sensitive period - hypotheses.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 20
 Sensitive period and language acquisition MA - 2014
Sensitive period and language acquisition MA - 2014
 OUTLINE Glimpses of history: study of the sensitive period Main hypotheses and their evidence Modern approach The stages of sensitive period, its features and 1 st language acquisition Bilingualism/polyglottism: secrets of foreign language acquisition
OUTLINE Glimpses of history: study of the sensitive period Main hypotheses and their evidence Modern approach The stages of sensitive period, its features and 1 st language acquisition Bilingualism/polyglottism: secrets of foreign language acquisition
 The critical period hypothesis was first proposed by neurologist Wilder Penfield and co-author Lamar Roberts in their 1959 book Speech and Brain Mechanisms!
The critical period hypothesis was first proposed by neurologist Wilder Penfield and co-author Lamar Roberts in their 1959 book Speech and Brain Mechanisms!
 Eric Heinz Lenneberg (19 September 1921 – 31 May 1975) linguist & neurologist pioneered ideas on language acquisition and cognitive psychology (concept of innateness). The University of Chicago and Harvard University.
Eric Heinz Lenneberg (19 September 1921 – 31 May 1975) linguist & neurologist pioneered ideas on language acquisition and cognitive psychology (concept of innateness). The University of Chicago and Harvard University.
 Hypothesis (CPH) embodying two ideas: The biological basis responsible for language development can establish the critical period for the language acquisition, between the age of 18 months and early puberty During the critical period the child’s presence in the linguistically supportive environment is necessary as it leads into the successful language development. Evidence: 1) traumatic aphasia 2) down’s syndrome
Hypothesis (CPH) embodying two ideas: The biological basis responsible for language development can establish the critical period for the language acquisition, between the age of 18 months and early puberty During the critical period the child’s presence in the linguistically supportive environment is necessary as it leads into the successful language development. Evidence: 1) traumatic aphasia 2) down’s syndrome
 Details Critical period is an ideal time window to acquire language in a linguistically rich environment, after which further language acquisition becomes much more difficult and effortful. There are maturational constraints on the time a first language can be acquired. Language acquisition relies on neuroplasticity. An individual can acquire a first language if presented with adequate stimuli.
Details Critical period is an ideal time window to acquire language in a linguistically rich environment, after which further language acquisition becomes much more difficult and effortful. There are maturational constraints on the time a first language can be acquired. Language acquisition relies on neuroplasticity. An individual can acquire a first language if presented with adequate stimuli.
