8c2f3aa1deacbf30a7c597b84015dd7c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 64
 Sensation & Perception Mr. Miller & Ms. Conaway AP Psychology – Chapter 6 (Myers, 9 th ed) Ocean Lakes High School Virginia Beach, VA Tons of Illusions! Flash-Lag Effect
Sensation & Perception Mr. Miller & Ms. Conaway AP Psychology – Chapter 6 (Myers, 9 th ed) Ocean Lakes High School Virginia Beach, VA Tons of Illusions! Flash-Lag Effect
 Thinking Question Day 1 If you had to give up 1 sense, which would you least be willing to give up and why? Most willing?
Thinking Question Day 1 If you had to give up 1 sense, which would you least be willing to give up and why? Most willing?
 How many SENSES do we have? Energy Senses • Vision = light • Hearing = sound waves • Touch = pressure Chemical Senses • Taste • Smell Body Position & Balance • Kinesthetic • Vestibular
How many SENSES do we have? Energy Senses • Vision = light • Hearing = sound waves • Touch = pressure Chemical Senses • Taste • Smell Body Position & Balance • Kinesthetic • Vestibular
 Absolute Threshold Detected @ rate of 50% Stimulus Absolute Threshold Vision A candle seen at 30 miles on a dark, clear night (only 3 photons of light!) Hearing The tick of a watch at 20 feet under quiet conditions Taste One teaspoon of sugar in 2 gallons of water Smell One drop of perfume diffused into a three-room apartment Touch The wing of a fly falling on your cheek from a distance of 0. 5 inch
Absolute Threshold Detected @ rate of 50% Stimulus Absolute Threshold Vision A candle seen at 30 miles on a dark, clear night (only 3 photons of light!) Hearing The tick of a watch at 20 feet under quiet conditions Taste One teaspoon of sugar in 2 gallons of water Smell One drop of perfume diffused into a three-room apartment Touch The wing of a fly falling on your cheek from a distance of 0. 5 inch
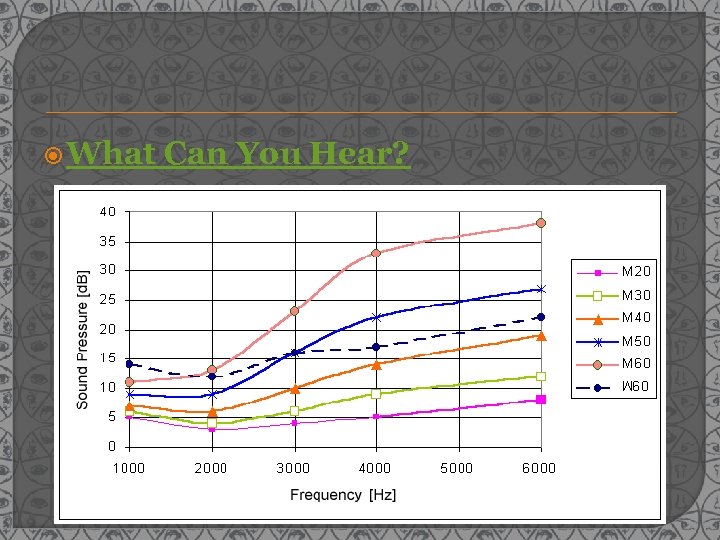 What Can You Hear?
What Can You Hear?
 Subliminal Demonic songs? messages in • Backwards Songs Movies with it? Greater liking for geometric shapes flashed subliminally (Kunst-Wilson & Zajonc, 1980) “Brainwashing” possible… not
Subliminal Demonic songs? messages in • Backwards Songs Movies with it? Greater liking for geometric shapes flashed subliminally (Kunst-Wilson & Zajonc, 1980) “Brainwashing” possible… not
 Researchers can study blindsight in the lab by using electromagnetic stimulation on normally sighted people to reproduce temporary blindness. They can then measure the subjects' ability to sense objects that they cannot see. Experience it How about just being blind? Blind people process Braille in the visual cortex, too! Blindsight
Researchers can study blindsight in the lab by using electromagnetic stimulation on normally sighted people to reproduce temporary blindness. They can then measure the subjects' ability to sense objects that they cannot see. Experience it How about just being blind? Blind people process Braille in the visual cortex, too! Blindsight
 Change Blindness Lots of Short Video Examples! • Original Door Study Basketball http: //www 2. psych. ubc. ca/~r ensink/flicker/download/ Some other examples…
Change Blindness Lots of Short Video Examples! • Original Door Study Basketball http: //www 2. psych. ubc. ca/~r ensink/flicker/download/ Some other examples…
 Blindness Activity Pair up One should be the observer, one should be “blind” You should find the… • • • 1) Schola 2) Computer Lab 101 3) Library 4) Gym Concession Stand 5) Social Studies Department Office Switch roles after you have found the location Be back in 10 minutes total…so back at…
Blindness Activity Pair up One should be the observer, one should be “blind” You should find the… • • • 1) Schola 2) Computer Lab 101 3) Library 4) Gym Concession Stand 5) Social Studies Department Office Switch roles after you have found the location Be back in 10 minutes total…so back at…
 JNDs & Weber’s Law = Detect diffs @ rate of 50% EXAMPLES of JNDs: • Light = 8% • Weight = 2 % • Taste = 20% Pitch = 1/3 of 1% Loudness = 10 % 100 th Birthday! 100 db…how much more until you noticed? 3 Quarters, 2 Envelopes and a Pair of Shoes Applied Psych: Salesman…Suit ($300) or Sweater ($75)…if you want the customer to buy both, which do you show first and why?
