cca6fd944dc3ececfa768d5eb99732d0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 Sensor Network Querying Dina Q Goldin University of Connecticut, USA March 17, 2003
Sensor Network Querying Dina Q Goldin University of Connecticut, USA March 17, 2003
 The Invisible Computer • The most user-friendly computer is one we don’t see • Advocated in mid-1990’s by Michael Dertouzos, director of MIT's Laboratory for Computer Science for 25 years. • Does that make sense?
The Invisible Computer • The most user-friendly computer is one we don’t see • Advocated in mid-1990’s by Michael Dertouzos, director of MIT's Laboratory for Computer Science for 25 years. • Does that make sense?
 Outline • Computing in the 21 st century • Sensors and sensor networks • Sensor network querying
Outline • Computing in the 21 st century • Sensors and sensor networks • Sensor network querying
 The Disappearing Computer • More and more processors are not on desktops • Processors in cars, in cellular telephones, in toys • Even the computer itself can “dissolve” into an entertainment system - digital TV screen and speakers - CPU on shelf - wireless keyboard on lap
The Disappearing Computer • More and more processors are not on desktops • Processors in cars, in cellular telephones, in toys • Even the computer itself can “dissolve” into an entertainment system - digital TV screen and speakers - CPU on shelf - wireless keyboard on lap
 Home Computer of Tomorrow 1. Flat wall screens for TV/computer in many rooms 2. Connected to an out-of-sight CPU by LAN 3. Multiple speakers embedded in/around screen for 3 D sound effects 4. Screen can act as an (open) window when not in use 5. Natural input interface -- voice/pointing (no keyboard needed)
Home Computer of Tomorrow 1. Flat wall screens for TV/computer in many rooms 2. Connected to an out-of-sight CPU by LAN 3. Multiple speakers embedded in/around screen for 3 D sound effects 4. Screen can act as an (open) window when not in use 5. Natural input interface -- voice/pointing (no keyboard needed)
 House as a Web Site • Processors in various appliances • All networked (locally, and to wireless hub) • Appliances can communicate with outside world - Security system calls you or police - “Smart recycling bin” orders more food • Can log onto your house site to control them - Turn heat up - Turn coffeemaker on (already a reality)
House as a Web Site • Processors in various appliances • All networked (locally, and to wireless hub) • Appliances can communicate with outside world - Security system calls you or police - “Smart recycling bin” orders more food • Can log onto your house site to control them - Turn heat up - Turn coffeemaker on (already a reality)
 Cars of Tomorrow • GPS to know position • Wireless connection to obtain traffic conditions • Sensors: - distance to cars / people / obstacles - indoor/outdoor temperatures - road traction • Screen to show sensor readings / maps • Radio used for warnings / directions • Automatic controls based on sensor readings
Cars of Tomorrow • GPS to know position • Wireless connection to obtain traffic conditions • Sensors: - distance to cars / people / obstacles - indoor/outdoor temperatures - road traction • Screen to show sensor readings / maps • Radio used for warnings / directions • Automatic controls based on sensor readings
 Sensors for/in the Body • Digital jewelry: – DCPU in watch, speaker in an earring, camera in glasses • Scenarios: – (salesmen) Identifies person approaching, whispers their name, position to you – (repair trainee) Identifies machine parts, projects visual instructions on glasses • Assumes powerful vision/voice recognition • Embedded microsensors – Track vital signs, blood levels – For at-risk people: sick, old, mountain climbers
Sensors for/in the Body • Digital jewelry: – DCPU in watch, speaker in an earring, camera in glasses • Scenarios: – (salesmen) Identifies person approaching, whispers their name, position to you – (repair trainee) Identifies machine parts, projects visual instructions on glasses • Assumes powerful vision/voice recognition • Embedded microsensors – Track vital signs, blood levels – For at-risk people: sick, old, mountain climbers
 Ambient Intelligence Intelligent environments of all kinds: • Highways - Where are the traffic jams? • Airports – Who is entering/leaving high-risk areas? • Large high-rise office complexes - Are there problems with heat/AC anywhere? • Oceans – Is a Tzunami on its way? • People
