 Senior Years ICT • • • • • • • Manitoba Curriculum Framework of Outcomes Darryl Gervais
Senior Years ICT • • • • • • • Manitoba Curriculum Framework of Outcomes Darryl Gervais
 Information and Communication Technology • Students learning to – solve problems – accomplish tasks – express creativity Education, Citizenship and Youth
Information and Communication Technology • Students learning to – solve problems – accomplish tasks – express creativity Education, Citizenship and Youth
 Why is there a new framework? • • Existing curriculum was old Large number of ICT SIC’s SY teachers were asking for outcomes Literacy with ICT Across the Curriculum Education, Citizenship and Youth
Why is there a new framework? • • Existing curriculum was old Large number of ICT SIC’s SY teachers were asking for outcomes Literacy with ICT Across the Curriculum Education, Citizenship and Youth
 Previous Curriculum - Computer • 1983 - Computer Science 205 • 1984 - Computer Science 305 • 1991 - Computer Applications and Technology 105 Education, Citizenship and Youth
Previous Curriculum - Computer • 1983 - Computer Science 205 • 1984 - Computer Science 305 • 1991 - Computer Applications and Technology 105 Education, Citizenship and Youth
 Previous Curriculum - Business • • • 1993 Introductory Keyboarding 15 G Advanced Keyboarding 25 G Software Applications 30 S Word Processing 30 G Advanced Word Processing 45 S Education, Citizenship and Youth
Previous Curriculum - Business • • • 1993 Introductory Keyboarding 15 G Advanced Keyboarding 25 G Software Applications 30 S Word Processing 30 G Advanced Word Processing 45 S Education, Citizenship and Youth
 School Initiated Courses • • Additional work for school staff Differences between schools Trends across school divisions Reflect local needs Education, Citizenship and Youth
School Initiated Courses • • Additional work for school staff Differences between schools Trends across school divisions Reflect local needs Education, Citizenship and Youth
 Literacy with ICT http: //www. edu. gov. mb. ca/k 12/tech/lict/index. html Education, Citizenship and Youth
Literacy with ICT http: //www. edu. gov. mb. ca/k 12/tech/lict/index. html Education, Citizenship and Youth
 Literacy with ICT • all K-8 students will develop their literacy with ICT • all K-8 teachers will provide opportunities for their students to develop literacy with ICT across the curriculum • all schools will report to parents about the development of their child’s literacy with ICT Education, Citizenship and Youth
Literacy with ICT • all K-8 students will develop their literacy with ICT • all K-8 teachers will provide opportunities for their students to develop literacy with ICT across the curriculum • all schools will report to parents about the development of their child’s literacy with ICT Education, Citizenship and Youth
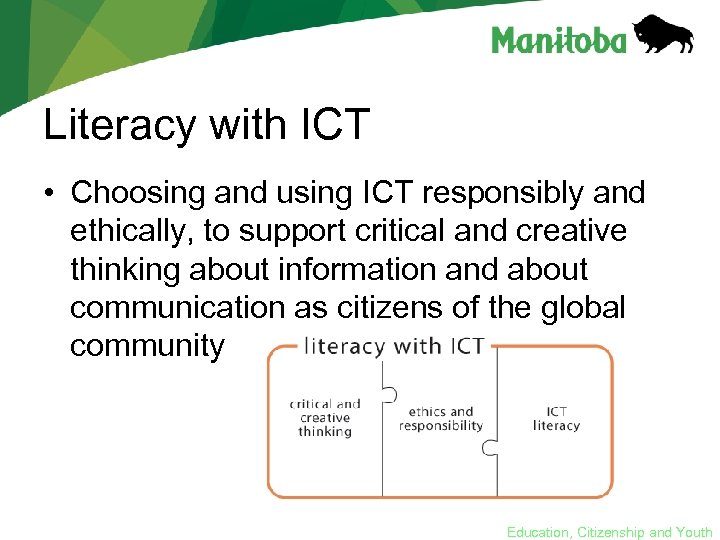 Literacy with ICT • Choosing and using ICT responsibly and ethically, to support critical and creative thinking about information and about communication as citizens of the global community Education, Citizenship and Youth
Literacy with ICT • Choosing and using ICT responsibly and ethically, to support critical and creative thinking about information and about communication as citizens of the global community Education, Citizenship and Youth
