f1264eb1ee98684f877c302b1718d4ad.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 10
 Sensitivity of Air Quality Model Predictions to Various Parameterizations of Vertical Eddy Diffusivity Zhiwei Han and Meigen Zhang Institute of Atmospheric Physics Chinese Academy of Science Beijing, China
Sensitivity of Air Quality Model Predictions to Various Parameterizations of Vertical Eddy Diffusivity Zhiwei Han and Meigen Zhang Institute of Atmospheric Physics Chinese Academy of Science Beijing, China
 Numerical experiment: • RAQMS (A Regional Air Quality Model System) 3 -d Eularian model with a spherical and terrain-following coordinate Advection, Diffusion, Dry deposition, multi-phase chemistry, cloud and scavenging etc. Han et al. (2006) Atmospheric Environment, Environmental Modelling & Software • PBL schemes 1. Medium-Range Forecasts (MRF), non-local first-order, countergradient term in Kz profile for the well mixed PBL, Hong and Pan (1996) 2. Gayno-Seaman(GSE), 1. 5 -order local closure, prognostic equation for TKE Shafran et al. (1998) 3. PBL similarity theory (B&D), (MCIP-CMAQ), Byun(1991), Byun and Dennis (1995)
Numerical experiment: • RAQMS (A Regional Air Quality Model System) 3 -d Eularian model with a spherical and terrain-following coordinate Advection, Diffusion, Dry deposition, multi-phase chemistry, cloud and scavenging etc. Han et al. (2006) Atmospheric Environment, Environmental Modelling & Software • PBL schemes 1. Medium-Range Forecasts (MRF), non-local first-order, countergradient term in Kz profile for the well mixed PBL, Hong and Pan (1996) 2. Gayno-Seaman(GSE), 1. 5 -order local closure, prognostic equation for TKE Shafran et al. (1998) 3. PBL similarity theory (B&D), (MCIP-CMAQ), Byun(1991), Byun and Dennis (1995)