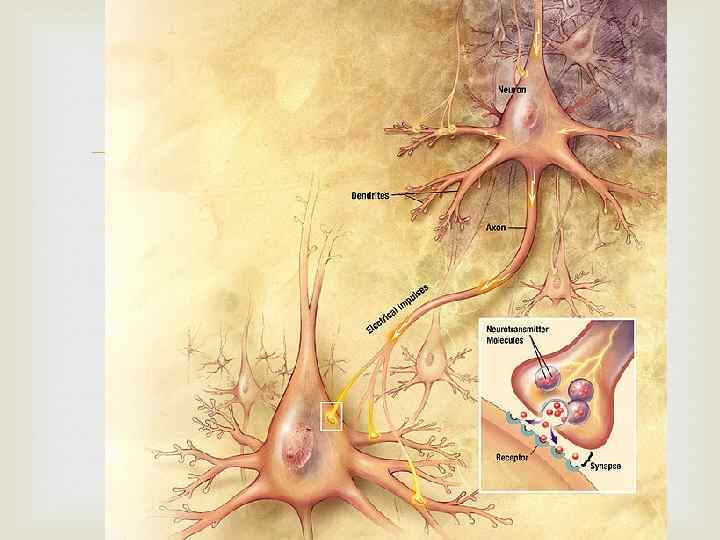
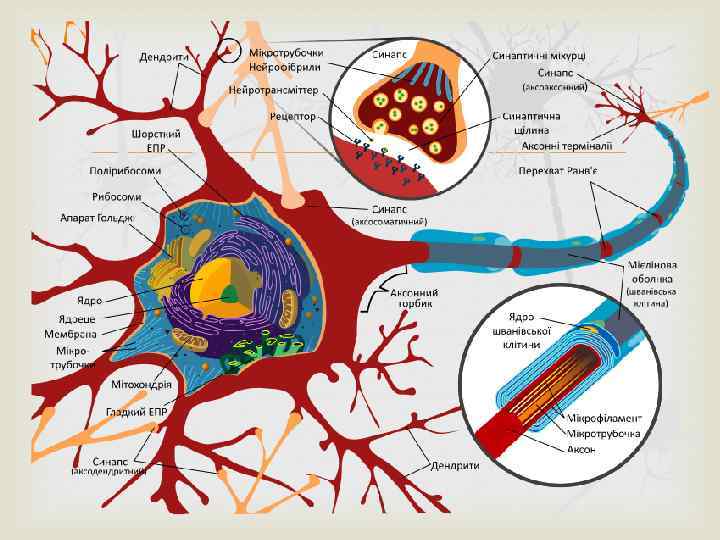
 Neuroplasticity is the ability of a particular part or region of a neuron to change in strength over time. Categories of plasticity: synaptic and non-synaptic. Synaptic plasticity deals directly with the strength of the connection between two neurons, including amount of neurotransmitter released from the presynaptic neuron, and the response generated in the postsynaptic neuron. Nonsynaptic plasticity involves modification of neuronal excitability in the axon, dendrites, and soma of an individual neuron, remote from the synapse
Neuroplasticity is the ability of a particular part or region of a neuron to change in strength over time. Categories of plasticity: synaptic and non-synaptic. Synaptic plasticity deals directly with the strength of the connection between two neurons, including amount of neurotransmitter released from the presynaptic neuron, and the response generated in the postsynaptic neuron. Nonsynaptic plasticity involves modification of neuronal excitability in the axon, dendrites, and soma of an individual neuron, remote from the synapse
 What changes and what preserves? time but can be restored Neuroplasticity declines with to a limited extent. (experiments by Anochin K. V. ) Lateralization of speech functions (J. Aitchison's metaphor – rooms in the house )
What changes and what preserves? time but can be restored Neuroplasticity declines with to a limited extent. (experiments by Anochin K. V. ) Lateralization of speech functions (J. Aitchison's metaphor – rooms in the house )
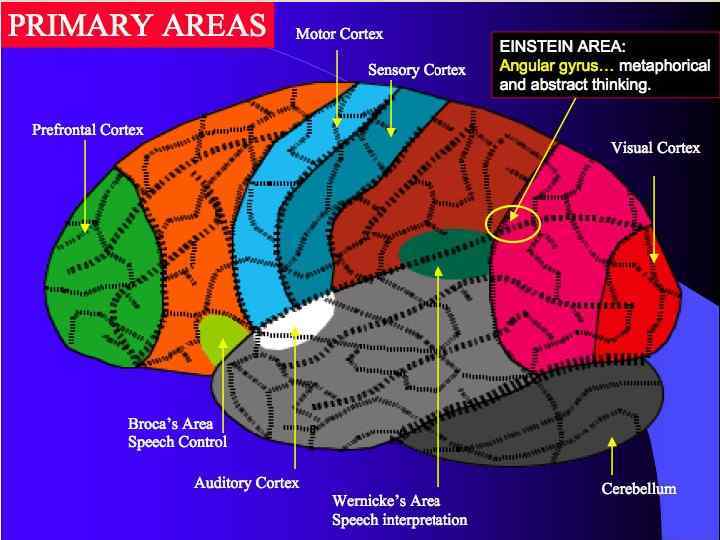 Cortical maps
Cortical maps
 Evidence for HCP Pre-lingual deafness Orphans Traumatic aphasia Down’s syndrome Lateralization of speech functions Hemispherectomy Wolf-children
Evidence for HCP Pre-lingual deafness Orphans Traumatic aphasia Down’s syndrome Lateralization of speech functions Hemispherectomy Wolf-children
 Wild/ feral children ‘the abandoned or isolated children who grow up without the normal condition for language learning, and so without language’ (Hudson, 2000. p. 175). There are two groups of ‘wild children’: those who grew up in jungles or forest those who grew up surrounded by the extreme social deprivation
Wild/ feral children ‘the abandoned or isolated children who grow up without the normal condition for language learning, and so without language’ (Hudson, 2000. p. 175). There are two groups of ‘wild children’: those who grew up in jungles or forest those who grew up surrounded by the extreme social deprivation
 Genie Wiley’s case, 2003
Genie Wiley’s case, 2003
 Rejection or confirmation She was eager to explore and socialize as she could. She won’t speak! But used non-verbal means! She was unable to straighten her arms and legs! Results of tests: about the level of a one-year-old, later 5 year-old. No syntax. She developed remarkable nonverbal communication skills (deep fascination with music, played with toys). Distinguished between plural and singular nouns, positive and negative sentence.