 Literacy with ICT Competencies • demonstrating critical thinking • demonstrating creative thinking • demonstrating ethics and responsibility Education, Citizenship and Youth
Literacy with ICT Competencies • demonstrating critical thinking • demonstrating creative thinking • demonstrating ethics and responsibility Education, Citizenship and Youth
 Literacy with ICT Big Ideas • • • Plan and Question Gather and Make Sense Produce to Show Understanding Communicate Reflect Ethics and Responsibility Social Implications Collaboration Motivation and Confidence Education, Citizenship and Youth
Literacy with ICT Big Ideas • • • Plan and Question Gather and Make Sense Produce to Show Understanding Communicate Reflect Ethics and Responsibility Social Implications Collaboration Motivation and Confidence Education, Citizenship and Youth
 Learning Continuum • A developmental learning continuum is an assessment tool FOR learning based on teacher observation. It describes what teachers see and hear students doing as they demonstrate their literacy Education, Citizenship and Youth
Learning Continuum • A developmental learning continuum is an assessment tool FOR learning based on teacher observation. It describes what teachers see and hear students doing as they demonstrate their literacy Education, Citizenship and Youth
 K – 8 Timeline • Continuum Development • 2004/5 - 16 teachers • Action Research • 2005/6 - 200+ teachers and school leaders • Implementation • • All 37 school divisions, reporting to parents 2006/7 - 15% teachers targeted 2007/8 – 70% teachers targeted 2008/9 – 100% teachers targeted Education, Citizenship and Youth
K – 8 Timeline • Continuum Development • 2004/5 - 16 teachers • Action Research • 2005/6 - 200+ teachers and school leaders • Implementation • • All 37 school divisions, reporting to parents 2006/7 - 15% teachers targeted 2007/8 – 70% teachers targeted 2008/9 – 100% teachers targeted Education, Citizenship and Youth
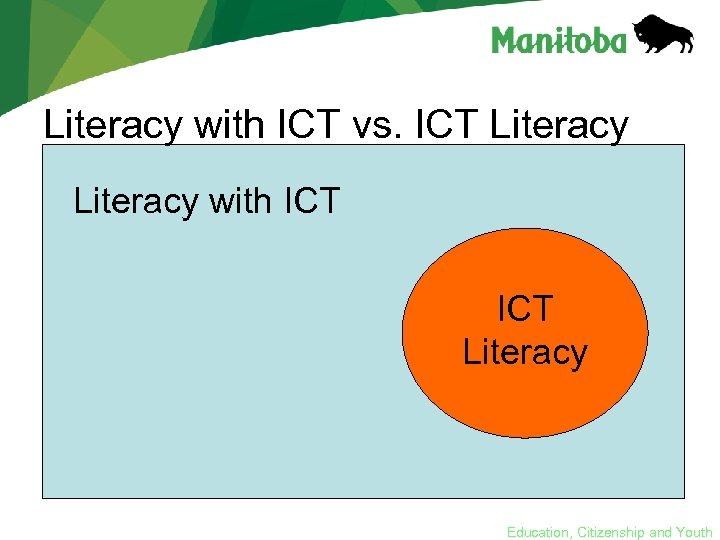 Literacy with ICT vs. ICT Literacy with ICT Literacy Education, Citizenship and Youth
Literacy with ICT vs. ICT Literacy with ICT Literacy Education, Citizenship and Youth
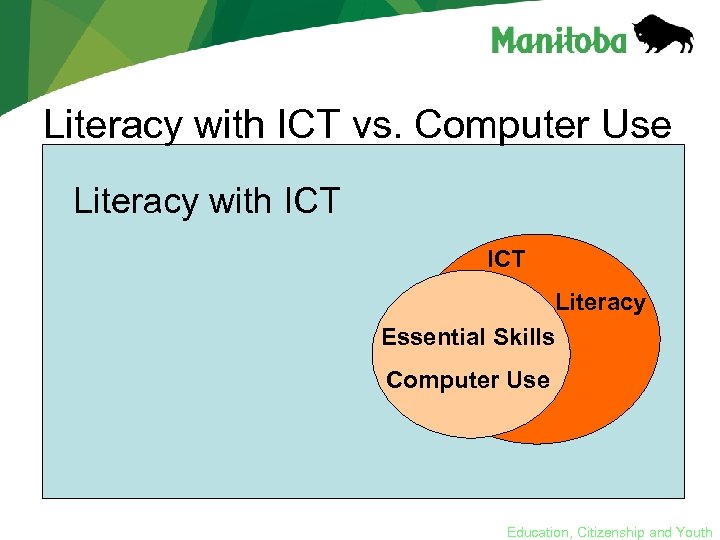 Literacy with ICT vs. Computer Use Literacy with ICT Literacy Essential Skills Computer Use Education, Citizenship and Youth
Literacy with ICT vs. Computer Use Literacy with ICT Literacy Essential Skills Computer Use Education, Citizenship and Youth
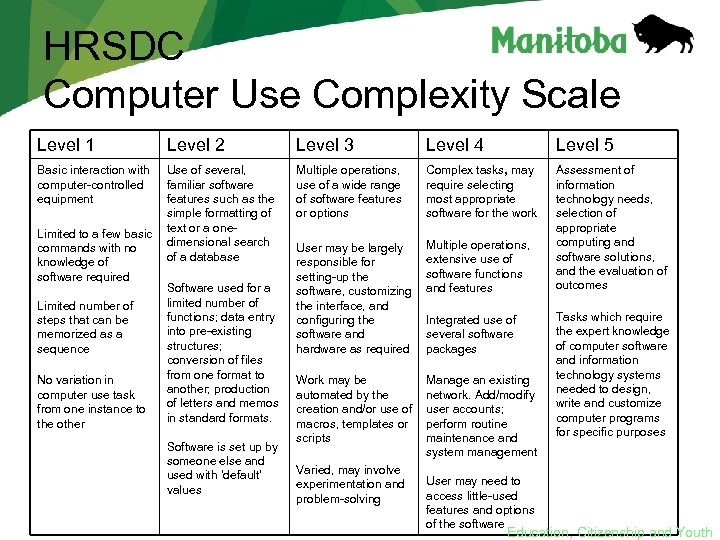 HRSDC Computer Use Complexity Scale Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Level 4 Level 5 Basic interaction with computer-controlled equipment Use of several, familiar software features such as the simple formatting of text or a onedimensional search of a database Multiple operations, use of a wide range of software features or options Complex tasks, may require selecting most appropriate software for the work User may be largely responsible for setting-up the software, customizing the interface, and configuring the software and hardware as required Multiple operations, extensive use of software functions