 • Other Options The study domain: 90ºE-145ºE, 15º-50ºN The study period: March 2001 Horizontal grid resolution: 0. 5º Vertical resolution: 16 layers to 10 km, with 9 layers <2. 5 km Emissions: Anthropogenic and biomass burning from Streets et al (2003) Boundary conditions: monthly means from Mozart II (constant at boundary) Meteorological fields: MM 5, FDDA applied (3 -d reanalysis nudging) • Model validation and sensitivity analysis Observations: ground level monitoring sites of Japan (Hedo) 5 flights of DC-8 and P-3 B from the TRACE-P experiment Obs in source regions ? Species: SO 2, NOx and O 3 Statistical measures: Correlation coeeficient (R), mean bias error (MBE) root mean square error (RMSE), normalized mean bias (NMB) normalized mean error (NME)
• Other Options The study domain: 90ºE-145ºE, 15º-50ºN The study period: March 2001 Horizontal grid resolution: 0. 5º Vertical resolution: 16 layers to 10 km, with 9 layers <2. 5 km Emissions: Anthropogenic and biomass burning from Streets et al (2003) Boundary conditions: monthly means from Mozart II (constant at boundary) Meteorological fields: MM 5, FDDA applied (3 -d reanalysis nudging) • Model validation and sensitivity analysis Observations: ground level monitoring sites of Japan (Hedo) 5 flights of DC-8 and P-3 B from the TRACE-P experiment Obs in source regions ? Species: SO 2, NOx and O 3 Statistical measures: Correlation coeeficient (R), mean bias error (MBE) root mean square error (RMSE), normalized mean bias (NMB) normalized mean error (NME)
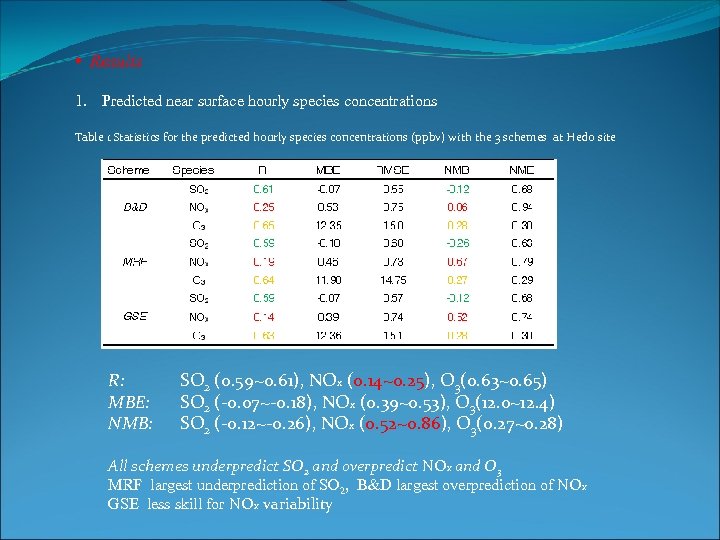 • Results 1. Predicted near surface hourly species concentrations Table 1 Statistics for the predicted hourly species concentrations (ppbv) with the 3 schemes at Hedo site R: MBE: NMB: SO 2 (0. 59~0. 61), NOx (0. 14~0. 25), O 3(0. 63~0. 65) SO 2 (-0. 07~-0. 18), NOx (0. 39~0. 53), O 3(12. 0~12. 4) SO 2 (-0. 12~-0. 26), NOx (0. 52~0. 86), O 3(0. 27~0. 28) All schemes underpredict SO 2 and overpredict NOx and O 3 MRF largest underprediction of SO 2, B&D largest overprediction of NOx GSE less skill for NOx variability
