6 Individual, State and Society.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 15

Separation of Powers

Branches of Government: • Judicial: interpret laws and settle disputes • Legislative: make laws • Executive: execute, enforce and administer laws Module Code and Module Title of Slides

Module Code and Module Title of Slides
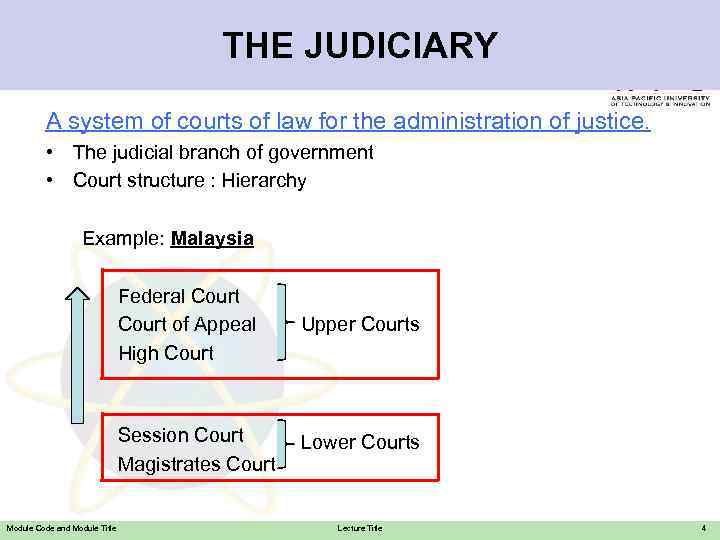
THE JUDICIARY A system of courts of law for the administration of justice. • The judicial branch of government • Court structure : Hierarchy Example: Malaysia Federal Court of Appeal High Court Session Court Magistrates Court Module Code and Module Title Upper Courts Lower Courts Lecture Title 4

Function of the Judiciary Interpret the law to disperse Justice WHO? HOW? ANY MONITORING SYSTEM? JURY SYSTEM? Important element of the Judiciary INDEPENDENCE OF THE JUDICIARY - Judgment to be given without fear and favour Module Code and Module Title Lecture Title 5

Others: Courts for particular purposes: – Industrial courts: Employment matters e. g. unfair dismissal – Special Courts (in Malaysia): ØMilitary Court: Martial law ØShariah Court: Islamic laws Module Code and Module Title Lecture Title 6

Apart from the formal courts: 1. Tribunal A Special Court or group of people who are officially chosen, especially by the government, to examine legal problems of a particular type e. g. (Consumer tribunal, Housing tribunal and War Tribunals). 2. Arbitration The parties opt(choose) for a private dispute resolution procedure instead of going to court. Arbitration is a procedure in which a dispute is submitted, by agreement of the parties, to one or more arbitrators who make a binding decision on the dispute. Module Code and Module Title Lecture Title 7
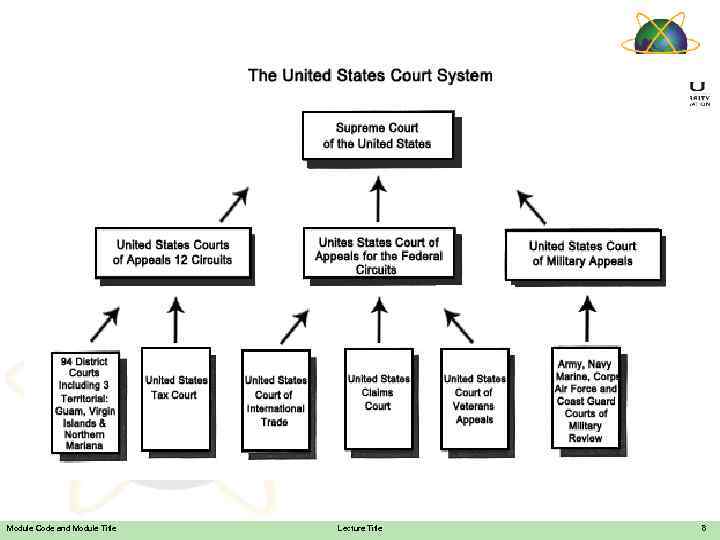
Module Code and Module Title Lecture Title 8

BAHRAIN - Shariah (Sunni & Shia) for personal matters of Muslims e. g. family & probate (dealing with property after death) - Civil & Criminal laws govern matters other than Shariah and for nonmuslims . Supreme Court of Appeal Higher Court of Appeal High Court Other : Military Court (March 2011) Module Code and Module Title Lecture Title 9

Module Code and Module Title Lecture Title 10

LEGISLATIVE A branch of government, having the powers to enact (make) laws. Examples: UNITED STATES: Congress is the legislative branch of the Government. House of representative Senate A Bill should be debated in Congress and voted by majority, then signed or vetoed by President of the US. What can Congress do if Bill is vetoed? Module Code and Module Title Lecture Title 11

UNITED KINGDOM Parliament House of Commons House of Lords MALAYSIA Parliament House of Representative Senate A Bill must be debated by both Houses & voted by Majority. It must then receive the Royal Assent & Sealed. Module Code and Module Title Lecture Title 12

Module Code and Module Title Lecture Title 13

THE EXECUTIVE The branch of the government that has its authority and responsibility for the daily administration of the state. Executes, or enforces the law. Chief of State Head of Government Cabinet/Council of Ministers UNITED STATES : PRESIDENT, VICE PRESIDENT & THE CABINET UNITED KINGDOM: MONARCH, PRIME MINISTER, THE CABINET MALAYSIA : MONARCH, PRIME MINISTER, THE CABINET IRAN : SUPREME LEADER, PRESIDENT, COUNCIL OF MINISTERS INDIA : PRESIDENT, PRIME MINISTER, THE CABINET Module Code and Module Title Lecture Title 14

Outcomes of the Lecturer • Students are able to describe the judiciary, executive and legislative body of governments. • Students are able to briefly discuss and compare the system of governance. Module Code and Module Title Lecture Title 15
6 Individual, State and Society.pptx