and features Assessment of information technology needs, selection of appropriate computing and software solutions, and the evaluation of outcomes Work may be automated by the creation and/or use of macros, templates or scripts Manage an existing network. Add/modify user accounts; perform routine maintenance and system management Limited to a few basic commands with no knowledge of software required Limited number of steps that can be memorized as a sequence No variation in computer use task from one instance to the other Software used for a limited number of functions; data entry into pre-existing structures; conversion of files from one format to another; production of letters and memos in standard formats. Software is set up by someone else and used with ‘default’ values Varied, may involve experimentation and problem-solving Integrated use of several software packages User may need to access little-used features and options of the software Tasks which require the expert knowledge of computer software and information technology systems needed to design, write and customize computer programs for specific purposes Education, Citizenship and Youth
HRSDC Computer Use Complexity Scale Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Level 4 Level 5 Basic interaction with computer-controlled equipment Use of several, familiar software features such as the simple formatting of text or a onedimensional search of a database Multiple operations, use of a wide range of software features or options Complex tasks, may require selecting most appropriate software for the work User may be largely responsible for setting-up the software, customizing the interface, and configuring the software and hardware as required Multiple operations, extensive use of software functions and features Assessment of information technology needs, selection of appropriate computing and software solutions, and the evaluation of outcomes Work may be automated by the creation and/or use of macros, templates or scripts Manage an existing network. Add/modify user accounts; perform routine maintenance and system management Limited to a few basic commands with no knowledge of software required Limited number of steps that can be memorized as a sequence No variation in computer use task from one instance to the other Software used for a limited number of functions; data entry into pre-existing structures; conversion of files from one format to another; production of letters and memos in standard formats. Software is set up by someone else and used with ‘default’ values Varied, may involve experimentation and problem-solving Integrated use of several software packages User may need to access little-used features and options of the software Tasks which require the expert knowledge of computer software and information technology systems needed to design, write and customize computer programs for specific purposes Education, Citizenship and Youth