Ambient Intelligence Intelligent environments of all kinds: • Highways - Where are the traffic jams? • Airports – Who is entering/leaving high-risk areas? • Large high-rise office complexes - Are there problems with heat/AC anywhere? • Oceans – Is a Tzunami on its way? • People
 Pervasive Computing • Computation in service of our needs: – Personal: Entertainment, daily activities, travel, house monitoring – Companies: Work efficiency, building monitoring – Scientific/medical: remote training / diagnosis, monitoring oceans - Governments: security, automatic gathering of statistics
Pervasive Computing • Computation in service of our needs: – Personal: Entertainment, daily activities, travel, house monitoring – Companies: Work efficiency, building monitoring – Scientific/medical: remote training / diagnosis, monitoring oceans - Governments: security, automatic gathering of statistics
 Pervasive Computing • Computing made easy - Interaction through natural modalities - Interaction during natural activities • Computing made invisible - Hidden in objects of everyday use - Distributed - Embedded in environments The computing paradigm for 21 st century
Pervasive Computing • Computing made easy - Interaction through natural modalities - Interaction during natural activities • Computing made invisible - Hidden in objects of everyday use - Distributed - Embedded in environments The computing paradigm for 21 st century
 Sensors • Essential part of pervasive computing • Computation – A small embedded computer with limited processing power and memory • Communication: – LAN, Wireless, Infrared / sound • Sensing – Temperature, pressure, magnetic field, noise levels, chemicals, etc.
Sensors • Essential part of pervasive computing • Computation – A small embedded computer with limited processing power and memory • Communication: – LAN, Wireless, Infrared / sound • Sensing – Temperature, pressure, magnetic field, noise levels, chemicals, etc.
 Sensor Constraints • A race to decrease: ü Size ü Price ü Energy consumption • A race to increase: ü Sensoring / transmitting abilities ü Computation power • Applications constrained by this tradeoff
Sensor Constraints • A race to decrease: ü Size ü Price ü Energy consumption • A race to increase: ü Sensoring / transmitting abilities ü Computation power • Applications constrained by this tradeoff
 Sensor Networks • • • Many sensors distributed in a region Performing a common task Local communication (between neighbors) Frequent failures Fault-tolerant distributed computing
Sensor Networks • • • Many sensors distributed in a region Performing a common task Local communication (between neighbors) Frequent failures Fault-tolerant distributed computing
 Monitoring Tasks • “Killer application” for sensor networks • Highways - Where are the traffic jams? • Airports – Who is entering/leaving high-risk areas? • Large high-rise office complexes - Are there problems with heat/AC anywhere? • Networks custom-engineered for each task
Monitoring Tasks • “Killer application” for sensor networks • Highways - Where are the traffic jams? • Airports – Who is entering/leaving high-risk areas? • Large high-rise office complexes - Are there problems with heat/AC anywhere? • Networks custom-engineered for each task
 Sensor Network Wish List • Robust performance – Failed sensors do not bring down the network • Ad-hoc routing – New sensors join the network on their own • Concerns also shared by mobile computing networks – Cell phones / PDAs / laptops / GPS devices • Established research area
Sensor Network Wish List • Robust performance – Failed sensors do not bring down the network • Ad-hoc routing – New sensors join the network on their own • Concerns also shared by mobile computing networks – Cell phones / PDAs / laptops / GPS devices • Established research area
 Monitoring Task Wish List • Ad-hoc computing – New sensor join the task on their own • Ad-hoc querying – Monitoring tasks can be initiated by user • Impossible while each task is customengineered • New approach is needed
Monitoring Task Wish List • Ad-hoc computing – New sensor join the task on their own • Ad-hoc querying – Monitoring tasks can be initiated by user • Impossible while each task is customengineered • New approach is needed