JNDs & Weber’s Law = Detect diffs @ rate of 50% EXAMPLES of JNDs: • Light = 8% • Weight = 2 % • Taste = 20% Pitch = 1/3 of 1% Loudness = 10 % 100 th Birthday! 100 db…how much more until you noticed? 3 Quarters, 2 Envelopes and a Pair of Shoes Applied Psych: Salesman…Suit ($300) or Sweater ($75)…if you want the customer to buy both, which do you show first and why?
 Top-Down and Bottom-Up Processing Aoccdrnig to rscheearch at Cmabrigde Uinervtisy, it deosn’t mttaer in waht oredr the ltteers in a wrod are, the olny iprmoetnt tihng is taht the frist and lsat ltteer be at the rghit pclae. The rset can be a total mses and you can sitll raed it wouthit a porbelm. Tihs is bcuseae the huamn mnid deos not raed ervey lteter by istlef, but the wrod as a wlohe.
Top-Down and Bottom-Up Processing Aoccdrnig to rscheearch at Cmabrigde Uinervtisy, it deosn’t mttaer in waht oredr the ltteers in a wrod are, the olny iprmoetnt tihng is taht the frist and lsat ltteer be at the rghit pclae. The rset can be a total mses and you can sitll raed it wouthit a porbelm. Tihs is bcuseae the huamn mnid deos not raed ervey lteter by istlef, but the wrod as a wlohe.
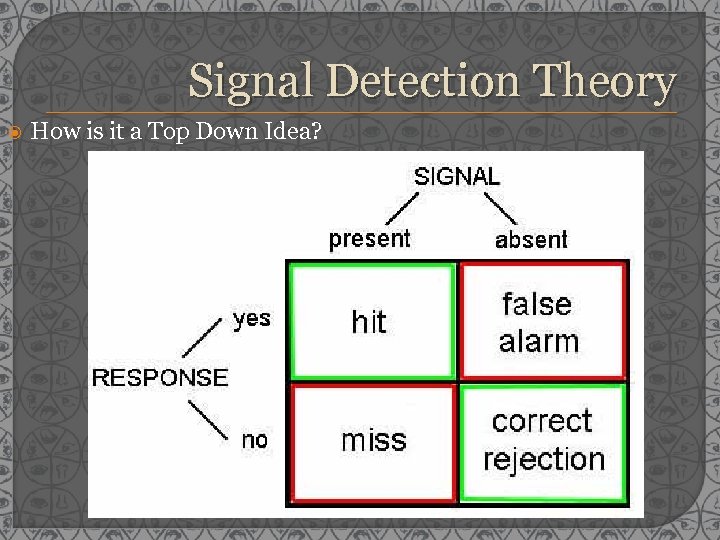 Signal Detection Theory How is it a Top Down Idea?
Signal Detection Theory How is it a Top Down Idea?
 Toe Top Down vs. Bottom Up Touching Demonstration Interlocked Arms Demonstration Nervous system does not come with automatic prewired sensory relationships
Toe Top Down vs. Bottom Up Touching Demonstration Interlocked Arms Demonstration Nervous system does not come with automatic prewired sensory relationships
 Sensory Adaptation Switch watch hands Friends’ houses smell funny? Cross-Adaptation OJ & Toothpaste Demonstration: Salt water becomes less salty, then drink regular water Eyes are always moving…if you mechanically keep them still, you will notice that things seem to disappear
Sensory Adaptation Switch watch hands Friends’ houses smell funny? Cross-Adaptation OJ & Toothpaste Demonstration: Salt water becomes less salty, then drink regular water Eyes are always moving…if you mechanically keep them still, you will notice that things seem to disappear
 Thinking Question Day 3 What’s your favorite color? Why? If you could only perceive 3 people’s faces, whose would they be and why? If you could only hear 1 song (or someone’s voice if you don’t like music), what would it be and why? If you could perceive only 1 type of taste, what would it be and why?
Thinking Question Day 3 What’s your favorite color? Why? If you could only perceive 3 people’s faces, whose would they be and why? If you could only hear 1 song (or someone’s voice if you don’t like music), what would it be and why? If you could perceive only 1 type of taste, what would it be and why?
 Movement Aftereffects (MAEs) Cause: adaptation of motion-specific detectors that are tuned to the direction of the movement of the stimuli being viewed TRIPPY!
Movement Aftereffects (MAEs) Cause: adaptation of motion-specific detectors that are tuned to the direction of the movement of the stimuli being viewed TRIPPY!