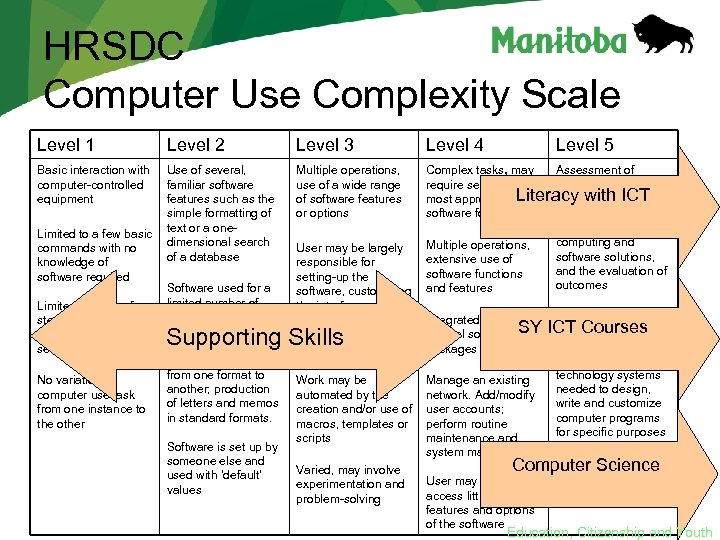 HRSDC Computer Use Complexity Scale Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Level 4 Basic interaction with computer-controlled equipment Use of several, familiar software features such as the simple formatting of text or a onedimensional search of a database Multiple operations, use of a wide range of software features or options Complex tasks, may Assessment of require selecting information most appropriate. Literacy with needs, technology ICT software for the work selection of appropriate computing and Multiple operations, software solutions, extensive use of and the evaluation of software functions outcomes and features Limited to a few basic commands with no knowledge of software required Limited number of steps that can be memorized as a sequence No variation in computer use task from one instance to the other Software used for a limited number of functions; data entry into pre-existing structures; conversion of files from one format to another; production of letters and memos in standard formats. User may be largely responsible for setting-up the software, customizing the interface, and configuring the software and hardware as required Supporting Skills Software is set up by someone else and used with ‘default’ values Work may be automated by the creation and/or use of macros, templates or scripts Varied, may involve experimentation and problem-solving Level 5 Integrated use of several software SY packages Manage an existing network. Add/modify user accounts; perform routine maintenance and system management Tasks which require ICTexpert knowledge the Courses of computer software and information technology systems needed to design, write and customize computer programs for specific purposes Computer Science User may need to access little-used features and options of the software Education, Citizenship and Youth
HRSDC Computer Use Complexity Scale Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Level 4 Basic interaction with computer-controlled equipment Use of several, familiar software features such as the simple formatting of text or a onedimensional search of a database Multiple operations, use of a wide range of software features or options Complex tasks, may Assessment of require selecting information most appropriate. Literacy with needs, technology ICT software for the work selection of appropriate computing and Multiple operations, software solutions, extensive use of and the evaluation of software functions outcomes and features Limited to a few basic commands with no knowledge of software required Limited number of steps that can be memorized as a sequence No variation in computer use task from one instance to the other Software used for a limited number of functions; data entry into pre-existing structures; conversion of files from one format to another; production of letters and memos in standard formats. User may be largely responsible for setting-up the software, customizing the interface, and configuring the software and hardware as required Supporting Skills Software is set up by someone else and used with ‘default’ values Work may be automated by the creation and/or use of macros, templates or scripts Varied, may involve experimentation and problem-solving Level 5 Integrated use of several software SY packages Manage an existing network. Add/modify user accounts; perform routine maintenance and system management Tasks which require ICTexpert knowledge the Courses of computer software and information technology systems needed to design, write and customize computer programs for specific purposes Computer Science User may need to access little-used features and options of the software Education, Citizenship and Youth