• Results 1. Predicted near surface hourly species concentrations Table 1 Statistics for the predicted hourly species concentrations (ppbv) with the 3 schemes at Hedo site R: MBE: NMB: SO 2 (0. 59~0. 61), NOx (0. 14~0. 25), O 3(0. 63~0. 65) SO 2 (-0. 07~-0. 18), NOx (0. 39~0. 53), O 3(12. 0~12. 4) SO 2 (-0. 12~-0. 26), NOx (0. 52~0. 86), O 3(0. 27~0. 28) All schemes underpredict SO 2 and overpredict NOx and O 3 MRF largest underprediction of SO 2, B&D largest overprediction of NOx GSE less skill for NOx variability
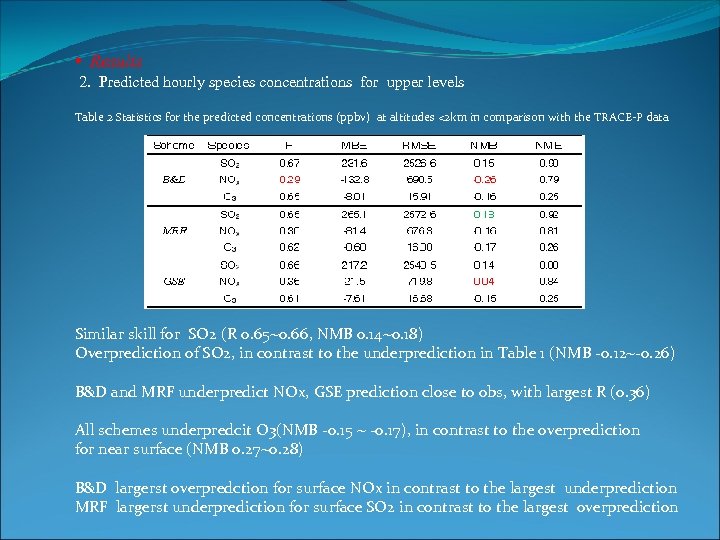 • Results 2. Predicted hourly species concentrations for upper levels Table 2 Statistics for the predicted concentrations (ppbv) at altitudes <2 km in comparison with the TRACE-P data Similar skill for SO 2 (R 0. 65~0. 66, NMB 0. 14~0. 18) Overprediction of SO 2, in contrast to the underprediction in Table 1 (NMB -0. 12~-0. 26) B&D and MRF underpredict NOx, GSE prediction close to obs, with largest R (0. 36) All schemes underpredcit O 3(NMB -0. 15 ~ -0. 17), in contrast to the overprediction for near surface (NMB 0. 27~0. 28) B&D largerst overpredction for surface NOx in contrast to the largest underprediction MRF largerst underprediction for surface SO 2 in contrast to the largest overprediction
• Results 2. Predicted hourly species concentrations for upper levels Table 2 Statistics for the predicted concentrations (ppbv) at altitudes <2 km in comparison with the TRACE-P data Similar skill for SO 2 (R 0. 65~0. 66, NMB 0. 14~0. 18) Overprediction of SO 2, in contrast to the underprediction in Table 1 (NMB -0. 12~-0. 26) B&D and MRF underpredict NOx, GSE prediction close to obs, with largest R (0. 36) All schemes underpredcit O 3(NMB -0. 15 ~ -0. 17), in contrast to the overprediction for near surface (NMB 0. 27~0. 28) B&D largerst overpredction for surface NOx in contrast to the largest underprediction MRF largerst underprediction for surface SO 2 in contrast to the largest overprediction