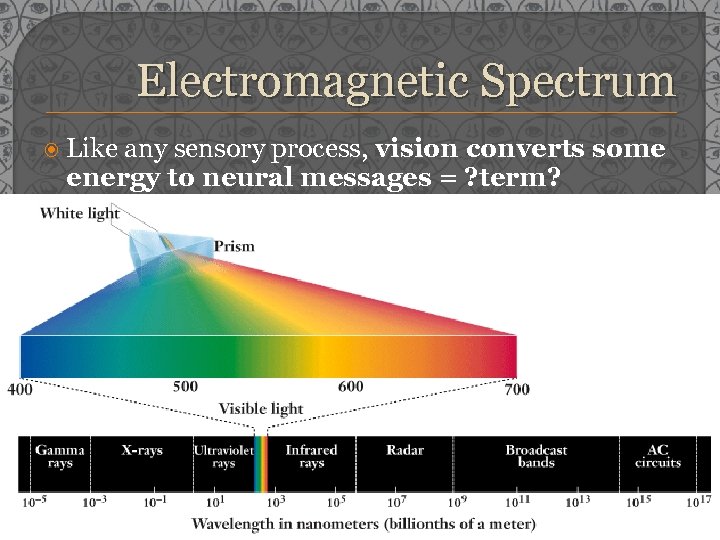 Electromagnetic Spectrum Like any sensory process, vision converts some energy to neural messages = ? term?
Electromagnetic Spectrum Like any sensory process, vision converts some energy to neural messages = ? term?
 Color NOTHING has color!! …rather color is our interpretation of reflected wavelengths of light • So, trees are “green” because they reflect the “green” wavelength of light; they keep in everything else Amplitude = how much energy (or photons) the light contains = Brightness (rods) Wavelength = determines hue (cones) • Shorter than “visible light” = UV-rays, X-rays • Longer than “visible light” = infrared, microwaves, radio waves • Colors short to long = violet (400 nm), indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange, and red (700 nm) NM = billionths of a meter
Color NOTHING has color!! …rather color is our interpretation of reflected wavelengths of light • So, trees are “green” because they reflect the “green” wavelength of light; they keep in everything else Amplitude = how much energy (or photons) the light contains = Brightness (rods) Wavelength = determines hue (cones) • Shorter than “visible light” = UV-rays, X-rays • Longer than “visible light” = infrared, microwaves, radio waves • Colors short to long = violet (400 nm), indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange, and red (700 nm) NM = billionths of a meter
 Fun Breathing And Square a related one (Motion Binding) Hollow Faces Hermann Grid AND Hermann Grid But, curiously, not as often (1: 3 vs. 9: 10) in schizophrenics
Fun Breathing And Square a related one (Motion Binding) Hollow Faces Hermann Grid AND Hermann Grid But, curiously, not as often (1: 3 vs. 9: 10) in schizophrenics
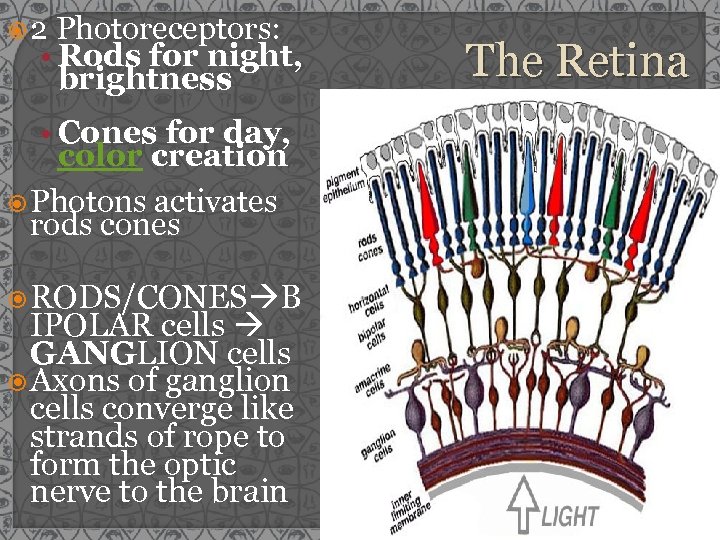 2 Photoreceptors: • Rods for night, brightness • Cones for day, color creation Photons activates rods cones RODS/CONES B IPOLAR cells GANGLION cells Axons of ganglion cells converge like strands of rope to form the optic nerve to the brain The Retina
2 Photoreceptors: • Rods for night, brightness • Cones for day, color creation Photons activates rods cones RODS/CONES B IPOLAR cells GANGLION cells Axons of ganglion cells converge like strands of rope to form the optic nerve to the brain The Retina
 Distribution of Rods & Cones Demonstration—Guess the Marker What are the function of cones? Rods? Where are the cones distributed? Rods? What does “fovea” mean? BLIND SPOT demonstration: • 2) Blindspot – next slide • 3) Not the Blind Spot. . . but still pretty darn sweet Magic Eye (not at all related)
Distribution of Rods & Cones Demonstration—Guess the Marker What are the function of cones? Rods? Where are the cones distributed? Rods? What does “fovea” mean? BLIND SPOT demonstration: • 2) Blindspot – next slide • 3) Not the Blind Spot. . . but still pretty darn sweet Magic Eye (not at all related)

 You can eliminate the blind spot But only if you are an octopus…!
You can eliminate the blind spot But only if you are an octopus…!