 Infusion of ICT • research in the last 20 years has shown that the most effective way to develop literacy with ICT is to use models that focus on learning rather than on technology • the pedagogy of Literacy with ICT encourages movement from technology as supplementary to the curriculum to a model that infuses the curriculum with ICT Education, Citizenship and Youth
Infusion of ICT • research in the last 20 years has shown that the most effective way to develop literacy with ICT is to use models that focus on learning rather than on technology • the pedagogy of Literacy with ICT encourages movement from technology as supplementary to the curriculum to a model that infuses the curriculum with ICT Education, Citizenship and Youth
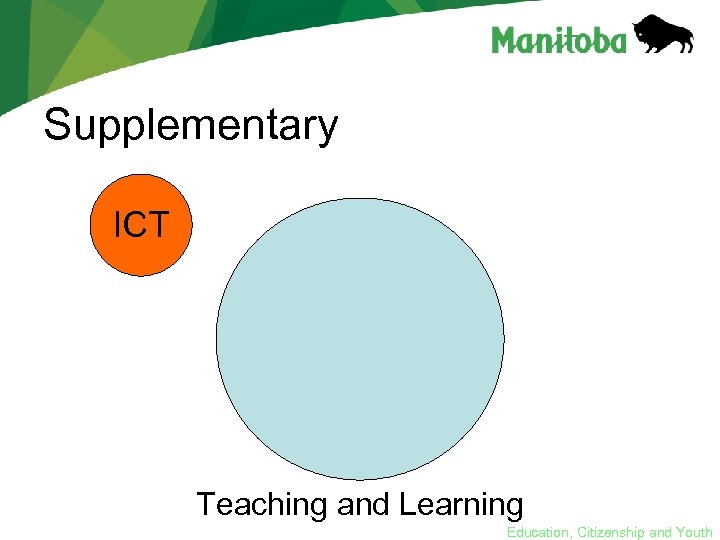 Supplementary ICT Teaching and Learning Education, Citizenship and Youth
Supplementary ICT Teaching and Learning Education, Citizenship and Youth
 Supplementary ICT Teaching and Learning Education, Citizenship and Youth
Supplementary ICT Teaching and Learning Education, Citizenship and Youth
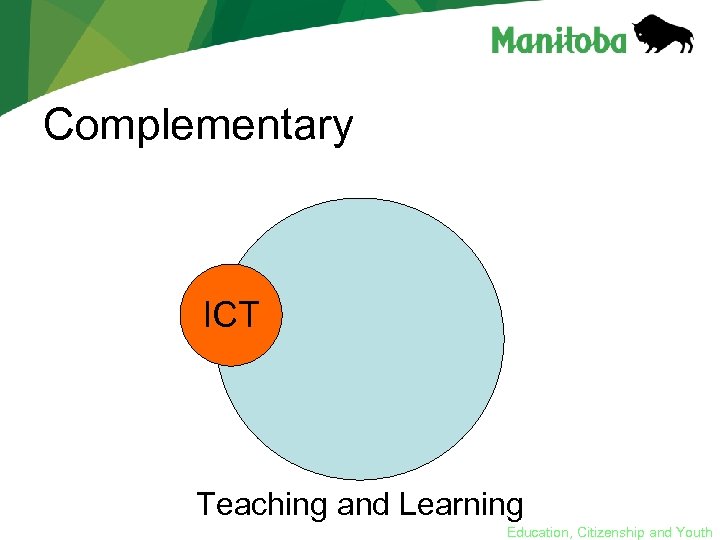 Complementary ICT Teaching and Learning Education, Citizenship and Youth
Complementary ICT Teaching and Learning Education, Citizenship and Youth
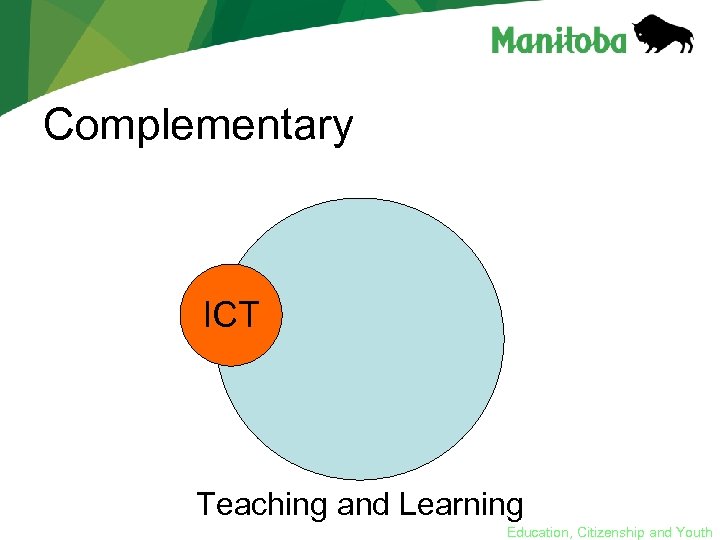 Complementary ICT Teaching and Learning Education, Citizenship and Youth
Complementary ICT Teaching and Learning Education, Citizenship and Youth
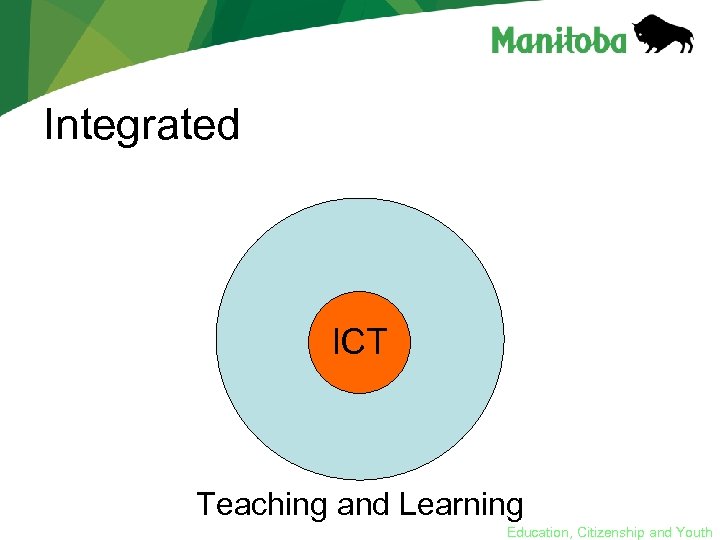 Integrated ICT Teaching and Learning Education, Citizenship and Youth
Integrated ICT Teaching and Learning Education, Citizenship and Youth
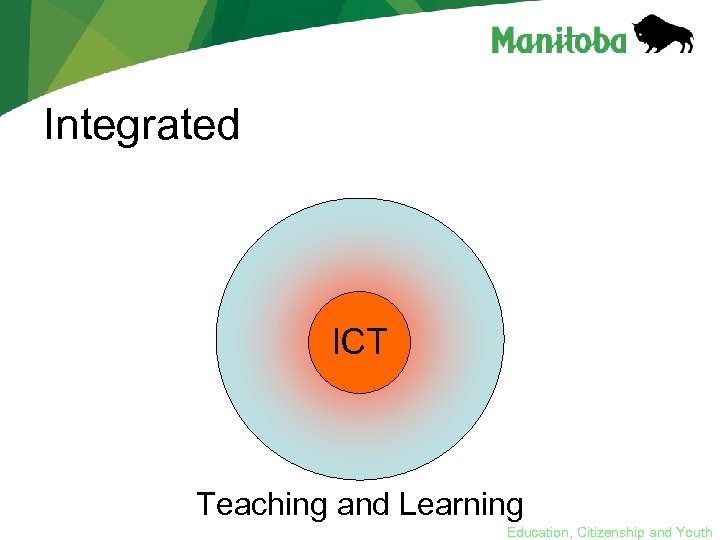 Integrated ICT Teaching and Learning Education, Citizenship and Youth
Integrated ICT Teaching and Learning Education, Citizenship and Youth
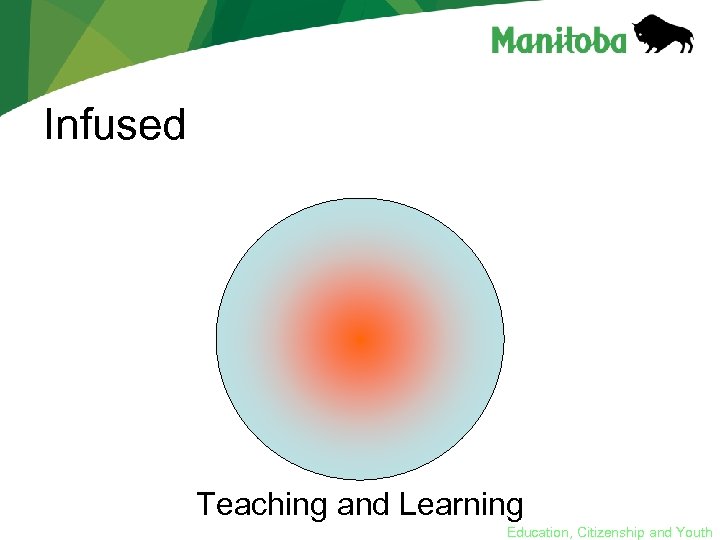 Infused Teaching and Learning Education, Citizenship and Youth
Infused Teaching and Learning Education, Citizenship and Youth
 Senior Years Infusion • In the workplace, ICT is infused throughout the activities of the organization. Using ICT is not a task separate from all other work. • In Senior Years, ICT needs to be infused across the curriculum. • Senior Years ICT courses support the infusion of ICT across the Senior Years curriculum. Education, Citizenship and Youth
Senior Years Infusion • In the workplace, ICT is infused throughout the activities of the organization. Using ICT is not a task separate from all other work. • In Senior Years, ICT needs to be infused across the curriculum. • Senior Years ICT courses support the infusion of ICT across the Senior Years curriculum. Education, Citizenship and Youth
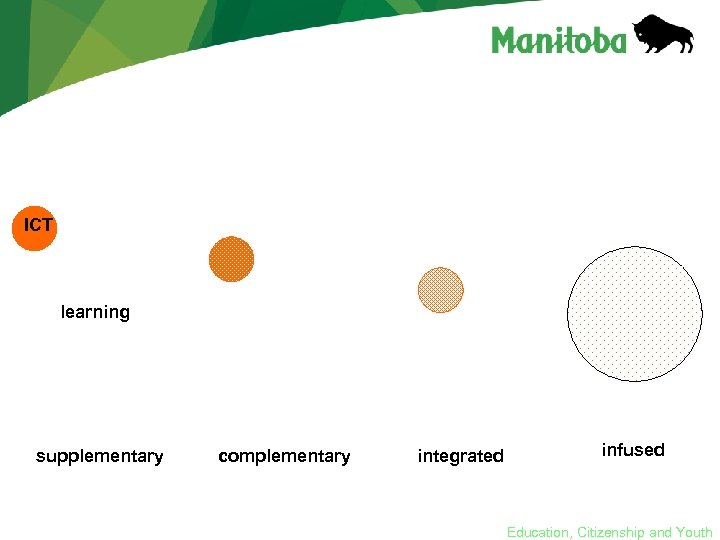 ICT learning supplementary complementary integrated infused Education, Citizenship and Youth
ICT learning supplementary complementary integrated infused Education, Citizenship and Youth
