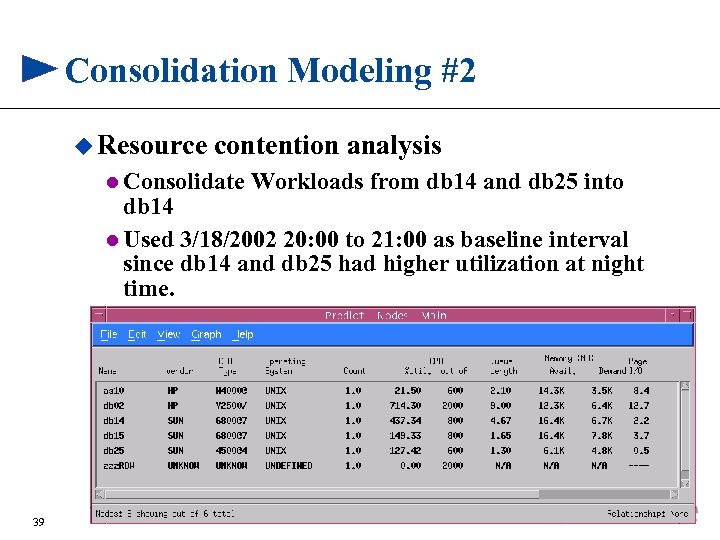 Consolidation Modeling #2 u Resource contention analysis l Consolidate Workloads from db 14 and db 25 into db 14 l Used 3/18/2002 20: 00 to 21: 00 as baseline interval since db 14 and db 25 had higher utilization at night time. 39
Consolidation Modeling #2 u Resource contention analysis l Consolidate Workloads from db 14 and db 25 into db 14 l Used 3/18/2002 20: 00 to 21: 00 as baseline interval since db 14 and db 25 had higher utilization at night time. 39
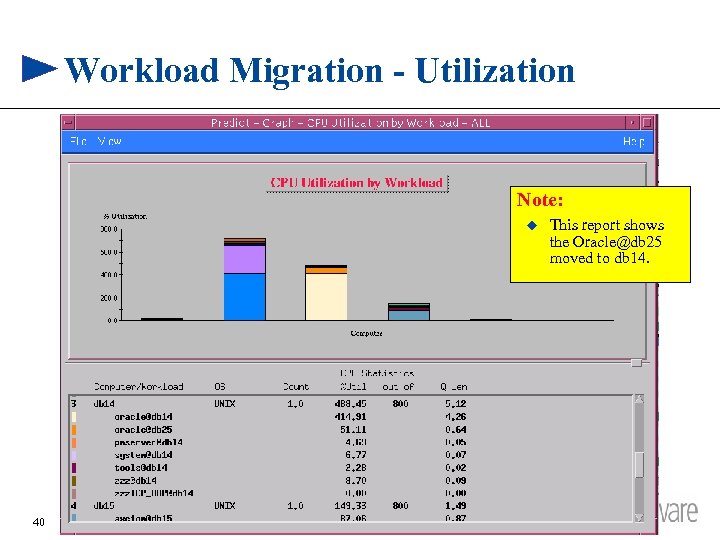 Workload Migration - Utilization Note: u 40 This report shows the Oracle@db 25 moved to db 14.
Workload Migration - Utilization Note: u 40 This report shows the Oracle@db 25 moved to db 14.