 Eye-ness Which eye is your dominant eye… 1) Select an object that is a few feet away from you 2) Stare at the object and then point to the object using your index finger. 3) When your eyes are focused on the object and not on your finger, you will see two blurry fingers in your line of sight. 4) Now, close one eye and then close the other eye. Expected results: with 1 of your eyes closed, your index finger will point exactly at the object, however, when the other eye is closed, your finger will point at an area slightly shifted to the side of the object…
Eye-ness Which eye is your dominant eye… 1) Select an object that is a few feet away from you 2) Stare at the object and then point to the object using your index finger. 3) When your eyes are focused on the object and not on your finger, you will see two blurry fingers in your line of sight. 4) Now, close one eye and then close the other eye. Expected results: with 1 of your eyes closed, your index finger will point exactly at the object, however, when the other eye is closed, your finger will point at an area slightly shifted to the side of the object…

 Another problem: Prosopagnosia Complete sensation but incomplete perception Best example is the inability to recognize faces
Another problem: Prosopagnosia Complete sensation but incomplete perception Best example is the inability to recognize faces
 Color Vision Trichromatic: 3 color combos (RGB) Dichromatic: See things in 2 colors combos • Red-green (most common) • Yellow-blue (dogs) Monochromatic – sees only light & dark (gray, black, white, etc. ) (rats)
Color Vision Trichromatic: 3 color combos (RGB) Dichromatic: See things in 2 colors combos • Red-green (most common) • Yellow-blue (dogs) Monochromatic – sees only light & dark (gray, black, white, etc. ) (rats)
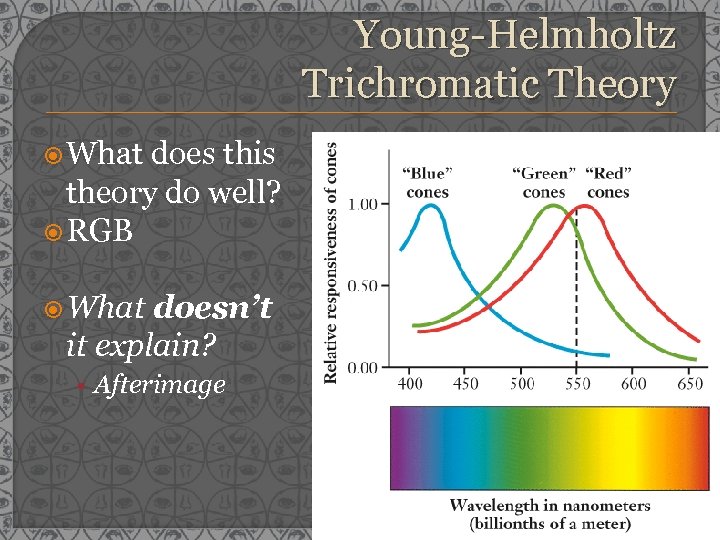 Young-Helmholtz Trichromatic Theory What does this theory do well? RGB What doesn’t it explain? • Afterimage
Young-Helmholtz Trichromatic Theory What does this theory do well? RGB What doesn’t it explain? • Afterimage
 Interesting Stuff Why eat carrots? • Contains carotene which produces rhodopsin, the photochemical in rods (helps night vision) Rods don’t respond to red light, so night watchmen (sailors) often wear “red” goggles to allow time (45 minutes) for rhodopsin to replenish to allow for “night vision”
Interesting Stuff Why eat carrots? • Contains carotene which produces rhodopsin, the photochemical in rods (helps night vision) Rods don’t respond to red light, so night watchmen (sailors) often wear “red” goggles to allow time (45 minutes) for rhodopsin to replenish to allow for “night vision”
 DOGS Color Vision CATS Color Vision Animal Stuff Nocturnal animals can’t see red. Turn white light on at night (makes them sleep) Turn red light on during day (when they are awake, so we can see them!)
DOGS Color Vision CATS Color Vision Animal Stuff Nocturnal animals can’t see red. Turn white light on at night (makes them sleep) Turn red light on during day (when they are awake, so we can see them!)
 Welcome! Today’s quiz will be in a different format. I will explain it after the bell rings. You will need your own sheet of paper.
Welcome! Today’s quiz will be in a different format. I will explain it after the bell rings. You will need your own sheet of paper.
 HW Quiz: 1) Is it a face or a vase? Which term best applies to this “dual” image? 2) What is this apparatus called?
HW Quiz: 1) Is it a face or a vase? Which term best applies to this “dual” image? 2) What is this apparatus called?
 3) If you are in a car staring out the side window (hopefully not while actually driving), what depth perception cue tells allows you to interpret the difference in speed seen in your lower visual field vs. the higher visual field as a sign of depth? 4)
3) If you are in a car staring out the side window (hopefully not while actually driving), what depth perception cue tells allows you to interpret the difference in speed seen in your lower visual field vs. the higher visual field as a sign of depth? 4)
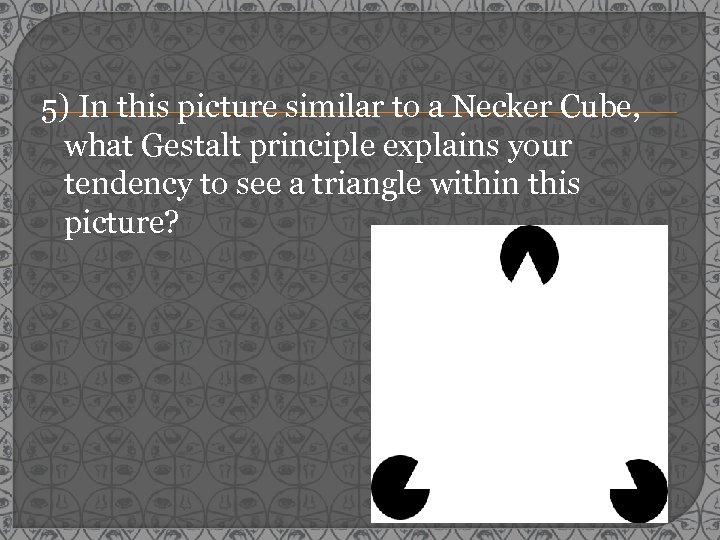 5) In this picture similar to a Necker Cube, what Gestalt principle explains your tendency to see a triangle within this picture?