 Challenges • Professional Development for Teachers – Personal ICT Literacy/Computer Use – Personal Literacy with ICT – Assisting students to become Literate with ICT • Professional Development for School Leaders – Personal ICT Literacy/Computer Use – Personal Literacy with ICT – Assisting teachers • Informing and Educating Parents Education, Citizenship and Youth
Challenges • Professional Development for Teachers – Personal ICT Literacy/Computer Use – Personal Literacy with ICT – Assisting students to become Literate with ICT • Professional Development for School Leaders – Personal ICT Literacy/Computer Use – Personal Literacy with ICT – Assisting teachers • Informing and Educating Parents Education, Citizenship and Youth
 Solutions • Workshops about ICT • School Divisions • Teacher Special Area Groups • Microsoft Teacher Mentor Program • Support for Teaching Literacy with ICT • Implementation teams in every school division • Peer Coaching • Online information • Information for Parents • Online • Print Education, Citizenship and Youth
Solutions • Workshops about ICT • School Divisions • Teacher Special Area Groups • Microsoft Teacher Mentor Program • Support for Teaching Literacy with ICT • Implementation teams in every school division • Peer Coaching • Online information • Information for Parents • Online • Print Education, Citizenship and Youth
 Funding of Schools 2007/2008 • Professional Development Support, $1. 3 M • The greater of – $10 per eligible pupil in K-8 and – $15, 000 per division • To assist with the training of teachers to incorporate ICT and report student outcomes to parents Education, Citizenship and Youth
Funding of Schools 2007/2008 • Professional Development Support, $1. 3 M • The greater of – $10 per eligible pupil in K-8 and – $15, 000 per division • To assist with the training of teachers to incorporate ICT and report student outcomes to parents Education, Citizenship and Youth
 New ICT Courses • Reinforce and extend the ICT knowledge, skills and attitudes developed in K – 8 • Support learning in all courses • Explore interests Education, Citizenship and Youth
New ICT Courses • Reinforce and extend the ICT knowledge, skills and attitudes developed in K – 8 • Support learning in all courses • Explore interests Education, Citizenship and Youth
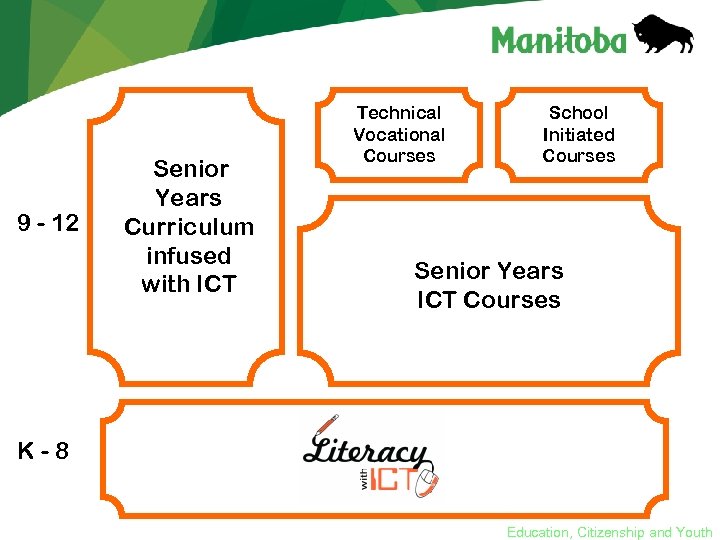 9 - 12 Senior Years Curriculum infused with ICT Technical Vocational Courses School Initiated Courses Senior Years ICT Courses K-8 Education, Citizenship and Youth
9 - 12 Senior Years Curriculum infused with ICT Technical Vocational Courses School Initiated Courses Senior Years ICT Courses K-8 Education, Citizenship and Youth
 New ICT Courses • • Applying ICT 1 & 2 Keyboarding Print Communications Digital Pictures Digital Film Making Desktop Publishing Web Design Interactive Websites • • Data Collection and Analysis Relational Databases 2 D Animation 3 D Modeling Broadcast Media Interactive Media Computer Science Education, Citizenship and Youth
New ICT Courses • • Applying ICT 1 & 2 Keyboarding Print Communications Digital Pictures Digital Film Making Desktop Publishing Web Design Interactive Websites • • Data Collection and Analysis Relational Databases 2 D Animation 3 D Modeling Broadcast Media Interactive Media Computer Science Education, Citizenship and Youth