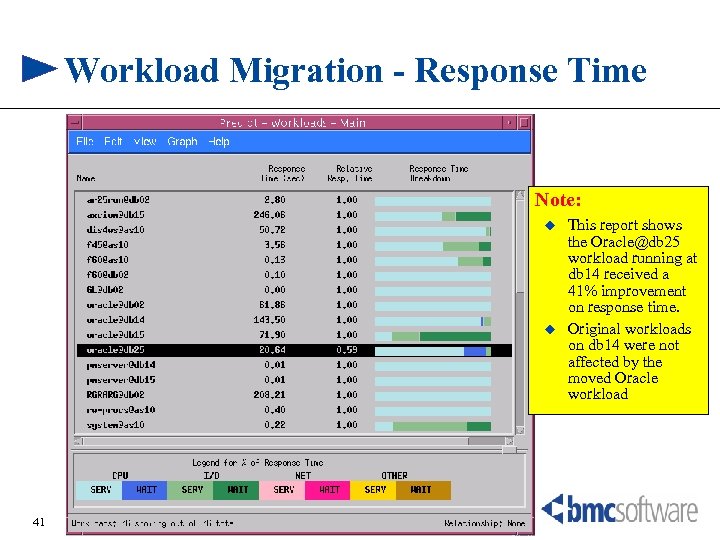 Workload Migration - Response Time Note: u u 41 This report shows the Oracle@db 25 workload running at db 14 received a 41% improvement on response time. Original workloads on db 14 were not affected by the moved Oracle workload
Workload Migration - Response Time Note: u u 41 This report shows the Oracle@db 25 workload running at db 14 received a 41% improvement on response time. Original workloads on db 14 were not affected by the moved Oracle workload
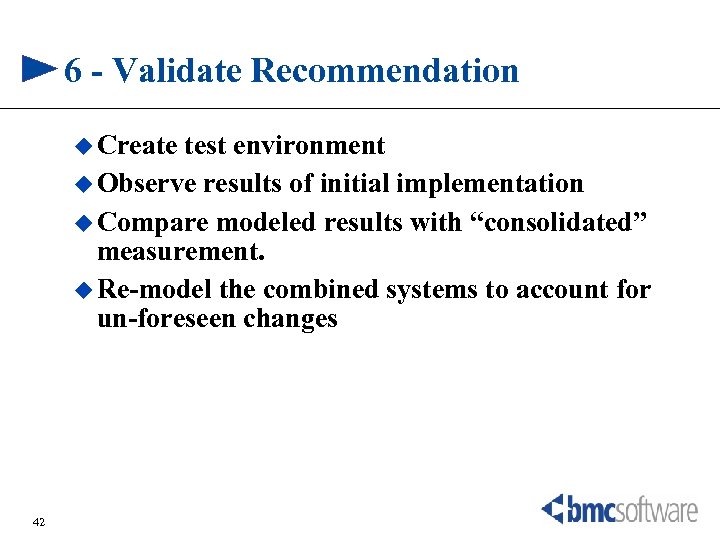 6 - Validate Recommendation u Create test environment u Observe results of initial implementation u Compare modeled results with “consolidated” measurement. u Re-model the combined systems to account for un-foreseen changes 42
6 - Validate Recommendation u Create test environment u Observe results of initial implementation u Compare modeled results with “consolidated” measurement. u Re-model the combined systems to account for un-foreseen changes 42
 Server Consolidation Review Six steps to Success u 1. Baseline current performance Collect detailed performance data u 2. Characterize workload l System, utility, application, database, etc. l u 3. Analyze resource usage level l u Time Series Graphical Analysis Peaks, batch windows, trends, growth pattern Workloads profiles 4. Combine systems for sizing Server and Workload stacking u 5. Consolidation modeling l Resource contention analysis l Response time degradation analysis l Growth sensitivity analysis l 43 u 6. Validate recommendation
Server Consolidation Review Six steps to Success u 1. Baseline current performance Collect detailed performance data u 2. Characterize workload l System, utility, application, database, etc. l u 3. Analyze resource usage level l u Time Series Graphical Analysis Peaks, batch windows, trends, growth pattern Workloads profiles 4. Combine systems for sizing Server and Workload stacking u 5. Consolidation modeling l Resource contention analysis l Response time degradation analysis l Growth sensitivity analysis l 43 u 6. Validate recommendation
 STORAGE Consolidation Too? BMC’s Application Centric Storage Management (ACSM) products can be leveraged to consolidate the storage side… 44
STORAGE Consolidation Too? BMC’s Application Centric Storage Management (ACSM) products can be leveraged to consolidate the storage side… 44
 PATROL Performance Management Summary An established process u An integrated suite of products and services to manage mission critical client/server applications. A proven methodology u Performance platforms and capacity management across multiple Multi-functional u Performance Analysis u Daily Performance Visualization u Interactive Performance Prediction High degree of process automation 45
PATROL Performance Management Summary An established process u An integrated suite of products and services to manage mission critical client/server applications. A proven methodology u Performance platforms and capacity management across multiple Multi-functional u Performance Analysis u Daily Performance Visualization u Interactive Performance Prediction High degree of process automation 45
 ROI’s Ensure consistent approach to take on server consolidation projects u ROI: Reduce risks and costs Enable IT staff to understand performance information and evaluate alternatives effectively u ROI: Better IT Performance/$ Ratio Empower IT staff to plan for and justify expenditures with confidence u ROI: 46 Timely hardware/software acquisitions
ROI’s Ensure consistent approach to take on server consolidation projects u ROI: Reduce risks and costs Enable IT staff to understand performance information and evaluate alternatives effectively u ROI: Better IT Performance/$ Ratio Empower IT staff to plan for and justify expenditures with confidence u ROI: 46 Timely hardware/software acquisitions