5) In this picture similar to a Necker Cube, what Gestalt principle explains your tendency to see a triangle within this picture?
 Opponent Process Theory After leaving the cones Some Ganglion cells—excited by input from red cones, inhibited by input from green cones (red-green opponent process) Blue-Yellow Black-White What does it explain? • Afterimages What DOESN’T explain? • Colorblindness – we now know this is VERY complicated…let’s take a look at how complicated it is and be glad you don’t have to memorize this stuff
Opponent Process Theory After leaving the cones Some Ganglion cells—excited by input from red cones, inhibited by input from green cones (red-green opponent process) Blue-Yellow Black-White What does it explain? • Afterimages What DOESN’T explain? • Colorblindness – we now know this is VERY complicated…let’s take a look at how complicated it is and be glad you don’t have to memorize this stuff
 Stare at this
Stare at this

 Figure 4 -4 Test for Color Blindness Slide 38
Figure 4 -4 Test for Color Blindness Slide 38
 HEARING: some basic definitions Amplitude = strength of a sound (Loudness) • Decibel = 1/10 of a bel, a unit of measurement named after the inventor Bell • 0 = absolute threshold level 20 d. B = soft whisper 60 d. B = regular conversation Frequency = number of cycles in a sound wave (Pitch) • Hertz = cycles of sounds waves per second • Pitch = high or low (longer wave is lower, shorter is higher)
HEARING: some basic definitions Amplitude = strength of a sound (Loudness) • Decibel = 1/10 of a bel, a unit of measurement named after the inventor Bell • 0 = absolute threshold level 20 d. B = soft whisper 60 d. B = regular conversation Frequency = number of cycles in a sound wave (Pitch) • Hertz = cycles of sounds waves per second • Pitch = high or low (longer wave is lower, shorter is higher)
 Helmholtz’s Place Theory Different frequencies make different parts of the basilar membrane vibrate • High frequencies, @start of cochlea • Low frequencies spread out across cochlea, peaking @end of it Larger the cochlea, the better the ability to hear low freq sound • Cats & Dogs have smaller cochleas (hear HIGH pitch stuff) • The vacuum cleaner freaks out the cat because it produces very high pitch
Helmholtz’s Place Theory Different frequencies make different parts of the basilar membrane vibrate • High frequencies, @start of cochlea • Low frequencies spread out across cochlea, peaking @end of it Larger the cochlea, the better the ability to hear low freq sound • Cats & Dogs have smaller cochleas (hear HIGH pitch stuff) • The vacuum cleaner freaks out the cat because it produces very high pitch
 Frequency theory Frequency of vibrations? • If freq = 100 waves/s, then 100 impulses/s to the brain Problem: Neurons cannot fire over 1000 times/s, so how do we hear over 1000 Hz? (speech = 4000 Hz) • Volley Principle: Neurons alternate firing like soldiers, so that their combined their frequency = something above 1000/s In the end, it is probably both theories
Frequency theory Frequency of vibrations? • If freq = 100 waves/s, then 100 impulses/s to the brain Problem: Neurons cannot fire over 1000 times/s, so how do we hear over 1000 Hz? (speech = 4000 Hz) • Volley Principle: Neurons alternate firing like soldiers, so that their combined their frequency = something above 1000/s In the end, it is probably both theories
 Sound Localization DEMONSTRATION Car honking? Emergency Sirens? WHY? Parallel processing: • Timing difference in one neural pathway • Intensity differences in another • Info merged in temporal lobe
Sound Localization DEMONSTRATION Car honking? Emergency Sirens? WHY? Parallel processing: • Timing difference in one neural pathway • Intensity differences in another • Info merged in temporal lobe
 Tinnitus Defined = persistent sound in one or both ears…sound does not come from external source • High pitched hiss, ring, buzz, or roar • Continuous or pulsating (often coinciding with the heartbeat) • Sound originates in the inner ear and is triggered by the auditory nerve Causes: side effect of taking aspirin!, wax in outer ear, ear infection, impacted teeth, infected sinuses or tonsils, nerve disorders, arteriosclerosis, hypertension, loud noise, head injury, antibiotic drugs, Meniere’s disease (eventually causes hearing loss), otitis (inflammation of the ear) Explanation: Science News