 Applying ICT 1 & 2 (15 F) • Reinforce and extend the ICT knowledge, attitudes, and skills that they have developed in K-8, and prepare them for further studies in ICT Education, Citizenship and Youth
Applying ICT 1 & 2 (15 F) • Reinforce and extend the ICT knowledge, attitudes, and skills that they have developed in K-8, and prepare them for further studies in ICT Education, Citizenship and Youth
 Keyboarding (25 S) • Use touch-keying techniques to improve accuracy and speed with a keyboard Education, Citizenship and Youth
Keyboarding (25 S) • Use touch-keying techniques to improve accuracy and speed with a keyboard Education, Citizenship and Youth
 Print Communications (25 S) • Plan and create documents for personal and business communications Education, Citizenship and Youth
Print Communications (25 S) • Plan and create documents for personal and business communications Education, Citizenship and Youth
 Digital Pictures (25 S) • Convey a message through an original digital image Education, Citizenship and Youth
Digital Pictures (25 S) • Convey a message through an original digital image Education, Citizenship and Youth
 Digital Film Making (25 S) • Tell stories by combining sound, still images, moving images, text, graphics, and animation into a video product Education, Citizenship and Youth
Digital Film Making (25 S) • Tell stories by combining sound, still images, moving images, text, graphics, and animation into a video product Education, Citizenship and Youth
 Desktop Publishing (35 S) • Plan and create published print documents Education, Citizenship and Youth
Desktop Publishing (35 S) • Plan and create published print documents Education, Citizenship and Youth
 Web Design (35 S) • Design, develop, and publish a simple website Education, Citizenship and Youth
Web Design (35 S) • Design, develop, and publish a simple website Education, Citizenship and Youth
 Interactive Websites (35 S) • Design, develop, and publish a website to display and gather data Education, Citizenship and Youth
Interactive Websites (35 S) • Design, develop, and publish a website to display and gather data Education, Citizenship and Youth
 Data Collection and Analysis (35 S) • Collect, organize, manipulate and analyze data to solve problems Education, Citizenship and Youth
Data Collection and Analysis (35 S) • Collect, organize, manipulate and analyze data to solve problems Education, Citizenship and Youth
 Relational Databases (35 S) • Plan, create, and use a relational database Education, Citizenship and Youth
Relational Databases (35 S) • Plan, create, and use a relational database Education, Citizenship and Youth
 2 D Animation (35 S) • Create two-dimensional animations Education, Citizenship and Youth
2 D Animation (35 S) • Create two-dimensional animations Education, Citizenship and Youth
 3 D Modeling (35 S) • Model three-dimensional objects Education, Citizenship and Youth
3 D Modeling (35 S) • Model three-dimensional objects Education, Citizenship and Youth
 Broadcast Media (35 S) • Plan, develop, and broadcast multimedia Education, Citizenship and Youth
Broadcast Media (35 S) • Plan, develop, and broadcast multimedia Education, Citizenship and Youth