 Sensor Network Querying • A single general-purpose platform to enable sensor network users to perform all the monitoring activities mentioned above – A single (extensible) query language – A single (extensible) OS/DB engine – No more custom engineering • New & exciting research area
Sensor Network Querying • A single general-purpose platform to enable sensor network users to perform all the monitoring activities mentioned above – A single (extensible) query language – A single (extensible) OS/DB engine – No more custom engineering • New & exciting research area
 Axioms of SN Querying • User sees network as a single intelligent information system – Sensors as sources of data – Monitoring tasks as data processing • Ad-hoc querying of sensor networks - Each task specified by user, not customengineered - Multiple tasks can be present at once • Separation of engineering concerns – physical level (routing, communication) – logical level (data processing) – our focus
Axioms of SN Querying • User sees network as a single intelligent information system – Sensors as sources of data – Monitoring tasks as data processing • Ad-hoc querying of sensor networks - Each task specified by user, not customengineered - Multiple tasks can be present at once • Separation of engineering concerns – physical level (routing, communication) – logical level (data processing) – our focus
 Sensors As Data • Sensors form a database relation – Sensors(Node. ID, locn, temp, pressure, …. ) • Syntax as for regular relations – Employees(Emp. ID, birthdate, salary, …) • Data semantics is dynamic – Temperature and pressure are streams of continuously changing values
Sensors As Data • Sensors form a database relation – Sensors(Node. ID, locn, temp, pressure, …. ) • Syntax as for regular relations – Employees(Emp. ID, birthdate, salary, …) • Data semantics is dynamic – Temperature and pressure are streams of continuously changing values
 Monitoring Tasks as Queries • User asks queries in a query language – Return average temperature of each room in building • Syntax similar to regular database query languages – Such as SQL • Query semantics is continuous – Query “lives” in the network – Continuously reevaluated as sensor data dynamically changes
Monitoring Tasks as Queries • User asks queries in a query language – Return average temperature of each room in building • Syntax similar to regular database query languages – Such as SQL • Query semantics is continuous – Query “lives” in the network – Continuously reevaluated as sensor data dynamically changes
 Examples Find the average temperature in all the rooms that are dark SELECT room. Number, AVG(temp) FROM sensors WHERE light = OFF GROUPBY room. Number EPOCH DURATION 30 s
Examples Find the average temperature in all the rooms that are dark SELECT room. Number, AVG(temp) FROM sensors WHERE light = OFF GROUPBY room. Number EPOCH DURATION 30 s
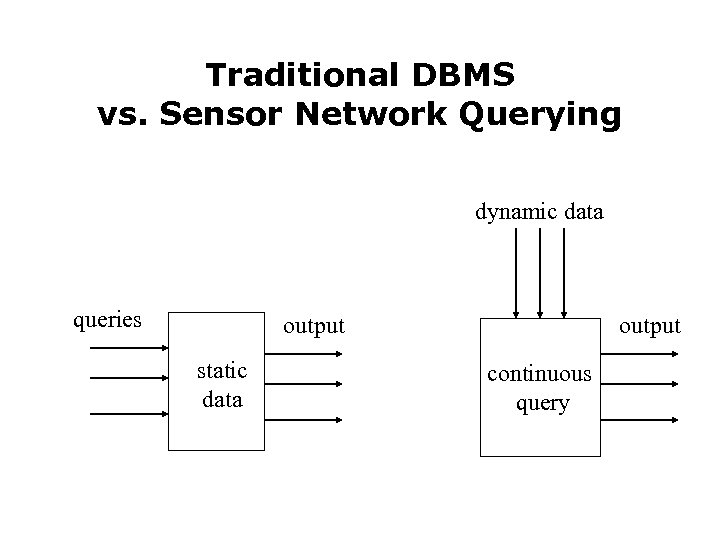 Traditional DBMS vs. Sensor Network Querying dynamic data queries output static data output continuous query
Traditional DBMS vs. Sensor Network Querying dynamic data queries output static data output continuous query
 Distributed DB Engine… • Each sensor has an OS – for managing routing, communication, etc – for controlling sensors – such as Tiny. OS (UC Berkeley) • Each sensor has a DB processor – remembers all queries “alive” in the network – evaluates each of them continuously – such as Tiny. DB (UC Berkeley) • New sensors join the network seamlessly
Distributed DB Engine… • Each sensor has an OS – for managing routing, communication, etc – for controlling sensors – such as Tiny. OS (UC Berkeley) • Each sensor has a DB processor – remembers all queries “alive” in the network – evaluates each of them continuously – such as Tiny. DB (UC Berkeley) • New sensors join the network seamlessly
 Coupled to Central Processor • • Entry point into sensor network User interacts with network via a CP Additional (static) data stored at CP Sensors are routed in a single tree whose root is connected to CP • Some data processing is centralized (at the CP), other localized (at the sensors)
Coupled to Central Processor • • Entry point into sensor network User interacts with network via a CP Additional (static) data stored at CP Sensors are routed in a single tree whose root is connected to CP • Some data processing is centralized (at the CP), other localized (at the sensors)