Tinnitus Defined = persistent sound in one or both ears…sound does not come from external source • High pitched hiss, ring, buzz, or roar • Continuous or pulsating (often coinciding with the heartbeat) • Sound originates in the inner ear and is triggered by the auditory nerve Causes: side effect of taking aspirin!, wax in outer ear, ear infection, impacted teeth, infected sinuses or tonsils, nerve disorders, arteriosclerosis, hypertension, loud noise, head injury, antibiotic drugs, Meniere’s disease (eventually causes hearing loss), otitis (inflammation of the ear) Explanation: Science News
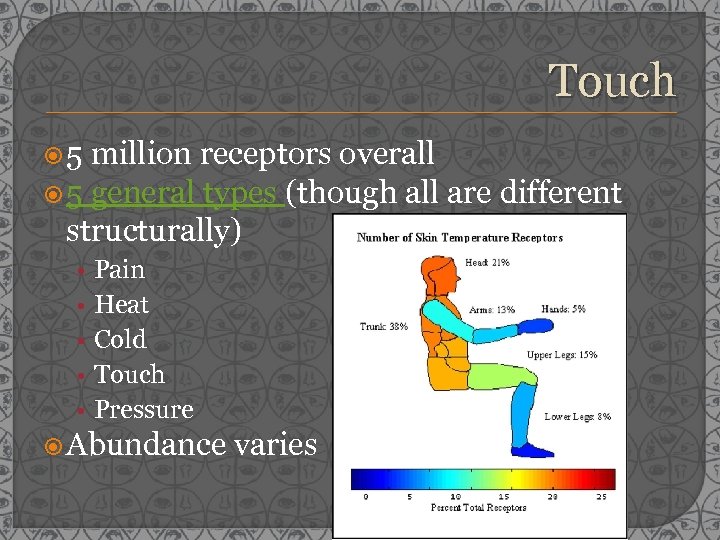 Touch 5 million receptors overall 5 general types (though all are different structurally) • • • Pain Heat Cold Touch Pressure Abundance varies
Touch 5 million receptors overall 5 general types (though all are different structurally) • • • Pain Heat Cold Touch Pressure Abundance varies
 Touch Thresholds 2 Point Thresholds (Guide 16) 2 toothpicks, 1 cm apart • Touch cheek, then calf • Touch fingertips, then forearm 2 toothpicks (or same pencils), 1 inch apart on crease of elbow • Keep distance between toothpicks equal, “draw” them to the middle and index fingers
Touch Thresholds 2 Point Thresholds (Guide 16) 2 toothpicks, 1 cm apart • Touch cheek, then calf • Touch fingertips, then forearm 2 toothpicks (or same pencils), 1 inch apart on crease of elbow • Keep distance between toothpicks equal, “draw” them to the middle and index fingers
 The Aristotle Illusion Cross index, middle finger Touch small spherical object between them (end of a ballpoint pen)
The Aristotle Illusion Cross index, middle finger Touch small spherical object between them (end of a ballpoint pen)
 More Top Down Concepts Interlocking Hands Purpose: Nervous system does not come with prewired sensory relationships
More Top Down Concepts Interlocking Hands Purpose: Nervous system does not come with prewired sensory relationships
 Pain…In the beginning: Descartes: Pain is a physical phenomenon of injured nerves sending impulses to the brain • He was right…kinda! Nociceptors – sensory receptors for “hurtful” stimuli including temperatures, pressures, and chemicals Usually respond either to chemical, thermal, or mechanical environments upon reaching a particular “pain” threshold • Noxious heat or cold • Excess pressure / breaks in the skin Sleeping nociceptors – like the others, but can’t be activated unless tissue inflammation surrounds it (meaning the tissue is damaged)
Pain…In the beginning: Descartes: Pain is a physical phenomenon of injured nerves sending impulses to the brain • He was right…kinda! Nociceptors – sensory receptors for “hurtful” stimuli including temperatures, pressures, and chemicals Usually respond either to chemical, thermal, or mechanical environments upon reaching a particular “pain” threshold • Noxious heat or cold • Excess pressure / breaks in the skin Sleeping nociceptors – like the others, but can’t be activated unless tissue inflammation surrounds it (meaning the tissue is damaged)
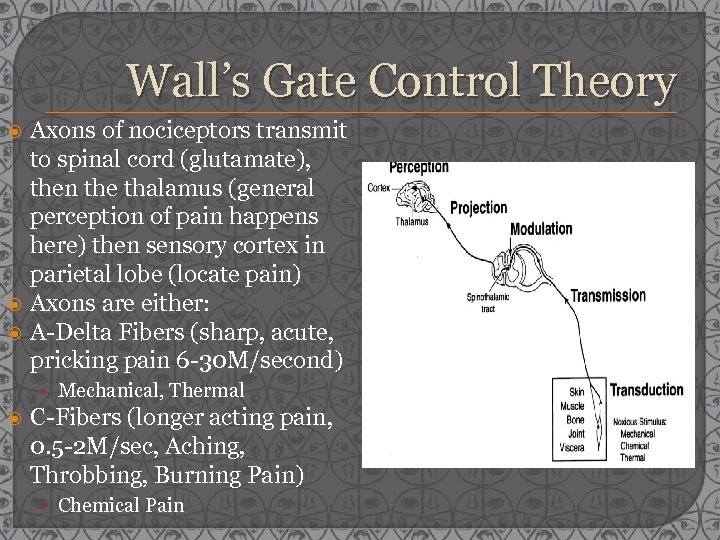 Wall’s Gate Control Theory Axons of nociceptors transmit to spinal cord (glutamate), then the thalamus (general perception of pain happens here) then sensory cortex in parietal lobe (locate pain) Axons are either: A-Delta Fibers (sharp, acute, pricking pain 6 -30 M/second) • Mechanical, Thermal C-Fibers (longer acting pain, 0. 5 -2 M/sec, Aching, Throbbing, Burning Pain) • Chemical Pain
Wall’s Gate Control Theory Axons of nociceptors transmit to spinal cord (glutamate), then the thalamus (general perception of pain happens here) then sensory cortex in parietal lobe (locate pain) Axons are either: A-Delta Fibers (sharp, acute, pricking pain 6 -30 M/second) • Mechanical, Thermal C-Fibers (longer acting pain, 0. 5 -2 M/sec, Aching, Throbbing, Burning Pain) • Chemical Pain
 Brain Briefly on Headaches does not actually have any nocioceptive tissue = cannot perceive pain So headaches CANNOT = stimulation of pain fibers in the brain itself The membrane surrounding CNS, dura matter, has pain receptors Evolutionary, probably any injury that was severe enough to be able to cause pain in the brain would probably kill you first anyway