 Interactive Media (35 S) • Plan, develop, and publish interactive media products Education, Citizenship and Youth
Interactive Media (35 S) • Plan, develop, and publish interactive media products Education, Citizenship and Youth
 Computer Science (20 S, 30 S, 40 S) • Solve problems, learn and use programming languages and techniques Education, Citizenship and Youth
Computer Science (20 S, 30 S, 40 S) • Solve problems, learn and use programming languages and techniques Education, Citizenship and Youth
 Implementation timeline • September 2005 - Computer Science • September 2008 – Senior Years ICT Education, Citizenship and Youth
Implementation timeline • September 2005 - Computer Science • September 2008 – Senior Years ICT Education, Citizenship and Youth
 Implementation • School and Division decide: – Which optional courses to offer – Local prerequisites – Recognition of prior learning – Assessment Education, Citizenship and Youth
Implementation • School and Division decide: – Which optional courses to offer – Local prerequisites – Recognition of prior learning – Assessment Education, Citizenship and Youth
 Implementation Possibilities • Stand-alone courses • Combine ICT and non-ICT courses – To support learning in non-ICT courses – To follow a theme – To support project based learning • Challenge for credit Education, Citizenship and Youth
Implementation Possibilities • Stand-alone courses • Combine ICT and non-ICT courses – To support learning in non-ICT courses – To follow a theme – To support project based learning • Challenge for credit Education, Citizenship and Youth
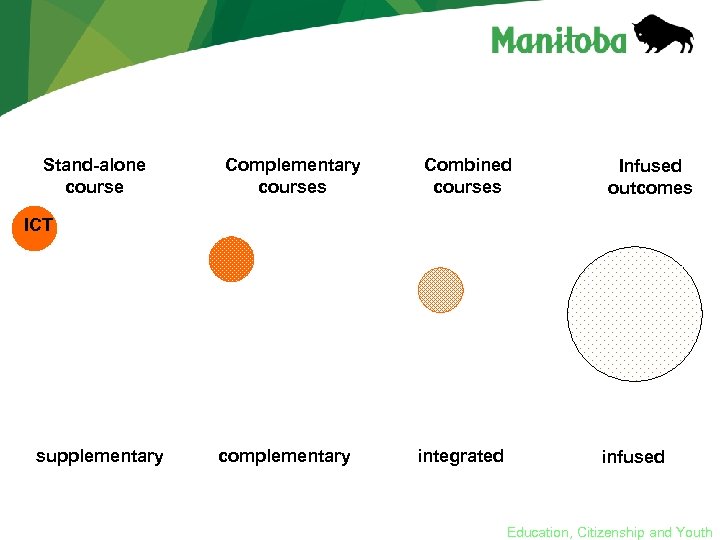 Stand-alone course Complementary courses Combined courses Infused outcomes ICT supplementary complementary integrated infused Education, Citizenship and Youth
Stand-alone course Complementary courses Combined courses Infused outcomes ICT supplementary complementary integrated infused Education, Citizenship and Youth
 School Initiated Courses (SICs) • Schools may still submit ICT SIC’s • SIC learning outcomes must go beyond the learning outcomes in the framework • At least 50% of the learning outcomes in a SIC must be different than the learning outcomes in the curriculum framework Education, Citizenship and Youth
School Initiated Courses (SICs) • Schools may still submit ICT SIC’s • SIC learning outcomes must go beyond the learning outcomes in the framework • At least 50% of the learning outcomes in a SIC must be different than the learning outcomes in the curriculum framework Education, Citizenship and Youth
 Professional Learning Community • Forum for discussion and sharing • http: //webct. merlin. mb. ca/webct • Request access to the community – Email dgervais@gov. mb. ca Education, Citizenship and Youth
Professional Learning Community • Forum for discussion and sharing • http: //webct. merlin. mb. ca/webct • Request access to the community – Email dgervais@gov. mb. ca Education, Citizenship and Youth
 Education, Citizenship and Youth
Education, Citizenship and Youth
 Darryl Gervais dgervais@gov. mb. ca Distance Learning and Information Technologies Education, Citizenship and Youth
Darryl Gervais dgervais@gov. mb. ca Distance Learning and Information Technologies Education, Citizenship and Youth