Rejection or confirmation She was eager to explore and socialize as she could. She won’t speak! But used non-verbal means! She was unable to straighten her arms and legs! Results of tests: about the level of a one-year-old, later 5 year-old. No syntax. She developed remarkable nonverbal communication skills (deep fascination with music, played with toys). Distinguished between plural and singular nouns, positive and negative sentence.
 Pronounced two/three-word sentences. But: She could not produce correct wh-questions: ‘Where is may I have penny? ’ (Curtiss, 1977) Failed to understand passive constructions and distinction marked by tenses Grammar was deficient in both production and comprehension: ‘Mama wash hair in sink’ ‘Father take piece wood. Hit. Cry. ’ (Curtiss, 1977).
Pronounced two/three-word sentences. But: She could not produce correct wh-questions: ‘Where is may I have penny? ’ (Curtiss, 1977) Failed to understand passive constructions and distinction marked by tenses Grammar was deficient in both production and comprehension: ‘Mama wash hair in sink’ ‘Father take piece wood. Hit. Cry. ’ (Curtiss, 1977).
 Nativists vs. empiricists Jonson&Newport, 1989 L. is nature: the maturational state hypothesis – (Early in life people have a superior capacity for acquiring language. This capacity disappears or declines with maturation. ) L. is nurture: the exercise hypothesis (Early in life people have a superior capacity for acquiring language and if it’s exercised during this time further language-learning abilities will remain intact throughout life. If not, it will disappear or decline with maturation)
Nativists vs. empiricists Jonson&Newport, 1989 L. is nature: the maturational state hypothesis – (Early in life people have a superior capacity for acquiring language. This capacity disappears or declines with maturation. ) L. is nurture: the exercise hypothesis (Early in life people have a superior capacity for acquiring language and if it’s exercised during this time further language-learning abilities will remain intact throughout life. If not, it will disappear or decline with maturation)
 nd 2 language acquisition hypothesis The interference hypothesis – 2 nd language learning is (to some extend) inhibited (затримуватись, гальмуватись) by prior attainment in a first language.
nd 2 language acquisition hypothesis The interference hypothesis – 2 nd language learning is (to some extend) inhibited (затримуватись, гальмуватись) by prior attainment in a first language.
 Other theories Social interactionist theory - by Lev Vygotsky and Jerome Bruner The relational frame theory (RFT) - (Hayes, Barnes. Holmes, Roche, 2001) - via a system of inherent reinforcement Emergentist theories, such as Mac. Whinney's competition model Chunking theories (the incremental acquisition of meaningful chunks of elementary constituents)
Other theories Social interactionist theory - by Lev Vygotsky and Jerome Bruner The relational frame theory (RFT) - (Hayes, Barnes. Holmes, Roche, 2001) - via a system of inherent reinforcement Emergentist theories, such as Mac. Whinney's competition model Chunking theories (the incremental acquisition of meaningful chunks of elementary constituents)
 Yevhenii Plakhotniuk Thanks!!!
Yevhenii Plakhotniuk Thanks!!!