Brain Briefly on Headaches does not actually have any nocioceptive tissue = cannot perceive pain So headaches CANNOT = stimulation of pain fibers in the brain itself The membrane surrounding CNS, dura matter, has pain receptors Evolutionary, probably any injury that was severe enough to be able to cause pain in the brain would probably kill you first anyway
 Stop complaining and take something… How does aspirin work? • Actually doesn’t work in the brain • Blocks the production of prostaglandins throughout the body • Prostaglandins (named by a Swede who thought they were produced in the prostate) are in virtually every cell of the body…they produce inflammation, pain, and fever when triggered by appropriate stimuli • Aspirin blocks them from doing this
Stop complaining and take something… How does aspirin work? • Actually doesn’t work in the brain • Blocks the production of prostaglandins throughout the body • Prostaglandins (named by a Swede who thought they were produced in the prostate) are in virtually every cell of the body…they produce inflammation, pain, and fever when triggered by appropriate stimuli • Aspirin blocks them from doing this
 Can plants feel pain? Since pain is defined as a signal of present or impending tissue damage affected by a harmful stimulus, the ability to experience pain or irritation is observable in most multicellular organisms. Even some plants have the ability to retract from a noxious stimulus. Whether this sensation of pain is equivalent to the human experience is debatable.
Can plants feel pain? Since pain is defined as a signal of present or impending tissue damage affected by a harmful stimulus, the ability to experience pain or irritation is observable in most multicellular organisms. Even some plants have the ability to retract from a noxious stimulus. Whether this sensation of pain is equivalent to the human experience is debatable.
 Taste (Gustation) Types of sensations: Sweet, Sour, Salty, Bitter, & Umami Supertasters
Taste (Gustation) Types of sensations: Sweet, Sour, Salty, Bitter, & Umami Supertasters
 Smell (Olfaction) Anosmia – no sense of smell (2 million Americans) • Most common cause = head trauma 10 million olfactory neurons, each having 1000 different possible types of receptors 4 other ways to detect chemicals in the air (kinda like smell, but not what we think of when we say “smell”) • Vomeronasal organ – snakes forked tongues collect scent molecules and deposit them here on the roof of their mouths; in mammals its in the nasal cavity • Septal organ of Masera – ? • Nervus terminalils – ? • Tigeminal nerve – irritating odors
Smell (Olfaction) Anosmia – no sense of smell (2 million Americans) • Most common cause = head trauma 10 million olfactory neurons, each having 1000 different possible types of receptors 4 other ways to detect chemicals in the air (kinda like smell, but not what we think of when we say “smell”) • Vomeronasal organ – snakes forked tongues collect scent molecules and deposit them here on the roof of their mouths; in mammals its in the nasal cavity • Septal organ of Masera – ? • Nervus terminalils – ? • Tigeminal nerve – irritating odors

 Thinking Question Imagine that you are outside on a clear night in which there are no clouds, and there is a bright FULL MOON. Pretend that on a table in front of you are objects that range in size from a BB to a beach ball as follows: 1. BB 2. Pea 3. Dime 4. Penny 5. Nickel 6. Quarter 7. Golf ball 8. Baseball 9. Softball 10. Small salad plate 11. Large dinner plate 12. Frisbee 13. Basketball 14. Beach ball Please pretend that you are going to pick one of these things that WHEN HELD AT ARM’S LENGTH JUST COVERS UP THE MOON. Imagine that you are picking one that when you hold it in your hand will JUST BARELY COVER UP THE MOON so that you can no longer see it. Write down the object you selected.
Thinking Question Imagine that you are outside on a clear night in which there are no clouds, and there is a bright FULL MOON. Pretend that on a table in front of you are objects that range in size from a BB to a beach ball as follows: 1. BB 2. Pea 3. Dime 4. Penny 5. Nickel 6. Quarter 7. Golf ball 8. Baseball 9. Softball 10. Small salad plate 11. Large dinner plate 12. Frisbee 13. Basketball 14. Beach ball Please pretend that you are going to pick one of these things that WHEN HELD AT ARM’S LENGTH JUST COVERS UP THE MOON. Imagine that you are picking one that when you hold it in your hand will JUST BARELY COVER UP THE MOON so that you can no longer see it. Write down the object you selected.