 Query Optimization • Traditionally: - minimize computation time / disk accesses • In sensor networks: - minimize power consumption • Sensor power consumption – Computation – Sensing (various modalities) – Communication (receiving, transmitting)
Query Optimization • Traditionally: - minimize computation time / disk accesses • In sensor networks: - minimize power consumption • Sensor power consumption – Computation – Sensing (various modalities) – Communication (receiving, transmitting)
 Events • Will play important role in SN querying • As part of query specification ON EVENT door-open(loc) [QUERY DESCRIPTION] • As optimization technique [monitor for sounds every 30 sec] BETWEEN EVENTS door-open, door-closed [monitor for sounds every 1 sec]
Events • Will play important role in SN querying • As part of query specification ON EVENT door-open(loc) [QUERY DESCRIPTION] • As optimization technique [monitor for sounds every 30 sec] BETWEEN EVENTS door-open, door-closed [monitor for sounds every 1 sec]
 Aggregation • Impossible to continuously collect raw sensor data (information overload) • Aggregation – family of operators to summarize data – Min, max, average • In-network aggregation for optimal query evaluation
Aggregation • Impossible to continuously collect raw sensor data (information overload) • Aggregation – family of operators to summarize data – Min, max, average • In-network aggregation for optimal query evaluation
 In-network Aggregation • Aggregate computed gradually – as values routed back to CP • Additional information carried along – to allow “partial” aggregation • Example: computing average – Carry
In-network Aggregation • Aggregate computed gradually – as values routed back to CP • Additional information carried along – to allow “partial” aggregation • Example: computing average – Carry
 Spatial Data • Spatial Databases store spatial data – Locations (of fire stations) – Regions (towns, lakes) – Lines (roads, rivers) • Spatial data will play larger role in SN querying • Dynamic spatial data – Contour maps – Tracking paths – Sensor locations (for mobile sensors) • Challenge: querying over dynamic spatial data
Spatial Data • Spatial Databases store spatial data – Locations (of fire stations) – Regions (towns, lakes) – Lines (roads, rivers) • Spatial data will play larger role in SN querying • Dynamic spatial data – Contour maps – Tracking paths – Sensor locations (for mobile sensors) • Challenge: querying over dynamic spatial data
 Example Queries over Dynamic Spatial Data • When there is an unusually loud sound, return the path that is followed by the source of this sound • Identify when we have a growing area of decreased pressure that exceeds some specified tolerances • Track the area where the average daily temperature has been exceeding its expected value by some specified tolerance for a specified period of time.
Example Queries over Dynamic Spatial Data • When there is an unusually loud sound, return the path that is followed by the source of this sound • Identify when we have a growing area of decreased pressure that exceeds some specified tolerances • Track the area where the average daily temperature has been exceeding its expected value by some specified tolerance for a specified period of time.
 Georouting • For reducing communication during broadcasts of spatial data • Maintain bounding box at each sensor, over locations of sensors in its routing subtree • Use it to filter out spatial data that falls outside the bounding box • Results in very significant savings
Georouting • For reducing communication during broadcasts of spatial data • Maintain bounding box at each sensor, over locations of sensors in its routing subtree • Use it to filter out spatial data that falls outside the bounding box • Results in very significant savings
 The Future: Active Sensor Networks • Sensors become mobile robots • Multiple communication modalities – Sound, wireless, infrared, smell • Can act upon their environments – Move things, turn switches, deposit color or scent • Interacting with our environment – Rather than just monitoring
The Future: Active Sensor Networks • Sensors become mobile robots • Multiple communication modalities – Sound, wireless, infrared, smell • Can act upon their environments – Move things, turn switches, deposit color or scent • Interacting with our environment – Rather than just monitoring