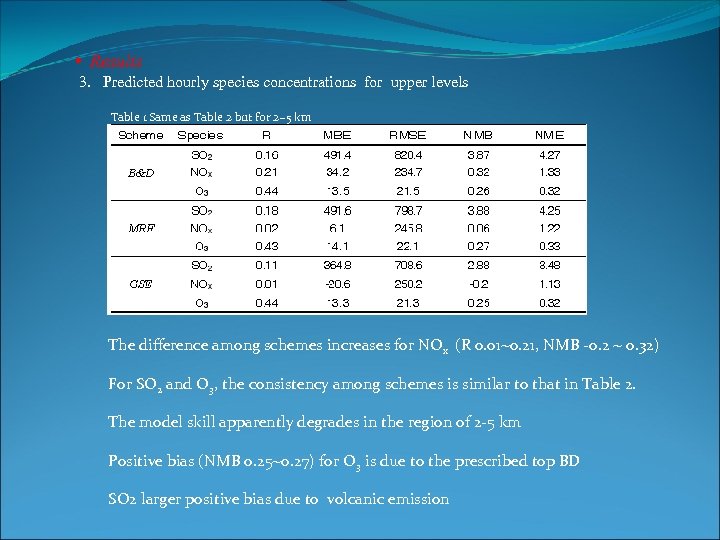 • Results 3. Predicted hourly species concentrations for upper levels Table 1 Same as Table 2 but for 2~5 km The difference among schemes increases for NOx (R 0. 01~0. 21, NMB -0. 2 ~ 0. 32) For SO 2 and O 3, the consistency among schemes is similar to that in Table 2. The model skill apparently degrades in the region of 2 -5 km Positive bias (NMB 0. 25~0. 27) for O 3 is due to the prescribed top BD SO 2 larger positive bias due to volcanic emission
• Results 3. Predicted hourly species concentrations for upper levels Table 1 Same as Table 2 but for 2~5 km The difference among schemes increases for NOx (R 0. 01~0. 21, NMB -0. 2 ~ 0. 32) For SO 2 and O 3, the consistency among schemes is similar to that in Table 2. The model skill apparently degrades in the region of 2 -5 km Positive bias (NMB 0. 25~0. 27) for O 3 is due to the prescribed top BD SO 2 larger positive bias due to volcanic emission
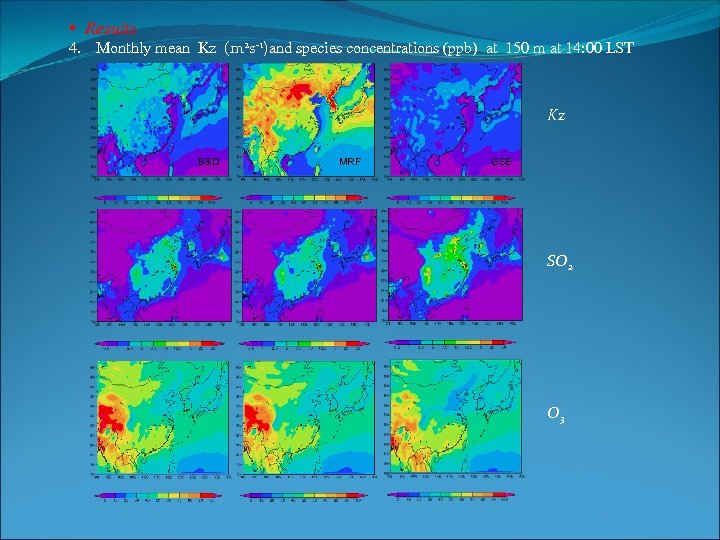 • Results 4. Monthly mean Kz (m 2 s-1)and species concentrations (ppb) at 150 m at 14: 00 LST Kz B&D MRF GSE SO 2 O 3
• Results 4. Monthly mean Kz (m 2 s-1)and species concentrations (ppb) at 150 m at 14: 00 LST Kz B&D MRF GSE SO 2 O 3
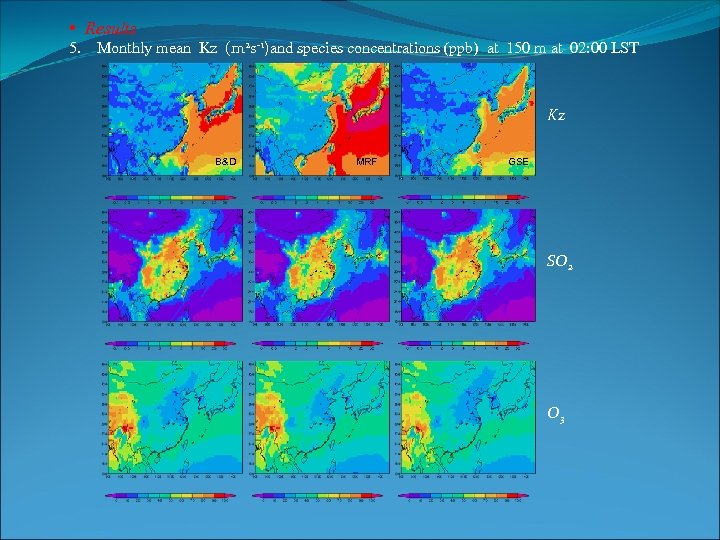 • Results 5. Monthly mean Kz (m 2 s-1)and species concentrations (ppb) at 150 m at 02: 00 LST Kz B&D MRF GSE SO 2 O 3
• Results 5. Monthly mean Kz (m 2 s-1)and species concentrations (ppb) at 150 m at 02: 00 LST Kz B&D MRF GSE SO 2 O 3
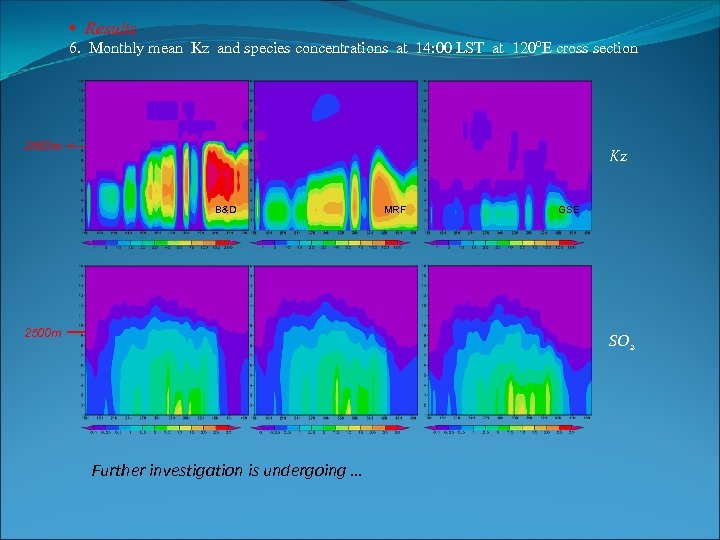 • Results 6. Monthly mean Kz and species concentrations at 14: 00 LST at 120ºE cross section 2500 m Kz B&D 2500 m MRF GSE SO 2 Further investigation is undergoing …
• Results 6. Monthly mean Kz and species concentrations at 14: 00 LST at 120ºE cross section 2500 m Kz B&D 2500 m MRF GSE SO 2 Further investigation is undergoing …
 Thank you !
Thank you !