 Flavor: The Interaction of Taste & Smell Demonstration
Flavor: The Interaction of Taste & Smell Demonstration
 Pheromones Received by olfactory system, vomeronasal system, taste, inhalation, absorption through the skin, chemorecetors RELEASERS: • Attractans / Repellants – sexual, maternal, fear, social status, recently rewarded/frustrated • Aggression-Inhibiting/Promoting – androgen dependent urinary pheromone promoting intramale aggression in mice and estrogendependent pheromones that inhibit aggression in mice
Pheromones Received by olfactory system, vomeronasal system, taste, inhalation, absorption through the skin, chemorecetors RELEASERS: • Attractans / Repellants – sexual, maternal, fear, social status, recently rewarded/frustrated • Aggression-Inhibiting/Promoting – androgen dependent urinary pheromone promoting intramale aggression in mice and estrogendependent pheromones that inhibit aggression in mice
 PRIMERS (slow acting effects, all in mice) • Puberty inhibition – grouped females inhibit the • • • sexual maturation of young female mice Puberty acceleration Estrus-Suppression Estrus-Induction Pregnancy Blocking – exposure to scent of strange male in absence of scent of original stud can induce abortion up to Day 15 of a 21 Day mouse pregnancy Adrenal Hypertrophy
PRIMERS (slow acting effects, all in mice) • Puberty inhibition – grouped females inhibit the • • • sexual maturation of young female mice Puberty acceleration Estrus-Suppression Estrus-Induction Pregnancy Blocking – exposure to scent of strange male in absence of scent of original stud can induce abortion up to Day 15 of a 21 Day mouse pregnancy Adrenal Hypertrophy
 Human Pheromones? Androstenol – excreted in urine, armpit sweat • Seems to attract women, repel men, make subjects rate women’s photographs more sexy/attractive, increase frequency of copulation in exposed subjects • Can buy this in a can at agricultural supply stores Studies show when sprayed in a movie theater, women are more likely to sit in the sprayed seats, men less likely May explain intermale-aggression at English soccer matches (lines get long, don’t want to miss anything, lots of drinking = pee where you are) Is found in colognes (and even 1 perfume)!
Human Pheromones? Androstenol – excreted in urine, armpit sweat • Seems to attract women, repel men, make subjects rate women’s photographs more sexy/attractive, increase frequency of copulation in exposed subjects • Can buy this in a can at agricultural supply stores Studies show when sprayed in a movie theater, women are more likely to sit in the sprayed seats, men less likely May explain intermale-aggression at English soccer matches (lines get long, don’t want to miss anything, lots of drinking = pee where you are) Is found in colognes (and even 1 perfume)!

 A Body Position and Movement 6 th sense: kinesthesis = awareness aroused by movements of and feedback from muscles, tendons, & joints Proprioception – stretch (muscles) receptors • Activity 1: Close eyes, raise both hands above head. Keep fingers of left hand entirely still. With right hand, touch index fingertip to nose, then touch your left hand thumb with your right index finger…try each finger • Activity 2: X on paper…close eyes…hand up high…mark a dot • Activity 3: Write “Proprioception”: close eyes…on same line, write “Proprioception” Explanation: proprioceptors in muscles, tendons, joints judge your body positions in all these activities
A Body Position and Movement 6 th sense: kinesthesis = awareness aroused by movements of and feedback from muscles, tendons, & joints Proprioception – stretch (muscles) receptors • Activity 1: Close eyes, raise both hands above head. Keep fingers of left hand entirely still. With right hand, touch index fingertip to nose, then touch your left hand thumb with your right index finger…try each finger • Activity 2: X on paper…close eyes…hand up high…mark a dot • Activity 3: Write “Proprioception”: close eyes…on same line, write “Proprioception” Explanation: proprioceptors in muscles, tendons, joints judge your body positions in all these activities
 Vestibular Sense A 7 th sense! = Vestibular sense = monitors the head’s (and thus the body’s) position and movement • Semicircular canals (3 -D pretzel) in the inner ear contains the sensory system for this • Vestibular sacs connect the canals with the cochlea (fluid-filled)…so, when the head rotates or tilts, this feels it Spinny bat: You feel dizzy because you are spinning, causing the fluid to spin, you stop moving, but the fluid keeps spinning…something is off…you feel dizzy • Sends messages to the cerebellum Waterman of England contracted viral infection that destroyed nerves enabling him to sense light touch and body position • He can only stand / move when the lights are on • If lights go out, he crumples to the floor DEMONSTRATION: • Stand up • Right heel in front of your left toes • Close eyes!
Vestibular Sense A 7 th sense! = Vestibular sense = monitors the head’s (and thus the body’s) position and movement • Semicircular canals (3 -D pretzel) in the inner ear contains the sensory system for this • Vestibular sacs connect the canals with the cochlea (fluid-filled)…so, when the head rotates or tilts, this feels it Spinny bat: You feel dizzy because you are spinning, causing the fluid to spin, you stop moving, but the fluid keeps spinning…something is off…you feel dizzy • Sends messages to the cerebellum Waterman of England contracted viral infection that destroyed nerves enabling him to sense light touch and body position • He can only stand / move when the lights are on • If lights go out, he crumples to the floor DEMONSTRATION: • Stand up • Right heel in front of your left toes • Close eyes!
 Synesthesia • Stimulation of one modality leads to perceptual experience in another. • For example: Seeing specific letters or numbers in specific colors See a “ 5” in black ink on a white background as red A “k” may always appear greenish-blue Video
Synesthesia • Stimulation of one modality leads to perceptual experience in another. • For example: Seeing specific letters or numbers in specific colors See a “ 5” in black ink on a white background as red A “k” may always appear greenish-blue Video


